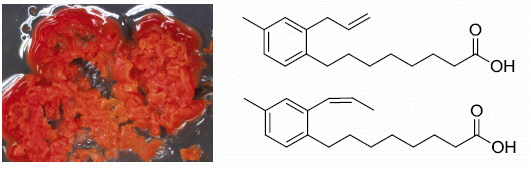
Solwaric Acids A and B, Antibacterial Aromatic Acids from a Marine Solwaraspora sp.
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Bacterial Strain Selection and Structure Elucidation
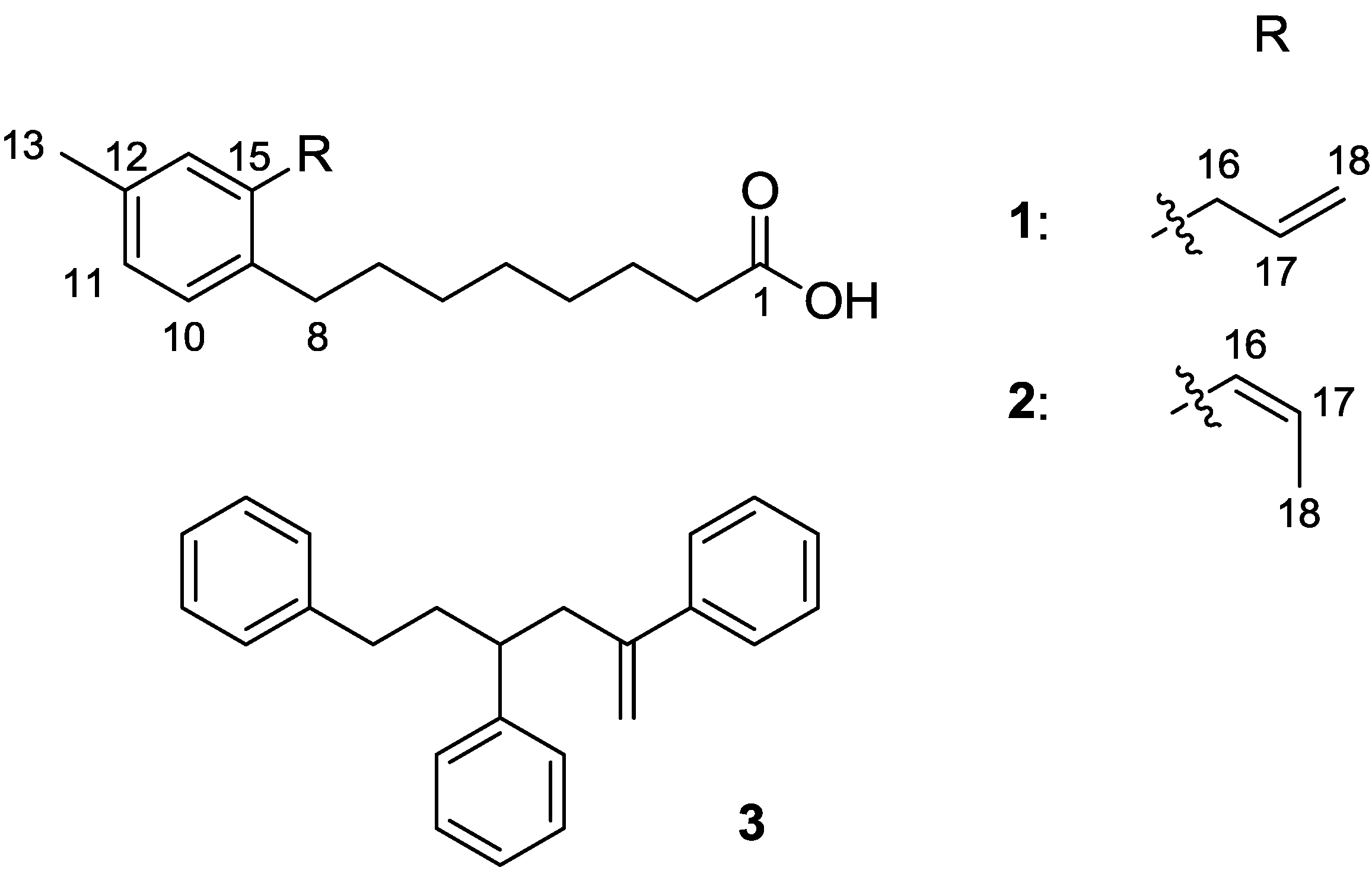
| Position | 1 | 2 | COSY | HMBC | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| δC, mult. | δH (J in Hz) | δC, mult. | δH (J in Hz) | ||||
| 1 | 180.1, C | 180.5, C | |||||
| 1-OH | 9.34, s | ||||||
| 2 | 34.4, CH2 | 2.33, t (6.6) | 34.8, CH2 | 2.29, t (6.6) | 3 | 3, 4 | |
| 3 | 24.9, CH2 | 1.60, m | 25.0, CH2 | 1.59, m | 2, 4 | 2, 4 | |
| 4 | 29.2, CH2 | 1.30, m | 29.3, CH2 | 1.30, m | 3 | ||
| 5 | 29.4, CH2 | 1.30, m | 29.4, CH2 | 1.30, m | |||
| 6 | 29.9, CH2 | 1.30, m | 29.6, CH2 | 1.30, m | 7 | ||
| 7 | 31.3, CH2 | 1.51, m | 30.9, CH2 | 1.48, m | 8 | 9 | |
| 8 | 32.5, CH2 | 2.52, t (7.6) | 33.2, CH2 | 2.50, t (7.6) | 7 | 6, 9, 10 | |
| 9 | 137.9, C | 138.1, C | |||||
| 10 | 129.4, CH | 7.02, d (7.2) | 129.0, CH | 7.04, d (7.2) | 11 | 8, 12 | |
| 11 | 127.2, CH | 6.95, d (7.2) | 127.6, CH | 6.96, d (7.2) | 10 | 14 | |
| 12 | 135.5, C | 134.7, C | |||||
| 13 | 21.2, CH3 | 2.27, s | 21.2, CH3 | 2.30, s | 11, 12, 14 | ||
| 14 | 130.4, CH | 6.94, s | 130.3, CH | 6.97, s | 9, 13 | ||
| 15 | 137.5, C | 136.1, C | |||||
| 16 | 37.2, CH2 | 3.33, br d (6.4) | 129.1, CH | 6.47, br d (11.4) | 17 | 12, 14, 18 | |
| 17 | 137.7, CH | 5.93, tdd (6.4, 10.1, 16.9) | 126.9, CH | 5.77, dq (11.4, 7.0) | 16, 18 | 18 | |
| 18 | 115.7, CH2 | 5.04, tdd (1.7, 1.7, 10.1) | 14.6, CH3 | 1.71, dd (1.8, 7.0) | 17 | 16, 17 | |
| 5.00, tdd (1.7, 1.7, 16.9) | |||||||
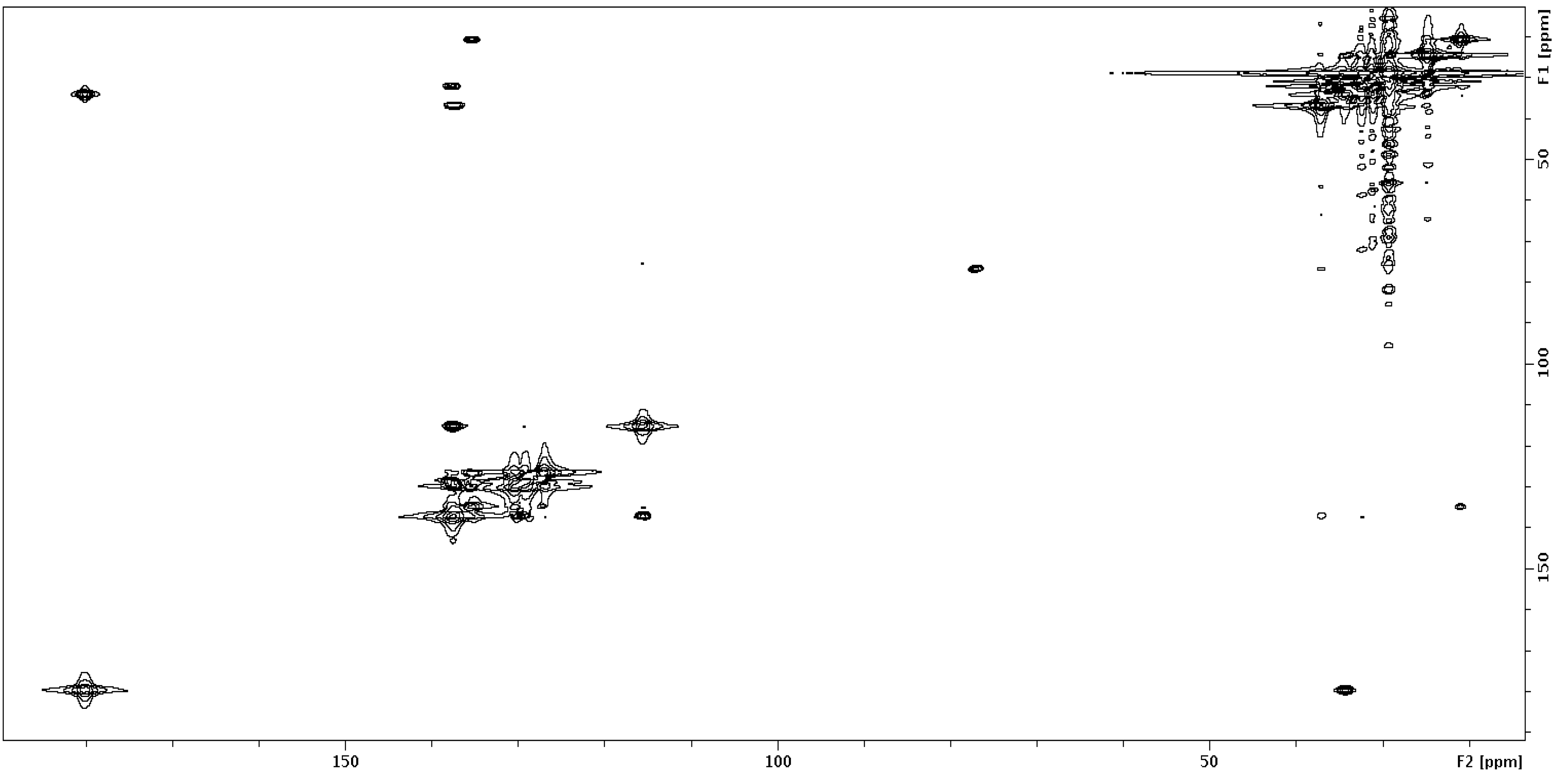
2.2. 13C–13C gCOSY
2.3. Biological Activity
| MRSA | MSSA | E. coli | P. aeruginosa | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 32 | 64 | 128 | 128 |
| 2 | 32 | 64 | 128 | 128 |
| 3 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 |
3. Experimental Section
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Biological Material
3.3. Sequencing
3.4. Fermentation, Extraction, and Isolation
3.5. Antibacterial Assay
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Files
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Deaths by Cause, Sex, and Mortality Stratum in WHO Regions, Estimates for 2002: World Health Report—2004; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004; p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, R.; Coast, J. The true cost of antimicrobial resistance. Br. Med. J. 2013, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Center for Disease Control and Prevention. Available online: http://www.cdc.gov/drugresistance/threat-report-2013/ (accessed on 13 December 2013).
- Boucher, H.W.; Talbot, G.H.; Bradley, J.S.; Edwards, J.E., Jr.; Gilbert, D.; Rice, L.B.; Scheld, M.; Spellberg, B.; Bartlett, J. Bad bugs, no drugs: No ESKAPE! An update from the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 48, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Stefani, S.; Chung, D.R.; Lindsay, J.A.; Friedrich, A.W.; Kearns, A.M.; Westh, H.; MacKenzie, F.M. Meticillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA): Global epidemiology and harmonisation of typing methods. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2012, 39, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köck, R.; Becker, K.; Cookson, B.; van Gemert-Pijnen, J.E.; Harbarth, S.; Kluytmans, J.; Mielke, M.; Peters, G.; Skov, R.L.; Struelens, M.J.; et al. Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA): Burden of disease and control challenges in Europe. Euro Surveill. 2010, 15, 19688–19696. [Google Scholar]
- Klevens, R.M.; Morrison, M.A.; Nadle, J.; Petit, S.; Gershman, K.; Ray, S.; Harrison, L.H.; Lynfield, R.; Dumyati, G.; Townes, J.M.; et al. Invasive methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections in the United States. JAMA 2007, 298, 1763–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Kraker, M.E.A.; Wolkewitz, M.; Davey, P.G.; Koller, W.; Berger, J.; Nagler, J.; Icket, C.; Kalenic, S.; Horvatic, J.; Seifert, H.; et al. Clinical impact of antimicrobial resistance in European hospitals: Excess mortality and length of hospital stay related to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus bloodstream infections. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 1598–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staudinger, H.; Steinhofer, A. Über hochpolymere verbindungen. 107. Mitteilung. Beiträge zur kenntnis der polystyrole. Justus Liebigs Ann. Chem. 1935, 517, 35–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayo, F.R. The dimerization of styrene. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1968, 90, 1289–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayer, W.A.; Muir, D.J.; Chakravarty, P. Phenolic and other metabolites of Phellinus pini, a fungus pathogenic to pine. Phytochemistry 1996, 42, 1321–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Name, W.G. The ascidians of the Bermuda Islands. Trans. Connecticut Acad. Sci. 1902, 11, 325–412. [Google Scholar]
- Iwata, F.; Sato, S.; Mukai, T.; Yamada, S.; Takeo, J.; Abe, A.; Okita, T.; Kawahara, H. Lorneic acids, trialkyl-substituted aromatic acids from a marine-derived actinomycete. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 2046–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenzel, S.C.; Bode, H.B. Novel polyene carboxylic acids from Streptomyces. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 1631–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehnaz, S.; Saleem, R.S.; Yameen, B.; Pianet, I.; Schnakenbur, G.; Pietraszkiewicz, H.; Valeriote, F.; Josten, M.; Sahl, H.G.; Franzblau, S.G.; et al. Lahorenoic acids A–C, ortho-dialkyl-substituted aromatic acids from the biocontrol strain Pseudomonas aurantiaca PB-St2. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raju, R.; Gromyko, O.; Fedorenko, V.; Luzhetskyy, A.; Müller, R. Lorneic acids C and D, new trialkyl-substituted aromatic acids isolated from a terrestrial Streptomyces sp. J. Antibiot. 2013, 66, 347–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.H.; Fleming, I. Spectroscopic Methods in Organic Chemistry, 4th ed.; McGraw-Hill Book Company Limited: London, UK, 1987; pp. 143–146. [Google Scholar]
- Bugni, T.S.; Bernan, V.S.; Greenstein, M.; Janso, J.E.; Maiese, W.M.; Mayne, C.L.; Ireland, C.M. Brocaenols A–C: Novel polyketides from a marine-derived Penicillium brocae. J. Org. Chem. 2003, 68, 2014–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, S.W.; Köck, M. NMR studies of phakellins and isophakellins. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 1524–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bifulco, G.; Riccio, R.; Martin, G.E.; Buevich, A.V.; Williamson, R.T. Quantum chemical calculations of 1JCC coupling constants for the stereochemical determination of organic compounds. Org. Lett. 2013, 15, 654–657. [Google Scholar]
- Harrison, P.J.; Waters, R.E.; Taylor, F.J.R. A broad spectrum artificial seawater medium for coastal and open ocean phytoplankton. J. Phycol. 1980, 16, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reasoner, D.J.; Geldreich, E.E. A new medium for the enumeration and subculture of bacteria from potable water. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1985, 49, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Maldonado, L.A.; Fragoso-Yáñez, D.; Pérez-García, A.; Rosellón-Druker, J.; Quintana, E.T. Antinobacterial diversity from marine sediments collected in Mexico. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2009, 95, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyche, T.P.; Hou, Y.; Braun, D.; Cohen, H.C.; Xiong, M.P.; Bugni, T.S. First natural analogs of the cytotoxic thiodepsipeptide thiocoraline A from a marine Verrucosispora sp. J. Org. Chem. 2011, 76, 6542–6547. [Google Scholar]
- National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards. Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria that Grow Aerobically, 7th ed.NCCLS: Villanova, PA, USA, 2006; Approved standard M7-A7.
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Ellis, G.A.; Wyche, T.P.; Fry, C.G.; Braun, D.R.; Bugni, T.S. Solwaric Acids A and B, Antibacterial Aromatic Acids from a Marine Solwaraspora sp. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 1013-1022. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12021013
Ellis GA, Wyche TP, Fry CG, Braun DR, Bugni TS. Solwaric Acids A and B, Antibacterial Aromatic Acids from a Marine Solwaraspora sp. Marine Drugs. 2014; 12(2):1013-1022. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12021013
Chicago/Turabian StyleEllis, Gregory A., Thomas P. Wyche, Charles G. Fry, Doug R. Braun, and Tim S. Bugni. 2014. "Solwaric Acids A and B, Antibacterial Aromatic Acids from a Marine Solwaraspora sp." Marine Drugs 12, no. 2: 1013-1022. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12021013
APA StyleEllis, G. A., Wyche, T. P., Fry, C. G., Braun, D. R., & Bugni, T. S. (2014). Solwaric Acids A and B, Antibacterial Aromatic Acids from a Marine Solwaraspora sp. Marine Drugs, 12(2), 1013-1022. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12021013