Marine Nucleosides: Structure, Bioactivity, Synthesis and Biosynthesis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
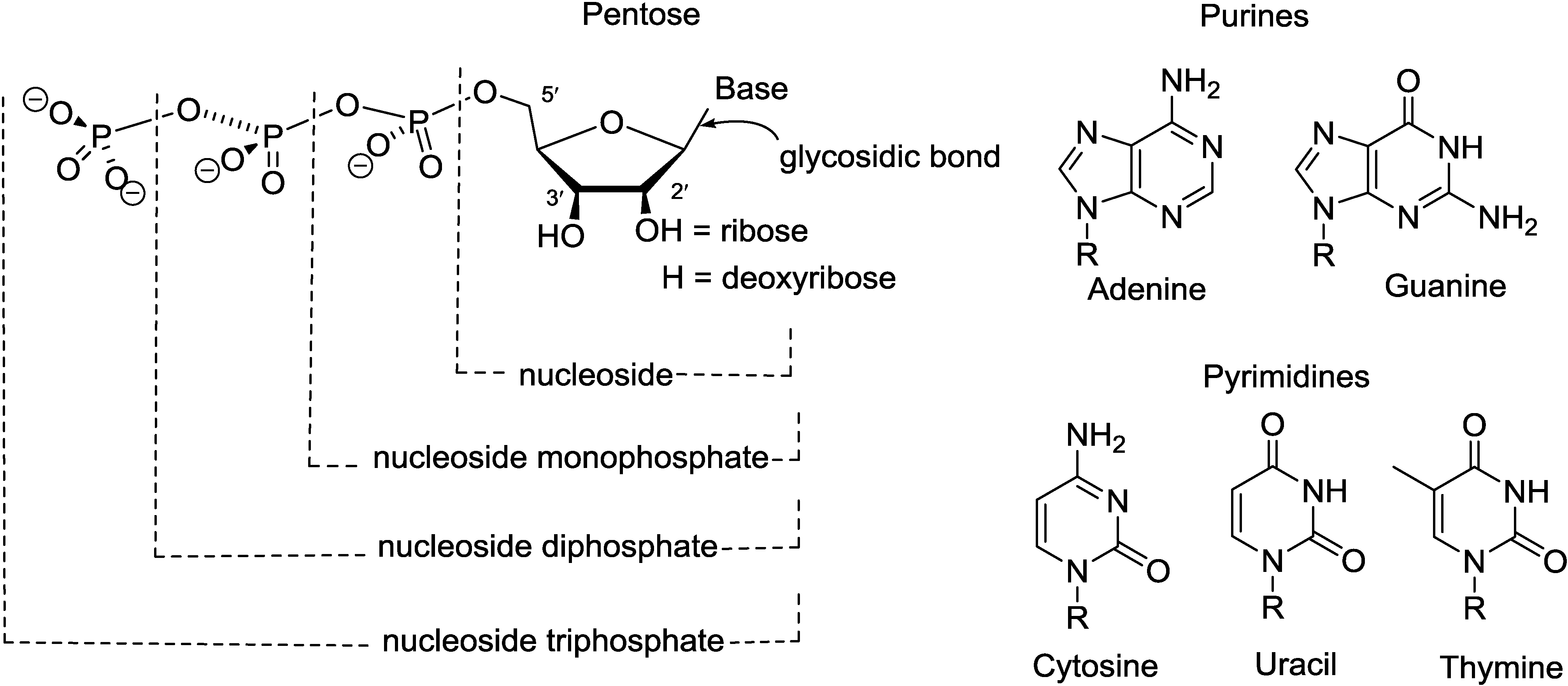
2. Purine Nucleosides
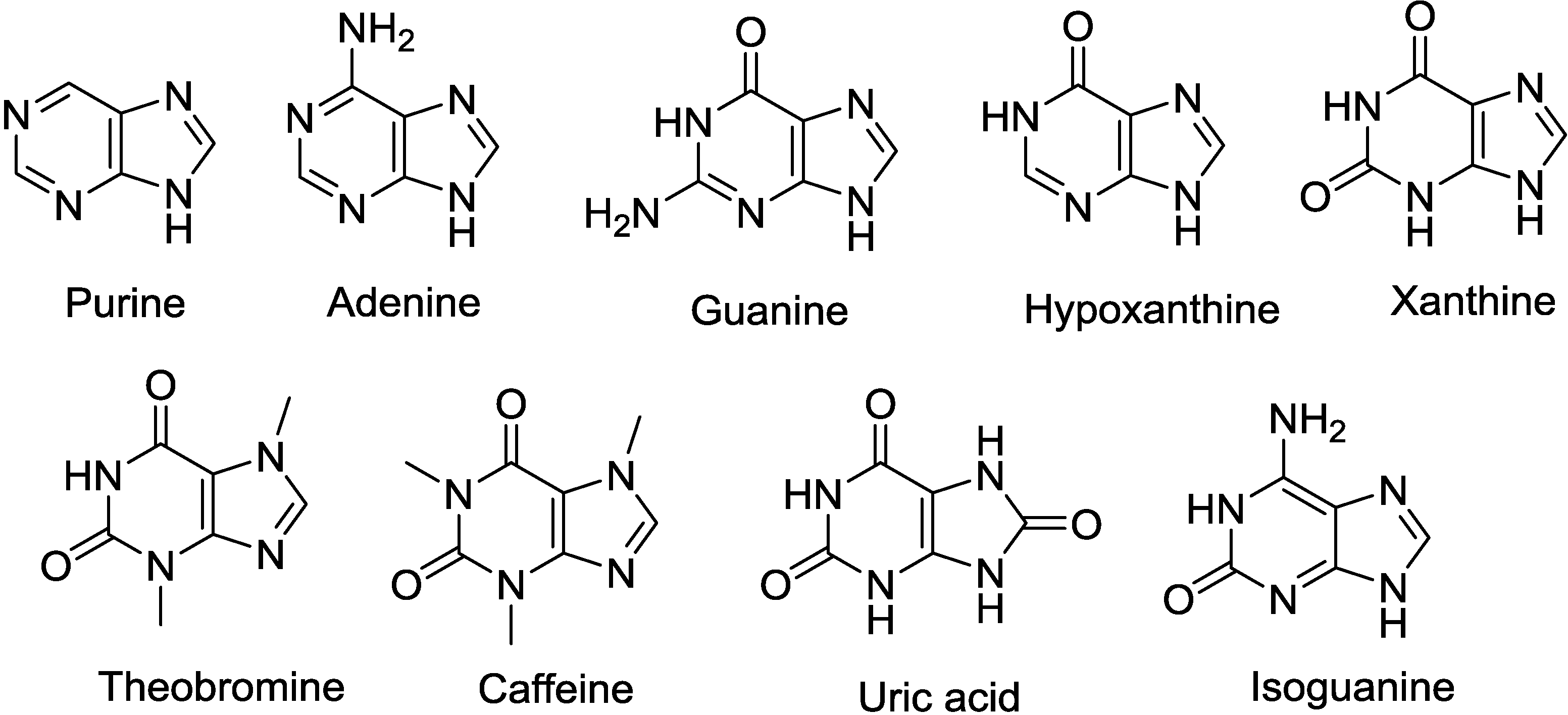
2.1. Purine-d-Arabinosides

2.2. Purine-2′-Deoxyribosides

2.3. Purine-1-β-d-Ribosides
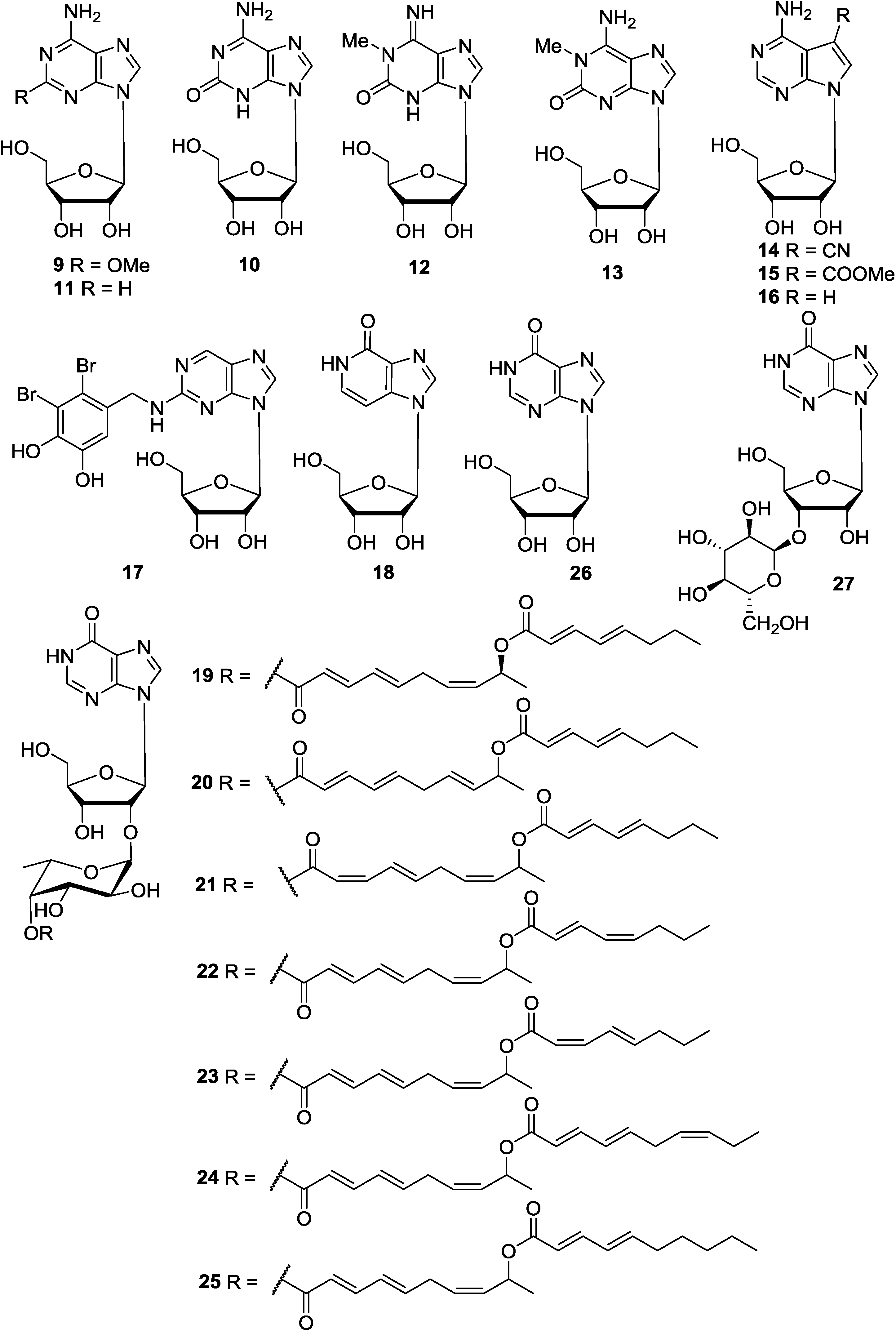
2.4. Purine Nucleoside Analogues
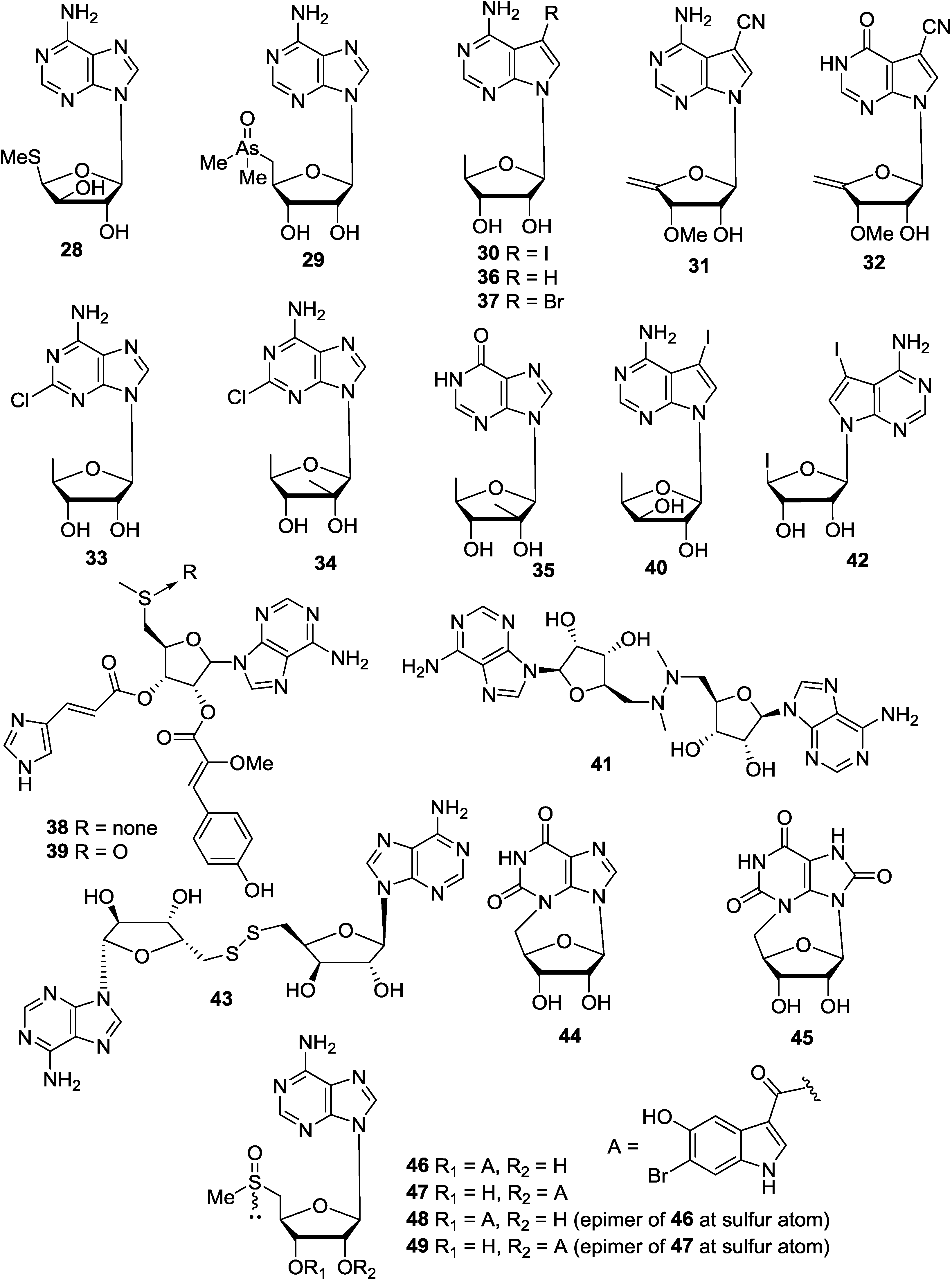
3. Pyrimidine Nucleosides
3.1. Pyrimidine-d-Arabinosides
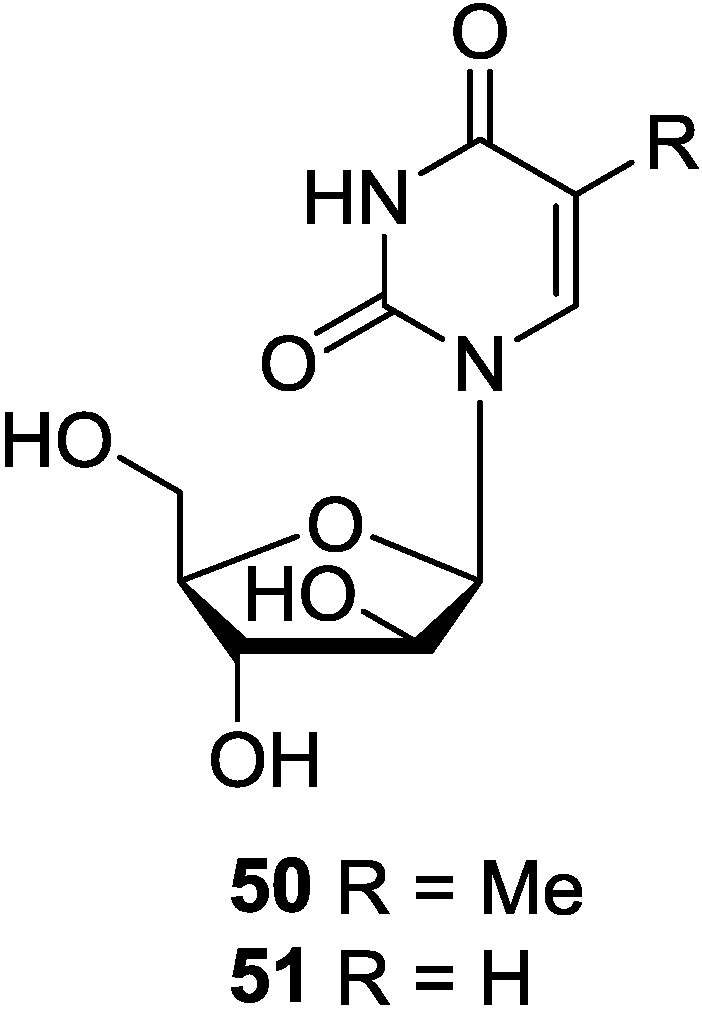
3.2. Pyrimidine-2′-Deoxyribosides
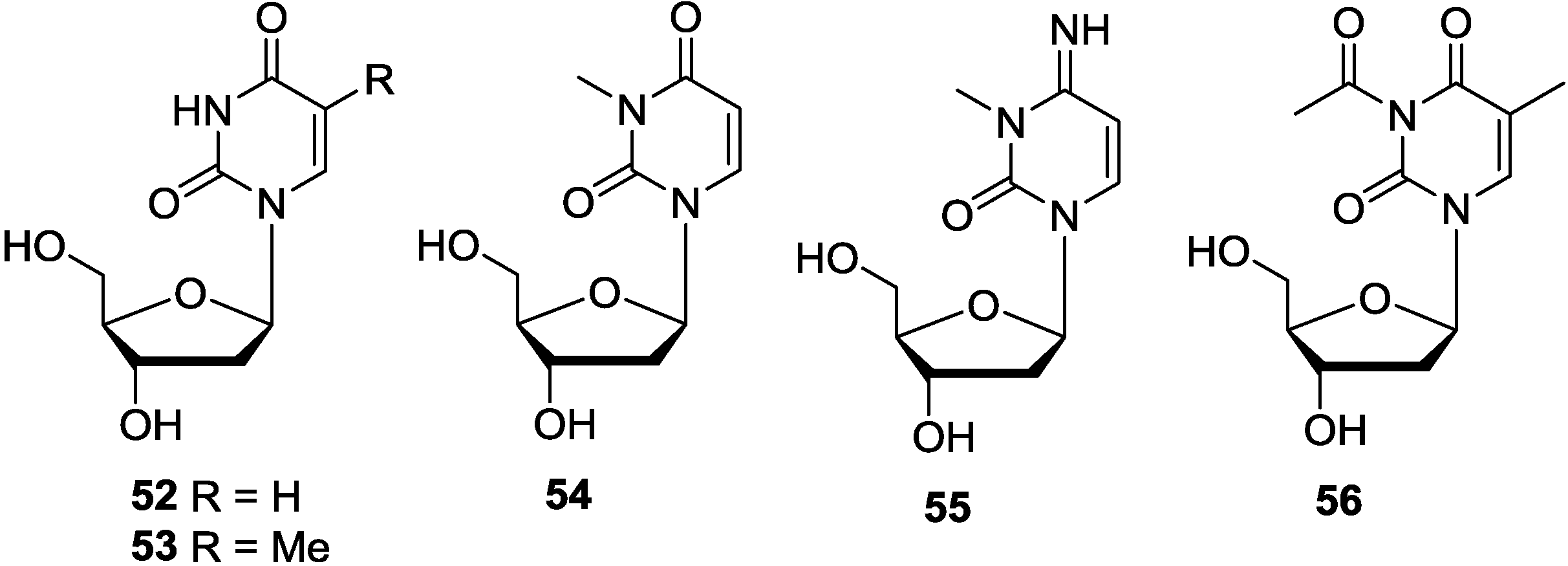
3.3. Pyrimidine-1-β-d-Ribosides

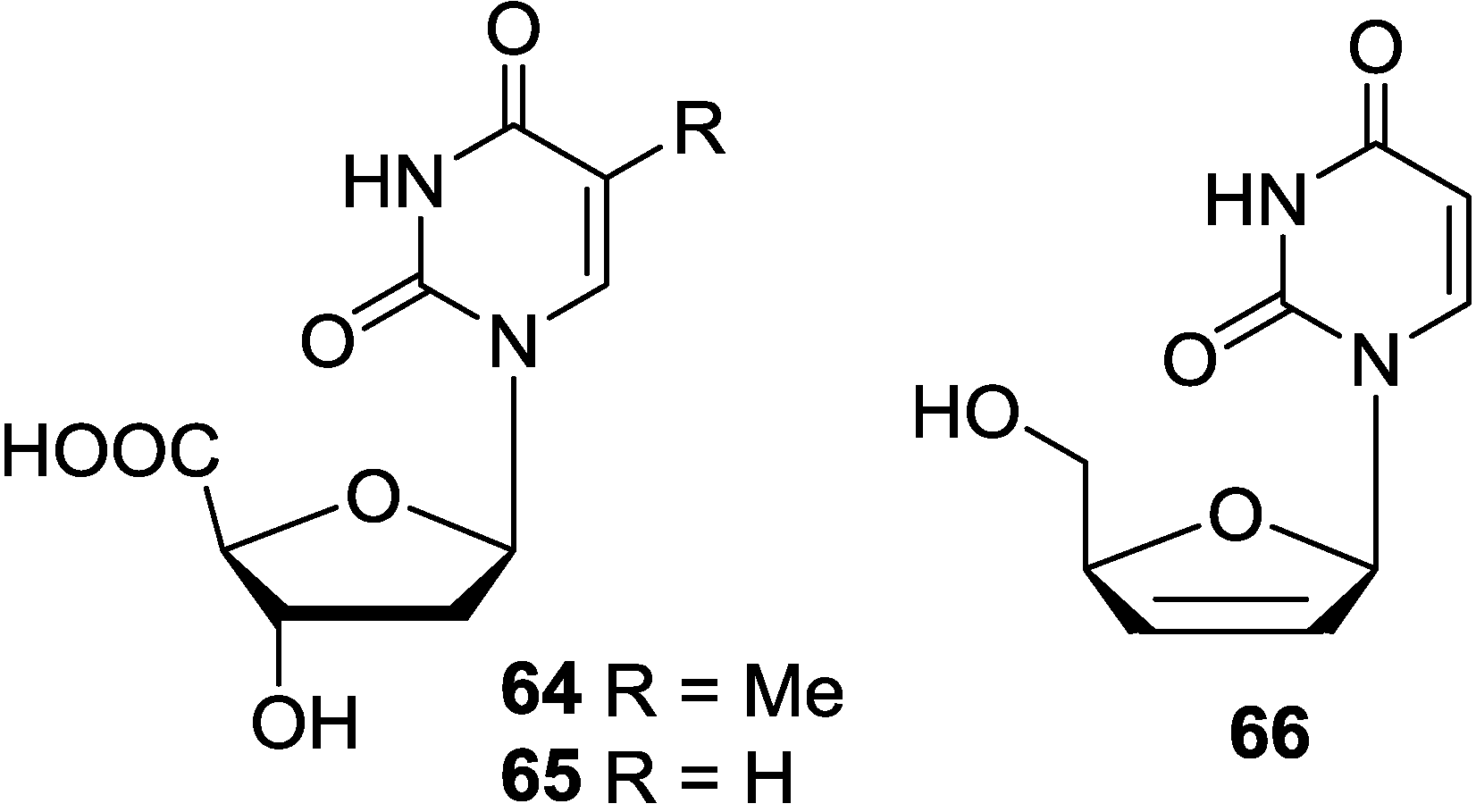
3.4. Analogues of Pyrimidine Nucleosides
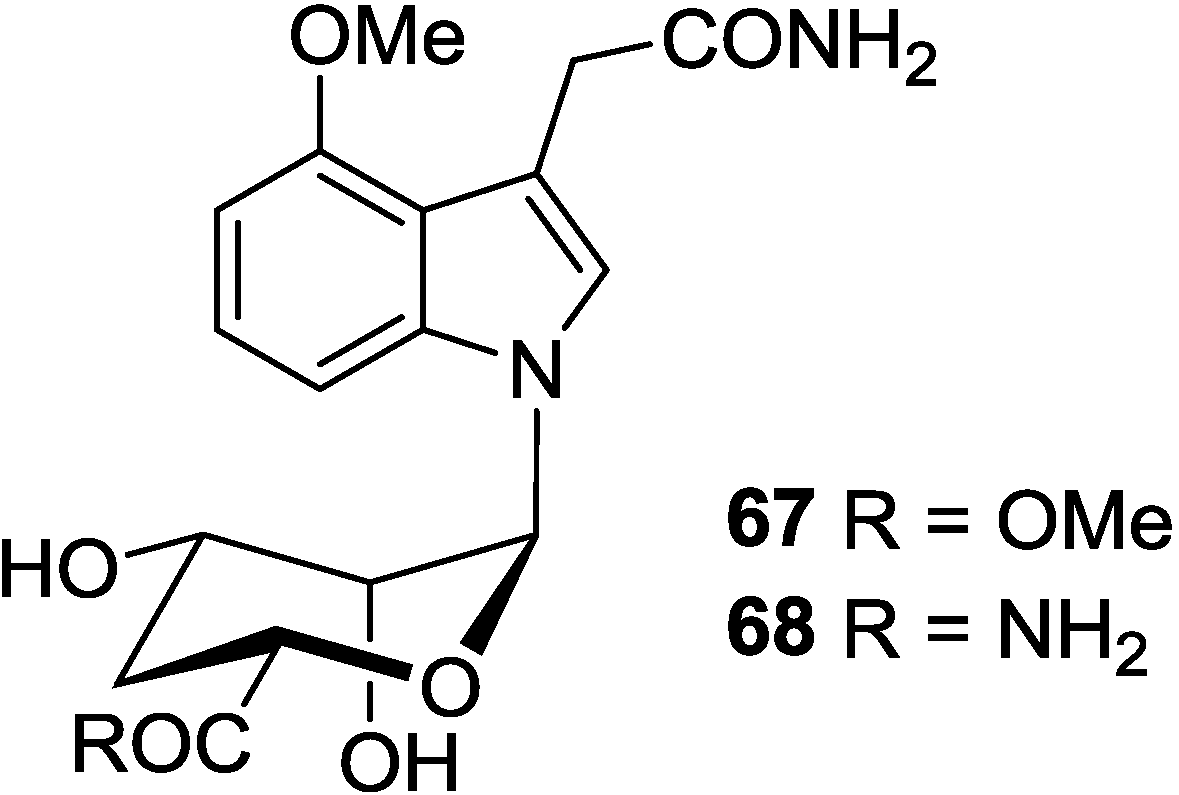
4. Indole Nucleosides
5. Synthesis
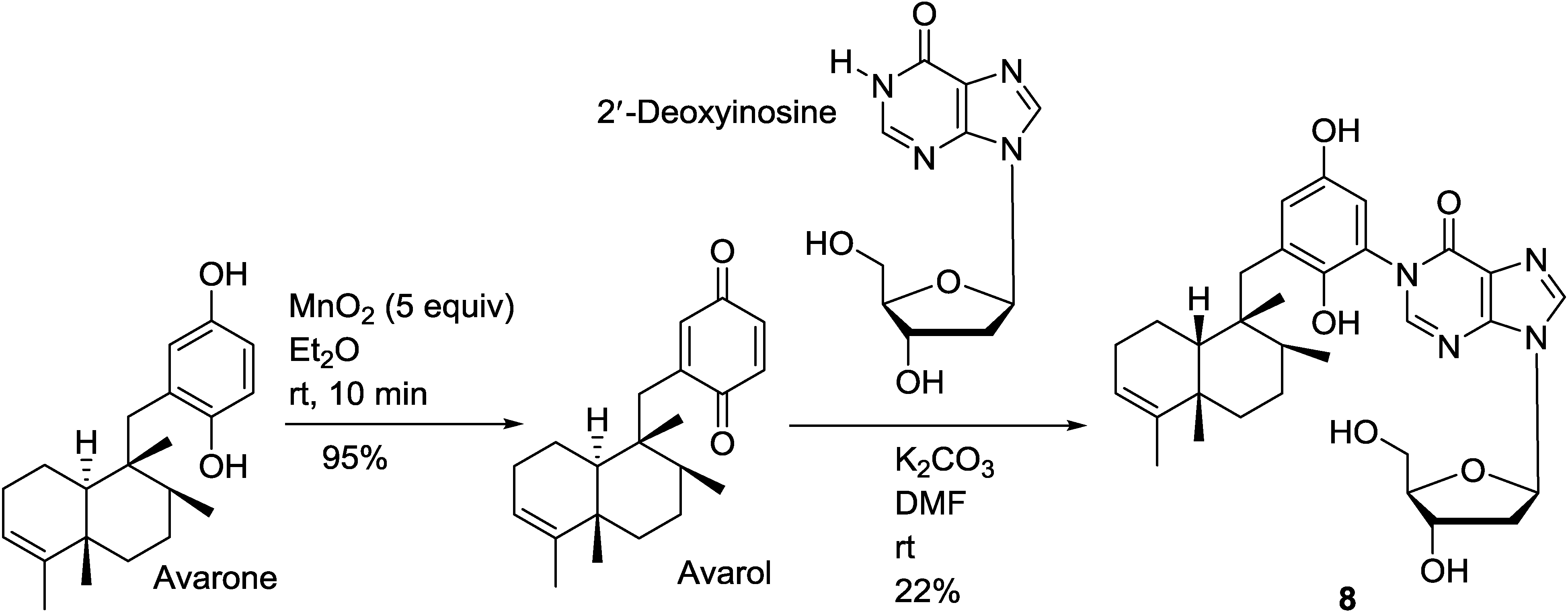
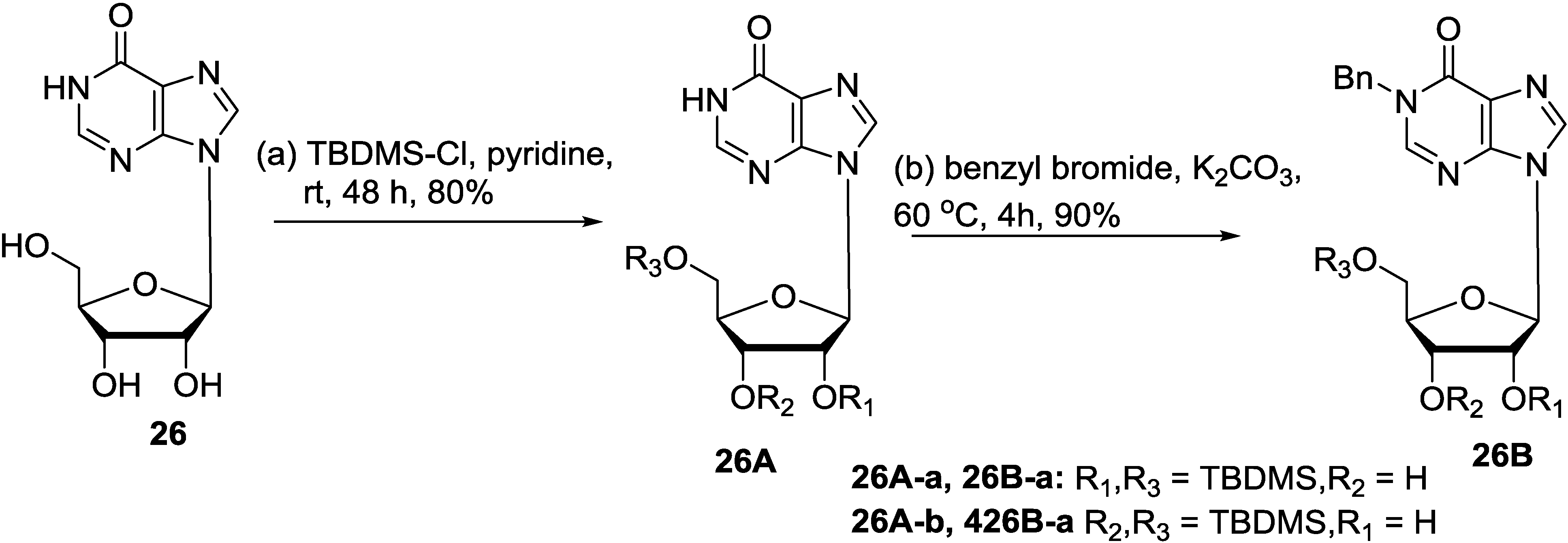
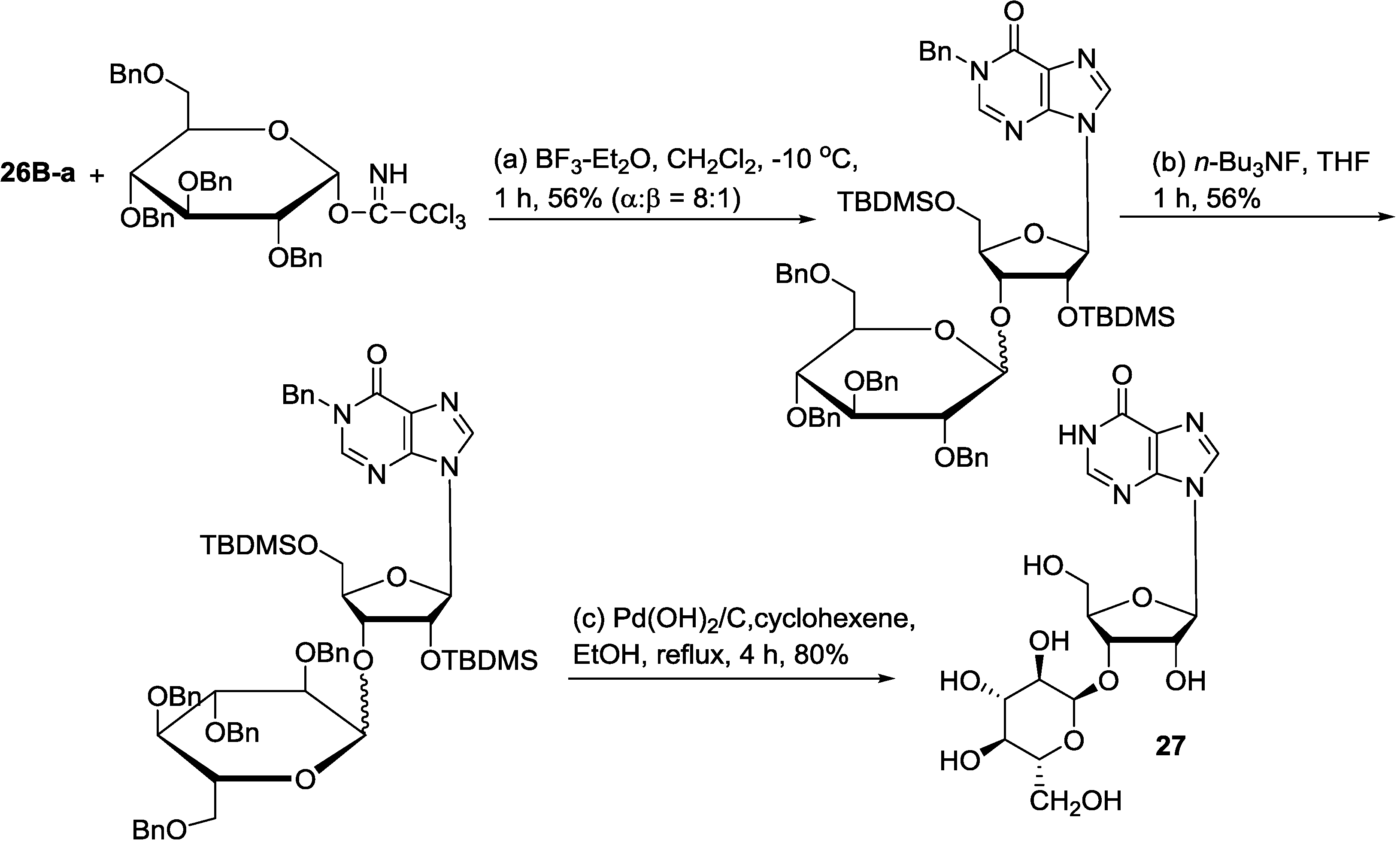

6. Biosynthetic Pathways
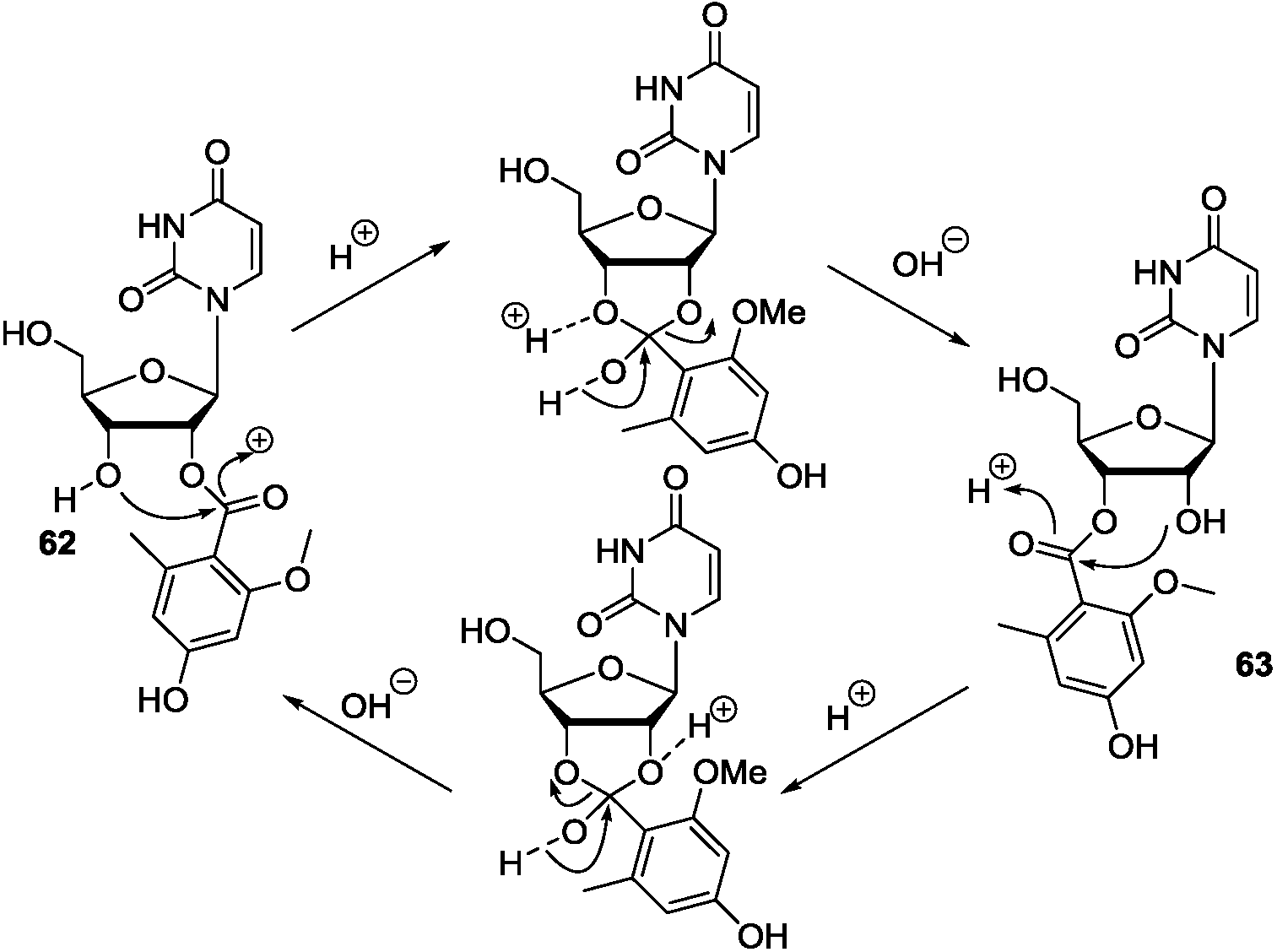
7. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kukhanova, M.K. Anti-HIV nucleoside drugs: A retrospective view into the future. Mol. Biol. 2012, 46, 768–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damaraju, V.L.; Damaraju, S.; Young, J.D.; Baldwin, S.A.; Mackey, J.; Sawyer, M.B.; Cass, C.E. Nucleoside anticancer drugs: The role of nucleoside transporters in resistance to cancer chemotherapy. Oncogene 2003, 22, 7524–7536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooperwood, J.S.; Gumina, G.; Boudinot, F.D.; Chu, C.K. Nucleoside and Nucleotide Prodrugs. In Recent Advances in Nucleosides: Chemistry and Chemotherapy; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2002; pp. 91–147. [Google Scholar]
- Huryn, D.M.; Okabe, M. Aids-driven nucleoside chemistry. Chem. Rev. 1992, 92, 1745–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrofoglio, L.A.; Gillaizeau, I.; Saito, Y. Palladium-assisted routes to nucleosides. Chem. Rev. 2003, 103, 1875–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikhailopulo, I.A.; Miroshnikov, A.I. New trends in nucleoside biotechnology. Acta Nat. 2010, 2, 36–58. [Google Scholar]
- Faulkner, D.J. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 1993, 10, 497–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isono, K. Nucleoside antibiotics—Structure, biologicalactivity, and biosynthesis. J. Antibiot. 1988, 41, 1711–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isono, K. Current progress on nucleoside antibiotics. Pharmacol. Ther. 1991, 52, 269–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Advanced preclinical and clinical trials of natural products and related compounds from marine sources. Curr. Med. Chem. 2004, 11, 1693–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Marine natural products and related compounds in clinical and advanced preclinical trials. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 1216–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proksch, P.; Edrada-Ebel, R.A.; Ebel, R. Drugs from the sea—Opportunities and obstacles. Mar. Drugs 2003, 1, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kijjoa, A.; Sawangwong, P. Drugs and cosmetics from the sea. Mar. Drugs 2004, 2, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmann, W.; Feeney, R.J. The isolation of a new thymine pentoside from sponges. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1950, 72, 2809–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhakuni, D.S.; Rawat, D.S. Bioactive Marine Natural Products; Springer: New Delhi, India, 2005; pp. 208–234. [Google Scholar]
- Cimino, G.; de Rosa, S.; de Stefano, S. Antiviral agents from a gorgonian, Eunicella cavolini. Experientia 1984, 40, 339–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.W.; Benitez, A.; Goodman, L.; Baker, B.R. Potential anticancer agents .40. Synthesis of the β-anomer of 9-(d-arabinofuranosyl)-adenine. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1960, 82, 2648–2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ch’ien, L.T.; Cannon, N.J.; Charamella, L.J.; Dismukes, W.E.; Whitley, R.J.; Buchanan, R.A.; Alford, C.A. Effect of adenine arabinoside on severe Herpesvirus hominis infections in man. J. Infect. Dis. 2004, 190, 1362–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsimberidou, A.M.; Keating, M.J.; Giles, F.J.; Wierda, W.G.; Ferrajoli, A.; Lerner, S.; Beran, M.; Andreeff, M.; Kantarjian, H.M.; O’Brien, S. Fludarabine and mitoxantrone for patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Cancer Am. Cancer Soc. 2004, 100, 2583–2591. [Google Scholar]
- Plosker, G.L.; Figgitt, D.P. Oral fludarabine. Drugs 2003, 63, 2317–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitley, R.; Aford, C.; Hess, F.; Buchanan, R. Vidarbine: A preliminary review of its pharmacological properties and therapeutic use. Drugs 1980, 20, 267–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farmer, P.B.; Suhadoln, R.J. Nucleoside antibiotics—Biosynthesis of arabinofuranosyladenine by Streptomyces antibioticus. Biochemistry 1972, 11, 911–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farmer, P.B.; Uematsu, T.; Hogenkam, H.P.; Suhadoln, R.J. Nucleoside antibiotics—Epimerization of carbon 2′ of adenosine during biosynthesis of 9-β-d-arabinofuranosyladenine by Streptomyces antibioticus. J. Biol. Chem. 1973, 248, 1844–1847. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zemlicka, J. Unusual analogues of nucleosides: Chemistry and biological activity. In Recent Advances in Nucleosides: Chemistry and Chemotherapy; Chu, C.K., Ed.; Elsevier Science B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2002; pp. 327–357. [Google Scholar]
- Weinheimer, A.J.; Chang, C.W.; Matson, J.A.; Kaul, P.N. Marine cardioactive agents—Adenosine and 2′-deoxyadenosine from Dasychalina cyathina. Lloydia 1978, 41, 488–490. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huang, R.M.; Zhou, X.F.; Peng, Y.; Yang, X.W.; Xu, T.H.; Liu, Y.H. Nucleosides from the marine sponge Callyspongia sp. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2011, 46, 1010–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmann, W.; Burke, D.C. Contributions to the study of marine products. The nucleosides of sponges .4. Spongosine. J. Org. Chem. 1956, 21, 226–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Searle, P.A.; Molinski, T.F. Isolation of spongosine and 2′-deoxyspongosine from a Western Australian sponge of the order Hadromerida (Tethyidae). J. Nat. Prod. 1994, 57, 1452–1454. [Google Scholar]
- Kondo, K.; Shigemori, H.; Ishibashi, M.; Kobayashi, J. Aplysidine, a new nucleoside from the Okinawan marine sponge Aplysina sp. Tetrahedron 1992, 48, 7145–7148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Koning, H.P.; Bridges, D.J.; Burchmore, R.J. Purine and pyrimidine transport in pathogenic protozoa: From biology to therapy. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2005, 29, 987–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.Q.; Deng, Z.W.; Ii, J.; Fu, H.Z.; Lin, H.W. Chemical constituents from starfish Asterias rollestoni. J. Chin. Pharm. Sci. 2004, 13, 81–86. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Dong, J.; Zhou, X.F.; Lee, K.J.; Huang, R.M.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Y.H. Nucleosides from the marine sponge Haliclona sp. Z. Naturforsch C 2009, 64, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Diaz-Marrero, A.R.; Austin, P.; van Soest, R.; Matainaho, T.; Roskelley, C.D.; Roberge, M.; Andersen, R.J. Avinosol, a meroterpenoid-nucleoside conjugate with antiinvasion activity isolated from the marine sponge Dysidea sp. Org. Lett. 2006, 8, 3749–3752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergmann, W.; Feeney, R.J. Contributions to the study of marine products: The nucleosides of sponges. J. Org. Chem. 1951, 16, 981–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.R.; Tang, H.F.; Feng, J.T.; Li, Y.S.; Lin, H.W.; Fan, X.P.; Zhang, X. Neritinaceramides A-E, new ceramides from the marine bryozoan Bugula neritina inhabiting South China Sea and their cytotoxicity. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 1987–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergmann, W.; Stempien, M.F. Contributions to the study of marine products: The nucleosides of sponges. 5. The synthesis of spongosine. J. Org. Chem. 1957, 22, 1575–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaeffer, H.J.; Thomas, H.J. Synthesis of potential anticancer agents. 15. Ribonucleosides of 2-substituted purines. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1958, 80, 4896–4899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, A.; Nomoto, Y.; Ueda, T. Nucleosides and nucleotides: Synthesis of 2-cyanoadenosines and 8-cyanoadenosines and their derivatives. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1979, 27, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stimac, A.; Leban, I.; Kobe, J. An efficient stereospecific method for the synthesis of 8-aza-3-deazaguanine nucleosides from glycosyl azides. Synlett 1999, 7, 1069–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuhrman, F.A.; Fuhrman, G.J.; Nachman, R.J.; Mosher, H.S. Isoguanosine—Isolation from an animal. Science 1981, 212, 557–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ewing, P.L.; Schlenk, F.; Emerson, G.A. Comparison of smooth muscle effects of crotonoside (isoguanosine) and adenosine. J. Pharm. Exp. Ther. 1949, 97, 379–383. [Google Scholar]
- Kaul, P.N. Biomedical potential of the sea. Pure Appl. Chem. 1982, 54, 1963–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohisalo, J.J. Regulatory functions of adenosine. Med. Biol. 1987, 65, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Deckert, J.; Morgan, P.F.; Marangos, P.J. Adenosine uptake site heterogeneity in the mammalian CNS—Uptake Inhibitors as probes and potential neuropharmaceuticals. Life Sci. 1988, 42, 1331–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinn, R.J.; Gregson, R.P.; Cook, A.F.; Bartlett, R.T. Isolation and synthesis of 1-methylisoguanosine, a potent pharmacologically active constituent from the marine sponge Tedania digitata. Tetrahedron Lett. 1980, 21, 567–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bairdlambert, J.; Marwood, J.F.; Davies, L.P.; Taylor, K.M. 1-Methylisoguanosine—Orally active marine natural product with skeletal-muscle and cardiovascular effects. Life Sci. 1980, 26, 1069–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, P.L.; Yen, M.H.; Shyu, W.S.; Chern, J.W. Doridosine derivatives—Binding at adenosine receptors and in vivo effects. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1993, 243, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuhrman, F.A.; Fuhrman, G.J.; Kim, Y.H.; Pavelka, L.A.; Mosher, H.S. Doridosine—New hypotensive N-methylpurine riboside from the nudibranch Anisodoris nobilis. Science 1980, 207, 193–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.H.; Nachman, R.J.; Pavelka, L.; Mosher, H.S.; Fuhrman, F.A.; Fuhrman, G.J. Doridosine, 1-methylisoguanosine, from Anisodoris nobilis—Structure, pharmacological properties and synthesis. J. Nat. Prod. 1981, 44, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, L.P.; Taylor, K.M.; Gregson, R.P.; Quinn, R.J. Stimulation of guinea pig brain adenylate cyclase by adenosine analogs with potent pharmacological activity in vivo. Life Sci. 1980, 26, 1079–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, A.F.; Bartlett, R.T.; Gregson, R.P.; Quinn, R.J. 1-Methylisoguanosine, a pharmacologically active agent from a marine sponge. J. Org. Chem. 1980, 45, 4020–4025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grozinger, K.; Freter, K.R.; Farina, P.; Gladczuk, A. Synthesis of 7-substituted and 9-substituted 1-methylisoguanines from 4(5)-amino-5(4)-cyanoimidazole. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 1983, 18, 221–226. [Google Scholar]
- Jamieson, D.; Davis, P. Inhibition of nerve-mediated contractions in isolated guinea pig ileum by 1-methylisoguanosine, a novel purine from a sponge. Eur. J. Pharm. 1980, 67, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartlett, R.T.; Cook, A.F.; Holman, M.J.; Mccomas, W.W.; Nowoswait, E.F.; Poonian, M.S.; Bairdlambert, J.A.; Baldo, B.A.; Marwood, J.F. Synthesis and pharmacological evaluation of a deries of snalogs of 1-methylisoguanosine. J. Med. Chem. 1981, 24, 947–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohkuma, K. Chemical structure of toyocamycin. J. Antibiot. 1960, 13, 361–361. [Google Scholar]
- Bergstrom, D.E.; Brattesani, A.J.; Ogawa, M.K.; Schweickert, M.J. Pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine nucleoside antibiotic analogs—Synthesis viaorganopalladium intermediates derived from 5-mercuritubercidin. J. Org. Chem. 1981, 46, 1423–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabriskie, T.M.; Ireland, C.M. The isolation and structure of modified bioactive nucleosides from Jaspis johnstoni. J. Nat. Prod. 1989, 52, 1353–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biabani, M.F.; Gunasekera, S.P.; Longley, R.E.; Wright, A.E.; Pomponi, S.A. Tubercidin, a cytotoxic agent from the marine sponge Caulospongia biflabellata. Pharm. Biol. 2002, 40, 302–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.L.; Ma, M.; Wang, S.J.; Li, S.; Cao, P.; Yang, Y.C.; Lu, Y.; Shi, J.G.; Xu, N.J.; Fan, X.; et al. Bromophenols coupled with derivatives of amino acids and nucleosides from the red alga Rhodomela confervoides. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 691–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minakawa, N.; Matsuda, A. Nucleosides and nucleotides: Convenient syntheses of 3-deazaadenosine, 3-deazaguanosine, and 3-deazainosine via ring-closure of 5-ethynyl-1-β-d-ribofuranosylimidazole-4-carboxamide or carbonitrile. Tetrahedron 1993, 49, 557–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AbouHussein, Dina. R.; Diaa, J.B.; Youssef, T.A. Nucleoside constituents of the Egyptian tunicate Eudistoma laysani. Nat. Prod. Sci. 2007, 13, 229–233. [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi, J.; Doi, Y.; Ishibashi, M. Shimofuridin A, a nucleoside derivative embracing an acylfucopyranoside unit isolated from the Okinawan marine tunicate Aplidium multiplicatum. J. Org. Chem. 1994, 59, 255–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapp, S.; Gore, V.K. Synthesis of the shimofuridin nucleoside disaccharide. J. Org. Chem. 1996, 61, 6744–6747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doi, Y.; Ishibashi, M.; Kobayashi, J. Isolation and structure of shimofuridins B–G from the Okinawan marine tunicate Aplidium multiplicatum. Tetrahedron 1994, 50, 8651–8656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogi, T.; Margiastuti, P.; Teruya, T.; Taira, J.; Suenaga, K.; Ueda, K. Isolation of C-11 cyclopentenones from two didemnidspecies, Lissoclinum sp. and Diplosoma sp. Mar. Drugs 2009, 7, 816–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.H.; Yoo, S.M.; Park, I.S.; Kim, Y.H. A new inosine disaccharide from the crustacean Ligia exotica: Isolation and structure elucidation by total synthesis. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 1188–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cimino, G.; Crispino, A.; Destefano, S.; Gavagnin, M.; Sodano, G. A naturally-occurring analog of methylthioadenosine (MTA) from the nudibranch mollusk Doris verrucosa. Experientia 1986, 42, 1301–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgome, J.A.; Shortnacy, A.T.; Thomas, H.J. Analogs of 5′-deoxy-5′-(methylthio)adenosine. J. Med. Chem. 1974, 17, 1197–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francesconi, K.A.; Stick, R.V.; Edmonds, J.S. An arsenic-containing nucleoside from the kidney of the giant clam, Tridacna maxima. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Comm. 1991, 14, 928–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazlauskas, R.; Murphy, P.T.; Wells, R.J.; Baird-Lambert, J.A.; Jamieson, D.D. Halogenated pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine nucleosides from marine organisms. Aust. J. Chem. 1983, 36, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, Y.; Fusetani, N.; Matsunaga, S.; Hashimoto, K. Bioactive marine metabolites, Mycalisine A and mycalisine B, novel nucleosides which inhibit cell-division of fertilized starfish eggs, from the marine sponge Mycale sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 1985, 26, 3483–3486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichiba, T.; Nakao, Y.; Scheuer, P.J.; Sata, N.U.; Kellyborges, M. Kumusine, a chloroadenine riboside from a sponge, Theonella sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 1995, 36, 3977–3980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Searle, P.A.; Molinski, T.F. Trachycladine A and trachycladine B—2′-C-methyl-5′-deoxyribofuranosyl nucleosides from the marine sponge Trachycladus laevispirulifer. J. Org. Chem. 1995, 60, 4296–4298. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell, S.S.; Pomerantz, S.C.; Concepcion, G.P.; Ireland, C.M. Tubercidin analogs from the ascidian Didemnum voeltzkowi. J. Nat. Prod. 1996, 59, 1000–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kehraus, S.; Gorzalka, S.; Hallmen, C.; Iqbal, J.; Muller, C.E.; Wright, A.D.; Wiese, M.; Konig, G.M. Novel amino acid derived natural products from the ascidian Atriolum robustum: Identification and pharmacological characterization of a unique adenosine derivative. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 2243–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margiastuti, P.; Ogi, T.; Teruya, T.; Taira, J.; Suenaga, K.; Ueda, K. An unusual iodinated 5′-deoxyxylofuranosyl nucleoside from an Okinawan ascidian, Diplosoma sp. Chem. Lett. 2008, 37, 448–449, correction in 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, M.A. A new adenosyl-alkaloid from Ostrea rivularis. Nat. Prod. Res. 2006, 20, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, C.S.; Gunaherath, G.M. K.B.; Piggott, A.M.; Khalil, Z.; Conte, M.; Capon, R.J. 9-(5′-Deoxy-5′-thio-β-d-xylofuranosyl)adenine disulfide from the Southern Australian marine sponge Trachycladus laevispirulifer: The first natural occurrence of a nucleoside disulfide. Aust. J. Chem. 2010, 63, 873–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capon, R.J.; Trotter, N.S. N3,5′-cycloxanthosine, the first natural occurrence of a cyclonucleoside. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 1689–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menna, M.; Aiello, A.; D’Aniello, F.; Fattorusso, E.; Imperatore, C.; Luciano, P.; Vitalone, R. Further investigation of the mediterranean sponge Axinella polypoides: Isolation of a new cyclonucleoside and a new betaine. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 2509–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.L.; La Kim, E.; Wang, H.; Hong, J.; Shin, S.; Lee, C.K.; Jung, J.H. Epimeric methylsulfinyladenosine derivatives from the marine ascidian Herdmania momus. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 4701–4704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aswell, J.F.; Allen, G.P.; Jamieson, A.T.; Campbell, D.E.; Gentry, G.A. Antiviral activity of arabinosylthymine in herpesviral replication: Mechanism of action in vivo and in vitro. Antimicrob. Agent Chemother. 1977, 12, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.L.; Iltis, J.P.; Rapp, F. Differential effect of arabinofuranosylthymine of the replication of human herpesviruses. J. Virol. 1977, 23, 679–684. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bergmann, W.; Burke, D.C. Contributions to the study of marine products: The nucleosides of sponges .3. Spongothymidine and spongouridine. J. Org. Chem. 1955, 20, 1501–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utagawa, T.; Morisawa, H.; Miyoshi, T.; Yoshinaga, F.; Yamazaki, A.; Mitsugi, K. Novel and simple method for the preparation of adenine arabinoside by bacterial transglycosylation reaction. FEBS Lett. 1980, 109, 261–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tono, H.; Cohen, S.S. Activity of nucleoside phosphorylase on 1-β-d-arabinosyluracil within Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem. 1962, 237, 1271–1282. [Google Scholar]
- Declercq, E.; Krajewska, E.; Descamps, J.; Torrence, P.F. Anti-herpes activity of deoxythymidine analogs—Specific dependence on virus-induced deoxythymidine kinase. Mol. Pharmacol. 1977, 13, 980–984. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Komori, T.; Sanechika, Y.J.; Ito, Y.S.; Matsuo, J.J.; Nohara, T.; Kawasaki, T.; Schulten, H.R. Biologisch aktive glykoside aus Asteroidea, I. Strukturen eines neuen cerebrosidgemischs und von nucleosiden aus dem seestern Acanthaster planci. Leibigs Ann. Chem. 1980, 1980, 653–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lidgren, G.; Bohlin, L.; Christophersen, C. Studies of Swedish marine organisms, biologically active compounds from the marine sponge Geodia baretti. J. Nat. Prod. 1988, 51, 1277–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Li, Q.L.; Ji, N.Y.; Liu, B.; Zhang, W.; Cao, X.P. Deoxyuridines from the marine sponge associated actinomycete Streptomyces microflavus. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 690–695. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, A.F.; Wu, M.H.; Wu, Y.C.; Dai, C.F.; Sheu, J.H. Metabolites with cytotoxic activity from the Formosan soft coral Cladiella australis. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2006, 53, 489–494. [Google Scholar]
- Ilan, E.Z.; Torres, M.R.; Prudhomme, J.; Le Roch, K.; Jensen, P.R.; Fenical, W. Farnesides A and B, sesquiterpenoid nucleoside ethers from a marine-rerived Streptomyces sp. strain CNT-372 from Fiji. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 1815–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Fu, X.M.; Kong, C.J.; Wang, C.Y. Nucleoside derivatives from the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus versicolor. Nat. Prod. Res. 2014, 28, 895–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicola, D.; Antonio, G.; Françoise, L.; Francesco, P. 2′-Deoxynucleoside uronic acids from the ascidian Aplidium (= Amaroucium) fuscum. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B 1986, 84, 11–13. [Google Scholar]
- Schumacher, R.W.; Harrigan, B.L.; Davidson, B.S. Kahakamides A and B, new neosidomycin metabolites from a marine-derived actinomycete. Tetrahedron Lett. 2001, 42, 5133–5135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davoll, J.; Lythgoe, B.; Todd, A.R. Experiments on the synthesis of purine nucleosides: A synthesis of guanosine. J. Chem. Soc. 1948, 1685–1687. [Google Scholar]
- Ling, T.T.; Xiang, A.X.; Theodorakis, E.A. Enantioselective total synthesis of avarol and avarone. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1999, 38, 3089–3091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narukulla, R.; Shuker, D.E.G.; Xu, Y.Z. Post-synthetic and site-specific modification of endocyclic nitrogen atoms of purines in DNA and its potential for biological and structural studies. Nucleic. Acids Res. 2005, 33, 1767–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knapp, S. Synthesis of complex nucleoside antibiotics. Chem. Rev. 1995, 95, 1859–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogilvie, K.K.; Entwistle, D.W. Silyl protecting groups in nucleoside and nucleotide chemistry, isomerization of tert-butyldimethylsilyl protecting groups in ribonucleosides. Carbohydr. Res. 1981, 89, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Rahman, S.Z.; Nouraldeen, A.M.; Abo-Elwafa, A.A.; Ahmed, A.E. Acrylonitrile-induced reversible inhibition of uridine uptake by isolated rat intestinal epithelial-cells. Toxicol. Vitro 1994, 8, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, R.E.; Robins, R.K. Purine nucleosides, preparation and reactions of some 9-β-d-ribofuranosyl-3,5′-purine cyclonucleosides. J. Org. Chem. 1963, 28, 3483–3486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampton, A.; Nichol, A.W. Nucleotides, preparation and optical rotatory dispersion of some 9-β-d-ribofuranosyl-3,5′-purine cyclonucleosides. J. Org. Chem. 1967, 1967, 32, 1688–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmonds, J.S.; Francesconi, K.A. Transformations of arsenic in the marine-environment. Experientia 1987, 43, 553–557. [Google Scholar]
- Cullen, W.R.; Reimer, K.J. Arsenic speciation in the environment. Chem. Rev. 1989, 89, 713–764. [Google Scholar]
- Challenger, F. Biological Methylation. Chem. Rev. 1945, 36, 315–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantoni, G.L. The nature of the active methyl donor formed enzymatically from l-methionine and adenosinetriphosphate. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1952, 74, 2942–2943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, H.; Akira, K.; Shinohara, Y.; Kasuya, Y.; Hashimoto, T. Kinetics of intramolecular acyl migration of 1-β-O-acyl glucuronides of (R)- and (S)-2-phenylpropionic acids. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2001, 24, 852–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, A.D.; Denu, J.M. Structural identification of 2′- and 3′-O-acetyl-ADP-ribose as novel metabolites derived from the Sir2 family of β-NAD(+)-dependent histone/protein deacetylases. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 18535–18544. [Google Scholar]
- Sauve, A.A.; Celic, I.; Avalos, J.; Deng, H.T.; Boeke, J.D.; Schramm, V.L. Chemistry of gene silencing: The mechanism of NAD(+)-dependent deacetylation reactions. Biochemistry 2001, 40, 15456–15463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spahnlangguth, H.; Benet, L.Z. Acyl glucuronides revisited—Is the glucuronidation process a toxification as well as a detoxification mechanism. Drug Metab. Rev. 1992, 24, 5–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, R.-M.; Chen, Y.-N.; Zeng, Z.; Gao, C.-H.; Su, X.; Peng, Y. Marine Nucleosides: Structure, Bioactivity, Synthesis and Biosynthesis. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 5817-5838. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12125817
Huang R-M, Chen Y-N, Zeng Z, Gao C-H, Su X, Peng Y. Marine Nucleosides: Structure, Bioactivity, Synthesis and Biosynthesis. Marine Drugs. 2014; 12(12):5817-5838. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12125817
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Ri-Ming, Yin-Ning Chen, Ziyu Zeng, Cheng-Hai Gao, Xiangdong Su, and Yan Peng. 2014. "Marine Nucleosides: Structure, Bioactivity, Synthesis and Biosynthesis" Marine Drugs 12, no. 12: 5817-5838. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12125817
APA StyleHuang, R.-M., Chen, Y.-N., Zeng, Z., Gao, C.-H., Su, X., & Peng, Y. (2014). Marine Nucleosides: Structure, Bioactivity, Synthesis and Biosynthesis. Marine Drugs, 12(12), 5817-5838. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12125817




