Investigating Diet as the Source of Tetrodotoxin in Pleurobranchaea maculata
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results

| Scientific Name | Common name/Description | Habitat | TTX Level (mg kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Echinodermata | |||
| Australostichopus mollis | Sea cucumber | Reef | 0 |
| Stegnaster inflatus | Orange elevated cushion star | Reef | 0 |
| Patiriella regularis | Common cushion star | Reef and MS | 0 |
| Coscinasterias calamaria | 11 Arm star | Reef and MS | 0 |
| Evechinus chloroticus | Sea urchin (Kina) | Reef | 0 |
| Echinocardium australe | Heart urchin | MS | 0 |
| Arachnoides zelandiae | Sand Dollar | Reef | 0.25 |
| Mollusca | |||
| Cominella virgata | Whelk | Reef | 0 |
| Musculista senhousia | Asian date mussel | MS | 0 |
| Saccostrea glomerata | Rock oysters | Reef | 0 |
| Cymatium spengleri | Whelk | Reef | 0 |
| Penion sulcatus | Whelk | Reef | 0 |
| Cominella adspersa | Whelk | Reef and MS | 0 |
| Turbo smaragdus | Cats eye | Reef | Trace |
| Haminoea zealandiae | Bubble shell slugs | Reef | 0 |
| Cellana radians | Limpets | Reef | 0 |
| Acanthochitona zelandica | Chiton | Reef | 0 |
| Cryptoconchus porosus | Chiton | Reef | 0 |
| Polychaeta | |||
| Perinereis amblyodonta | Polychaete | Reef | 0 |
| Crustacea | |||
| Plagusia chabrus | Red rock crab | Reef | 0 |
| Ovalipes catharus | Paddle Crab | MS | 0 |
| Petrolisthes elongatus | Porcelain crab | Reef | 0 |
| Chamaesipho columna | Barnacles | Reef | 0 |
| Macrophthalmus hirtipes | Crab | MS | Trace |
| Pagurus sp. | Hermit crabs | Reef | 0 |
| Callianassa filholi | Burrowing shrimp | MS | 0 |
| Crustacea | |||
| Plagusia chabrus | Red rock crab | Reef | 0 |
| Corallina officinalis | Coralline turf algae | Reef | Trace |
| Other | |||
| Sediment from M. senhousia beds | MS | 0 | |
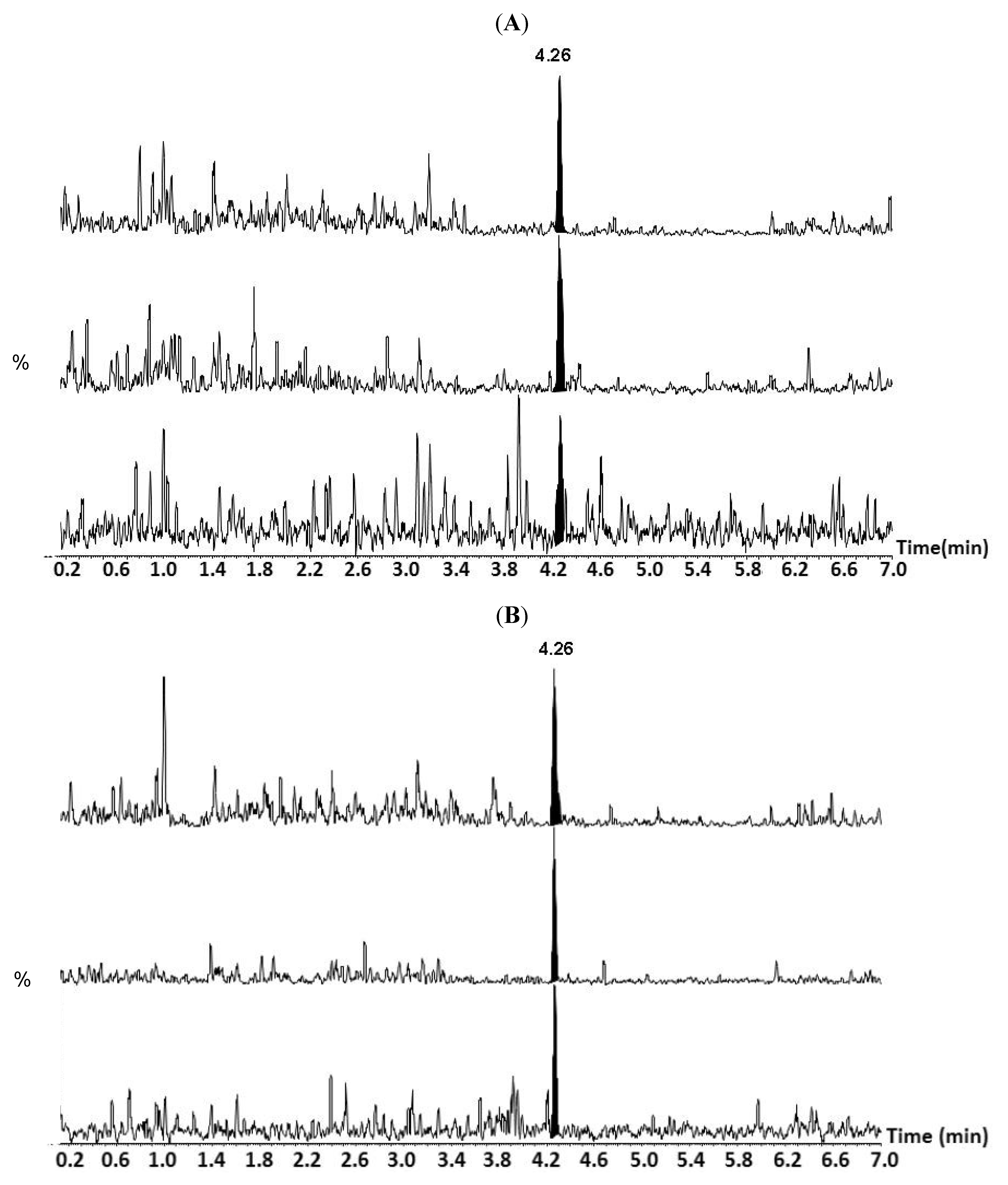
| Scientific or Record Name | Common Name/Description | TTX or C9 level (mg kg−1) |
|---|---|---|
| Echinodermata | ||
| Patiriella regularis | Regular seastar | ND |
| Coscinasterias calamaria | Spiny star | ND |
| Echinocardium australe | Heart urchin | ND |
| Arachnoides zelandiae | Snapper biscuit | ND |
| Botryllus schlosseri | Star ascidian | ND |
| Stichopus mollis | Sea cucumber | ND |
| Porifera | ||
| Polymastia sp. | Common sponge | ND |
| Unknown orange sponge | Sponge | ND |
| Mollusca | ||
| Perna canaliculus | GreenshellTM mussel | ND |
| Bursatella leachii | Ragged Sea Hare | ND |
| Buccinulum lineum | Lined whelk | ND |
| Cockle shell | Cockle shell | ND |
| Zelithophaga truncata | Bivalve | ND |
| Atrina zelandica | Horse mussel | ND |
| Cleidothaerus albidus | Bivalve | ND |
| Mytilus galloprovincialis | Blue mussel | ND |
| Crassostrea gigas | Pacific oyster | ND |
| Sigapatella novazelandiae | Circular slipper limpet | ND |
| Polychaeta | ||
| Thelepus spectabilis | Polychaete | ND |
| Annelida | ND | |
| Chaetopterus sp. | Parchment worms | ND |
| Crustacea | ||
| Crab inside gastropod | Crab | ND |
| Pagurus novazelandiae | New Zealand hermit crab | ND |
| Algae | ||
| Codium fragile | Green alga | ND |
| Colpomenia sinuosa | Brown alga | ND |
| Laurencia thyrsifera | Red alga | ND |
| Lithothamnion sp. | Encrusting red alga | ND |
| Lithothamnion sp. | Encrusting red alga | ND |
| Plocamium sp. | Red alga | ND |
| Sargassum sinclairii | Brown alga | ND |
| Unknown brown algae | Alga | ND |
| Unknown red algae | Alga | ND |
| Other | ||
| Beania discodermiae | Bryozoan | ND |
| Biofilm from gastropod | ND | |
| Biofilm from rock | ND | |
| Biofilm from Scallop shell | ND | |
| Biofilm from shell | ND | |
| Ciona intestinalis | Sea squirt | ND |
| Cnemidocarpa bicornuta | Sea squirt | ND |
| Mussel biofilm | ND | |
| Pecten novazelandiae (biofilm) | Scallop | ND |
| Plumularia setacea | Hydroid | ND |
| Rock with biofilm | ND | |
| Sargassum epifauna | ND | |
| Sediment—top of the tube (1 cm) | ND | |
| Sediment—top of the tube (3 cm) | ND | |
| Styela plicata | Tunicate | ND |
| Unknown ascidian | ND |
3. Discussion
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Field Sampling and Laboratory Conditions
4.2. Preparation of Tetrodotoxin-Containing Food
4.3. Spiked Recovery Experiment
4.4. Feeding Experiment
4.5. Dissection, Tetrodotoxin Extraction and Analysis
4.6. Statistical Analysis
4.7. Environmental Surveys
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Noguchi, T.; Arakawa, O. Tetrodotoxin—Distribution and accumulation in aquatic organisms, and cases of human intoxication. Mar. Drugs 2008, 6, 220–242. [Google Scholar]
- Ito, K.; Okabe, S.; Asakawa, M.; Bessho, K.; Taniyama, S.; Shida, Y.; Ohtsuka, S. Detection of tetrodotoxin (TTX) from two copepods infecting the grass puffer Takifugu niphobles: TTX attracting the parasites? Toxicon 2006, 48, 620–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoo, A. Studies on a toxin of the globefish. III—Isolation of spheroidine from the ovary of Spheroides Rubripes. Nippon Kagaku Zasshi 1950, 71, 590–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, H.V.; Takata, Y.; Sato, S.; Fukuyo, Y.; Kodama, M. Frequent occurrence of the tetrodotoxin-bearing horseshoe crab Carcinoscorpius rotundicauda in Vietnam. Fish. Sci. 2009, 75, 435–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosher, H.S.; Fuhrman, F.A.; Buchwald, H.D.; Fischer, H.G. Tarichatoxin—Tetrodotoxin: A potent neurotoxin. Science (N. Y.) 1964, 144, 1100–1110. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, D.F.; Lu, S.C.; Jeng, S.S. Occurrence of tetrodotoxin in the gastropods Rapana rapiformis and R. venosa venosa. Mar. Biol. 1991, 111, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanifin, C.T.; Yotsu-Yamashita, M.; Yasumoto, T.; Brodie, E.D., III; Brodie, E.D., Jr. Toxicity of dangerous prey: Variation of tetrodotoxin levels within and among populations of the newt Taricha granulosa. J. Chem. Ecol. 1999, 25, 2161–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, T.; Arakawa, O.; Daigo, K.; Hashimoto, K. Local differences in toxin composition of a xanthid crab Atergatis floridus inhabiting Ishigaki Island, Okinawa. Toxicon 1986, 24, 705–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Liu, Y.; Gong, Q.-L.; Zhou, L.; Wang, Z.-P. Toxicity of cultured puffer fish and seasonal variations in China. Aquacult. Res. 2011, 42, 1186–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, S.A.; Taylor, D.I.; McNabb, P.; Walker, J.; Adamson, J.; Cary, S.C. Tetrodotoxin concentrations in Pleurobranchaea maculata: Temporal, spatial and individual variability from New Zealand populations. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, T.; Hamada, S.; Yamamori, K. Local Variation of Toxicity of the Puffer Fish Fugu niphobles. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 1982, 48, 1179–1179. [Google Scholar]
- Saito, T.; Kohama, T.; Ui, K.; Watabe, S. Distribution of tetrodotoxin in the xanthid crab (Atergatis floridus) collected in the coastal waters of Kanagawa and Wakayama Prefectures. Comp. Biochem. Phys. D 2006, 1, 158–162. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, B.L.; Caldwell, R.L. Intra-organismal distribution of tetrodotoxin in two species of blue-ringed octopuses (Hapalochlaena fasciata and H. lunulata). Toxicon 2009, 54, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanifin, C.T.; Brodie, E.D., III; Brodie, E.D., Jr. Tetrodotoxin levels in eggs of the rough-skin newt, Taricha granulosa, are correlated with female toxicity. J. Chem. Ecol. 2003, 29, 1729–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, B.L.; Lovenburg, V.; Huffard, C.L.; Caldwell, R.L. Chemical defense in pelagic octopus paralarvae: Tetrodotoxin alone does not protect individual paralarvae of the greater blue-ringed octopus (Hapalochlaena lunulata) from common reef predators. Chemoecology 2011, 21, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardall, B.L.; Brodie, E.D., Jr.; Brodie, E.D., III; Hanifin, C.T. Secretion and regeneration of tetrodotoxin in the rough-skin newt (Taricha granulosa). Toxicon 2004, 44, 933–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanifin, C.T.; Brodie, E.D., III; Brodie, E.D., Jr. Tetrodotoxin levels of the rough-skin newt, Taricha granulosa, increase in long-term captivity. Toxicon 2002, 40, 1149–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gall, B.G.; Stokes, A.N.; French, S.S.; Brodie, E.D., III; Brodie, E.D., Jr. Predatory caddisfly larvae sequester tetrodotoxin from their prey, eggs of the rough-skinned newt (Taricha granulosa). J. Chem. Ecol. 2012, 38, 1351–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, S.; Arakawa, O.; Takatani, T.; Tachibana, K.; Yagi, M.; Tanigawa, A.; Noguchi, T. Toxification of cultured puffer fish Takifugu rubripes by feeding on tetrodotoxin-containing diet. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 2005, 71, 815–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, T.; Narita, H.; Maruyama, J.; Hashimoto, K. Tetrodotoxin in the starfish Astropecten polyacanthus, in association with toxification of a trumpet shell, “Boshubora” Charonia sauliae. Bull. Jap. Soc. Sci. Fish. 1982, 48, 1173–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, B.L.; Brodie, E.D., Jr.; Brodie, E.D., III. A resistant predator and its toxic prey: Persistence of newt toxin leads to poisonous (not venomous) snakes. J. Chem. Ecol. 2004, 30, 1901–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.J.; Jeong, D.Y.; Kim, W.S.; Kim, H.D.; Kim, C.H.; Park, W.W.; Park, Y.H.; Kim, K.S.; Kim, H.M.; Kim, D.S. A tetrodotoxin-producing Vibrio strain, LM-1, from the puffer fish Fugu vermicularis radiatus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 1698–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Yi, R. Bacillus horikoshii, a tetrodotoxin-producing bacterium isolated from the liver of puffer fish. Ann. Microbiol. 2009, 59, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, T.; Jeon, J.K.; Arakawa, O.; Sugita, H.; Deguchi, Y.; Shida, Y.; Hashimoto, K. Occurrence of tetrodotoxin and anhydrotetrodotoxin in Vibrio sp. isolated from the intestines of a xanthid crab, Atergatis floridus. J. Biochem. 1986, 99, 311–314. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.-J.; Yu, R.-C.; Luo, X.; Zhou, M.-J.; Lin, X.-T. Toxin-screening and identification of bacteria isolated from highly toxic marine gastropod Nassarius semiplicatus. Toxicon 2008, 52, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.L.; Xie, L.P.; Xia, G.L.; Zhang, J.F.; Nie, Y.C.; Hu, J.C.; Wang, S.J.; Zhang, R.Q. A new tetrodotoxin-producing actinomycete, Nocardiopsis dassonvillei, isolated from the ovaries of puffer fish Fugu rubripes. Toxicon 2005, 45, 851–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Xu, J.; Liang, S.; Ren, D.; Yan, X.; Bao, B. A novel TTX-producing Aeromonas isolated from the ovary of Takifugu obscurus. Toxicon 2010, 56, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasumoto, T.; Yasumura, D.; Yotsu, M.; Michishita, T.; Endo, A.; Kotaki, Y. Bacterial production of tetrodotoxin and anhydrotetrodotoxin. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1986, 50, 793–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, T.; Arakawa, O.; Takatani, T. Toxicity of pufferfish Takifugu rubripes cultured in netcages at sea or aquaria on land. Comp. Biochem. Phys., D 2006, 1, 153–157. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, B.; Hanifin, C.; Brodie, E., Jr.; Brodie, E., III. Predators usurp prey defenses? Toxicokinetics of tetrodotoxin in common garter snakes after consumption of rough-skinned newts. Chemoecology 2012, 22, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kono, M.; Matsui, T.; Furukawa, K.; Yotsu-Yamashita, M.; Yamamori, K. Accumulation of tetrodotoxin and 4,9-anhydrotetrodotoxin in cultured juvenile kusafugu Fugu niphobles by dietary administration of natural toxic komonfugu Fugu poecilonotus liver. Toxicon 2008, 51, 1269–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, T.; Hamada, S.; Konosu, S. Difference in accumulation of puffer fish toxin and crystalline tetrodotoxin in the puffer fish, Fugu rubripes rubripes. Bull. Jap. Soc. Sci. Fish. 1981, 47, 535–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, T.; Taketsugu, S.; Sato, H.; Yamamori, K.; Kodama, K.; Ishii, A.; Hirose, H.; Shimizu, C. Toxification of cultured puffer fish by the administration of tetrodotoxin-producing bacteria. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 1990, 56, 705. [Google Scholar]
- Yamamori, K.; Kono, M.; Furukawa, K.; Matsui, T. The toxification of juvenile cultured kusafugu Takifugu niphobles by oral administration of crystalline tetrodotoxin. Shokuhin Eiseigaku Zasshi 2004, 45, 73–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, B.L.; Hanifin, C.T.; Brodie, E.D., Jr.; Caldwell, R.L. Ontogeny of tetrodotoxin levels in blue-ringed octopuses: Maternal investment and apparent independent production in offspring of Hapalochlaena lunulata. J. Chem. Ecol. 2011, 37, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.H.; Brown, G.B.; Mosher, H.S.; Fuhrman, F.A. Tetrodotoxin: Occurrence in atelopid frogs of Costa Rica. Science (N. Y.) 1975, 189, 151–152. [Google Scholar]
- McNabb, P.; Selwood, A.I.; Munday, R.; Wood, S.A.; Taylor, D.I.; MacKenzie, L.A.; van Ginkel, R.; Rhodes, L.L.; Cornelisen, C.; Heasman, K.; et al. Detection of tetrodotoxin from the grey side-gilled sea slug—Pleurobranchaea maculata, and associated dog neurotoxicosis on beaches adjacent to the Hauraki Gulf, Auckland, New Zealand. Toxicon 2010, 56, 466–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, D.I.; Wood, S.A.; McNabb, P. Population Surveys of Pleurobranchaea maculata and Tetrodotoxin in Waitemata Harbour. In Prepared for Auckland Council, Cawthron Report No. 2006; Cawthron Institute: Nelson, New Zealand, 2011; p. 11. [Google Scholar]
- Soong, T.W.; Venkatesh, B. Adaptive evolution of tetrodotoxin resistance in animals. Trends Genet. 2006, 22, 621–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bricelj, V.M.; Connell, L.; Konoki, K.; MacQuarrie, S.P.; Scheuer, T.; Catterall, W.A.; Trainer, V.L. Sodium channel mutation leading to saxitoxin resistance in clams increases risk of PSP. Nature 2005, 434, 763–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geffeney, S.L.; Fujimoto, E.; Brodie, E.D.; Ruben, P.C. Evolutionary diversification of TTX-resistant sodium channels in a predator–prey interaction. Nature 2005, 434, 759–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiomi, K.; Yamaguchi, S.; Kikuchi, T.; Yamamori, K.; Matsui, T. Occurrence of tetrodotoxin-binding high molecular weight substances in the body fluid of shore crab (Hemigrapsus sanguineus). Toxicon 1992, 30, 1529–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, T.; Tanuma, D.; Tsutsumi, K; Jeon, J.K.; Ishizaki, S.; Nagashima, Y. Plasma protein binding of tetrodotoxin in the marine puffer fish Takifugu rubripes. Toxicon 2010, 55, 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yotsu-Yamashita, M.; Sugimoto, A.; Terakawa, T.; Shoji, Y.; Miyazawa, T.; Yasumoto, T. Purification, chracterization, and cDNA cloning of a novel soluble saxitoxin and tetrodotoxin binding protein from plasma of the puffer fish, Fugu pardalis. Eur. J. Biochem. 2001, 268, 5937–5959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yotsu-Yamashita, M.; Okoshi, N.; Watanabe, K.; Araki, N.; Yamaki, H.; Shoji, Y.; Terakawa, T. Localization of pufferfish saxitoxin and tetrodotoxin binding protein (PSTBP) in the tissues of the pufferfish, Takifugu pardalis, analyzed by immunohistochemical staining. Toxicon 2013, 72, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, S.A.; Casas, M.; Taylor, D.I.; McNabb, P.; Salvitti, L.; Ogilvie, S.; Cary, S.C. Depuration of tetrodotoxin and changes in bacterial communities in Pleurobranchea maculata adults and egg masses maintained in captivity. J. Chem. Ecol. 2012, 38, 1342–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, D.-F.; Kao, C.-Y.; Yang, H.-C.; Jeng, S.-S.; Noguchi, T.; Hashimoto, K. Toxicity of puffer in Taiwan. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 1992, 58, 1541–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khor, S.; Wood, S.A.; Salvitti, L.; Ragg, N.L.C.; Taylor, D.; McNabb, P.; Cary, S.C. Development of a non-lethal biopsy technique for estimating total tetrodotoxin concentrations in the grey side-gilled sea slug Pleurobranchaea maculata. Toxicon 2013, 74, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNabb, P.S.; Taylor, D.I.; Ogilvie, S.C.; Wilkinson, L.; Anderson, A.; Hamon, D.; Wood, S.A.; Peake, B.M. First detection of tetrodotoxin in the bivalve Paphies australis by liquid chromatography coupled to triple quadrupole mass spectrometry with and without pre-column hydrolysis. J. AOAC Int. 2013, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Chau, R.; Kalaitzis, J.A.; Wood, S.A.; Neilan, B.A. Diversity and biosynthetic potential of culturable microbes associated with toxic marine animals. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 2695–2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Khor, S.; Wood, S.A.; Salvitti, L.; Taylor, D.I.; Adamson, J.; McNabb, P.; Cary, S.C. Investigating Diet as the Source of Tetrodotoxin in Pleurobranchaea maculata. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 1-16. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12010001
Khor S, Wood SA, Salvitti L, Taylor DI, Adamson J, McNabb P, Cary SC. Investigating Diet as the Source of Tetrodotoxin in Pleurobranchaea maculata. Marine Drugs. 2014; 12(1):1-16. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhor, Serena, Susanna A. Wood, Lauren Salvitti, David I. Taylor, Janet Adamson, Paul McNabb, and Stephen Craig Cary. 2014. "Investigating Diet as the Source of Tetrodotoxin in Pleurobranchaea maculata" Marine Drugs 12, no. 1: 1-16. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12010001
APA StyleKhor, S., Wood, S. A., Salvitti, L., Taylor, D. I., Adamson, J., McNabb, P., & Cary, S. C. (2014). Investigating Diet as the Source of Tetrodotoxin in Pleurobranchaea maculata. Marine Drugs, 12(1), 1-16. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12010001






