Sarcophyolides B–E, New Cembranoids from the Soft Coral Sarcophyton elegans
Abstract
:1. Introduction
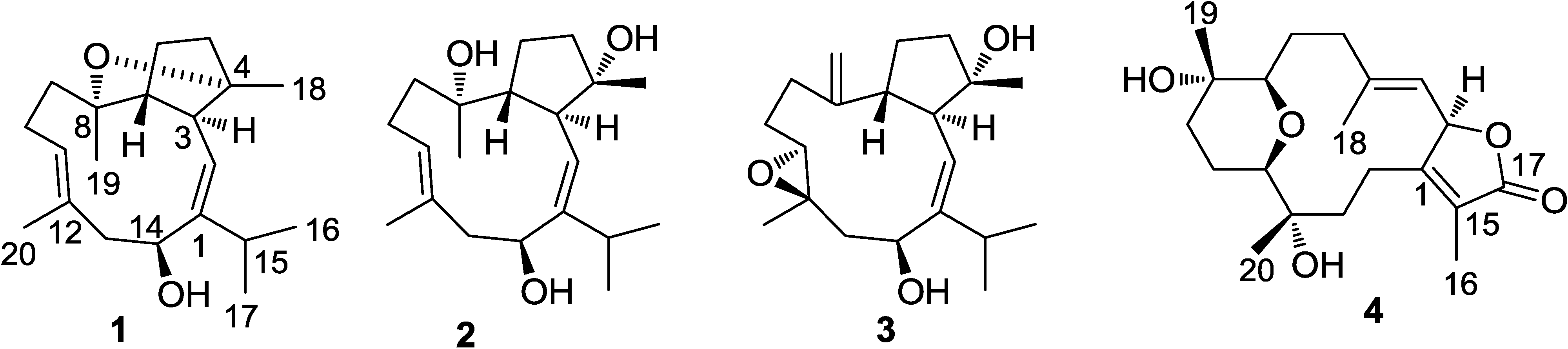
2. Results and Discussion
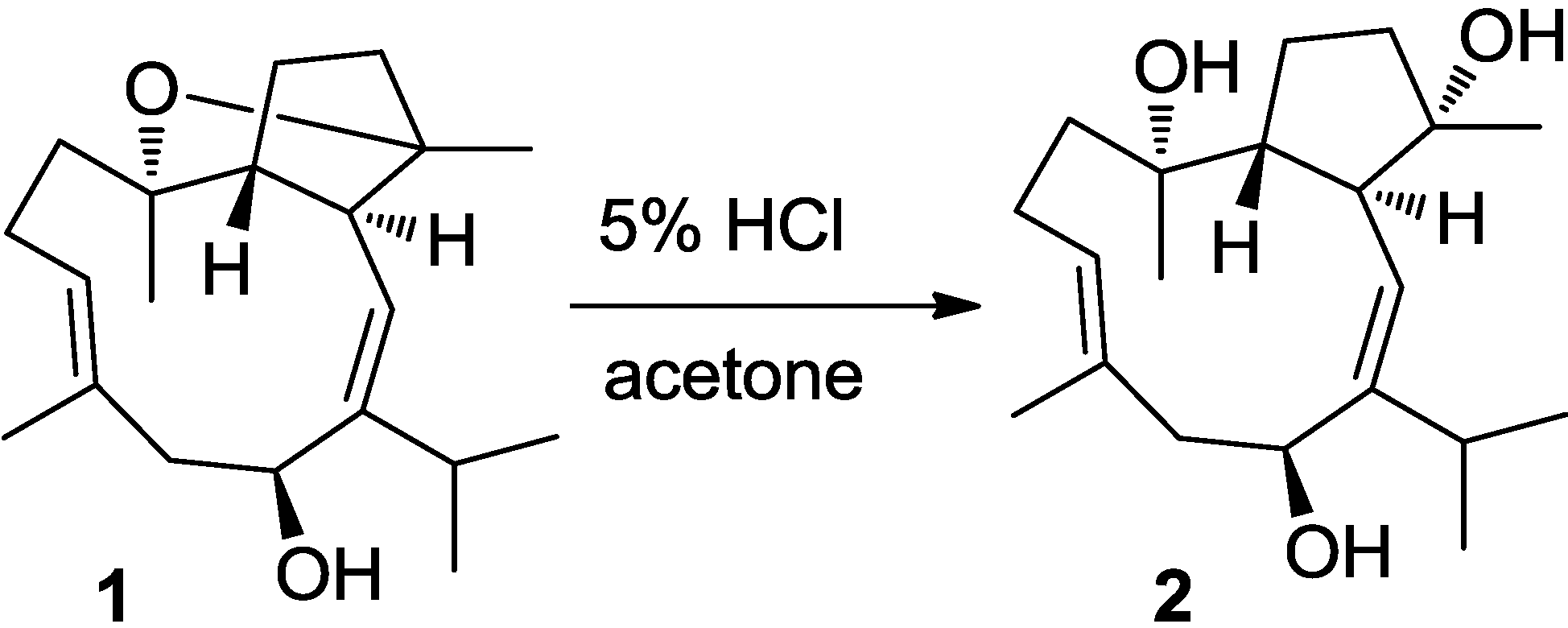
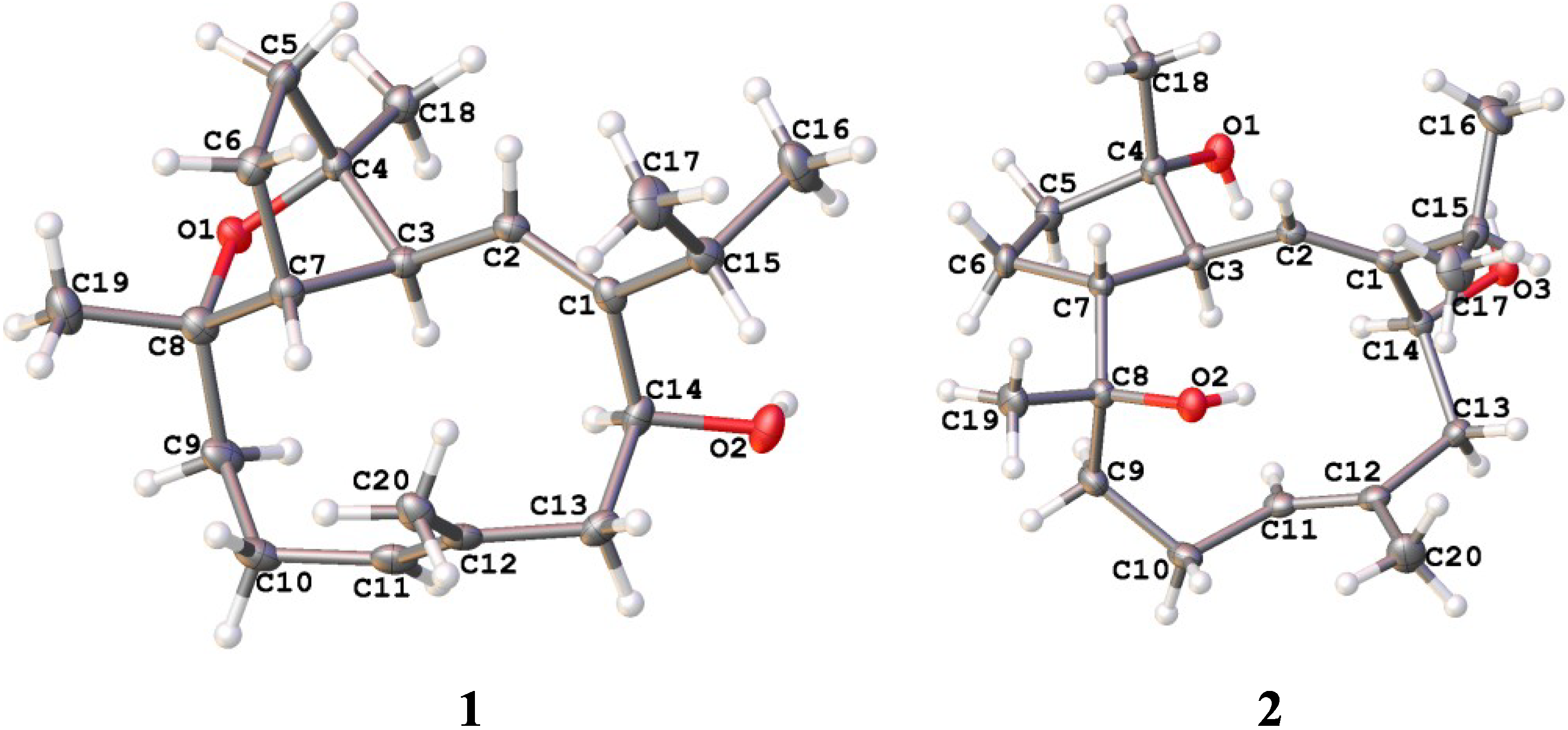
2.1. Structural Elucidation of New Compounds
| No. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 5.26 d (11.5) | 5.28 d (9.5) | 5.09 d (10.4) | 5.50 d (10.0) |
| 3 | 3.11 brd (11.5) | 2.64 dd (9.5,10.5) | 2.77 dd (10.4,10.4) | 5.00 d (10.0) |
| 5 | 1.55 m | 1.76 m | 1.85 m | 2.16 m |
| 1.74 m | 1.78 m | 1.80 m | 2.20 m | |
| 6 | 1.68 m | 1.35 m | 1.70 m | 1.43 m |
| 1.74 m | 1.74 m | 1.82 m | 1.96 m | |
| 7 | 1.90 m | 1.97 ddd (8.5,10.0,10.5) | 2.50 m | 3.02 brd (10.0) |
| 9 | 1.90 m | 1.62 ddd (3.0,5.0,14.0) | 2.25 m | 1.48 m |
| 1.92 m | 1.82 brdd (10.0,14.0) | 2.20 m | 1.46 m | |
| 10 | 2.00 m | 2.05 m | 2.45 m | 1.34 m |
| 2.02 m | 2.41 ddd (8.0, 10.0, 12.0) | 1.40 m | 1.67 m | |
| 11 | 5.49 dd (3.0,5.0) | 5.36 dd (4.5, 8.0) | 2.88 dd (4.2, 9.8) | 3.14 d (8.5) |
| 13 | 2.00 dd (9.0,11.5) | 2.09 dd (11.5, 13.0) | 2.13 d (13.3) | 1.48 m |
| 2.62 brd (11.5) | 2.50 dd (3.0, 13.0) | 1.50 dd (10.7, 13.3) | 1.73 m | |
| 14 | 5.04 brd (9.0) | 4.86 dd (3.0, 11.5) | 3.83 d (10.7) | 1.93 m |
| 2.45 m | ||||
| 15 | 2.68 qq (7.0, 7.0) | 2.56 qq (7.0, 7.0) | 2.49 qq (6.8, 6.8) | |
| 16 | 1.12 d (7.0) | 1.09 d (7.0) | 1.03 d (6.9) | |
| 17 | 1.13 d (7.0) | 1.15 d (7.0) | 1.14 d (6.9) | 1.73 s |
| 18 | 1.19 s | 1.11 s | 1.17 s | 1.78 s |
| 19 | 1.23 s | 1.15 s | 4.96 brs | 0.98 s |
| 4.91 brs | ||||
| 20 | 1.60 s | 1.73 s | 1.49 s | 0.98 s |
| No. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 150.6 qC | 149.8 qC | 150.9 qC | 165.8 qC |
| 2 | 120.9 CH | 126.2 CH | 124.9 CH | 80.1 CH |
| 3 | 53.2 CH | 49.7 CH | 50.8 CH | 120.0 CH |
| 4 | 87.6 qC | 81.5 qC | 81.3 qC | 144.2 qC |
| 5 | 32.8 CH2 | 39.7 CH2 | 40.1 CH2 | 36.2 CH2 |
| 6 | 21.1 CH2 | 24.4 CH2 | 25.4 CH2 | 24.7 CH2 |
| 7 | 49.6 CH | 56.3 CH | 54.6 CH | 83.9 CH |
| 8 | 82.8 qC | 74.7 qC | 147.4 qC | 68.8 qC |
| 9 | 43.5 CH2 | 34.2 CH2 | 24.1 CH2 | 40.8 CH2 |
| 10 | 24.0 CH2 | 23.4 CH2 | 27.5 CH2 | 23.4 CH2 |
| 11 | 133.0 CH | 129.9 CH | 59.5 CH | 80.5 CH |
| 12 | 128.0 qC | 131.0 qC | 58.1 qC | 71.8 qC |
| 13 | 43.5 CH2 | 43.0 CH2 | 45.6 CH2 | 37.3 CH2 |
| 14 | 72.9 CH | 70.8 CH | 67.8 CH | 20.6 CH2 |
| 15 | 26.9 CH | 26.4 CH | 26.7 CH | 121.7 qC |
| 16 | 25.3 CH3 | 24.7 CH3 | 24.4 CH3 | 9.0 CH3 |
| 17 | 25.7 CH3 | 26.4 CH3 | 26.4 CH3 | 174.9 qC |
| 18 | 19.1 CH3 | 23.0 CH3 | 24.1 CH3 | 16.7 CH3 |
| 19 | 25.1 CH3 | 31.7 CH3 | 111.2 CH2 | 20.5 CH3 |
| 20 | 20.0 CH2 | 18.8 CH3 | 17.1 CH3 | 23.9 CH3 |
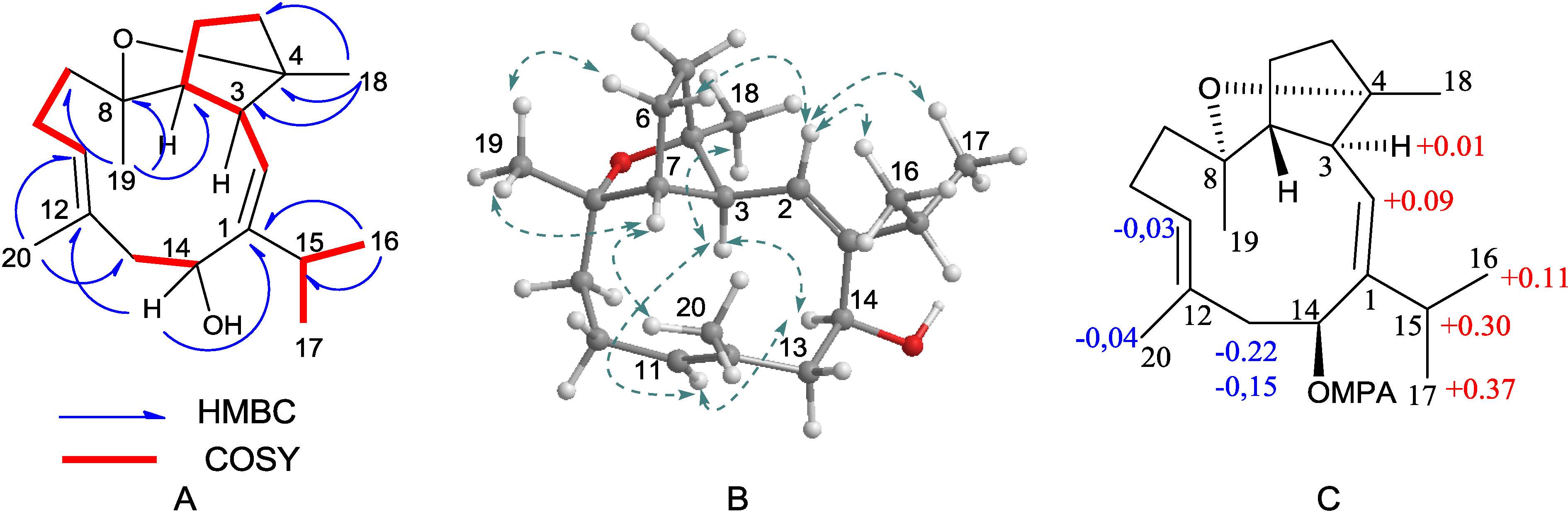
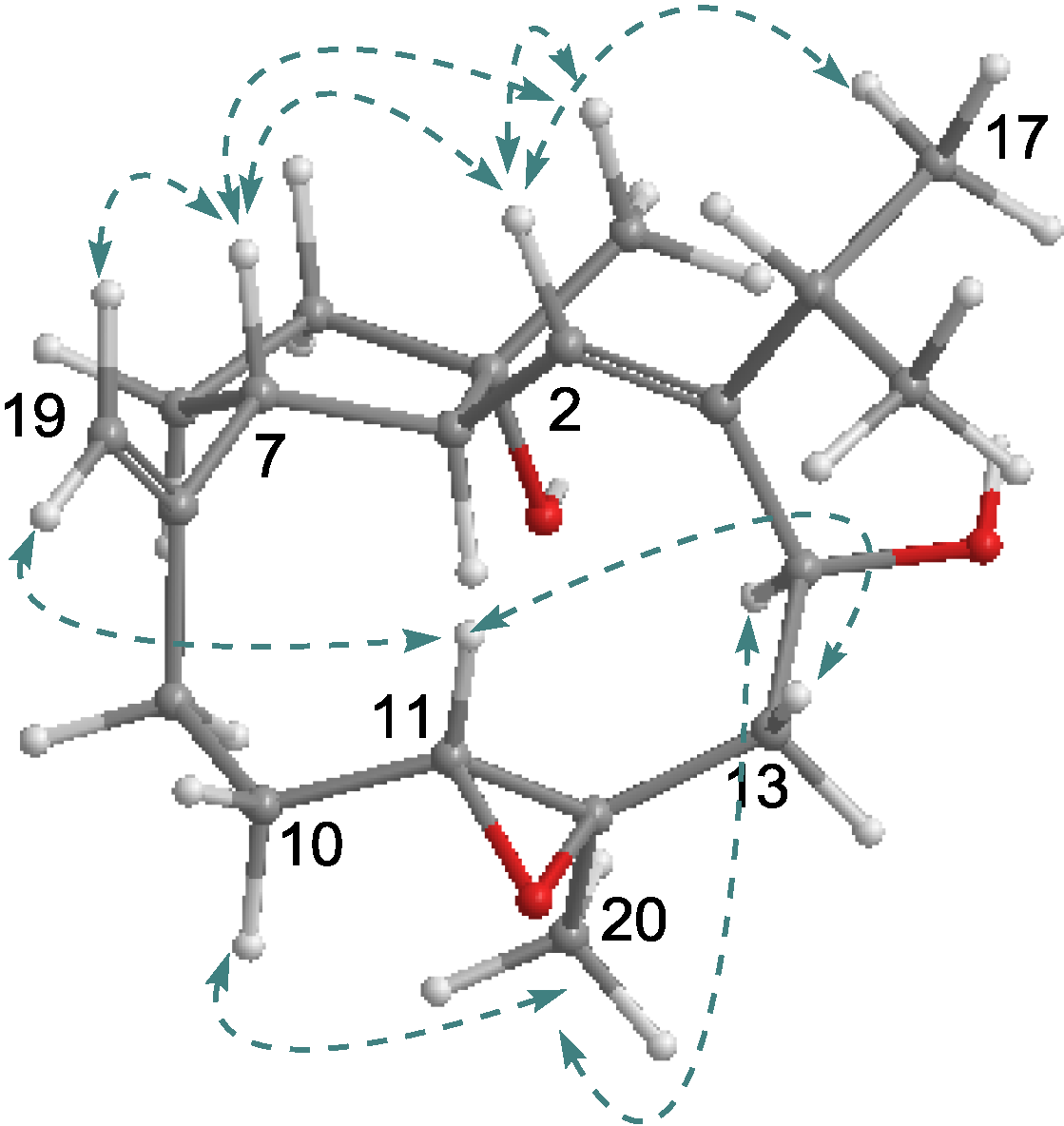
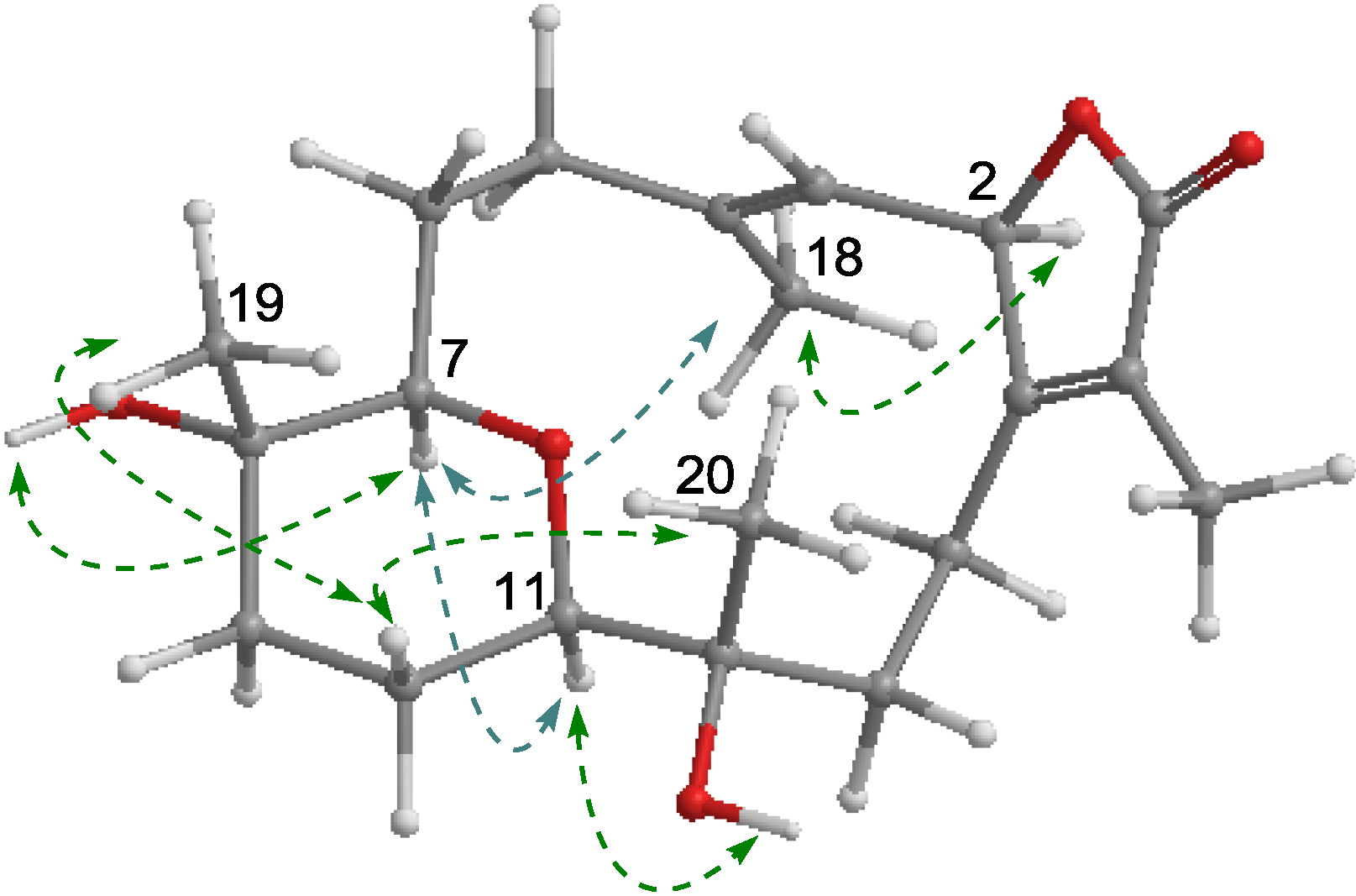
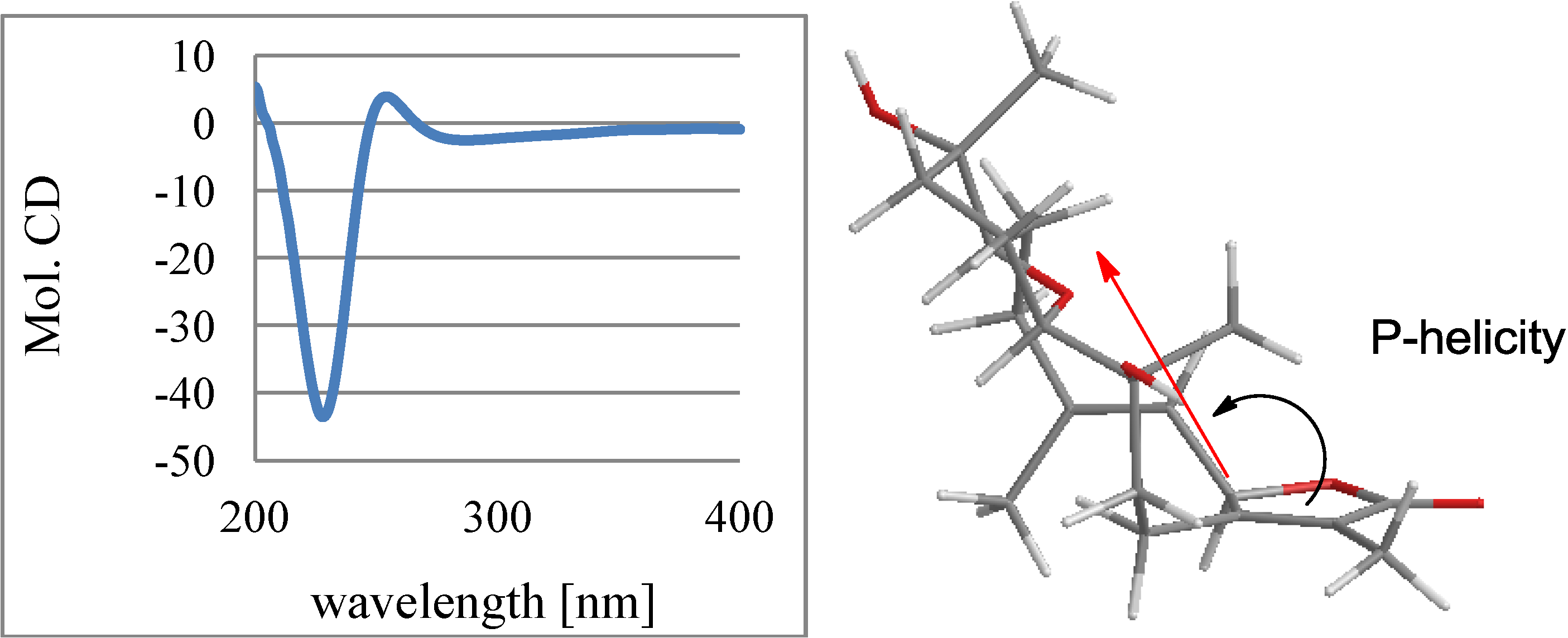
2.2. Cytotoxic Results
3. Experimental Section
3.1. General
3.2. Animal Material
3.3. Extraction and Isolation
3.4. Cytotoxic Bioassays
3.5. Mosher Reaction
3.6. Chemical Conversion
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roethle, P.A.; Trauner, D. The chemistry of marine furanocembranoids, pseudopteranes, gersolanes, and related natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2008, 25, 298–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iguchi, K. Yonarolide: A new marine norditerpenoid possessing a novel tricyclic skeleton, from the Okinawan soft coral of the genus, Sinularia. Tetrahedron Lett. 1995, 36, 8807–8808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjaneyulu, A.S.R.; Rao, G.V. Chemical constituents of the soft coral species of Sarcophyton genus: A review. J. Indian Chem. Soc. 1997, 74, 272–278. [Google Scholar]
- Kelman, D.; Kashman, Y.; Rosenberg, E.; Kushmaro, A.; Loya, Y. Antimicrobial activity of Red Sea corals. Mar. Biol. 2006, 149, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleury, B.G.; Coll, J.C.; Sammarco, P.W.; Tentori, E.; Duquesne, S. Complementary (secondary) metabolites in an octocoral competing with a scleractinian coral: Effects of varying nutrient regimes. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2004, 303, 115–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthoni, U.; Bock, K.; Christophersen, C.; Duus, J.O.; Kjaer, E.B.; Nielsen, P.H. Structure of a novel antifouling epoxy cembrenoid diterpene from a Sarcophyton sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 1991, 32, 2825–2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Su, J.; Lu, Y.; Wen, Z.; Dai, C.; Kuo, Y.; Sheu, J. Cytotoxic and anti-inflammatory cembranoids from the Dongsha Atoll soft coral Sarcophyton crassocaule. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 1936–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, J.; Su, J.; Liang, Y.; Yang, X.; Zheng, K.; Zeng, L. Cytotoxic diterpenoids from the soft coral Sarcophyton crassocaule. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 1476–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duh, C.; Wang, S.; Chung, S.; Chou, G.; Dai, C. Cytotoxic cembrenolides and steroids from the Formosan soft coral Sarcophyton crassocaule. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 1634–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawant, S.S.; Youssef, D.T.A.; Reiland, J.; Ferniz, M.; Marchetti, D.; El Sayed, K.A. Biocatalytic and antimetastatic studies of the marine cembranoids sarcophine and 2-epi-16-deoxysarcophine. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 1010–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grkovic, T.; Whitson, E.L.; Rabe, D.C.; Gardella, R.S.; Bottaro, D.P.; Linehan, W.M.; McMahon, J.B.; Gustafson, K.R.; McKee, T.C. Identification and evaluation of soft coral diterpenes as inhibitors of HIF-2α induced gene expression. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 21, 2113–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badria, F.A.; Guirguis, A.N.; Perovic, S.; Steffen, R.; Muller, W.E.G.; Schroder, H.C. Sarcophytolide: A new neuroprotective compound from the soft coral Sarcophyton glaucum. Toxicology 1998, 131, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badria, F.A.; Guirguis, A.N.; El-Naggar, W.A. Antibacterial and antifungal agents from Egyptian marine organisms. Int. J. Pharmacol. 1997, 35, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, M.; Iwanaga, T.; Hatanaka, M.; Nakano, A.; Morihara, K.; Takemura, K. Distribution of sarcophytol A in soft coral of the Sarcophyton genus. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2000, 64, 858–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.F.; Kuo, Y.H.; Dai, C.; Sheu, J. Oxygenated terpenoids from a Formosan soft coral Sinularia gibberosa. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 1208–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Liu, D.; Tian, L.; Wei, Y.; Proksch, P.; Zeng, J.; Lin, W. Venezuelines A–G, new phenoxazine-based alkaloids and aminophenols from Streptomyces venezuelae and the regulation of gene target Nur77. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 301–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawant, S.S.; Sylvester, P.W.; Avery, M.A.; Desai, P.; Youssef, D.T.A.; El Sayed, K.A. Bioactive rearranged and halogenated semisynthetic derivatives of the marine natural product sarcophine. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 2017–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, A.D.; Pina, I.C.; Acosta, A.L.; Ramirez, C.; Soto, J.J. Synthesis of analogues of eunicea γ-cembranolides containing cyclic ethers via saponification. J. Org. Chem. 2001, 66, 648–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osabe, K.; Kobayashi, M. Marine terpenes and terpenoids. VIII. Transannular cyclization of 3,4-epoxy-1,7,11-cembratriene systems. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1989, 37, 1192–1196. [Google Scholar]
- Bie, W.; Deng, Z.; Xu, M.; Lin, W. Structural elucidation of a new cembranoid diterpene from the Chinese soft coral Sarcophyton sp. J. Chin. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 17, 221–224. [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein, J.; Shmeuli, U.; Zadock, E.; Kashman, Y.; Néeman, I. Sarcophine, a new epoxy cembranolide from marine origin. Tetrahedron 1974, 30, 2817–2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawronski, J.K.; Oeveren, A.; Deen, H.; Leung, C.W.; Feringa, B. Simple circular dichroic method for the determination of absolute configuration of 5-substituted 2(5H)-furanones. J. Org. Chem. 1996, 61, 1513–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegazya, M.E.; El-Beih, A.A.; Moustafad, A.Y.; Hamdy, A.A.; Alhammady, M.A.; Selim, R.M.; Abdel-Rehim, M.; Paré, P.W. Cytotoxic cembranoids from the red sea soft coral Sarcophyton glaucum. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2011, 6, 1809–1812. [Google Scholar]
- Khalid, A.E.S.; Mark, T. Structurally novel bioconversion products of the marine natural product sarcophine effectively inhibit JB6 cell transformation. J. Org. Chem. 1998, 63, 7449–7455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, M.; Kondo, K.; Osabe, K.; Mitsuhashi, H. Marine terpenes and terpenoids. V. Oxidation of sarcophytol A, a potent anti-tumor-promoter from the soft coral Sarcophyton glaucum. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1988, 36, 2331–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, M.; Iesaka, T.; Nakano, E. Marine terpenes and terpenoids. IX. Structures of six new cembranoids, sarcophytols F, K, P, Q, R and S, from the soft coral Sarcophyton glaucum. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1989, 37, 2053–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Wang, S.; Cheng, S.; Duh, C. Lobocrasol, a new diterpenoid from the soft coral Lobophytum crassum. Org. Lett. 2009, 11, 3012–3014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Supplementary Files
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Xi, Z.; Bie, W.; Chen, W.; Liu, D.; Ofwegen, L.V.; Proksch, P.; Lin, W. Sarcophyolides B–E, New Cembranoids from the Soft Coral Sarcophyton elegans. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 3186-3196. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11093186
Xi Z, Bie W, Chen W, Liu D, Ofwegen LV, Proksch P, Lin W. Sarcophyolides B–E, New Cembranoids from the Soft Coral Sarcophyton elegans. Marine Drugs. 2013; 11(9):3186-3196. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11093186
Chicago/Turabian StyleXi, Zhifang, Wei Bie, Wei Chen, Dong Liu, Leen Van Ofwegen, Peter Proksch, and Wenhan Lin. 2013. "Sarcophyolides B–E, New Cembranoids from the Soft Coral Sarcophyton elegans" Marine Drugs 11, no. 9: 3186-3196. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11093186
APA StyleXi, Z., Bie, W., Chen, W., Liu, D., Ofwegen, L. V., Proksch, P., & Lin, W. (2013). Sarcophyolides B–E, New Cembranoids from the Soft Coral Sarcophyton elegans. Marine Drugs, 11(9), 3186-3196. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11093186







