Integrated Metagenomic and Metatranscriptomic Analyses of Microbial Communities in the Meso- and Bathypelagic Realm of North Pacific Ocean
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Overview of Data Generation and Analysis
| Sampling Sites | Position | Depth (m) | Sampling Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| CT04 | 44°29′34.80′′ N, 125°8′49.61″ W | 1181–1194 | 7/23/2008, 21:00–21:24GMT |
| CT05 | 44°34′1.02″ N, 125°9′3.75″ W | 785–790 | 7/27/2008, 3:05–7:21GMT |
| CT06 | 44°33′52.99″ N, 125°9′3.73″ W | 763–789 | 7/27/2008, 3:12–7:31GMT |
| CT12 | 45°51′57.01″ N, 129°47′19.47″ W | 1840–1913 | 8/2/2008, 00:01–00:24GMT |
| DNA | RNA | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CT04 | CT05 | CT06 | CT12 | CT04 | CT05 | CT06 | CT12 | |
| Total reads | 61,650 | 46,012 | 50,491 | 40,049 | 12,804 | 13,722 | 18,367 | 33,509 |
| Ave. length (bp) | 217 ± 143 | 228 ± 145 | 252 ± 156 | 236 ± 144 | 170 ± 113 | 184 ± 120 | 177 ± 124 | 202 ± 121 |
| Ave. GC% | 49 ± 8 | 50 ± 8 | 48 ± 8 | 48 ± 8 | 49 ± 6 | 36 ± 6 | 49 ± 7 | 48 ± 6 |
| Failed QC | 15,938 | 11,537 | 11,133 | 0 | 3745 | 4421 | 5443 | 0 |
| Annotated protein | 8545 | 7328 | 9070 | 12,720 | 201 | 0 | 0 | 10,300 |
| Unknown protein | 18,581 | 14,359 | 17,011 | 15,723 | 4602 | 5790 | 6981 | 13,569 |
| Ribosomal RNA | 1505 | 1042 | 999 | 2811 | 1932 | 1009 | 3663 | 6175 |
| Unknown | 17,081 | 11,746 | 12,278 | 8795 | 2324 | 2502 | 2280 | 3465 |
| Metagenome (%) | Metatranscriptome (%) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CT04 | CT05 | CT06 | CT12 | CT04 | CT05 | CT06 | CT12 | |
| Archaea | 1.31 | 1.97 | 4.23 | 1.60 | 1.24 | 0.80 | 0.64 | 1.05 |
| Bacteria | 26.56 | 30.27 | 34.30 | 24.16 | 23.06 | 9.42 | 17.14 | 19.98 |
| Eukaryotes | 69.94 | 65.73 | 58.73 | 71.92 | 73.45 | 87.54 | 81.40 | 78.37 |
| Viruses | 0.41 | 0.29 | 0.47 | 0.44 | 0.30 | 0.50 | 0.23 | 0.25 |
| Others * | 1.78 | 1.74 | 2.26 | 1.88 | 1.96 | 1.77 | 0.59 | 0.35 |
2.2. Metagenomic Analysis of the Deep-Sea Prokaryotic Communities
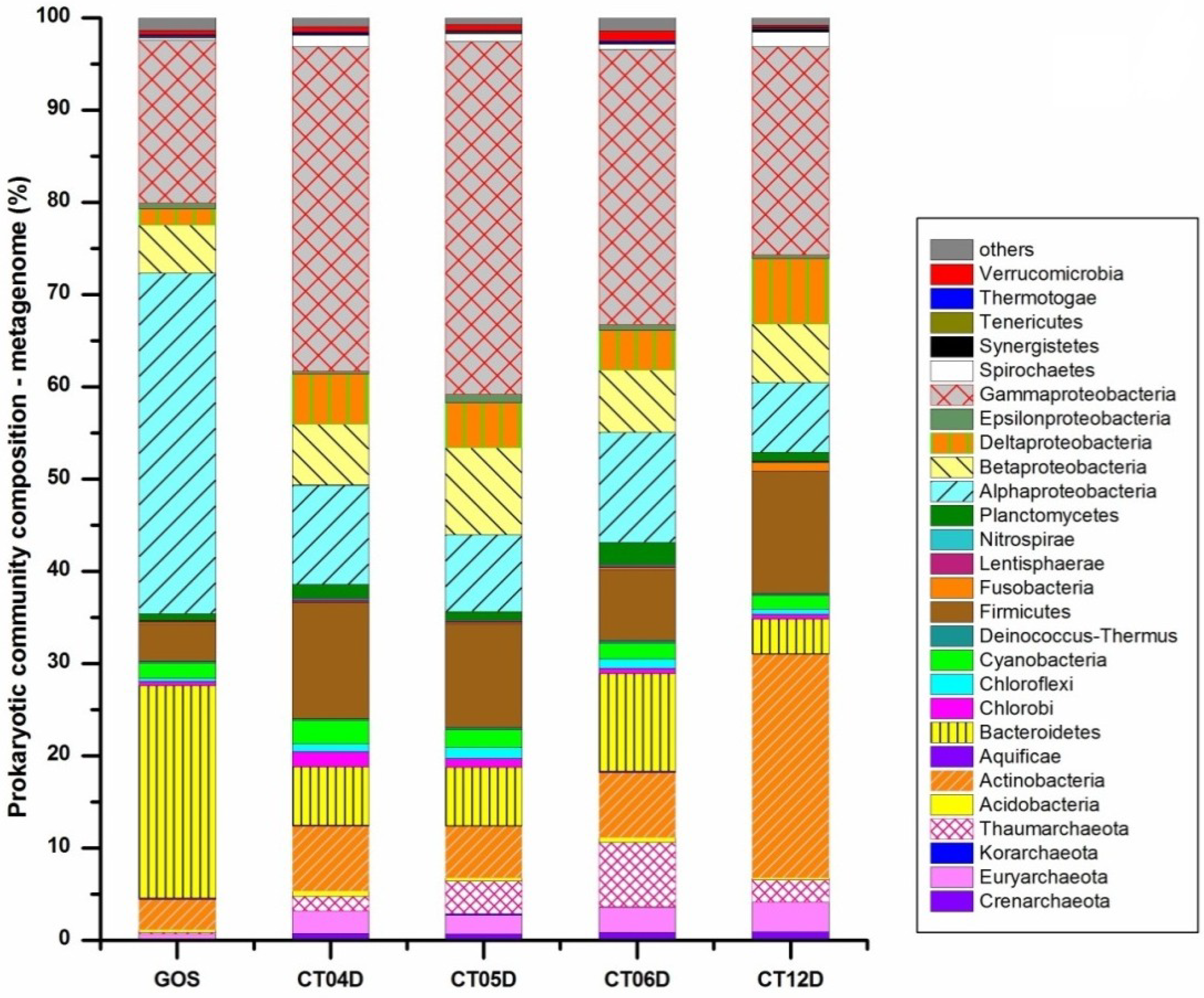
2.3. Metatranscriptomic Analysis of the Deep-Sea Prokaryotic Communities
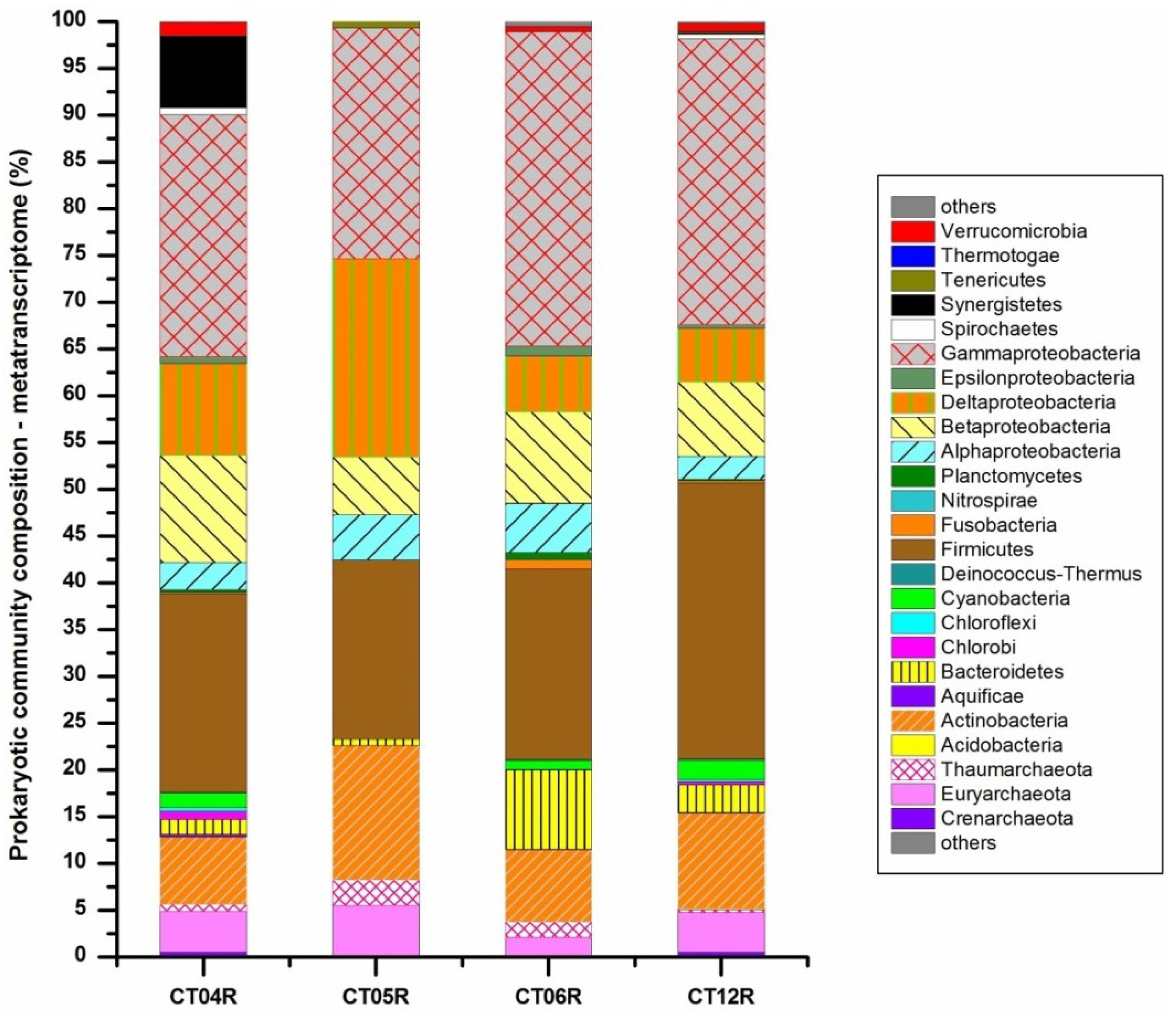
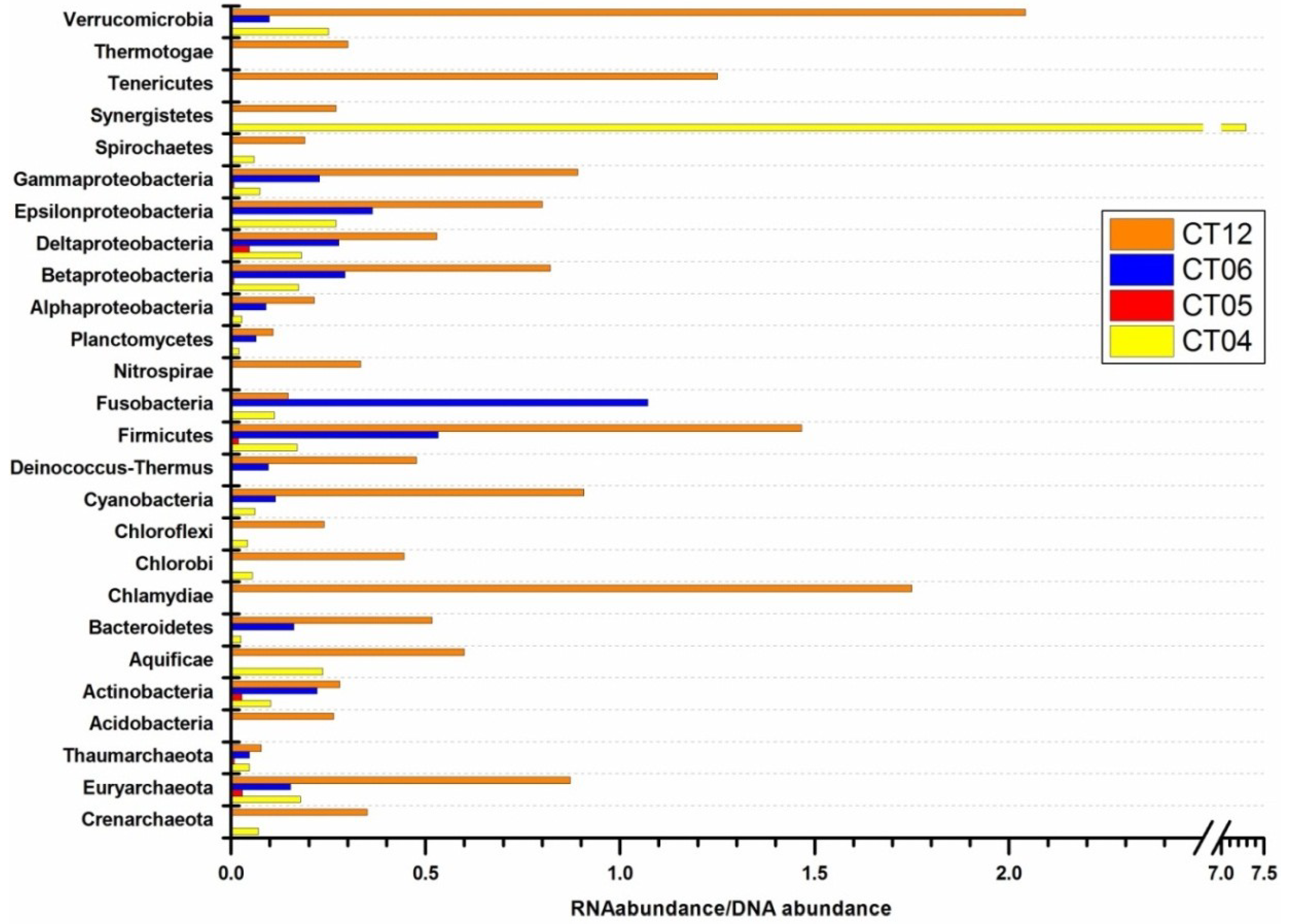
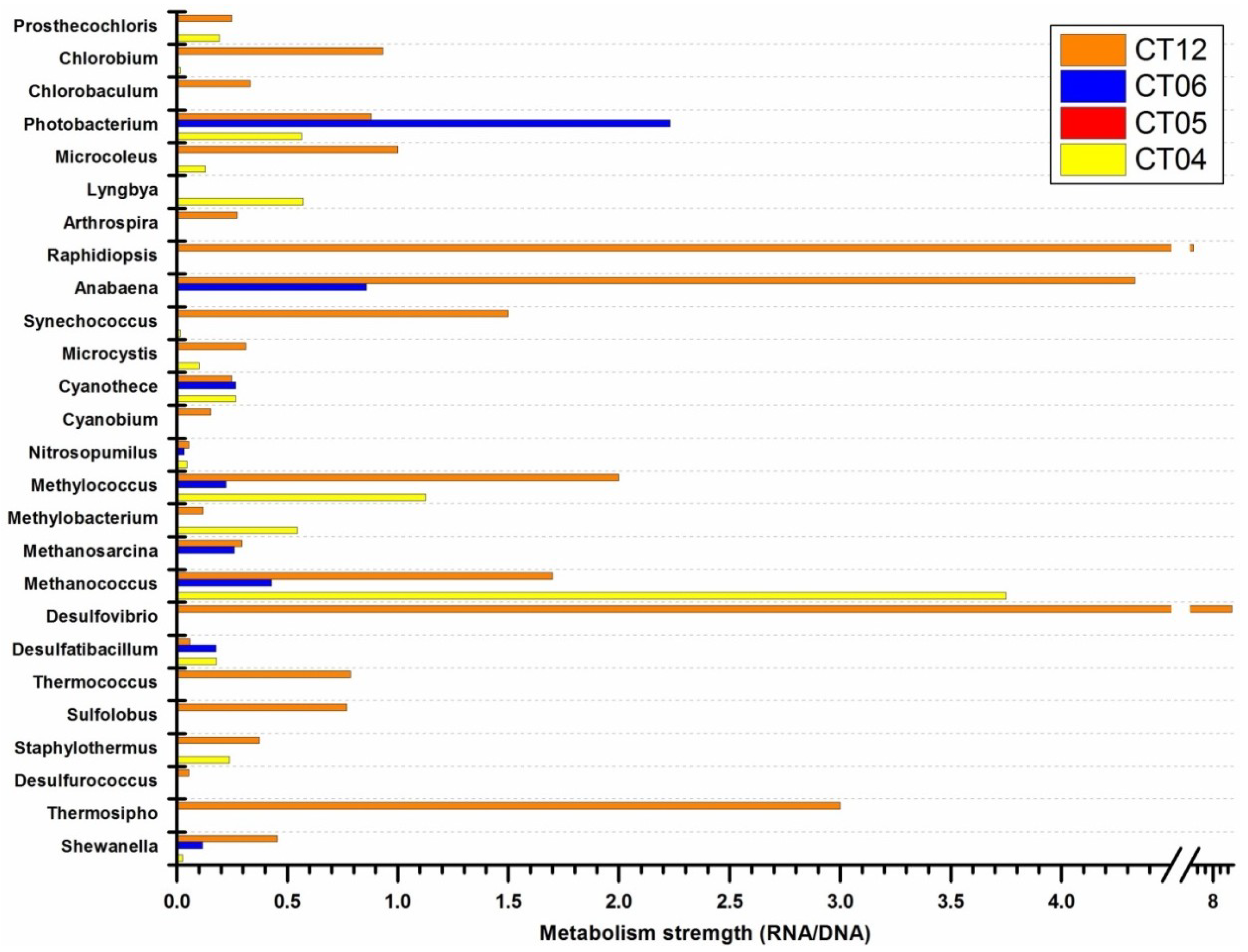
2.4. Integrated Metagenomic and Metatranscriptomic Analysis of Prokaryotic Communities in Deep-Sea Water
2.4.1. Cell Wall/Membrane/Envelope Biogenesis
2.4.2. Signal Transduction Mechanisms
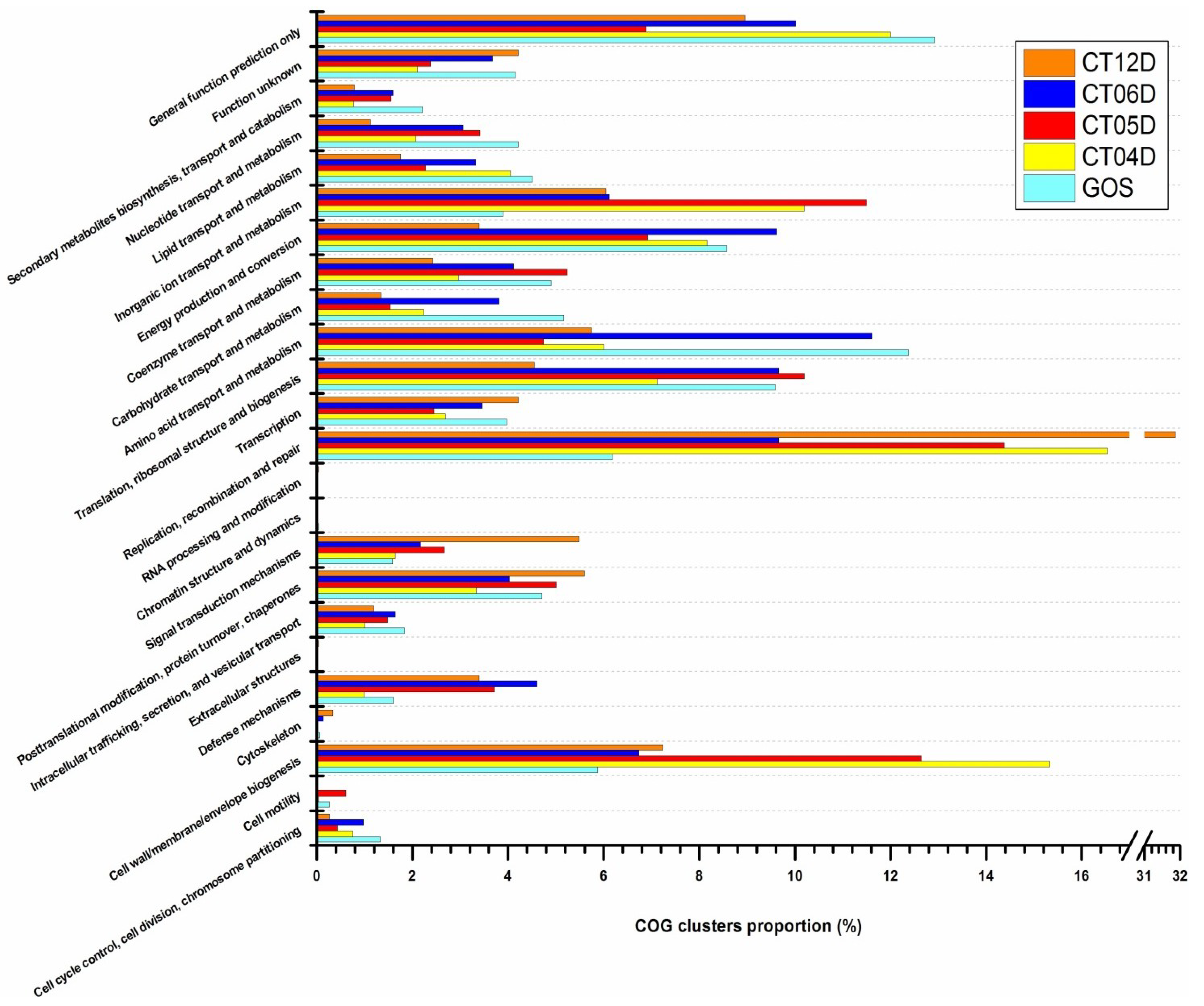
2.4.3. Replication, Recombination, and Repair
2.4.4. Inorganic ion Transport and Metabolism
| Metagenomics | Metatranscriptomics | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CT04 | CT05 | CT06 | CT12 | CT04 | CT05 | CT06 | CT12 | |
| Unique COG Functions Identified | 401 | 406 | 876 | 528 | 8 | 2 | 20 | 85 |
| Sequences Assigned to COG Functions | 5971 | 5745 | 2336 | 2841 | 166 | 6 | 306 | 877 |
2.5. Active Presence of Photosynthetic Bacteria in Deep-Sea Water
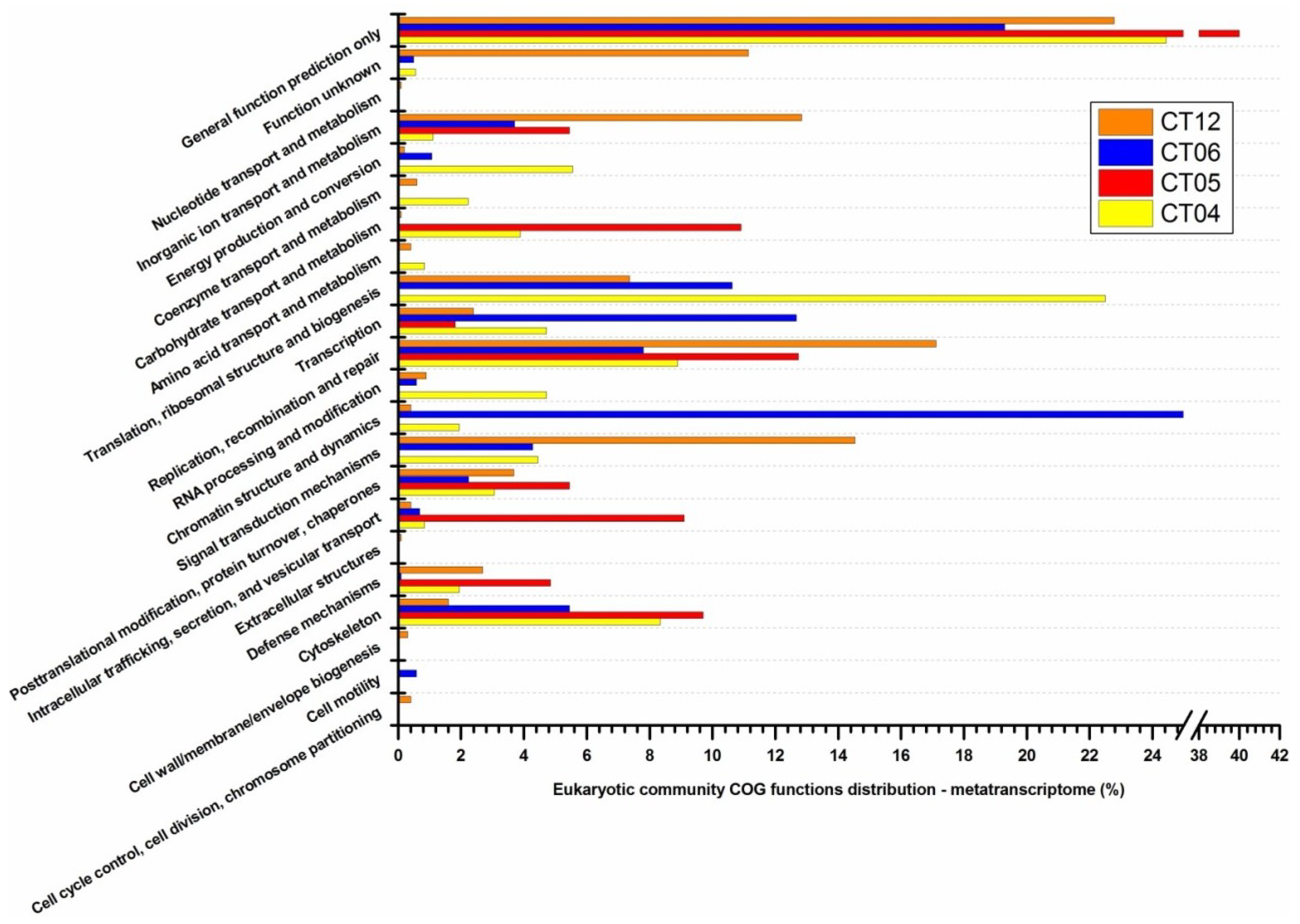
2.6. Taxonomic and Functional Study of the Deep-Sea Eukaryotic Community
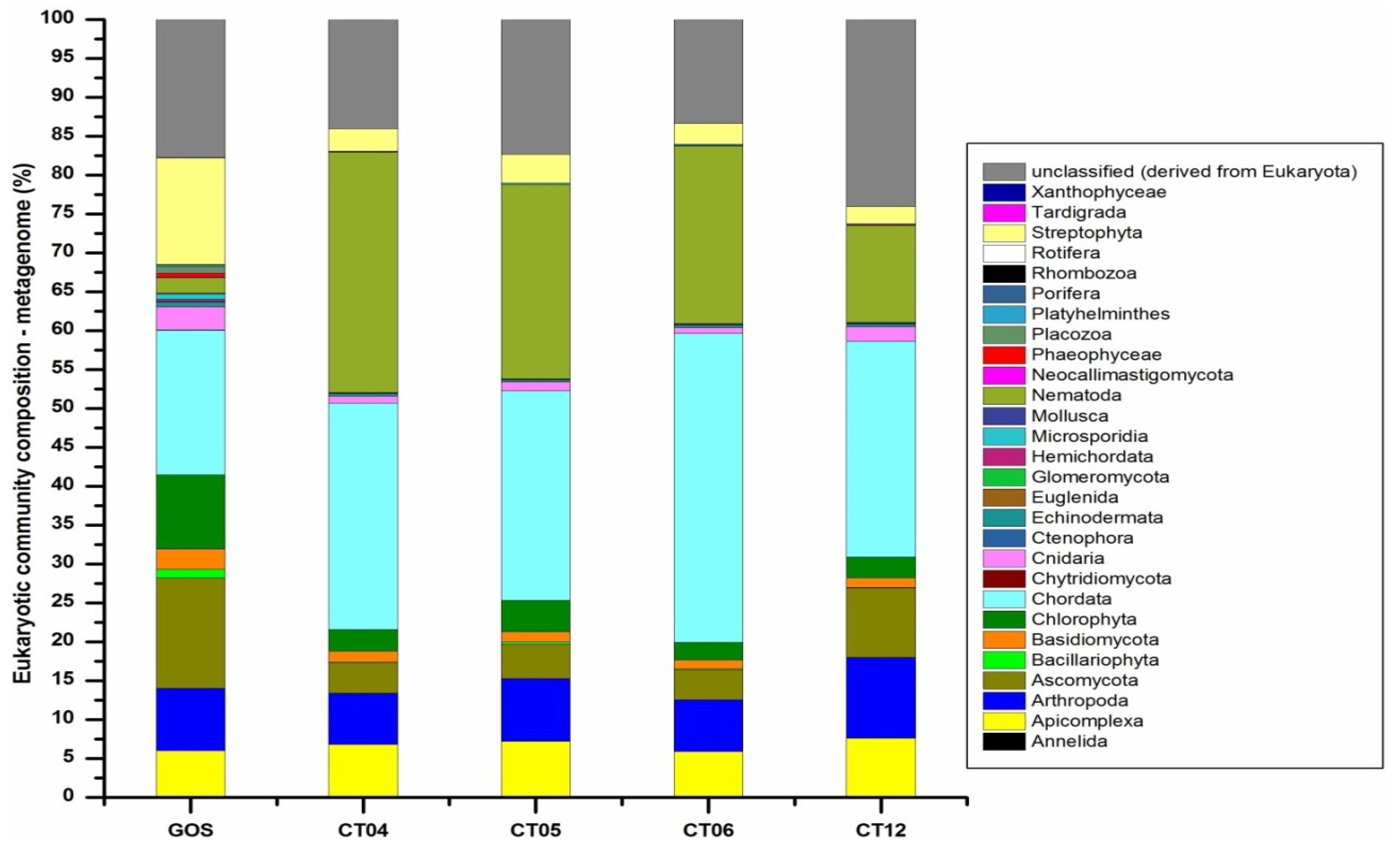
| Level 1 | Level 2 | CT04 | CT05 | CT06 | CT12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cellular processes and signaling | Cell cycle control, cell division, chromosome partitioning | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.12 |
| Cell wall/membrane/envelope biogenesis | 60.87 | 0 | 19.46 | 40.53 | |
| Defense mechanisms | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.12 | |
| Intracellular trafficking, secretion, and vesicular transport | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.23 | |
| Posttranslational modification, protein turnover, chaperones | 12.17 | 0 | 4.70 | 1.51 | |
| Signal transduction mechanisms | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.51 | |
| Information storage and processing | Replication, recombination and repair | 21.74 | 0 | 27.52 | 26.13 |
| Transcription | 0 | 33.33 | 14.09 | 3.83 | |
| Translation, ribosomal structure and biogenesis | 0 | 66.67 | 0 | 0.35 | |
| Metabolism | Amino acid transport and metabolism | 0.87 | 0 | 4.70 | 0.58 |
| Carbohydrate transport and metabolism | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.46 | |
| Energy production and conversion | 0.87 | 0 | 7.38 | 0 | |
| Inorganic ion transport and metabolism | 0 | 0 | 9.06 | 12.89 | |
| Lipid transport and metabolism | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.12 | |
| Secondary metabolites biosynthesis, transport and catabolism | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.46 | |
| Poorly characterized | Function unknown | 3.48 | 0 | 9.73 | 3.95 |
| General function prediction only | 0 | 0 | 3.36 | 7.20 |
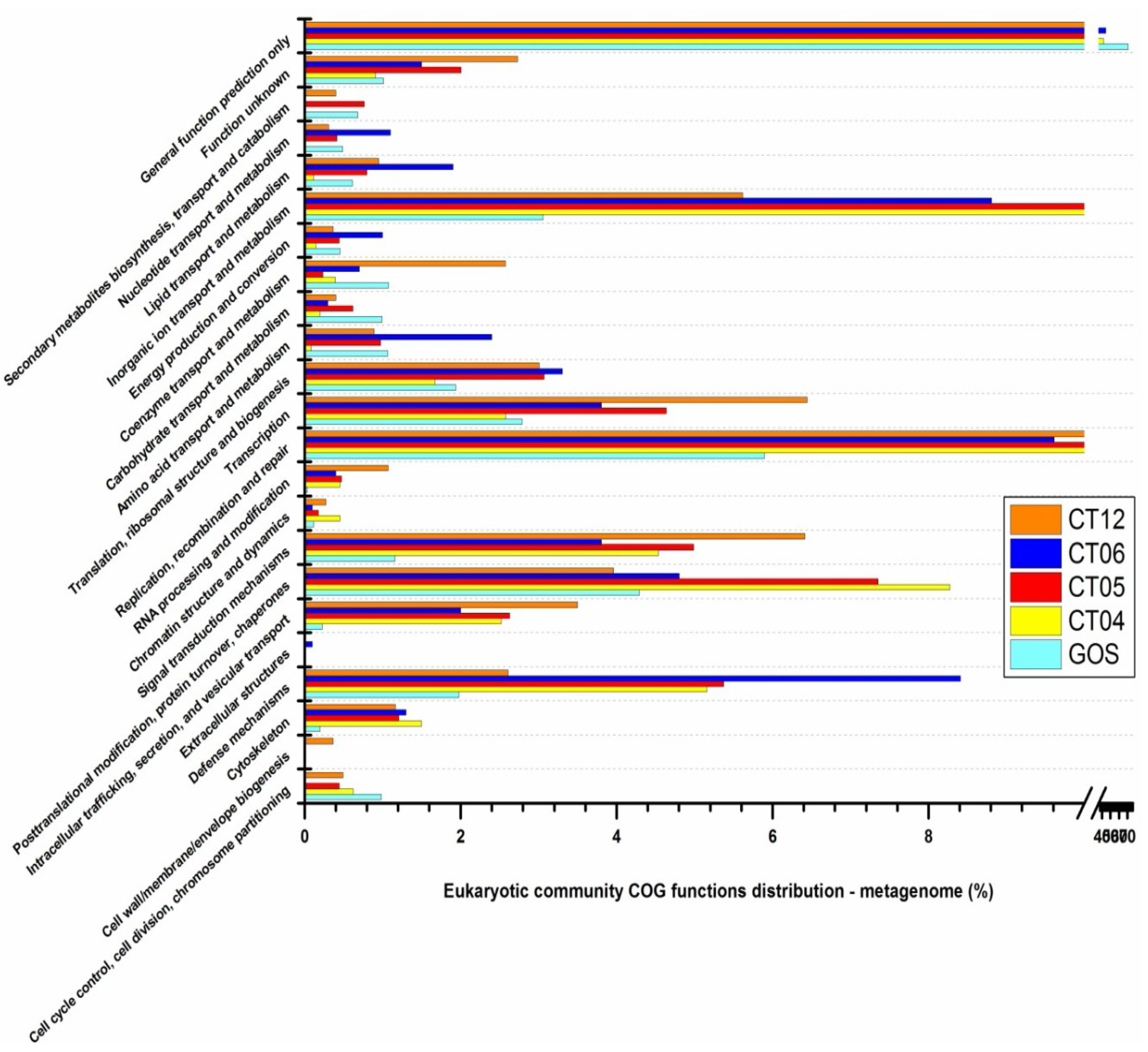
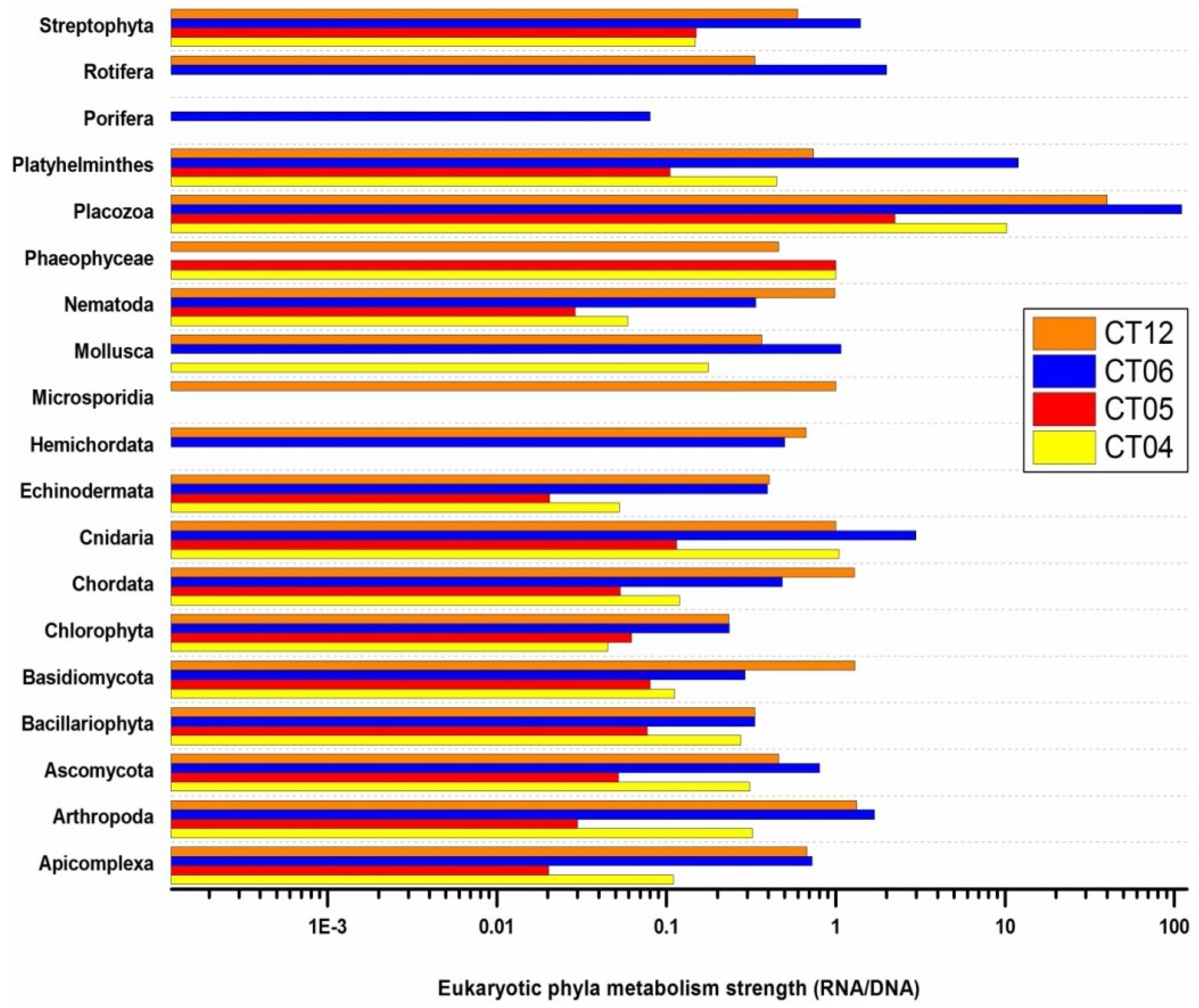
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Microbial Sample Collection and DNA/RNA Isolation
3.2. DNA/RNA Amplification, Second Strand cDNA Synthesis, and Quality Examination
3.3. Pyrosequencing
3.4. Data Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Orcutt, B.N.; Sylvan, J.B.; Knab, N.J.; Edwards, K.J. Microbial ecology of the dark ocean above, at, and below the Seafloor. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2011, 75, 361–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aristegui, J.; Gasol, J.M.; Duarte, C.M.; Herndl, G.J. Microbial oceanography of the dark ocean’s pelagic realm. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2009, 54, 1501–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arístegui, J.; Duarte, C.M.; Agustí, S.; Doval, M.; Alvarez-Salgado, X.A.; Hansell, D.A. Dissolved organic carbon support of respiration in the dark ocean. Science 2002, 298, 1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arístegui, J.; Duarte, C.M.; Gasol, J.M.; Alonso-Sáez, L. Active mesopelagic prokaryotes support high respiration in the subtropical northeast Atlantic Ocean. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teske, A.; Durbin, A.; Ziervogel, K.; Cox, C.; Arnosti, C. Microbial community composition and function in permanently cold seawater and sediments from an arctic fjord of Svalbard. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 2008–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haefner, B. Drugs from the deep: Marine natural products as drug candidates. Drug Discov. Today 2003, 8, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenical, W.; Jensen, P.R. Developing a new resource for drug discovery: Marine actinomycete bacteria. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2006, 2, 666–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schattenhofer, M.; Fuchs, B.M.; Amann, R.; Zubkov, M.V.; Tarran, G.A.; Pernthaler, J. Latitudinal distribution of prokaryotic picoplankton populations in the Atlantic Ocean. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 11, 2078–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massana, R.; Pedrós-Alió, C. Unveiling new microbial eukaryotes in the surface ocean. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2008, 11, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díez, B.; Pedrós-Alió, C.; Massana, R. Study of genetic diversity of eukaryotic picoplankton in different oceanic regions by small-subunit rRNA gene cloning and sequencing. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 2932–2941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frias-Lopez, J.; Shi, Y.; Tyson, G.W.; Coleman, M.L.; Schuster, S.C.; Chisholm, S.W.; Delong, E.F. Microbial community gene expression in ocean surface waters. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 3805–3810. [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert, J.A.; Field, D.; Huang, Y.; Edwards, R.; Li, W.; Gilna, P.; Joint, I. Detection of large numbers of novel sequences in the metatranscriptomes of complex marine microbial communities. PLoS One 2008, 3, e3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poretsky, R.S.; Gifford, S.; Rinta-Kanto, J.; Vila-Costa, M.; Moran, M.A. Analyzing gene expression from marine microbial communities using environmental transcriptomics. J. Vis. Exp. JoVE 2009, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vila-Costa, M.; Rinta-Kanto, J.M.; Sun, S.; Sharma, S.; Poretsky, R.; Moran, M.A. Transcriptomic analysis of a marine bacterial community enriched with dimethylsulfoniopropionate. ISME J. 2010, 4, 1410–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, F.J.; Ulloa, O.; Delong, E.F. Microbial metatranscriptomics in a permanent marine oxygen minimum zone. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 14, 23–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinta-Kanto, J.M.; Sun, S.; Sharma, S.; Kiene, R.P.; Moran, M.A. Bacterial community transcription patterns during a marine phytoplankton bloom. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 14, 228–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, S.; Rupek, P.; Richter, D.C.; Urich, T.; Gilbert, J.A.; Meyer, F.; Wilke, A.; Huson, D.H. Functional analysis of metagenomes and metatranscriptomes using SEED and KEGG. BMC Bioinforma. 2011, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; McCarren, J.; Delong, E.F. Transcriptional responses of surface water marine microbial assemblages to deep-sea water amendment. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 14, 191–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Cuadrado, A.-B.; López-García, P.; Alba, J.-C.; Moreira, D.; Monticelli, L.; Strittmatter, A.; Gottschalk, G.; Rodríguez-Valera, F. Metagenomics of the deep Mediterranean, a warm bathypelagic habitat. PLoS One 2007, 2, e914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roussel, E.G.; Konn, C.; Charlou, J.-L.; Donval, J.-P.; Fouquet, Y.; Querellou, J.; Prieur, D.; Bonavita, M.-A.C. Comparison of microbial communities associated with three Atlantic ultramafic hydrothermal systems. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2011, 77, 647–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eloe, E.A.; Fadrosh, D.W.; Novotny, M.; Zeigler Allen, L.; Kim, M.; Lombardo, M.-J.; Yee-Greenbaum, J.; Yooseph, S.; Allen, E.E.; Lasken, R.; Williamson, S.J.; Bartlett, D.H. Going deeper: Metagenome of a hadopelagic microbial community. PLoS One 2011, 6, e20388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawagucci, S.; Yoshida, Y.T.; Noguchi, T.; Honda, M.C.; Uchida, H.; Ishibashi, H.; Nakagawa, F.; Tsunogai, U.; Okamura, K.; Takaki, Y.; Nunoura, T.; Miyazaki, J.; Hirai, M.; Lin, W.; Kitazato, H.; Takai, K. Disturbance of deep-sea environments induced by the M9.0 Tohoku Earthquake. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danovaro, R.; Dell’anno, A.; Pusceddu, A.; Fabiano, M. Nucleic acid concentrations (DNA, RNA) in the continental and deep-sea sediments of the eastern Mediterranean: Relationships with seasonally varying organic inputs and bacterial dynamics. Deep Sea Res. Part Ocean. Res. Pap. 1999, 46, 1077–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Gao, W.; Zhang, W.; Meldrum, D.R. Optimization of whole-transcriptome amplification from low cell density deep-sea microbial samples for metatranscriptomic analysis. J. Microbiol. Methods 2011, 84, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urich, T.; Lanzén, A.; Qi, J.; Huson, D.H.; Schleper, C.; Schuster, S.C. Simultaneous assessment of soil microbial community structure and function through analysis of the meta-transcriptome. PLoS One 2008, 3, e2527. [Google Scholar]
- Morse, A.M.; Carballo, V.; Baldwin, D.A.; Taylor, C.G.; McIntyre, L.M. Comparison between NuGEN’s WT-Ovation Pico and one-direct amplification systems. J. Biomol. Tech. 2010, 21, 141–147. [Google Scholar]
- Skalitzky, C.; Watt, M.-A. Evaluation of RNA Amplification Methods for NimbleGen Gene Expression Microarray Analysis, 2010. Roche NimbleGen. Available online: http://www.nimblegen.com/products/lit/NG_GeneExp_TechNote_RNAAmplification_101310.pdf (accessed on 5 May 2013).
- DeLong, E.F.; Preston, C.M.; Mincer, T.; Rich, V.; Hallam, S.J.; Frigaard, N.-U.; Martinez, A.; Sullivan, M.B.; Edwards, R.; Brito, B.R.; et al. Community genomics among stratified microbial assemblages in the ocean’s interior. Science 2006, 311, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusch, D.B.; Halpern, A.L.; Sutton, G.; Heidelberg, K.B.; Williamson, S.; Yooseph, S.; Wu, D.; Eisen, J.A.; Hoffman, J.M.; Remington, K.; et al. The sorcerer II global ocean sampling expedition: Northwest Atlantic through eastern tropical Pacific. PLoS Biol. 2007, 5, e77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.V.; Philip, G.K.; Bunge, J.A.; Smith, M.C.; Bissett, A.; Lauro, F.M.; Fuhrman, J.A.; Donachie, S.P. Microbial community structure in the North Pacific ocean. ISME J. 2009, 3, 1374–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, L.; Xu, X.-W.; Jiang, X.-W.; Wang, C.-S.; Zhang, D.-S.; Ni, J.-Y.; Wu, M. Microbial diversity in deep-sea sediment from the cobalt-rich crust deposit region in the Pacific Ocean. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2011, 78, 565–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schippers, A.; Kock, D.; Höft, C.; Köweker, G.; Siegert, M. Quantification of Microbial Communities in Subsurface Marine Sediments of the Black Sea and off Namibia. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karner, M.B.; DeLong, E.F.; Karl, D.M. Archaeal dominance in the mesopelagic zone of the Pacific Ocean. Nature 2001, 409, 507–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herndl, G.J.; Reinthaler, T.; Teira, E.; van Aken, H.; Veth, C.; Pernthaler, A.; Pernthaler, J. Contribution of Archaea to total prokaryotic production in the deep Atlantic Ocean. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 2303–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pester, M.; Rattei, T.; Flechl, S.; Gröngröft, A.; Richter, A.; Overmann, J.; Reinhold-Hurek, B.; Loy, A.; Wagner, M. amoA-Based consensus phylogeny of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and deep sequencing of amoA genes from soils of four different geographic regions. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 14, 525–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber, N.; Galloway, J.N. An earth-system perspective of the global nitrogen cycle. Nature 2008, 451, 293–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purkhold, U.; Pommerening-Röser, A.; Juretschko, S.; Schmid, M.C.; Koops, H.P.; Wagner, M. Phylogeny of all recognized species of ammonia oxidizers based on comparative 16S rRNA and amoA sequence analysis: implications for molecular diversity surveys. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 5368–5382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schleper, C.; Nicol, G.W. Ammonia-oxidising archaea—Physiology, ecology and evolution. Adv. Microb. Physiol. 2010, 57, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pester, M.; Schleper, C.; Wagner, M. The Thaumarchaeota: An emerging view of their phylogeny and ecophysiology. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2011, 14, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkpatrick, J.; Oakley, B.; Fuchsman, C.; Srinivasan, S.; Staley, J.T.; Murray, J.W. Diversity and distribution of planctomycetes and related bacteria in the suboxic zone of the Black Sea. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 3079–3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, N.; Strous, M.; Crépeau, V.; Kartal, B.; Birrien, J.-L.; Schmid, M.; Lesongeur, F.; Schouten, S.; Jaeschke, A.; Jetten, M.; et al. Presence and activity of anaerobic ammonium-oxidizing bacteria at deep-sea hydrothermal vents. ISME J. 2009, 3, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuerst, J.A.; Webb, R.I.; van Niftrik, L.; Jetten, M.S.M.; Strous, M. Anammoxosomes of anaerobic ammonium-oxidizing planctomycetes. Microbiol. Monogr. 2006, 2, 259–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuypers, M.M.M.; Lavik, G.; Woebken, D.; Schmid, M.; Fuchs, B.M.; Amann, R.; Jørgensen, B.B.; Jetten, M.S.M. Massive nitrogen loss from the Benguela upwelling system through anaerobic ammonium oxidation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 6478–6483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gärtner, A.; Blümel, M.; Wiese, J.; Imhoff, J.F. Isolation and characterisation of bacteria from the Eastern Mediterranean deep sea. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2011, 100, 421–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, C.; Wiezer, A.; Strittmatter, A.W.; Daniel, R. Phylogenetic diversity and metabolic potential revealed in a glacier ice metagenome. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 7519–7526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Steindler, L.; Thrash, J.C.; Halsey, K.H.; Smith, D.P.; Carter, A.E.; Landry, Z.C.; Giovannoni, S.J. One carbon metabolism in SAR11 pelagic marine bacteria. PLoS One 2011, 6, e23973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viklund, J.; Ettema, T.J.G.; Andersson, S.G.E. Independent genome reduction and phylogenetic reclassification of the oceanic SAR11 Clade. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2012, 29, 599–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laghdass, M.; Catala, P.; Caparros, J.; Oriol, L.; Lebaron, P.; Obernosterer, I. High contribution of SAR11 to microbial activity in the North West Mediterranean Sea. Microb. Ecol. 2012, 63, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, F.; Paarmann, D.; D’Souza, M.; Olson, R.; Glass, E.M.; Kubal, M.; Paczian, T.; Rodriguez, A.; Stevens, R.; Wilke, A.; et al. The metagenomics RAST server—A public resource for the automatic phylogenetic and functional analysis of metagenomes. BMC Bioinforma. 2008, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhou, H.; Meng, J.; Peng, X.; Jiang, L.; Sun, P.; Zhang, C.; Van Nostrand, J.D.; Deng, Y.; He, Z.; et al. GeoChip-Based analysis of metabolic diversity of microbial communities at the Juan de Fuca Ridge hydrothermal vent. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci.USA 2009, 106, 4840–4845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrenk, M.O.; Kelley, D.S.; Delaney, J.R.; Baross, J.A. Incidence and diversity of microorganisms within the walls of an active deep-sea sulfide chimney. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 3580–3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Wang, F.; Guo, L.; Chen, Z.; Sievert, S.M.; Meng, J.; Huang, G.; Li, Y.; Yan, Q.; Wu, S.; et al. Comparative metagenomics of microbial communities inhabiting deep-sea hydrothermal vent chimneys with contrasting chemistries. ISME J. 2010, 5, 414–426. [Google Scholar]
- El-Hajj, Z.W.; Tryfona, T.; Allcock, D.J.; Hasan, F.; Lauro, F.M.; Sawyer, L.; Bartlett, D.H.; Ferguson, G.P. Importance of proteins controlling initiation of DNA replication in the growth of the high-pressure-loving bacterium Photobacterium profundum SS9. J. Bacteriol. 2009, 191, 6383–6393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domigan, L.J.; Scally, S.W.; Fogg, M.J.; Hutton, C.A.; Perugini, M.A.; Dobson, R.C.J.; Muscroft-Taylor, A.C.; Gerrard, J.A.; Devenish, S.R.A. Characterisation of dihydrodipicolinate synthase (DHDPS) from Bacillus anthracis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1794, 1510–1516. [Google Scholar]
- Wolanin, P.M.; Thomason, P.A.; Stock, J.B. Histidine protein kinases: Key signal transducers outside the animal kingdom. Genome Biol. 2002, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, B.L.; Zhulin, I.B. PAS domains: Internal sensors of oxygen, redox potential, and light. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 1999, 63, 479–506. [Google Scholar]
- Heusipp, G.; Fälker, S.; Schmidt, M.A. DNA adenine methylation and bacterial pathogenesis. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2007, 297, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakai, R.; Abe, T.; Takeyama, H.; Naganuma, T. Metagenomic analysis of 0.2-μm-passable microorganisms in deep-sea hydrothermal fluid. Mar. Biotechnol. 2011, 13, 900–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, V.; Braun, M. Active transport of iron and siderophore antibiotics. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2002, 5, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jannasch, H. Microbial Interactions with Hydrothermal Fluids. In Seafloor Hydrothermal Systems: Physical, Chemical, Biological, and Geological Interactions; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 1995; pp. 273–296. [Google Scholar]
- Konstantinidis, K.T.; Braff, J.; Karl, D.M.; DeLong, E.F. Comparative metagenomic analysis of a microbial community residing at a depth of 4,000 meters at station ALOHA in the North Pacific subtropical gyre. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 5345–5355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herndl, G.J.; Agogu, H.; Baltar, F.; Reinthaler, T.; Sintes, E.; Varela, M.M. Regulation of aquatic microbial processes: The “microbial loop” of the sunlit surface waters and the dark ocean dissected. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2008, 53, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, D.A.; Zaikova, E.; Howes, C.G.; Song, Y.C.; Wright, J.J.; Tringe, S.G.; Tortell, P.D.; Hallam, S.J. Metagenome of a versatile chemolithoautotroph from expanding oceanic dead zones. Science 2009, 326, 578–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilibić, I.; Šantić, D. Deep water ventilation traced by Synechococcus cyanobacteria. Ocean Dyn. 2008, 58, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Shi, X.; Wu, J.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, W.; Meldrum, D.R. Phylogenetic and gene expression analysis of cyanobacteria and diatoms in the twilight waters of the temperate northeast Pacific Ocean. Microb. Ecol. 2011, 62, 765–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koblížek, M.; Komenda, J.; Masojídek, J.; Pechar, L. Cell aggregation of the cyanobacterium Synechococcus elongatus: Role of the electron transport chain. J. Phycol. 2001, 36, 662–668. [Google Scholar]
- Amacher, J.; Neuer, S.; Lomas, M. DNA-based molecular fingerprinting of eukaryotic protists and cyanobacteria contributing to sinking particle flux at the Bermuda Atlantic time-series study. Deep Sea Res. Part II 2013, 93, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bass, D.; Howe, A.; Brown, N.; Barton, H.; Demidova, M.; Michelle, H.; Li, L.; Sanders, H.; Watkinson, S.C.; Willcock, S.; Richards, T.A. Yeast forms dominate fungal diversity in the deep oceans. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2007, 274, 3069–3077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gestal, C.; Pascual, S.; Hochberg, F.G. Aggregata bathytherma sp. nov. (Apicomplexa: Aggregatidae), a new coccidian parasite associated with a deep-sea hydrothermal vent octopus. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2010, 91, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takishita, K.; Yubuki, N.; Kakizoe, N.; Inagaki, Y.; Maruyama, T. Diversity of microbial eukaryotes in sediment at a deep-sea methane cold seep: Surveys of ribosomal DNA libraries from raw sediment samples and two enrichment cultures. Extremophiles Life Extreme Cond. 2007, 11, 563–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Buron, I.; Morand, S. Deep-Sea hydrothermal vent parasites: Why do we not find more? Parasitology 2004, 128, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambshead, P.J.D.; Boucher, G. Marine nematode deep-sea biodiversity—Hyperdiverse or hype? J. Biogeogr. 2003, 30, 475–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merckx, B.; Goethals, P.; Steyaert, M.; Vanreusel, A.; Vincx, M.; Vanaverbeke, J. Predictability of marine nematode biodiversity. Ecol. Model. 2009, 220, 1449–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanreusel, A.; de Groote, A.; Gollner, S.; Bright, M. Ecology and biogeography of free-living nematodes associated with chemosynthetic environments in the deep sea: A review. PLoS One 2010, 5, e12449. [Google Scholar]
- Schierwater, B.; de Jong, D.; Desalle, R. Placozoa and the evolution of Metazoa and intrasomatic cell differentiation. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2009, 41, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eitel, M.; Schierwater, B.; Eitel, M.; Schierwater, B. The phylogeography of the Placozoa suggests a taxon-rich phylum in tropical and subtropical waters. Mol. Ecol. 2010, 19, 2315–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, Y.K. Occurrence in the field of a long-term, year-round, stable population of placozoans. Biol. Bull. 2004, 206, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Calvez, T.; Burgaud, G.; Mahé, S.; Barbier, G.; Vandenkoornhuyse, P. Fungal diversity in deep-sea hydrothermal ecosystems. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 6415–6421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhadury, P.; Bik, H.; Lambshead, J.D.; Austen, M.C.; Smerdon, G.R.; Rogers, A.D. Molecular diversity of fungal phylotypes co-amplified alongside nematodes from coastal and deep-sea marine environments. PLoS One 2011, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takishita, K.; Tsuchiya, M.; Reimer, J.D.; Maruyama, T. Molecular evidence demonstrating the basidiomycetous fungus Cryptococcus curvatus is the dominant microbial eukaryote in sediment at the Kuroshima Knoll methane seep. Extremophiles Life Extreme Cond. 2006, 10, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Supplementary Files
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, J.; Gao, W.; Johnson, R.H.; Zhang, W.; Meldrum, D.R. Integrated Metagenomic and Metatranscriptomic Analyses of Microbial Communities in the Meso- and Bathypelagic Realm of North Pacific Ocean. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 3777-3801. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11103777
Wu J, Gao W, Johnson RH, Zhang W, Meldrum DR. Integrated Metagenomic and Metatranscriptomic Analyses of Microbial Communities in the Meso- and Bathypelagic Realm of North Pacific Ocean. Marine Drugs. 2013; 11(10):3777-3801. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11103777
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Jieying, Weimin Gao, Roger H. Johnson, Weiwen Zhang, and Deirdre R. Meldrum. 2013. "Integrated Metagenomic and Metatranscriptomic Analyses of Microbial Communities in the Meso- and Bathypelagic Realm of North Pacific Ocean" Marine Drugs 11, no. 10: 3777-3801. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11103777
APA StyleWu, J., Gao, W., Johnson, R. H., Zhang, W., & Meldrum, D. R. (2013). Integrated Metagenomic and Metatranscriptomic Analyses of Microbial Communities in the Meso- and Bathypelagic Realm of North Pacific Ocean. Marine Drugs, 11(10), 3777-3801. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11103777





