A New Spatane Diterpenoid from the Cultured Soft Coral Sinularia leptoclados
Abstract
:1. Introduction

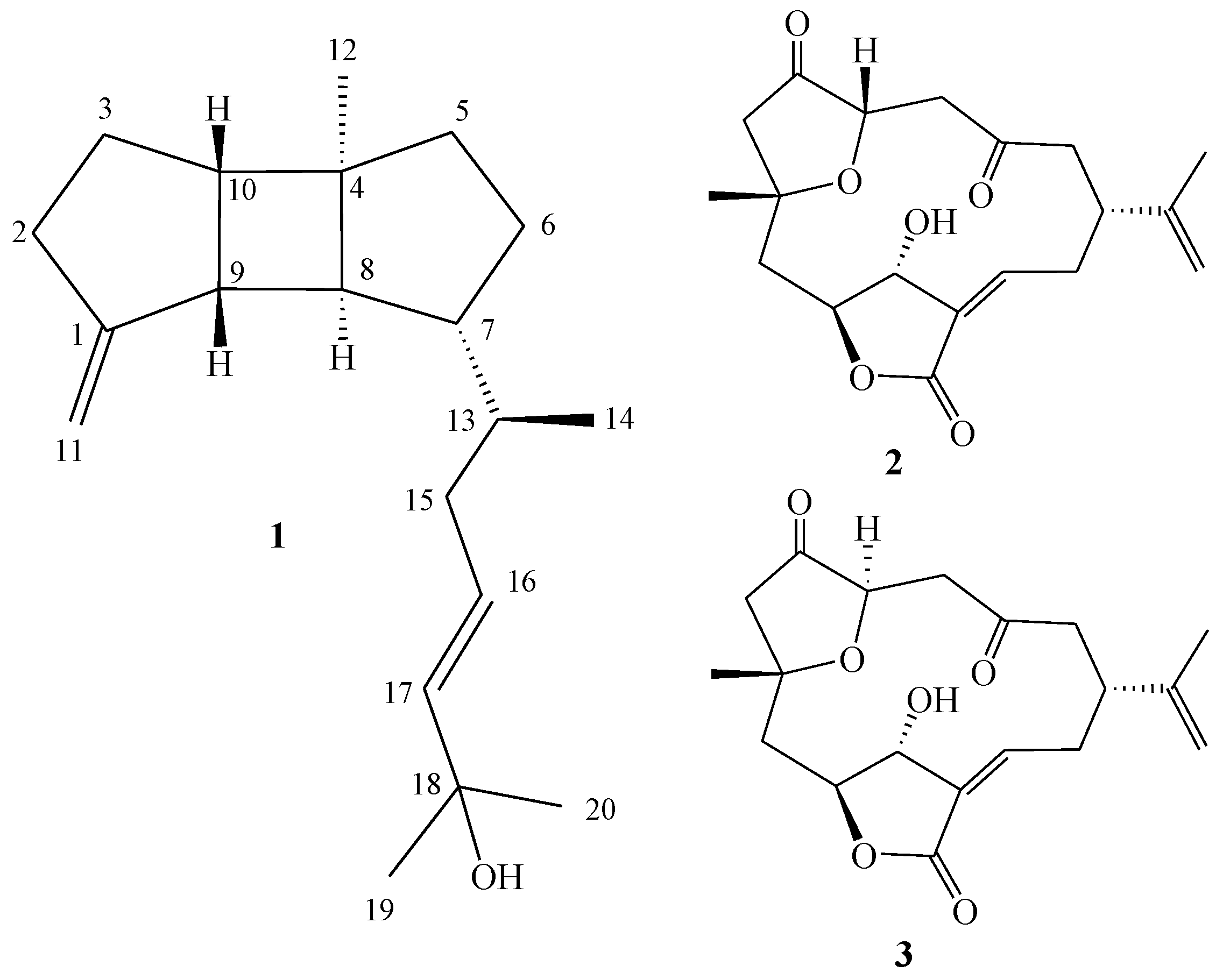
2. Results and Discussion
| δH (J in Hz) a | δC (mult.) b | δH (J in Hz) c | δC (mult.) d | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 157.5 (C) | 157.8 (C) | ||
| 2 | 2.54 m; 2.28 m | 33.7 (CH2) | 2.55 m; 2.27 m | 34.4 (CH2) |
| 3 | 1.81 m; 1.59 m | 27.2 (CH2) | 1.74 m; 1.52 m | 28.0 (CH2) |
| 4 | 43.1 (C) | 43.8 (C) | ||
| 5 | 1.50 m | 42.0 (CH2) | 1.48 m | 42.7 (CH2) |
| 6 | 1.89 m; 1.55 m | 29.7 (CH2) | 1.84 m; 1.54 m | 30.6 (CH2) |
| 7 | 1.62 m | 54.5 (CH) | 1.62 m | 55.3 (CH) |
| 8 | 1.62 m | 55.0 (CH) | 1.67 m | 55.8 (CH) |
| 9 | 2.35 m | 47.8 (CH) | 2.46 m | 48.6 (CH) |
| 10 | 2.32 m | 45.7 (CH) | 2.24 m | 46.4 (CH) |
| 11 | 4.74 s; 4.70 s | 103.7 (CH2) | 4.89 s; 4.87 s | 104.8 (CH2) |
| 12 | 1.00 s | 21.6 (CH3) | 0.94 s | 22.0 (CH3) |
| 13 | 1.20 m | 36.3 (CH) | 1.20 m | 37.4 (CH) |
| 14 | 0.83 d (6.5) | 17.8 (CH3) | 0.88 d (6.5) | 18.4 (CH3) |
| 15 | 2.15 ddd (13.5, 3.5, 3.5); 1.74 m | 38.2 (CH2) | 2.27 m; 1.85 m | 39.1 (CH2) |
| 16 | 5.58 m | 125.8 (CH) | 5.90 m | 125.1 (CH) |
| 17 | 5.58 m | 139.2 (CH) | 5.90 m | 142.0 (CH) |
| 18 | 70.7 (C) | 70.1 (C) | ||
| 19 | 1.31 s | 29.9 (CH3) | 1.53 s | 31.3 (CH3) |
| 20 | 1.31 s | 29.8 (CH3) | 1.53 s | 31.2 (CH3) |



| 4 b | 5 b | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| position | δH (J in Hz) | δC (mult.) | δH (J in Hz) | δC (mult.) |
| 22a | 1.74 m | 39.0 (CH2) | 2.13 dddd (14.8, 9.9, 8.8, 1.7) | 34.6 (CH2) |
| 22b | 2.17 ddd (14.0, 3.3, 3.3) | 2.38 dddd (14.8, 6.1, 3.8, 1.7) | ||
| 23 | 5.60 m | 125.6 (CH) | 5.31 ddd (12.1, 8.8, 6.1) | 130.2 (CH) |
| 24 | 5.60 m | 139.4 (CH) | 5.53 ddd (12.1, 1.7, 1.7) | 137.4 (CH) |
| 25 | 70.7 (C) | 71.6 (C) | ||
| 26 | 1.31 s | 30.0 (CH3) | 1.36 s | 31.3 (CH3) |
| 27 | 1.32 s | 29.9 (CH3) | 1.37 s | 31.1 (CH3) |
| Cell Lines | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compound | DLD-1 | HCT-116 | T-47D | K-562 |
| 1 | NA b | NA b | 15.4 | 12.8 |
| 2 | NA b | NA b | NA b | NA b |
| 3 | NA b | NA b | NA b | NA b |
| Doxorubicin a | 0.42 | 0.89 | 0.28 | 0.14 |
3. Experimental Section
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Animal Material
3.3. Extraction and Separation
3.4. Cytotoxicity Testing
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
Supplementary Files
References
- Blunt, J.W.; Copp, B.R.; Keyzers, R.A.; Munro, M.H.G.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2012, 29, 144–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, A.D.; Nielson, J.L.; Tapiolas, D.M.; Liptrot, C.H.; Motti, C.A. A great barrier reef Sinularia sp. yields two new cytotoxic diterpenes. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 1619–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, T.-R.; Tsai, F.-J.; Lin, J.-J.; Huang, H.H.; Chiu, C.-C.; Su, J.-H.; Yang, Y.-T.; Chen, J.-F.; Wong, B.-S.; Wu, Y.-J. Induction of apoptosis by 11-dehydrosinulariolide via mitochondrial dysregulation and ER stress pathways in human melanoma Cells. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 1883–1898. [Google Scholar]
- Su, J.-H.; Wen, Z.-H. Bioactive cembrane-based diterpenoids from the soft coral Sinularia triangula. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 944–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, C.-H.; Chou, K.-J.; Huang, C.-Y.; Wen, Z.-H.; Hsu, C.-H.; Wu, Y.-C.; Dai, C.-F.; Sheu, J.-H. Bioactive cembranoids from the soft coral Sinularia crassa. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 1955–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.-Y.; Huang, K.-J.; Wang, S.-K.; Wen, Z.-H.; Chen, P.-W.; Duh, C.-Y. Antiviral and anti-inflammatory metabolites from the soft coral Sinularia capillosa. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 771–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Yu, S.; Liu, D.; van Ofwegen, L.; Proksch, P.; Lin, W. Sinularones A–I, new cyclopentenone and butenolide derivatives from a marine soft coral Sinularia sp. and their antifouling activity. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 1331–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.-W.; Wu, Y.-C.; Chiang, M.Y.; Su, J.-H.; Wang, W.-H.; Fang, T.-Y.; Sheu, J.-H. Eunicellin-based diterpenoids from the cultured soft coral Klyxum simplex. Tetrahedron 2009, 65, 7016–7022. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.-W.; Chao, C.-H.; Su, J.-H.; Wen, Z.-H.; Sung, P.-J.; Sheu, J.-H. Anti-inflammatory eunicellin-based diterpenoids from the cultured soft coral Klyxum simplex. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2010, 8, 2363–2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.-W.; Chao, C.-H.; Su, J.-H.; Tsai, C.-W.; Wang, W.-H.; Wen, Z.-H.; Hsieh, C.-H.; Sung, P.-J.; Wu, Y.-C.; Sheu, J.-H. Klysimplexins I-T, eunicellin-based diterpenoids from the cultured soft coral Klyxum simplex. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2011, 9, 834–844. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.-W.; Huang, C.-Y.; Wen, Z.-H.; Su, J.-H.; Wang, W.-H.; Sung, P.-J.; Wu, Y.-C.; Sheu, J.-H. Klysimplexins U-X, eunicellin-based diterpenoids from the cultured soft coral Klyxum simplex. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2011, 84, 1237–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.-H.; Lin, Y.-F.; Lu, Y.; Huang, C.-Y.; Wang, W.-H.; Fang, T.-Y.; Sheu, J.-H. Oxygenated cembranoids from the cultured and wild-type soft corals Sinularia flexibilis. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2009, 57, 1189–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.-H.; Lu, Y.; Lin, W.-Y.; Wang, W.-H.; Sung, P.-J.; Sheu, J.-H. A cembranoid, trocheliophorol, from the cultured soft coral Sarcophyton trocheliophoru. Chem. Lett. 2010, 39, 172–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.-L.; Su, J.-H. Tetrahydrofuran cembranoids from the cultured soft coral Lobophytum crassum. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 2526–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Pattenden, G. Novel macrocyclic and polycyclic norcembranoid diterpenes from Sinularia species of soft coral: Structural relationships and biosynthetic speculations. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2011, 28, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, S.; Satoh, H.; Hongo, Y.; Koshino, H. Structural revision of terpenoids with a (3Z)-2-methyl-3-penten-2-ol moiety by the synthesis of (23E)- and (23Z)-cycloart-23-ene-3β,25-diols. J. Org. Chem. 2007, 72, 4578–4581. [Google Scholar]
- Alley, M.C.; Scudiero, D.A.; Monks, A.; Hursey, M.L.; Czerwinski, M.J.; Fine, D.L.; Abbott, B.J.; Mayo, J.G.; Shoemaker, R.H.; Boyd, M.R. Feasibility of drug screening with panels of human tumor cell lines using a microculture tetrazolium assay. Cancer Res. 1988, 48, 589–601. [Google Scholar]
- Scudiero, D.A.; Shoemaker, R.H.; Paull, K.D.; Monks, A.; Tierney, S.; Nofziger, T.H.; Currens, M.J.; Seniff, D.; Boyd, M.R. Evaluation of a soluble tetrazolium/formazan assay for cell growth and drug sensitivity in culture using human and other tumor cell lines. Cancer Res. 1988, 48, 4827–4833. [Google Scholar]
- Gerwick, W.H.; Fenical, W.; Engen, D.V.; Clardy, J. Isolation and structure of spatol, a potent inhibitor of cell replication from the brown seaweed Spatoglossum schmittii. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1980, 102, 7991–7993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rosa, S.; Iodice, C.; Khalaghdoust, M.; Oryan, S.; Rustaiyan, A. Spatane diterpenoids from the brown alga Stoechospermum marginatum (Dictyotaceae). Phytochemistry 1999, 51, 1009–1012. [Google Scholar]
- Yamase, H.; Umemoto, K.; Ooi, T.; Kusumi, T. Structures and absolute stereochemistry of five new secospatanes and a spatane isolated from the brown alga Dilophus okamurai DAWSON. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1999, 47, 813–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkateswarlu, Y.; Biabani, M. A spatane diterpene from the brown alga Stoechospermum marginatum. Phytochemistry 1995, 40, 331–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanaltena, I.A.; Mcgivern, J. New spatane-derived diterpenoids from the Australian brown alga Dictyota fenestrata. Aust. J. Chem. 1992, 45, 541–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurata, K.; Suzuki, M.; Shiraishi, K.; Taniguchi, K. Spatane-type diterpenes with biological activity from the brown alga Dilophus okamurai. Phytochemistry 1988, 27, 1321–1324. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, C.B.; Pullaiah, K.C.; Surapaneni, R.K.; Suryaprabha, R.; Raju, V.S.N. A new spatane diterpenoid from Stoechospermum marginatum C. Agardh. Indian J. Chem. Sect. B 1987, 26, 79–80. [Google Scholar]
- Gerwick, W.H.; Fenical, W. Spatane diterpenoids from the tropical marine algae Spatoglossum schmittii and Spatoglossum howleii (Dictyotaceae). J. Org. Chem. 1983, 48, 3325–3329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerwick, W.H.; Fenical, W.; Sultanbawa, M.U.S. Spatane diterpenoids from the tropical marine alga Stoechospermum marginatum (Dictyotaceae). J. Org. Chem. 1981, 46, 2233–2241. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Sheng, L.; Wang, C.-Y.; Zhou, Y.-B.; Huang, H.; Li, X.-B.; Li, J.; Mollo, E.; Gavagnin, M.; Guo, Y.-W. Diterpenes from the Hainan soft coral Lobophytum cristatum Tixier-Durivault. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 2089–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samples Availability: Available from the authors.
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsai, T.-C.; Wu, Y.-J.; Su, J.-H.; Lin, W.-T.; Lin, Y.-S. A New Spatane Diterpenoid from the Cultured Soft Coral Sinularia leptoclados. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 114-123. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11010114
Tsai T-C, Wu Y-J, Su J-H, Lin W-T, Lin Y-S. A New Spatane Diterpenoid from the Cultured Soft Coral Sinularia leptoclados. Marine Drugs. 2013; 11(1):114-123. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11010114
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsai, Tsung-Chang, Yu-Jen Wu, Jui-Hsin Su, Wei-Tung Lin, and Yun-Sheng Lin. 2013. "A New Spatane Diterpenoid from the Cultured Soft Coral Sinularia leptoclados" Marine Drugs 11, no. 1: 114-123. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11010114
APA StyleTsai, T.-C., Wu, Y.-J., Su, J.-H., Lin, W.-T., & Lin, Y.-S. (2013). A New Spatane Diterpenoid from the Cultured Soft Coral Sinularia leptoclados. Marine Drugs, 11(1), 114-123. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11010114





