Isolation and Characterization of a Lycopene ε-Cyclase Gene of Chlorella (Chromochloris) zofingiensis. Regulation of the Carotenogenic Pathway by Nitrogen and Light
Abstract
:1. Introduction

2. Results
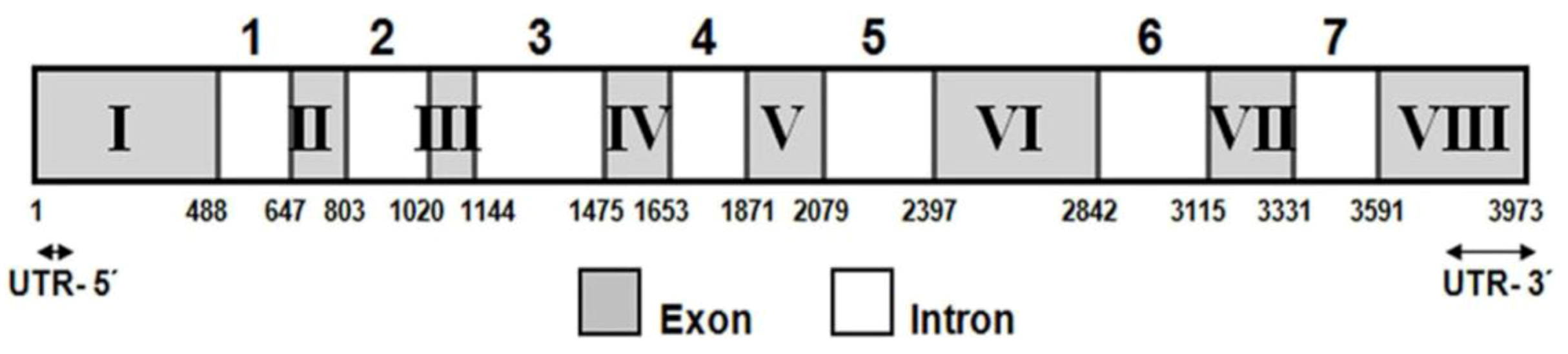
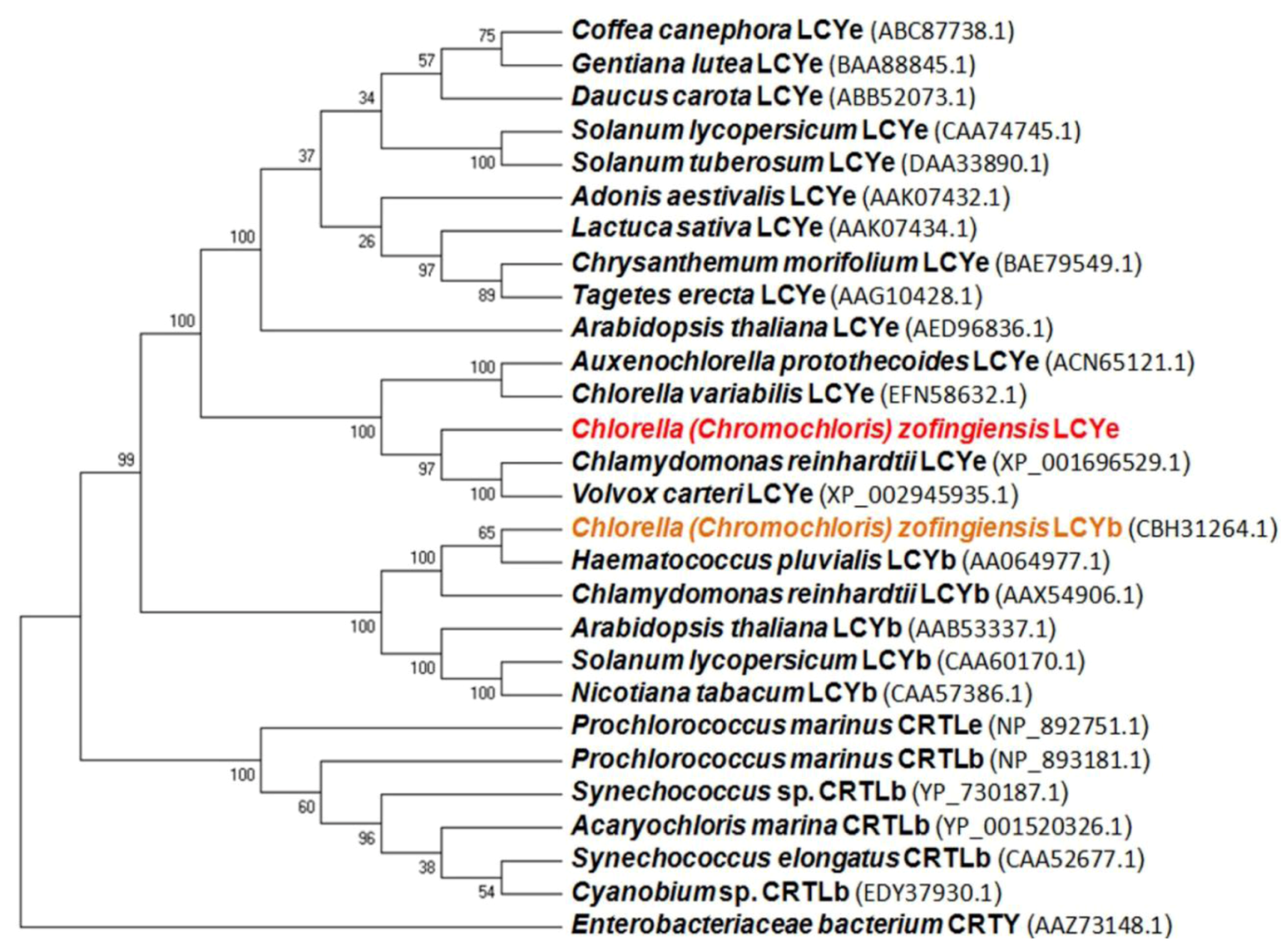
2.1. Isolation and Characterization of the lcy-e Gene and Deduced Protein from C. zofingiensis
| Primer | Sequence (5′→3′) |
|---|---|
| Partial lcy-e fragment | |
| lcy-e-1F | AACCGCGTGTTCCTGGARGARACNTG |
| lcy-e-1R | TGGCACAGCAGCTCCATNCCRAA |
| 5′ and 3′ RACE | |
| GSP-F | GGCATCAAAGTCACACGCATACACG |
| GSP-R | ACTGAACCCTGTGGCGGGATGCACC |
| NGSP-F | ACCCTCAGCAAACCAGCCTATTACAGCT |
| NGSP-R | CTTGAAAGGCAGTGCTGGCTTAGCTA |
| Genomic DNA amplification | |
| lcy-e-2F | ACATGGGGACACCAGCAGCAACTG |
| lcy-e-2R | GCGAGGGGGTTGTGACTGCATCT |
| lcy-e-3F | CCAGCAAGACAAGCTCGCAGCAATG |
| lcy-e-3R | TGCACAGATCCACGAGGTGCTGGC |
| lcy-e-4F | GTGTTACTTTGGTGAGGGCAATCAGGTC |
| lcy-e-4R | CCACAAGCCATCATTAGCATTCGGGTGG |
| lcy-e-5F | GTTCATGGATTACAGAAGGCACCACACAGG |
| lcy-e-5R | TGACTCCCTGACAATGCTTGCACCGC |
| lcy-e-6F | TGGTGCATCCTGCCACAGGGTTCA |
| lcy-e-6R | CACCAGTCATAGCTGATTCCTTACTGCTCC |
| lcy-e-7F | GATCCTGCTGGCAGATACCTAATCAGTC |
| lcy-e-7R | GCAACTCTTGGCTTAAAGCTAGGTGC |
| PCR for probe preparation | |
| Czlcy-e-S-F | CCAGCAAGACAAGCTCGCAGCAATG |
| Czlcy-e-S-R | TGCACAGATCCACGAGGTGCTGGC |
| Genetic complementation-pQE-80L a | |
| pQE-lcy-e-F | gagctcATGGGGACACCAGCAGCAACTGTA |
| pQE-lcy-e-R | aagcttTCACTGTTGCACCTGTGTTGCTGC |
| Czlcy-e expression | |
| RT-Czlcy-e-F | TCAAAGCACAGGCGAACAAACA |
| RT-Czlcy-e-R | AACGTCGGGACCTATAAGTCCG |
| Czlcy-b expression | |
| RT-Czlcy-b-F | CGCAGGCGAAAAATTCCTGTCA |
| RT-Czlcy-b-R | TAAGGAATGTCACACCGCTGGC |
| Czpsy expression | |
| RT-Czpsy-F | CACCAGGTTGTCAGAGTCCA |
| RT-Czpsy-R | ACTAGTGTGTTGCTGACTCT |
| Czpds expression | |
| RT-Czpds-F | GCCAGAAAAGATCCAATTTG |
| RT-Czpds-R | CATGCTTCTCCCGCAAGAAC |
| CzchyB expression | |
| RT-CzchyB-F | ATTGGAGGAGTGTTTGGCATGGAG |
| RT-CzchyB-R | AGATATCGTTGGCCTCGAATGGTC |
| Czbkt expression | |
| RT-Czbkt-F | GTGGTTTGGCAGGTTTATGT |
| RT-Czbkt-R | AGAACAATCGGAACGCACTG |

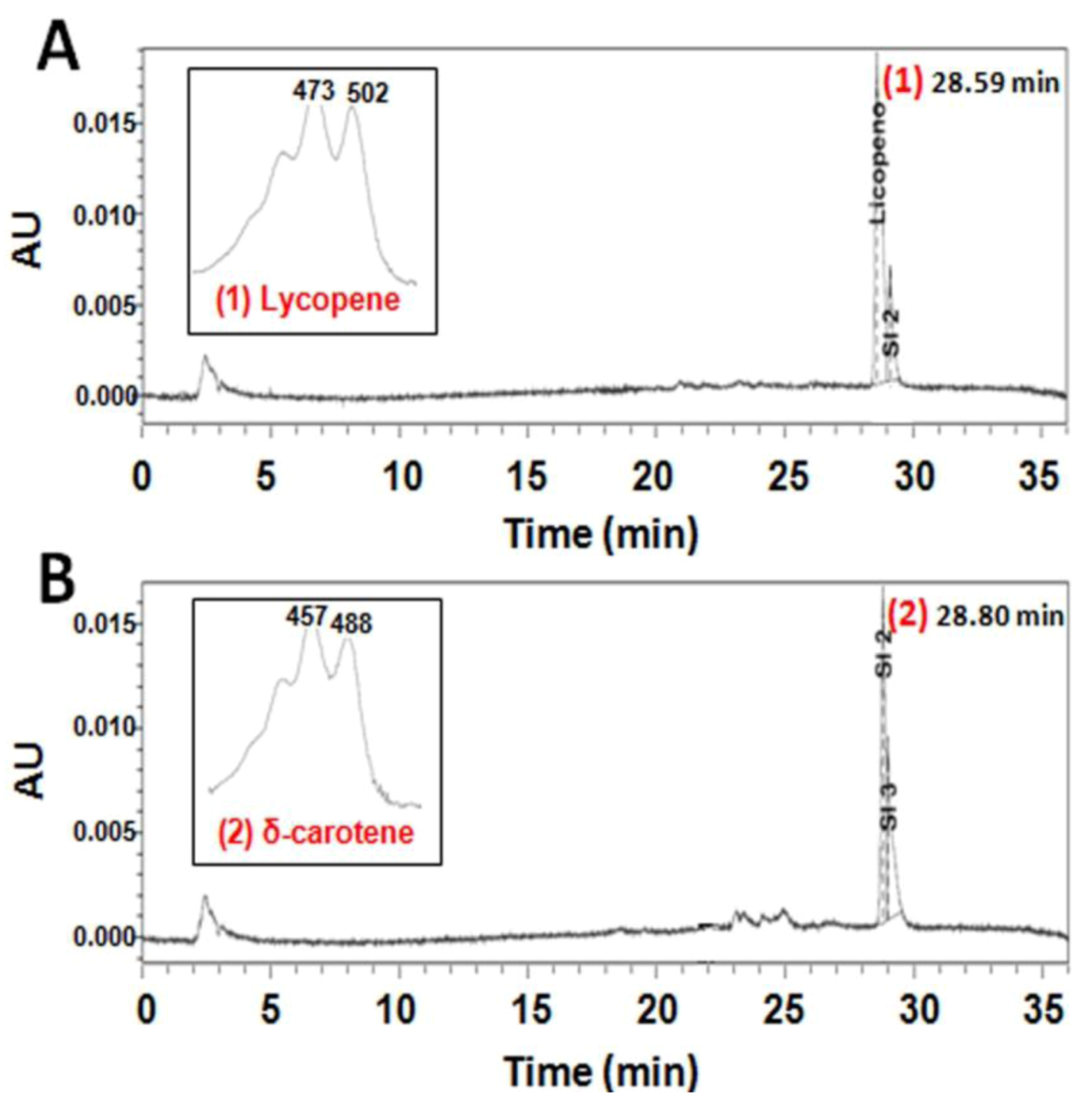
2.2. Functional Analysis of the CzLCYe in E. coli
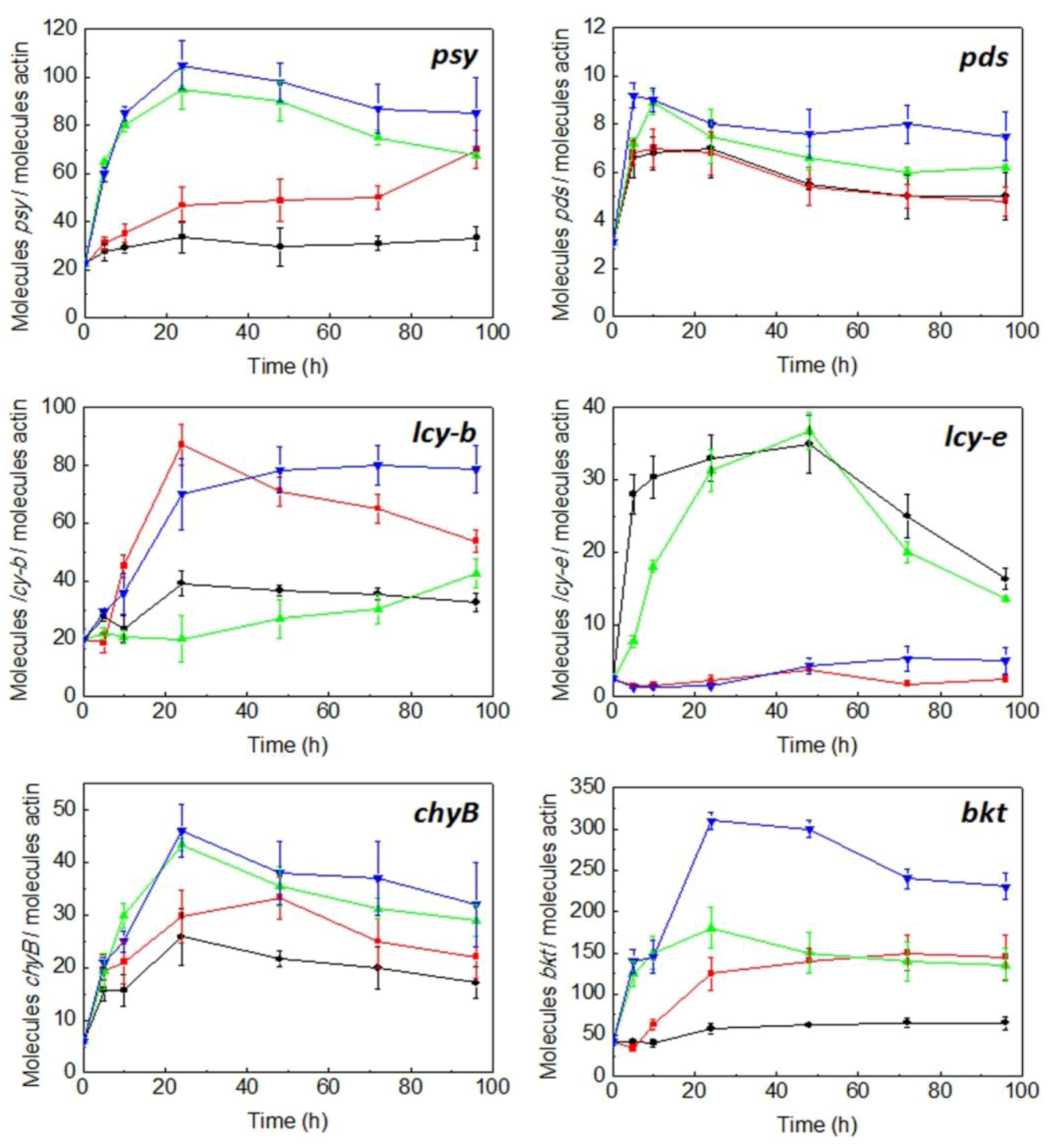
2.3. Expression of Carotenogenic Genes: Effect of Irradiance and Nitrogen
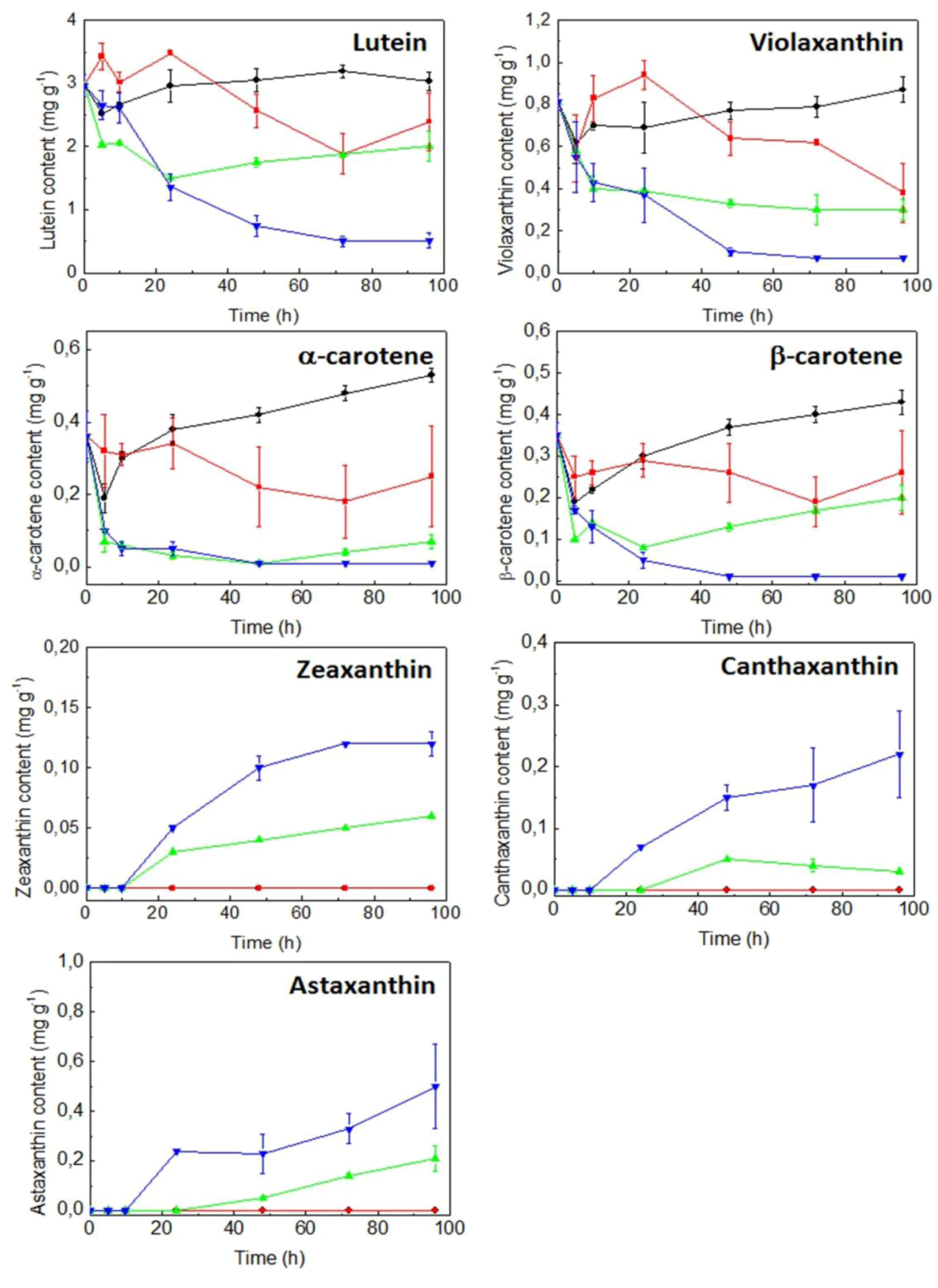
3. Discussion
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Strains and Culture Conditions
4.2. Genomic DNA and RNA Isolation and cDNA Preparation
4.3. Cloning of C. zofingiensis lcy-e cDNA and Genomic Gene
4.4. Nucleotide Sequence Accession Numbers
4.5. Southern Blot Analysis
4.6. Functional Analysis of Czlcy-e cDNA by Heterologous Expression in E. coli
4.7. Quantitative RT-PCR
4.8. Analytical Methods
4.8.1. Cell Concentration and Dry Weight Determinations
4.8.2. Carotenoid Extraction and HPLC Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Frank, H.A.; Cogdell, R.J. Carotenoids in photosynthesis. Photochem. Photobiol. 1996, 63, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazzonelli, C. Carotenoids in nature: Insights from plants and beyond. Funct. PlantBiol. 2011, 38, 833–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, A.; Polle, J.; Tran, D.; Cushman, J.C.; Jin, E.; Valera, J. The unicellular green alga Dunaliella salina Teod. as a model for abiotic stress tolerance: Genetic advances and future perspectives. Algae 2011, 26, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, P.D.; Romer, S.; Shipton, C.A.; Mills, P.B.; Kiano, J.W.; Misawa, N.; Drake, R.G.; Schuch, W.; Bramley, P.M. Evaluation of transgenic tomato plants expressing an additional phytoene synthase in a fruit specific-manner. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 1092–1097. [Google Scholar]
- Sandmann, G.; Romer, S.; Fraser, P.D. Understanding carotenoid metabolism as a necessity for genetic engineering of crop plants. Metab. Eng. 2006, 8, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordero, B.F.; Couso, I.; Leon, R.; Rodriguez, H.; Vargas, M.A. Enhancement of carotenoids biosynthesis in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii by nuclear transformation using a phytoene synthase gene isolated from Chlorella zofingiensis. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 91, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, F.; Wurtzel, E.T. Isolation and characterization of the Z-ISO gene encoding a missing component of carotenoid biosynthesis in plants. Plant Physiol. 2010, 153, 66–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harjes, C.E.; Rocheford, T.R.; Bai, L.; Brutnell, T.P.; Kandianis, C.B.; Sowinski, S.G.; Stapleton, A.E.; Vallabhaneni, R.; Williams, M.; Wurtzel, E.T. Natural genetic variation in lycopene ε-cyclase tapped for maize biofortification. Science 2008, 319, 330–333. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Smith, J.J.; Tian, L.; DellaPenna, D. The evolution and function of carotenoid hydroxylases in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Physiol. 2009, 50, 463–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Vonshak, A.; Rachel, G.; Hirshberg, J.; Cohen, Z.; Boussiba, S. The biosynthetic pathway of astaxanthin in a green alga Haematococcus pluvialis as indicated by inhibition with diphenylamine. Plant Cell Physiol. 1995, 36, 1519–1524. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, E.A.; Schroeder, W.A. Microbial carotenoids. Adv. Biochem. Eng. Biotechnol. 1995, 53, 119–178. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.C.; Wang, Y.; Sandmann, G.; Chen, F. Isolation and characterization of a carotenoid oxygenase gene from Chlorella zofingiensis (Chlorophyta). Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 71, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Huang, J.; Sandmann, G.; Chen, F. Glucose sensing and the mitochondrial alternative pathway are involved in the regulation of astaxanthin biosynthesis in the dark-grown Chlorella zofingiensis (Chlorophyceae). Planta 2008, 228, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojima, K.; Breitenbach, J.; Visser, H.; Setoguchi, Y.; Tabata, K.; Hoshino, T.; van den Berg, J.; Sandmann, G. Cloning of the astaxanthin synthase gene from Xanthophyllomyces dendrorhous (Phaffia rhodozyma) and its assignment as a β-carotene 3-hydroxylase/4-ketolase. Mol. Gen. Genomics 2006, 275, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerin, M.; Huntley, M.E.; Olaizola, M. Haematococcus astaxanthin applications for human health and nutrition. Trends Biotechnol. 2003, 21, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmedilla, B.; Granado, F.; Blanco, I.; Vaquero, M. Lutein, but not α-tocopherol, supplementation improves visual function in patients with age-related cataracts: A 2-y double blind, placebo-controlled study. Nutrition 2003, 19, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rise, M.; Cohen, E.; Vishkautsan, M.; Cojocaru, M.; Gottlieb, H.E.; Arad, S.M. Accumulation of secondary carotenoids in Chlorella zofingiensis. J. Plant Physiol. 1994, 144, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar, E.; Rise, M.; Vishkautsan, M.; Arad, S. Pigment and structural changes in Chlorella zofingiensis upon light and nitrogen stress. J. Plant Physiol. 1995, 146, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orosa, M.; Valero, J.F.; Herrero, C.; Abalde, J. Comparison of the accumulation of astaxanthin in Haematococcus pluvialis and other microalgae under N-starvation and high light conditions. Biotechnol. Lett. 2001, 23, 1079–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Campo, J.A.; Rodríguez, H.; Moreno, J.; Vargas, M.A.; Rivas, J.; Guerrero, M.G. Accumulation of astaxanthin and lutein in Chlorella zofingiensis (Chlorophyta). Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2004, 64, 848–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordero, B.F.; Obraztsova, I.; Couso, I.; Leon, R.; Vargas, M.A.; Rodriguez, H. Enhancement of lutein production in Chlorella sorokiniana (Chorophyta) by improvement of culture conditions and random mutagenesis. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 1607–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.C.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Chen, F. Isolation and characterization of the phytoene desaturase gene as a potential selective marker for genetic engineering of the astaxanthin-producing green alga Chlorella zofingiensis (Chlorophyta). J. Phycol. 2008, 44, 684–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, N.; Wang, Y.; Huang, J.C.; Chen, F. Sugar-based growth, astaxanthin accumulation and carotenogenic transcription of heterotrophic Chlorella zofingiensis (Chlorophyta). Proc. Biochem. 2008, 43, 1288–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Huang, J.; Sandmann, G.; Chen, F. High-Light and sodium chloride stress differentially regulate the biosynthesis of astaxanthin in Chlorella zofingiensis (Chlorophyceae). J. Phycol. 2009, 45, 635–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordero, B.F.; Obraztsova, I.; Martin, L.; Couso, I.; Leon, R.; Vargas, M.A.; Rodriguez, H. Isolation and characterization of a lycopene β-cyclase gene from the astaxanthin-producing green alga Chlorella zofingiensis (Chlorophyta). J. Phycol. 2010, 46, 1229–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber, H.; Goetinck, S.D.; Kirk, D.L.; Schmitt, R. The nitrate reductase-encoding gene of Volvox carteri: Map location, sequence and induction kinetics. Gene 1992, 120, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasteiger, E.; Hoogland, C.; Gattiker, A.; Duvaud, S.; Wilkins, M.R.; Appel, R.D.; Bairoch, A. Protein Identification and Analysis Tools on the ExPASy Server. In The Proteomics Protocols Handbook; Walker, J., Walker, M., Eds.; Humana Press: New Jersey, NJ, USA, 2005; pp. 571–607. [Google Scholar]
- Tamura, K.; Peterson, D.; Peterson, N.; Stecher, G.; Nei, M.; Kumar, S. MEGA5: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2011, 28, 2731–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, F.X., Jr.; Gantt, E. One ring or two? Determination of ring number in carotenoids by lycopene ε-cyclases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 2905–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stickforth, P.; Steiger, S.; Hess, W.R.; Sandmann, G. A novel type of lycopene ε-cyclase in the marine cyanobacterium Prochlorococcus marinus MED4. Arch. Microbiol. 2003, 179, 409–415. [Google Scholar]
- Bannai, H.; Tamada, Y.; Maruyama, O.; Nakai, K.; Miyano, S. Extensive feature detection of N-terminal protein sorting signals. Bioinformatics 2002, 18, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emanuelsson, O.; Nielsen, H.; von Hejne, G. ChloroP, a neural network-based method for predicting chloroplast transit peptides and their cleavage sites. Protein Sci. 1999, 8, 978–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Heijne, G. Membrane protein structure prediction: Hydrophobicity analysis and the “positive inside” rule. J. Mol. Biol. 1992, 225, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, F.X., Jr.; Pogson, B.; Sun, Z.; McDonald, K.A.; DellaPenna, D.; Gantt, E. Functional analysis of the β- and ε-lycopene cyclase enzymes of Arabidopsis reveals a mechanism for control of cyclic carotenoid formation. Plant Cell 1996, 8, 1613–1626. [Google Scholar]
- Takaichi, S. Carotenoids in algae: Distributions, biosyntheses and functions. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 1101–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Shi, C.; Gan, Z.; Shi, X. Cloning and analysis of the gene encoding lycopene epsilon cyclase in Chlorella protothecoides CS-41. Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao 2009, 49, 1180–1189. [Google Scholar]
- Sandmann, G. Molecular evolution of carotenoid biosynthesis from bacteria to plants. Physiol. Plant 2002, 116, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krubasik, P.; Sandmann, G. A carotenogenic gene cluster from Brevibacterium linens with novel lycopene cyclase genes involved in the synthesis of aromatic carotenoids. Mol. Gen. Genet. 2000, 263, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maresca, J.A.; Graham, J.E.; Wu, M.; Eisen, J.; Bryant, D.A. Identification of a new family of lycopene cyclases in photosynthetic bacteria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 11784–11789. [Google Scholar]
- Pogson, B.J.; McDonald, K.; Truong, M.; Britton, G.; DellaPenna, D. Arabidopsis carotenoid mutants demonstrate lutein is not essential for photosynthesis in higher plants. Plant Cell 1996, 8, 1627–1639. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, B.; Lydiate, D.J.; Young, L.W.; Schafer, U.A.; Hannoufa, A. Enhancing the carotenoid content of Brassica napus seeds by downregulating lycopene ε-cyclase. Transgenic Res. 2008, 17, 573–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diretto, G.; Tavazza, R.; Welsch, R.; Pizzichini, D.; Mourgues, F.; Papacchioli, V.; Beyer, P.; Giuliano, G. Metabolic engineering of potato tuber carotenoids through tuberspecific silencing of lycopene ε-cyclase. BMC Plant Biol. 2006, 6, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farre, G.; Sanahuja, G.; Naqvi, S.; Bai, C.; Capell, T.; Zhu, C.; Christou, P. Travel advice on the road to carotenoids in plants. Plant Sci. 2010, 179, 28–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pogson, B.J.; Rissler, M. Genetic manipulation of carotenoid biosynthesis and photoprotection. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B 2000, 355, 1395–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidhyavathi, R.; Venkatachalam, L.; Sarada, R.; Ravishankar, G.A. Regulation of carotenoid biosynthetic genes expression and carotenoid accumulation in the green alga Haematococcus pluvialis under nutrient stress conditions. J. Exp. Bot. 2008, 59, 1409–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinbrenner, J.; Linden, H. Light induction of carotenoid biosynthesis genes in the green alga Haematococcus pluvialis: Regulation by photosynthetic redox control. Plant Mol. Biol. 2003, 52, 343–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, A.; Coesel, A.; Marques, A.; Rodrigues, M.; Baumgartner, A.; Noronha, J.; Rauter, A.; Brenig, B.; Varela, J. Isolation and characterization of a stress-inducible Dunaliella salina Lcy-β gene encoding a functional lycopene β-cyclase. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 79, 819–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coesel, S.N.; Baumgartner, A.C.; Teles, L.M.; Ramos, A.; Henriques, N.M.; Cancela, L.; Valera, J. Nutrient limitation is the main regulatory factor for carotenoid accumulation and for Psy and Pds steady state transcript levels in Dunaliella salina (Chlorophyta) exposed to high light and salt stress. Mar. Biotechnol. 2008, 10, 602–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goss, R.; Jakob, T. Regulation and function of xanthophylls cycle-dependent photoprotection in algae. Photosynth. Res. 2010, 106, 103–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fucikova, K.; Lewis, L.A. Intersection of Chlorella, Muriella and Bracteacoccus: Resurrecting the genus Chromochloris KOL et CHODAT (Chlorophyceae, Chlorophyta). Fottea 2012, 12, 83–93. [Google Scholar]
- Arnon, D.I.; McSwain, B.D.; Tsujimoto, H.Y.; Wada, K. Photochemical activity and components of membrane preparations from blue-green algae. I. Coexistence of two photosystems in relation to chlorophyll a and removal of phycocyanin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1974, 357, 231–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, F.X., Jr.; Sun, Z.; Chamovitz, D.; Hirschberg, J.; Gantt, E. Molecular structure and enzymatic function of lycopene cyclise from the cyanbacterium Synechococcus sp. strain PCC 7942. Plant Cell 1994, 6, 1107–1121. [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham, F.X., Jr.; Gantt, E. A portfolio of plasmids for identification and analysis of carotenoid pathway enzymes: Adonis aestivalis as a case study. Photosynth. Res. 2007, 92, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambrook, J.; Fritsch, E.F.; Maniatis, T. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual; Nolan, C., Ed.; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: New York, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, G.; Zhang, X.; Sui, Z.; Mao, Y. Inhibition of pds gene expression via the RNA interference approach in Dunaliella salina (Chlorophyta). Mar. Biotechnol. 2008, 10, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samples Availability: Available from the authors.
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Cordero, B.F.; Couso, I.; Leon, R.; Rodriguez, H.; Vargas, M.A. Isolation and Characterization of a Lycopene ε-Cyclase Gene of Chlorella (Chromochloris) zofingiensis. Regulation of the Carotenogenic Pathway by Nitrogen and Light. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 2069-2088. https://doi.org/10.3390/md10092069
Cordero BF, Couso I, Leon R, Rodriguez H, Vargas MA. Isolation and Characterization of a Lycopene ε-Cyclase Gene of Chlorella (Chromochloris) zofingiensis. Regulation of the Carotenogenic Pathway by Nitrogen and Light. Marine Drugs. 2012; 10(9):2069-2088. https://doi.org/10.3390/md10092069
Chicago/Turabian StyleCordero, Baldo F., Inmaculada Couso, Rosa Leon, Herminia Rodriguez, and Maria Angeles Vargas. 2012. "Isolation and Characterization of a Lycopene ε-Cyclase Gene of Chlorella (Chromochloris) zofingiensis. Regulation of the Carotenogenic Pathway by Nitrogen and Light" Marine Drugs 10, no. 9: 2069-2088. https://doi.org/10.3390/md10092069
APA StyleCordero, B. F., Couso, I., Leon, R., Rodriguez, H., & Vargas, M. A. (2012). Isolation and Characterization of a Lycopene ε-Cyclase Gene of Chlorella (Chromochloris) zofingiensis. Regulation of the Carotenogenic Pathway by Nitrogen and Light. Marine Drugs, 10(9), 2069-2088. https://doi.org/10.3390/md10092069





