Glycosides from Marine Sponges (Porifera, Demospongiae): Structures, Taxonomical Distribution, Biological Activities and Biological Roles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Tetracyclic Triterpene Glycosides
2.1. The Order Astrophorida
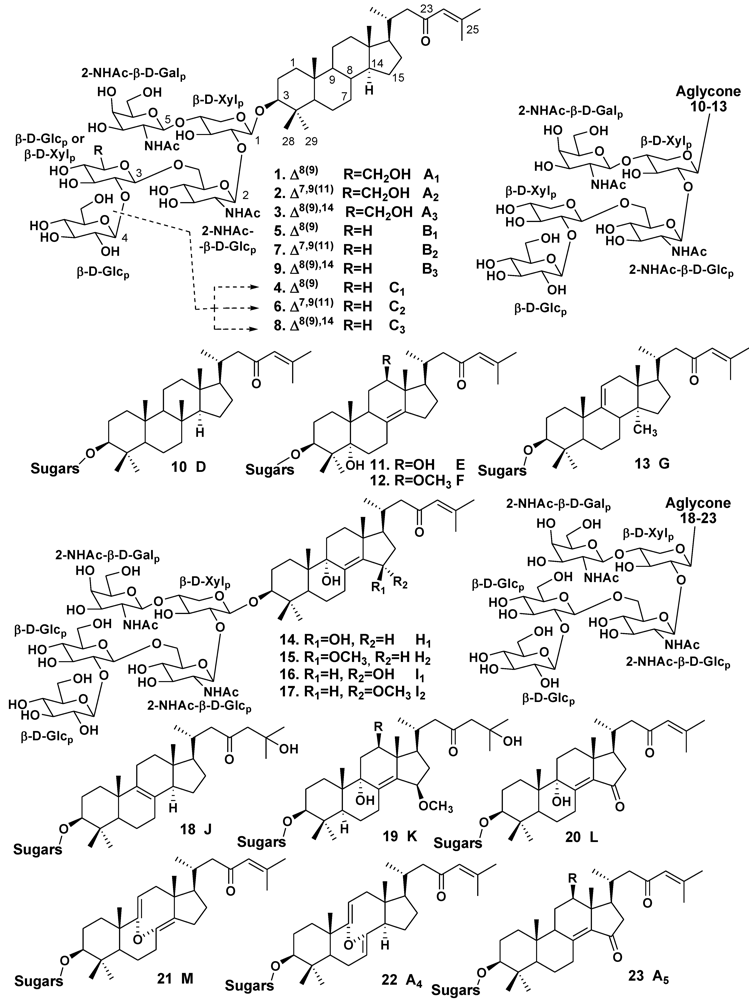
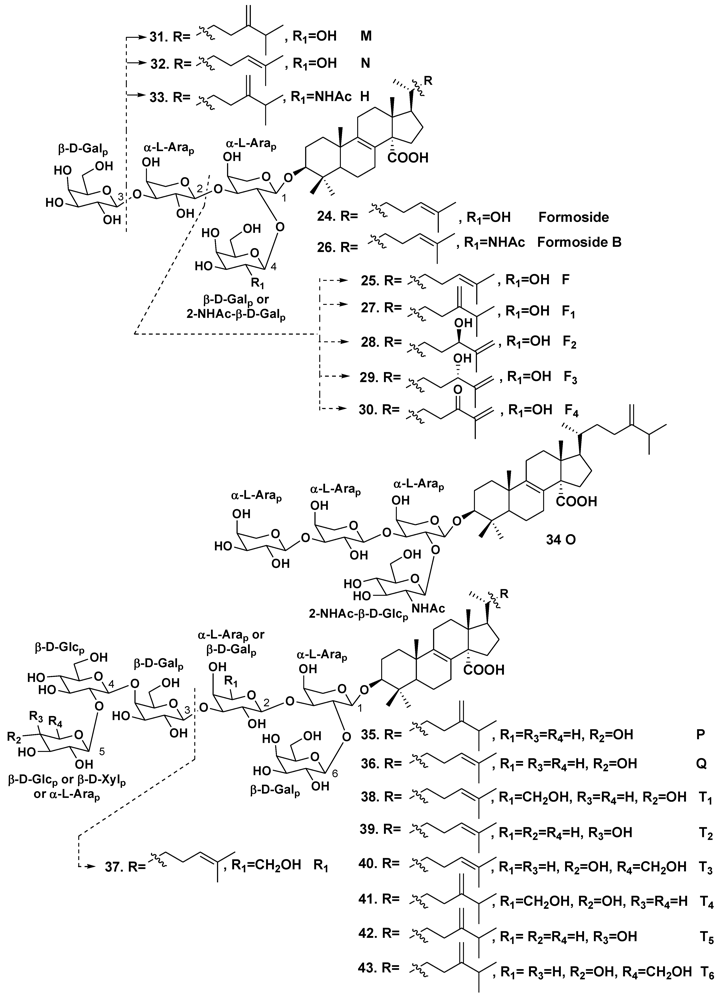
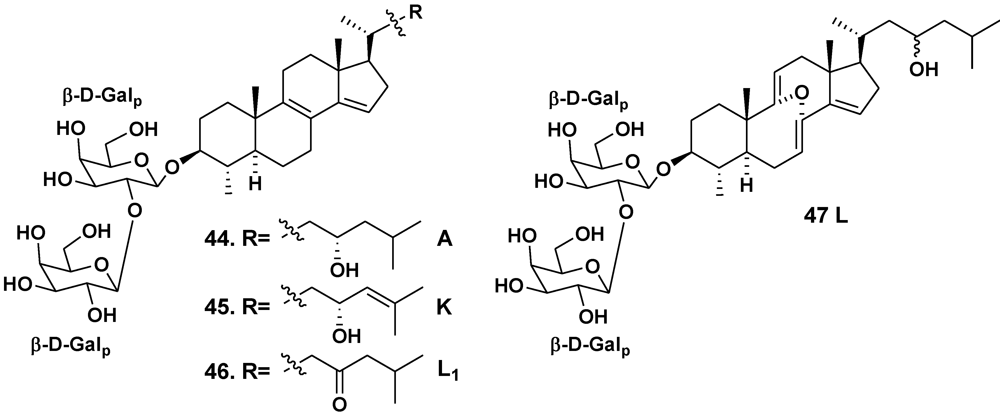

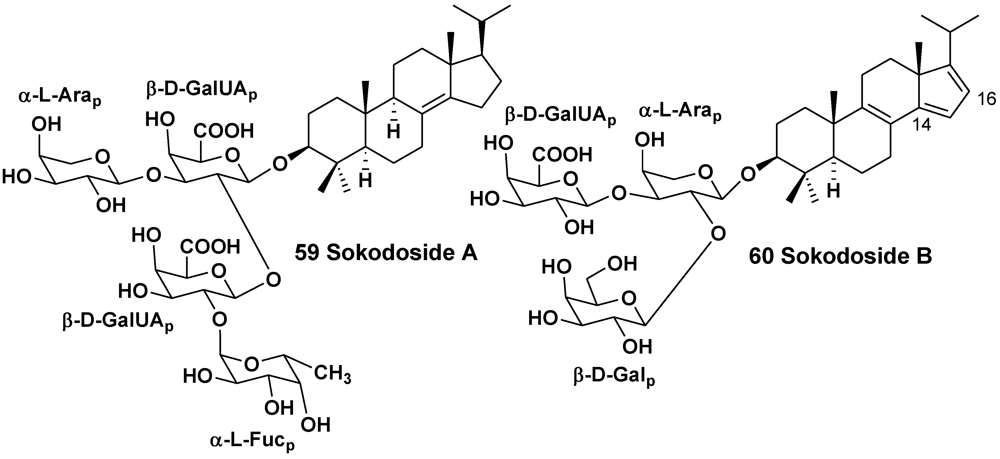
2.2. The Order Poecilosclerida

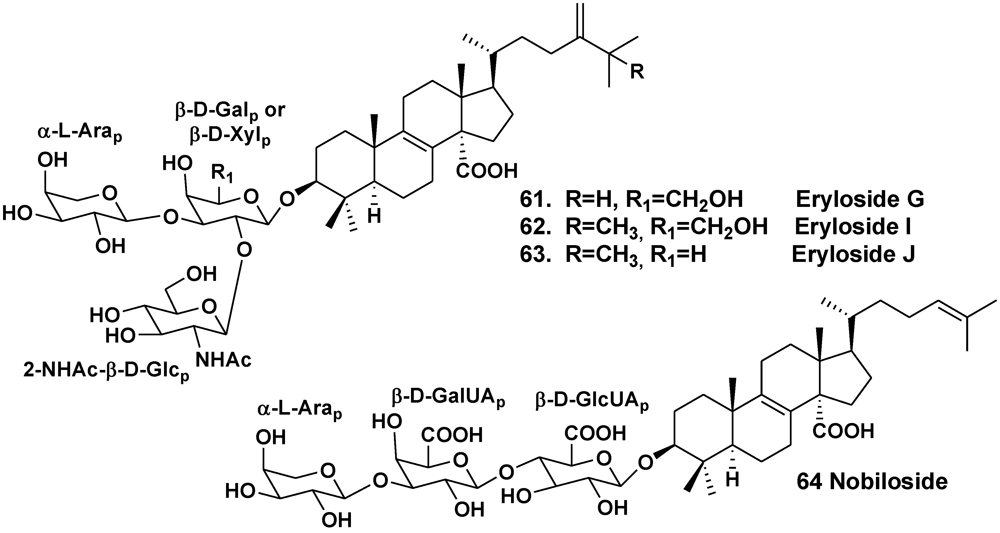
3. Other Triterpene Glycosides from Sponges
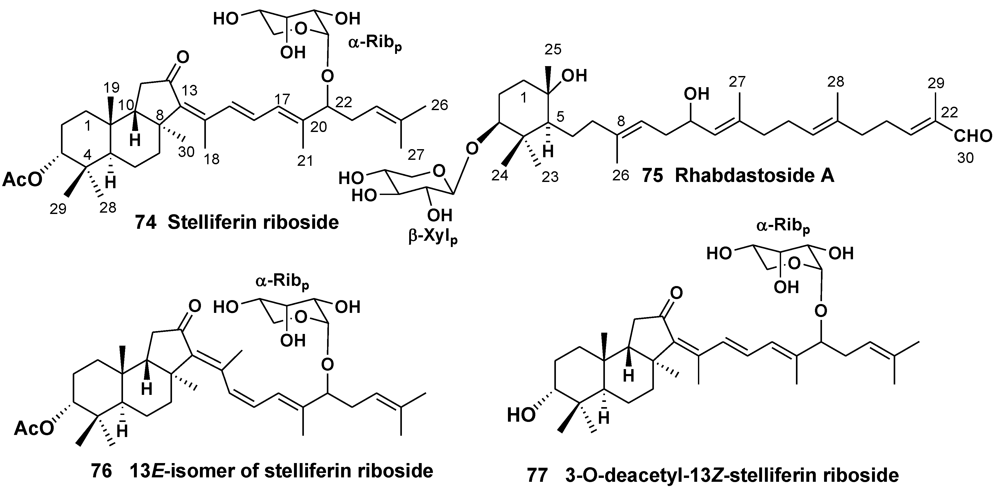
3.1. Orders Astrophorida and Halichondrida
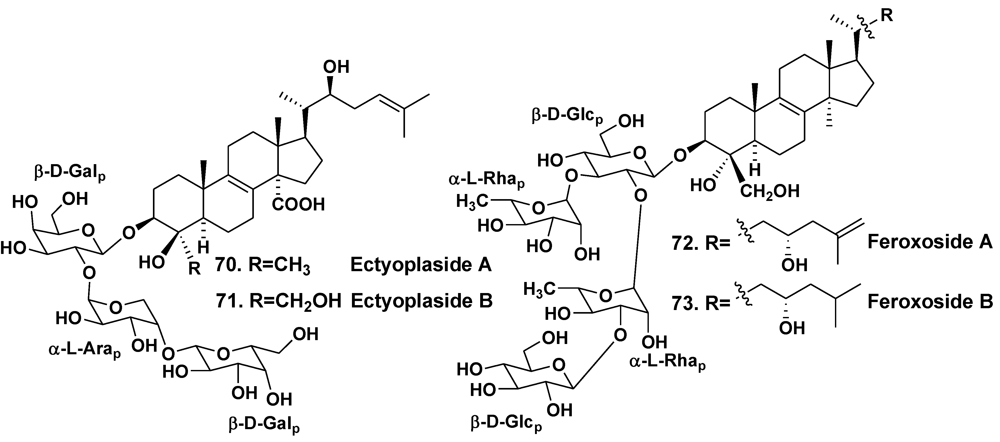
3.2. The Order Haplosclerida
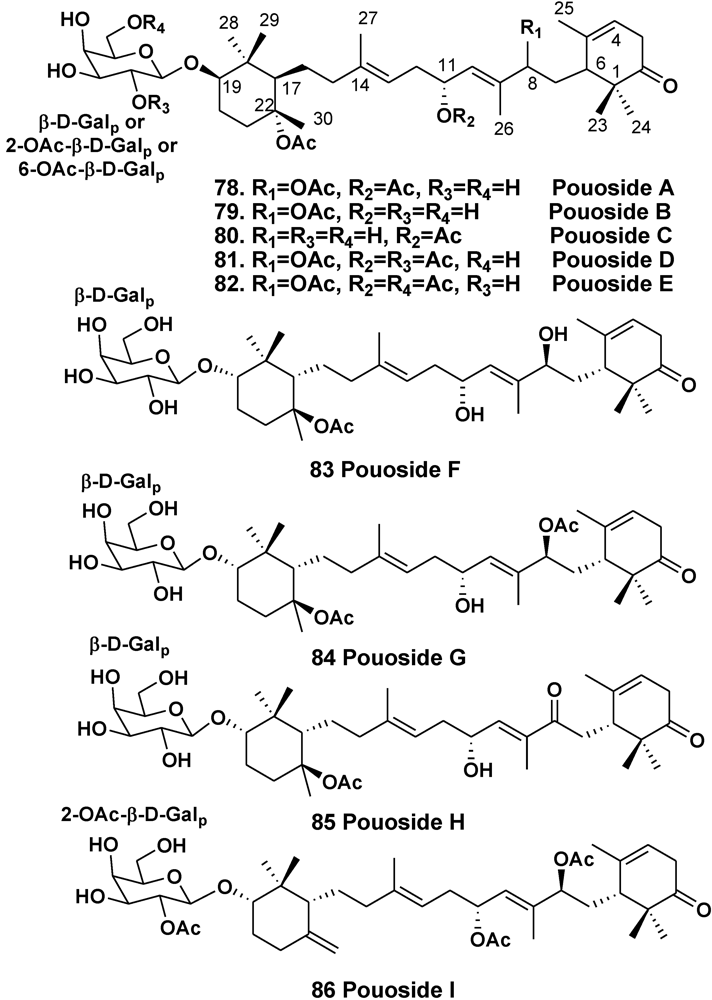
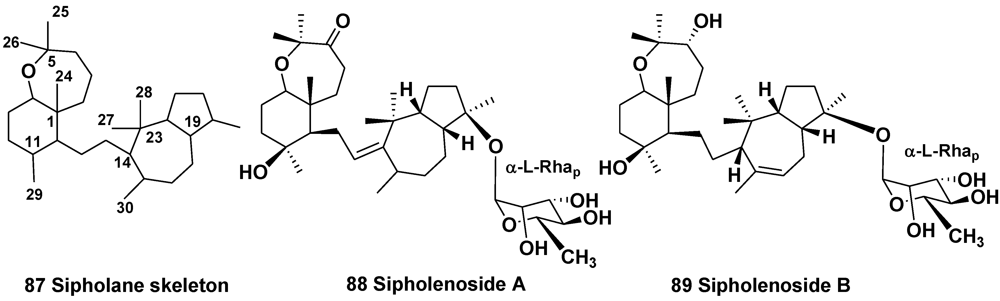
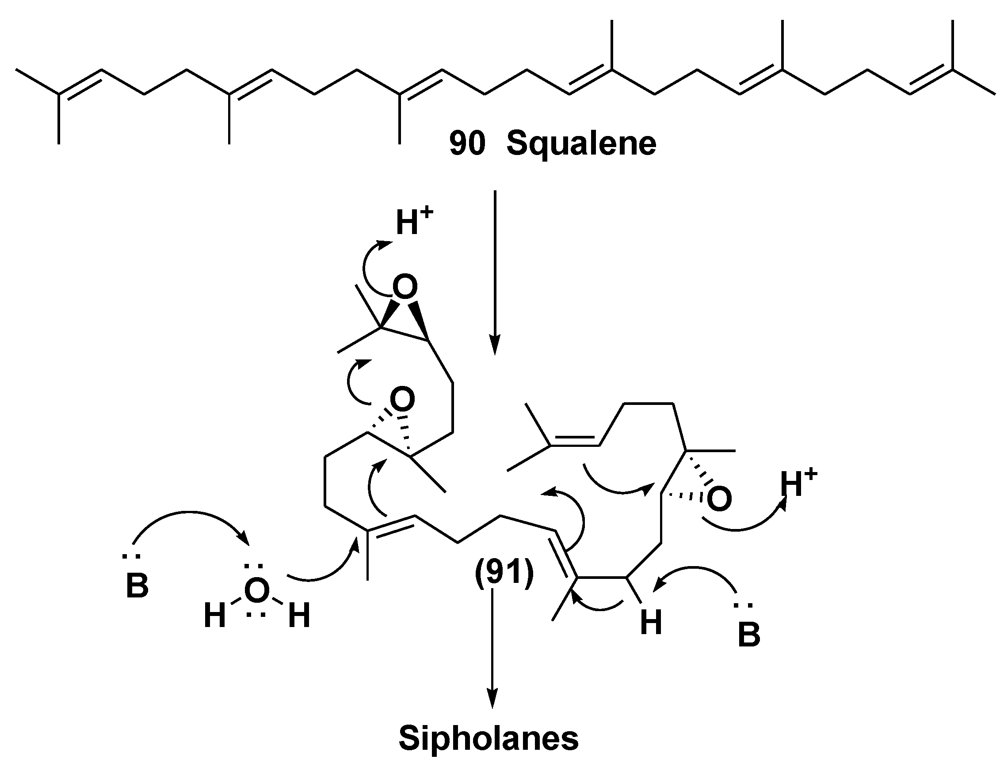

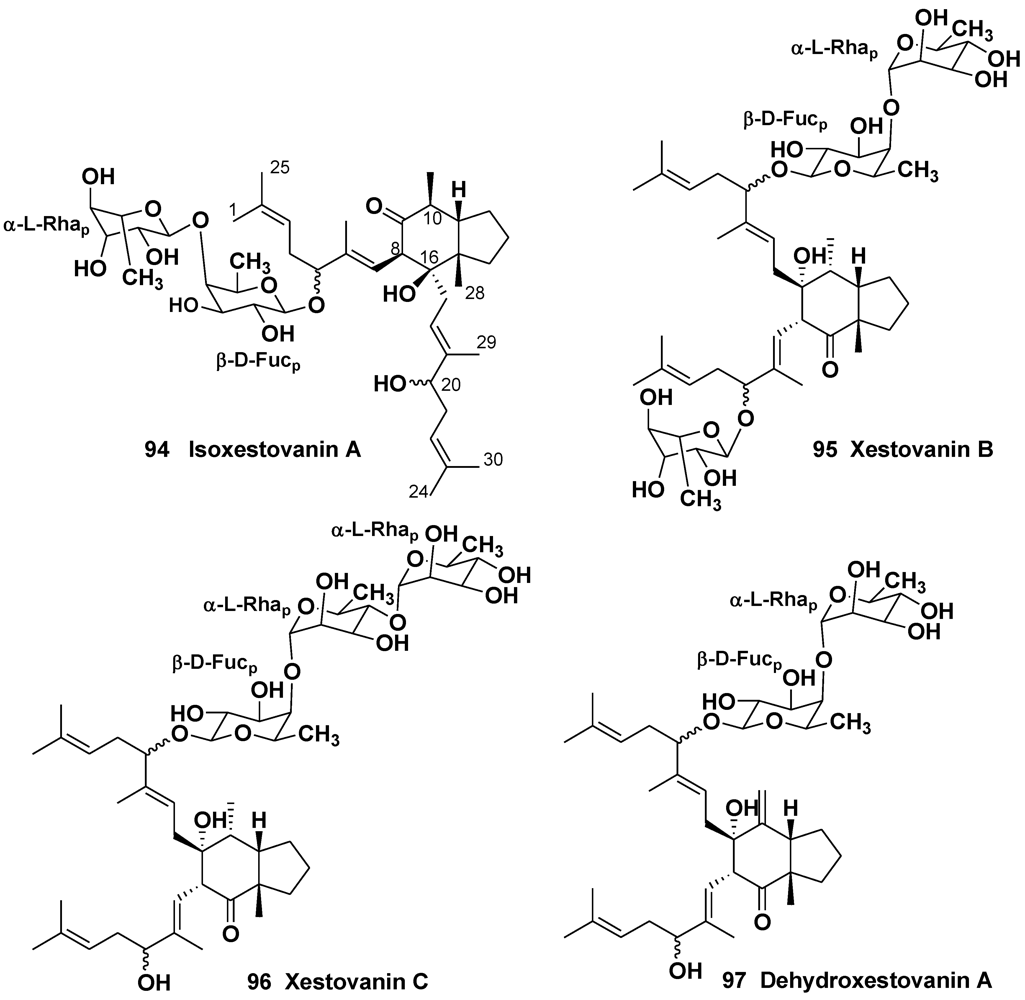
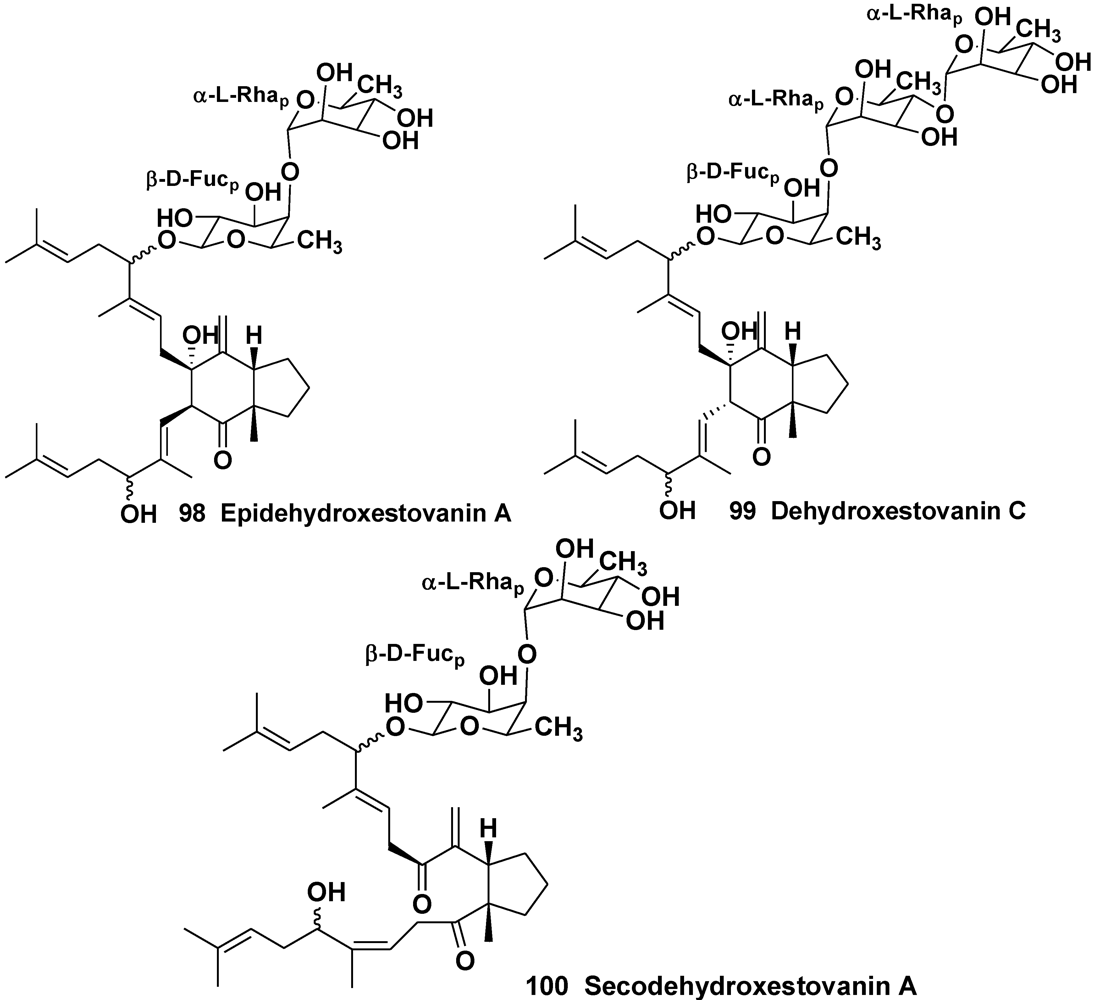
4. Steroid Glycosides from Sponges
4.1. The order Astrophorida
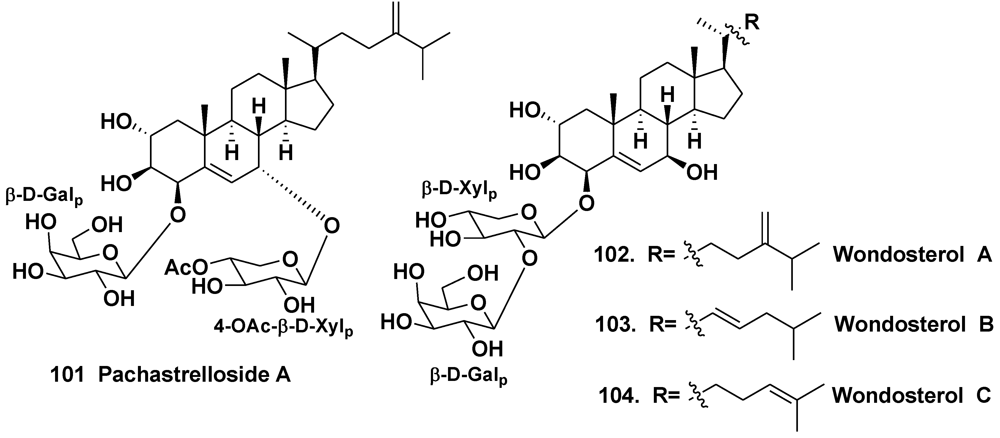
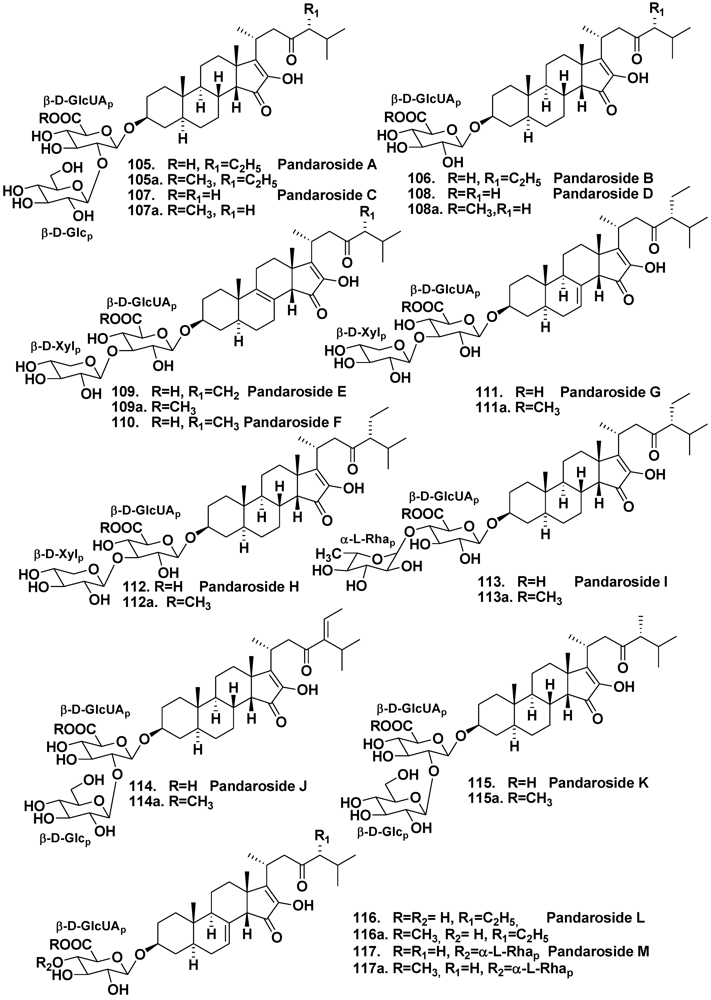
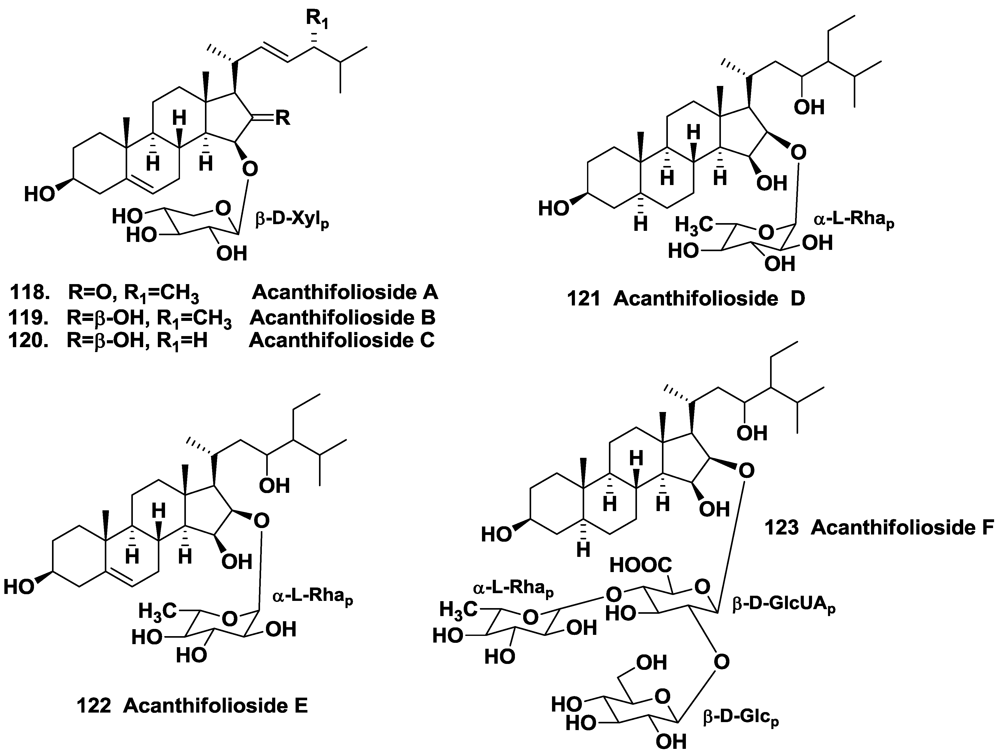
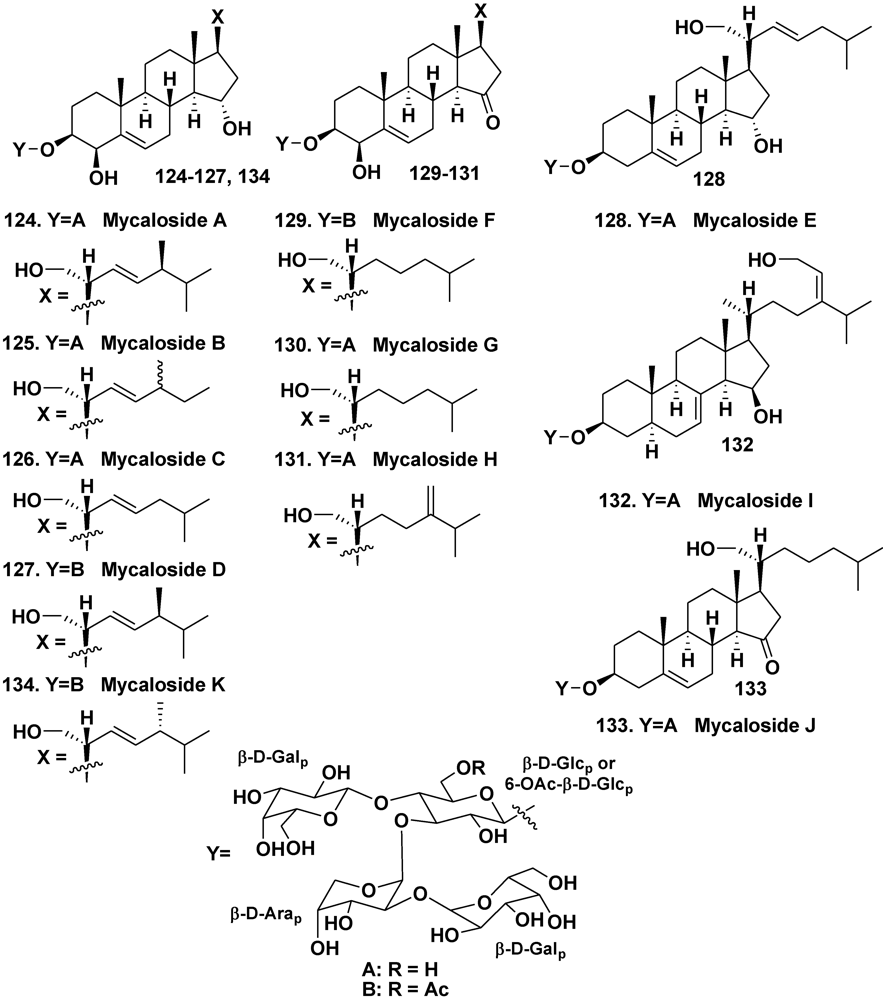
4.2. The Order Halichondrida

5. Glycosides of Non-Isoprenoid Aglycones
5.1. “Atypical” Glycolipids
5.1.1. The Order Astrophorida

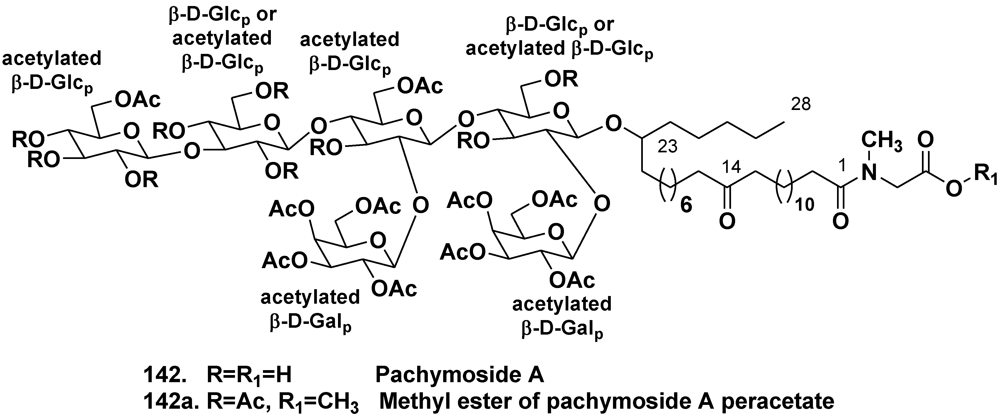
5.1.2. The Order Poecilosclerida
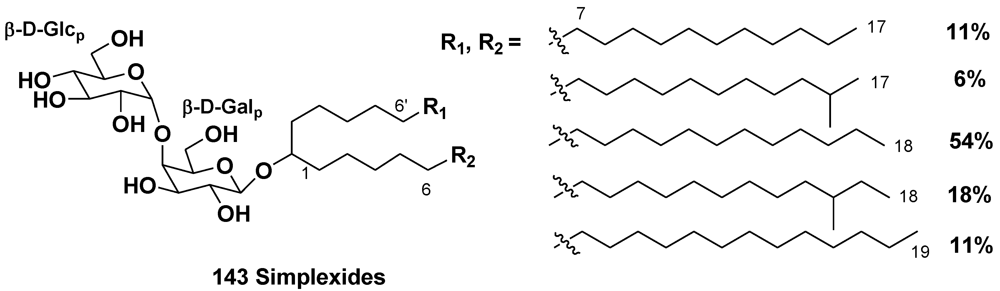
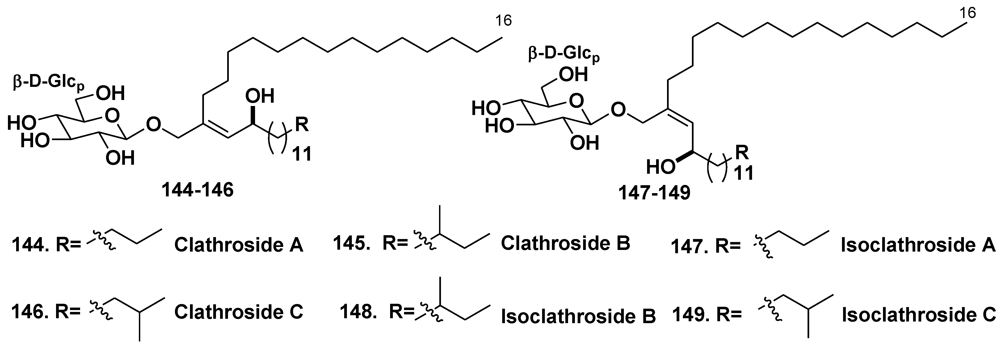
5.1.3. The Order Agelasida
5.2. Glycosides of Macrolides
5.2.1. The Order Astrophorida
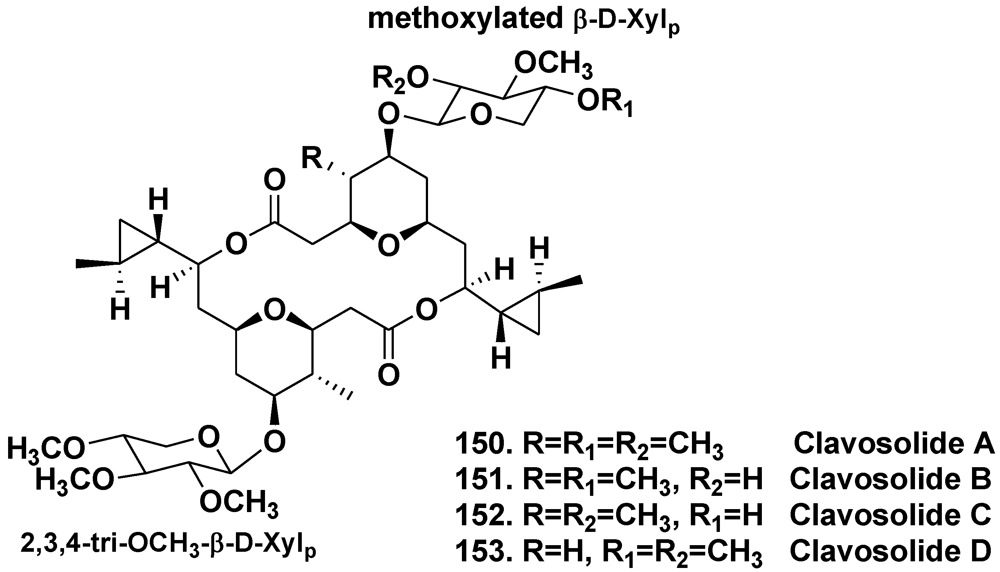
5.2.2. The Order Poecilosclerida
5.3. Bipolar Glycolipids
5.3.1. The Order Haplosclerida
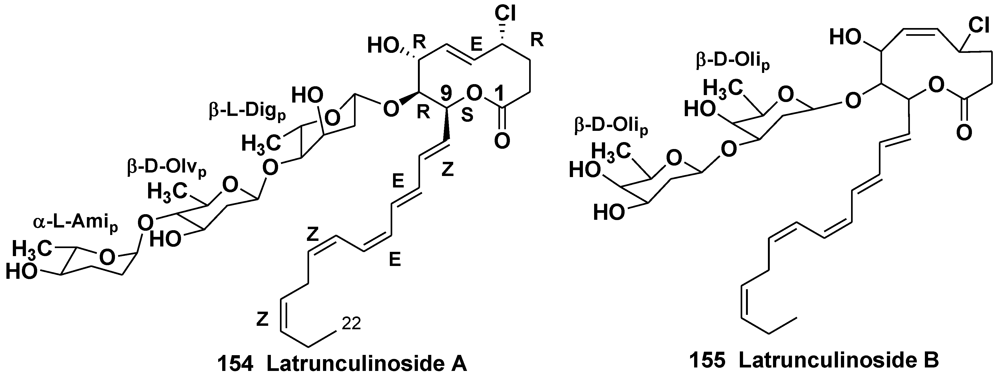
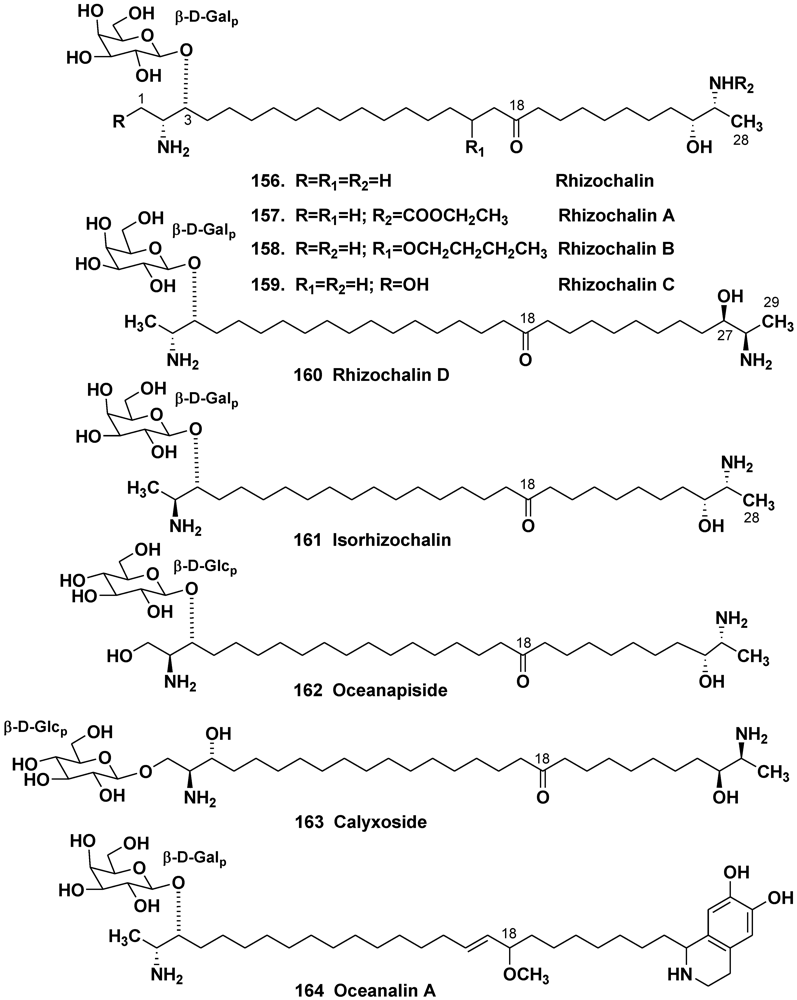
5.3.2. The Order Astrophorida
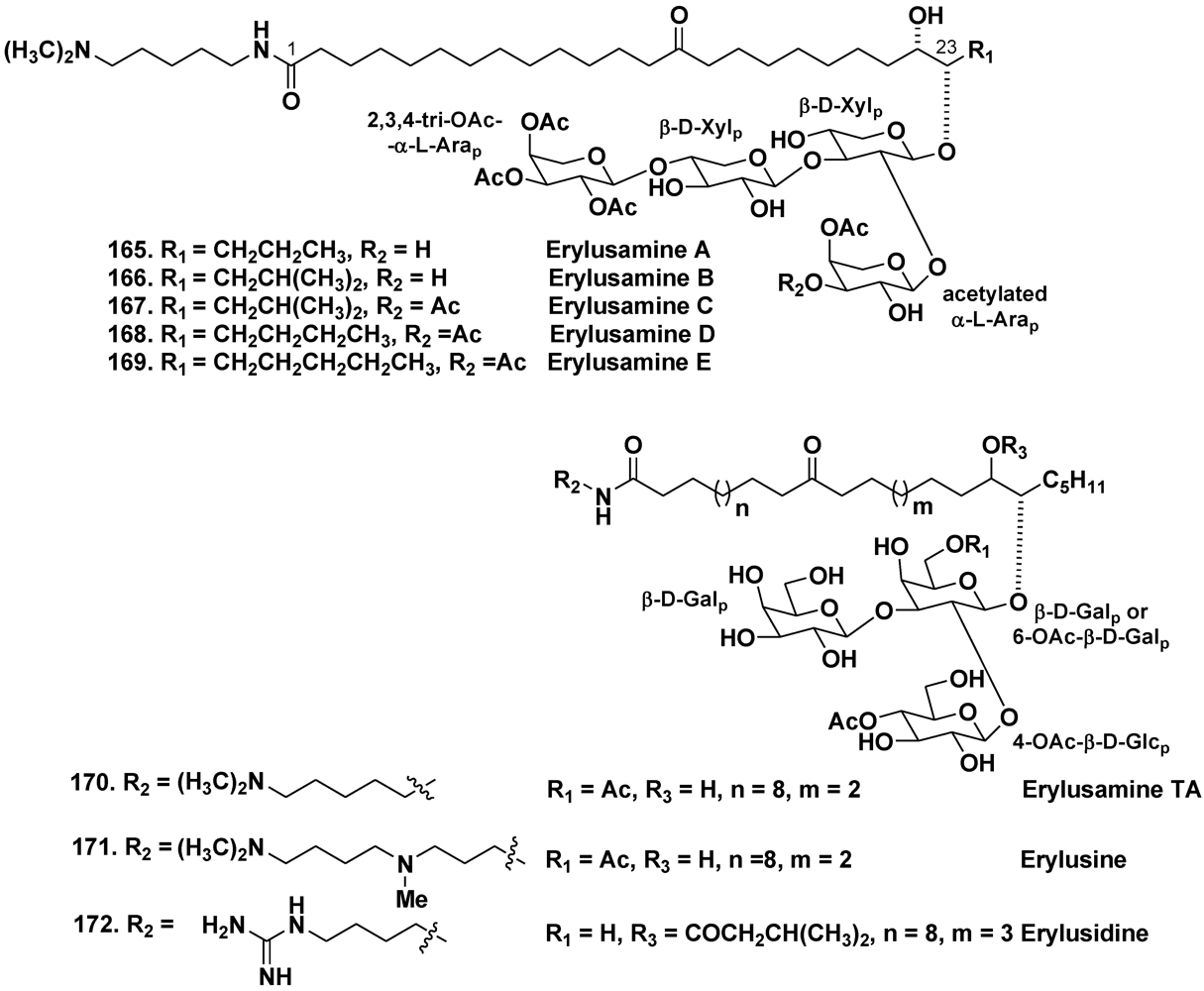
6. Taxonomic Distribution of Glycosides in Sponges
| Taxon | Place of collection | Glycosides | Reference | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Order Astrophorida | |||||
| Family Ancorinidae | |||||
| Melophlus sp. | Guam Island, Truk Lagoon | 1 | [13] | ||
| Melophlus | Palau Islands | 1, 4, 5 | [12] | ||
| sarasinorum | |||||
| – | – | 1–9 | [15] | ||
| – | Solomon Islands | 5, 10–13 | [16] | ||
| – | Guam Island | 1, 3, 14–17 | [17] | ||
| – | Sulawesi Island | 1, 3, 15–21 | [14] | ||
| – | Reef Scott, North-Western Coast of Australia | 1–3, 20–23 | [18] | ||
| Family Geodiidae | |||||
| Erylus formosus | Bahamas Islands | 24 | [19] | ||
| – | – | 25 | [22] | ||
| – | – | 24, 26 | [23] | ||
| – | Puerto Morelos, the Caribbean Sea | 25, 27–36 | [24] | ||
| – | – | 24, 37–43 | [25] | ||
| Erylus lendenfeldi | Gulf of Eilat, Red Sea | 44 | [27] | ||
| – | Red Sea, north of Hurghada | 44–46 | [28] | ||
| – | Gulf of Aqaba, Red Sea | 45, 47 | [29] | ||
| Erylus goffrilleri | Bahama Islands | 48 | [30] | ||
| – | Arresife-Seko Reef, Cuba | 49–56 | [31] | ||
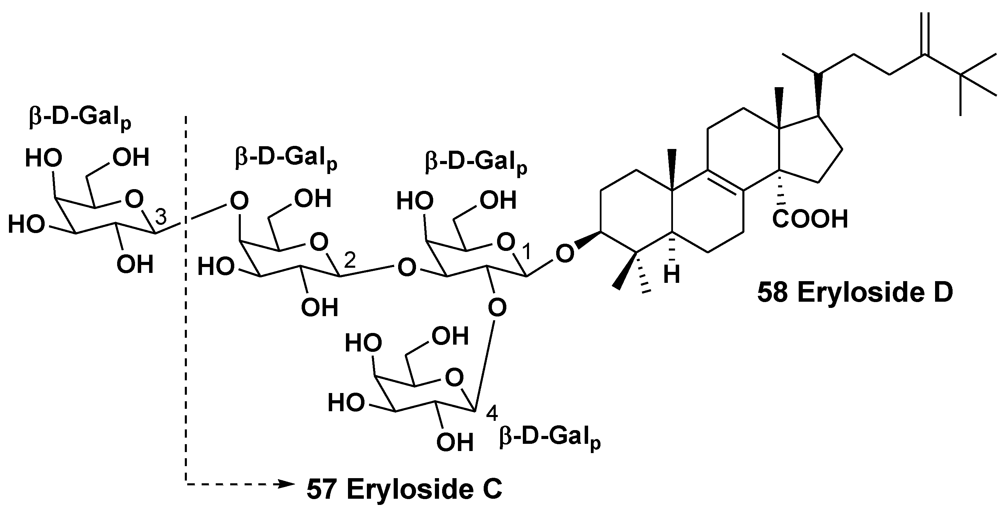
| Erylus sp. | South of New Caledonia | 57, 58 | [32] | ||
| Erylus placenta | Hachijo Island, South Japan | 59, 60 | [33] | ||
| Erylus nobilis | Jaeju Island, South Korea | 33, 61–63 | [26] | ||
| – | Shikine-jima Island, 200 km south of Tokyo, Japan | 64 | [35] | ||
| Order Poecilosclerida | |||||
| Family Mycalidae | |||||
| Ulosa sp. | Madagascar | 65–69 | [37,38,39] | ||
| Family Raspaillidae | |||||
| Ectyoplasia ferox | San Salvador Island, Bahamas | 70, 71 | [40] | ||
| – | Grand Bahama Island | 72, 73 | [41] | ||
7. Biological Roles of Sponge Glycosides
8. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Stonik, V.A. Some terpenoid and steroid derivatives from echinoderms and sponges. Pure Appl. Chem. 1986, 58, 423–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stonik, V.A.; Kalinin, V.I.; Avilov, S.A. Toxins from sea cucumbers (Holothuroids): Chemical structures, properties, taxonomic distribution, biosynthesis and evolution. J. Nat. Toxins 1999, 8, 235–248. [Google Scholar]
- Moraes, G.; Northcote, P.T.; Kalinin, V.I.; Avilov, S.A.; Silchenko, A.S.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Stonik, V.A.; Levin, V.S. Structure of the major triterpene glycoside from the sea cucumber Stichopus mollis and evidence to reclassify this species into the new genus Australostichopus. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2004, 32, 637–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avilov, S.A.; Kalinin, V.I.; Smirnov, A.V. Use of triterpene glycosides for resolving taxonomic problems in the sea cucumber genus Cucumaria (Holothurioidea, Echinodermata). Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2004, 32, 715–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinin, V.I.; Silchenko, A.S.; Avilov, S.A.; Stonik, V.A.; Smirnov, A.V. Sea cucumbers triterpene glycosides, the recent progress in structural elucidation and chemotaxonomy. Phytochem. Rev. 2005, 4, 221–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonov, A.S.; Avilov, S.A.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Anastyuk, S.D.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Kalinin, V.I.; Taboada, S.; Bosh, A.; Avila, C.; Stonik, V.A. Triterpene glycosides from Antarctic sea cucumbers. 2. Structure of achlioniceosides A1, A2 and A3 from the sea cucumber Achlionice violaescupidata (=Rhipidothuria racowitzai). J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 33–38. [Google Scholar]
- Minale, L.; Riccio, R.; Zollo, F. Steroid oligoglycosides and polyhydroxysteroids from the echinoderms. Fortschr. Chem. Org. Naturst. 1993, 62, 75–308. [Google Scholar]
- Stonik, V.A. Marine polar steroids. Russ. Chem. Rev. 2001, 70, 673–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanchina, N.V.; Kicha, A.A.; Stonik, V.A. Steroid glycosides from marine organisms. Steroids 2011, 76, 425–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebada, S.S.; Lin, W.H.; Proksch, P. Bioactive sesteterpenes and triterpenes from marine sponges: Occurence and pharmacological significance. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 313–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, J.N.A.; Van Soest, R.W.M. Systema Porifera: A Guide to the Classification of Sponges; Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers: Dordrecht, Netherlands, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Kitagawa, I.; Kobayashi, M.; Okamoto, Y.; Yoshikawa, M.; Hamamoto, Y. Structures of sapasinosides A1, B1, and C1, new norlanostane-triterpenoid olygoglycosides from the Palauan marine sponge Asteropus sarasinos. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1987, 35, 5036–5039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, F.J.; Ksebati, M.B.; Gunasekera, S.P.; Agarwal, S. Sarasinoside A1: A saponin containing amino sugars isolated from a sponge. J. Org. Chem. 1988, 53, 5941–5947. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, H.-F.; Edrada, R.A.; Ebel, R.; Nimtz, M.; Wray, V.; Proksch, P. Norlanostane triterpenoidal saponins from the marine sponge Melophlus sarassinorum. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, M.; Okamoto, Y.; Kitagawa, I. Marine natural products. XXVIII. The structures of sarasinosides A1, A2, A3, B1, B2, B3, C1, C2, and C3, nine new norlanostane-triterpenoidal olygoglycosides from the Palauan marine sponge Asteropus sarasinosum. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1991, 39, 2867–2877. [Google Scholar]
- Espada, A.; Jimenez, C.; Rodriguez, J.; Crews, P.; Riguera, R. Sarasinosides D-G: Four new triterpenoid saponins from the sponge Asteropus sarasinosum. Tetrahedron 1992, 48, 8685–8696. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.-S.; Seo, Y.; Cho, K.W.; Rho, J.-R.; Shin, J.; Paul, V.J. New triterpenoid saponins from the sponge Melophlus isis. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 915–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santalova, E.A.; Denisenko, V.A.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Berdyshev, D.V.; Stonik, V.A. Two new sarasinosides from the sponge Melophlus sarasinorum. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2006, 1, 265–271. [Google Scholar]
- Jaspars, M.; Crews, P. A triterpene tetrasaccharide, formoside, from the Caribbean choristida sponge Erylus formosu. Tetrahedron Lett. 1994, 35, 7501–7504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.-F.; Kobayashi, J.; Nakamura, H.; Ohizumi, Y.; Hirata, Y.; Sasaki, T. Penasterol, a novel antileukemic sterol from the Okinawan marine sponge Penares sp. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. I 1988, 2403–2406. [Google Scholar]
- Shoji, N.; Umeyama, A.; Motoki, S.; Arihara, S.; Ishida, T.; Nomoto, K.; Kobayashi, J.; Takei, M. Potent inhibitors of histamine release, two novel triterpenoids from the Okinawan marine sponge Penares incrustans. J. Nat. Prod. 1992, 55, 1682–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stead, P.; Hiscox, S.; Robinson, P.S.; Pike, N.B.; Sidebottom, P.J.; Roberts, A.D.; Taylor, N.L.; Wright, A.E.; Pomponi, S.A.; Langley, D. Eryloside F, a novel penasterol disaccharide possessing potent thrombin receptor antagonist activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2000, 10, 661–664. [Google Scholar]
- Kubanek, J.; Fenical, W.; Pawlik, J.R. New antifeedant triterpene glycosides from the Caribbean sponge Erylus formosus. Nat. Prod. Lett. 2001, 15, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonov, A.S.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Stonik, V.A.; Afiyatullov, S.S.; Aminin, D.L.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Mollo, E.; Cimino, G. Isolation and structures of erylosides from the Caribbean sponge Erylus formosus. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonov, A.S.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Kalinin, V.I.; Stonik, V.A.; Mollo, E.; Cimino, G. New triterpene oligoglycosides from the Caribbean sponge Erylus formosus. Carbohydrate Res. 2011, 346, 2182–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.; Lee, H.-S.; Woo, L.; Rho, J.-R.; Seo, Y.; Cho, K.W.; Sim, C.J. New triterpenoid saponins from the sponge Erylus nobilis. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 767–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmely, S.; Roll, M.; Loya, Y.; Kashman, Y. The structure of eryloside A, a new antitumor and antifungal 4-methylated steroidal glycoside from the sponge Erylus lendenfeldi. J. Nat. Prod. 1989, 52, 167–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandler, J.S.; Forsburg, S.L.; Faulkner, D.J. Bioactive steroidal glycosides from the marine sponge Erylus lendenfeldi. Tetrahedron 2005, 61, 1199–1206. [Google Scholar]
- Fouad, M.; Al-Trabeen, K.; Badran, M.; Wray, V.; Edrada, R.A.; Proksch, P.; Ebel, R. New steroidal saponins from the sponge Erylus lendenfeldi. ARKIVOC 2004, 2004, 17–27. [Google Scholar]
- Gulavita, N.K.; Wright, A.E.; Kelly-Borges, M.; Longley, R.E. Eryloside E from an Atlantic sponge Erylus goffrilleri. Tetrahedron Lett. 1994, 35, 4299–4302. [Google Scholar]
- Afiyatullov, S.S.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Antonov, A.S.; Ponomarenko, L.P.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Aminin, D.L.; Krasokhin, V.B.; Nosova, V.M.; Kisin, A.V. Isolation and structures of erylosides from the Caribbean sponge Erylus goffrilleri. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 1871–1877. [Google Scholar]
- D’Auria, M.V.; Paloma, L.G.; Minale, L.; Riccio, R. Structure characterization by two-dimentional NMR spectroscopy, of two marine triterpene olygoglycosides from a Pacific sponge of the genus Erylus. Tetrahedron 1992, 48, 491–498. [Google Scholar]
- Okada, Y.; Matsunaga, S.; van Soest, R.W.M.; Fusetani, N. Sokodosides, steroid glycosides with an isopropyl chain, from the marine sponge Erylus placenta. J. Org. Chem. 2006, 71, 4884–4888. [Google Scholar]
- Dasgupta, S.; Pramanik, K.; Mikhopadhyay, B. Oiligosaccharides through reactivity tuning: Convergent synthesis of the trisaccharides of the steroid glycoside sokodoside B isolated from marine sponge Erylus placenta. Tetrahedron 2007, 63, 12310–12316. [Google Scholar]
- Takada, K.; Nakao, Y.; Matsunaga, S.; van Soest, R.W.M.; Fusetani, N. Nobiloside, a new neuraminidase inhibitory triterpenoidal saponin from the marine sponge Erylus nobilis. J. Nat. Prod. 2002, 65, 411–413. [Google Scholar]
- Mandal, S.; Das, R.; Mukhopadhyay, B. Synthesis of two trisaccharides related to the triterpenoid saponin eryloside isolated from the sponge Erylus nobilis. Tetrahedron Asymm. 2011, 22, 1108–1113. [Google Scholar]
- Antonov, A.S.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Stonik, V.A.; Evtushenko, E.V.; Elyakov, G.B. Structure of Ulososide A—New triterpene glycoside from the sponge Ulosa sp. Izvestia AN SSSR. Ser. Khim. 1994, 1326–1329. [Google Scholar]
- Antonov, A.S.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Stonik, V.A. Ulososide B, a new unusual norlanostane-triterpene glycoside and its genuine aglycone from the Madagascar sponge Ulosa sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 1998, 39, 3807–3808. [Google Scholar]
- Antonov, A.S.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Stonik, V.A. New triterpene glycosides from the sponge Ulosa sp. Bioorgan. Khimiya. 2002, 28, 209–214. [Google Scholar]
- Cafieri, F.; Fattorusso, E.; Taglialatela-Scafati, O. Ectyoplasides A–B—Unique triterpene olygoglycosides from the Caribbean sponge Ectyoplasia ferox. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 1999, 231–238. [Google Scholar]
- Campagnuolo, C.; Fattorusso, E.; Taglialatela-Scafari, O. Feroxosides A–B, two norlanostane tetraglycosides from the Caribbean sponge Ectyoplasia ferox. Tetrahedron 2001, 57, 4049–4055. [Google Scholar]
- Ravi, B.N.; Wells, R.J.; Croft, K.D. Malabaricane triterpenes from a Fijian collection of the sponge Jaspis stellifera. J. Org. Chem. 1981, 46, 1998–2001. [Google Scholar]
- McCabe, T.; Clardy, J.; Minale, L.; Pizza, C.; Zollo, F.; Riccio, R. A triterpenoid pigment with isomalabaricane skeleton from the marine sponge Stelletta sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 1982, 23, 3307–3310. [Google Scholar]
- Tabudravu, J.N.; Jaspars, M. Stelliferin riboside, a triterpene monosaccharide isolated from the Fijian sponge Geodia globostellifera. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 813–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirashima, M.; Tsuda, K.; Hamada, T.; Okumara, H.; Furukawa, T.; Akiyama, S.; Tajitsu, Y.; Ikeda, R.; Komatsu, M.; Doe, M.; et al. Cytotoxic isomalabaricane derivatives and a monocyclic triterpene glycoside from a sponge Rhabdastrella globostellata. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 1512–1518. [Google Scholar]
- Clement, J.A.; Li, M.; Hecht, S.M.; Kingston, D.G.I. Bioactive isomalabaricane triterpenoids from Rhabdastrella globostellata that stabilize the binding of DNA polymerase β to DNA. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 373–376. [Google Scholar]
- Fouad, M.; Edrada, R.A.; Ebel, R.; Wray, V.; Muller, W.E.G.; Lin, W.H.; Proksch, P. Cytotoxic isomalabaricane triterpenoids from the marine sponge Rhabdastrella globostellata. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ksebati, M.B.; Schmitz, F.J.; Gunasekera, S.P. Pouosides A–E, novel triterpene galactosides from a marine sponge Asteropus sp. J. Org. Chem. 1988, 53, 3917–3921. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.-H.; Jang, K.H.; Lee, Y.-J.; Lee, H.-S.; Sim, C.J.; Oh, K.-B.; Shin, J. Triterpene galactoside of the pouoside class and corresponding aglycones from the sponge Lipastrotethya sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 2563–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shmueli, U.; Carmely, A.; Groweiss, A.; Kashman, Y. Sipholenol and sipholenone, two new triterpenes from the marine sponge Siphonochalina siphonella (Levi). Tetrahedron Lett. 1981, 22, 709–712. [Google Scholar]
- Kashman, Y.; Groweiss, A.; Carmely, S.; Kinamoni, Z.; Czarkie, D.; Rotem, M. Recent research in marine natural products from the Red Sea. Pure Appl. Chem. 1982, 54, 1995–2010. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez, J.J.; Souto, M.L.; Norte, M. Marine polyether triterpenes. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2000, 17, 235–246. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, S.; Laphookheio, S.; Shi, Z.; Fu, L.; Akiyama, S.; Chen, Z.S.; Youssef, D.T.A.; Rob, W.M.; van Soest, R.W.M.; El Sayed, K.A. Reversal of P-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance by sipholane triterpenoids. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 928–931. [Google Scholar]
- Kashman, Y.; Yosief, T.; Carmeli, S. New triterpenoids from the Red Sea sponge Siphonochalina siphonella. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 175–180. [Google Scholar]
- Ohtani, I.; Kusumi, T.; Kashman, Y.; Kakisawa, H. A new aspect of the high-field NMR application of Mosher’s method. The absolute configuration of marine terpenoid sipholenol A. J. Org. Chem. 1991, 56, 1296–1298. [Google Scholar]
- Northcote, P.T.; Andersen, R.J. Xestovanin A and secoxestovanin A, triterpenoid glycosides with new carbon skeletons from the sponge Xestospongia vanilla. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1989, 111, 6276–6280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, S.A.; Northcote, P.T.; Andersen, R.J. Triterpenoid glycosides from the Northeastern Pacific marine sponge Xestospongia vanilla. Can. J. Chem. 1991, 69, 1352–1364. [Google Scholar]
- Hirota, H.; Takayama, S.; Miyashiro, S.; Ozaki, Y.; Ikegami, S. Structure of a novel steroidal saponin, pachastrelloside A, obtained from a marine sponge of the genus Pachastrella. Tetrahedron Lett. 1990, 31, 3321–3324. [Google Scholar]
- Ryu, G.; Choi, B.W.; Lee, B.H.; Hwang, K.-H.; Lee, U.C.; Jeong, D.S.; Lee, N.H. Wondosterols A–C, three steroidal glycosides from a Korean marine two-sponge association. Tetrahedron 1999, 55, 13171–13178. [Google Scholar]
- Cachet, N.; Regalado, E.L.; Genta-Jouve, G.; Mehiri, M.; Amade, P.; Thomas, O.P. Steroidal glycosides from the marine sponge Pandaros acanthifolium. Steroids 2009, 74, 746–750. [Google Scholar]
- Regalado, E.L.; Tasdemir, D.; Kaiser, M.; Cachet, N.; Amade, P.; Thomas, O.P. Antiprotozoal steroidal saponins from the marine sponge Pandaros acanthifolium. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 1404–1410. [Google Scholar]
- Regalado, E.; Turk, T.; Tasdemir, D.; Gorjanc, M.; Kaiser, M.; Thomas, O.P.; Fernandez, R.; Amade, P. Cytotoxic and haemolytic steroidal glycosides from the Caribbean sponge Pandaros acanthifolium. Steroids 2011, 76, 1389–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regalado, E.; Jimenez-Romero, C.; Genta-Jouve, G.; Tasdemir, D.; Amade, P.; Nogueiras, C.; Thomas, O.P. Acanthifoliosides, minor steroidal saponins from the sponge Pandaros acanthifolium. Tetrahedron 2011, 67, 1011–1018. [Google Scholar]
- Stonik, V.A.; Makarieva, T.N.; Antonov, A.S.; Elyakov, G.B. Steroidal saponins from the sponge Mycale purpurea. Khimiya Prirod. Soedin. 1981, 1, 104–105. [Google Scholar]
- Kalinovsky, A.I.; Antonov, A.S.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Evtuschenko, E.V.; Stonik, V.A. Mycaloside A, a new steroid oligoglycoside with an unprecedented structure from the Caribbean sponge Mycale laxissima. Tetrahedron Lett. 2002, 43, 523–525. [Google Scholar]
- Antonov, A.S.; Afiyatullov, S.S.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Ponomarenko, L.P.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Aminin, D.L.; Stonik, V.A. ycalosides B–J, eight new spermostatic steroid oligoglycosides from the sponge Mycale laxissima. J. Nat. Prod. 2003, 66, 1082–1088. [Google Scholar]
- Afiyatullov, S.S.; Antonov, A.S.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Dmitrenok, P.S. Two new steroid oligoglycosides from the Caribbean sponge Mycale laxissima. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2008, 3, 1581–1586. [Google Scholar]
- Yeung, B.K.S.; Hamann, M.T.; Scheuer, P.J.; Kelly-Borges, M. Hapaioside: 19-norpregnane glycoside from the sponge Cribrochalina olemda. Tetrahedron 1994, 50, 12593–12598. [Google Scholar]
- Gabant, M.; Schmitz-Afonso, I.; Gallard, J.-F.; Menou, J.-L.; Laurent, D.; Debitus, C.; Al-Mourabit, A. Sulfated steroids: Ptilosteroids A–C and ptilosaponosodes A and B from the Solomon Islands marine sponge Ptilocaulis spiculifer. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 760–763. [Google Scholar]
- Linington, R.G.; Robertson, M.; Gauthier, A.; Finlay, B.B.; van Soest, R.; Andersen, R.J. Caminoside A, an antimicrobial glycolipid isolated from the marine sponge Caminus sphaeroconia. Org. Lett. 2002, 4, 4089–4092. [Google Scholar]
- Linington, R.G.; Robertson, M.; Gauthier, A.; Finlay, B.B.; MacMillan, J.B.; Molinski, T.F.; van Soest, R.; Andersen, R.J. Caminosides B–D, antimicrobial glycolipids isolated from the marine sponge Caminus sphaeroconia. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 173–177. [Google Scholar]
- MacMillan, J.B.; Linington, R.G.; Andersen, R.J.; Molinski, T.F. Stereochemical assignment in acyclic lipids across long distance by circular dichroism: absolute stereochemistry of the aglycone of caminoside A. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 5946–5951. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Han, X.; Yu, B. First total synthesis of caminoside A, an antimicrobial glycolipid from sponge. Synlett 2005, 3, 437–440. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Zong, C.; Song, G.; Lv, G.; Chun, Y.; Wang, P.; Ding, N.; Li, Y. Total synthesis of caminoside B, a novel antimicrobial glycolipid isolated from the marine sponge Caminus sphaeroconia. Carbohydrate Res. 2010, 345, 750–760. [Google Scholar]
- Warabi, K.; Zimmerman, W.T.; Shen, J.; Gauthier, A.; Robertson, M.; Finlay, B.B.; van Soest, R.; Andersen, R.J. Pachymoside A—a novel glycolipid isolated from the marine sponge Pachymatisma johnstonia. Can. J. Chem. 2004, 82, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantino, V.; Fattorusso, E.; Mangoni, A.; Di Rosa, M.; Ianaro, A. Glycolipids from Sponges. VII. Simplexides, novel immunosuppressive glycolipids from the Caribbean sponge Plakortis simplex. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 1999, 9, 271–276. [Google Scholar]
- Costantino, V.; Fattorusso, E.; Imperatore, C.; Mangoni, A. Glycolipids from sponges. Part 17. Clathrosides and isoclathrosides, unique glycolipids from the Caribbean sponge Agelas clathrodes. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, M.R.; Faulkner, D.J. Clavosolides A and B, dimeric macrolides from the Philippines sponge Myriastra clavosa. J. Nat. Prod. 2002, 65, 386–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erickson, K.L.; Gustafson, K.R.; Pannell, L.K.; Beutler, J.A.; Boyd, M.R. New dimeric macrolide glycosides from the marine sponge Myriastra clavosa. J. Nat. Prod. 2002, 65, 1303–1306. [Google Scholar]
- Rezanka, T.; Dembitsky, V.M. Ten-membered substituted cyclic 2-oxecanone (decalactone) derivatives from Latrunculia corticata, a Red Sea sponge. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2003, 2144–2152. [Google Scholar]
- Makarieva, T.N.; Denisenko, V.A.; Stonik, V.A.; Milgrom, Y.M.; Rashkes, Y.V. hizochalin, a novel secondary metabolite of mixed biosynthesis from the sponge Rhizochalina incrustata. Tetrahedron Lett. 1989, 30, 6581–6584. [Google Scholar]
- Makarieva, T.N.; Guzii, A.G.; Denisenko, V.A.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Santalova, E.A.; Pokanevich, E.V.; Molinski, T.F.; Stonik, V.A. Rhizochalin A, a novel two-headed sphingolipid from the sponge Rhizochalina incrustata. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 255–257. [Google Scholar]
- Makarieva, T.N.; Guzii, A.G.; Denisenko, V.A.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Stonik, V.A. New two-headed sphingolipid-like compounds from the marine sponge Oceanapia sp. Russ. Chem. Bull. 2008, 57, 669–673. [Google Scholar]
- Makarieva, T.N.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Zakharenko, A.M.; Denisenko, V.A.; Guzii, A.G.; Li, R.; Skepper, C.K.; Molinski, T.F.; Stonik, V.A. Rhizochalins C and D from the sponge Rhizochalina incrustata. A rare threo-sphingolipid and a facile method for determination of the carbonyl position in α,ω-bifunctionalized ketosphingolipids. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 1991–1998. [Google Scholar]
- Molinski, T.F.; Makarieva, T.N.; Stonik, V.A. (–)-Rhizochalin is a dimeric enantiomorphic (2R)-sphingolipid: Absolute configuration of pseudo-C2V-symmetric bis-2-amino-3-alkanols by CD. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2000, 39, 4076–4079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarieva, T.N.; Zakharenko, A.M.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Guzii, A.G.; Denisenko, V.A.; Savina, A.S.; Dalisay, D.S.; Molinski, T.F.; Stonik, V.A. Isorhizochalin, a minor unprecedented bipolar sphingolipid of stereodivergent biogenesis from the Rhizochalina incrustata. Lipids 2009, 44, 1155–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholas, G.M.; Hong, T.W.; Molinski, T.F.; Lerch, M.L.; Cancilla, M.T.; Lebrilla, C.B. Oceanapiside, an antifungal bis-α,ω-amino alcohol glycoside from the marine sponge Oceanapia phillipensis. J. Nat. Prod. 1999, 62, 1678–1681. [Google Scholar]
- Nicholas, G.M.; Molinski, T.F. Enantiodivergent biosynthesis of the dimeric sphingolipid oceanapiside from the marine sponge Oceanapia phillipensis. Determination of remote stereochemistry. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 4011–4019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, B.-N.; Mattern, M.P.; Johnson, R.K.; Kingston, D.G.I. Structure and stereochemistry of a novel bioactive sphingolipid from a Calyx sp. Tetrahedron 2001, 57, 9549–9554. [Google Scholar]
- Makarieva, T.N.; Denisenko, V.A.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Guzii, A.G.; Santalova, E.A.; Stonik, V.A.; MacMillan, J.B.; Molinski, T.F. Oceanalin A, a hybrid α,ω-bifunctionalized sphingoid tetrahydroisoquinoline β-glycoside from the marine sponge Oceanapia sp. Org. Lett. 2005, 7, 2897–2900. [Google Scholar]
- Fedorov, S.N.; Makarieva, T.N.; Guzii, A.G.; Shubina, L.K.; Kwak, J.Y.; Stonik, V.A. Marine two-headed sphingolipid-like compound rhizochalin inhibits EGF-induced transformation of JB6 P+ Cl41 cells. Lipids 2009, 44, 777–785. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, J.-O.; Shastina, V.; Park, J.-I.; Han, J.-Y.; Makarieva, T.; Fedorov, S.; Rasskazov, V.; Stonik, V.; Kwak, J.-Y. Differential induction of apoptosis of leukemic cells by rhizochalin, two headed sphingolipids from sponge and its derivatives. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2009, 32, 955–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibirtsev, J.T.; Shastina, V.V.; Menzorova, N.I.; Makarieva, T.N.; Rasskazov, V.A. Ca2+, Mg2+-dependent DNase involvement in apoptotic effects in spermatozoa of sea urchin Strongylocentrotus intermedius induced by two-headed sphingolipid rhizochalin. Mar. Biotechnol. 2011, 13, 536–543. [Google Scholar]
- Fusetani, N.; Sata, N.; Asai, N.; Matsunaga, S. Isolation and structure elucidation of erylusamine B, a new class of marine natural products, which blocked an IL-6 receptor, from the marine sponge Erylus placenta Thiele. Tetrahedron Lett. 1993, 34, 4067–4070. [Google Scholar]
- Sata, N.; Asai, N.; Matsunaga, S.; Fusetani, N. Erylusamines, IL-6 receptor antagonists, from the marine sponge, Erylus placenta. Tetrahedron 1994, 50, 1105–1110. [Google Scholar]
- Goobes, R.; Rudi, A.; Kashman, Y. Three new glycolipids from a Red Sea sponge of the genus Erylus. Tetrahedron 1996, 52, 7921–7928. [Google Scholar]
- Kubanek, J.; Pawlik, J.R.; Eve, T.M.; Fenical, W. Triterpene glycosides defend the Caribbean reef sponge Erylus formosus from predatory fishes. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2000, 207, 69–77. [Google Scholar]
- Pawlik, J.R. The chemical ecology of sponges on Caribbean reefs: Natural products shape natural systems. BioScience 2011, 61, 888–898. [Google Scholar]
- Kubanek, J.; Whalen, K.E.; Engel, S.; Kelly, S.R.; Henkel, T.R.; Fenical, W.; Pawlik, J.R. Multiple defensive roles for triterpene glycosides from two Caribbean sponges. Oecologia 2002, 131, 125–136. [Google Scholar]
- Engel, S.; Pawlik, J.R. Allelopathic activities of sponge extracts. Mar. Ecol. 2000, 207, 273–281. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, S.R.; Jensen, P.R.; Henkel, T.P.; Fenical, W.; Pawlik, J.R. Effects of Caribbean sponge extracts on bacterial attachment. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2003, 31, 175–182. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, S.A.P.; Hatt, H.; Kubanek, J.; McCarty, N.A. Reconstitution of a chemical defense signaling pathway in a heterologous system. J. Exp. Biol. 2008, 211, 599–605. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, S.P.; Haack, K.K.V.; Halstead-Nissloch, G.W.; Bernard, K.F.; Hatt, H.; Kubanek, J.; McCarty, N.A. Identification of RL-TGR, a coreceptor involved in aversive chemical signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 12339–12344. [Google Scholar]
- Samples Availability: Available from the authors.
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Kalinin, V.I.; Ivanchina, N.V.; Krasokhin, V.B.; Makarieva, T.N.; Stonik, V.A. Glycosides from Marine Sponges (Porifera, Demospongiae): Structures, Taxonomical Distribution, Biological Activities and Biological Roles. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 1671-1710. https://doi.org/10.3390/md10081671
Kalinin VI, Ivanchina NV, Krasokhin VB, Makarieva TN, Stonik VA. Glycosides from Marine Sponges (Porifera, Demospongiae): Structures, Taxonomical Distribution, Biological Activities and Biological Roles. Marine Drugs. 2012; 10(8):1671-1710. https://doi.org/10.3390/md10081671
Chicago/Turabian StyleKalinin, Vladimir I., Natalia V. Ivanchina, Vladimir B. Krasokhin, Tatyana N. Makarieva, and Valentin A. Stonik. 2012. "Glycosides from Marine Sponges (Porifera, Demospongiae): Structures, Taxonomical Distribution, Biological Activities and Biological Roles" Marine Drugs 10, no. 8: 1671-1710. https://doi.org/10.3390/md10081671
APA StyleKalinin, V. I., Ivanchina, N. V., Krasokhin, V. B., Makarieva, T. N., & Stonik, V. A. (2012). Glycosides from Marine Sponges (Porifera, Demospongiae): Structures, Taxonomical Distribution, Biological Activities and Biological Roles. Marine Drugs, 10(8), 1671-1710. https://doi.org/10.3390/md10081671








