A Lactose-Binding Lectin from the Marine Sponge Cinachyrella Apion (Cal) Induces Cell Death in Human Cervical Adenocarcinoma Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effects of CaL on Cell Proliferation of Tumor Cells Lines
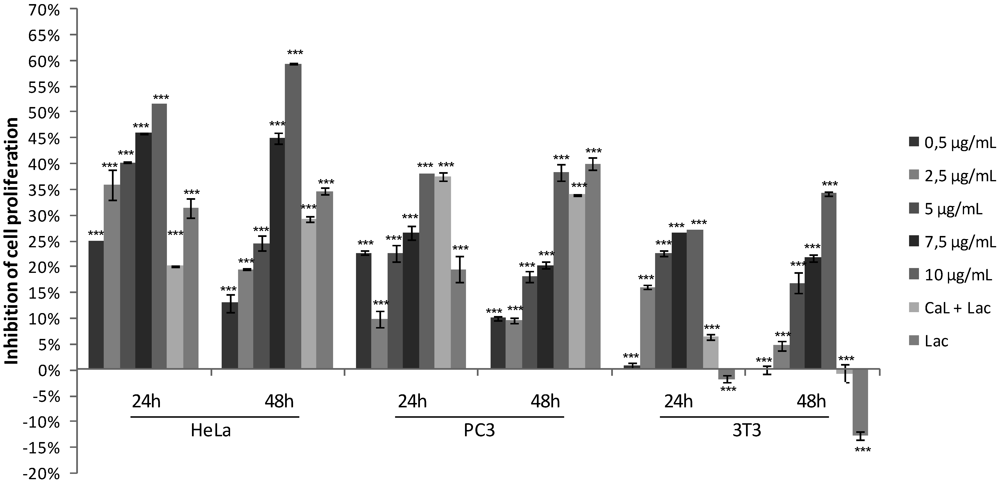
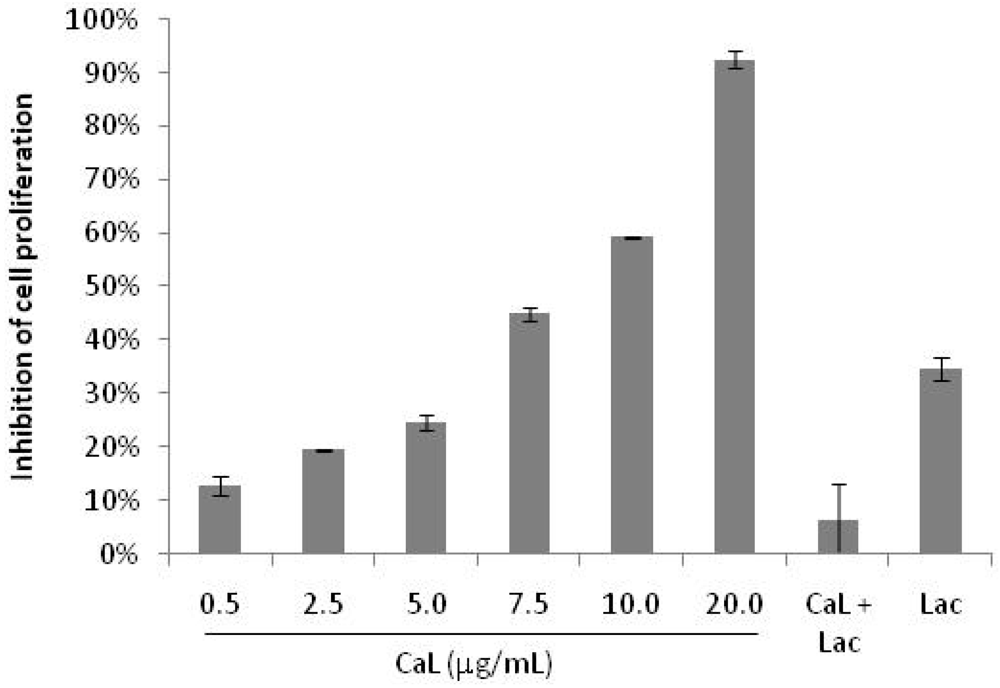
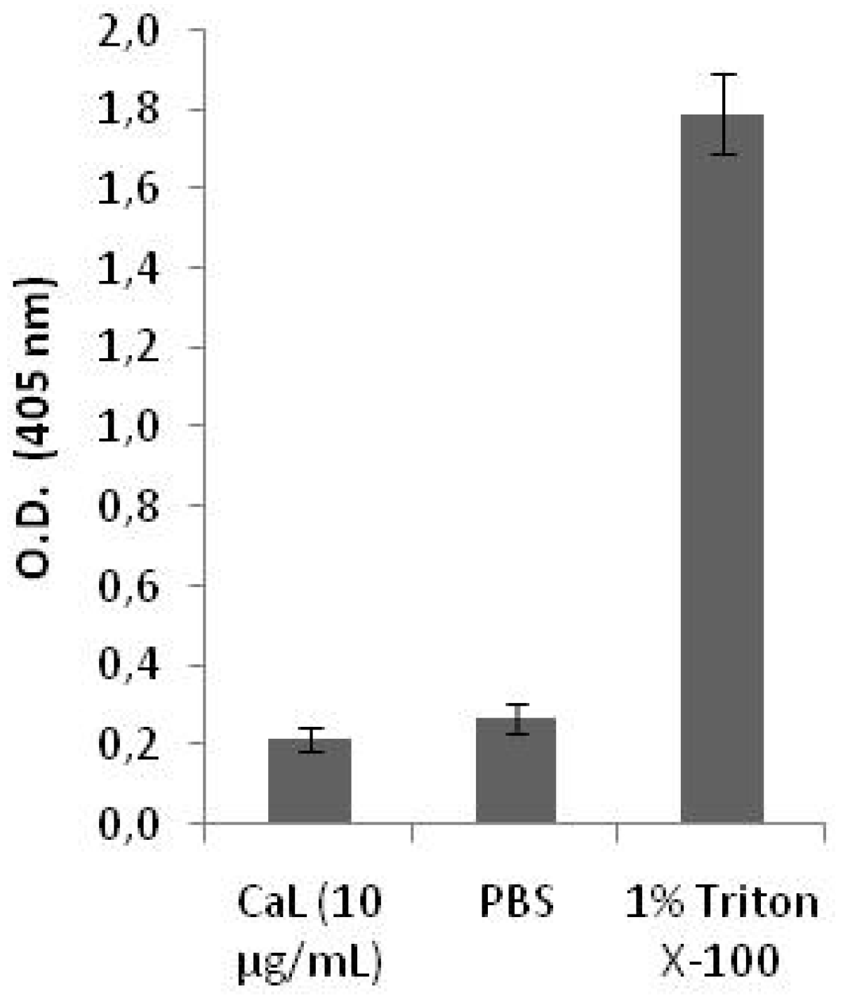
2.2. Cytotoxicity on Human Peripheral Blood Cells and Hemolytic Activity of CaL
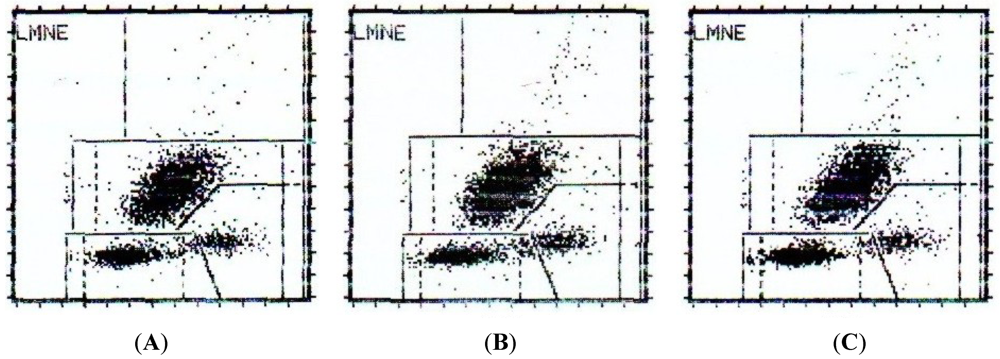
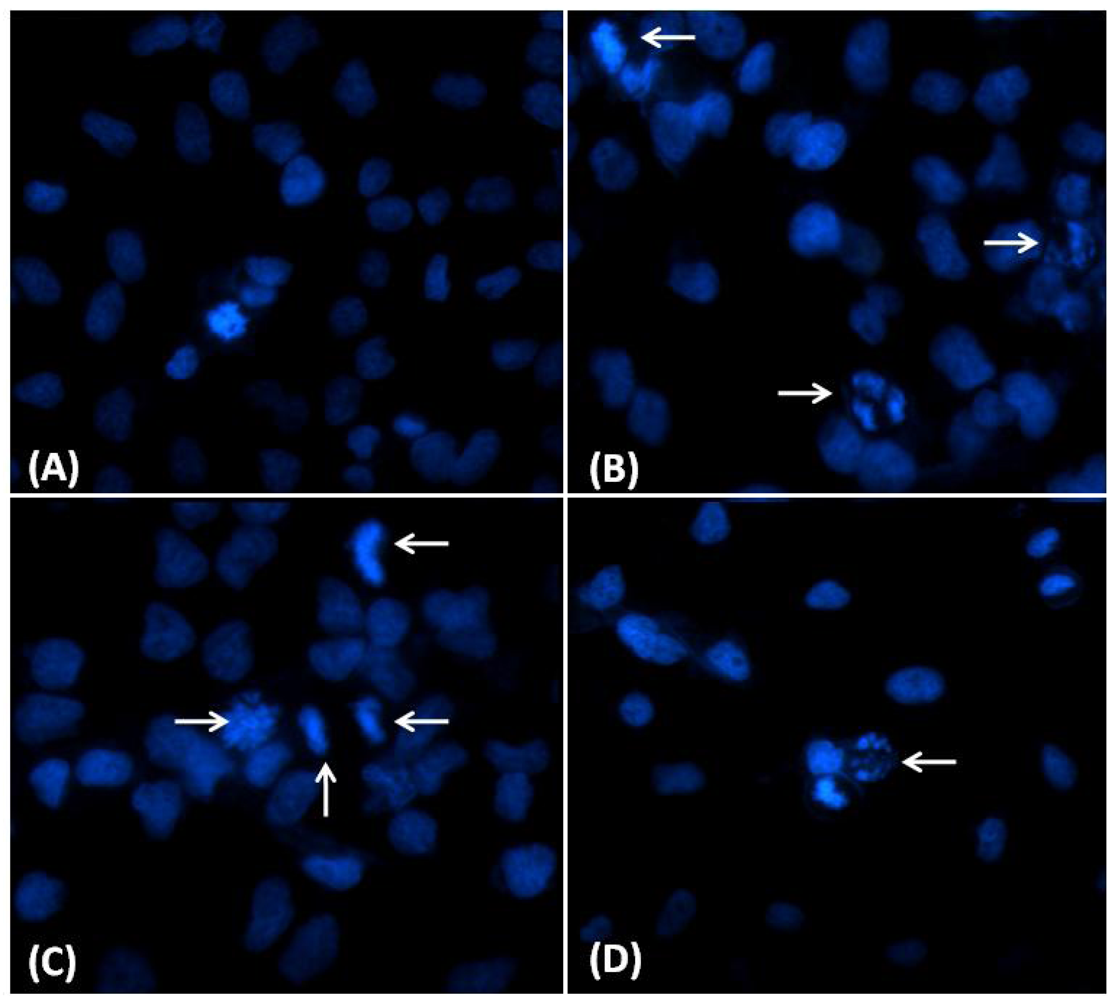
2.3. Nuclear Morphological Changes Induced by CaL in HeLa Cells
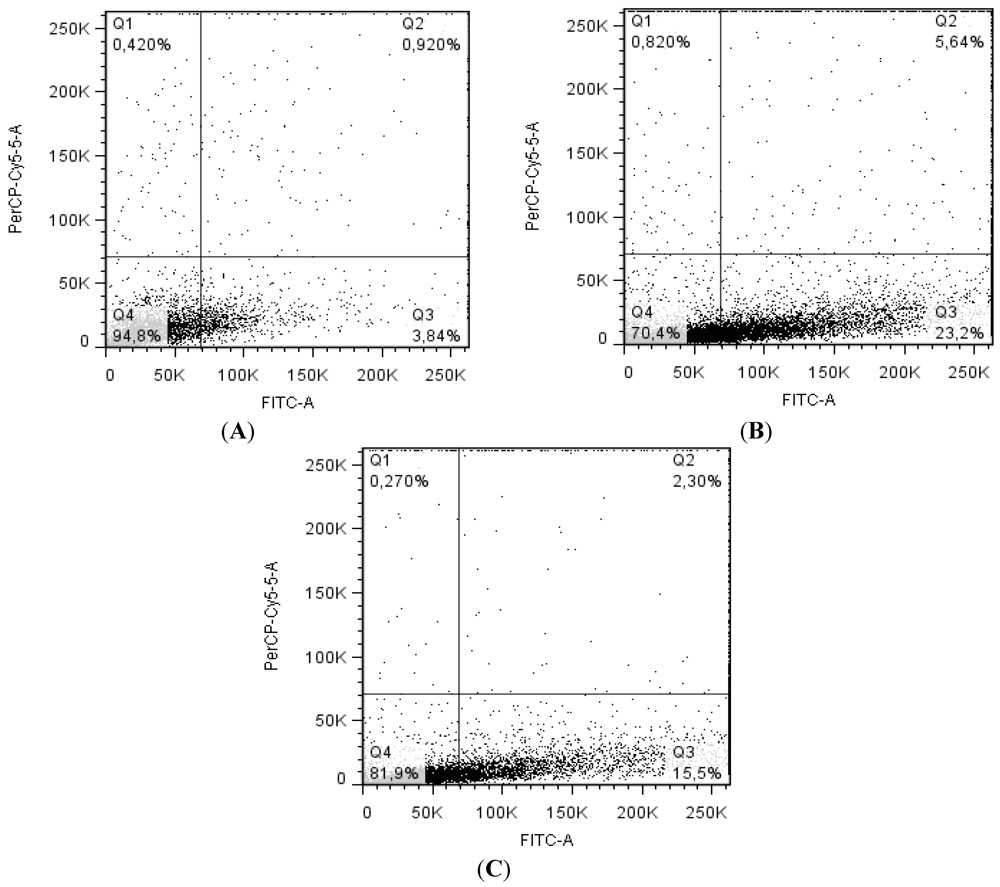
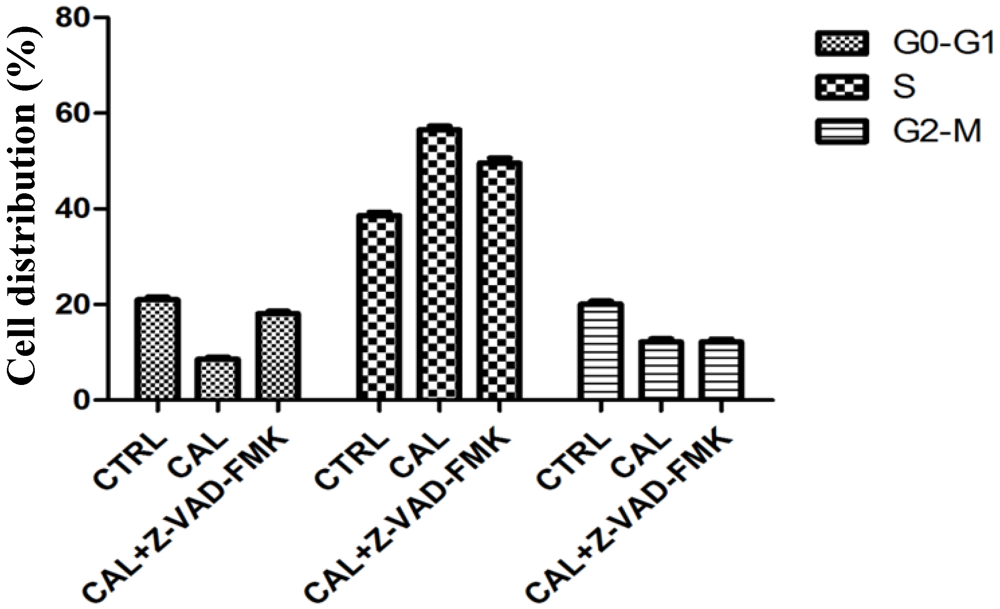
2.4. Balance between Apoptosis and Necrosis by Double Staining Annexin V-FITC/PI and Cell Cycle Analysis
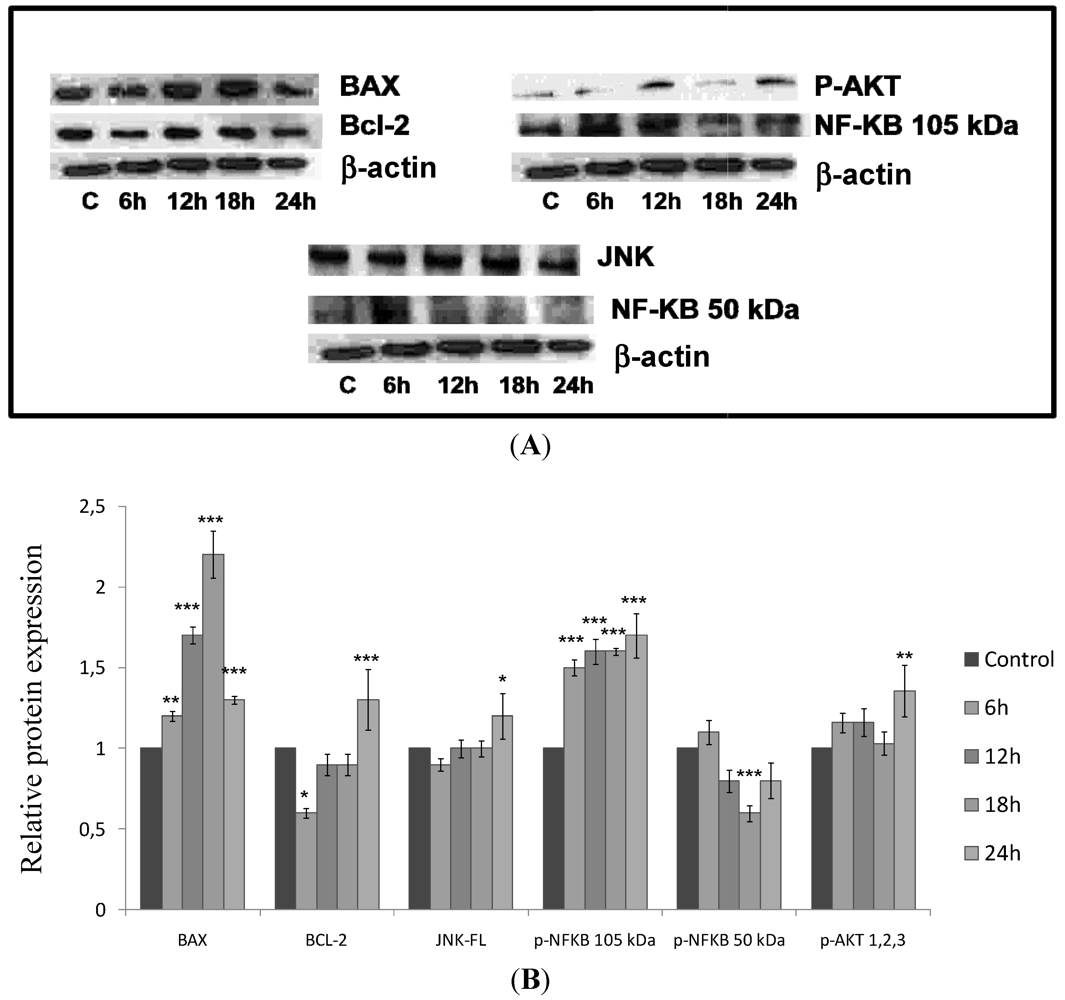
2.5. CaL Effects in Activation of Proteins Related to Apoptosis in HeLa Cells
3. Discussions
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Materials
4.2. Preparation of Marine Sponge Cinachyrella apion Lectin (CaL)
4.3. Cell Culture
4.4. Cell Growth Inhibition Assay
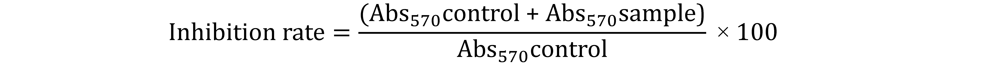
4.5. Cytotoxicity of Human Peripheral Blood Cells and Hemolytic Activity in Vitro
4.6. Evaluation of Indicators of Apoptosis by Incubation with DAPI
4.7. Annexin V-FITC/PI Double Staining and Analysis by Flow Cytometry
4.8. Cell Cycle Analysis
4.9. Western Blotting
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusion
Acknowledgments
References
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell 2000, 100, 57–70. [Google Scholar]
- Clardy, J.; Walsh, C. Lessons from natural molecules. Nature 2004, 432, 829–837. [Google Scholar]
- Hatakeyama, T.; Nagatomo, H.; Yamasaki, N. Interaction of the hemolytic lectin CEL-III from the marine invertebrate Cucumaria echinata with the erythrocyte membrane. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 3560–3564. [Google Scholar]
- Muta, T.; Miyata, T.; Misumi, Y.; Tokunaga, F.; Nakamura, T.; Toh, Y.; Ikehara, Y.; Iwanaga, S. Limulus factor C. An endotoxin-sensitive serine protease zymogen with a mosaic structure of complement-like, epidermal growth factor-like, and lectin-like domains. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 6554–6561. [Google Scholar]
- Takagi, T.; Nakamura, A.; Deguchi, R.; Kyozuka, K. Isolation, characterization, and primary structure of three major proteins obtained from Mytilus edulis sperm. J. Biochem. 1994, 116, 598–605. [Google Scholar]
- Giga, Y.; Ikai, A.; Takahashi, K. The complete amino acid sequence of echinoidin, a lectin from the coelomic fluid of the sea urchin Anthocidaris crassispina. Homologies with mammalian and insect lectins. J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 6197–6203. [Google Scholar]
- Atta, A.M.; Barralnetto, M.; Peixinho, S.; Sousaatta, M.L.B. Isolation and functional-characterization of a mitogenic lectin from the marine sponge cinachyrella-alloclada. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 1989, 22, 379–385. [Google Scholar]
- Bretting, H.; Donadey, C.; Vacelet, J.; Jacobs, G. Investigations on the occurrence of lectins in marine sponges with special regard to some species of the family axinellidae. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1981, 70, 69–76. [Google Scholar]
- Engel, M.; Bachmann, M.; Schroder, H.C.; Rinkevich, B.; Kljajic, Z.; Uhlenbruck, G.; Muller, W.E.G. A novel galactose-specific and arabinose-specific lectin from the sponge pellina-semitubulosa—Isolation, characterization and immunobiological properties. Biochimie 1992, 74, 527–537. [Google Scholar]
- Pajic, I.; Kljajic, Z.; Dogovic, N.; Sladic, D.; Juranic, Z.; Gasic, M.J. A novel lectin from the sponge Haliclona cratera: Isolation, characterization and biological activity. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2002, 132, 213–221. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, C.N.; Li, W.; Liu, H.; Zhang, W.; Dou, J.L.; Bai, X.F.; Du, Y.G.; Ma, X.J. A normal mucin-binding lectin from the sponge Craniella australiensis. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2006, 143, 9–16. [Google Scholar]
- Queiroz, A.F.S.; Silva, R.A.; Moura, R.M.; Dreyfuss, J.L.; Paredes-Gamero, E.J.; Souza, A.C.S.; Tersariol, I.L.S.; Santos, E.A.; Nader, H.B.; Justo, G.Z.; et al. Growth inhibitory activity of a novel lectin from Cliona varians against K562 human erythroleukemia cells. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2009, 63, 1023–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renan, M.J. How many mutations are required for tumorigenesis? Implications from human cancer data. Mol. Carcinog. 1993, 7, 139–146. [Google Scholar]
- Green, D.R.; Kroemer, G. Pharmacological manipulation of cell death: Clinical applications in sight? J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 2610–2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Natural products from marine invertebrates and microbes as modulators of antitumor targets. Curr. Drug Targets 2006, 7, 279–304. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, C.V.; Justo, G.Z.; Souza, A.C.; Queiroz, K.C.; Zambuzzi, W.F.; Aoyama, H.; Peppelenbosch, M.P. Natural compounds as a source of protein tyrosine phosphatase inhibitors: Application to the rational design of small-molecule derivatives. Biochimie 2006, 88, 1859–1873. [Google Scholar]
- Strohl, W.R. The role of natural products in a modern drug discovery program. Drug Discov. Today 2000, 5, 39–41. [Google Scholar]
- Justo, G.Z.; Ferreira, C.V. Coagulation and cancer therapy: The potential of natural compounds. Curr. Genomics 2005, 6, 461–469. [Google Scholar]
- Bantel, H.; Engels, I.H.; Voelter, W.; Schulze-Osthoff, K.; Wesselborg, S. Mistletoe lectin activates caspase-8/FLICE independently of death receptor signaling and enhances anticancer drug-induced apoptosis. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 2083–2090. [Google Scholar]
- Hajto, T.; Hostanska, K.; Berki, T.; Palinkas, L.; Boldizsar, F.; Nemeth, P. Oncopharmacological perspectives of a plant lectin (viscum album agglutinin-I): Overview of recent results from in vitro experiments and in vivo animal models, and their possible relevance for clinical applications. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2005, 2, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.A.; Lee, W.H.; Choi, T.H.; Rhee, S.H.; Park, K.Y.; Choi, Y.H. Involvement of p21WAF1/CIP1, pRB, Bax and NF-κB in induction of growth arrest and apoptosis by resveratrol in human lung carcinoma A549 cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2003, 23, 1143–1149. [Google Scholar]
- Lavastre, V.; Pelletier, M.; Saller, R.; Hostanska, K.; Girard, D. Mechanisms involved in spontaneous and Viscum album agglutinin-I-induced human neutrophil apoptosis: Viscum album agglutinin-I accelerates the loss of antiapoptotic Mcl-1 expression and the degradation of cytoskeletal paxillin and vimentin proteins via caspases. J. Immunol. 2002, 168, 1419–1427. [Google Scholar]
- Miyoshi, N.; Koyama, Y.; Katsuno, Y.; Hayakawa, S.; Mita, T.; Ohta, T.; Kaji, K.; Isemura, M. Apoptosis induction associated with cell cycle dysregulation by rice bran agglutinin. J. Biochem. 2001, 130, 799–805. [Google Scholar]
- Ohba, H.; Moriwaki, S.; Bakalova, R.; Yasuda, S.; Yamasaki, N. Plant-derived abrin-a induces apoptosis in cultured leukemic cell lines by different mechanisms. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2004, 195, 182–193. [Google Scholar]
- Park, R.; Kim, M.S.; So, H.S.; Jung, B.H.; Moon, S.R.; Chung, S.Y.; Ko, C.B.; Kim, B.R.; Chung, H.T. Activation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase 1 (JNK1) in mistletoe lectin II-induced apoptosis of human myeloleukemic U937 cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2000, 60, 1685–1691. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, P.V.; Jayaraj, R.; Bhaskar, A.S.; Kumar, O.; Bhattacharya, R.; Saxena, P.; Dash, P.K.; Vijayaraghavan, R. Mechanism of ricin-induced apoptosis in human cervical cancer cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2005, 69, 855–865. [Google Scholar]
- Medeiros, D.S.; Medeiros, T.L.; Ribeiro, J.K.; Monteiro, N.K.; Migliolo, L.; Uchoa, A.F.; Vasconcelos, I.M.; Oliveira, A.S.; de Sales, M.P.; Santos, E.A. A lactose specific lectin from the sponge Cinachyrella apion: Purification, characterization, N-terminal sequences alignment and agglutinating activity on Leishmania promastigotes. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 2010, 155, 211–216. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, C.; Sun, H.; Tong, X.; Qi, Y. An antitumour lectin from the edible mushroom Agrocybe aegerita. Biochem. J. 2003, 374, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Hang, D.; Guo, C.; Chen, Z. Fate of mesenchymal stem cells transplanted to osteonecrosis of femoral head. J. Orthop. Res. 2009, 27, 442–446. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, R. Mechanisms of BCR-ABL in the pathogenesis of chronic myelogenous leukaemia. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2005, 5, 172–183. [Google Scholar]
- Priyadarsini, R.V.; Murugan, R.S.; Maitreyi, S.; Ramalingam, K.; Karunagaran, D.; Nagini, S. The flavonoid quercetin induces cell cycle arrest and mitochondria-mediated apoptosis in human cervical cancer (HeLa) cells through p53 induction and NF-κB inhibition. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 649, 84–91. [Google Scholar]
- Ogden, C.A.; deCathelineau, A.; Hoffmann, P.R.; Bratton, D.; Ghebrehiwet, B.; Fadok, V.A.; Henson, P.M. C1q and mannose binding lectin engagement of cell surface calreticulin and CD91 initiates macropinocytosis and uptake of apoptotic cells. J. Exp. Med. 2001, 194, 781–795. [Google Scholar]
- Hadari, Y.R.; Arbel-Goren, R.; Levy, Y.; Amsterdam, A.; Alon, R.; Zakut, R.; Zick, Y. Galectin-8 binding to integrins inhibits cell adhesion and induces apoptosis. J. Cell Sci. 2000, 113, 2385–2397. [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz, R.E.; Wojciechowicz, D.C.; Picon, A.I.; Schwarz, M.A.; Paty, P.B. Wheatgerm agglutinin-mediated toxicity in pancreatic cancer cells. Br. J. Cancer 1999, 80, 1754–1762. [Google Scholar]
- Kessel, D.; Luo, Y. Cells in cryptophycin-induced cell-cycle arrest are susceptible to apoptosis. Cancer Lett. 2000, 151, 25–29. [Google Scholar]
- Liua, W.; Ho, J.C.; Ng, T. Suppression of cell cycle progression by a fungal lectin: Activation of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2001, 61, 33–37. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, S.Y.; Lai, W.W.; Chou, C.C.; Kuo, H.M.; Li, T.M.; Chung, J.G.; Yang, J.H. Sodium ascorbate inhibits growth via the induction of cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human malignant melanoma A375.S2 cells. Melanoma Res. 2006, 16, 509–519. [Google Scholar]
- Fuke, H.; Shiraki, K.; Sugimoto, K.; Tanaka, J.; Beppu, T.; Yoneda, K.; Yamamoto, N.; Ito, K.; Masuya, M.; Takei, Y. Jak inhibitor induces S phase cell-cycle arrest and augments TRAIL-induced apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 363, 738–744. [Google Scholar]
- FlowJo, version 7.6.3, Tree Star, Inc.: Ashland, OR, USA, 1997.
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, C.V.; Bos, C.L.; Versteeg, H.H.; Justo, G.Z.; Duran, N.; Peppelenbosch, M.P. Molecular mechanism of violacein-mediated human leukemia cell death. Blood 2004, 104, 1459–1464. [Google Scholar]
- GraphPad InStat, version 3.05 for Windows, GraphPad Software: San Diego, CA, USA, 2000.
- Samples Availability: Available from the authors.
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Rabelo, L.; Monteiro, N.; Serquiz, R.; Santos, P.; Oliveira, R.; Oliveira, A.; Rocha, H.; Morais, A.H.; Uchoa, A.; Santos, E. A Lactose-Binding Lectin from the Marine Sponge Cinachyrella Apion (Cal) Induces Cell Death in Human Cervical Adenocarcinoma Cells. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 727-743. https://doi.org/10.3390/md10040727
Rabelo L, Monteiro N, Serquiz R, Santos P, Oliveira R, Oliveira A, Rocha H, Morais AH, Uchoa A, Santos E. A Lactose-Binding Lectin from the Marine Sponge Cinachyrella Apion (Cal) Induces Cell Death in Human Cervical Adenocarcinoma Cells. Marine Drugs. 2012; 10(4):727-743. https://doi.org/10.3390/md10040727
Chicago/Turabian StyleRabelo, Luciana, Norberto Monteiro, Raphael Serquiz, Paula Santos, Ruth Oliveira, Adeliana Oliveira, Hugo Rocha, Ana Heloneida Morais, Adriana Uchoa, and Elizeu Santos. 2012. "A Lactose-Binding Lectin from the Marine Sponge Cinachyrella Apion (Cal) Induces Cell Death in Human Cervical Adenocarcinoma Cells" Marine Drugs 10, no. 4: 727-743. https://doi.org/10.3390/md10040727
APA StyleRabelo, L., Monteiro, N., Serquiz, R., Santos, P., Oliveira, R., Oliveira, A., Rocha, H., Morais, A. H., Uchoa, A., & Santos, E. (2012). A Lactose-Binding Lectin from the Marine Sponge Cinachyrella Apion (Cal) Induces Cell Death in Human Cervical Adenocarcinoma Cells. Marine Drugs, 10(4), 727-743. https://doi.org/10.3390/md10040727




