Bioactive Hydroperoxyl Cembranoids from the Red Sea Soft Coral Sarcophyton glaucum
Abstract
:1. Introduction
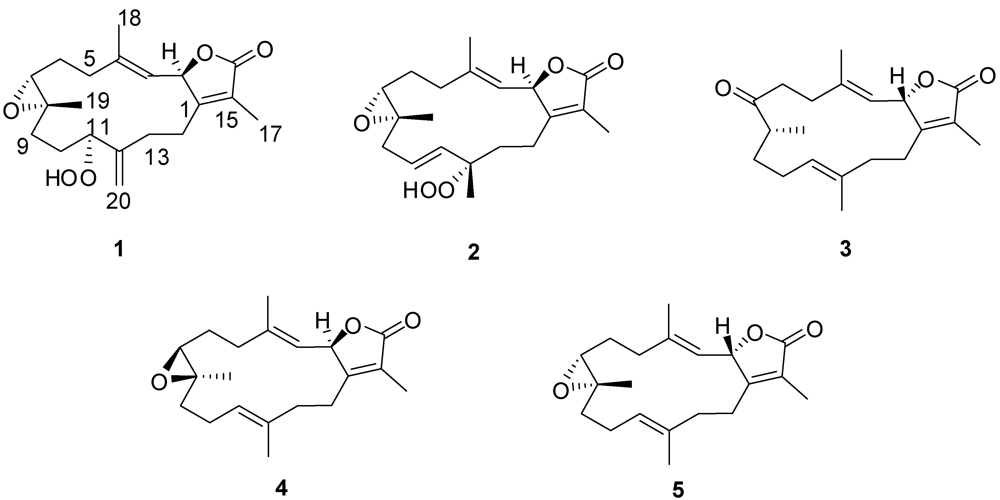
2. Results and Discussion
 +12.6 (c 0.09, CHCl3). The HR-FAB-MS exhibited a [M + Na]+ ion at m/z 371.18281, indicating a molecular formula of C20H28O5Na and seven degrees of unsaturation that was supported by NMR data. An IR spectrum indicated the presence of an α,β-unsaturated-γ-lactone (1750 and 1686 cm−1), a carbonyl (1707 cm−1), an olefin (1669 cm−1), an epoxide (1256 cm−1) and a broad absorption band for OH stretching (3000–3353 cm−1). The 13C NMR and DEPT spectrum (Table 1) exhibited 20 carbon signals establishing: three methyls, seven methylenes, four methines, and six quaternary carbons. The spectrum also revealed the presence of an exomethylene functionality at δC 113.4/144.5, two oxymethine carbons at δC 60.8 and 86.5, one oxygenated quaternary carbon at δC 61.1, and two olefinic carbons at δC 119.6 and 146.0.
+12.6 (c 0.09, CHCl3). The HR-FAB-MS exhibited a [M + Na]+ ion at m/z 371.18281, indicating a molecular formula of C20H28O5Na and seven degrees of unsaturation that was supported by NMR data. An IR spectrum indicated the presence of an α,β-unsaturated-γ-lactone (1750 and 1686 cm−1), a carbonyl (1707 cm−1), an olefin (1669 cm−1), an epoxide (1256 cm−1) and a broad absorption band for OH stretching (3000–3353 cm−1). The 13C NMR and DEPT spectrum (Table 1) exhibited 20 carbon signals establishing: three methyls, seven methylenes, four methines, and six quaternary carbons. The spectrum also revealed the presence of an exomethylene functionality at δC 113.4/144.5, two oxymethine carbons at δC 60.8 and 86.5, one oxygenated quaternary carbon at δC 61.1, and two olefinic carbons at δC 119.6 and 146.0.| Position | 1 | 2 | 3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| δH (J in Hz) | δC | δH (J in Hz) | δC | δH (J in Hz) | δC | |
| 1 | -- | 162.2 | -- | 162.5 | -- | 163.3 |
| 2 | 5.50 (d, 15.0) | 78.9 | 5.44 (d, 16.0) | 79.2 | 5.47 (dd, 1.5, 10.0) | 78.9 |
| 3 | 5.09 (d, 15.0) | 119.6 | 4.98 (d, 16.0) | 118.9 | 5.12 (brd, 10.5) | 122.1 |
| 4 | -- | 146.0 | -- | 146.7 | -- | 141.9 |
| 5 | 2.20 (m) | 35.9 | 2.02 (m) | 37.1 | 2.66 (m) | 37.9 |
| 2.39 (m) | 2.38 (dt, 4.5, 13.5) | 2.76 (m) * | ||||
| 6 | 2.59 (td, 5, 13.5) | 25.4 | 1.77 (m) | 25.0 | 2.06 (m) | 32.8 |
| 2.39 (m) | 2.73 (m) * | |||||
| 7 | 2.50 (d, 4.5, 8.5) | 60.8 | 2.53 (dd, 5.0, 6.0) | 59.0 | -- | 212.1 |
| 8 | -- | 61.1 | -- | 59.2 | 2.44 (m) | 46.6 |
| 9 | 1.30 (m) | 32.1 | 2.25 (m) | 39.0 | 1.56 (m) | 32.4 |
| 1.79 (m) | 2.46 (m) | 1.95 (m) | ||||
| 10 | 1.50 (m) | 26.7 | 5.42 (ddd, 16.0, 10.5, 7.5) | 124.6 | 1.88 (brd, 11.0) | 26.5 |
| 1.70 (m) | 2.26 (m) | |||||
| 11 | 4.35 (t like, 5) | 86.5 | 5.56 (d, 16.0) | 136.1 | 4.78 (td, 7.5, 1) | 124.1 |
| 12 | -- | 144.5 | -- | 84.0 | -- | 134.9 |
| 13 | 2.07 (m) | 30.1 | 1.41 (dd, 4) * | 37.6 | 1.92 (m) | 36.1 |
| 2.20 (m) | 2.07 (td, 13.0, 4.5) | 2.00 (m) | ||||
| 14 | 2.07 (m) | 24.8 | 2.42 (m) * | 21.2 | 2.16 (brt, 12.0) | 26.1 |
| 1.50 (m) | 2.50 (m) * | 2.60 (m) | ||||
| 15 | -- | 124.2 | -- | 123.8 | -- | 122.3 |
| 16 | -- | 174.5 | -- | 174.9 | -- | 175.0 |
| 17 | 1.85 (s) | 8.9 | 1.87 (brs) | 9.1 | 1.82 (t, 1.5) | 8.9 |
| 18 | 1.94 (s) | 16.0 | 1.89 (s) | 16.2 | 1.84 (s) | 16.2 |
| 19 | 1.27 (s) | 16.7 | 1.30 (s) | 18.2 | 1.06 (d, 7.5) | 18.8 |
| 20 | 5.12 (s) | 113.4 | 1.43 (s) | 22.8 | 1.60 (s) | 15.7 |
| 5.16 (s) | ||||||
| -OOH | 8.25 (brs) | -- | 7.70 (brs) | -- | -- | -- |
 ) and HMBC (
) and HMBC (  ) correlations of 1–3.
) correlations of 1–3.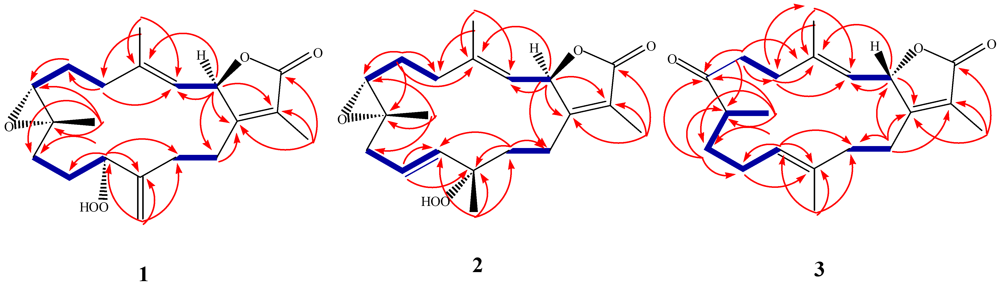
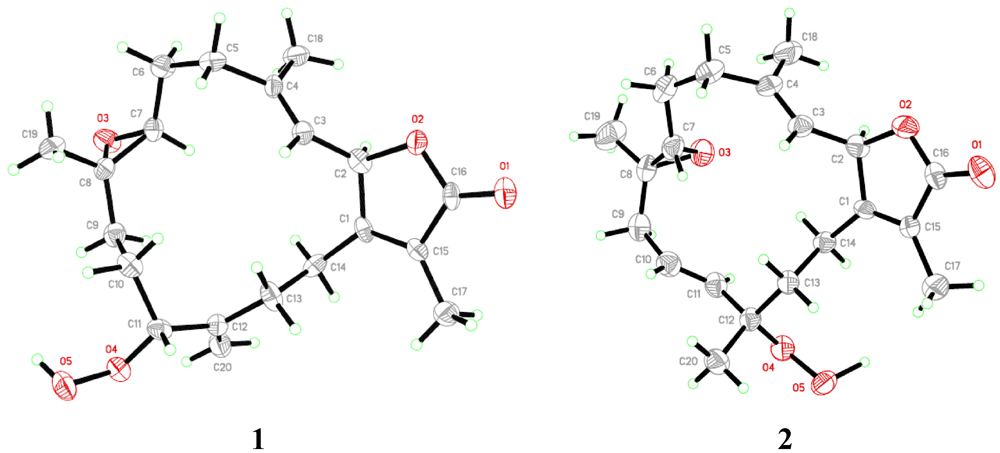
 −20.1 (c 0.1, CHCl3) with much of the spectral data identical to 1 (Table 1). The HR-FAB-MS showed an [M + Na]+ ion at m/z 371.18293 indicating a molecular formula C20H8O5Na and seven degrees of unsaturation that was supported by NMR data. The analysis of 1H, 13C NMR and DEPT spectra revealed the presence of four methyls, five methylenes, five methines (two of them oxygenated, δC 59.0, and 79.2) , and six quaternary carbons (two of them oxygenated, δC 59.2, and 84.0). NMR spectra also revealed the presence of four olefinic functionalities at δC 118.9, 124.6, 136.1 and 146.7. The presence of an α,β-unsaturated-γ-lactone functionality was assigned based on NMR parallels with 1. From HMBC (Figure 1), a methyl unit (1.43, s; H3-20) was observed proximal to C-12 determined from correlations between C-12 (δC 84.0) and H3-20 (1.43, s), H-11 (5.56, d, J = 16.0 Hz), H-10 (5.42, ddd, J = 16.0, 10.5, 7.5 Hz), H-13 (2.07, td, J = 13.0, 4.5 Hz; 1.41, dd, J = 4 Hz, overlapped with H3-18). HMBC correlations (Figure 1) were also observed between C-7 (δC 59.0) and H-6 (1.77, m, 2H), H-5 (2.02, m; 2.38, dt, J = 4.5, 13.5 Hz), H3-19 (1.30, s), and H2-9 (2.25, m; 2.46, m), and C-8 (δC 59.2) and H-7 (2.53, dd, J = 5.0, 6.0 Hz), H2-9 (2.25, m; 2.46, m), H-10 (5.42), and H2-6 (1.77, m, 2H) indicating the same epoxide location as in 1 bridging C-7 and C-8. The olefinic proton signal at δH 5.56 (H-11, d, J = 16.0 Hz) showed an HMBC correlation with an oxygenated carbon at δC 84.0 (C-12), a methyl signal at δC 22.8 (C-20), and an olefinic carbon at δC 124.6 (C-10) establishing that the peroxyl and double bond functionalities are located at C-12 and C-10/C-11, respectively.
−20.1 (c 0.1, CHCl3) with much of the spectral data identical to 1 (Table 1). The HR-FAB-MS showed an [M + Na]+ ion at m/z 371.18293 indicating a molecular formula C20H8O5Na and seven degrees of unsaturation that was supported by NMR data. The analysis of 1H, 13C NMR and DEPT spectra revealed the presence of four methyls, five methylenes, five methines (two of them oxygenated, δC 59.0, and 79.2) , and six quaternary carbons (two of them oxygenated, δC 59.2, and 84.0). NMR spectra also revealed the presence of four olefinic functionalities at δC 118.9, 124.6, 136.1 and 146.7. The presence of an α,β-unsaturated-γ-lactone functionality was assigned based on NMR parallels with 1. From HMBC (Figure 1), a methyl unit (1.43, s; H3-20) was observed proximal to C-12 determined from correlations between C-12 (δC 84.0) and H3-20 (1.43, s), H-11 (5.56, d, J = 16.0 Hz), H-10 (5.42, ddd, J = 16.0, 10.5, 7.5 Hz), H-13 (2.07, td, J = 13.0, 4.5 Hz; 1.41, dd, J = 4 Hz, overlapped with H3-18). HMBC correlations (Figure 1) were also observed between C-7 (δC 59.0) and H-6 (1.77, m, 2H), H-5 (2.02, m; 2.38, dt, J = 4.5, 13.5 Hz), H3-19 (1.30, s), and H2-9 (2.25, m; 2.46, m), and C-8 (δC 59.2) and H-7 (2.53, dd, J = 5.0, 6.0 Hz), H2-9 (2.25, m; 2.46, m), H-10 (5.42), and H2-6 (1.77, m, 2H) indicating the same epoxide location as in 1 bridging C-7 and C-8. The olefinic proton signal at δH 5.56 (H-11, d, J = 16.0 Hz) showed an HMBC correlation with an oxygenated carbon at δC 84.0 (C-12), a methyl signal at δC 22.8 (C-20), and an olefinic carbon at δC 124.6 (C-10) establishing that the peroxyl and double bond functionalities are located at C-12 and C-10/C-11, respectively.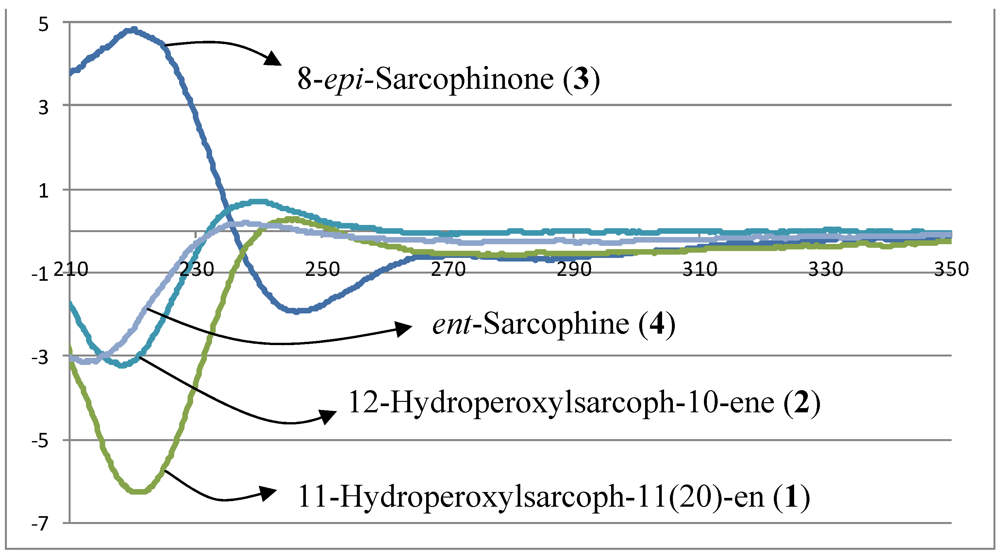
 +19.2 (c 0.1, CHCl3). The HR-FAB-MS showed an [M + Na]+ ion at m/z 339.19313 suggesting a molecular formula of C20H28O3Na that was supported by NMR data. Spectral data suggested that 3 was similar to the sarcophinone previously isolated from the soft coral Sarchophyton molle Tix [23], except for an up-field shift for H3-19 (δH 1.06) and an increase in its coupling constant (7.5 Hz) in comparison with sarcophinone H3-19 (δH 1.13, J = 6.4 Hz). This up-field shift for such a methyl attached to a methine carbon can be explained by an alternative stereochemistry since the β-configuration methyl group is down-field relative to the α-stereochemistry [23,24].
+19.2 (c 0.1, CHCl3). The HR-FAB-MS showed an [M + Na]+ ion at m/z 339.19313 suggesting a molecular formula of C20H28O3Na that was supported by NMR data. Spectral data suggested that 3 was similar to the sarcophinone previously isolated from the soft coral Sarchophyton molle Tix [23], except for an up-field shift for H3-19 (δH 1.06) and an increase in its coupling constant (7.5 Hz) in comparison with sarcophinone H3-19 (δH 1.13, J = 6.4 Hz). This up-field shift for such a methyl attached to a methine carbon can be explained by an alternative stereochemistry since the β-configuration methyl group is down-field relative to the α-stereochemistry [23,24]. 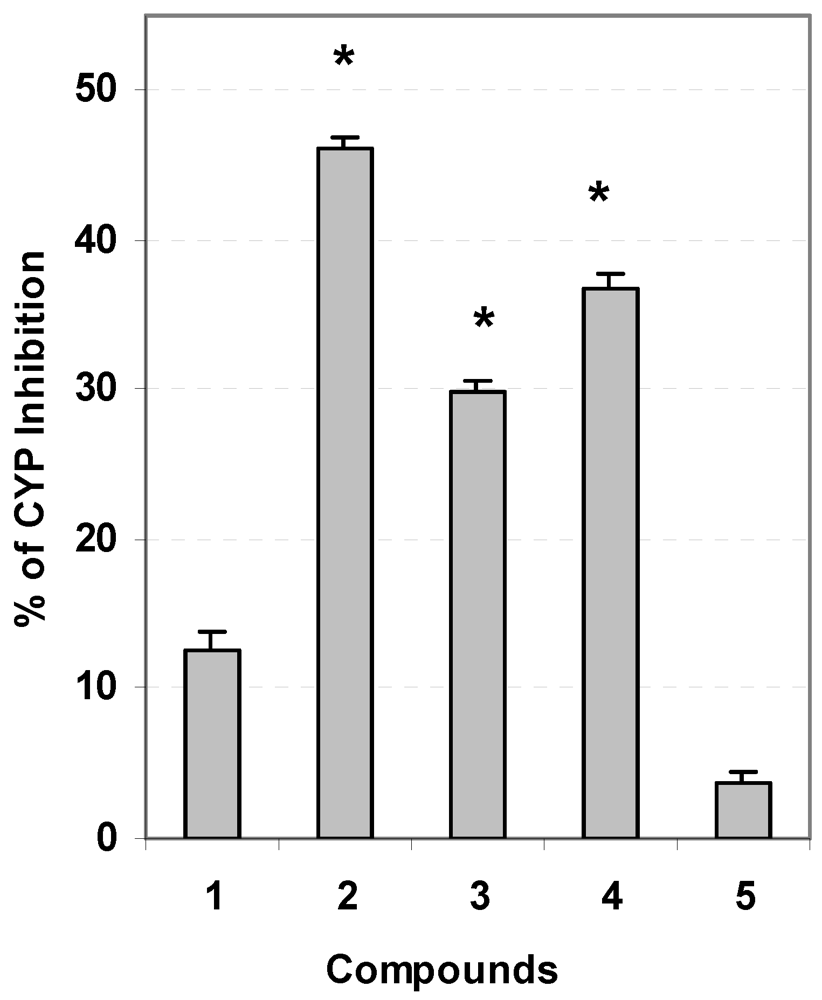
3. Experimental Section
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Animal Material
3.3. Extraction and Separation
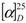 = +12.6 (c 0.09, CHCl3); IR (KBr) νmax 3353, 3000, 1750, 1707, 1686, 1669, 1256 cm−1; 1H NMR and 13C NMR data, see Table 1; HR-FAB-MS [M + Na]+ m/z 371.18281 (41%) (calc. 371.18284, C20H28O5Na).
= +12.6 (c 0.09, CHCl3); IR (KBr) νmax 3353, 3000, 1750, 1707, 1686, 1669, 1256 cm−1; 1H NMR and 13C NMR data, see Table 1; HR-FAB-MS [M + Na]+ m/z 371.18281 (41%) (calc. 371.18284, C20H28O5Na).3.3.1. Single-Crystal X-ray Crystallography of 1
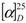 = −20.1 (c 0.1, CHCl3); IR (KBr) νmax 3353, 3000, 1750, 1707, 1686, 1669, 1256 cm−1; 1H NMR and 13C NMR data, see Table 1; HR-FAB-MS [M + Na]+ m/z 371.18293 (33%) (calc. 371.18290, C20H28O5Na).
= −20.1 (c 0.1, CHCl3); IR (KBr) νmax 3353, 3000, 1750, 1707, 1686, 1669, 1256 cm−1; 1H NMR and 13C NMR data, see Table 1; HR-FAB-MS [M + Na]+ m/z 371.18293 (33%) (calc. 371.18290, C20H28O5Na).3.3.2. Single-Crystal X-ray Crystallography of 2
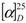 = +19.2 (c 0.1, CHCl3); IR (KBr) νmax 1730, 1700, 1410, 1230, 960 cm−1; 1H NMR and 13C NMR data, see Table 1; HR-FAB-MS [M + Na]+ m/z 339.19313 (100%) (calc. 339.19317, C20H28O5Na).
= +19.2 (c 0.1, CHCl3); IR (KBr) νmax 1730, 1700, 1410, 1230, 960 cm−1; 1H NMR and 13C NMR data, see Table 1; HR-FAB-MS [M + Na]+ m/z 339.19313 (100%) (calc. 339.19317, C20H28O5Na).3.4. Cell Culture
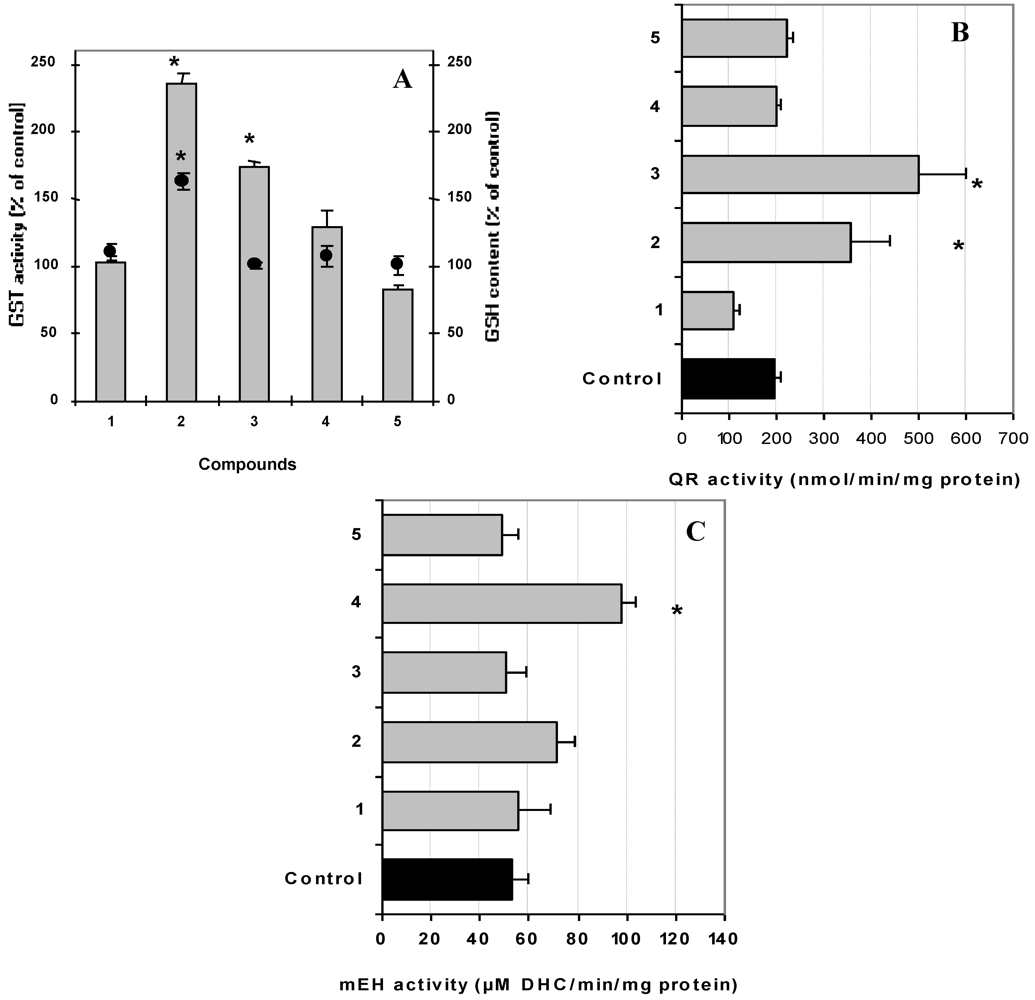
3.5. Evaluation of Carcinogen Metabolizing Enzymes
3.6. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
- Samples Availability: Available from the authors.
Supplementary Files
References
- Edwards, A.J.; Head, S.M. Key Environments-Red Sea; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1987; p. 440. [Google Scholar]
- Roethle, P.A.; Trauner, D. The chemistry of marine furanocembranoids, pseudopteranes, gersolanes, and related natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2008, 25, 298–317. [Google Scholar]
- Blunt, J.W.; Copp, B.R.; Hu, W.P.; Munro, M.H.G.; Northcote, P.T.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2008, 25, 35–94. [Google Scholar]
- Gross, H.; Wright, A.D.; Beil, W.; Koenig, G.M. Two new bicyclic cembranolides from a new Sarcophyton species and determination of the absolute configuration of sarcoglaucol-16-one. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2004, 2, 1133–1138. [Google Scholar]
- Sawant, S.; Youssef, D.; Mayer, A.; Sylvester, P.; Wali, V.; Arant, M.; El Sayed, K. Anticancer and anti-inflammatory sulfur-containing semisynthetic derivatives of sarcophine. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2006, 54, 1119–1123. [Google Scholar]
- Sawant, S.S.; Youssef, D.T.A.; Reiland, J.; Ferniz, M.; Marchetti, D.; El Sayed, K.A. Biocatalytic and antimetastatic studies of the marine cembranoids sarcophine and 2-epi-16-deoxysarcophine. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 1010–1013. [Google Scholar]
- Wahlberg, I.; Eklund, A.M. Cembranoids, pseudopteranoids, and cubitanoids of natural occurrence. Prog. Chem. Org. Nat. 1992, 59, 141–294. [Google Scholar]
- El Sayed, K.A.; Hamann, M.T.; Waddling, C.A.; Jensen, C.; Lee, S.K.; Dunstan, C.A.; Pezzuto, J.M. Structurally novel bioconversion products of the marine natural product sarcophine effectively inhibit JB6 cell transformation. J. Org. Chem. 1998, 63, 7449–7455. [Google Scholar]
- Grote, D.; Soliman, H.S.M.; Shaker, K.H.; Hamza, M.; Seifert, K. Cembranoid diterpenes and a briarane diterpene from corals. Nat. Prod. Res. 2005, 20, 285–291. [Google Scholar]
- Neeman, I.; Fishelson, I.; Kashman, Y. Sarcophine—a new toxin from the soft coral Sarcophyton glaucum (alcyonaria). Toxicon 1974, 12, 593–598. [Google Scholar]
- Erman, A.; Neeman, I. Inhibition of phosphofructokinase by the toxic cembranolide sarcophine isolated from the soft-bodied coral Sarcophyton glaucum. Toxicon 1976, 15, 207–215. [Google Scholar]
- El Sayed, K.A.; Orabi, K.Y.; Dunbar, D.C.; Hammann, M.T.; Avery, M.A.; Sabnis, Y.A.; Mossa, J.S.; El feraly, F.S. Transformation of lactone to lactam in sarcophine and antimalarial activity of resulting N-substituted azasarcophines. Tetrahedron 2002, 58, 3699–3708. [Google Scholar]
- Fahmy, H.; Khalifa, S.I.; Konoshima, T.; Zjawiony, J.K. An improved synthesis of 7,8-epoxy-1,3,11-cembratriene-15R(α),16-diol, a cembranoid of marine origin with a potent cancer chemopreventive activity. Mar. Drugs 2004, 2, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Katsuyama, I.; Fahmy, H.; Zjawiony, J.K.; Khalifa, S.I.; Kilada, R.W.; Konoshima, T.; Takasaki, M.; Harakuni, T. Semisynthesis of new sarcophine derivatives with chemopreventive activity. J. Nat. Prod. 2002, 65, 1809–1814. [Google Scholar]
- Abouzied, A.M.; Sawant, S.S.; Sylvester, P.W.; Avery, M.A.; Desai, P.; Youssef, D.T.A.; El Sayed, K.A. Bioactive rearranged and halogenated semisynthetic derivatives of the marine natural product sarcophine. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 2017–2023. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, W.K.; Sporn, M.B. Recent advances in chemoprevention of cancer. Science 1997, 278, 1073–1077. [Google Scholar]
- Arif, J.M.; Al-Hazzani, A.A; Kunhi, M.; Al-Khodairy, F. Novel marine compounds: Anticancer or genotoxic? J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2004, 2, 93–98. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, S.W.; Shi, Y.P.; Li, X.M.; Wang, B.G. A novel hydroperoxyl-substituted cembranolide diterpene from marine soft coral Lobophytum crassum. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2005, 1, 1489–1491. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, L.-G.; Liu, H.L.; Guo, Y.W.; Mollo, E. New cembranoids from the hainan soft coral Sarcophyton glaucum. Helv. Chim. Acta 2009, 92, 1085–1091. [Google Scholar]
- Bowden, B.F.; Coll, J.C.; Mitchell, S.J. Studies of Australian soft corals. XVIII. Further cembranoid diterpenes from soft corals of the genus Sarcophyton. Aust. J. Chem. 1980, 33, 879–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashman, Y.; Zadock, E.; Neeman, I. New cembrane derivatives of marine origin. Tetrahedron 1974, 30, 3615–3620. [Google Scholar]
- Kamel, H.N.; Ferreira, D.; Garcia-Fernandez, L.F.; Slattery, M. Cytotoxic diterpenoids from the hybrid soft coral Sinularia maxima × Sinularia polydactyla. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 1223–1227. [Google Scholar]
- Su, J.Y.; Yan, S.J.; Zeng, L.M. New diterpene lactone from the soft coral Sarcophyton molle Tix. Dur. Chem. J. Chin. Univ. 2001, 22, 1515–1517. [Google Scholar]
- Nii, K.; Tagami, K.; Kijima, M.; Munakata, T.; Ooi, T.; Kusumi, T. Acid-catalyzed reactions of sarcophytoxide, a marine cembranoid: An apparently enantio-directive reaction, unusual products and stereochemical reconsideration of epoxide-ketone rearrangement. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2008, 81, 562–573. [Google Scholar]
- Czarkie, D.; Carmely, S.; Groweiss, A.; Kashman, Y. Attempted acid-catalyzed transannular reactions in the cembranoids. Tetrahedron 1985, 41, 1049–1056. [Google Scholar]
- Swapnali, S.S.; Sylvester, P.W.; Avery, M.A.; Desai, P.; Youssef, D.T.A.; El Sayed, K.A. Bioactive rearranged and halogenated semisynthetic derivatives of the marine natural product sarcophine. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 2017–2023. [Google Scholar]
- Rooseboom, M.; Commandeur, J.N.M.; Vermeulen, N.P.E. Enzyme-catalyzed activation of anticancer prodrugs. Pharmacol. Rev. 2004, 56, 53–102. [Google Scholar]
- Cannady, E.A.; Dyer, C.A.; Christian, P.J.; Sipes, G.; Hoyer, P.B. Expression and activity of microsomal epoxide hydrolase in follicles isolated from mouse ovaries. Toxicol. Sci. 2002, 68, 24–31. [Google Scholar]
- Henry, N.F.M.; Lonsdale, K. International Tables for X-ray Crystallography; Kynoch Press: Birmingham, UK, 1952; Volume 1, p. 78. [Google Scholar]
- Crespi, C.L.; Miller, V.P.; Penman, B.W. Microtiter plate assays for inhibition of human, drug-metabolizing cytochromes P450. Anal. Biochem. 1997, 248, 188–190. [Google Scholar]
- Gerhäuser, C.; Klimo, K.; Heiss, E.; Neumann, I.; Gamal-Eldeen, A.; Knauft, J.; Liu, J.-U.; Sitthimonchai, S.; Frank, N. Mechanism-based in vitro screening of potential cancer chemopreventive agents. Mutat. Res. 2003, 523–524, 163–172. [Google Scholar]
- Habig, W.H.; Pabst, M.J.; Jakoby, W.B. Glutathione S-transferases. The first enzymatic step in mercapturic acid formation. J. Biol. Chem. 1974, 249, 7130–7139. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Smith, P.K.; Krohn, R.I.; Hermanson, G.T.; Mallia, A.K.; Gartner, F.H.; Provenzano, M.D.; Fujimoto, E.K.; Goeke, N.M.; Olson, B.J.; Klenk, D.C. Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal. Biochem. 1985, 150, 76–85. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, R.; Mandlekar, S.; Lei, W.; Fahl, W.E.; Tan, T.-H.; Kong, A.T. p38 Mitogen-activated protein kinase negatively regulates the induction of phase II drug-metabolizing enzymes that detoxify carcinogens. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 2322–2327. [Google Scholar]
- Inoue, N.; Yamada, K.; Imai, K.; Aimoto, T. Sex hormone-related control of hepatic EH activities in mice. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 1993, 16, 1004–1007. [Google Scholar]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Hegazy, M.-E.F.; Eldeen, A.M.G.; Shahat, A.A.; Abdel-Latif, F.F.; Mohamed, T.A.; Whittlesey, B.R.; Paré, P.W. Bioactive Hydroperoxyl Cembranoids from the Red Sea Soft Coral Sarcophyton glaucum. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 209-222. https://doi.org/10.3390/md10010209
Hegazy M-EF, Eldeen AMG, Shahat AA, Abdel-Latif FF, Mohamed TA, Whittlesey BR, Paré PW. Bioactive Hydroperoxyl Cembranoids from the Red Sea Soft Coral Sarcophyton glaucum. Marine Drugs. 2012; 10(1):209-222. https://doi.org/10.3390/md10010209
Chicago/Turabian StyleHegazy, Mohamed-Elamir F., Amira M. Gamal Eldeen, Abdelaaty A. Shahat, Fathy F. Abdel-Latif, Tarik A. Mohamed, Bruce R. Whittlesey, and Paul W. Paré. 2012. "Bioactive Hydroperoxyl Cembranoids from the Red Sea Soft Coral Sarcophyton glaucum" Marine Drugs 10, no. 1: 209-222. https://doi.org/10.3390/md10010209
APA StyleHegazy, M.-E. F., Eldeen, A. M. G., Shahat, A. A., Abdel-Latif, F. F., Mohamed, T. A., Whittlesey, B. R., & Paré, P. W. (2012). Bioactive Hydroperoxyl Cembranoids from the Red Sea Soft Coral Sarcophyton glaucum. Marine Drugs, 10(1), 209-222. https://doi.org/10.3390/md10010209








