Establishment of an Assay with Ultrahigh Sensitivity for Detecting sEV-Derived PD-L1 as a Serum Biomarker for Lung Cancer—A Pilot Study Using TN-cyclon™
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Specimens
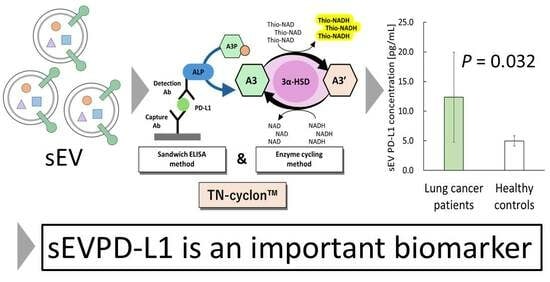
2.2. TN-cyclonTM for Recombinant PD-L1
2.3. Isolation of sEVs
2.4. Western Blotting
2.5. Measurement of sEV Size
2.6. Measurement of sEVPD-L1
2.7. Measurement of sPD-L1
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
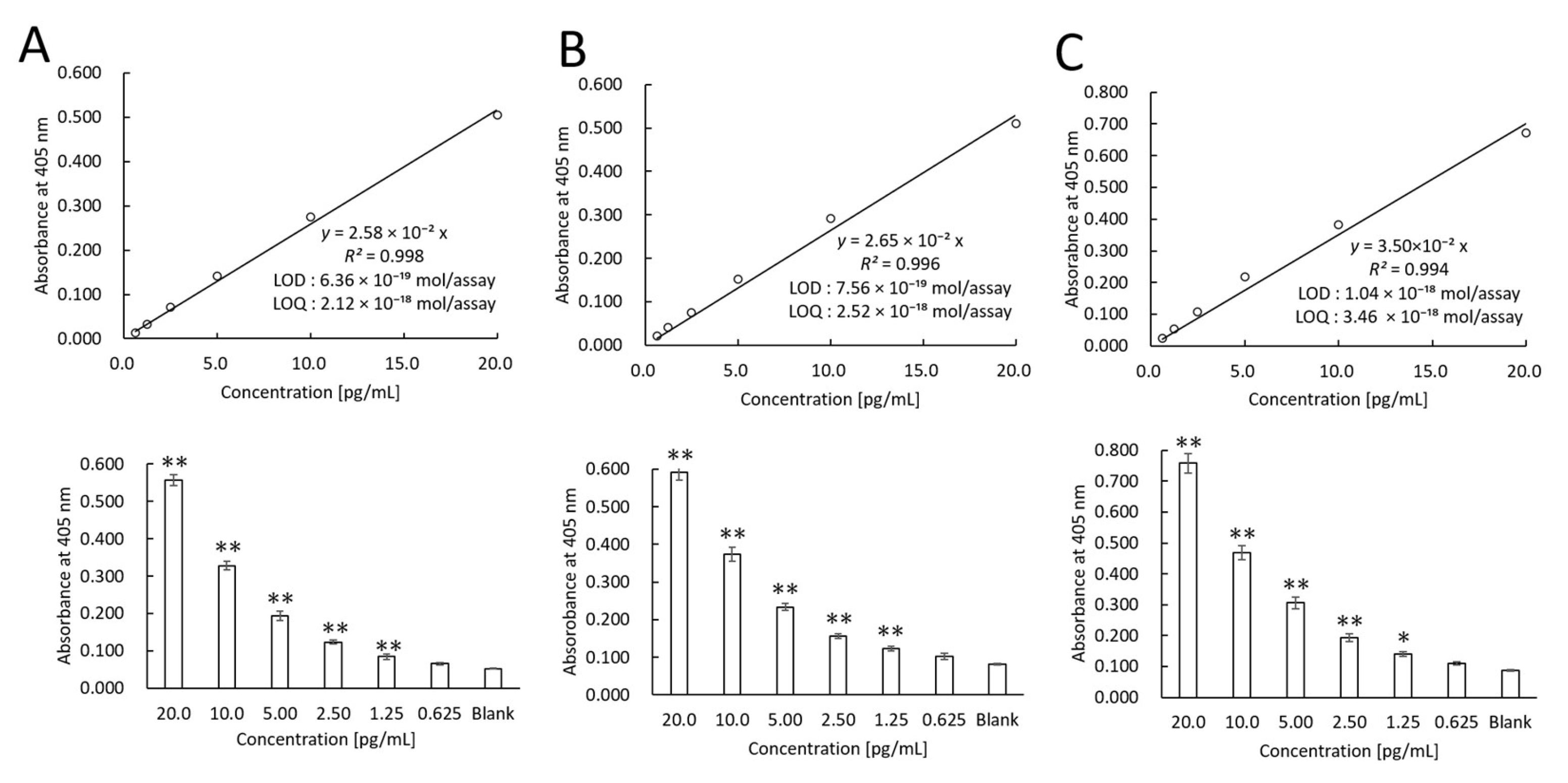
3.1. Recombinant PD-L1 Measurements Using TN-cyclonTM
3.2. Characteristics of sEVs
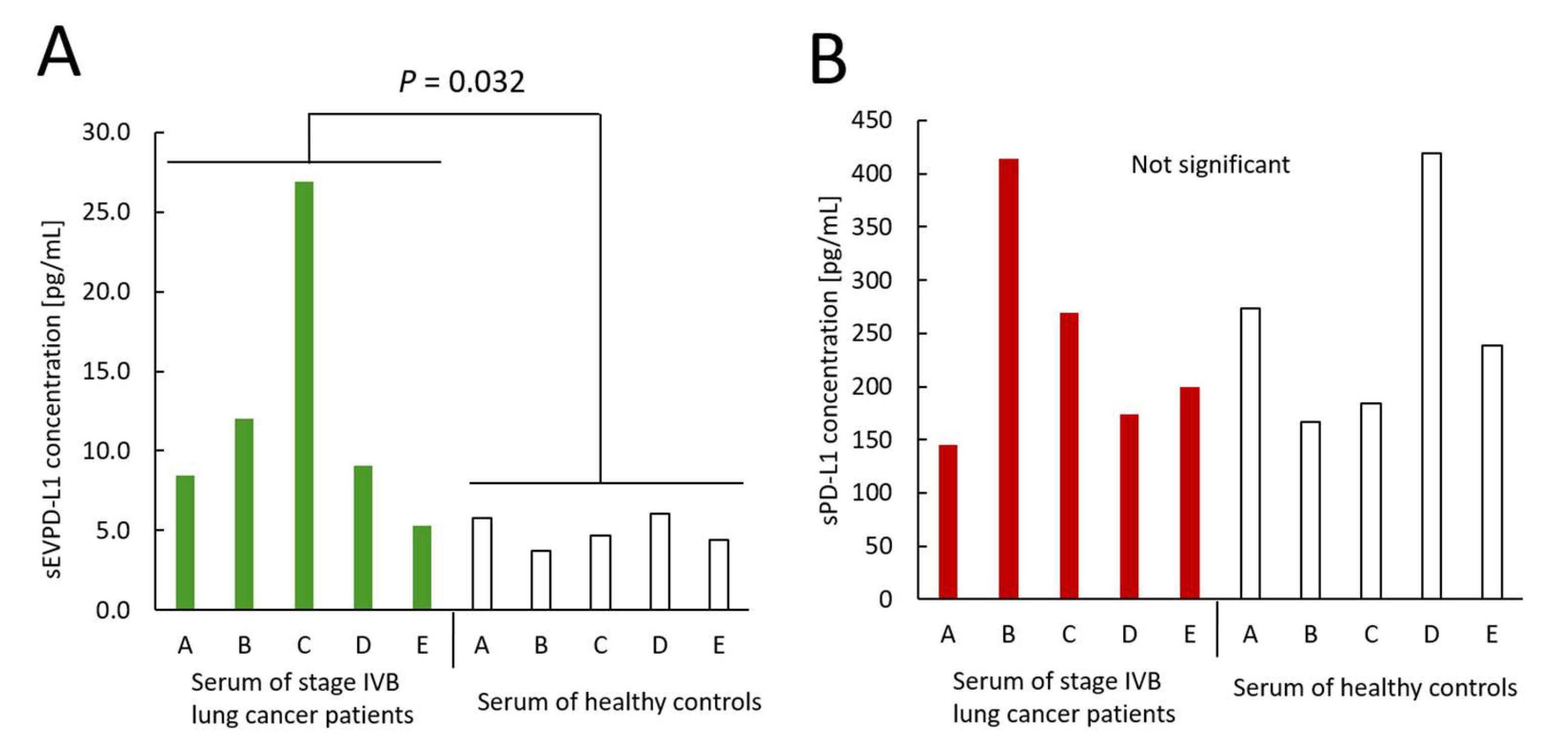
3.3. Measurements of sEVPD-L1 and sPD-L1 Derived from Sera Obtained from Lung Cancer Patients and Healthy Controls
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BCA | Bicinchoninic acid |
| CV | Coefficient of variation |
| DLS | Dynamic light scattering |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| HSD | Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase |
| IHC | Immunohistochemistry |
| LOD | Limit of detection |
| LOQ | Limit of quantification |
| NSCLC | Non-small-cell lung cancer |
| PD-1 | Programmed death-1 |
| PD-L1 | Programmed death ligand-1 |
| sEV | Small extracellular vesicle |
| sPD-L1 | Soluble form of PD-L1 |
| sEVPD-L1 | PD-L1 in small extracellular vesicles |
| TN-cyclonTM | Ultrasensitive ELISA combined with thio-NAD cycling |
Appendix A
| Sample ID | Donation Date | Gender | Age | Ethnicity | Location | Histological Diagnosis | TNM | Stage | Smoking History | Family History | Medical History | Treatment | Date of Surgery |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 13 March 2023 | M | 62 | Caucasian | lower lobe of the left lung, brain and bones mets | adenocarcinoma | T4N2M1c | IVB | no | grandmother- gastric cancer | hypertension | no | no |
| B | 10 May 2023 | M | 66 | Caucasian | upper lobe of the right lung, bones, brain mets | adenocarcinoma | T4N2M1c | IVB | 45 years 1 pack/day | no | varicose veins | no | no |
| C | 11 August 2023 | M | 60 | Caucasian | upper lobe of the left lung, adrenal gland and brain mets | adenocarcinoma | T4N2M1c | IVB | no | no | hypertension, diabetes mellitus type 2, chronic bronchitis | no | no |
| D | 13 September 2023 | M | 60 | Caucasian | upper lobe of the right lung, brain and bone mets | adenocarcinoma | T4NxM1c | IVB | 40 years 1pack/day | no | chronic gastritis, thymus cyst, chronic bronchitis | no | 13 Sep-tember 2023 |
| E | 5 December 2023 | M | 68 | Caucasian | lower lobe of the left lung, right lung, brain mets | adenocarcinoma | T4N3M1c | IVB | 40 years 1 pack/day | no | chronic gastritis | 4 December 2023—1 course paclitaxel, carboplatin | no |
| Sample ID | Donation Date | Blood Type | Gender | Age | Ethnicity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 31 July 2023 | A+ | M | 68 | Caucasian |
| B | 8 August 2023 | A+ | M | 66 | Caucasian |
| C | 31 July 2023 | A+ | M | 62 | Caucasian |
| D | 6 August 2023 | A+ | M | 60 | Caucasian |
| E | 31 July 2023 | A+ | M | 60 | Caucasian |
References
- Dermani, F.K.; Samadi, P.; Rahmani, G.; Kohlan, A.K.; Najafi, R. PD-1/PD-L1 immune checkpoint: Potential target for cancer therapy. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 1313–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borghaei, H.; Paz-Ares, L.; Horn, L.; Spigel, D.R.; Steins, M.; Ready, N.E.; Chow, L.Q.; Vokes, E.E.; Felip, E.; Holgado, E.; et al. Nivolumab versus docetaxel in advanced nonsquamous non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1627–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topalian, S.L.; Hodi, F.S.; Brahmer, J.R.; Gettinger, S.N.; Smith, D.C.; McDermott, D.F.; Powderly, J.D.; Carvajal, R.D.; Sosman, J.A.; Atkins, M.B.; et al. Safety, activity, and immune correlates of anti-PD-1 antibody in cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 2443–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbst, R.S.; Baas, P.; Kim, D.W.; Felip, E.; Pérez-Gracia, J.L.; Han, J.Y.; Molina, J.; Kim, J.H.; Arvis, C.D.; Ahn, M.J.; et al. Pembrolizumab versus docetaxel for previously treated, PD-L1-positive, advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (KEYNOTE-010): A randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2016, 387, 1540–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.P.; Kurzrock, R. PD-L1 expression as a predictive biomarker in cancer immunotherapy. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2015, 14, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Széles, Á.; Fazekas, T.; Váncsa, S.; Váradi, M.; Kovács, P.T.; Krafft, U.; Grünwald, V.; Hadaschik, B.; Csizmarik, A.; Hegyi, P.; et al. Pre-treatment soluble PD-L1 as a predictor of overall survival for immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2023, 72, 1061–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.Y.; Kim, S.; Keam, B.; Kim, T.M.; Kim, D.W.; Heo, D.S. Soluble PD-L1 is a predictive and prognostic biomarker in advanced cancer patients who receive immune checkpoint blockade treatment. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 19712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mildner, F.O.; Sykora, M.M.; Hackl, H.; Amann, A.; Zelger, B.; Sprung, S.; Buch, M.L.; Nocera, F.; Moser, P.; Maier, H.; et al. Soluble PD-L1 shows no association to relapse and overall survival in early stage non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Lung Cancer 2024, 196, 107955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, T.; Inoue, E.; Ohkuma, R.; Kobayashi, S.; Tsunoda, T.; Wada, S. Soluble PD-L1 changes in advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with PD-1 inhibitors: An individual patient data meta-analysis. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1308381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Che, X.; Qu, J.; Hou, K.; Wen, T.; Li, Z.; Li, C.; Wang, S.; Xu, L.; Liu, Y.; et al. Exosomal PD-L1 retains immunosuppressive activity and is associated with gastric cancer prognosis. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2019, 26, 3745–3755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.M.; Yang, Y. Exosomal PD-L1 in cancer and other fields: Recent advances and perspectives. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1395332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.W.; Wei, P.; Guo, Y.; Shi, D.; Yu, B.H.; Su, Y.F.; Li, X.Q.; Zhou, X.Y. Clinical significance of circulating exosomal PD-L1 and soluble PD-L1 in extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal-type. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2020, 10, 4498–4512. [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Kyosei, Y.; Ogawa, R.; Okita, K.; Yoshimura, T.; Ito, E. Ultrasensitive protein-level detection for respiratory infectious viruses. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1445771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makioka, D.; Inada, M.; Awano, M.; Saito, E.; Shinoda, T.; Abe, S.; Yoshimura, T.; Müller, M.; Sasagawa, T.; Ito, E. Quantification of HPV16 E7 oncoproteins in urine specimens from women with cervical intraepithelial neoplasia. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsurusawa, N.; Iha, K.; Sato, A.; Tsai, H.Y.; Sonoda, H.; Watabe, S.; Yoshimura, T.; Wu, D.C.; Lin, M.W.; Ito, E. Ultrasensitive detection of GRP78 in exosomes and observation of migration and proliferation of cancer cells by application of GRP78-containing exosomes. Cancers 2022, 14, 3887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Signorelli, D.; Ghidotti, P.; Proto, C.; Brambilla, M.; De Toma, A.; Ferrara, R.; Galli, G.; Ganzinelli, M.; Lo Russo, G.; Prelaj, A.; et al. Circulating CD81-expressing extracellular vesicles as biomarkers of response for immune-checkpoint inhibitors in advanced NSCLC. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 987639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quanterix Corporation. Simoa PD-L1 Data Sheet HD-1/HD-X Rev03. Available online: https://www.quanterix.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/Simoa_PD-L1_Data_Sheet_HD-1_HD-X_Rev03.pdf (accessed on 31 May 2025).
- Abcam. Human PD-L1 ELISA Kit [28-8]. Available online: https://www.abcam.com/en-us/products/elisa-kits/human-pd-l1-elisa-kit-28-8-ab277712 (accessed on 31 May 2025).
- Proteintech. Human PD-L1 ELISA Kit (KE00074). Available online: https://www.ptglab.com/products/Human-PD-L1-ELISA-Kit-KE00074.htm (accessed on 31 May 2025).
- Li, C.; Li, C.; Zhi, C.; Liang, W.; Wang, X.; Chen, X.; Lv, T.; Shen, Q.; Song, Y.; Lin, D.; et al. Clinical significance of PD-L1 expression in serum-derived exosomes in NSCLC patients. J. Transl. Med. 2019, 17, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ćeriman Krstić, V.; Jovanović, D.; Samardžić, N.; Gajić, M.; Kotur Stevuljević, J.; Klisic, A.; Soldatović, I.; Radončić, D.; Roksandić Milenković, M.; Šeha, B.; et al. The potential role of sPD-L1 as a predictive biomarker in EGFR-positive non-small-cell lung cancer. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, T.; Nonomura, R.; Tabata, T.; Yoshimura, N.; Hata, S.; Shimada, H.; Nakamura, Y. Study of the clinicopathological features of soluble PD-L1 in lung cancer patients. J. Rural Med. 2023, 18, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.L.; Liu, J.Y.; Chen, G. Small extracellular vesicle PD-L1 in cancer: The knowns and unknowns. NPJ Precis. Oncol. 2022, 6, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ancın, B.; Özercan, M.M.; Yılmaz, Y.M.; Uysal, S.; Kumbasar, U.; Sarıbaş, Z.; Dikmen, E.; Doğan, R.; Demircin, M. The correlation of serum sPD-1 and sPD-L1 levels with clinical, pathological characteristics and lymph node metastasis in nonsmall cell lung cancer patients. Turk. J. Med. Sci. 2022, 52, 1050–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumagai, S.; Togashi, Y.; Kamada, T.; Sugiyama, E.; Nishinakamura, H.; Takeuchi, Y.; Vitaly, K.; Itahashi, K.; Maeda, Y.; Matsui, S.; et al. The PD-1 expression balance between effector and regulatory T cells predicts the clinical efficacy of PD-1 blockade therapies. Nat. Immunol. 2020, 21, 1346–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Okita, K.; Arita, H.; Sudo, K.; Yoshimura, T.; Ito, E. Establishment of an Assay with Ultrahigh Sensitivity for Detecting sEV-Derived PD-L1 as a Serum Biomarker for Lung Cancer—A Pilot Study Using TN-cyclon™. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 564. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47070564
Okita K, Arita H, Sudo K, Yoshimura T, Ito E. Establishment of an Assay with Ultrahigh Sensitivity for Detecting sEV-Derived PD-L1 as a Serum Biomarker for Lung Cancer—A Pilot Study Using TN-cyclon™. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025; 47(7):564. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47070564
Chicago/Turabian StyleOkita, Kyo, Hasumi Arita, Keita Sudo, Teruki Yoshimura, and Etsuro Ito. 2025. "Establishment of an Assay with Ultrahigh Sensitivity for Detecting sEV-Derived PD-L1 as a Serum Biomarker for Lung Cancer—A Pilot Study Using TN-cyclon™" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47, no. 7: 564. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47070564
APA StyleOkita, K., Arita, H., Sudo, K., Yoshimura, T., & Ito, E. (2025). Establishment of an Assay with Ultrahigh Sensitivity for Detecting sEV-Derived PD-L1 as a Serum Biomarker for Lung Cancer—A Pilot Study Using TN-cyclon™. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 47(7), 564. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47070564