The Antidiabetic Mechanisms of Cinnamon Extract: Insights from Network Pharmacology, Gut Microbiota, and Metabolites
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Cinnamon Extract Preparation and Chemical Composition Determination
2.3. Network Pharmacological Analysis
2.4. Animals and Treatments
2.5. Biochemical Analysis of Blood Samples
2.6. Pathological Examination
2.7. Immunohistochemistry Staining
2.8. Gut Microbiota Assay
2.9. Determination of Fecal SCFAs
2.10. Determination of BAs in Fecal Samples
2.11. Western Blotting
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. The Chemical Makeup and Quantification of the EC
3.2. Identification of Active Compounds and Target Discovery
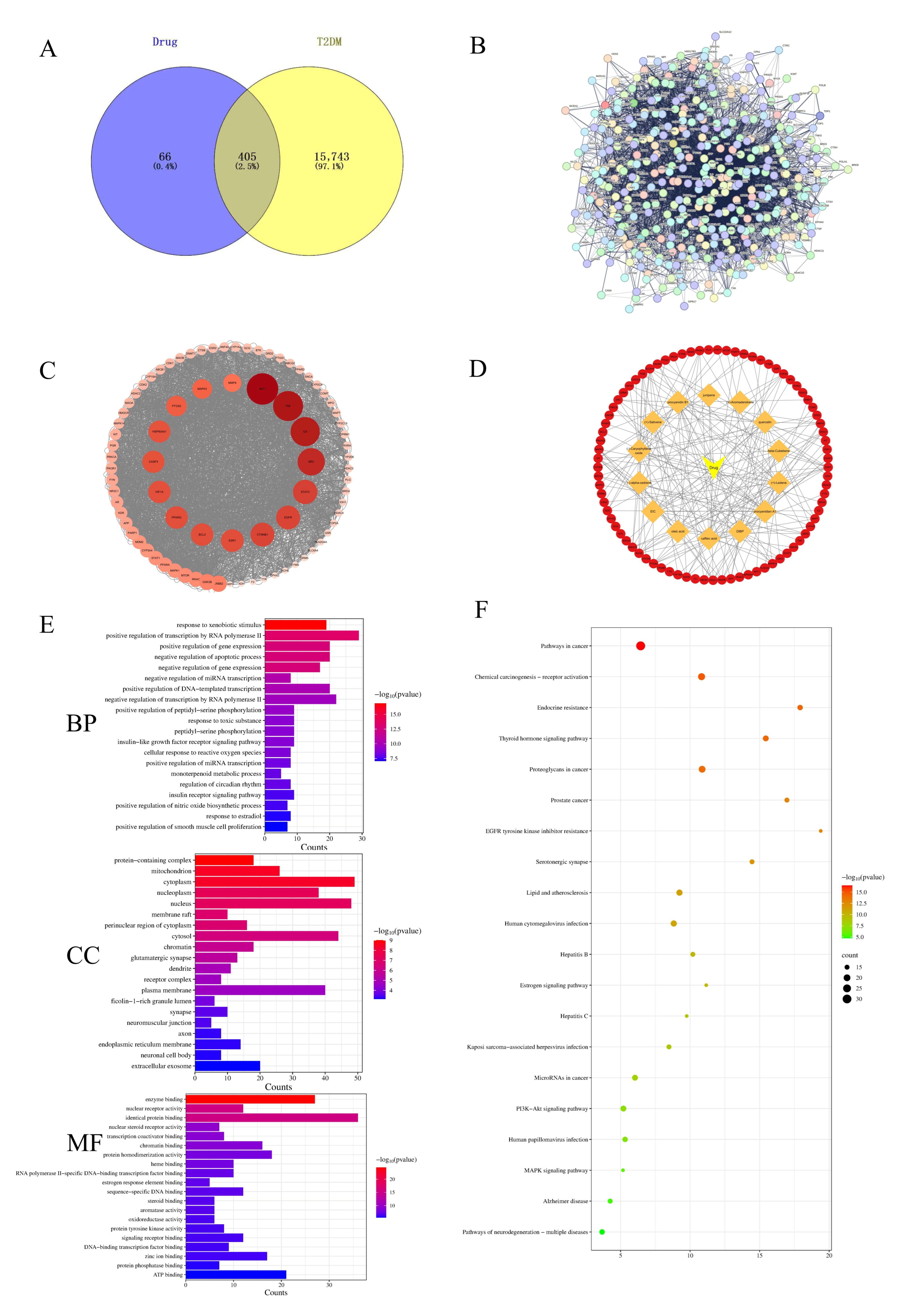
3.2.1. Screening of T2DM-Related Targets Corresponding to EC
3.2.2. Analysis of EC’s Multi-Component and Diverse Target Role in Treating T2DM
3.2.3. Enrichment Analyses of GO and KEGG Pathways
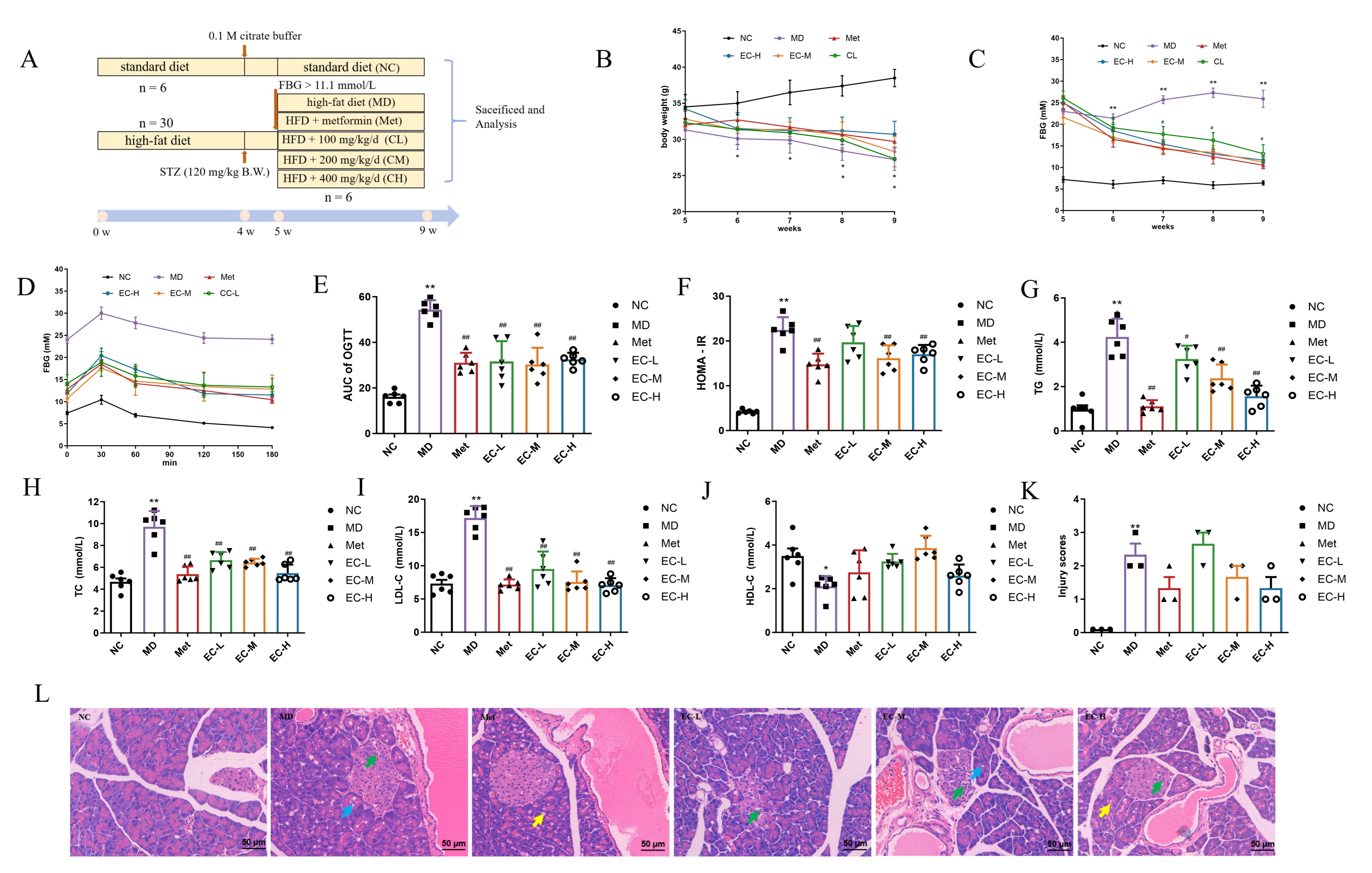
3.3. Effects of EC on BW, FBG, OGTT, and Serum Indices
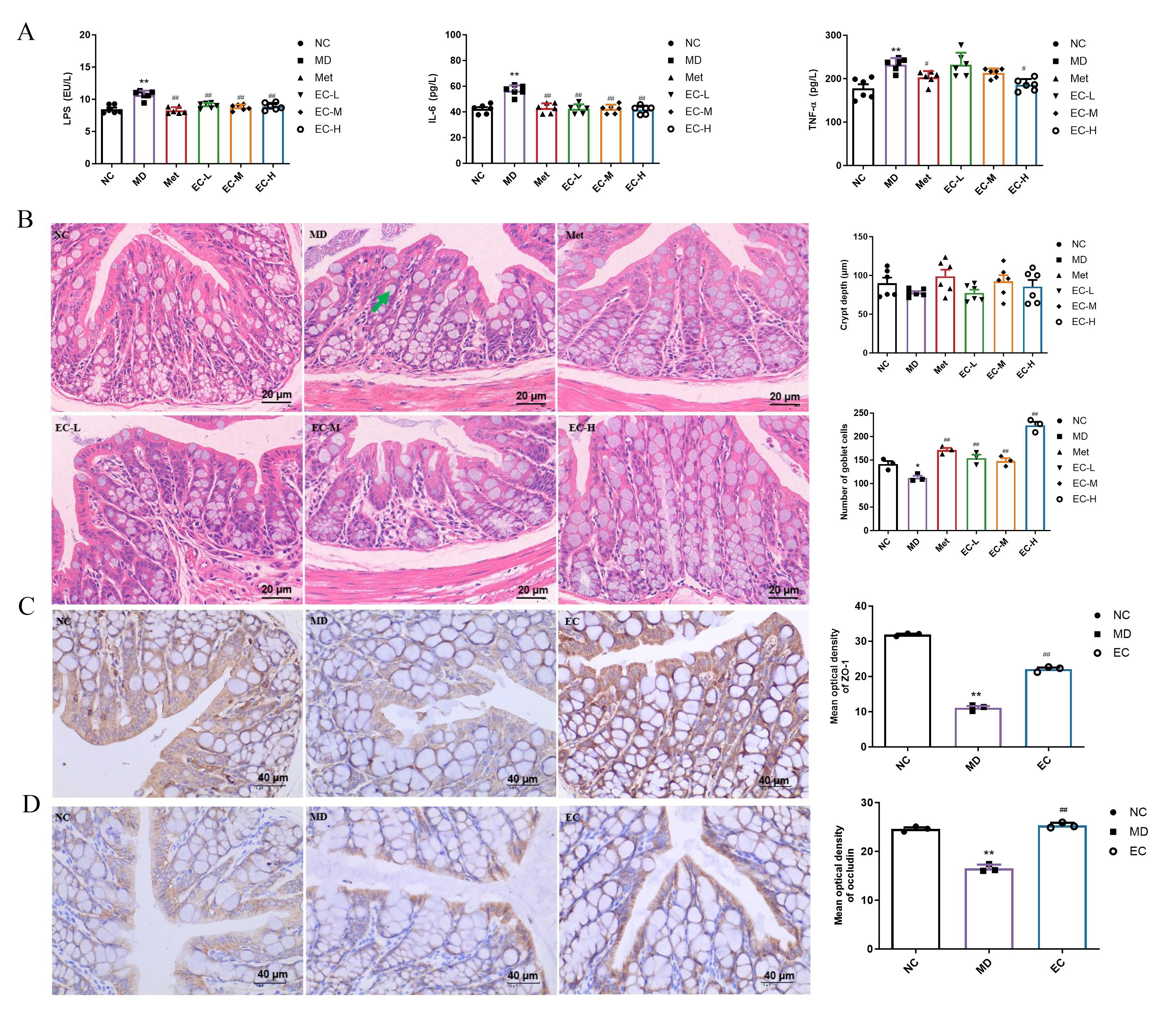
3.4. EC Inhibited Inflammation and Improved Intestinal Barrier Damage
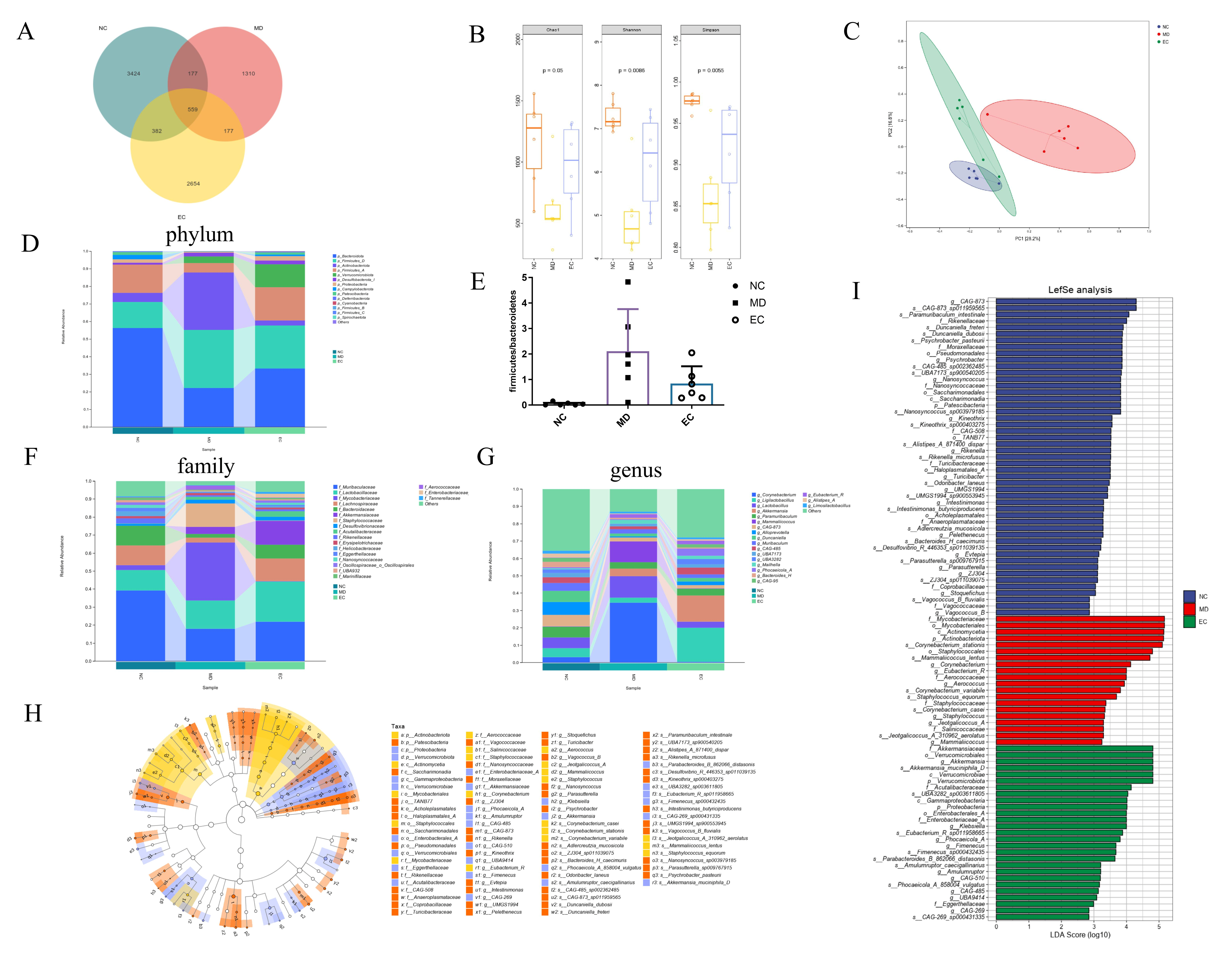
3.5. EC Modulated the Gut Microbiota in T2DM Mice
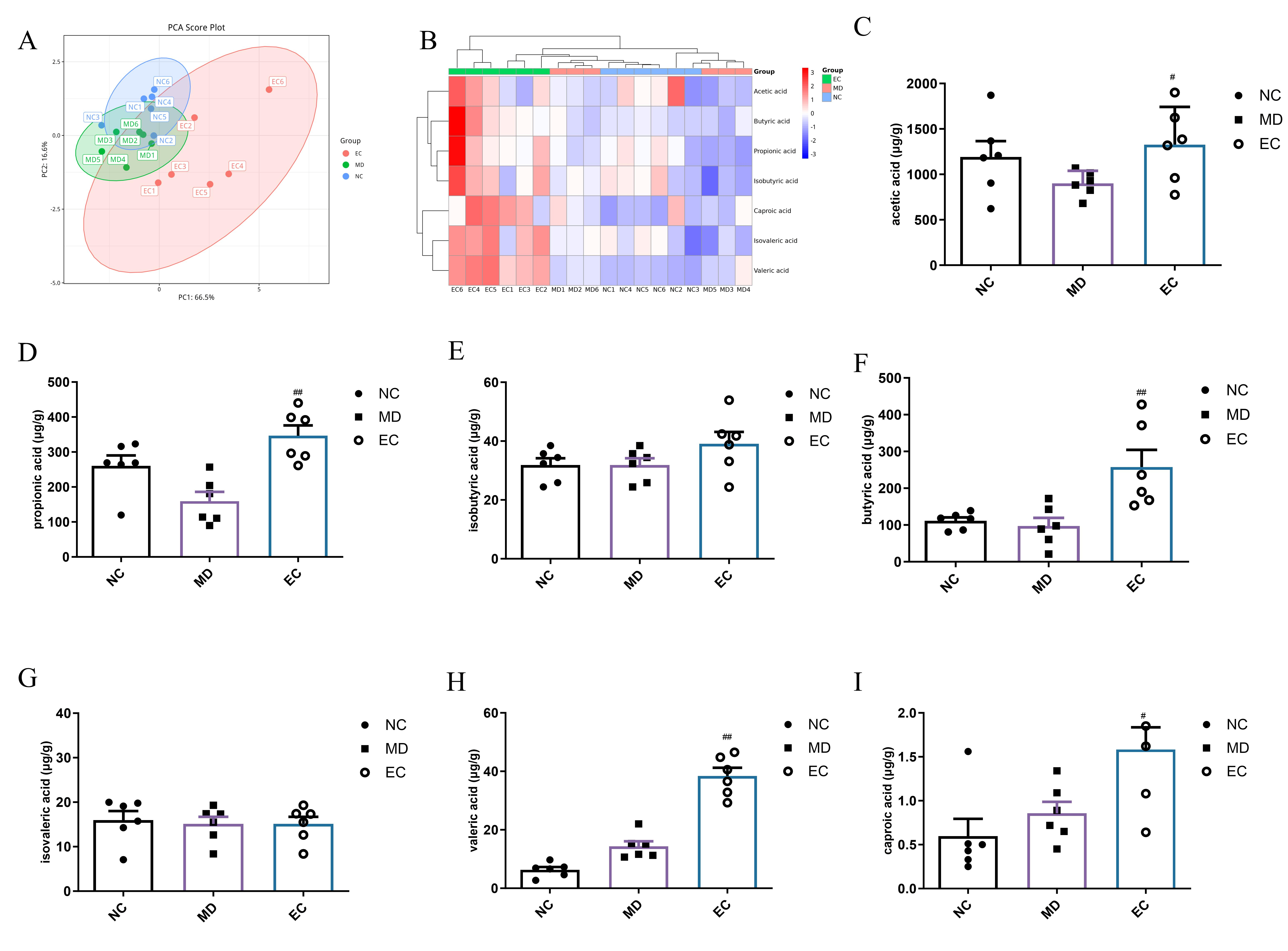
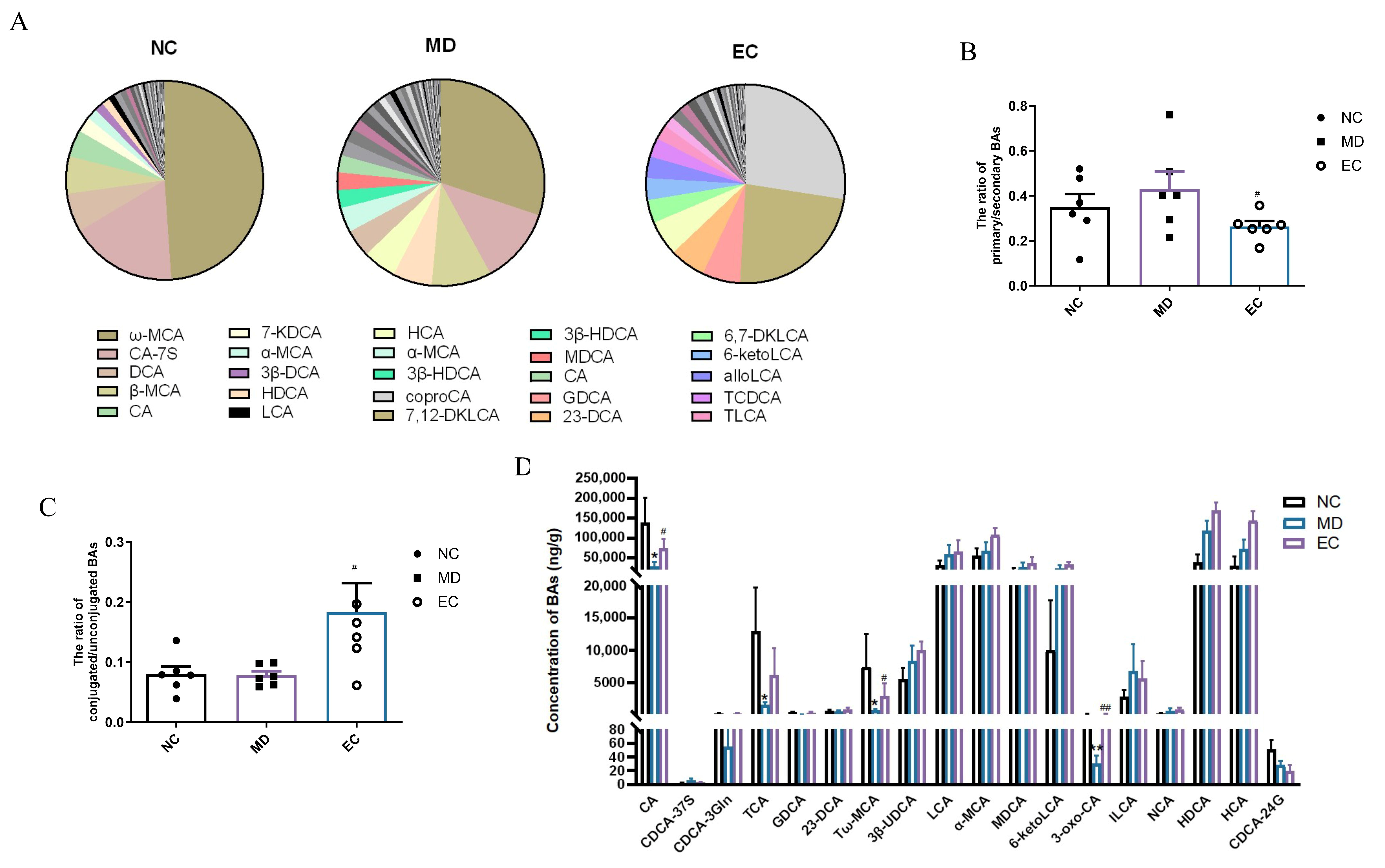
3.6. EC Increased the SCFA Content and Affected the Profile of BAs in the Feces of T2DM Mice
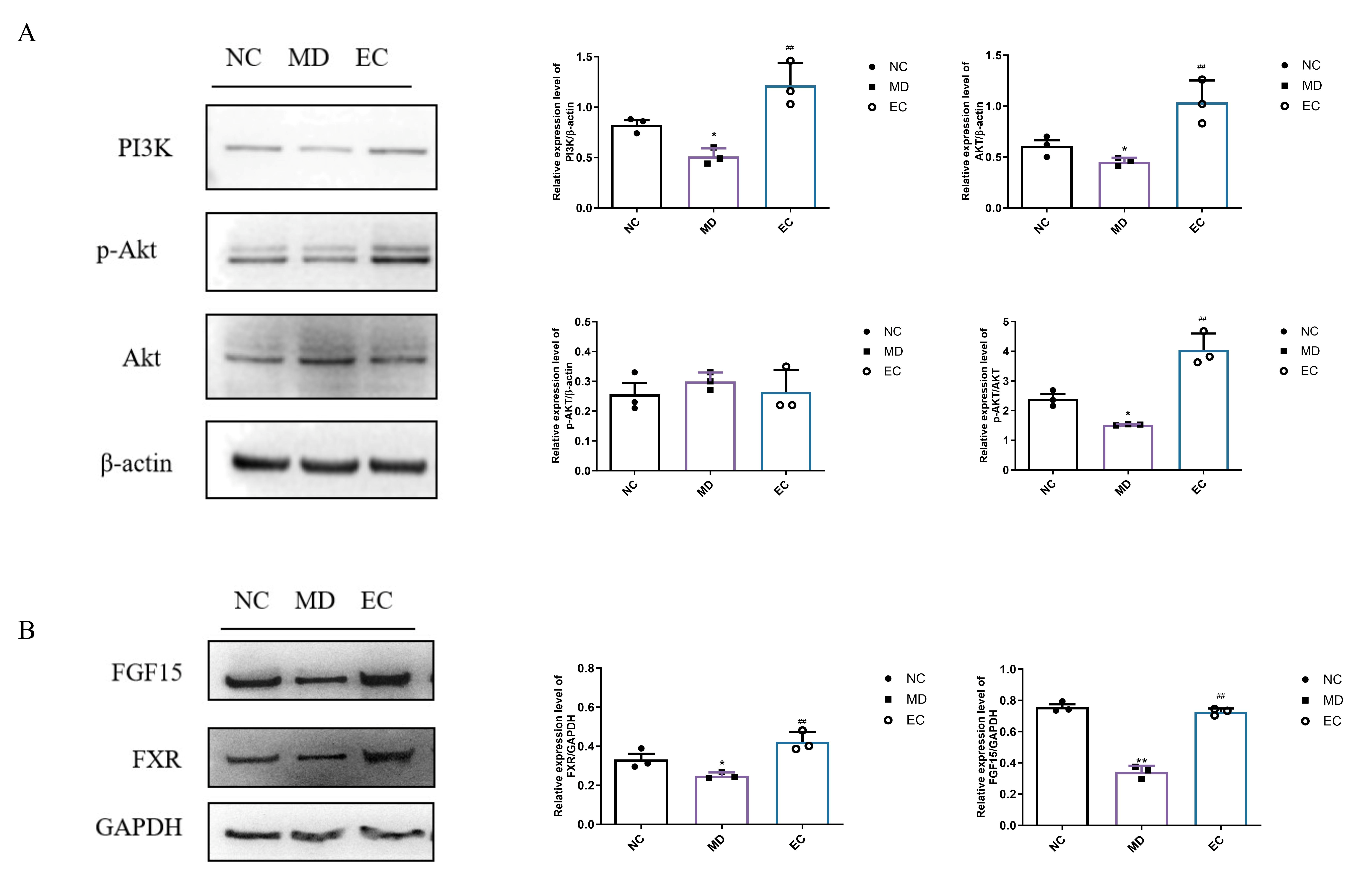
3.7. EC Activated Hepatic PI3K/AKT and Colon BA/FXR/FGF15 Signaling Pathways
3.8. Spearman’s Correlation Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| T2DM | type 2 diabetes mellitus |
| EC | ethanol extract of cinnamon |
| BW | body weight |
| HFD | high-fat diet |
| FBG | fasting blood glucose |
| OGTT | oral glucose tolerance test |
| HOMA-IR | homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance |
| TC | total cholesterol |
| TG | total triglyceride |
| LDL-C | low-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| HDL-C | high-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| TNF-α | tumor necrosis factor-α |
| SCFAs | short-chain fatty acids |
| STZ | streptozotocin |
| MS | mass spectrometry |
| PPI | protein–protein interaction |
| GO | Gene Ontology |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
| H&E | Hematoxylin and eosin |
| BAs | bile acids |
| CA | cholic acid |
| FXR | farnesoid X receptor |
| FGF15 | fibroblast growth factor 15 |
| PI3K | phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase |
| AKT | protein kinase B |
| ZO-1 | zonula occludens-1 |
References
- Oswal, N.; Lizardo, K.; Dhanyalayam, D.; Ayyappan, J.-P.; Thangavel, H.; Heysell, S.K.; Nagajyothi, J.F. Host metabolic changes during mycobacterium tuberculosis infection cause insulin resistance in adult mice. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.-H.; He, S.-F.; Liu, L.; Huang, J.-R. Saponin monomers: Potential candidates for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications. Phytother. Res. 2024, 38, 3564–3582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Froldi, G. View on Metformin: Antidiabetic and pleiotropic effects, pharmacokinetics, side effects, and sex-related differences. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Fan, L.; Fan, S.; Wang, J.; Luo, T.; Tang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Yu, L. Cinnamomum cassia presl: A review of its traditional uses, phytochemistry, pharmacology and toxicology. Molecules 2019, 24, 3473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, Z.; Khan, J.-A.; Arshad, A.; Asif, P.; Rashid, H.; Arshad, M.-I. Protective effects of cinnamomum zeylanicum l. (Darchini) in acetaminophen-induced oxidative stress, hepatotoxicity and nephrotoxicity in mouse model. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 109, 2285–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newerli-Guz, J.; Smiechowska, M. Health benefits and risks of consuming spices on the example of black pepper and cinnamon. Foods 2022, 11, 2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Yang, L.; Zheng, S.; Hou, A.; Man, W.; Zhang, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, X.; Yu, H.; Jiang, H. A review: The botany, ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry, pharmacology of cinnamomi cortex. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 27461–27497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Geng-Ji, J.-J.; Quan, Y.-Y.; Qi, L.-M.; Sun, Q.; Huang, Q.; Jiang, H.-M.; Sun, Z.-J.; Liu, H.-M.; Xie, X. Role of potential bioactive metabolites from traditional Chinese medicine for type 2 diabetes mellitus: An overview. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1023713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachid, A.-P.; Moncada, M.; Mesquita, M.; Brito, J.; Bernardo, M.-A.; Silva, M.-L. Effect of aqueous cinnamon extract on the postprandial glycemia levels in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A randomized controlled trial. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-C.; Chen, B.-H. A comparative study on improving streptozotocin-induced type 2 diabetes in rats by hydrosol, extract and nanoemulsion prepared from cinnamon leaves. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Pedersen, O. Gut microbiota in human metabolic health and disease. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 55–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massey, W.; Brown, J.-M. The gut microbial endocrine organ in type 2 diabetes. Endocrinology 2021, 162, bqaa235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perler, B.-K.; Friedman, E.-S.; Wu, G.-D. The role of the gut microbiota in the relationship between diet and human health. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2023, 85, 449–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, K.; Choi, H.-N.; Cho, S.-R.; Yim, J.-E. Association of firmicutes/bacteroidetes ratio with body mass index in Korean type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. Metabolites 2024, 14, 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandaliya, D.-K.; Seshadri, S. Short chain fatty acids, pancreatic dysfunction and type 2 diabetes. Pancreatology 2019, 19, 280–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.-Y.; Hu, J.-L.; Leng, T.; Liu, S.; Xie, M.-Y. Rosa roxburghii-edible fungi fermentation broth attenuates hyperglycemia, hyperlipidemia and affects gut microbiota in mice with type 2 diabetes. Food Biosci. 2023, 52, 102342–102354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, T.; Liu, C.-S.; Hu, Y.-N.; Luo, Z.-Y.; Chen, F.-L.; Yuan, L.-X.; Tan, X.M. Coix seed polysaccharides alleviate type 2 diabetes mellitus via gut microbiota-derived short-chain fatty acids activation of igf1/pi3k/akt signaling. Food Res. Int. 2021, 150, 110717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Chen, J.; Chen, Y.; Xie, J.; Xue, P.; Ao, T.; Chang, X.; Hu, X.; Yu, Q. Metabonomics combined with 16s rrna sequencing to elucidate the hypoglycemic effect of dietary fiber from tea residues. Food Res. Int. 2022, 155, 111122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, W.; Huang, Y.; Chen, S.; Teng, T.; Shi, Y.; Sun, Z.; Xu, Y. Mechanisms of rhizoma coptidis against type 2 diabetes mellitus explored by network pharmacology combined with molecular docking and experimental validation. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 20849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acquah, C.; Dzuvor, C.; Tosh, S.; Agyei, D. Anti-diabetic effects of bioactive peptides: Recent advances and clinical implications. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 2158–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, S.-A.; Khan, S.; Wani, S.-A. Controlling diabetes with the aid of medicinal herbs: A critical compilation of a decade of research. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 12552–12566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, M.-L.; Bernardo, M.-A.; Singh, J.; de Mesquita, M.-F. Cinnamon as a complementary therapeutic approach for dysglycemia and dyslipidemia control in type 2 diabetes mellitus and its molecular mechanism of action: A review. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Vasudeva, N.; Sharma, S. GC-MS analysis and screening of antidiabetic, antioxidant and hypolipidemic potential of Cinnamomum tamala oil in streptozotocin induced diabetes mellitus in rats. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2012, 11, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuzcu, Z.; Orhan, C.; Sahin, N.; Juturu, V.; Sahin, K. Cinnamon polyphenol extract inhibits hyperlipidemia and inflammation by modulation of transcription factors in high-fat diet-fed rats. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2017, 2017, 1583098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, D.-T.; Tung, T.-H.; Jiesisibieke, Z.-L.; Chien, C.-W.; Liu, W.-Y. Safety of Cinnamon: An Umbrella Review of Meta-Analyses and Systematic Reviews of Randomized Clinical Trials. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 790901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackonochie, M.; Rodriguez-Mateos, A.; Mills, S.; Rolfe, V. A scoping review of the clinical evidence for the health benefits of culinary doses of herbs and spices for the prevention and treatment of metabolic syndrome. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, R.; Chen, X.; Ren, H.; Wang, C.; Min, R.; Zhang, X. Network pharmacology, molecular docking and experimental validation to elucidate the anti-t2dm mechanism of lanxangia tsaoko. Fitoterapia 2024, 178, 106117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Cao, Q.; Xiong, X.; Zhao, P.; Shen, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, N. Fluoxetine regulates glucose and lipid metabolism via the pi3k-akt signaling pathway in diabetic rats. Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 22, 3073–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Miao, Q.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, M. Effects of chitosan guanidine on blood glucose regulation and gut microbiota in T2DM. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 279 Pt 3, 135422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.-B.; Xie, P.; Guo, M.; Li, F.-F.; Xiao, M.-Y.; Qi, Y.-S.; Pei, W.-J.; Luo, H.-T.; Gu, Y.-L.; Piao, X.-L. Protective effect of heat-processed gynostemma pentaphyllum on high fat diet-induced glucose metabolic disorders mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1215150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Zeng, R.; Gou, X.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, J.; Nhamdriel, T.; Fan, G. The total alkaloids of berberidis cortex alleviate type 2 diabetes mellitus by regulating gut microbiota, inflammation and liver gluconeogenesis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2025, 337 Pt 3, 118957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Jia, H.; Li, J.; Yu, M.; Yang, Y.; Tian, D.; Zhang, H.; Zou, Z. Cecal gut microbiota and metabolites might contribute to the severity of acute myocardial ischemia by impacting the intestinal permeability, oxidative stress, and energy metabolism. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Bian, X.; Wu, W.; Lv, L.; Li, Y.; Ye, J.; Jiang, X.; Wang, Q.; Shi, D.; Fang, D.; et al. Protective effect of lactobacillus salivarius li01 on thioacetamide-induced acute liver injury and hyperammonaemia. Microb. Biotechnol. 2020, 13, 1860–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, F.; Han, W.; Zhan, G.; Li, S.; Jiang, X.; Wang, L.; Xiang, S.; Zhu, B.; Yang, L.; Luo, A.; et al. Abnormal gut microbiota composition contributes to the development of type 2 diabetes mellitus in db/db mice. Aging 2019, 11, 10454–10467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Cheng, C.; Li, R.; Chen, Z.; Tang, K.; Du, G. The role of akkermansia muciniphila in maintaining health: A bibliometric study. Front. Med. 2025, 12, 1484656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Li, Q.; Yi, H.; Kuang, T.; Tang, Y.; Fan, G. Gut microbiota-derived metabolites as key actors in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 149, 112839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, J.; Rani, K.; Datt, C. Molecular link between dietary fibre, gut microbiota and health. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2020, 47, 6229–6237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wang, C.; Mao, Z.; Huo, W.; Yang, T.; Li, Y.; Xing, W.; Li, L. Association of the short-chain fatty acid levels and dietary quality with type 2 diabetes: A case-control study based on henan rural cohort. Br. J. Nutr. 2024, 131, 1668–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Lahham, S.-H.; Peppelenbosch, M.-P.; Roelofsen, H.; Vonk, R.-J.; Venema, K. Biological effects of propionic acid in humans; Metabolism, potential applications and underlying mechanisms. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1801, 1175–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weitkunat, K.; Schumann, S.; Nickel, D.; Kappo, K.-A.; Petzke, K.-J.; Kipp, A.P.; Blaut, M.; Klaus, S. Importance of propionate for the repression of hepatic lipogenesis and improvement of insulin sensitivity in high-fat diet-induced obesity. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2016, 60, 2611–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gao, X.; Zhang, X.; Xiao, Y.; Huang, J.; Yu, D.; Li, X.; Hu, H.; Ge, T.; Li, D.; et al. Gut microbiota dysbiosis is associated with altered bile acid metabolism in infantile cholestasis. Msystems 2019, 4, e00463-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tawulie, D.; Jin, L.; Shang, X.; Li, Y.; Sun, L.; Xie, H.; Zhao, J.; Liao, J.; Zhu, Z.; Cui, H.; et al. Jiang-tang-san-huang pill alleviates type 2 diabetes mellitus through modulating the gut microbiota and bile acids metabolism. Phytomedicine 2023, 113, 154733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mousavi, S.M.; Jayedi, A.; Bagheri, A.; Zargarzadeh, N.; Wong, A.; Persad, E.; Akhgarjand, C.; Koohdani, F. What is the influence of cinnamon supplementation on liver enzymes? A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Phytother. Res. 2021, 35, 5634–5646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Liu, H.; Liu, C.; Wang, L.; Ma, R.; Chen, B.; Li, L.; Niu, J.; Fu, M.; Zhang, D.; et al. Cinnamaldehyde in diabetes: A review of pharmacology, pharmacokinetics and safety. Pharmacol. Res. 2017, 122, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
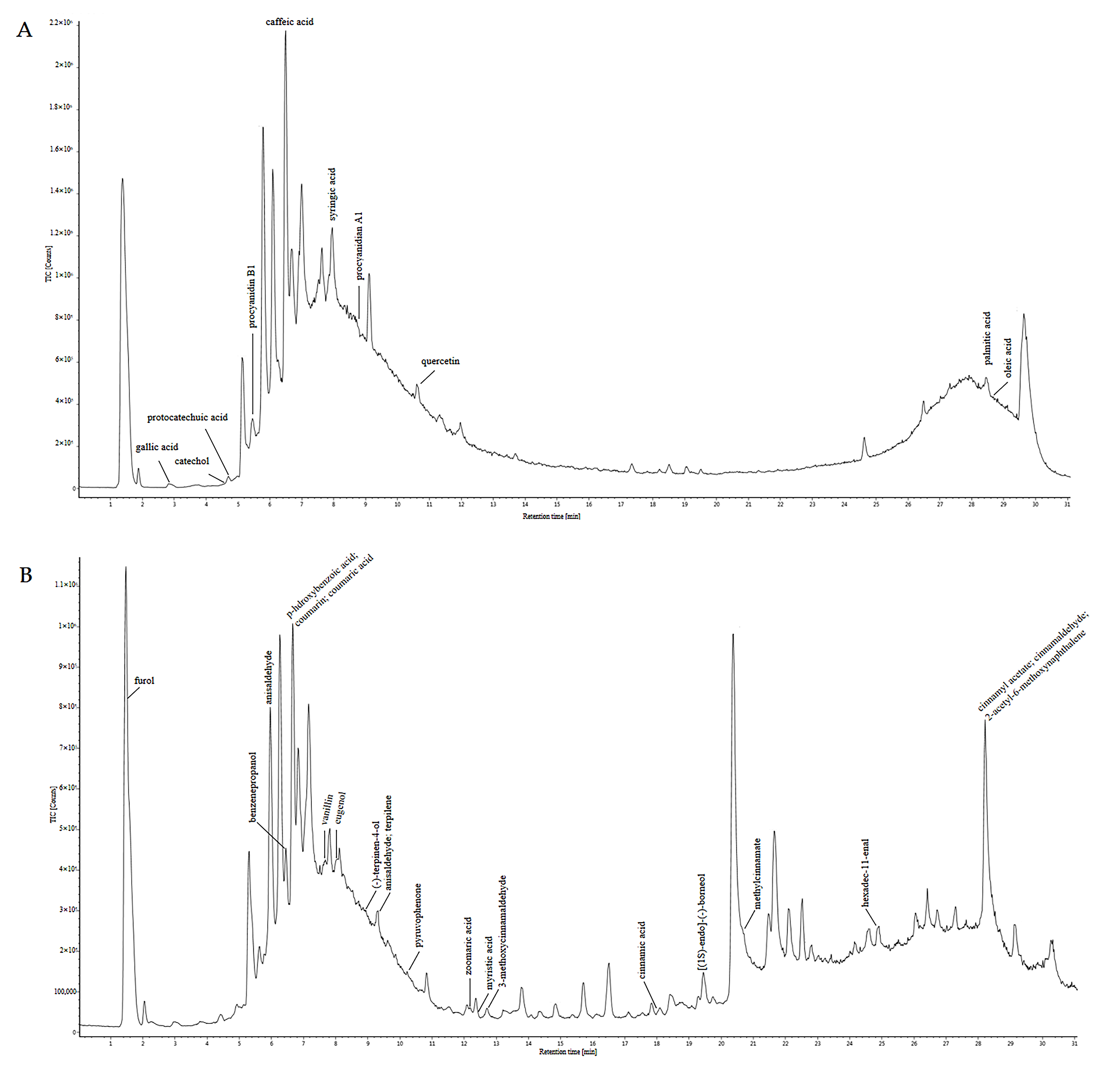
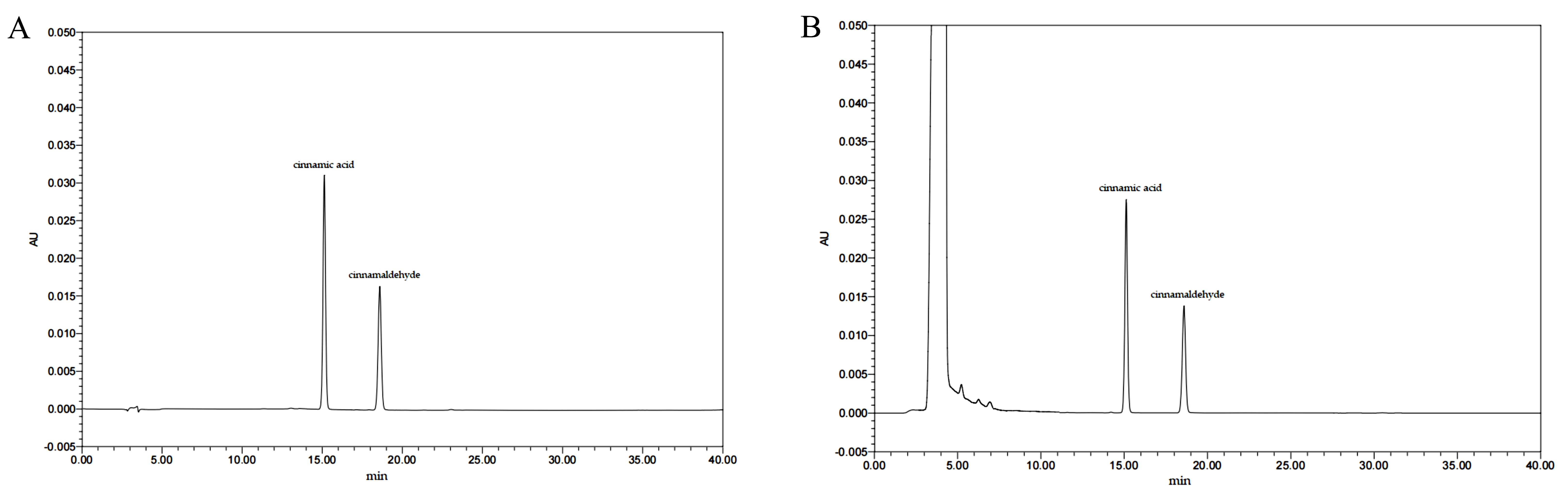

| Compounds | Content (mg/g) | Regression Equation | R2 | Linear Range (μg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| cinnamic acid | 6.269 ± 0.213 | Y = 72537X + 9229.1 | 0.9997 | 1–20 |
| cinnamaldehyde | 6.133 ± 0.155 | Y = 46534X + 4356.1 | 0.9998 | 1–20 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, R.; Yang, K.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, N.; Yu, L.; Liu, S.; Hu, Y.; Qin, B. The Antidiabetic Mechanisms of Cinnamon Extract: Insights from Network Pharmacology, Gut Microbiota, and Metabolites. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 543. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47070543
Wang R, Yang K, Liu X, Zhang Y, Chen Y, Wang N, Yu L, Liu S, Hu Y, Qin B. The Antidiabetic Mechanisms of Cinnamon Extract: Insights from Network Pharmacology, Gut Microbiota, and Metabolites. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025; 47(7):543. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47070543
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Rong, Kuan Yang, Xuefeng Liu, Yiye Zhang, Yunmei Chen, Nana Wang, Lili Yu, Shaojing Liu, Yaqi Hu, and Bei Qin. 2025. "The Antidiabetic Mechanisms of Cinnamon Extract: Insights from Network Pharmacology, Gut Microbiota, and Metabolites" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47, no. 7: 543. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47070543
APA StyleWang, R., Yang, K., Liu, X., Zhang, Y., Chen, Y., Wang, N., Yu, L., Liu, S., Hu, Y., & Qin, B. (2025). The Antidiabetic Mechanisms of Cinnamon Extract: Insights from Network Pharmacology, Gut Microbiota, and Metabolites. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 47(7), 543. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47070543





