Abstract
This study aims to investigate the mechanism by which the total flavones of Rhododendron (TFR) protect against cerebral ischemic injury through the endothelial-derived H2S-mediated regulation of RhoA phosphorylation at the Ser188 and Rho kinase 2 (ROCK2) phosphorylation at Thr436. For experimental design, mouse or rat cerebrovascular endothelial cells (ECs) were cultured with or without neurons and subjected to hypoxia/reoxygenation (H/R) injury. The vasodilation of the cerebral basilar artery was assessed. Cerebral ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury was induced in mice by bilateral carotid artery ligation, followed by Morris water maze and open field behavioral assessments. The protein levels of cystathionine-γ-lyase (CSE), 3-mercaptopyruvate sulfurtransferase (3-MST), RhoA, ROCK2, p-RhoA (RhoA phosphorylated at Ser188), and p-ROCK2 (ROCK2 phosphorylated at Thr436) were quantified. Additionally, the activities of RhoA and ROCK2 were measured. Notably, TFR significantly inhibited H/R-induced H2S reduction and suppressed the increased expression and activity of RhoA and ROCK2 in ECs, effects attenuated by CSE or 3-MST knockout. Moreover, TFR-mediated cerebrovascular dilation was reduced by RhoA or ROCK2 inhibitors, while the protective effect of TFR against cerebral I/R injury in mice was markedly attenuated by the heterozygous knockout of ROCK2. In the ECs-co-cultured neurons, the inhibition of TFR on H/R-induced neuronal injury and decrease in H2S level in the co-culture was attenuated by the knockout of CSE or 3-MST in the ECs. TFR notably inhibited the H/R-induced upregulation of neuronal RhoA, ROCK2, and p-ROCK2 protein levels, as well as the activities of RhoA and ROCK2, while reversing the decrease in p-RhoA. However, the knockout of CSE or 3-MST in the ECs significantly attenuated the inhibition of TFR on these increases. Furthermore, 3-MST knockout in ECs attenuated the TFR-mediated suppression of p-RhoA reduction. Additionally, CSE or 3-MST knockout in ECs exacerbated H/R-induced neuronal injury, reduced H2S level in the co-culture system, and increased RhoA activity and ROCK2 expression in neurons. In summary, TFR protected against ischemic cerebral injury by endothelial-derived H2S promoting the phosphorylation of RhoA at Ser188 but inhibited the phosphorylation of ROCK2 at Thr436 to inhibit the RhoA-ROCK2 pathway in neurons.
1. Introduction
Ischemic brain injury is a prevalent cause of mortality and disability worldwide, significantly impacting human health and life quality [1]. Chinese herbal medicine has a long history of use in the prevention and treatment of ischemic cerebrovascular diseases, with advantages in multi-target and multi-component comprehensive therapeutic effects [2,3]. Extracting active ingredients from Chinese herbal medicines has been an important approach for discovering new drugs in the treatment of ischemic brain injury [4]. The total flavones of Rhododendron (TFR), an effective component of flavonoids extracted from Rhododendron, mainly consists of quercetin, hyperoside, rutin, and other flavonoids, and is a significant medicinal resource [5]. In multiple cerebral ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury models [6,7,8], TFR exerts significant protective effects against ischemic brain injury by enhancing hydrogen sulfide (H2S) production and inducing cerebral vasodilation. However, its exact mechanism requires further investigation, particularly on which downstream signaling pathway of H2S involves the protective effect of TFR.
The production of endogenous H2S occurs through the direct enzymatic desulfhydration of cysteine, which is catalyzed by cystathionine-γ-lyase (CSE) and cystathionine-β-synthase (CBS). Additionally, an indirect desulfhydration process is facilitated by 3-mercaptopyruvate sulfurtransferase (3-MST) in the presence of reductants within mitochondria [9]. CBS is predominantly located in nerve cells [10], while CSE serves as the primary H2S-produing enzyme in blood vessels and mainly expresses in vascular endothelium [11]. However, 3-MST can exist in various cell types, including vascular endothelial cells (ECs) [12]. Therefore, the generation of endothelial-derived H2S is mainly catalyzed by CSE and 3-MST.
Previous studies conducted by our research group indicate that the inhibition of the RhoA-Rho kinase (ROCK) pathway may play a critical role in H2S-induced cerebral vasodilation and neuroprotective effects [13,14,15]. The RhoA-ROCK signaling pathway serves as a key target for cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases [16,17], is extensively distributed throughout the nervous system, and is intricately associated with neuronal physiological functions as well as the repair and regeneration of nerve axons [18,19,20]. ROCK has two subtypes, namely ROCK1 and ROCK2, with ROCK2 primarily being distributed in the brain and blood vessels [21,22]. Therefore, the RhoA-ROCK2 signaling pathway may serve as the primary mechanism through which H2S exerts its effects on regulating cerebral vascular function and providing protection against ischemic brain injury.
Protein phosphorylation, catalyzed by kinases, transfers phosphate groups from ATP to specific residues (serine, threonine, and tyrosine) on target proteins, whereas dephosphorylation, mediated by phosphatases, removes these groups [23]. These processes are essential mechanisms for regulating protein activity and function.
The phosphorylation of RhoA at Ser188 inhibits its activation and translocation from the cytoplasm to the cell membrane [24]. Additionally, the phosphorylation of ROCK2 at specific sites plays a crucial role in the regulation of its activity [25,26]. Our recent research revealed that exogenous H2S can inhibit the phosphorylation of ROCK2 at Thr436 in neurons, thereby playing a protective role in neuronal hypoxia/reoxygenation (H/R) damage [27]. TFR promotes H2S production to exert protective effects against cerebral I/R injury [7]; however, whether this protection occurs via the endothelial-derived H2S-mediated inhibition of the RhoA-ROCK2 pathway and its detailed mechanism still remain unclear. Therefore, the present study was designed to investigate the role of endothelial-derived H2S in inhibiting the RhoA-ROCK2 pathway for TFR-mediated protection against ischemic cerebral injury, focusing on the novel mechanism of regulating phosphorylation at the RhoA Ser188 and ROCK2 Thr436 residues.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Drugs
The flowers of Rhododendron simsii Planch., authenticated by Prof. Shoujin Liu from the Department of Traditional Chinese Medicine Material Resources at Anhui University of Traditional Chinese Medicine (Hefei, China), were collected from the Dabie Mountains in Anhui Province, China. A voucher specimen (xH080843) has been deposited in the Herbarium of the Department of Pharmacology at Anhui Medical University. The extraction of TFR was carried out by Hefei Heyuan Medicine Technology Co., Ltd. (Hefei, China), with UV spectrophotometric analysis confirming a total flavonoid content exceeding 85%. The key pharmacoactive components in TFR were further characterized using ultra-performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS) via a Waters ACQUITY UPLC system integrated with an AB6500 Plus triple quadrupole mass spectrometer for precise compositional profiling. Sodium hydrosulfide (NaHS, catalog number: 161527) and DL-propargylglycine (PPG, catalog number: P7888) were purchased from Sigma Aldrich Chemical Co., Ltd. (St. Louis, MO, USA). Anti-ROCK2 antibodies (lot number: TD-M10-010), anti-p-ROCK2 (Thr436) antibodies (lot number: TD-M10-011), and anti-CSE antibodies (catalog number: BD-PN0625) were purchased from Suzhou Bo’aolong Technology Co., Ltd. (Suzhou, China). Anti-p-RhoA (Ser188) antibodies (catalog number: ab41435), anti-RhoA antibodies (catalog number: ab187027), and Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) (catalog number: ab228554) were purchased from Abcam (San Francisco, California, USA). Anti 3-MST antibodies (catalog number: sc-376168) were purchased from Santa Cruz Biotechnology (Santa Cruz, CA, USA). LDH test kit (catalog number: A020-2-2) was obtained from Nanjing Jiancheng Biotechnology Research Institute Co., Ltd. (Nanjing, China). RhoA activity (catalog number: MM-45317M2), ROCK2 activity (catalog number: MM-0886R2), H2S (catalog number: MM-21189R1), and NSE (catalog number: MM-0069R1) assay kits were obtained from Jiangsu Meimian Industrial, Co., Ltd. (Yancheng, China). CCG-1423 (catalog number: C5803) was purchased from ApexBio (Houston, TX, USA). KD-025 (catalog number: HY-15307) was purchased from MedChemExpress (Shanghai, China).
2.2. Animals
Neonatal Sprague Dawley (SD) rats born within 24 h and adult SD rats were bought from the Experimental Animal Center of Anhui Medical University. Wild-type (WT), ROCK2 heterozygote knockout (ROCK2 HK) and CSE knockout (CSE KO) mice, and WT and 3-MST knockout (3-MST KO) rats were obtained from Shanghai Biomodel Organism Science & Technology Development Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China) All animals were housed in the Animal Center of Anhui Medical University, where they had unrestricted access to food and water. The environmental conditions for raising the animals were maintained at a humidity level of 54 ± 2% and a temperature of 22 ± 2 °C. The experiments received approval from the Ethical Committee of Anhui Medical University, and all experimental protocols adhered to the regulations established by the Animal Care and Use Committee at Anhui Medical University. These protocols comply with the guidelines outlined in the “Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals,” published by the US National Institutes of Health (NIH Publication No. 85-23, revised 2011).
The homozygous knockout of the ROCK2 gene is lethal; therefore, the experiment utilized heterozygotes. The CSE KO mouse model, widely used in H2S research, benefits from mature gene editing technology and well-characterized phenotypes [28,29]. Meanwhile, an existing study supports the application of 3-MST knockout rats in experimental research [30]. Given the species differences between rats and mice relevant to these three gene knockout models, this study employs two distinct experimental groups: one based on rats and the other on mice. These models have been clearly delineated and utilized separately in each experiment.
2.3. Isolation and Cultivation of ECs
The cerebrovascular ECs were isolated and cultured according to a previously established method [30] with some modifications. The rats or mice were anesthetized with pentobarbital sodium, decapitated, disinfected, and their cerebral cortices were placed in pre-cooled Petri dishes containing phosphate-buffered saline (PBS). The basilar artery, middle cerebral artery vessels, and other microscopic vessels were meticulously excised under a microscope. A total of 500 µL of PBS was added to a 1.5 mL centrifuge tube containing the freshly isolated blood vessel segment, which was subsequently cut into smaller pieces using ophthalmic scissors. Sterilized collagenase was introduced into the centrifuge tube along with the blood vessel segment before sealing it securely. The centrifuge tube was then placed in a water bath at 37 °C for digestion, with gentle shaking occurring every five min throughout this process. Following digestion, the mixture was subjected to centrifugation at 1400 r/min for ten min, then the supernatant was discarded and replaced with 1 mL of endothelial cell medium added to the pellet prior to transferring it into a culture bottle. After an incubation period of 24 h, non-adherent cells and tissue debris were removed by changing the medium, subsequently, cell morphology and growth were monitored every two to three days, with fluid changes performed as necessary. Once cell density reached approximately 80%, primary cultured cerebral vascular ECs were passed into a 6-well plate and identified through immunofluorescence techniques.
2.4. H/R Injury Model
When the cell culture reached the experimental requirements, after 24 h of pretreatment, the original medium was aspirated and replaced with a sugar-free medium. The cells were then cultured in a low-oxygen incubator (1% O2, 95% N2, 4% CO2, 37 °C) for 4 h. At the end of the incubation, the sugar-free medium was discarded and replaced with complete medium and placed in a normal incubator for 12 h for the next experiment.
WT mice cerebrovascular ECs were divided into the following groups: control group, H/R group, and 0.1 μmol/L [31] ROCK2 inhibitor KD-025 group.
WT and ROCK2 HK mice cerebrovascular ECs were, respectively, assigned to the following groups: control group and H/R group.
These two experiments were designed to investigate the effects of the ROCK2 inhibitor and ROCK2 HK on the protein expressions of CSE and 3-MST, as well as H2S production in cerebrovascular ECs subjected to H/R injury.
WT and CSE KO mice cerebrovascular ECs were, respectively, divided into four groups: control group, H/R group, 200 μmol/L [27] NaHS group, and 810 mg/L [7] TFR group.
WT and 3-MST KO rats cerebrovascular ECs were, respectively, divided into four groups: control group, H/R group, 200 μmol/L NaHS group, and 810 mg/L TFR group.
The two aforementioned experiments were designed to investigate the roles of CSE and 3-MST in TFR-promoted H2S production, as well as their association with the RhoA-ROCK2 signaling pathway in cerebrovascular ECs.
2.5. Cultivation of Hippocampal Neurons
The primary hippocampal neurons were cultured as previously described [32]. Several neonatal rats were captured within 24 h of birth. Following the administration of anesthesia, their skin was disinfected by immersion in 75% alcohol, and the brains were promptly excised through decapitation. The hippocampal tissues were meticulously excised in a pre-cooled Petri dish with PBS. A small glass bottle was prepared for autoclaving and drying, into which 0.125% trypsin solution was added. Subsequently, the removed hippocampal tissue was transferred to this small glass bottle with the 0.125% trypsin solution. The tissue was then cut using surgical scissors and allowed to rest on the table for 2 min. Following this, the glass bottle was placed in a cell incubator at 37 °C for digestion, which lasted between 15 and 20 min. During the digestion process, gentle shaking of the glass bottle occurred every 5 min to ensure thorough digestion. After completion of digestion, an equal volume of complete medium was added to terminate the enzymatic activity. The culture medium was gently aspirated using a pipette and set aside on the table. To remove insoluble matter, a nylon filter cloth with a mesh size of 200 mesh was employed; subsequently, centrifugation at room temperature at 1200 r/min for 5 min followed. Post centrifugation, the supernatant was discarded while complete medium was introduced back into the precipitate to re-suspend cells thoroughly by gentle mixing with a pipette gun before counting. Cell counts were adjusted to approximately 5 × 105 cells/mL. The cell suspension was then seeded into pre-coated polylysine 6-well plates and cultured in a cell incubator maintained at 37 °C with an atmosphere of 5% CO2. After an incubation period of 24 h, media changes were performed using basic medium, thereafter, media changes continued every two days.
2.6. Co-Culture System
In this study, the Transwell co-culture system of hippocampal neurons and cerebral vascular ECs was established. The 6-well plate was chosen for the co-culture system, with a pet membrane featuring a pore size of 0.4 μm selected for the Transwell chamber. Primary hippocampal neurons were directly seeded onto the pore plate. After 7 days of cell growth, primary cultured cerebral vascular ECs were dissociated with pancreatic enzyme and then seeded in the upper chamber of the Transwell system placed on top of the pore plate, successfully establishing a co-culture system with cerebral vascular ECs in the upper chamber and hippocampal neurons in the lower chamber. The co-culture system was maintained in a 5% CO2 incubator at 37 °C for 24 h before subsequent experimental procedures.
Neurons+ECsWT and Neurons+ECsCSE KO co-cultured cells were divided into a control group and H/R group, respectively.
Neurons+ECsWT and Neurons+ECs3-MST KO co-cultured cells were divided into a control group and H/R group, respectively.
The above two experiments observed the effects of CSE and 3-MST KO cerebrovascular ECs on H2S content, H/R injury, and RhoA-ROCK2 pathway in the co-cultured neurons.
Neurons+ECsWT and Neurons+ECsCSE KO co-cultured cells were divided into a control group, H/R group, 200 μmol/L NaHS group, and 810 mg/L TFR group.
Neurons+ECsWT and Neurons+ECs3-MST KO co-cultured cells were divided into a control group, H/R group, 200 μmol/L NaHS group, and 810 mg/L TFR group.
Two types of H2S synthetases, CSE and 3-MST, are predominantly expressed in cerebrovascular ECs. In order to clarify the specific role of TFR in promoting H2S catalyzed by CSE and 3-MST in ECs in neuronal H/R injury, rat neurons were co-cultured with WT, CSE KO, and 3-MST KO ECs in the above two experiments. Then, NaHS and TFR were added into the ECs culture medium, and CBS inhibitor aminooxyacid and 3-MST inhibitor L-aspartic acid was added into the neurons culture medium to exclude the interference of H2S produced by neurons on experimental results.
2.7. Determination of Cell Viability and Biochemical Measurement
The viability of cells was detected at 450 nm using a CCK-8 assay kit. We tested the content of neuron-specific enolase (NSE), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), and H2S according to assay kits and the manufacturer’s protocols. The activity of RhoA and ROCK2 were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kits, and all procedures followed the manufacturer’s guidelines.
2.8. Western Blotting
Western blotting analysis was used to measure the protein expressions of CSE, 3-MST, RhoA, p-RhoA (Ser188), ROCK2, and p-ROCK2 (Thr436). The total proteins were separated using SDS-PAGE (Beyotime, Nanjing, China), transferred to polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membranes (Millipore, Boston, MA, USA). The membranes were blocked with 5% skim milk in tris-buffered saline with Tween-20 (TBST) for 1 h, then shortly washed and hatched overnight at 4 °C with specific primary antibodies. After washing three times with TBST, the membranes were hatched with a secondary antibody in TBST solution for 1 h at 37 °C and then washed. The bands were visualized using an enhanced chemiluminescence kit (Thermo, Rockford, IL, USA). The intensity of immunoreactive bands was quantified with the use of image J software (Fiji distribution, NIH Image, Bethesda, MD, USA https://imagej.net/ij/ accessed on 9 June 2025). Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) and β-actin were selected as reference proteins based on their molecular weights relative to the target protein.
2.9. Vessel Experiment
According to a previous method [33], after euthanizing the animals, the brain was promptly removed and the basilar artery of the mouse or rat brain was isolated. The basilar artery was subsequently prepared into a cerebrovascular segment measuring approximately 3 mm in length. Subsequently, the cerebrovascular segment was inserted into two tungsten wires and mounted on a wire myograph in 5 mL chambers (DMT, Aarhus, Denmark) containing physiological salt dissolution (PSS) at 37 °C and continuously aerated with a mixture of 95% O2 and 5% CO2. Controlled by the measurement system’s software, the pressure within the vascular ring was gradually increased from 10 mmHg to 60 mmHg over a period of 30 min. This pressure then stabilized for an additional hour, during which time the PSS fluid in the tank was replaced every 15 min. After incubation with various drugs for 30 min, a contraction was induced with 30 mmol/L KCl. Once vascular ring contraction stabilized, TFR or NaHS at the required concentration was added to induce vasodilation. The percentage of vasodilation is calculated according to the following formula: the percentage of vasodilation = (blood vessel diameter after adding medication—blood vessel diameter after adding contraction agent)/(blood vessel diameter before adding contraction agent—blood vessel diameter after adding contraction agent) × 100%.
The basal arteries of rats were divided into the following groups: vehicle group, (10, 30, 90, 270, and 810 mg/L) TFR group, 1.0 μmol/L [34] CCG-1423 + TFR group, and 0.1 μmol/L KD-025 + TFR group. This experimental design aimed to investigate the effects of pretreatment with RhoA inhibitor and ROCK2 inhibitor on TFR-induced vasodilation.
The basal arteries of WT and ROCK2 HK mice were divided into a vehicle group and (1, 3.16, 10, 31.62, 100, 316, and 1000 μmol/L) NaHS group. This experiment was designed to investigate the changes in H2S-mediated cerebral vessel dilation in ROCK2 HK mice.
2.10. Cerebral I/R Model
The cerebral I/R model was established by 20 min of bilateral common carotid artery occlusion (2-VO) three times with 10 min intervals, as previously described [35]. Briefly, the mice were anesthetized with 0.35% pentobarbital sodium (0.1 mL/10 g) via intraperitoneal injection. A midline incision was then made in the neck to expose the bilateral common carotid arteries (BCCAs). The BCCAs were isolated and fully ligated with sutures for a duration of 20 min to induce occlusion, followed by 10 min of reperfusion. This I/R protocol was repeated three times. Subsequently, the ligatures were carefully removed to restore blood flow. Finally, the midline incision in the neck was sutured closed.
WT mice were randomly divided into the following groups: sham group, I/R group, and 120 mg/kg [9] TFR group.
ROCK2 HK mice were randomly divided into the following groups: sham group, I/R group, 120 mg/kg TFR group, and 50 mg/kg [32] PPG + 120 mg/kg TFR group.
The mice in the TFR treatment groups were administrated with 120 mg/kg TFR by gavage once a day for 14 days. In addition to TFR treatment, mice of the PPG + TFR group were intraperitoneally injected daily with 50 mg/kg PPG for 14 days after cerebral I/R. The mice in cerebral I/R group were administrated with the same volume of normal saline. At 1 h after the first administration, the 2-VO-treated cerebral I/R injury was established. Mice in the sham group underwent exposure of BCCAs but not ligation. A heating station was used to maintain the rectal temperature of mice at 37.0 ± 0.5 °C during the operations. The experiment was designed to observe the effect of ROCK2 HK on TFR against ischemic cerebral injury and the effect of CSE inhibitor PPG treatment on TFR.
Detailed methods for the in vivo animal experiments are provided in Appendix A.
2.11. Determination of Blood Flow in Brain Tissue
The blood flow in mouse brain tissue was assessed using laser speckle flow imaging. Following anesthesia with pentobarbital sodium, the head hair was shaved and the skin and fascia were incised along the sagittal suture from the center of the head. The connective tissue on the skull surface was removed, and the body temperature was maintained at 37.0 ± 0.2 °C. The imaging system’s laser source emits a wavelength of 785 nm, uniformly irradiating the area approximately 9 cm above the mouse skull. In the real-time perfusion map generated by Pim Soft V1.4 software, detection regions for both the left and right hemispheres of each mouse brain were selected, allowing for the recording of cerebral blood flow (CBF) in both hemispheres. Using pre ischemic blood flow in mice as the baseline blood flow, the following calculation was used: change rate of CBF = reperfusion blood flow/pre ischemic blood flow × 100%.
2.12. Morris Water Maze Assay
The Morris water maze assay was performed as previously described [36] with some modifications. The mice were placed in the water maze for the observation of their swimming behavior, utilizing computer tracking. Each mouse’s swimming time was restricted to 60 s, with the duration from the onset of exploration until reaching the platform defined as the escape latency period. If a mouse failed to locate the platform within 60 s, it was gently guided to the platform and allowed a maximum stay of 10 s to observe spatial cues related to learning and memory. Subsequent training sessions over 3 days followed a clockwise direction, with an interval of at least 20 min between each session. Following 4 consecutive days of spatial learning, on day 5, the platform was removed for a spatial exploration test during which mice were permitted to swim freely for 60 s after being gently placed into the water from quadrant one.
2.13. Open Field Test
The open field test was performed as previously described [37]. The open field apparatus was a square box and the length, width, and height of it were, respectively, 96 cm, 96 cm, and 50 cm. Experimental mice were put in the central area of the open field equipment and permitted to move freely for 3 min to adapt to the environment. Afterwards, the exploratory behavior of the mice was then evaluated by recording the total distance traveled by the mice in an additional 3 min and the percentage of distance traveled by the mice within the boundary region.
2.14. Randomized Block Design
WT and gene knockout cells were, respectively, randomly allocated to the control group and the experimental group at an identical inoculation concentration. Synchronization was performed to minimize experimental error and potential confounding factors, such as genetic differences between species (e.g., rats and mice), thereby ensuring the robustness of the results. At the conclusion of each experiment, the effect of TFR was assessed by calculating the absolute difference between the study indicators obtained in the TFR group and the H/R group.
2.15. Statistical Analysis
All data, presented as mean ± SD, were analyzed using GraphPad Prism 8.0 software (La Jolla, CA, USA). A t-test was used to compare the differences between the two groups. One-way analysis of variance with Tukey’s test for post test analysis were used for multi-group comparisons. A value of p < 0.05 or p < 0.01 was considered statistically significant.
3. Results
3.1. ROCK2-Mediated Inhibition in CSE and 3-MST Expressions and H2S Production in Mouse Cerebrovascular ECs
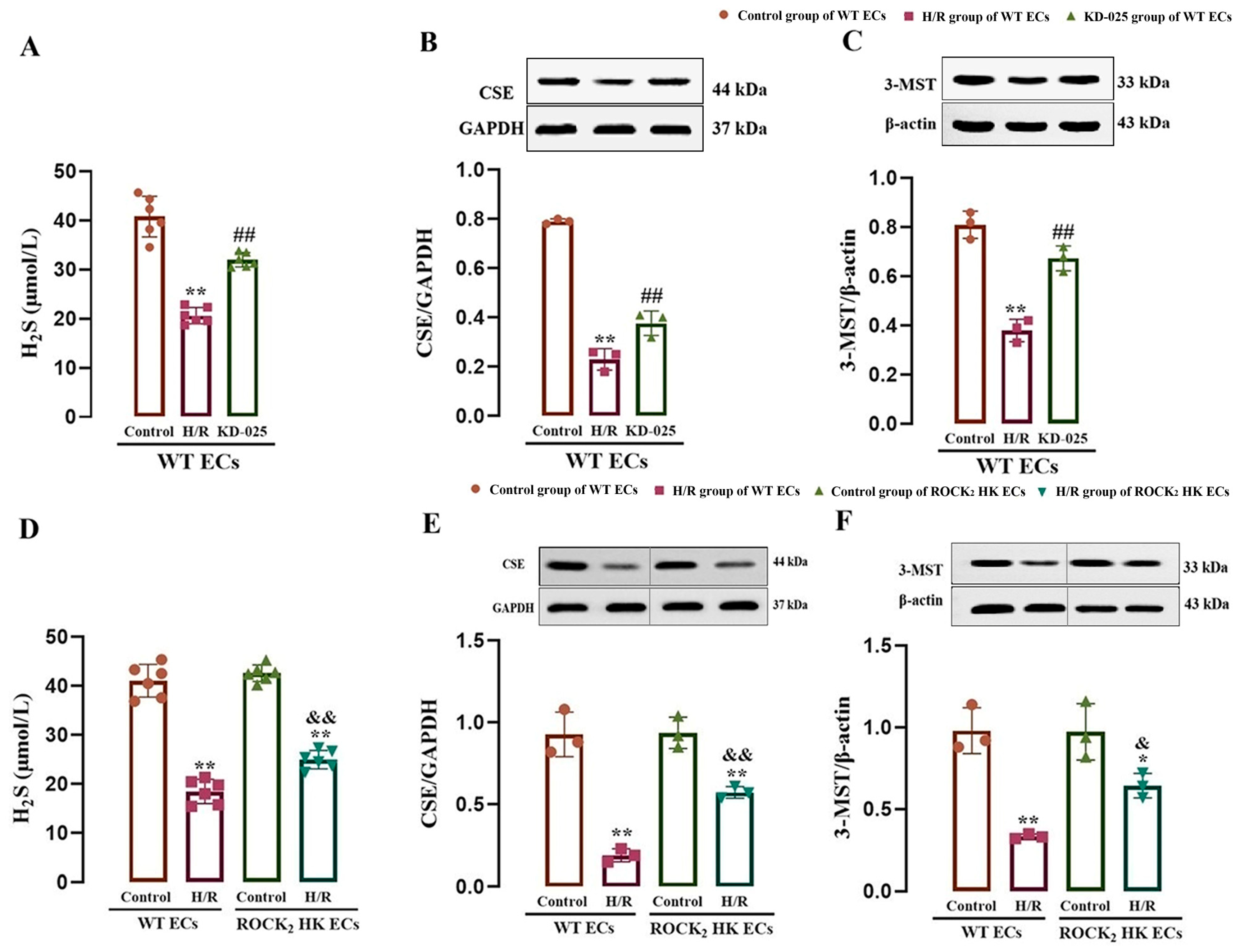
The correlation between ROCK2 and H2S production in mouse cerebrovascular ECs was examined using the ROCK2 inhibitor as well as WT and ROCK2 HK mice. As shown in Figure 1A–C, compared with the control group, H/R injury led to significant reductions in CSE and 3-MST protein expression and H2S content in the cerebrovascular ECs from the WT mice, which were markedly reversed by the ROCK2 inhibitor KD-025 (0.1 μmol/L) compared with the H/R group, suggesting that the inhibition of ROCK2 could enhance CSE and 3-MST protein expression and H2S production in mouse cerebrovascular ECs subjected to H/R injury.
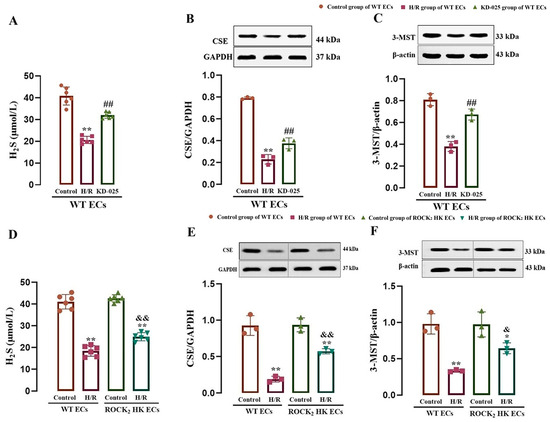
Figure 1.
Effects of ROCK2 inhibitor KD-025 and HK of ROCK2 on H2S production and CSE and 3-MST protein expression in the mouse cerebrovascular ECs subjected to H/R injury (mean ± SD, n = 6 or 3). (A–C) Effect of KD-025 on the H2S content and CSE and 3-MST protein expression in the ECs. (D–F) Effect of HK of ROCK2 on the H2S content and CSE and 3-MST protein expression in the ECs. KD-025: 0.1 μmol/L. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 vs. the control group; ## p < 0.01 vs. the H/R group; & p < 0.05, && p < 0.01 vs. the H/R group of WT ECs.
Figure 1D–F show that, in comparison with the control group, H/R injury resulted in significant reductions in CSE and 3-MST protein expression as well as H2S production in cerebrovascular ECs from the WT or ROCK2 HK mice, but the reductions in the ECs from the ROCK2 HK mice were remarkably attenuated compared with those in the ECs from the WT mice. The result suggested that the HK of ROCK2 could inhibit the reductions in CSE and 3-MST protein expression as well as H2S production in the ECs following H/R injury.
3.2. Effect of CSE or 3-MST KO on TFR Promoting H2S Production and Inhibiting the RhoA-ROCK2 Pathway in Mouse or Rat Cerebrovascular ECs Subjected to H/R Injury
Figure 1 clearly illustrates the inhibitory role of ROCK2 in H2S production within cerebrovascular ECs. To further explore this, we next investigated the regulatory effects of TFR-induced H2S on the RhoA-ROCK2 signaling pathway.
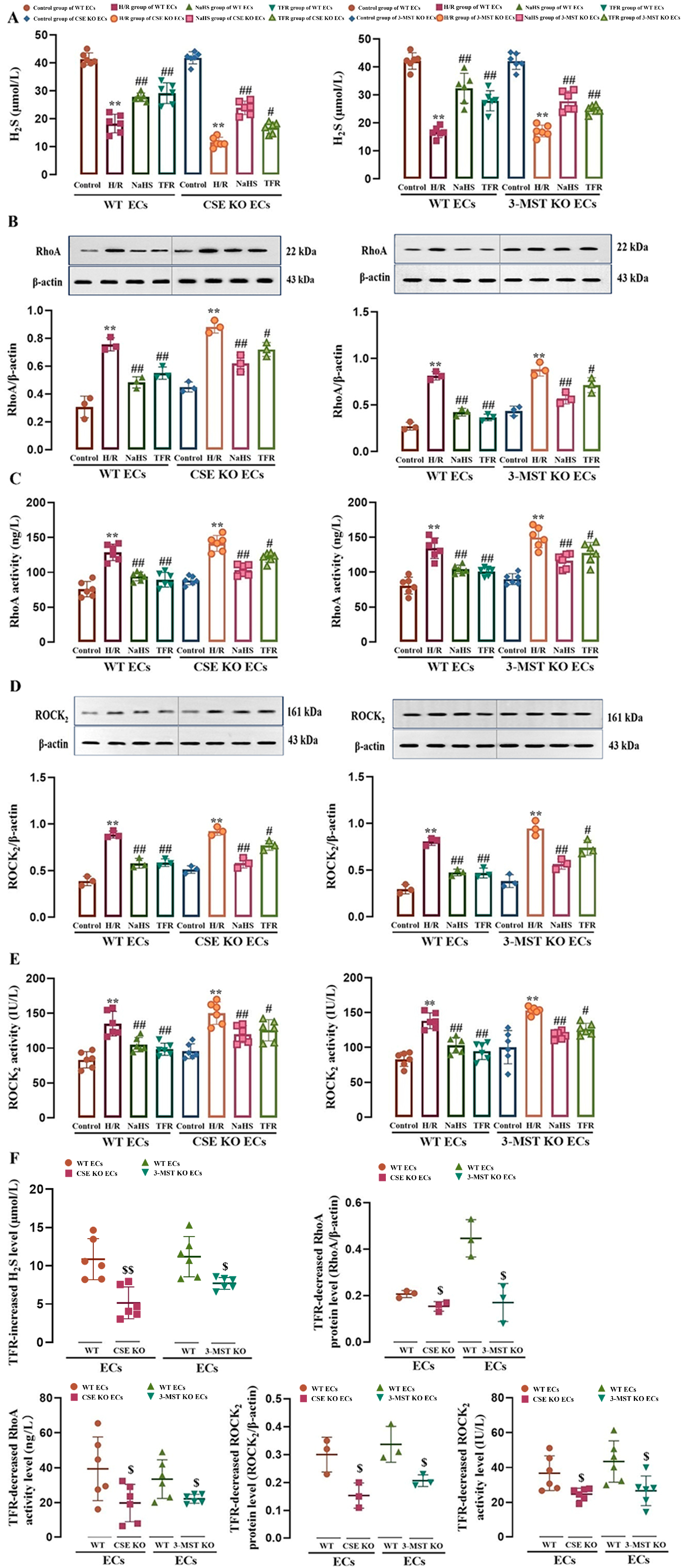
As shown in Figure 2A–E, H/R injury induced a significant decrease in H2S level and increases in RhoA and ROCK2 protein expression and activities in WT and CSE KO mouse cerebrovascular ECs and 3-MST KO rat cerebrovascular ECs, but these decreases and increases were markedly attenuated by treatment with TFR (810 mg/L) or H2S donor NaHS (200 μmol/L). The results demonstrated that, like NaHS, TFR could inhibit the upregulation of the RhoA-ROCK2 pathway in either WT or CSE KO or 3-MST KO ECs induced by H/R injury through H2S. The results of our paired experiment (Figure 2F) further showed that the TFR-caused increase in H2S level and decreases in protein expression and activities of RhoA and ROCK2 in the CSE KO or 3-MST KO ECs were substantially smaller than those in WT ECs. These results suggested that the KO of CSE or 3-MST attenuated the inhibitory effect of TFR on the H/R injury-induced decrease in H2S production and activation of the RhoA-ROCK2 pathway in mouse and rat cerebrovascular ECs.
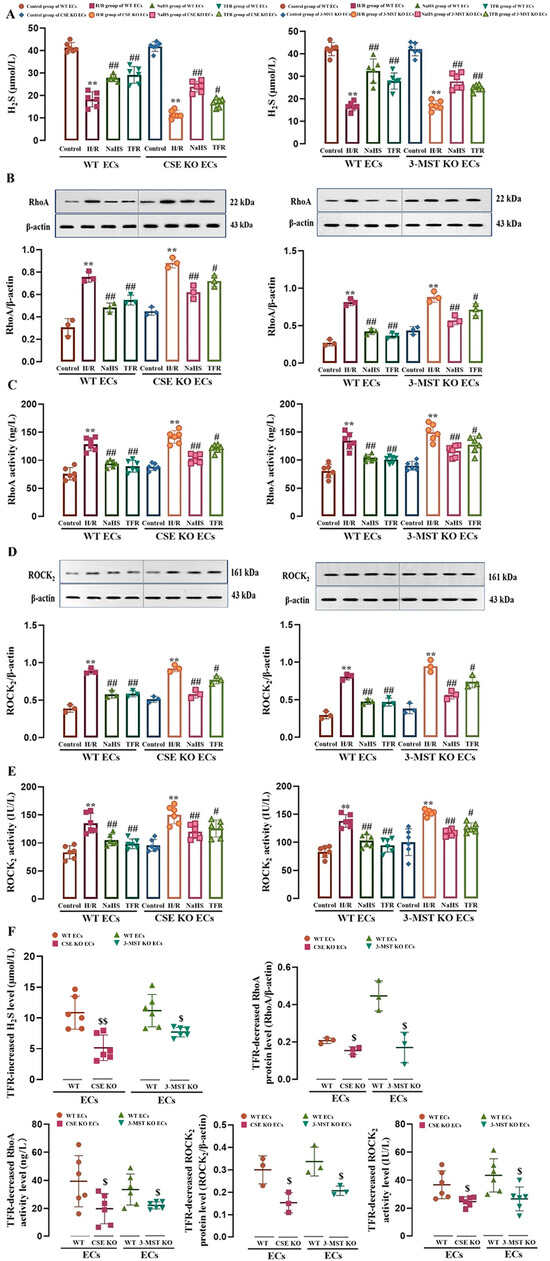
Figure 2.
Effects of TFR and NaHS on the H2S level as well as RhoA and ROCK2 protein expression and activities in WT and CSE KO mouse cerebrovascular ECs (or WT and 3-MST KO rat cerebrovascular ECs) subjected to H/R injury (mean ± SD, n = 6 or 3). (A) H2S level. (B) RhoA protein level. (C) RhoA activity. (D) ROCK2 protein level. (E) ROCK2 activity. (F) Comparison of the TFR-induced increase in H2S level and decreases in protein expression and activities of RhoA and ROCK2 in WT and CSE KO ECs (or WT and 3-MST KO ECs). NaHS: 200 μmol/L; TFR: 810 mg/L. ** p < 0.01 vs. the control group; # p < 0.05, ## p < 0.01 vs. the H/R group; $ p < 0.05, $$ p < 0.01 vs. the WT ECs group.
3.3. Effects of CCG-1423 and KD-025 on the Cerebral Vasodilation of TFR
Vascular ECs regulate vascular tone by secreting various regulatory factors [38]. Accordingly, at the vascular level, we further examined the role of TFR and its relationship with both H2S and the RhoA-ROCK2 pathway.
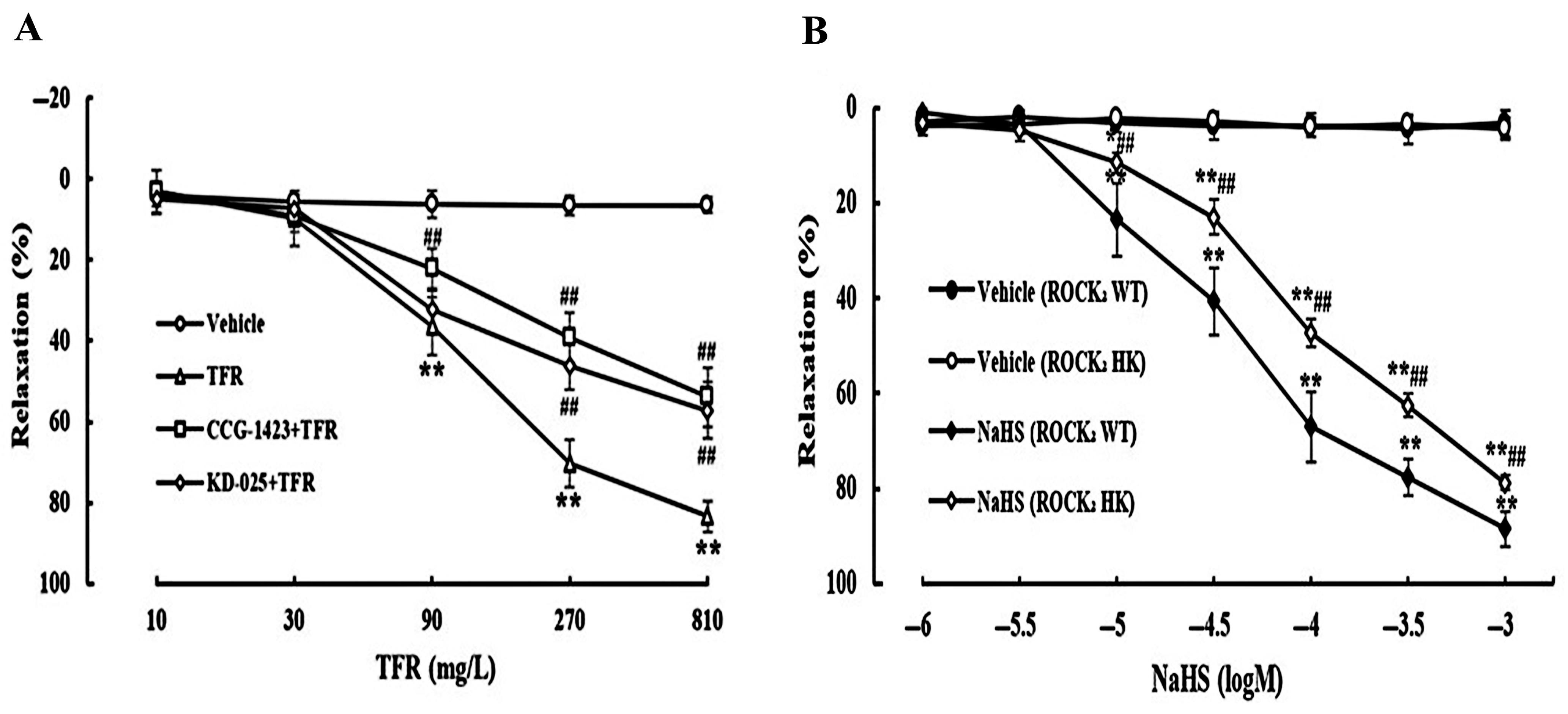
As shown in Figure 3A, TFR 90, 270, and 810 mg/L induced a significant vasorelaxation in the rat cerebral basilar artery, which was remarkably attenuated by the RhoA inhibitor CCG-1423 (1.0 μmol/L) or ROCK2 inhibitor KD-025 (0.1 μmol/L), suggesting the involvement of the RhoA-ROCK2 signaling pathway in the TFR-induced cerebral vasorelaxation in rats. Additionally, Figure 3B shows that at the ranges of 10~1000 μmol/L, NaHS could elicit an obvious vasodilation in the cerebral basilar arteries from both WT and ROCK2 HK mice, but the vasodilation of NaHS was significantly more attenuated in the artery from ROCK2 HK mice than that from WT mice. This is consistent with our previous finding that endothelial-derived H2S induces rat cerebral vasodilation by inhibiting the RhoA-ROCK pathway [34], and suggested that the cerebral vasodilation of TFR may be due to the inhibition of the RhoA-ROCK2 signaling pathway by endothelial-derived H2S.
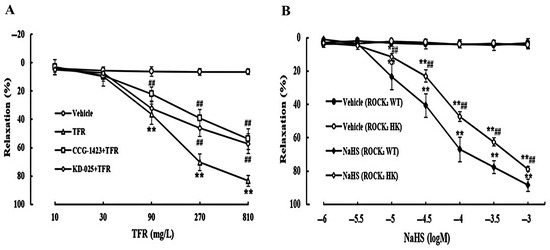
Figure 3.
Effects of RhoA inhibitor CCG-1423 and ROCK2 inhibitor KD-025 on vasodilation of TFR in rat cerebral basilar artery, and impact of HK of ROCK2 on the NaHS-induced cerebral vasorelaxation in mice (mean ± SD, n = 6). (A) Effects of CCG-1423 (1.0 μmol/L) or KD-025 (0.1 μmol/L) pretreatment on cerebral vasodilation of TFR in rats. (B) Effect of HK of ROCK2 on the NaHS-induced cerebral vasodilation in mice. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 vs. the vehicle group; ## p < 0.01 vs. the TFR group or the NaHS (ROCK2 WT) group.
3.4. Protective Effects of TFR Against Cerebral I/R Injury in WT and ROCK2 HK Mice
The involvement of the RhoA-ROCK2 pathway in the cerebral vasorelaxation induced by TFR suggests that this pathway may also contribute to the protective effects of TFR against cerebral I/R injury. Thus, this study investigated the role of ROCK2 in TFR-mediated cerebral protection in mice.
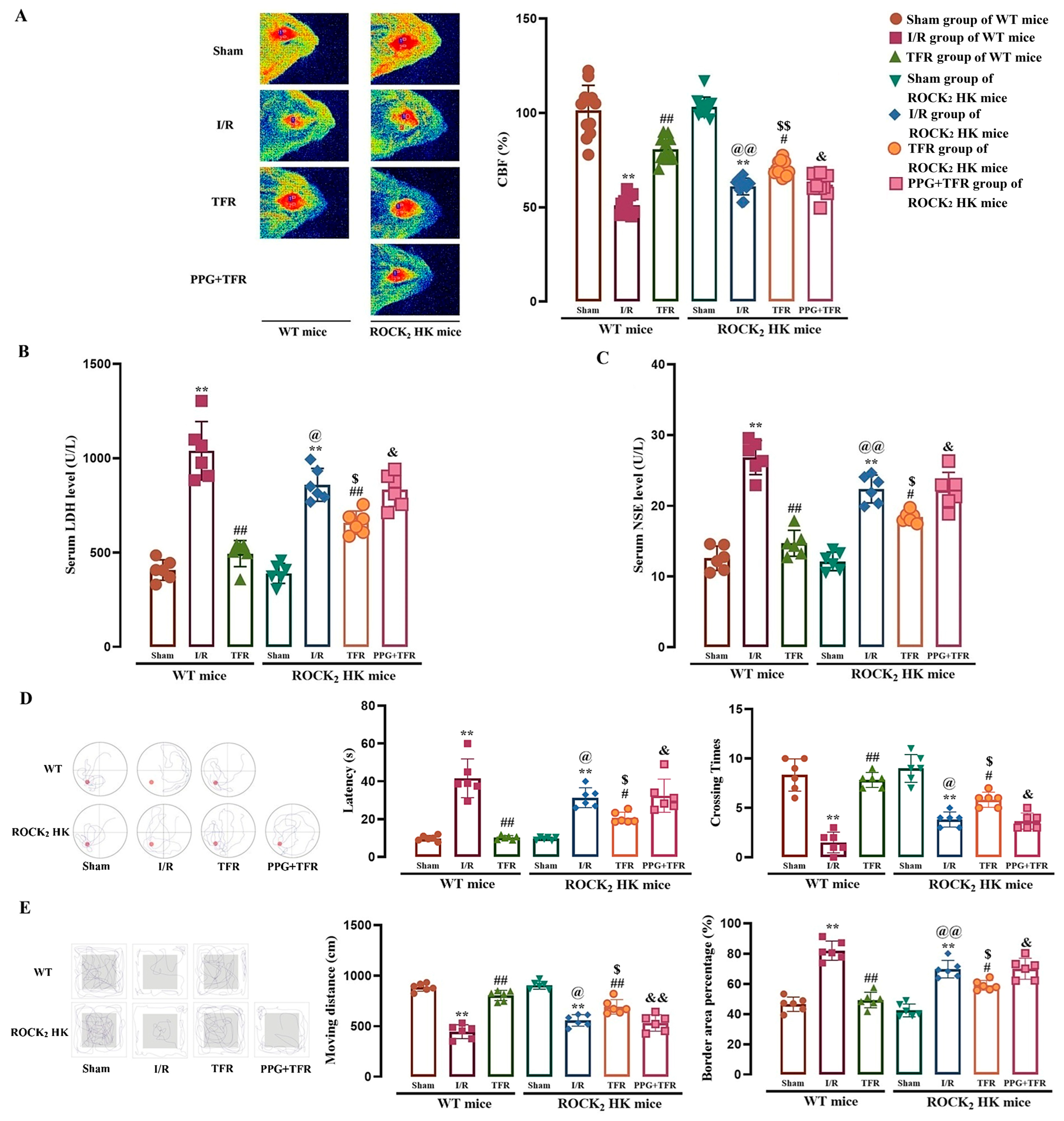
As depicted in Figure 4A–C, cerebral I/R injury significantly induced a decrease in CBF and increases in serum LDH and NSE activities in WT and ROCK2 HK mice. The water maze test (Figure 4D) showed that the platform reaching latency increased but the platform crossing times decreased in both WT and ROCK2 HK mice subjected to cerebral I/R injury compared with the sham group. The open field test (Figure 4E) showed that cerebral I/R injury resulted in a significant decrease in moving distances and a marked increase in border area percentage in these two types of mice. Notably, the administration of TFR (120 mg/kg) significantly mitigated both the decreases and increases observed, suggesting that TFR provides a protective effect against cerebral I/R injury.
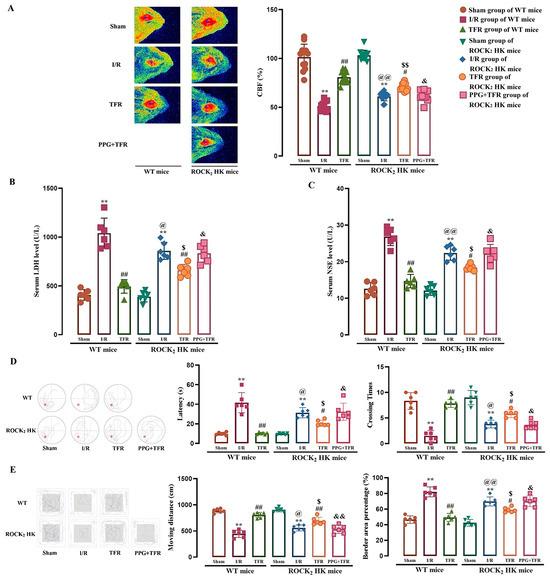
Figure 4.
Protective effect of TFR against brain I/R injury in WT and ROCK2 HK mice, and impact of PPG on the protection of TFR in ROCK2 HK mice (mean ± SD, n = 6). (A) CBF (Red areas represent relatively normal blood perfusion, while blue areas represent hypoperfusion, one detection area per left/right cerebral hemisphere in each mouse). (B) Serum LDH level. (C) Serum NSE level. (D) Water maze test. (E) Open field test. TFR: 120 mg/kg, PPG: 50 mg/kg. ** p < 0.01 vs. the sham group; # p < 0.05, ## p < 0.01 vs. the I/R group; @ p < 0.05, @@ p < 0.01 vs. the I/R group of WT mice; $ p < 0.05, $$ p < 0.01 vs. the TFR group of WT mice; & p < 0.05, && p < 0.01 vs. the TFR group of ROCK2 HK mice.
Figure 4 also shows that the cerebral I/R injury-induced decreases in CBF, spatial learning, memory functions, and exploratory behavior (such as platform reaching latency, platform crossing times, moving distances, and border area percentage) and increases in serum LDH and NSE activities were remarkably attenuated in ROCK2 HK mice compared with those in WT mice, and the amelioration of TFR on these indicators was markedly weaker in ROCK2 HK mice than that in WT mice. The results suggested that the HK of ROCK2 could reduce cerebral I/R injury, and ROCK2 was involved in the protection of TFR against brain I/R injury. Additionally, pretreatment with PPG (50 mg/kg), a CSE inhibitor, significantly attenuated the protection of TFR against cerebral I/R injury in ROCK2 HK mice, indicating that endogenous H2S might also participate in the protection of TFR in mice.
3.5. Effect of TFR on H/R Injury in the ECs-Co-Cultured Neurons and H2S Level in the Co-Cultured Medium
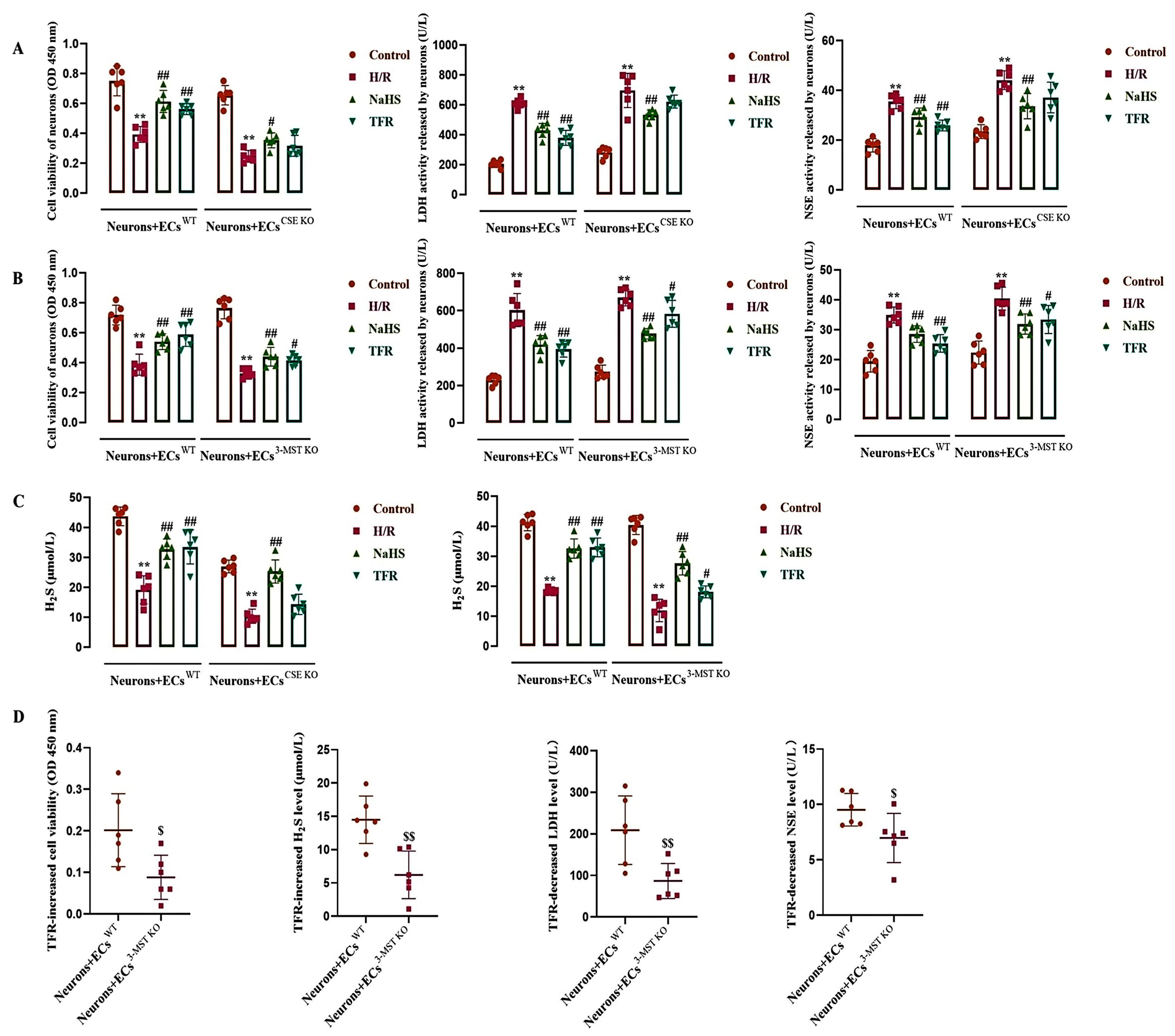
To observe the role of endothelial-derived H2S in H/R injury in neurons, the present study co-cultured rat neurons with WT and CSE KO (or 3-MST KO) cerebrovascular ECs, and then the H2S level in the co-cultured medium as well as neuronal vitality, LDH, and NSE activities were detected.
As shown in Figure 5A–C, during the co-culture of neurons with WT ECs, CSE KO ECs, or 3-MST KO ECs, H/R injury induced significant decreases in the neuronal vitality and the H2S level; at the same time, the activities of LDH and NSE in the neuronal supernatant were increased. Both NaHS (200 μmol/L) and TFR (810 mg/L) substantially inhibited the decreases in neuronal vitality and H2S level induced by H/R injury, as well as the increases in LDH and NSE activities observed in the neuronal supernatant during co-culture with WT ECs. Figure 5A,C shows that in the co-culture of neurons with CSE KO ECs, NaHS but not TFR significantly mitigated the reduction in neuronal vitality and H2S level, as well as the elevation of LDH and NSE activities in the neuronal supernatant induced by H/R injury. The results suggested that TFR could protect rat neurons from H/R injury through the CSE-produced H2S in the co-cultured ECs. Figure 5B,C shows that in the co-culture of neurons with 3-MST KO ECs, not only NaHS but also TFR significantly inhibited the H/R injury-decreased neuronal vitality and H2S level, and attenuated the increased LDH and NSE activities in the neuronal supernatant induced by H/R injury. Figure 5D further shows that the TFR-caused increases in decreased neuronal vitality and H2S level, as well as decreases in the increased LDH and NSE activities, were remarkably attenuated in the co-culture of neurons with 3-MST KO ECs compared with those in the co-culture of neurons with WT ECs. The results suggested that the 3-MST-produced H2S in the co-cultured ECs was also involved in the protection of TFR against H/R injury in rat neurons, but it seemed not as crucial as the CSE-produced H2S.
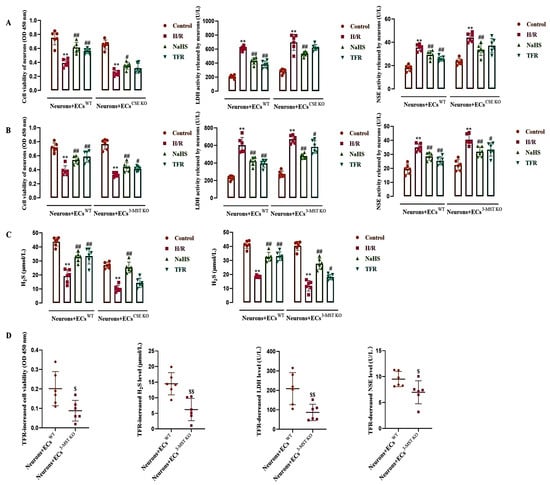
Figure 5.
Effects of TFR and NaHS on H/R injury in the rat neurons co-cultured with cerebrovascular ECs and H2S level in the co-cultured medium (mean ± SD, n = 6). (A) Effects of TFR and NaHS against H/R injury in the rat neurons co-cultured with WT and CSE KO ECs. (B) Effects of TFR and NaHS against H/R injury in the rat neurons co-cultured with WT and 3-MST KO ECs. (C) Effects of TFR and NaHS on the H2S level in the co-cultured medium. (D) Comparison of the TFR-induced increases in neuronal vitality and H2S level, along with the decreases in LDH and NSE activities, between the co-culture of neurons with WT ECs and that with 3-MST KO ECs. NaHS: 200 μmol/L; TFR: 810 mg/L. ** p < 0.01 vs. the control group; # p < 0.05, ## p < 0.01 vs. the H/R group; $ p < 0.05, $$ p < 0.01 vs. the Neurons+ECsWT group.
3.6. Impact of CSE or 3-MST KO in the ECs on the Effects of TFR on RhoA Expression, Activity, and Phosphorylation in the Co-Cultured Neurons Subjected to H/R Injury
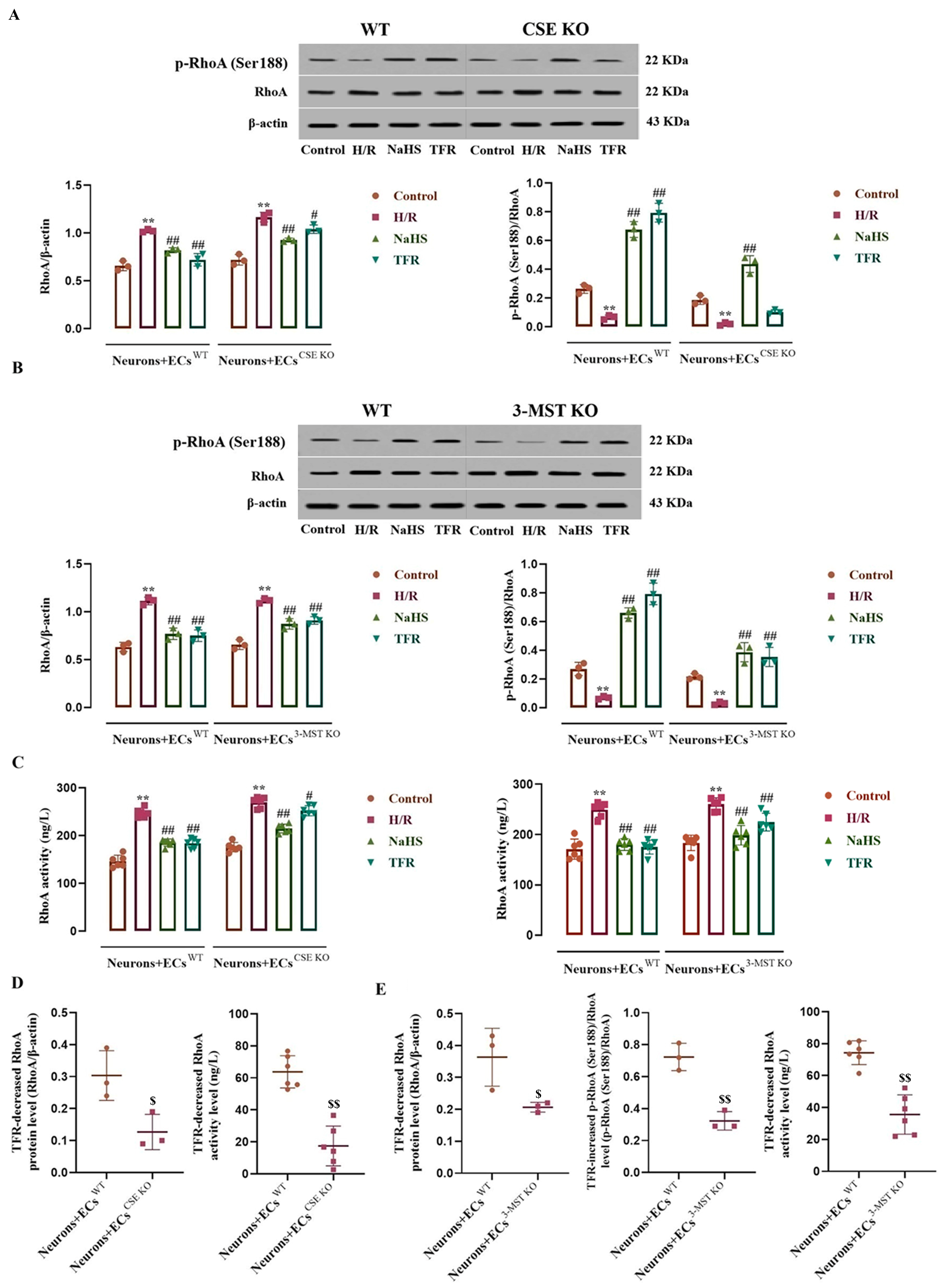
As shown in Figure 6A–C, compared with the control group, the neurons co-cultured with WT ECs, CSE KO ECs, or 3-MST KO ECs exhibited significant increases in RhoA protein level and activity, along with a decrease in p-RhoA (RhoA phosphorylated at Ser188) protein level following H/R injury, which were remarkably inhibited by NaHS (200 μmol/L). In the neurons co-cultured with WT ECs, TFR (810 mg/L) had notable inhibitory effects on these increases and decreases. Figure 6A–C also demonstrates that, although there were diminished trends in TFR’s inhibition of the increased RhoA protein level and activity in the neurons co-cultured with CSE KO ECs or with 3-MST KO ECs, as well as reduced trends in TFR’s inhibition of the decreased p-RhoA protein level in the neurons co-cultured with 3-MST KO ECs, significant differences remained when compared with the H/R group. However, Figure 6A shows that TFR lost its inhibitory effect on the H/R injury-induced decrease in p-RhoA protein level in the neurons co-cultured with CSE KO ECs. Furthermore, Figure 6D,E indicate that the decreases in RhoA protein level and activity caused by TFR in the neurons co-cultured with either CSE KO ECs or 3-MST KO ECs, as well as the increase in decreased p-RhoA protein level observed in the neurons co-cultured with 3-MST KO ECs, were significantly attenuated compared with those seen in the neurons co-cultured with WT ECs. These findings indicate that TFR may inhibit the upregulation of RhoA expression and activation, as well as the downregulation of RhoA phosphorylation induced by H/R injury in rat neurons, and this effect appears to be mediated through CSE and 3-MST in co-cultured ECs.
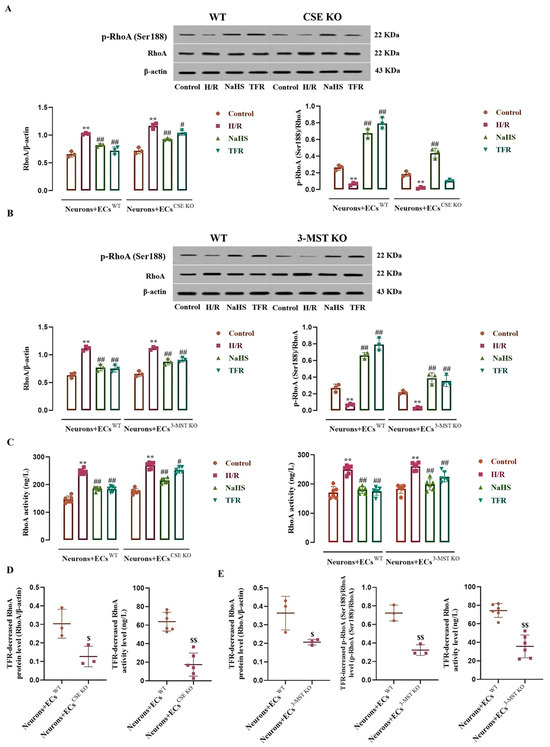
Figure 6.
Effects of TFR and NaHS on the RhoA protein expression, activity, and phosphorylation in the rat neurons co-cultured with cerebrovascular ECs subjected to H/R injury (mean ± SD, n = 3 or 6). (A) RhoA and p-RhoA (RhoA phosphorylated at Ser188) protein levels in the neurons co-cultured with WT ECs or CSE KO ECs. (B) RhoA and p-RhoA protein levels in the neurons co-cultured with WT ECs or 3-MST KO ECs. (C) RhoA activity in the neurons co-cultured with WT ECs, CSE KO ECs, and 3-MST KO ECs. (D) Comparison of the TFR-caused decreases in the H/R injury-increased RhoA protein level and activity in the neurons co-cultured with WT ECs and CSE KO ECs. (E) Comparison of the TFR-caused decreases in the H/R injury-increased RhoA protein level and activity and increase in the decreased p-RhoA protein level in the neurons co-cultured with WT ECs and 3-MST KO ECs. NaHS: 200 μmol/L; TFR: 810 mg/L. ** p < 0.01 vs. the control group; # p < 0.05, ## p < 0.01 vs. the H/R group; $ p < 0.05, $$ p < 0.01 vs. the Neurons+ECsWT group.
3.7. Effects of CSE or 3-MST KO in the ECs on TFR Inhibiting the H/R Injury-Increased ROCK2 Expression, Activity, and Phosphorylation in the Co-Cultured Neurons
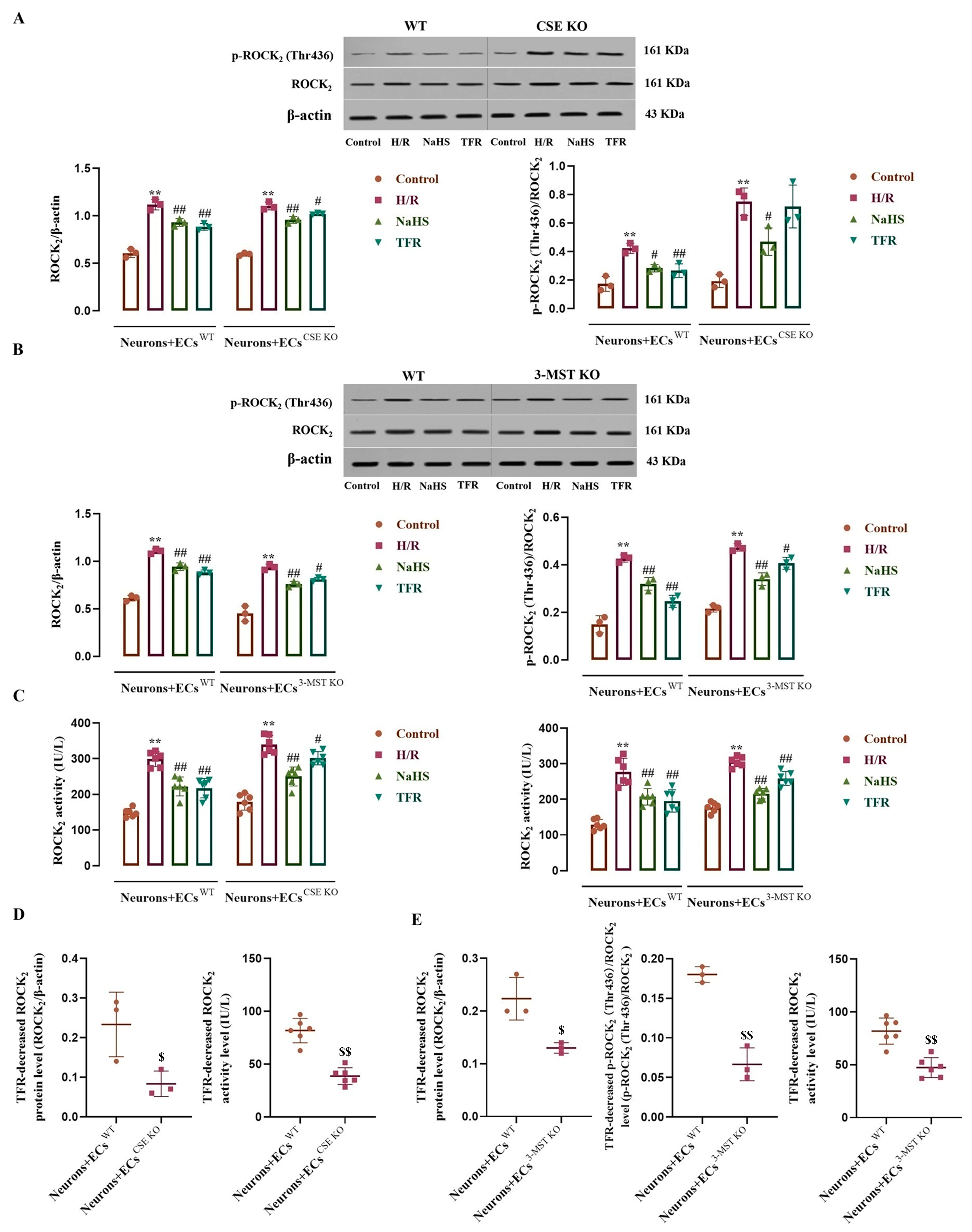
As shown in Figure 7A–C, H/R injury remarkably increased the ROCK2 and p-ROCK2 (ROCK2 phosphorylated at Thr436) protein levels and ROCK2 activity in the neurons co-cultured with WT ECs, CSE KO ECs, or 3-MST KO ECs compared with the control group. These increases were significantly inhibited by NaHS (200 μmol/L); except having no effect on the increased p-ROCK2 in the neurons co-cultured with CSE KO ECs, TFR (810 mg/L) notably attenuated the other increases. However, Figure 7D,E show that the TFR attenuated the H/R injury-increased ROCK2 and p-ROCK2 protein levels and ROCK2 activity, which were markedly weakened in the neurons co-cultured with CSE KO ECs or with 3-MST KO ECs compared with those in the neurons co-cultured with WT ECs. These results suggested that TFR could inhibit the H/R injury-increased ROCK2 expression, activity, and phosphorylation at the Thr436 site in rat neurons via the CSE and 3-MST in the co-cultured ECs.
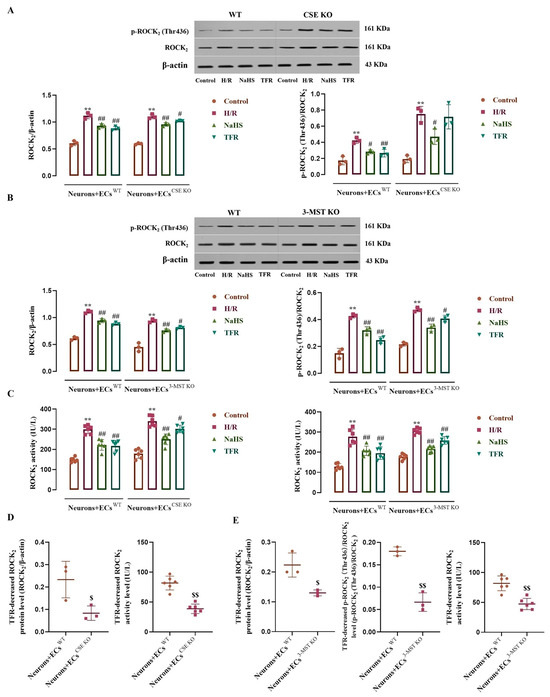
Figure 7.
Effects of TFR and NaHS on the H/R injury-increased ROCK2 protein expression, activity, and phosphorylation in the rat neurons co-cultured with cerebrovascular ECs (mean ± SD, n = 3 or 6). (A) ROCK2 and p-ROCK2 (ROCK2 phosphorylated at Thr436) protein levels in the neurons co-cultured with WT ECs or CSE KO ECs. (B) ROCK2 and p-ROCK2 protein levels in the neurons co-cultured with WT ECs or 3-MST KO ECs. (C) ROCK2 activity in the neurons co-cultured with WT ECs, CSE KO ECs, and 3-MST KO ECs. (D) Comparison of the TFR-decreased and the H/R injury-increased ROCK2 protein level and activity in the neurons co-cultured with WT ECs and CSE KO ECs. (E) Comparison of the TFR-decreased and the H/R injury-increased ROCK2 and p-ROCK2 protein levels and ROCK2 activity in the neurons co-cultured with WT ECs and 3-MST KO ECs. NaHS: 200 μmol/L; TFR: 810 mg/L. ** p < 0.01 vs. the control group; # p < 0.05, ## p < 0.01 vs. the H/R group; $ p < 0.05, $$ p < 0.01 vs. the Neurons+ECsWT group.
3.8. Effects of Endothelial-Derived H2S on H/R Injury and the RhoA-ROCK2 Pathway in the Co-Cultured Neurons
To observe the role of the RhoA-ROCK2 pathway in the effect of H2S produced by CSE or 3-MST in cerebrovascular ECs against neuronal H/R injury, the present study co-cultured rat neurons with WT, CSE KO, and 3-MST KO cerebrovascular ECs from both mice and rats.
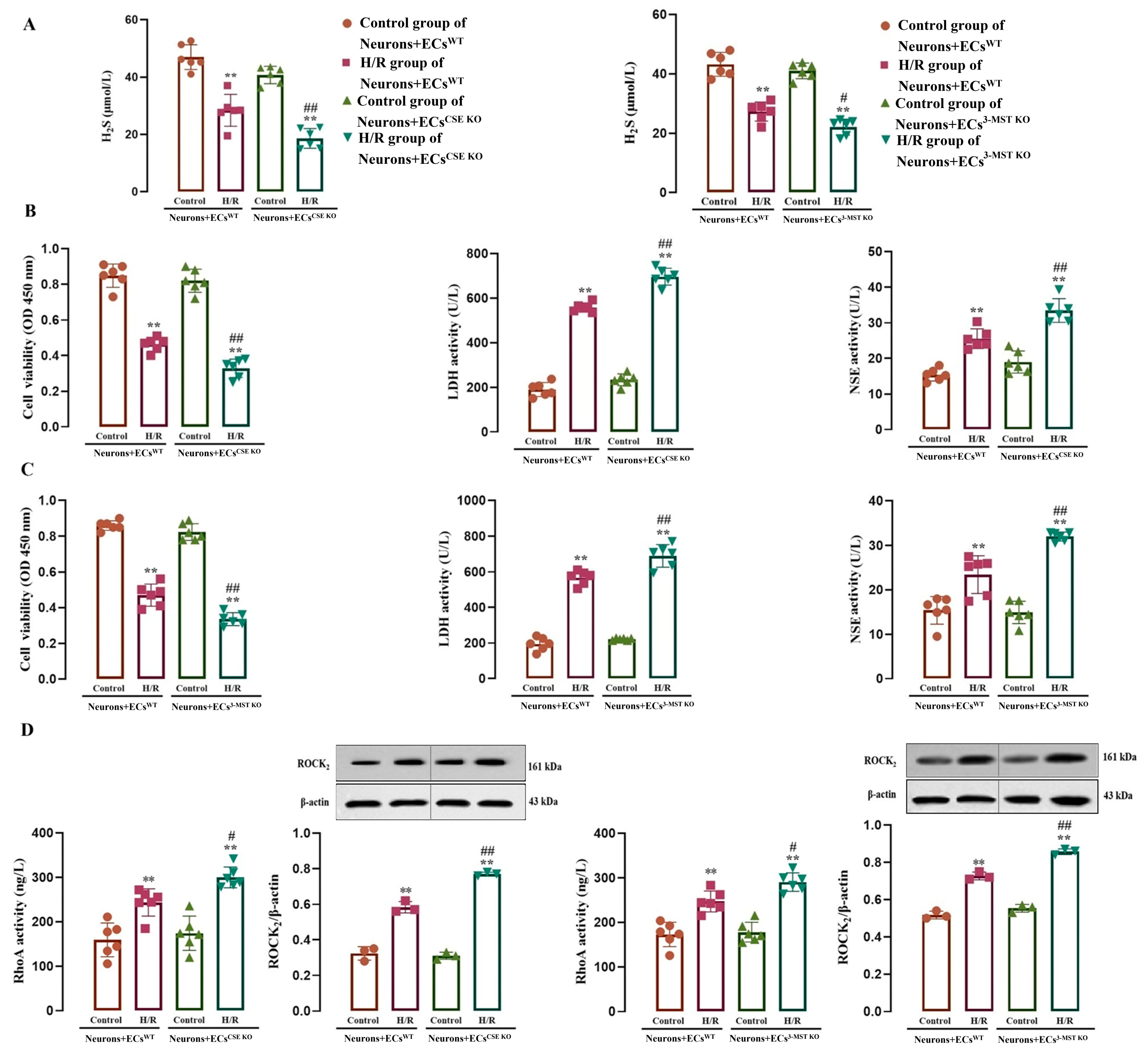
As shown in Figure 8, in the co-cultures of neurons with WT ECs, CSE KO ECs, and 3-MST KO ECs, the control groups did not show significant differences in H2S level and LDH and NSE activities in the culture medium, and no significant differences were observed in neuronal viability and RhoA activity and ROCK2 protein level in the co-cultured neurons. H/R exposure remarkably reduced the H2S level and neuronal viability, and increased the LDH, NSE, and RhoA activities and the ROCK2 protein level, suggesting that in the co-cultures, H/R exposure resulted in neuronal injury and the activation of the RhoA-ROCK2 pathway in the neurons, as well as a reduction in the H2S production.
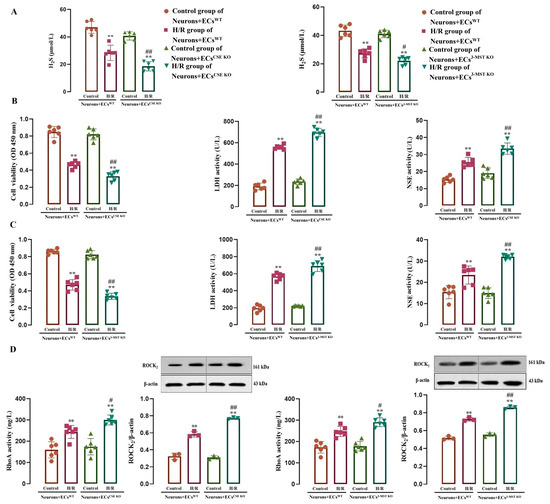
Figure 8.
Effect of the H2S produced by CSE or 3-MST in mouse or rat cerebrovascular ECs on H/R injury, RhoA activity, and ROCK2 protein expression in rat neurons co-cultured with the ECs (mean ± SD, n = 6 or 3). (A) H2S level in the co-cultured medium. (B) H/R injury in the neurons co-cultured with the WT ECs or CSE KO ECs. (C) H/R injury in the neurons co-cultured with the WT ECs or 3-MST KO ECs. (D) RhoA activity and ROCK2 protein level in neurons co-cultured with the WT ECs, CSE KO ECs, and 3-MST KO ECs. ** p < 0.01 vs. the control group; # p < 0.05, ## p < 0.01 vs. the H/R group in co-culture of Neurons+ECsWT.
Figure 8A–C further shows that the H/R exposure-induced decreases in the H2S level and neuronal viability and increases in the LDH and NSE activities were more significant in the co-culture of neurons with CSE KO ECs or 3-MST KO ECs than those in the co-culture of neurons with WT ECs, indicating that endothelial CSE and 3-MST mediated the H2S production in the co-cultured ECs during H/R injury and played a protective role against neuronal H/R injury. Figure 8D shows that during H/R injury, the RhoA activity and ROCK2 protein level also increased more significantly in the neurons co-cultured with CSE KO ECs or 3-MST KO ECs compared with those in the neurons co-cultured with WT ECs, suggesting that endothelial CSE and 3-MST exerted an inhibitory effect on the H/R injury-induced activation of the RhoA-ROCK2 pathway in co-cultured neurons.
4. Discussion
Ischemic brain injury includes neuronal and cerebral vascular damage, with cerebrovascular injury prior to neuronal lesion occurring [39,40]. Vascular ECs play a crucial role in the maintenance of cerebrovascular function. Injury to these cells leads to a decreased production of endothelial-derived relaxing factors, such as nitric oxide and H2S, resulting in impaired vasorelaxation, reduced CBF, and exacerbated ischemic brain injury [41]. A previous study showed that TFR had a protective effect against cerebral I/R injury, as indicated by the decrease in intracellular enzyme release from brain cells and the reduction in cerebral infarction [7]. Using a mouse model of cerebral I/R injury, the results of this study not only showed that TFR attenuated the releases of LDH and NSE from brain cells, but also, for the first time, reveal that TFR significantly mitigates spatial learning memory impairment and inquiry dysfunction induced by brain I/R injury in mice. Furthermore, the CSE inhibitor PPG markedly attenuates the protective effect of TFR on brain I/R injury in ROCK2 HK mice, suggesting that endogenous H2S is involved in the neuroprotective mechanism of TFR.
CBF is closely correlated to the occurrence and development of ischemic cerebral injury [42]. The present study indicated that TFR markedly increased the I/R injury-decreased CBF in WT and ROCK2 HK mice; this is beneficial to alleviate ischemic brain injury. Our vascular experiment further showed that TFR relaxed a rat cerebral artery, which is consistent with its increasing effect on the CBF. The RhoA-ROCK pathway is closely associated with cardiovascular and cerebrovascular physiological functions and pathological processes [43,44,45]. In the present study, the cerebral vasodilation of TFR in rats was markedly attenuated by the RhoA inhibitor CCG-1423 or ROCK2 inhibitor KD-025, suggesting an involvement of the RhoA-ROCK2 pathway in the TFR-induced cerebral vasorelaxation. In the cerebrovascular ECs of mice and rats, we observed that the KO of CSE or 3-MST substantially diminished TFR’s inhibitory effect on the reduction of H2S production and the activation of the RhoA-ROCK2 pathway induced by H/R injury. Combined with the result that PPG attenuated the increasing effect of TFR on the I/R injury-decreased CBF in ROCK2 HK mice, these data demonstrated that TFR promoted endothelial-derived H2S generation to inhibit the RhoA-ROCK2 pathway, thereby relaxing cerebral arteries and increasing CBF. This is one of the important mechanisms of the protective effect of TFR against ischemic brain injury.
The present study also observed that NaHS, an H2S donor, elicited an evident effect of inducing cerebral vasodilation in both WT and ROCK2 HK mice; however, this effect was significantly weaker in ROCK2 HK mice compared with WT mice. This is not only in agreement with a previous study that showed that endothelial-derived H2S can induce cerebral vasodilation by inhibiting the RhoA-ROCK pathway in rats [34], but also supports the above-mentioned finding that TFR relaxed cerebral arteries via promoting endothelial-derived H2S production to inhibit the RhoA-ROCK2 pathway.
There is a reciprocal inhibitory mechanism between H2S generation and the RhoA-ROCK pathway in the ECs, where endothelial-derived H2S inhibits the activation of the RhoA-ROCK pathway, and this pathway can in turn attenuate endothelial-derived H2S production [34]. This study demonstrated that the ROCK2 inhibitor KD-025 or the HK of ROCK2 significantly mitigated reductions in CSE and 3-MST protein expression, as well as H2S production in ECs following H/R injury, suggesting that the RhoA-ROCK2 pathway play a role in inhibiting the generation of H2S produced by endothelial CSE and 3-MST during H/R injury. This may contribute to the explanation for TFR relaxing the cerebral artery, as an increase in endothelial-derived H2S production induced by TFR mitigates the activation of the RhoA-ROCK2 pathway, which subsequently alleviates the inhibition on endothelial-derived H2S generation and enhances endothelium-dependent vasodilation in the cerebral arteries.
Endogenous H2S is not only an important endothelial-derived relaxing factor to act on blood vessels, but also a gaseous neurotransmitter for nerve cells. However, few studies have investigated the effects of endothelial-derived H2S on brain cells. In the co-culture of rat neurons with cerebrovascular ECs, our study showed that TFR had a significant protective effect against neuronal H/R injury; this is consistent with our previous study [46]. This study further suggests that the protective effect of TFR on neuronal H/R injury is mediated by H2S catalyzed by CSE and 3-MST in co-cultured ECs. It was also observed that both CSE- and 3-MST-catalyzed H2S play a role in the protective effect of TFR against neuronal H/R injury. However, following the KO of CSE in ECs, TFR no longer enhances H2S level in neurons or mitigates neuronal H/R damage. In contrast, after the KO of 3-MST, although the efficacy of TFR is diminished, it still increases H2S content in neurons and reduces neuronal damage from H/R. These findings suggest that TFR may primarily promote the production of H2S through CSE rather than via 3-MST within cerebrovascular ECs.
The overactivation of the RhoA-ROCK2 pathway in the brain leads to neuronal injury, whereas the inhibition of this pathway exerts a protective effect against cerebral I/R injury [47,48,49]. The phosphorylation of RhoA at Ser188 leads to an inactivation of itself and subsequent inhibitions on ROCK2 activity and expression, and H2S can protect rat neurons from H/R injury via promoting the phosphorylation of RhoA at Ser188 [24]. There are multiple phosphorylation sites in ROCK2, and phosphorylation at different sites does not obtain the same effects as ROCK2 activity. For instances, the phosphorylation at Tyr722 can inhibit ROCK2 activation [50], but the phosphorylation at Thr436 promotes the activation of ROCK2 and mediates the inhibitory effect of H2S on ROCK2 activity [27]. In the present study, the co-culture experiment indicated that TFR inhibited the H/R injury-induced increases in the RhoA and ROCK2 activities and p-ROCK2 (Thr436) protein level and decrease in the p-RhoA (Ser188) protein level in the neurons through the CSE and 3-MST in the co-cultured ECs. Together with the above-mentioned fact that endothelial-derived H2S is produced by CSE and 3-MST, these results demonstrated that TFR could inhibit the H/R injury-induced activation of the RhoA-ROCK2 pathway in the neurons through endothelial CSE- and 3-MST-produced H2S, which promotes the phosphorylation of RhoA at Ser188 and inhibits the phosphorylation of ROCK2 at Thr436, which aligns with our previous findings on the effects of exogenous H2S on the phosphorylation of RhoA at Ser188 and ROCK2 at Thr436 [24,27]. Furthermore, the present study also indicated that via the CSE and 3-MST in the co-cultured ECs, TFR attenuated the neuronal RhoA and ROCK2 protein levels increased by H/R injury. The results similarly indicated that TFR could inhibit the H/R injury-increased expression of the RhoA-ROCK2 pathway in the neurons through endothelial-derived H2S. Additionally, in the neurons and ECs co-culture systems, endothelial CSE and 3-MST were responsible for the production of H2S, which protected neurons from H/R injury by suppressing the H/R injury-induced upregulation of the RhoA-ROCK2 pathway. These findings collectively support the conclusion that TFR mitigates H/R injury-induced neuronal damage through the endothelial-derived H2S-mediated inhibition of the RhoA-ROCK2 signaling pathway.
While consistent with established mechanisms of the neuroprotective effects of neuronal CBS-derived H2S against ischemic brain injury [8] and exogenous H2S-mediated ROCK2 inhibition [27,50], our study innovatively identifies endothelial-derived H2S as the critical paracrine mediator regulating neuronal RhoA-ROCK2 signaling in a clinically relevant co-culture model. Nevertheless, the phosphorylase activity and other potential phosphorylation sites (e.g., the Tyr722 site) involved in ROCK2 have not been fully explored in this study. Additionally, although homozygous ROCK2 knockout results in embryonic lethality, the heterozygous model retains functional ROCK2 (~50% expression), which may obscure the full phenotypic consequences. These limitations will be addressed in our future investigations.
5. Conclusions
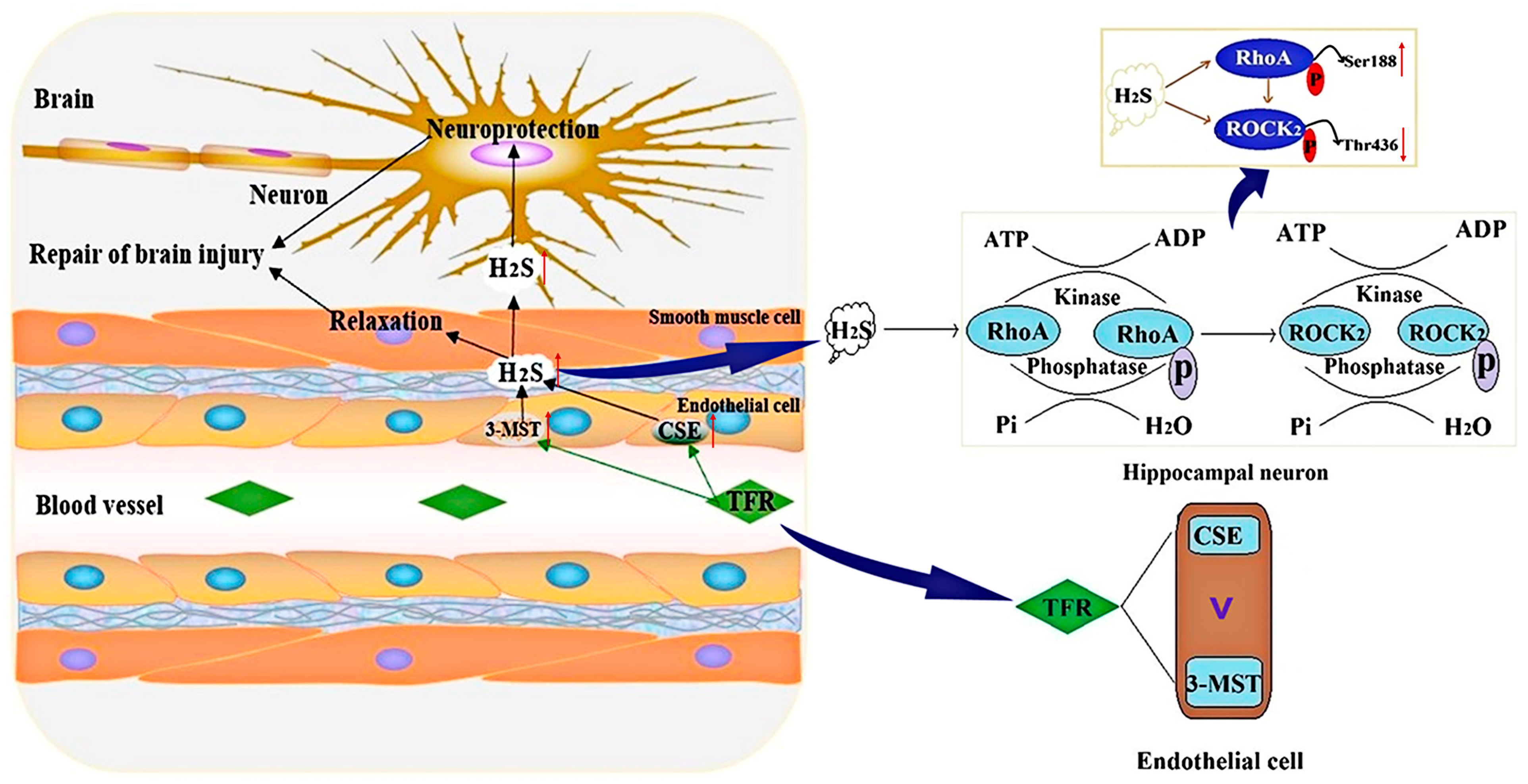
In conclusion, the present study demonstrated that TFR can suppress the RhoA-ROCK2 pathway by enhancing the production of H2S catalyzed by CSE and 3-MST in cerebrovascular ECs, thereby contributing to cerebrovascular relaxation and alleviating brain I/R injury. In addition, the endothelial-derived H2S promoted by TFR may be mainly catalyzed by CSE. TFR exerts a neuroprotective effect by promoting endothelial-derived H2S, which inhibits the activation and expression of the RhoA-ROCK2 pathway induced by H/R injury in neurons. The inhibitory effect of TFR on this pathway activation is at least partially mediated by endothelial-derived H2S facilitating the phosphorylation of RhoA at Ser188 while concurrently inhibiting the phosphorylation of ROCK2 at Thr436 (Figure 9). These findings are significant for elucidating the regulatory mechanism of the H2S–RhoA-ROCK2 pathway in TFR’s anti-ischemic brain injury effect and provide valuable reference for subsequent clinical investigations on TFR.
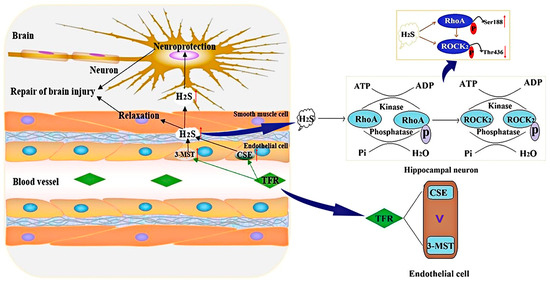
Figure 9.
Schematic representation of the protective mechanism of TFR against ischemic cerebral injury. By enhancing the production of H2S catalyzed by CSE and 3-MST in cerebrovascular ECs, TFR can promote the phosphorylation of RhoA at Ser188 while inhibiting the phosphorylation of ROCK2 at Thr436. This mechanism contributes to cerebrovascular relaxation and alleviates cerebral I/R injury.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.S., J.W., Z.C. and S.C.; methodology, X.S., J.W., Z.C. and S.C.; software, X.S., X.Z. and Y.L.; validation, X.S., J.W., Z.C. and S.C.; formal analysis, X.S., X.Z. and Y.L.; investigation, X.S., X.Z. and Y.L.; resources, J.W., Z.C. and S.C.; data curation, X.S., X.Z. and Y.L.; writing—original draft preparation, X.S., X.Z. and Y.L.; writing—review and editing, J.W., Z.C. and S.C.; visualization, X.S., J.W., Z.C. and S.C.; supervision, J.W., Z.C. and S.C.; project administration, J.W., Z.C. and S.C.; funding acquisition, J.W., Z.C. and S.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81973510), the Key Natural Science Research Projects of Anhui Universities (No. 2023AH050842), the Open Fund of Key Laboratory of Antiinflammatory and Immune Medicine, Ministry of Education, China (Anhui Medical University, No. Kfjj-2023-06), and the Clinical Research Project of Anhui University of Traditional Chinese Medicine in 2024 (No. 2024LC055).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The animal study protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of Anhui Medical University (Certification No. LLSC 20190575; Certification date: 1 March 2019).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets utilized and/or analyzed in the current study are available from the corresponding author(s) upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest in this work.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| 3-MST | 3-mercaptopyruvate sulfurtransferase |
| CBF | cerebral blood flow |
| CBS | cystathionine-β-synthase |
| CSE | cystathionine-γ-lyase |
| ECs | endothelial cells |
| H/R | hypoxia/reoxygenation |
| H2S | hydrogen sulfide |
| HK | heterozygote knockout |
| I/R | ischemia/reperfusion |
| KO | knockout |
| LDH | lactate dehydrogenase |
| NSE | neuron-specific enolase |
| ROCK | rho kinase |
| TFR | total flavones of Rhododendron |
| WT | wild-type |
Appendix A. In Vivo Animal Experimental Methods
Appendix A.1. Experimental Animals
WT and ROCK2 HK mice (C57BL/6J background) aged 8–10 weeks (body weight: 20–25 g) with a 1:1 female-to-male ratio were obtained from Shanghai Biomodel Organism Science & Technology Development Co., Ltd. All mice were housed in the Animal Center of Anhui Medical University under controlled environmental conditions (temperature: 22 ± 2 °C; humidity: 54 ± 2%) with free access to food and water. Prior to the experiment, animals were acclimatized to the facility for 7 days.
Appendix A.2. Experimental Design
Stratified randomization by sex and weight was performed using a computer-generated sequence. WT mice were randomly allocated to the following groups: sham group, I/R group, and 120 mg/kg TFR group. ROCK2 HK mice were randomly assigned to a sham group, I/R group, 120 mg/kg TFR group, and 50 mg/kg PPG + 120 mg/kg TFR group. The experimental unit was defined as the individual mouse, with all WT (3 groups × 6 mice) and ROCK2 HK (4 groups × 6 mice) animals independently housed and analyzed as single units. The target sample size (n = 6 per group) was determined by a priori power analysis using G*Power 3.1 software. Surgeons and outcome assessors were blinded to group assignments throughout the experiment.
Appendix A.3. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
Inclusion—all mice met the following conditions:
Healthy C57BL/6J mice (8–10 weeks old, body weight: 20–25 g), 50% male and 50% female.
No pre-operative neurological deficits.
Initial enrollment of 7–8 mice/group (target sample size: n = 6 per group) to account for potential attrition (e.g., intraoperative mortality or technical failure).
Exclusion:
Intraoperative mortality (occurred in <5% of cases; 2 mice excluded).
Postoperative body temperature abnormalities (>39.5 °C or <36.5 °C within 24 h).
Failed 2-VO surgery (verified by laser speckle blood flow imaging).
Appendix A.4. Blinding
During the experimental phase, surgeons were blinded to group assignments through the use of randomized coded labels. For data analysis, anonymized samples were independently evaluated by researchers who were unaware of the experimental conditions.
Appendix A.5. Outcome Measures
The unit for CBF was perfusion unit, where change rate of CBF = reperfusion blood flow/pre ischemic blood flow × 100%.
The units for serum LDH and NSE were both expressed as U/L.
The platform reaching latency was measured in second (s).
The number of times the mice crossed the location of the original hidden platform was recorded in “times”.
The moving distances of mice were measured in centimeters (cm).
The border area percentage was defined as the ratio of the distance traveled by mice in the border region to the total distance traveled.
References
- Stocchetti, N.; Zanier, E.R. Chronic impact of traumatic brain injury on outcome and quality of life: A narrative review. Crit. Care 2016, 20, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Jin, W. A comprehensive review of stroke-related signaling pathways and treatment in western medicine and traditional Chinese medicine. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1200061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Y.; Chen, J.; Shen, J. Herbal medicines for ischemic stroke: Combating inflammation as therapeutic targets. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2014, 9, 313–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.Y.; Zhou, S.F.; Gao, S.H.; Yu, Z.L.; Zhang, S.F.; Tang, M.K.; Sun, J.N.; Ma, D.L.; Han, Y.F.; Fong, W.F.; et al. New Perspectives on How to Discover Drugs from Herbal Medicines: CAM's Outstanding Contribution to Modern Therapeutics. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 627375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Xu, H.H.; Chen, X.L.; Hu, H.R.; Hu, K.M.; Chen, Z.W.; He, G.W. Total Flavone of Rhododendron Improves Cerebral Ischemia Injury by Activating Vascular TRPV4 to Induce Endothelium-Derived Hyperpolarizing Factor-Mediated Responses. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 2018, 8919867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; He, G.W.; Chen, Z.W. Protective Effect and Mechanism of Total Flavones from Rhododendron simsii Planch on Endothelium-Dependent Dilatation and Hyperpolarization in Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion and Correlation to Hydrogen Sulphide Release in Rats. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 2014, 904019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Zhang, J.H.; Hu, Y.Y.; Hu, D.H.; Gao, S.S.; Fan, Y.F.; Wang, Y.L.; Jiao, Y.; Chen, Z.W. Total Flavones of Rhododendron simsii Planch Flower Protect against Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury via the Mechanism of Cystathionine-gamma-Lyase-Produced H(2)S. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 2018, 8903849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Liu, B.; Ding, Y.; Li, X.; Sheng, J.; Guo, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wen, J. Total flavones of Rhododendron induce the transformation of A1/A2 astrocytes via promoting the release of CBS-produced H(2)S. Phytomedicine 2023, 111, 154666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, C.R.; Dillon, K.M.; Matson, J.B. A review of hydrogen sulfide (H(2)S) donors: Chemistry and potential therapeutic applications. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 149, 110–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, D.; Chu, X.; Bai, X.; Ma, W.; Yuan, H.; Qiu, J.; Liu, C.; Li, T.; Zhou, X.; Chen, W.; et al. l-Cysteine suppresses hypoxia-ischemia injury in neonatal mice by reducing glial activation, promoting autophagic flux and mediating synaptic modification via H(2)S formation. Brain Behav. Immun. 2018, 73, 222–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyson, R.M.; Palliser, H.K.; Wilding, N.; Kelly, M.A.; Chwatko, G.; Glowacki, R.; Berry, M.J.; Ni, X.; Wright, I.M.R. Microvascular circulatory dysregulation driven in part by cystathionine gamma-lyase: A new paradigm for cardiovascular compromise in the preterm newborn. Microcirculation 2019, 26, e12507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, S.P.; Dobariya, P.; Bellamkonda, H.; More, S.S. Role of 3-Mercaptopyruvate Sulfurtransferase (3-MST) in Physiology and Disease. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, J.Y.; Gao, S.S.; Chen, F.L.; Chen, S.; Wang, M.; Chen, Z.W. Role of CSE-Produced H(2)S on Cerebrovascular Relaxation via RhoA-ROCK Inhibition and Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Mice. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2019, 10, 1565–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, W.; Wen, J. H(2)S-mediated inhibition of RhoA/ROCK pathway and noncoding RNAs in ischemic stroke. Metab. Brain Dis. 2023, 38, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Wen, J. H(2)S-RhoA/ROCK Pathway and Glial Cells in Axonal Remyelination After Ischemic Stroke. Mol. Neurobiol. 2023, 60, 5493–5504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Magid, A.F. Rho kinase inhibitors: Potentially versatile therapy for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases and more. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 6, 371–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Chen, Z.; Wen, J. RhoA/ROCK signaling pathway and astrocytes in ischemic stroke. Metab. Brain Dis. 2021, 36, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, S.I.; Blaabjerg, M.; Freude, K.; Meyer, M. RhoA Signaling in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Cells 2022, 11, 1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, R.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Zou, Q.; Pu, Y.; Yu, C.; Cai, Z. Role of RhoA/ROCK signaling in Alzheimer’s disease. Behav. Brain Res. 2021, 414, 113481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, Y.; Yamashita, T. Axon growth inhibition by RhoA/ROCK in the central nervous system. Front. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, A.Y.; McLaurin, J. Rho-associated protein kinases as therapeutic targets for both vascular and parenchymal pathologies in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurochem. 2018, 144, 659–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, J.C.; Tonges, L.; Barski, E.; Michel, U.; Bahr, M.; Lingor, P. ROCK2 is a major regulator of axonal degeneration, neuronal death and axonal regeneration in the CNS. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ardito, F.; Giuliani, M.; Perrone, D.; Troiano, G.; Lo Muzio, L. The crucial role of protein phosphorylation in cell signaling and its use as targeted therapy (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 40, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wen, J.; Chen, Z. H2S protects hippocampal neurons against hypoxia-reoxygenation injury by promoting RhoA phosphorylation at Ser188. Cell Death Discov. 2021, 7, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, H.H.; Liang, S.W.; Chang, Z.F.; Lee, H.H. Ser1333 phosphorylation indicates ROCKI activation. J. Biomed. Sci. 2013, 20, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartmann, S.; Ridley, A.J.; Lutz, S. The Function of Rho-Associated Kinases ROCK1 and ROCK2 in the Pathogenesis of Cardiovascular Disease. Front. Pharmacol. 2015, 6, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, F.; Sheng, J.; Guo, Y.; Wen, J.; Chen, Z. Protection of H2S against Hypoxia/Reoxygenation Injury in Rat Hippocampal Neurons through Inhibiting Phosphorylation of ROCK2 at Thr436 and Ser575. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Li, Z.; Sharp, T.E., 3rd; Polhemus, D.J.; Carnal, J.; Moles, K.H.; Tao, Y.X.; Elrod, J.; Pfeilschifter, J.; Beck, K.F.; et al. Endothelial Cell Cystathionine gamma-Lyase Expression Level Modulates Exercise Capacity, Vascular Function, and Myocardial Ischemia Reperfusion Injury. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2020, 9, e017544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groger, M.; Hogg, M.; Abdelsalam, E.; Kress, S.; Hoffmann, A.; Stahl, B.; Calzia, E.; Wachter, U.; Vogt, J.A.; Wang, R.; et al. Effects of Sodium Thiosulfate During Resuscitation From Trauma-and-Hemorrhage in Cystathionine-gamma-Lyase Knockout Mice With Diabetes Type 1. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 878823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Chen, S.; Wen, J.Y.; Chen, Z.W. 3-Mercaptopyruvate sulfurtransferase/hydrogen sulfide protects cerebral endothelial cells against oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation-induced injury via mitoprotection and inhibition of the RhoA/ROCK pathway. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2020, 319, C720–C733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Patra, D.; Ghosh, P.; Banerjee, S.; Chowdhury, K.D.; Chakraborty, P.; Basu, A.; Sadhukhan, G.C. Activity of ROCKII not ROCKI promotes pulmonary metastasis of melanoma cells via modulating Smad2/3-MMP9 and FAK-Src-VEGF signalling. Cell. Signal. 2022, 97, 110389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, J.Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, S.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, Z.Y.; Zhang, F.; Xie, W.M.; Fan, Y.F.; Duan, J.S.; et al. Endothelium-derived hydrogen sulfide acts as a hyperpolarizing factor and exerts neuroprotective effects via activation of large-conductance Ca(2+) -activated K(+) channels. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 178, 4155–4175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, J.Y.; Wang, M.; Li, Y.N.; Jiang, H.H.; Sun, X.J.; Chen, Z.W. Vascular Protection of Hydrogen Sulfide on Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in Rats. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Guo, F.; Liu, X.; Xi, J.; Xue, M.; Guo, Y.; Wen, J.; Dong, L.; Chen, Z. Roles of the RhoA-ROCK Signaling Pathway in the Endothelial H(2)S Production and Vasodilation in Rat Cerebral Arteries. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 18498–18508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, K.; Wang, X.; Ding, Y.; Ren, Z.; Fang, J.; Sun, T.; Guo, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wen, J. CSE-Derived H(2)S Inhibits Reactive Astrocytes Proliferation and Promotes Neural Functional Recovery after Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in Mice Via Inhibition of RhoA/ROCK(2) Pathway. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2021, 12, 2580–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Tang, H.; Li, X.Y.; Deng, M.F.; Wei, N.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Y.F.; Wang, D.Q.; Fu, P.; Wang, J.Z.; et al. Targeting the HDAC2/HNF-4A/miR-101b/AMPK Pathway Rescues Tauopathy and Dendritic Abnormalities in Alzheimer's Disease. Mol. Ther. 2017, 25, 752–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Liu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Fang, F.; Li, X.; Wang, S.; Wen, J. Hydrogen sulphide protects mice against the mutual aggravation of cerebral ischaemia/reperfusion injury and colitis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 914, 174682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, S.; Randhawa, P.K.; Singh, N.; Jaggi, A.S. Preconditioning at a distance: Involvement of endothelial vasoactive substances in cardioprotection against ischemia-reperfusion injury. Life Sci. 2016, 151, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, C.; Jiang, J.; Xin, M.; Hao, J. Effect of TDP43-CTFs35 on Brain Endothelial Cell Functions in Cerebral Ischemic Injury. Mol. Neurobiol. 2022, 59, 4593–4611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulkadir, R.R.; Alwjwaj, M.; Othman, O.A.; Rakkar, K.; Bayraktutan, U. Outgrowth endothelial cells form a functional cerebral barrier and restore its integrity after damage. Neural Regen. Res. 2020, 15, 1071–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, M.; Hang, C.; Zhu, L.; Shi, J. Involvement of endothelial-derived relaxing factors in the regulation of cerebral blood flow. Neurol. Sci. 2011, 32, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tierradentro-Garcia, L.O.; Saade-Lemus, S.; Freeman, C.; Kirschen, M.; Huang, H.; Vossough, A.; Hwang, M. Cerebral Blood Flow of the Neonatal Brain after Hypoxic-Ischemic Injury. Am. J. Perinatol. 2023, 40, 475–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.Y.; Mo, D.; Tian, W.; Liu, X.X.; Zhou, Y.G.; Sun, Y.; Feng, Y.D.; Xiao, X.; Hao, X.W.; Zhang, H.N.; et al. Inhibition of RhoA/ROCK signaling pathway ameliorates hypoxic pulmonary hypertension via HIF-1alpha-dependent functional TRPC channels. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2019, 369, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Han, S.; Zheng, J.; Wang, H.; Li, S.; Li, J. EphA4 regulates white matter remyelination after ischemic stroke through Ephexin-1/RhoA/ROCK signaling pathway. Glia 2022, 70, 1971–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dokumacioglu, E.; Duzcan, I.; Iskender, H.; Sahin, A. RhoA/ROCK-1 Signaling Pathway and Oxidative Stress in Coronary Artery Disease Patients. Braz. J. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2022, 37, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Yu, X.M.; Chen, S.; Wen, J.Y.; Chen, Z.W. Total flavones of Rhododendron simsii Planch flower protect rat hippocampal neuron from hypoxia-reoxygenation injury via activation of BK(Ca) channel. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2020, 72, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Sun, L.; Ding, G.B.; Chen, L.; Jiang, L.; Wang, J.; Wu, J. Oxygen-Glucose Deprivation/Reoxygenation Induces Human Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cell Hyperpermeability Via VE-Cadherin Internalization: Roles of RhoA/ROCK2. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2019, 69, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sycheva, M.; Sustarich, J.; Zhang, Y.; Selvaraju, V.; Geetha, T.; Gearing, M.; Babu, J.R. Pro-Nerve Growth Factor Induces Activation of RhoA Kinase and Neuronal Cell Death. Brain Sci. 2019, 9, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Z. Effects of combined electroacupuncture and medication therapy on the RhoA/ROCK-2 signaling pathway in the striatal region of rats afflicted by cerebral ischemia. Brain Res. Bull. 2023, 205, 110828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, M.; Chen, S.; Xi, J.; Guan, Q.; Chen, W.; Guo, Y.; Chen, Z. Protection against Hypoxia-Reoxygenation Injury of Hippocampal Neurons by H2S via Promoting Phosphorylation of ROCK2 at Tyr722 in Rat Model. Molecules 2022, 27, 4567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).