Therapeutic Potential of Alpha-Lipoic Acid: Unraveling Its Role in Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Conditions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Properties of Alpha-Lipoic Acid (ALA)
3. ALA as an Antioxidant
4. Role of ALA in Inflammatory Diseases
4.1. ALA and Acute Pancreatitis
4.2. ALA and Joint Inflammation
4.3. ALA and Asthma
4.4. Effects of ALA in Sepsis and Associated Organ Injury
5. ALA and Cardiovascular Diseases
6. ALA and Neurological Disorders
7. ALA and Formation of H2S
8. Conclusions
9. Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Isenmann, E.; Trittel, L.; Diel, P. The effects of alpha lipoic acid on muscle strength recovery after a single and a short-term chronic supplementation—A study in healthy well-trained individuals after intensive resistance and endurance training. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2020, 17, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wollin, S.D.; Jones, P.J.H. α-Lipoic Acid and Cardiovascular Disease. J. Nutr. 2003, 133, 3327–3330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, L.J.; De, B.B.; Gunsalus, I.C.; Hornberger, C.S., Jr. Crystalline alpha-lipoic acid; a catalytic agent associated with pyruvate dehydrogenase. Science 1951, 114, 93–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bustamante, J.; Lodge, J.K.; Marcocci, L.; Tritschler, H.J.; Packer, L.; Rihn, B.H. α-Lipoic acid in liver metabolism and disease. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1998, 24, 1023–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiller, S.; DeKroon, R.; Hamlett, E.D.; Xu, L.; Osorio, C.; Robinette, J.; Winnik, W.; Simington, S.; Maeda, N.; Alzate, O. Alpha-lipoic acid supplementation protects enzymes from damage by nitrosative and oxidative stress. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Gen. Subj. 2016, 1860, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shay, K.P.; Moreau, R.F.; Smith, E.J.; Smith, A.R.; Hagen, T.M. Alpha-lipoic acid as a dietary supplement: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1790, 1149–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghibu, S.; Richard, C.; Vergely, C.; Zeller, M.; Cottin, Y.; Rochette, L. Antioxidant properties of an endogenous thiol: Alpha-lipoic acid, useful in the prevention of cardiovascular diseases. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2009, 54, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, P.R.; Stollmaier, J.G.; Christianson, D.W. Crystal structure of histone deacetylase 6 complexed with (R)-lipoic acid, an essential cofactor in central carbon metabolism. J. Biol. Chem. 2023, 299, 105228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafi, N.; Mehri, S.; Ghasemzadeh Rahbardar, M.; Hosseinzadeh, H. Effects of alpha lipoic acid on metabolic syndrome: A comprehensive review. Phytother. Res. 2022, 36, 2300–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, B.; Berkay Yılmaz, Y.; Antika, G.; Boyunegmez Tumer, T.; Fawzi Mahomoodally, M.; Lobine, D.; Akram, M.; Riaz, M.; Capanoglu, E.; Sharopov, F.; et al. Insights on the Use of α-Lipoic Acid for Therapeutic Purposes. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleiter, C.; Schug, B.; Hermann, R.; Elze, M.; Blume, H.; Gundert-Remy, U. Influence of food intake on the bioavailability of thioctic acid enantiomers. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1996, 50, 513–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maglione, E.; Marrese, C.; Migliaro, E.; Marcuccio, F.; Panico, C.; Salvati, C.; Citro, G.; Quercio, M.; Roncagliolo, F.; Torello, C.; et al. Increasing bioavailability of (R)-alpha-lipoic acid to boost antioxidant activity in the treatment of neuropathic pain. Acta Biomed. 2015, 86, 226–233. [Google Scholar]
- Capece, U.; Moffa, S.; Improta, I.; Di Giuseppe, G.; Nista, E.C.; Cefalo, C.M.A.; Cinti, F.; Pontecorvi, A.; Gasbarrini, A.; Giaccari, A.; et al. Alpha-Lipoic Acid and Glucose Metabolism: A Comprehensive Update on Biochemical and Therapeutic Features. Nutrients 2022, 15, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.-S.; Zhao, L.; Sui, J.; Li, X.; Huang, S.; Ding, H.; Zhu, H.; Chen, Z.-Y. Enzymatic Synthesis of a Novel Antioxidant Octacosanol Lipoate and Its Antioxidant Potency in Sunflower Oil. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 21781–21793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, W.-S.; Sun, Y.; Li, Z.; Yang, H.; Li, J.; Wang, Q.; Tan, C.; Zou, B. Enhanced antioxidant capacity of lipoic acid in different food systems through lipase-mediated esterification with phytosterols. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2022, 102, 7115–7125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanaida, M.; Lysiuk, R.; Mykhailenko, O.; Hudz, N.; Abdulsalam, A.; Gontova, T.; Oleshchuk, O.; Ivankiv, Y.; Shanaida, V.; Lytkin, D. Alpha-lipoic acid: An antioxidant with anti-aging properties for disease therapy. Curr. Med. Chem. 2025, 32, 23–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bast, A.; Haenen, G.R. Lipoic acid: A multifunctional antioxidant. Biofactors 2003, 17, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, P.; Dutta, S.; Moses, J.; Anandharamakrishnan, C. Recent developments in encapsulation of α-lipoic acid for enhanced bioavailability and stability. Qual. Assur. Saf. Crops Foods 2023, 15, 123–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, B.C.; Aruoma, O.I.; Evans, P.J.; O’Neill, C.; Van der Vliet, A.; Cross, C.E.; Tritschler, H.; Halliwell, B. Lipoic and dihydrolipoic acids as antioxidants. A critical evaluation. Free Radic. Res. 1994, 20, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navari-Izzo, F.; Quartacci, M.F.; Sgherri, C. Lipoic acid: A unique antioxidant in the detoxification of activated oxygen species. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2002, 40, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Superti, F.; Russo, R. Alpha-Lipoic Acid: Biological Mechanisms and Health Benefits. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tai, S.; Zheng, Q.; Zhai, S.; Cai, T.; Xu, L.; Yang, L.; Jiao, L.; Zhang, C. Alpha-Lipoic Acid Mediates Clearance of Iron Accumulation by Regulating Iron Metabolism in a Parkinson’s Disease Model Induced by 6-OHDA. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, K.F.B.; Akter, M.; Rahman, M.M.; Sikder, M.T.; Rahaman, M.S.; Yamasaki, S.; Kimura, G.; Tomihara, T.; Kurasaki, M.; Saito, T. Amelioration of Metal-Induced Cellular Stress by α-Lipoic Acid and Dihydrolipoic Acid through Antioxidative Effects in PC12 Cells and Caco-2 Cells. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szeląg, M.; Mikulski, D.; Molski, M. Quantum-chemical investigation of the structure and the antioxidant properties of α-lipoic acid and its metabolites. J. Mol. Model. 2012, 18, 2907–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skibska, B.; Kochan, E.; Stanczak, A.; Lipert, A.; Skibska, A. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of α-lipoic acid on lipopolysaccharide-induced oxidative stress in rat kidney. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. 2023, 71, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen Shay, K.; Moreau, R.F.; Smith, E.J.; Hagen, T.M. Is α-lipoic acid a scavenger of reactive oxygen species in vivo? Evidence for its initiation of stress signaling pathways that promote endogenous antioxidant capacity. IUBMB Life 2008, 60, 362–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, W.L.; Basit, H.; Zubair, M.; Burns, B. Pathology, inflammation. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.J.; Frei, B. Alpha-lipoic acid inhibits TNF-alpha-induced NF-kappaB activation and adhesion molecule expression in human aortic endothelial cells. FASEB J. 2001, 15, 2423–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, D.; Timmons, L.; Benson, J.T.; Dierkhising, R.A.; Chari, S.T. Incidence, prevalence, and survival of chronic pancreatitis: A population-based study. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 106, 2192–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, F.U.; Laemmerhirt, F.; Lerch, M.M. Etiology and Risk Factors of Acute and Chronic Pancreatitis. Visc. Med. 2019, 35, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.J.; Seo, S.W.; Choi, O.S.; Park, C.S. Alpha-lipoic acid protects against cholecystokinin-induced acute pancreatitis in rats. World J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 11, 4883–4885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulut, N.E.; Özkan, E.; Ekinci, O.; Dulundu, E.; Topaloğlu, Ü.; Şehirli, A.; Ercan, F.; Şener, G. Beneficial effects of alpha lipoic acid on cerulein-induced experimental acute pancreatitis in rats. Ulus. Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg. 2011, 17, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Lim, J.W.; Kim, H. α-lipoic acid inhibits cerulein/resistin-induced expression of interleukin-6 by activating peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ in pancreatic acinar cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2022, 26, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazes, J.M.W.; Luime, J.J. The epidemiology of early inflammatory arthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2011, 7, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hah, Y.S.; Sung, M.J.; Lim, H.S.; Jun, J.S.; Jeong, Y.G.; Kim, H.O.; Kim, J.; Hur, H.J.; Davaatseren, M.; Kwon, D.Y.; et al. Dietary alpha lipoic acid supplementation prevents synovial inflammation and bone destruction in collagen-induced arthritic mice. Rheumatol. Int. 2011, 31, 1583–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.Y.; Lee, C.-K.; Lee, K.-U.; Park, J.Y.; Cho, K.-J.; Cho, Y.S.; Lee, H.R.; Moon, S.H.; Moon, H.-B.; Yoo, B. Alpha-lipoic acid suppresses the development of collagen-induced arthritis and protects against bone destruction in mice. Rheumatol. Int. 2007, 27, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, H.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, H.N.; Kim, H.M.; Kwak, H.B.; Lee, S.; Kim, H.H.; Lee, Z.H. alpha-Lipoic acid inhibits inflammatory bone resorption by suppressing prostaglandin E2 synthesis. J. Immunol. 2006, 176, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.a.; Zhang, C.; Oo, W.M.; Fu, K.; Risberg, M.A.; Bierma-Zeinstra, S.M.; Neogi, T.; Atukorala, I.; Malfait, A.-M.; Ding, C.; et al. Osteoarthritis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2025, 11, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, M.; Zhang, W.; Qian, J. Therapeutic effect of α-lipoic acid on osteoarthritis patients and its influence on TLR 4/NF-κB and IL-23/IL-17 signaling pathway. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2019, 12, 1234–1241. [Google Scholar]
- Mirtaheri, E.; Gargari, B.P.; Kolahi, S.; Dehghan, P.; Asghari-Jafarabadi, M.; Hajalilou, M.; Shakiba Novin, Z.; Mesgari Abbasi, M. Effects of Alpha-Lipoic Acid Supplementation on Inflammatory Biomarkers and Matrix Metalloproteinase-3 in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2015, 34, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinyor, B.; Perez, L.C. Pathophysiology of asthma. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Sook Cho, Y.; Lee, J.; Lee, T.-H.; Young Lee, E.; Lee, K.-U.; Yeol Park, J.; Moon, H.-B. α-Lipoic acid inhibits airway inflammation and hyperresponsiveness in a mouse model of asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2004, 114, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Liao, X.; Wang, S.; Ni, Z.; Liang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Tao, D. Protective effect of maternal exposure to α-lipoic acid during pregnancy and lactation on susceptibility to OVAinduced neonatal asthma. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2022, 22, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Nguyen, T.; Piao, C.H.; Fan, Y.J.; Shin, D.-U.; Kim, S.Y.; Song, H.-J.; Song, C.H.; Shin, H.S.; Chai, O.H. Anti-allergic rhinitis activity of α-lipoic acid via balancing Th17/Treg expression and enhancing Nrf2/HO-1 pathway signaling. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahid, A.; Chambers, S.; Scott-Thomas, A.; Bhatia, M. Gut Microbiota and Liver Dysfunction in Sepsis: The Role of Inflammatory Mediators and Therapeutic Approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 13415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarino, M.; Perna, B.; Cesaro, A.E.; Maritati, M.; Spampinato, M.D.; Contini, C.; De Giorgio, R. 2023 Update on Sepsis and Septic Shock in Adult Patients: Management in the Emergency Department. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 3188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.-J.; Wei, H.; Hagen, T.; Frei, B. α-Lipoic acid attenuates LPS-induced inflammatory responses by activating the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 4077–4082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Guo, J.; Sun, H.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, R.; Yang, X. α-Lipoic acid attenuates LPS-induced liver injury by improving mitochondrial function in association with GR mitochondrial DNA occupancy. Biochimie 2015, 116, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petronilho, F.; Florentino, D.; Danielski, L.G.; Vieira, L.C.; Martins, M.M.; Vieira, A.; Bonfante, S.; Goldim, M.P.; Vuolo, F. Alpha-Lipoic Acid Attenuates Oxidative Damage in Organs After Sepsis. Inflammation 2016, 39, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadirci, E.; Altunkaynak, B.Z.; Halici, Z.; Odabasoglu, F.; Uyanik, M.H.; Gundogdu, C.; Suleyman, H.; Halici, M.; Albayrak, M.; Unal, B. Alpha-lipoic acid as a potential target for the treatment of lung injury caused by cecal ligation and puncture-induced sepsis model in rats. Shock 2010, 33, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Gao, L.; Jia, J.; Gong, X.; Zang, B.; Chen, W. α-Lipoic acid prolongs survival and attenuates acute kidney injury in a rat model of sepsis. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2014, 41, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Zhou, X.; Huang, J.; He, Y.; Wu, Q.; Huang, X.; Wu, K.; Wang, G.; Li, S.; Chen, X.; et al. Adjuvant Lipoic acid Injection in Sepsis treatment in China (ALIS study): Protocol for a randomised, single-blind, placebo-controlled trial. BMJ Open 2023, 13, e072897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, E.O.; Ballard, B.D.; Jan, A. Cardiovascular disease. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Vaduganathan, M.; Mensah, G.A.; Turco, J.V.; Fuster, V.; Roth, G.A. The Global Burden of Cardiovascular Diseases and Risk: A Compass for Future Health. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2022, 80, 2361–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudek, M.; Knutelska, J.; Bednarski, M.; Nowiński, L.; Zygmunt, M.; Bilska-Wilkosz, A.; Iciek, M.; Otto, M.; Żytka, I.; Sapa, J.; et al. Alpha lipoic acid protects the heart against myocardial post ischemia–reperfusion arrhythmias via KATP channel activation in isolated rat hearts. Pharmacol. Rep. 2014, 66, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Qi, B.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, X.; Feng, J.; Gao, W.; Li, T. α-Lipoic acid alleviates myocardial injury and induces M2b macrophage polarization after myocardial infarction via HMGB1/NF-kB signaling pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 121, 110435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skibska, B.; Goraca, A.; Skibska, A.; Stanczak, A. Effect of Alpha-Lipoic Acid on Rat Ventricles and Atria under LPS-Induced Oxidative Stress. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.; Sun, Z.; Tong, G.; Yi, W.; Ma, L.; Zhao, B.; Cheng, L.; Zhang, J.; Cao, F.; Yi, D. α-Lipoic acid reduces infarct size and preserves cardiac function in rat myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury through activation of PI3K/Akt/Nrf2 pathway. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Yin, L.; Sun, X.; Wu, J.; Dong, Z.; Hu, K.; Sun, A.; Ge, J. Alpha-lipoic acid protects against pressure overload-induced heart failure via ALDH2-dependent Nrf1-FUNDC1 signaling. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.J.; Lv, L.; Li, H.; Yu, D.M. Cardiac fibrosis and dysfunction in experimental diabetic cardiomyopathy are ameliorated by alpha-lipoic acid. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2012, 11, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ningrum, D.N.A.; Kung, W.-M. Challenges and Perspectives of Neurological Disorders. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naz, F.; Siddique, Y.H. Human Brain Disorders: A Review. Open Biol. J. 2020, 8, 6–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carocci, A.; Catalano, A.; Sinicropi, M.S.; Genchi, G. Oxidative stress and neurodegeneration: The involvement of iron. Biometals 2018, 31, 715–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifar, F.; Khalili, M.; Khaledyan, H.; Amiri Moghadam, S.; Izadi, A.; Azimi, A.; Shakouri, S.K. α-Lipoic acid, functional fatty acid, as a novel therapeutic alternative for central nervous system diseases: A review. Nutr. Neurosci. 2019, 22, 306–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, B.A.Q.; Santos, S.M.d.; Gato, L.d.S.; Espíndola, K.M.M.; Silva, R.K.M.d.; Davis, K.; Navegantes-Lima, K.C.; Burbano, R.M.R.; Romao, P.R.T.; Coleman, M.D.; et al. Alpha-Lipoic Acid Reduces Neuroinflammation and Oxidative Stress Induced by Dapsone in an Animal Model. Nutrients 2025, 17, 791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Dong, X.; Meng, Z.; Ji, L.; Kang, Y.; Liu, M.; Zhou, W.; Song, W. Alpha-lipoic acid alleviates cognitive deficits in transgenic APP23/PS45 mice through a mitophagy-mediated increase in ADAM10 α-secretase cleavage of APP. Alzheimer Res. Ther. 2024, 16, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, M.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yang, G. Alpha-lipoic acid improved motor function in MPTP-induced Parkinsonian mice by reducing neuroinflammation in the nigral and spinal cord. Neurosci. Lett. 2022, 781, 136669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-H.; He, Q.; Yu, J.-z.; Liu, C.-y.; Feng, L.; Chai, Z.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, H.-z.; Zhang, G.-X.; Xiao, B.-g.; et al. Lipoic acid protects dopaminergic neurons in LPS-induced Parkinson’s disease model. Metab. Brain Dis. 2015, 30, 1217–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrotra, A.; Kanwal, A.; Banerjee, S.K.; Sandhir, R. Mitochondrial modulators in experimental Huntington’s disease: Reversal of mitochondrial dysfunctions and cognitive deficits. Neurobiol. Aging 2015, 36, 2186–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salinthone, S.; Yadav, V.; Schillace, R.V.; Bourdette, D.N.; Carr, D.W. Lipoic acid attenuates inflammation via cAMP and protein kinase A signaling. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalili, M.; Azimi, A.; Izadi, V.; Eghtesadi, S.; Mirshafiey, A.; Sahraian, M.A.; Motevalian, A.; Norouzi, A.; Sanoobar, M.; Eskandari, G.; et al. Does Lipoic Acid Consumption Affect the Cytokine Profile in Multiple Sclerosis Patients: A Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Randomized Clinical Trial. Neuroimmunomodulation 2014, 21, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilska, A.; Dudek, M.; Iciek, M.; Kwiecień, I.; Sokołowska-Jezewicz, M.; Filipek, B.; Włodek, L. Biological actions of lipoic acid associated with sulfane sulfur metabolism. Pharmacol. Rep. 2008, 60, 225–232. [Google Scholar]
- Bilska-Wilkosz, A.; Iciek, M.; Kowalczyk-Pachel, D.; Górny, M.; Sokołowska-Jeżewicz, M.; Włodek, L. Lipoic Acid as a Possible Pharmacological Source of Hydrogen Sulfide/Sulfane Sulfur. Molecules 2017, 22, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, A.; Bhatia, M. Hydrogen Sulfide: A Versatile Molecule and Therapeutic Target in Health and Diseases. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zygmunt, M.; Dudek, M.; Bilska-Wilkosz, A.; Bednarski, M.; Mogilski, S.; Knutelska, J.; Sapa, J. Anti-inflammatory activity of lipoic acid in mice peritonitis model. Acta Pol. Pharm. 2013, 70, 899–904. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dugbartey, G.J.; Alornyo, K.K.; Adams, I.; Atule, S.; Obeng-Kyeremeh, R.; Amoah, D.; Adjei, S. Targeting hepatic sulfane sulfur/hydrogen sulfide signaling pathway with α-lipoic acid to prevent diabetes-induced liver injury via upregulating hepatic CSE/3-MST expression. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2022, 14, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Liu, K.; Xiao, L.; Jin, S.; Dong, J.; Teng, X.; Guo, Q.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Y. Alpha-lipoic acid regulates the autophagy of vascular smooth muscle cells in diabetes by elevating hydrogen sulfide level. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Basis Dis. 2018, 1864, 3723–3738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudek, M.; Bilska-Wilkosz, A.; Knutelska, J.; Mogilski, S.; Bednarski, M.; Zygmunt, M.; Iciek, M.; Sapa, J.; Bugajski, D.; Filipek, B.; et al. Are anti-inflammatory properties of lipoic acid associated with the formation of hydrogen sulfide? Pharmacol. Rep. 2013, 65, 1018–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
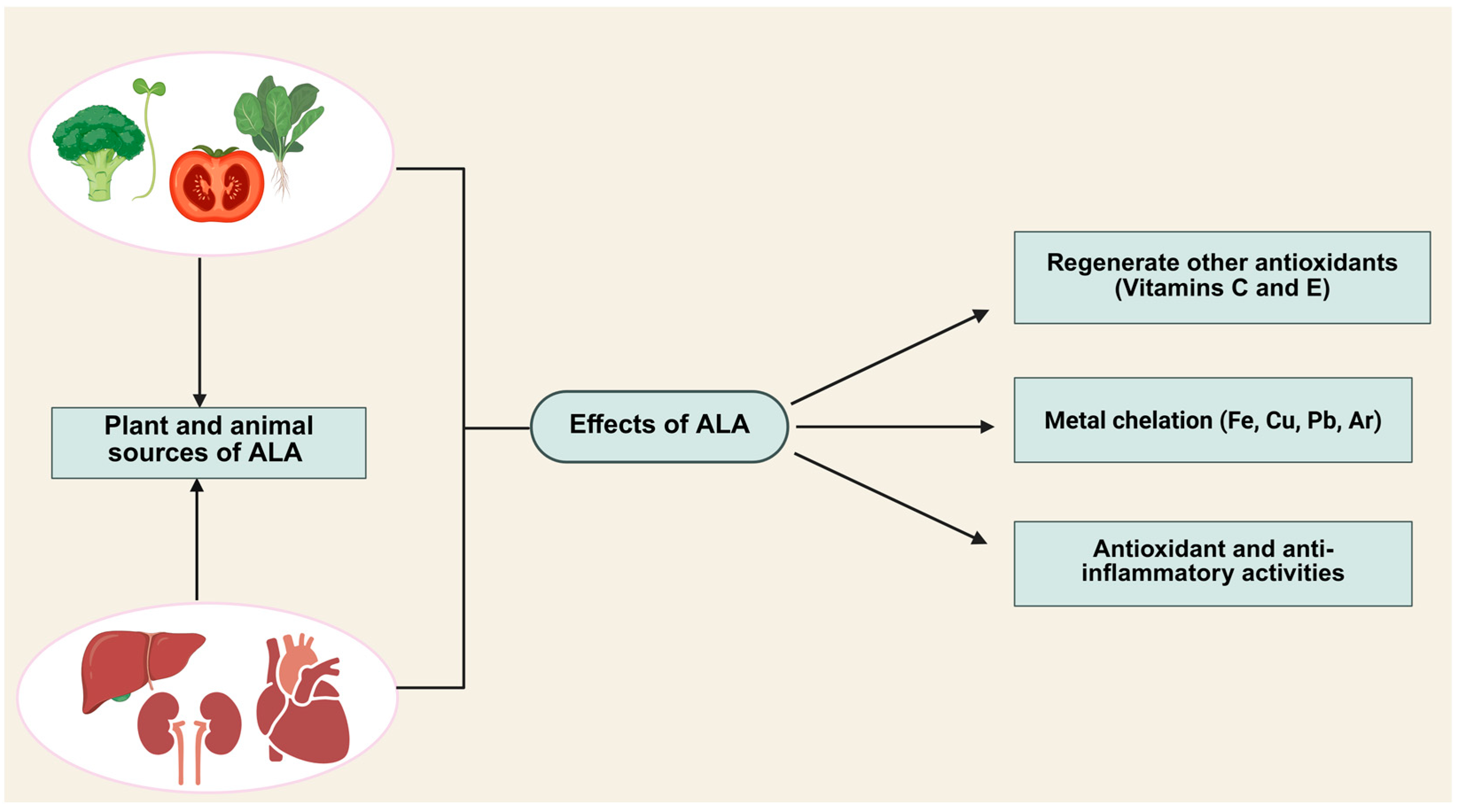
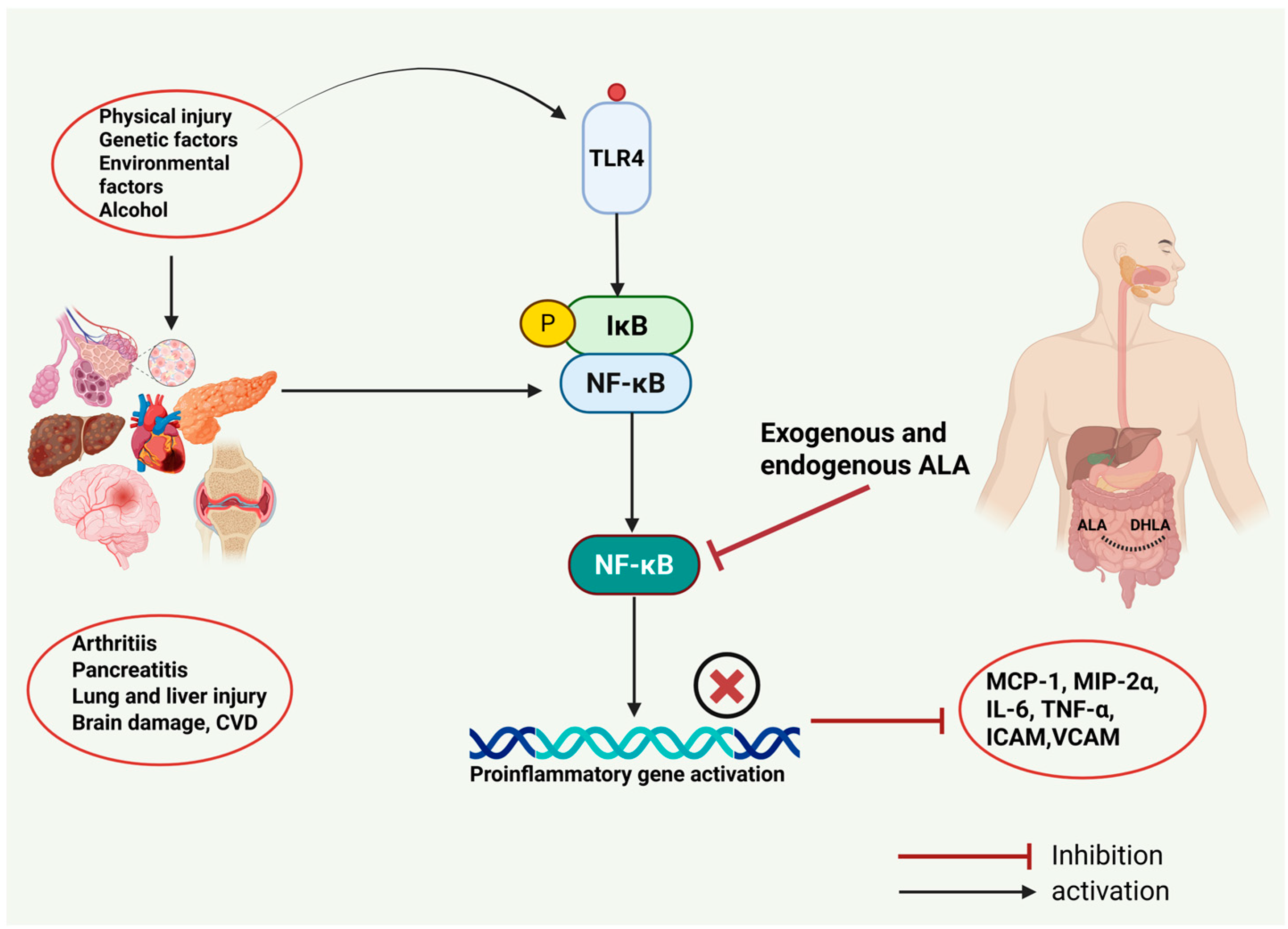
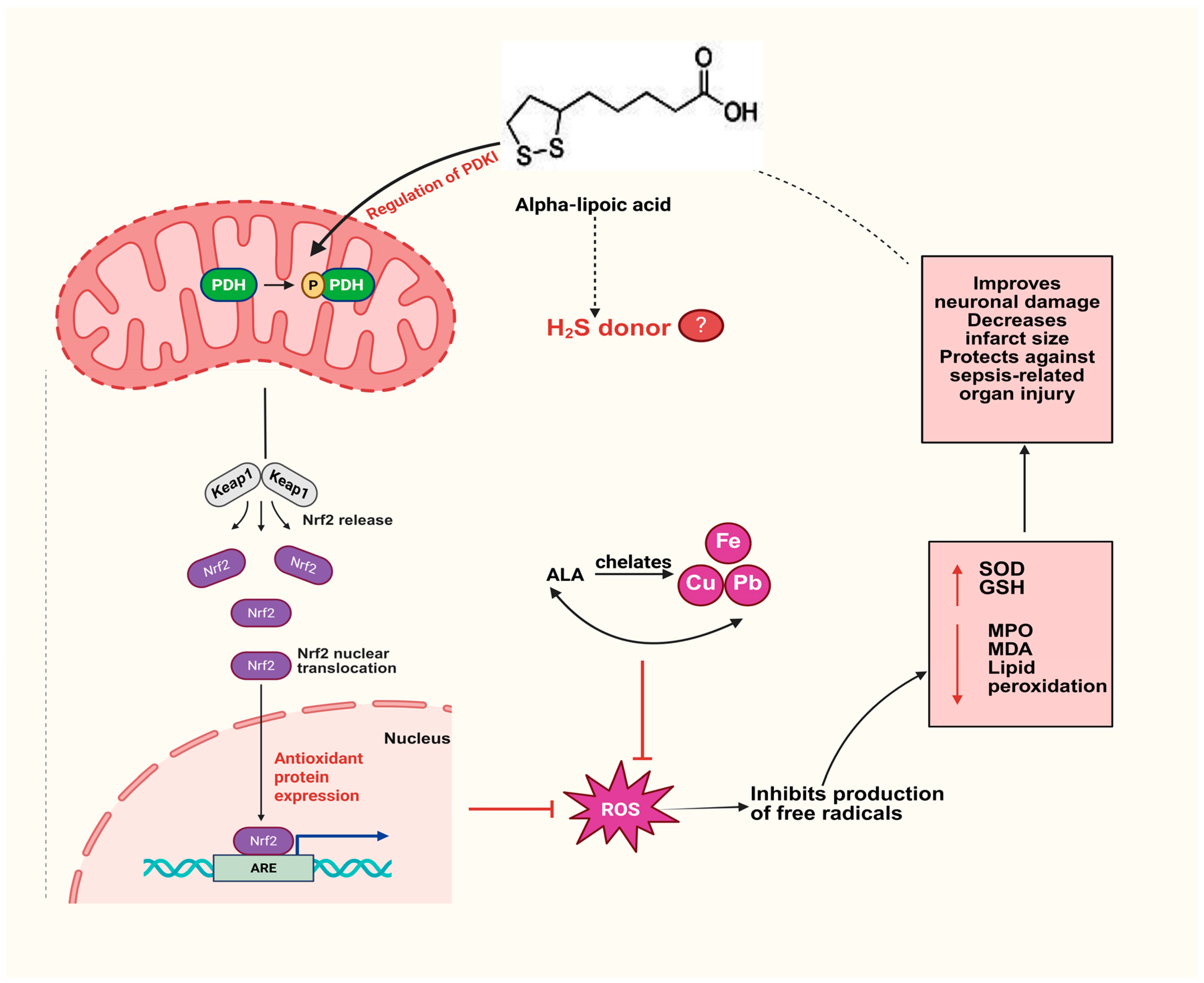
| Disease | Mechanism of Action | Disease Model | ALA Dose and Administration Route | Effects | Reference |
| Acute pancreatitis | Not completely understood | CKK-octapeptide-induced AP in rats (in vivo) | ALA was administered intraperitoneally at 1 mg/kg | Reduced levels of serum lipases and amylases and pancreatic weight–body weight ratio | [31] |
| Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects | Cerulein-induced AP in rats (in vivo) | ALA was administered intraperitoneally at dose of 100 mg/kg | Increased glutathione levels and decreased serum amylase and lipase levels and MDA and MPO activities Reduced necrosis and attenuated pancreatic tissue damage | [32] | |
| Activation of PPAR-γ signaling pathway | Cerulein/resistin-induced oxidative stress and inflammation in pancreatic acinar AR42J cells (in vitro) | Prophylactic treatment of AR42J cells with α-lipoic acid (at dose of 2 or 5 µM) | Decreased IL-6 expression and ROS production Increased expression of HO-1 and catalase | [33] | |
| Joint inflammation | Suppression of NF-κB signaling pathway | Collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) mouse model (in vivo) | 160 to 800 mg/kg per day (fed ALA diet) and 10 or 100 mg/kg (intraperitoneally) | Decreased production of IL-6, TNF-α, and IL-1β Decreased bone destruction and inhibition of production of TRAP-positive osteoclasts | [35,36] |
| Suppression of receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-B ligand (RANKL) expression | Osteoclastic bone damage with inflammation in mice and osteoclast cultures (in vivo and in vitro) | 10 µM and 50 µM (in vitro) and 25 mg/kg was administered intraperitoneally | Decreased PGE2 production and COX-2 activity | [37] | |
| Suppression of NF-κB and TLR-4 expression | 78 osteoarthritis patients (clinical study) | Oral administration of 0.6 g of ALA once | Decreased levels of serum TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-23, IL-6, and IL-17 | [39] | |
| Asthma | Antioxidant activities | OVA-induced allergic asthma mouse model (in vivo) | Different concentrations of ALA, i.e., 0%, 0.125%, 0.25%, 0.5%, and 1%, were administered through diet | Decreased intracellular ROS levels in lymphocytes, IL-4 and IL-5, eosinophils, neutrophils, and lymphocytes in BAL | [42] |
| Suppression of NF-κB signaling pathway | OVA-induced neonatal mice (in vivo) | 1% ALA was administered orally, mixed with mouse chow | Suppressed airway inflammation; lower wet-to-dry ratio in lungs; decreased levels of IL-4, IL-5, IL-13, and TNF-α; and lower levels of total IgE | [43] | |
| Activation of Nrf2/HO-1 and inhibition of NF-κB signaling pathway | (OVA)-induced allergic rhinitis (AR) mouse model (in vivo) | ALA was administered orally at various doses (2, 10, and 50 mg/kg) | Upregulation of Foxp3 and IL-10 Downregulation of IL-17, STAT3, and RORγ | [44] | |
| Sepsis-related organ injury | Activation of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway and suppression of NF-κB activity | LPS-induced endotoxemia mouse model (in vivo) | ALA was administered intraperitoneally at 100 mg/kg | Decreased levels of TNF-α, MCP-1, VCAM-1, ICAM-1, and E-selectin | [47] |
| Suppression of NF-κB activity | LPS-induced sepsis mouse model (in vivo) | ALA was administered intraperitoneally at 100 mg/kg | Acute liver injury Decreased levels of liver enzymes (ALT and AST) and TNF-α Improved mitochondrial function | [48] | |
| Antioxidant activities | CLP-induced sepsis model in rats (in vivo) | ALA was administered at dose of 200 mg/kg | Sepsis-associated acute kidney and liver injury Decreased MPO activity, lipid peroxidation in liver, and protein carbonylation in kidneys Increased SOD activity in kidneys | [49] | |
| Suppression of NF-κB activation | CLP-induced sepsis model in rats (in vivo) | ALA was administered by oral gavage at dose of 200 mg/kg | Acute lung injury Decreased TNF-α, IL-6, and MPO activity levels Increased GSH and SOD activities | [50] | |
| Cardiovascular diseases | Inhibition of NF-κB signaling pathway | LAD coronary artery ligation mouse model (in vivo) | ALA was administered intraperitoneally at dose of 30 mg/kg | Decreased infarct size and serum IL-1β, TNF-α, and CKMB levels | [56] |
| Suppression of JNK and p38 MAPK pathways | Streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats (in vivo) | ALA was administered intraperitoneally at dose of 100 mg/kg | Reduced cardiac fibrosis, improved heart function, restored ECM balance, and inhibited collagen deposition | [60] | |
| Activation of PI3K/Akt pathway | LAD coronary artery ligation-induced MI rat model (in vivo) | ALA was administered by tail vein injection at dose of 15 mg/kg | Decreased serum CKMB levels, LDH apoptosis, inflammation, and necrosis in cardiomyocytes | [58] | |
| Neurological diseases | Activation of autophagy and mitophagy | APP23/PS45 transgenic mouse model (in vivo) | ALA was administered intraperitoneally at dose of 5 mg/kg | Reduced amyloid plaque formation in brain and improved cognitive functions | [66] |
| Inhibition of NF-κB, iNOS, and TNF-α expression |
MPTP-induced neuroinflammation mouse model (in vivo) | ALA was administered intraperitoneally at dose of 50 mg/kg | Improved motor function and prevented activation of microglia in spinal cord and SN | [67] | |
| cAMP/PKA signaling pathway | 24 subjects suffering from MS (clinical study) | ALA was administered orally in form of capsules at dose of 600 mg | Markedly reduced IL-6 and IL-17 production and increased IL-10 synthesis | [70] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shahid, A.; Nasir, K.; Bhatia, M. Therapeutic Potential of Alpha-Lipoic Acid: Unraveling Its Role in Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Conditions. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 322. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47050322
Shahid A, Nasir K, Bhatia M. Therapeutic Potential of Alpha-Lipoic Acid: Unraveling Its Role in Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Conditions. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025; 47(5):322. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47050322
Chicago/Turabian StyleShahid, Aqsa, Khadeeja Nasir, and Madhav Bhatia. 2025. "Therapeutic Potential of Alpha-Lipoic Acid: Unraveling Its Role in Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Conditions" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47, no. 5: 322. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47050322
APA StyleShahid, A., Nasir, K., & Bhatia, M. (2025). Therapeutic Potential of Alpha-Lipoic Acid: Unraveling Its Role in Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Conditions. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 47(5), 322. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47050322






