Honokiol Inhibits Colorectal Cancer Cell Growth: Involvement of Hsp27 as a Molecular Target
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Isolation and Purification of HK
2.2. Analysis of HK
2.2.1. Qualitative Analysis on Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC)
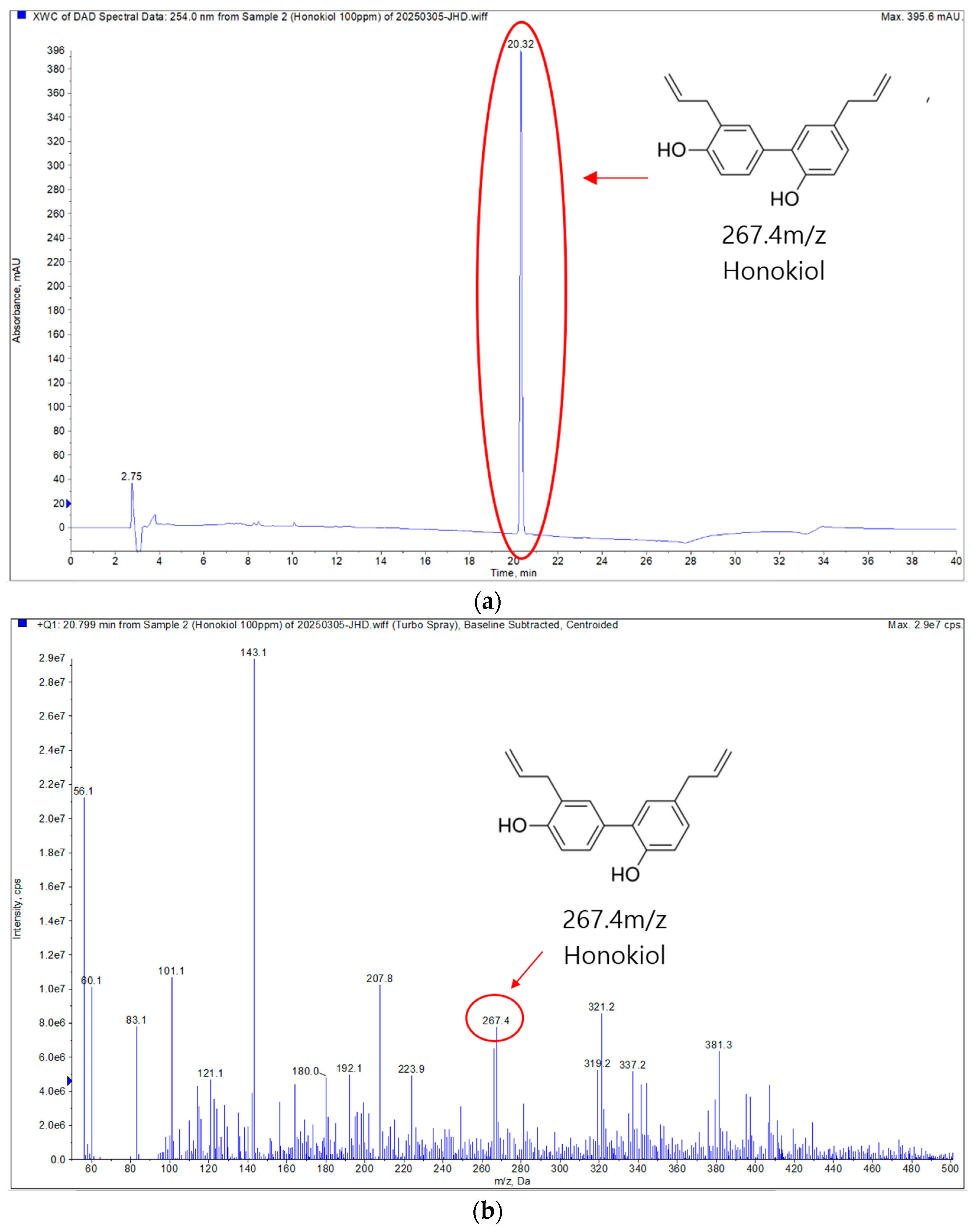
2.2.2. LC-MS/MS Analysis
2.2.3. NMR Analysis
2.2.4. Quantitative Analysis on High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
2.3. Reagents and Antibodies
2.4. Cell Lines and Cell Culture
2.5. Construction of Hsp27 Stable Knockdown CRC Cells
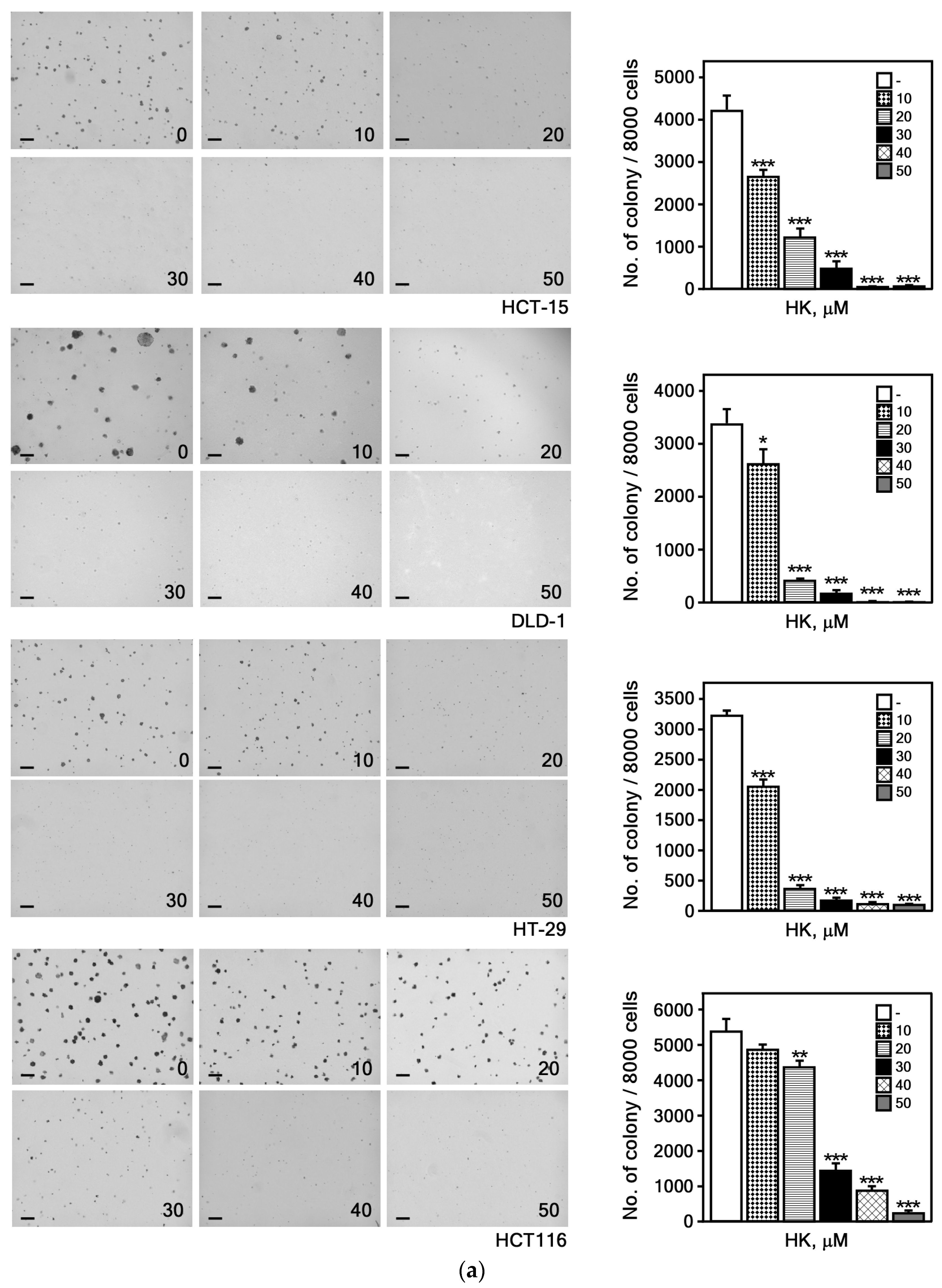
2.6. Anchorage-Independent CRC Cells Growing Assay
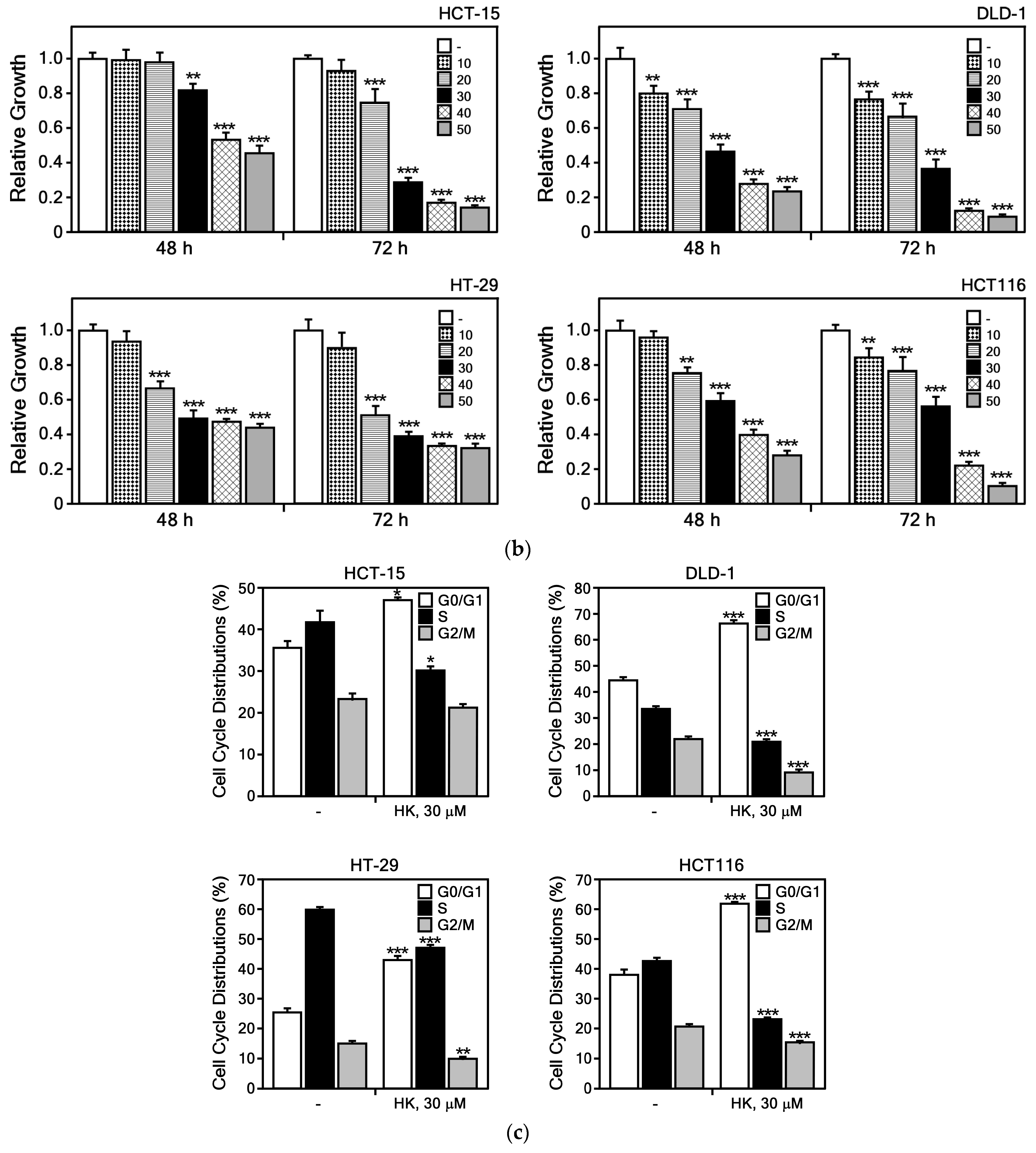
2.7. MTS Assay
2.8. Western Blot Analysis
2.9. Ex Vivo Pull-Down Assay
2.10. Site-Directed Mutagenesis
2.11. Cell Cycle Analysis
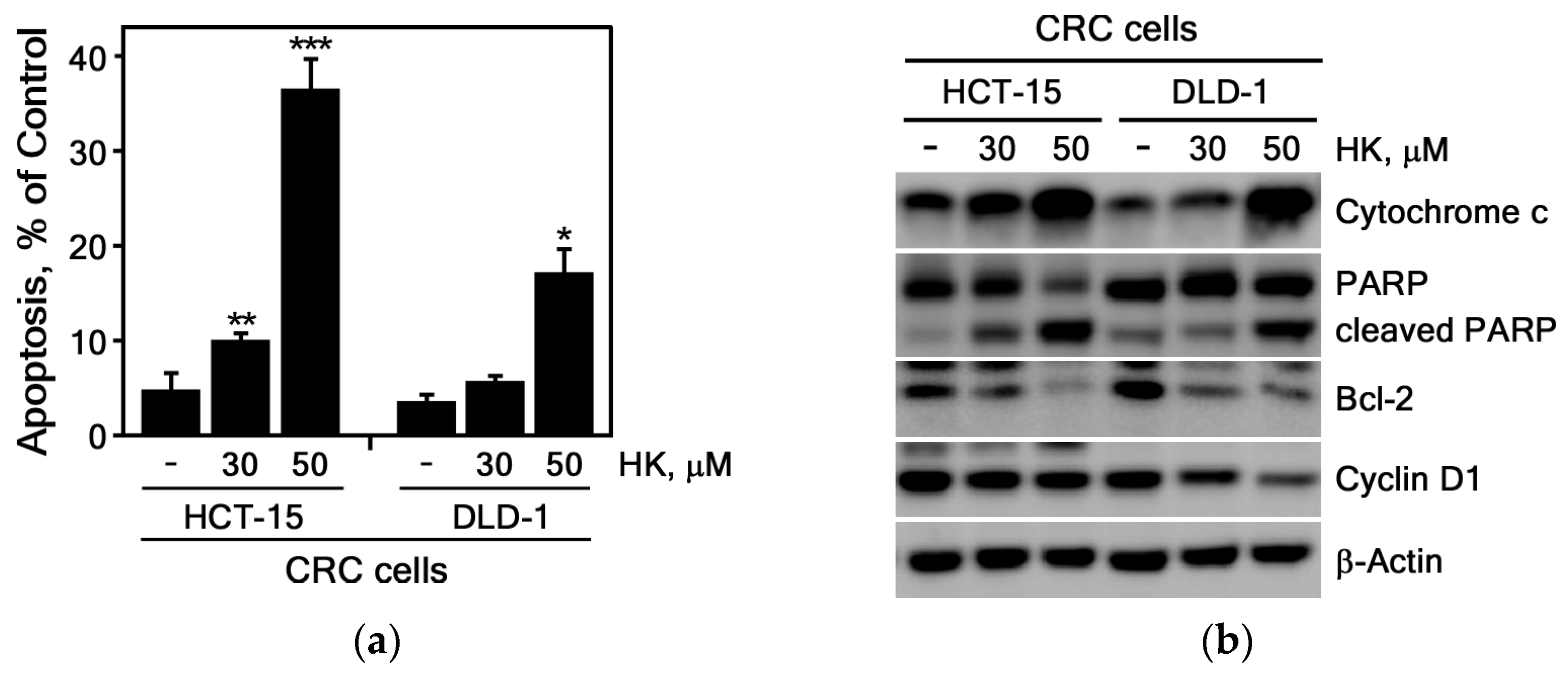
2.12. Apoptosis Analysis
2.13. Computational Modeling of Hsp27 with HK
2.14. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Isolation and Structural Characterization of HK
3.1.1. Purification of HK
3.1.2. Qualitative Analysis of Isolated Compound
3.1.3. NMR Analysis and Structural Elucidation of HK
3.1.4. Quantitative Chromatographic Analysis of M. officinalis 60% EtOH Extract (HPLC)
3.2. Biological Effects of HK on CRC Cells
3.2.1. HK Suppresses the Growth of CRC Cells
3.2.2. HK Induces Apoptosis in CRC Cells
3.3. Molecular Interaction Between HK and Hsp27
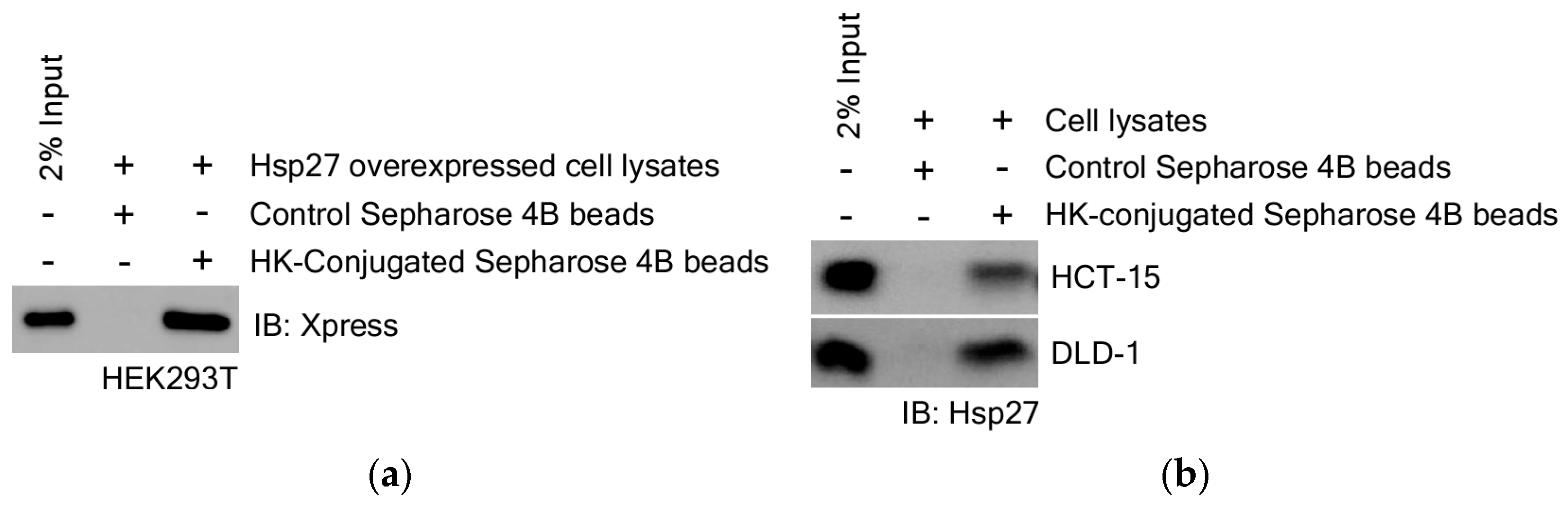
3.3.1. Identification for HK Direct Binding Protein
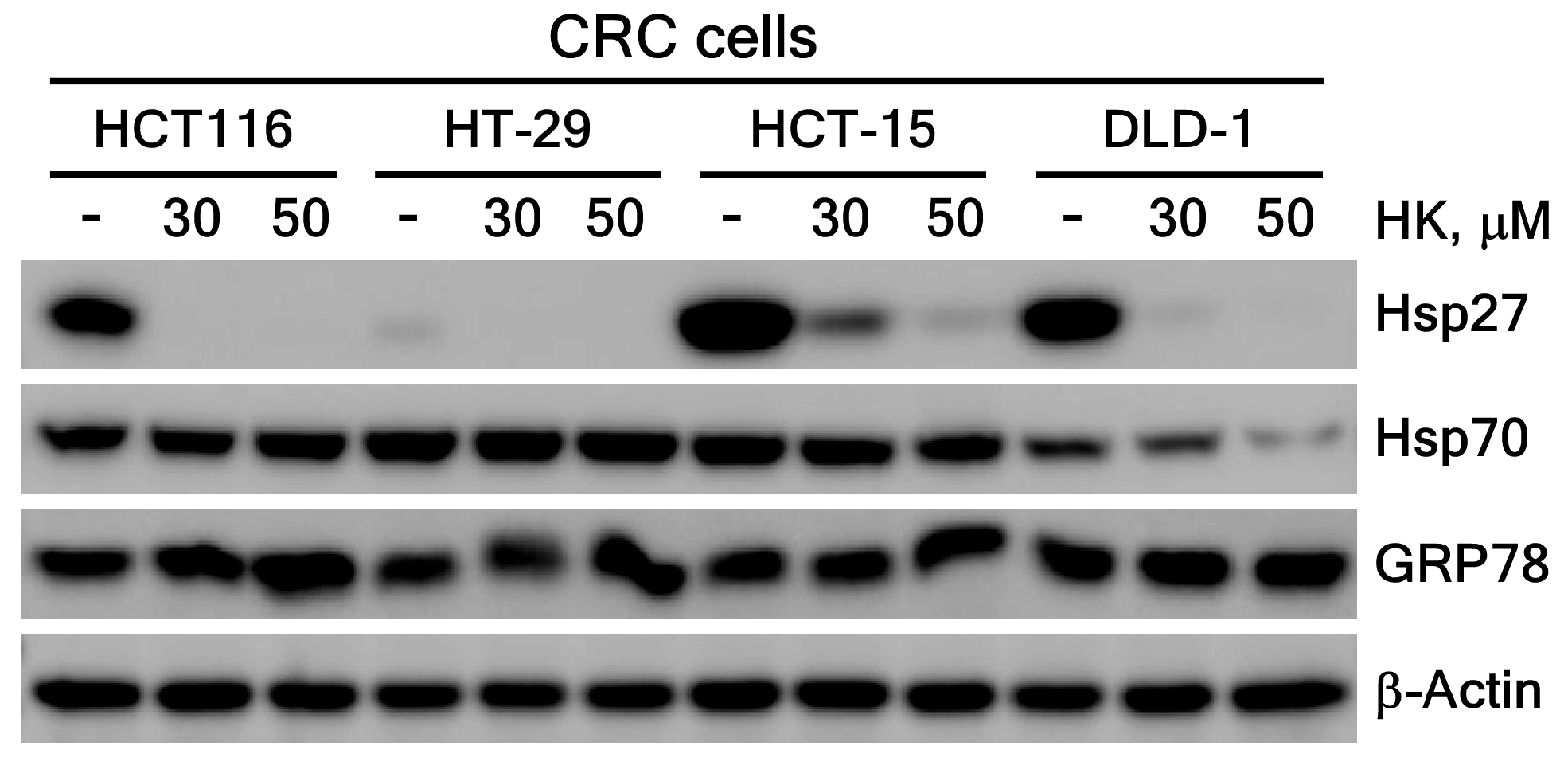
3.3.2. HK Suppresses Hsp27 Protein Expression Level
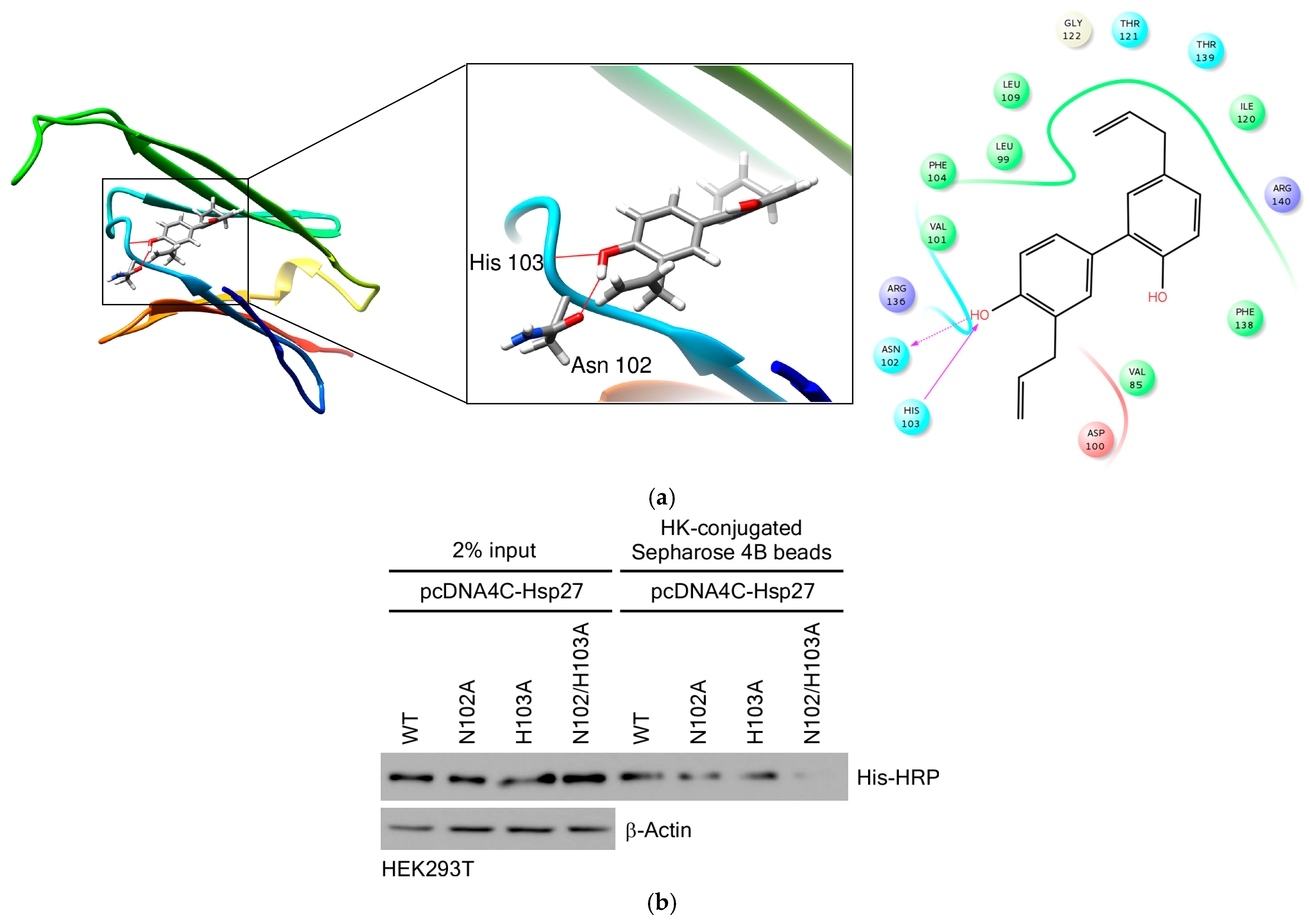
3.3.3. HK Directly Binds to Hsp27
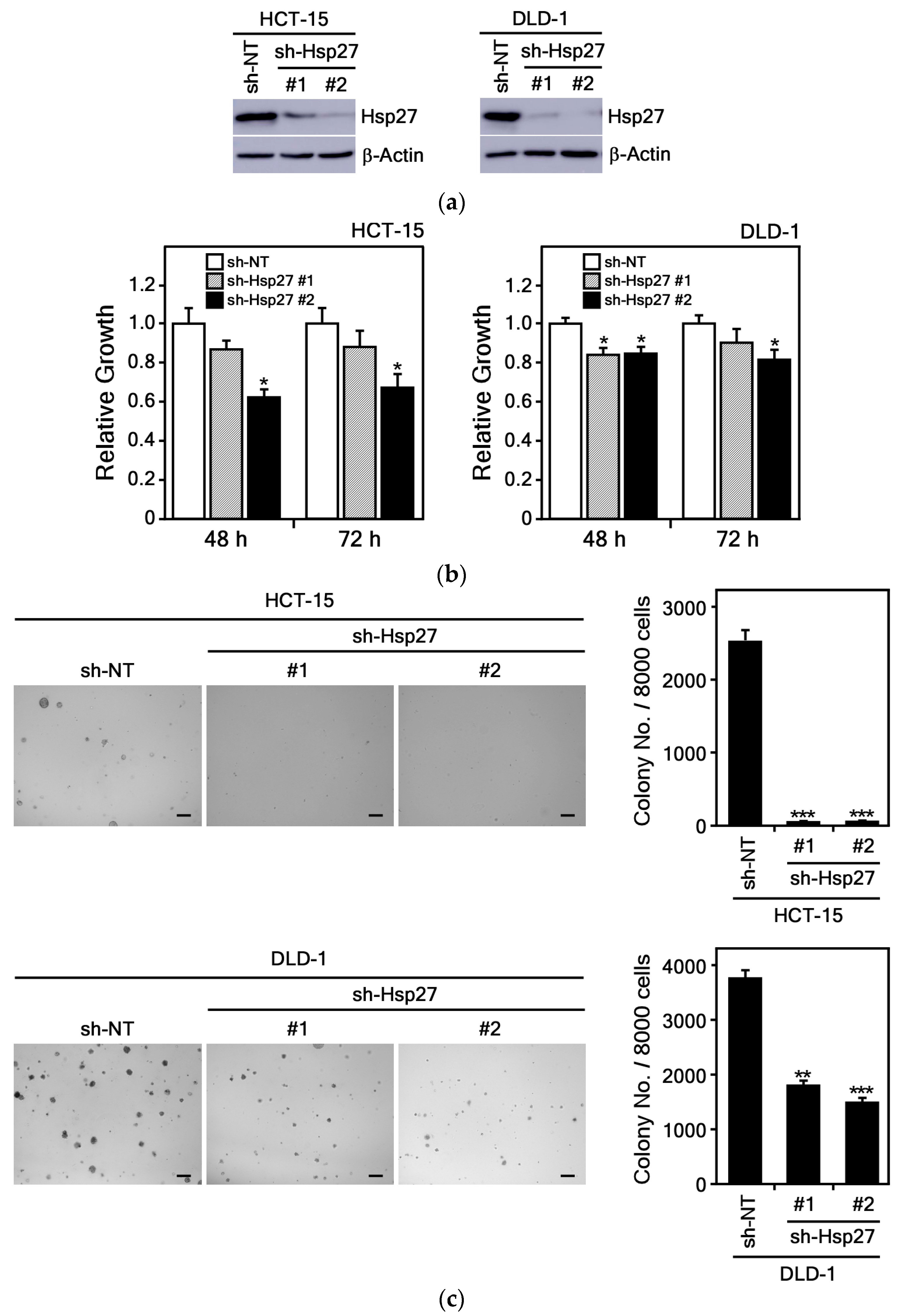
3.3.4. Hsp27 Knockdown Suppresses CRC Cell Growth
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HK | Honokiol |
| CRC | Colorectal cancer |
| HSPs | Heat Shock Proteins |
| Hsp27 | Heat shock protein 27 |
| HSP70 | Heat shock protein 70 |
| GRP78 | Glucose-regulating protein 78 |
| PARP | Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase |
| Bcl-2 | B-cell lymphoma-2 |
| IB | Immunoblotting |
| HEK293T | SV40 T antigen infected human embryonic kidney |
| His | Histidine |
| Asn | Asparagine |
| ODS column | Octadecylsilyl column |
| EtOH | Ethanol |
| TLC | Thin-layer chromatography |
| ECI | Extracted ion chromatogram |
| TIC | Total ion chromatogram |
| MPLC | Medium-performance liquid chromatography |
| HPLC | High-performance liquid chromatography |
| LC-MS/MS | Liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry |
| NMR | Nuclear magnetic resonance |
| PI | Propidium iodide |
| shRNA | Short hairpin RNA |
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gayet, J.; Zhou, X.P.; Duval, A.; Rolland, S.; Hoang, J.M.; Cottu, P.; Hamelin, R. Extensive characterization of genetic alterations in a series of human colorectal cancer cell lines. Oncogene 2001, 20, 5025–5032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sansom, O.J.; Meniel, V.S.; Muncan, V.; Phesse, T.J.; Wilkins, J.A.; Reed, K.R.; Vass, J.K.; Athineos, D.; Clevers, H.; Clarke, A.R. Myc deletion rescues Apc deficiency in the small intestine. Nature 2007, 446, 676–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xie, J. Targeting ferroptosis regulators by natural products in colorectal cancer. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1374722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Liu, C.; Wang, X.; Rong, K.; Zhu, M.; Duan, L.; Zheng, P.; Mi, Y. Exploring the mechanism of curcumin in the treatment of colon cancer based on network pharmacology and molecular docking. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1102581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarrica, A.; Kirika, N.; Romeo, M.; Salmona, M.; Diomede, L. Safety and Toxicology of Magnolol and Honokiol. Planta Medica 2018, 84, 1151–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Zhang, R.; Gu, X.; Zhao, Z.; Gao, Q.; Chen, M.; Wu, Q.; Xie, T.; Sui, X. Honokiol enhances the sensitivity of cetuximab in KRAS(G13D) mutant colorectal cancer through destroying SNX3-retromer complex. Theranostics 2024, 14, 5443–5460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, S.; Singh, S.; Piazza, G.A.; Contreras, C.M.; Panyam, J.; Singh, A.P. Honokiol: A novel natural agent for cancer prevention and therapy. Curr. Mol. Med. 2012, 12, 1244–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Ma, Y.; Liu, X.L.; Mu, L.; He, B.C.; Wu, K.; Sun, W.J. Anti-proliferative effect of honokiol on SW620 cells through upregulating BMP7 expression via the TGF-beta1/p53 signaling pathway. Oncol. Rep. 2020, 44, 2093–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Liu, P.; Deng, G.; Han, Y.; Chen, Y.; Cai, C.; Shen, H.; Deng, G.; Zeng, S. Honokiol induces ferroptosis in colon cancer cells by regulating GPX4 activity. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2021, 11, 3039–3054. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, R.; Fu, X.; Fan, J.; Wang, T.; Song, J.; Xu, T.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, S.Y. Semisynthesis and biological evaluation of novel honokiol thioethers against colon cancer cells HCT116 via inhibiting the transcription and expression of YAP protein. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2024, 107, 117762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrido, C.; Paul, C.; Seigneuric, R.; Kampinga, H.H. The small heat shock proteins family: The long forgotten chaperones. Int. J. Biochem. Cell. Biol. 2012, 44, 1588–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acunzo, J.; Katsogiannou, M.; Rocchi, P. Small heat shock proteins HSP27 (HspB1), alphaB-crystallin (HspB5) and HSP22 (HspB8) as regulators of cell death. Int. J. Biochem. Cell. Biol. 2012, 44, 1622–1631, Erratum in Int. J. Biochem. Cell. Biol. 2025, 5, 106862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, C.; Manero, F.; Gonin, S.; Kretz-Remy, C.; Virot, S.; Arrigo, A.P. Hsp27 as a negative regulator of cytochrome C release. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2002, 22, 816–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somu, P.; Mohanty, S.; Basavegowda, N.; Yadav, A.K.; Paul, S.; Baek, K.H. The Interplay between Heat Shock Proteins and Cancer Pathogenesis: A Novel Strategy for Cancer Therapeutics. Cancers 2024, 16, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodzek, P.; Damasiewicz-Bodzek, A.; Janosz, I.; Witek, L.; Olejek, A. Heat shock protein 27 (HSP27) in patients with ovarian cancer. Ginekol. Polska 2021, 92, 837–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Zhi, J.; Peng, X.; Zhong, X.; Xu, A. Clinical significance of HSP27 expression in colorectal cancer. Mol. Med. Rep. 2010, 3, 953–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, F.; Luo, D.; Li, Y.; Jin, Y.; Han, D.; Wang, Z.; Chen, B.; et al. HSPB1 facilitates chemoresistance through inhibiting ferroptotic cancer cell death and regulating NF-kappaB signaling pathway in breast cancer. Cell. Death Dis. 2023, 14, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baylot, V.; Andrieu, C.; Katsogiannou, M.; Taieb, D.; Garcia, S.; Giusiano, S.; Acunzo, J.; Iovanna, J.; Gleave, M.; Garrido, C.; et al. OGX-427 inhibits tumor progression and enhances gemcitabine chemotherapy in pancreatic cancer. Cell. Death Dis. 2011, 2, e221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, P.; Tian, Z. Atractylenolide I inhibits EMT and enhances the antitumor effect of cabozantinib in prostate cancer via targeting Hsp27. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 1084884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konda, J.D.; Olivero, M.; Musiani, D.; Lamba, S.; Di Renzo, M.F. Heat-shock protein 27 (HSP27, HSPB1) is synthetic lethal to cells with oncogenic activation of MET, EGFR and BRAF. Mol. Oncol. 2017, 11, 599–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Long, Y.; Liu, B.; Wang, X. Role of HSP27 in the multidrug sensitivity and resistance of colon cancer cells. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 19, 2021–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, D.H.; Lee, C.H.; Kwon, Y.; Kim, T.H.; Kim, E.J.; Jung, J.I.; Min, S.; Cheong, E.J.; Kim, S.; Kim, H.K.; et al. Effects of Alnus japonica Hot Water Extract and Oregonin on Muscle Loss and Muscle Atrophy in C2C12 Murine Skeletal Muscle Cells. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Liu, H.; Wang, P.; Hu, Y.; Yang, R.; Liu, F.; Kim, H.G.; Dong, Z.; Liu, K. Honokiol Inhibits Melanoma Growth by Targeting Keratin 18 in vitro and in vivo. Front. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 603472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berman, H.M.; Westbrook, J.; Feng, Z.; Gilliland, G.; Bhat, T.N.; Weissig, H.; Shindyalov, I.N.; Bourne, P.E. The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochberg, G.K.; Ecroyd, H.; Liu, C.; Cox, D.; Cascio, D.; Sawaya, M.R.; Collier, M.P.; Stroud, J.; Carver, J.A.; Baldwin, A.J.; et al. The structured core domain of alphaB-crystallin can prevent amyloid fibrillation and associated toxicity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E1562–E1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrödinger. Schrödinger Suite 2016; Schrödinger LLC.: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hua, H.; Chen, W.; Shen, L.; Sheng, Q.; Teng, L. Honokiol augments the anti-cancer effects of oxaliplatin in colon cancer cells. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2013, 45, 773–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Huang, H.; Park, S.; Zhang, H.; Park, S.; Kwon, W.; Kim, E.; Zhang, X.; Jang, S.; Yoon, D.; Choi, S.K.; et al. Targeting AKT with costunolide suppresses the growth of colorectal cancer cells and induces apoptosis in vitro and in vivo. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 40, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, S.; Lamb, H.K.; Brady, C.; Lefkove, B.; Bonner, M.Y.; Thompson, P.; Lovat, P.E.; Arbiser, J.L.; Hawkins, A.R.; Redfern, C.P. Inducing apoptosis of cancer cells using small-molecule plant compounds that bind to GRP78. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 109, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Couch, G.S.; Greenblatt, D.M.; Meng, E.C.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF Chimera--a visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Liu, L.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.F.; Yu, L.; Ding, Y.Q. Differential proteomic analysis of human colorectal carcinoma cell lines metastasis-associated proteins. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 133, 771–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontana, R.; Mattioli, L.B.; Biotti, G.; Budriesi, R.; Gotti, R.; Micucci, M.; Corazza, I.; Marconi, P.; Frosini, M.; Manfredini, S.; et al. Magnolia officinalis L. bark extract and respiratory diseases: From traditional Chinese medicine to western medicine via network target. Phytother. Res. 2023, 37, 2915–2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.L.; Man, K.M.; Huang, P.H.; Chen, W.C.; Chen, D.C.; Cheng, Y.W.; Liu, P.L.; Chou, M.C.; Chen, Y.H. Honokiol and magnolol as multifunctional antioxidative molecules for dermatologic disorders. Molecules 2010, 15, 6452–6465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheu, M.L.; Liu, S.H.; Lan, K.H. Honokiol induces calpain-mediated glucose-regulated protein-94 cleavage and apoptosis in human gastric cancer cells and reduces tumor growth. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, X.; Qi, M.; Huang, M.; Zhou, S.; Xiong, J. Honokiol Inhibits HIF-1alpha-Mediated Glycolysis to Halt Breast Cancer Growth. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 796763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pai, J.T.; Hsu, C.Y.; Hsieh, Y.S.; Tsai, T.Y.; Hua, K.T.; Weng, M.S. Suppressing migration and invasion of H1299 lung cancer cells by honokiol through disrupting expression of an HDAC6-mediated matrix metalloproteinase 9. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 1534–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Wu, T.; Ji, M.; Xiang, J.; Zou, Y.; Liao, Y. Honokiol suppress the PD-L1 expression to improve anti-tumor immunity in lung cancer. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 133, 112098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Wang, H.; Yang, F.; Gao, K.; Luo, S.; Bai, L.; Ma, K.; Liu, M.; Wu, S.; Chen, Z.; et al. Honokiol inhibits proliferation of colorectal cancer cells by targeting anoctamin 1/TMEM16A Ca2+ -activated Cl− channels. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 178, 4137–4154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.J.; Lin, C.I.; Wang, C.L.; Chao, J.I. Expression of survivin and p53 modulates honokiol-induced apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 2014, 115, 1888–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, N.; Xia, T.; Han, Y.; He, Q.J.; Zhao, R.; Ma, J.R. Synergistic antitumor effects of liposomal honokiol combined with cisplatin in colon cancer models. Oncol. Lett. 2011, 2, 957–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E.J.; Min, H.Y.; Chung, H.J.; Hong, J.Y.; Kang, Y.J.; Hung, T.M.; Youn, U.J.; Kim, Y.S.; Bae, K.; Kang, S.S.; et al. Down-regulation of c-Src/EGFR-mediated signaling activation is involved in the honokiol-induced cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2009, 277, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straume, O.; Shimamura, T.; Lampa, M.J.; Carretero, J.; Oyan, A.M.; Jia, D.; Borgman, C.L.; Soucheray, M.; Downing, S.R.; Short, S.M.; et al. Suppression of heat shock protein 27 induces long-term dormancy in human breast cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 8699–8704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, C.; Xu, Y.; Ge, H.; Li, G.; Wu, J. The clinicopathological and prognostic value of HSP27 in hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Onco Targets Ther. 2018, 11, 1293–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schweiger, T.; Nikolowsky, C.; Starlinger, P.; Traxler, D.; Zimmermann, M.; Birner, P.; Hegedus, B.; Dome, B.; Bergmann, M.; Mildner, M.; et al. Stromal expression of heat-shock protein 27 is associated with worse clinical outcome in patients with colorectal cancer lung metastases. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asada, Y.; Tsuruta, M.; Okabayashi, K.; Shigeta, K.; Ishida, T.; Shimada, T.; Suzumura, H.; Koishikawa, K.; Akimoto, S.; Hasegawa, H.; et al. Inhibition of Heat-shock Protein 27 Reduces 5-Fluorouracil-acquired Resistance in Human Colon Cancer Cells. Anticancer Res. 2021, 41, 1283–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, B.; Qi, C.; Liu, B.; Lin, Y.; Fu, T.; Zeng, Q. Increased HSP27 correlates with malignant biological behavior of non-small cell lung cancer and predicts patient’s survival. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiota, M.; Bishop, J.L.; Nip, K.M.; Zardan, A.; Takeuchi, A.; Cordonnier, T.; Beraldi, E.; Bazov, J.; Fazli, L.; Chi, K.; et al. Hsp27 regulates epithelial mesenchymal transition, metastasis, and circulating tumor cells in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 3109–3119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Tao, X.; Jin, G.; Jin, H.; Wang, N.; Hu, F.; Luo, Q.; Shu, H.; Zhao, F.; Yao, M.; et al. A Targetable Molecular Chaperone Hsp27 Confers Aggressiveness in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Theranostics 2016, 6, 558–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelj-Garolla, B.; Kumano, M.; Beraldi, E.; Nappi, L.; Rocchi, P.; Ionescu, D.N.; Fazli, L.; Zoubeidi, A.; Gleave, M.E. Hsp27 Inhibition with OGX-427 Sensitizes Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells to Erlotinib and Chemotherapy. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2015, 14, 1107–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Shen, F.; Qi, P.; Zhai, Z.; Wang, Z. miR-541-3p enhances the radiosensitivity of prostate cancer cells by inhibiting HSP27 expression and downregulating beta-catenin. Cell. Death Discov. 2021, 7, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karademir, D.; Ozgur, A. Small molecule heat shock protein 27 inhibitor J2 decreases ovarian cancer cell proliferation via induction of apoptotic pathways. Med. Oncol. 2023, 40, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocchi, P.; Beraldi, E.; Ettinger, S.; Fazli, L.; Vessella, R.L.; Nelson, C.; Gleave, M. Increased Hsp27 after androgen ablation facilitates androgen-independent progression in prostate cancer via signal transducers and activators of transcription 3-mediated suppression of apoptosis. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 11083–11093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parcellier, A.; Schmitt, E.; Gurbuxani, S.; Seigneurin-Berny, D.; Pance, A.; Chantome, A.; Plenchette, S.; Khochbin, S.; Solary, E.; Garrido, C. HSP27 is a ubiquitin-binding protein involved in I-kappaBalpha proteasomal degradation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2003, 23, 5790–5802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Lv, Z.; Weng, X.; Ye, S.; Shen, K.; Li, M.; Qin, Y.; Hu, C.; Zhang, C.; Wu, J.; et al. Hsp27 Acts as a Master Molecular Chaperone and Plays an Essential Role in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression. Digestion 2015, 92, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halasi, M.; Hitchinson, B.; Shah, B.N.; Varaljai, R.; Khan, I.; Benevolenskaya, E.V.; Gaponenko, V.; Arbiser, J.L.; Gartel, A.L. Honokiol is a FOXM1 antagonist. Cell. Death Dis. 2018, 9, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, X.; Jiang, X.; Zhao, M.; Su, K.; Tang, M.; Hong, F.; Ye, N.; Zhang, R.; Li, N.; Wang, L.; et al. Identification of the target protein and molecular mechanism of honokiol in anti-inflammatory action. Phytomedicine 2023, 109, 154617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.M.; Anandharaj, A.; Upadhyaya, P.; Kirtane, A.R.; Kim, J.H.; Hong, K.H.; Panyam, J.; Kassie, F. Honokiol suppresses lung tumorigenesis by targeting EGFR and its downstream effectors. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 57752–57769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermawan, A.; Putri, H.; Hanif, N.; Fatimah, N.; Prasetio, H.H. Identification of potential target genes of honokiol in overcoming breast cancer resistance to tamoxifen. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 1019025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Luo, W.; Liu, J.; Kang, X.; Yan, J.; Zhang, T.; Yang, L.; Shen, L.; Liu, D. The glucotoxicity protecting effect of honokiol in human hepatocytes via directly activating AMPK. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1043009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.J.; Wu, C.L.; Liu, J.F.; Fong, Y.C.; Hsu, S.F.; Li, T.M.; Su, Y.C.; Liu, S.H.; Tang, C.H. Honokiol induces cell apoptosis in human chondrosarcoma cells through mitochondrial dysfunction and endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cancer Lett. 2010, 291, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Yuan, J.; Gu, J.; Abbas, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zou, H.; Bian, J. Protective effect of honokiol on cadmium-induced liver injury in chickens. Poult. Sci. 2024, 103, 104066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frezzato, F.; Visentin, A.; Severin, F.; Pizzo, S.; Ruggeri, E.; Mouawad, N.; Martinello, L.; Pagnin, E.; Trimarco, V.; Tonini, A.; et al. Targeting of HSP70/HSF1 Axis Abrogates In Vitro Ibrutinib-Resistance in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Cancers 2021, 13, 5453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, B.; Li, H.; Xing, C.; Ye, H.; Feng, J.; Wu, J.; Lu, Z.; Fang, J.; Gao, S. Honokiol induces proteasomal degradation of AML1-ETO oncoprotein via increasing ubiquitin conjugase UbcH8 expression in leukemia. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2017, 128, 12–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Name | Full Hairpin Sequence (5′→3′) |
|---|---|
| Sh-NT | ccgggcaagctgaccctgaagttcactcgagtgaacttcagggtcagcttgcttttt |
| Sh-Hsp27 #1 | ccggcagtccaacgagatcaccatcctcgaggatggtgatctcgttggactgtttttg |
| Sh-Hsp27 #2 | ccgggatcaccatcccagtcaccttctcgagaaggtgactgggatggtgatctttttg |
| Primer Name | Sequence of Primers (5′→3′) | Description |
|---|---|---|
| N102A-FP | cctggatgtcgcccacttcgccccggacgagc | Forward primer |
| N102A-RP | gctcgtccggggcgaagtgggcgacatccagg | Reverse primer |
| H103A-FP | ggatgtcaacgccttcgccccggacgagctga | Forward primer |
| H103A-RP | tcagctcgtccggggcgaaggcgttgacatcc | Reverse primer |
| N102/H103A-FP | tccctggatgtcgccgccttcgccccggacgagctgaac | Forward primer |
| N102/H103A-FP | gttcagctcgtccggggcgaaggcggcgacatccaggga | Reverse primer |
| Identified Proteins | Peptides (95%) |
|---|---|
| Hsp27 | 1 |
| Hsp70 | 1 |
| NUP93 | 1 |
| KRT9 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, Y.; Jang, H.D.; An, D.H.; Lee, H.S.; Kim, H.-G.; Choi, S.E. Honokiol Inhibits Colorectal Cancer Cell Growth: Involvement of Hsp27 as a Molecular Target. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 921. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47110921
Kim Y, Jang HD, An DH, Lee HS, Kim H-G, Choi SE. Honokiol Inhibits Colorectal Cancer Cell Growth: Involvement of Hsp27 as a Molecular Target. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025; 47(11):921. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47110921
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Youngbin, Hyeon Du Jang, Da Hyeon An, Hyun Seo Lee, Hong-Gyum Kim, and Sun Eun Choi. 2025. "Honokiol Inhibits Colorectal Cancer Cell Growth: Involvement of Hsp27 as a Molecular Target" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47, no. 11: 921. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47110921
APA StyleKim, Y., Jang, H. D., An, D. H., Lee, H. S., Kim, H.-G., & Choi, S. E. (2025). Honokiol Inhibits Colorectal Cancer Cell Growth: Involvement of Hsp27 as a Molecular Target. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 47(11), 921. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47110921







