Melatonin Regulates Osteoblast Differentiation through the m6A Reader hnRNPA2B1 under Simulated Microgravity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Experimental Design
2.2. Micro-CT Scanning
2.3. Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
2.4. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.5. Cell Culture and In Vitro Differentiation
2.6. Two-Dimensional Clinorotation
2.7. Cell Transfection
2.8. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR) and Analysis
2.9. Western Blotting and Analysis
2.10. Alkaline Phosphatase Staining (ALP Staining)
2.11. ALP Activity Assay
2.12. Rescue Experiments
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
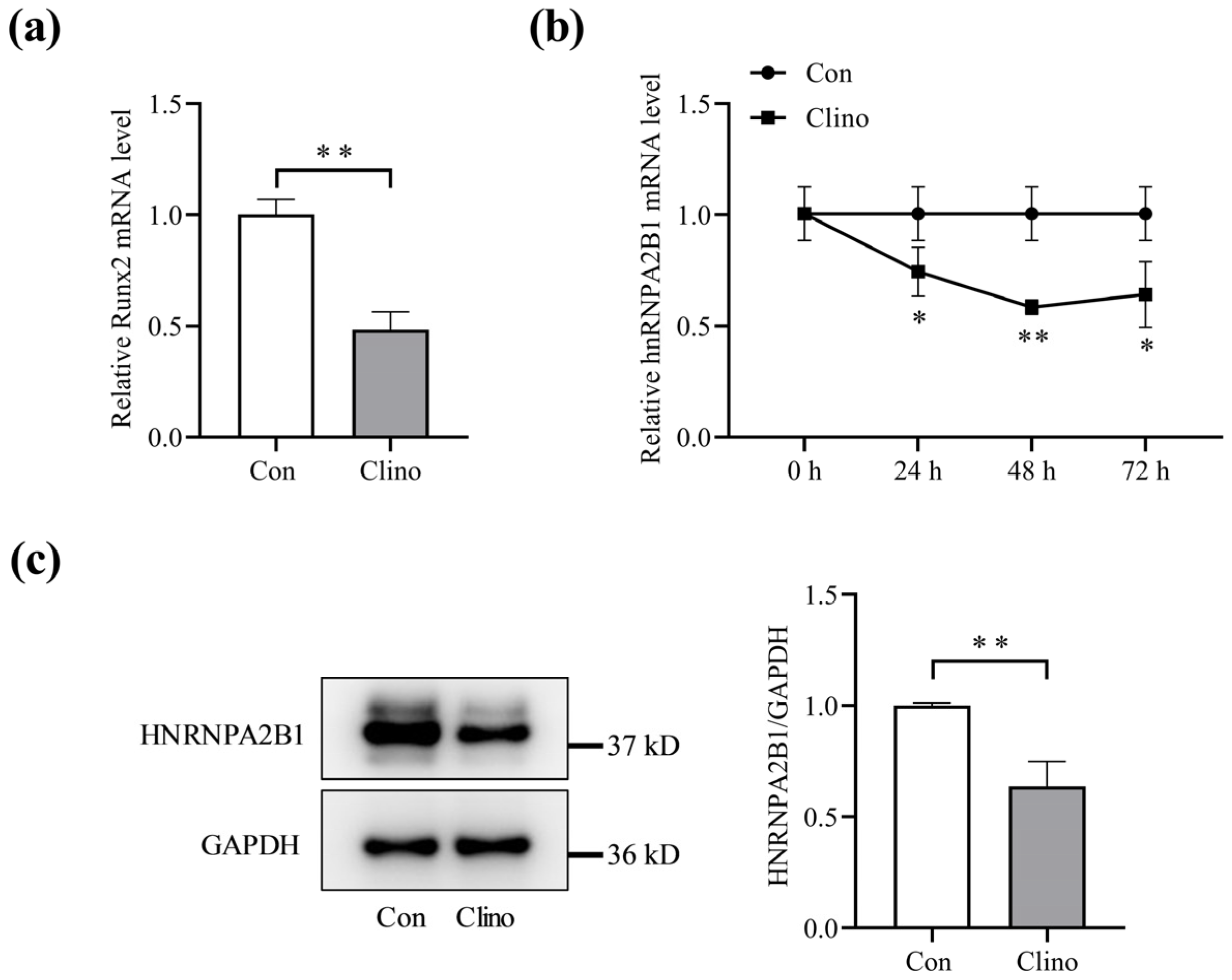
3.1. Expression of hnRNPA2B1 in Osteoblasts under Simulated Microgravity
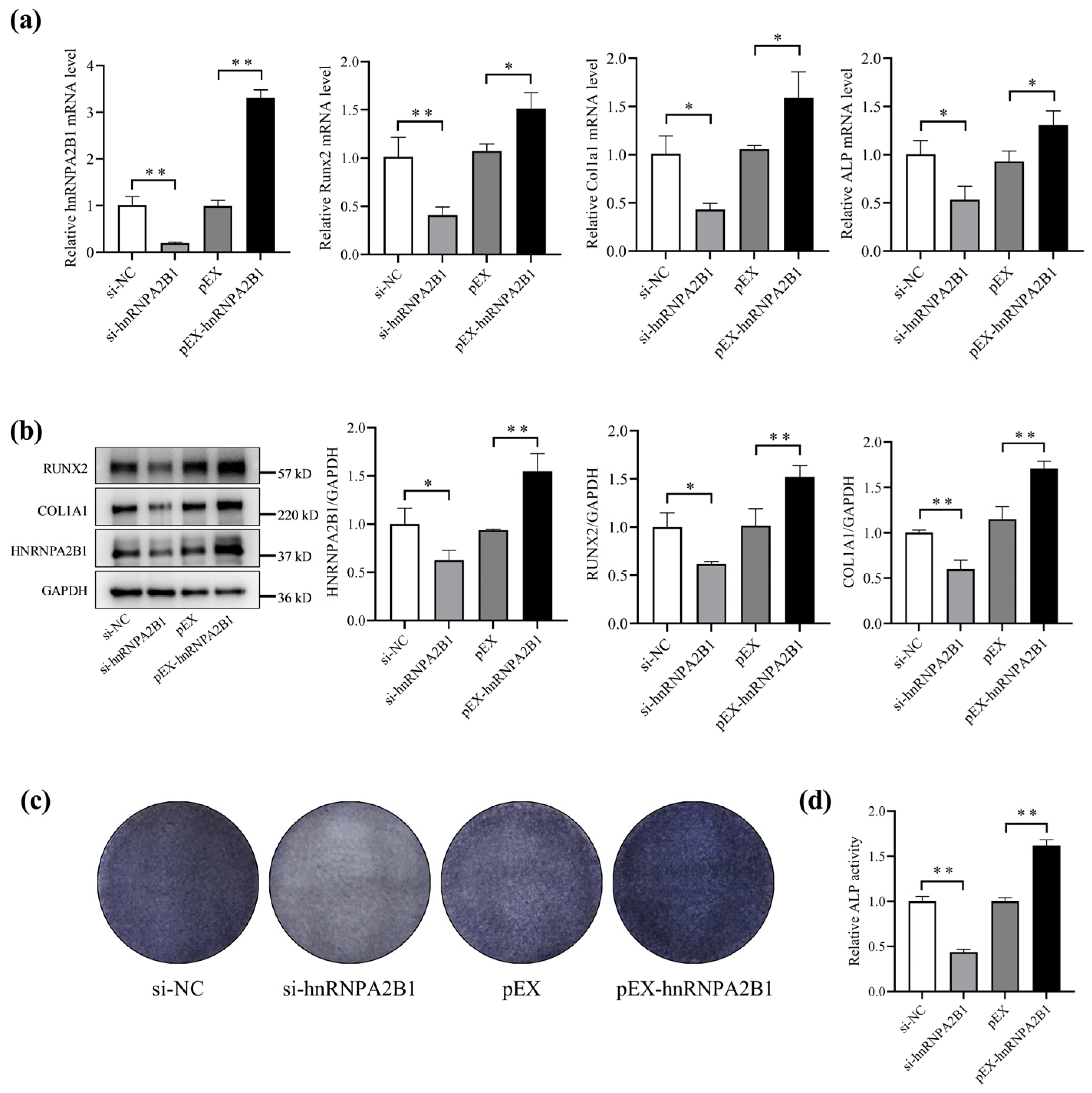
3.2. hnRNPA2B1 Regulates Osteoblast Differentiation
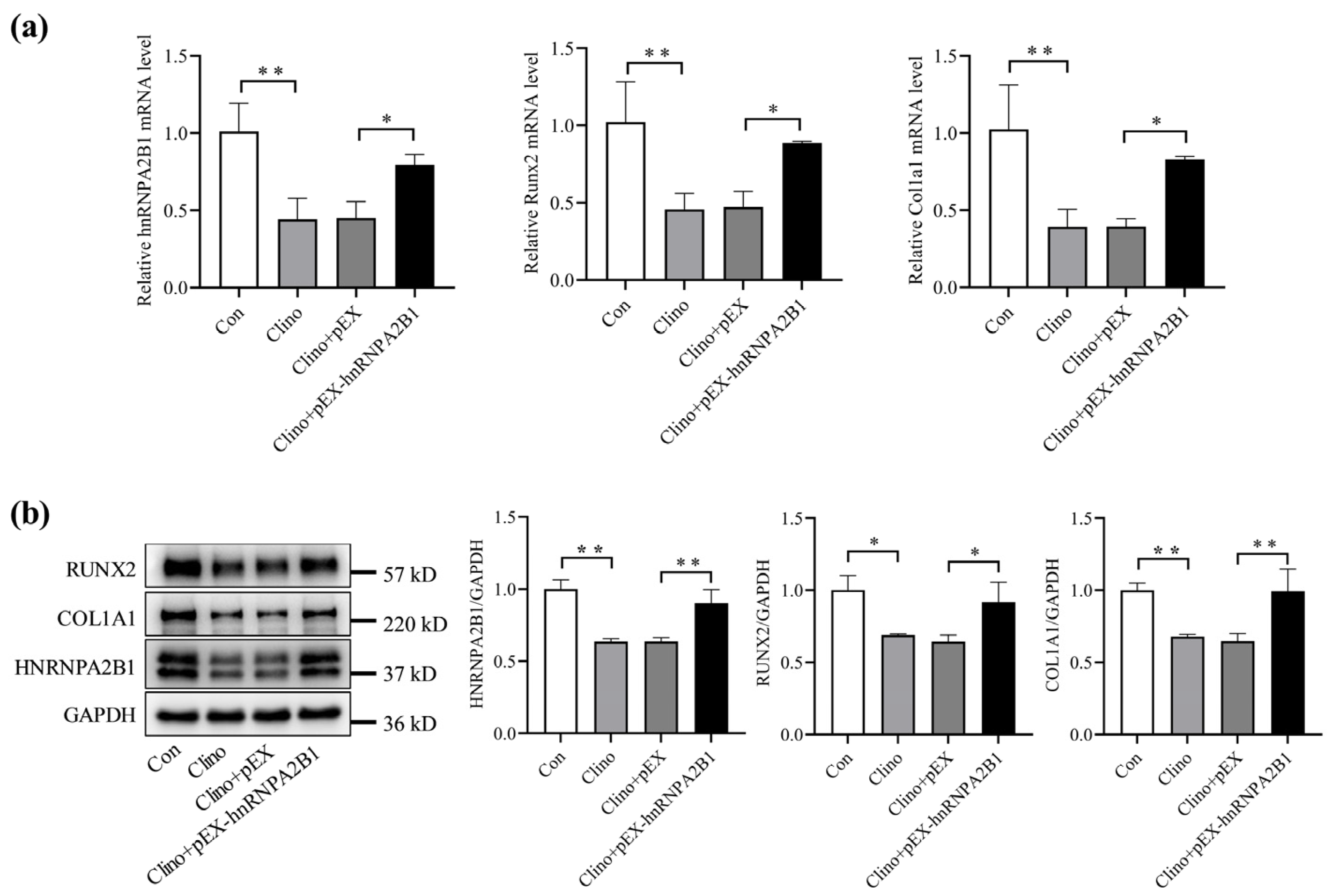
3.3. Overexpression of hnRNPA2B1 Attenuates the Inhibitory Effect of Simulated Microgravity on Osteoblast Differentiation in MC3T3-E1 Cells
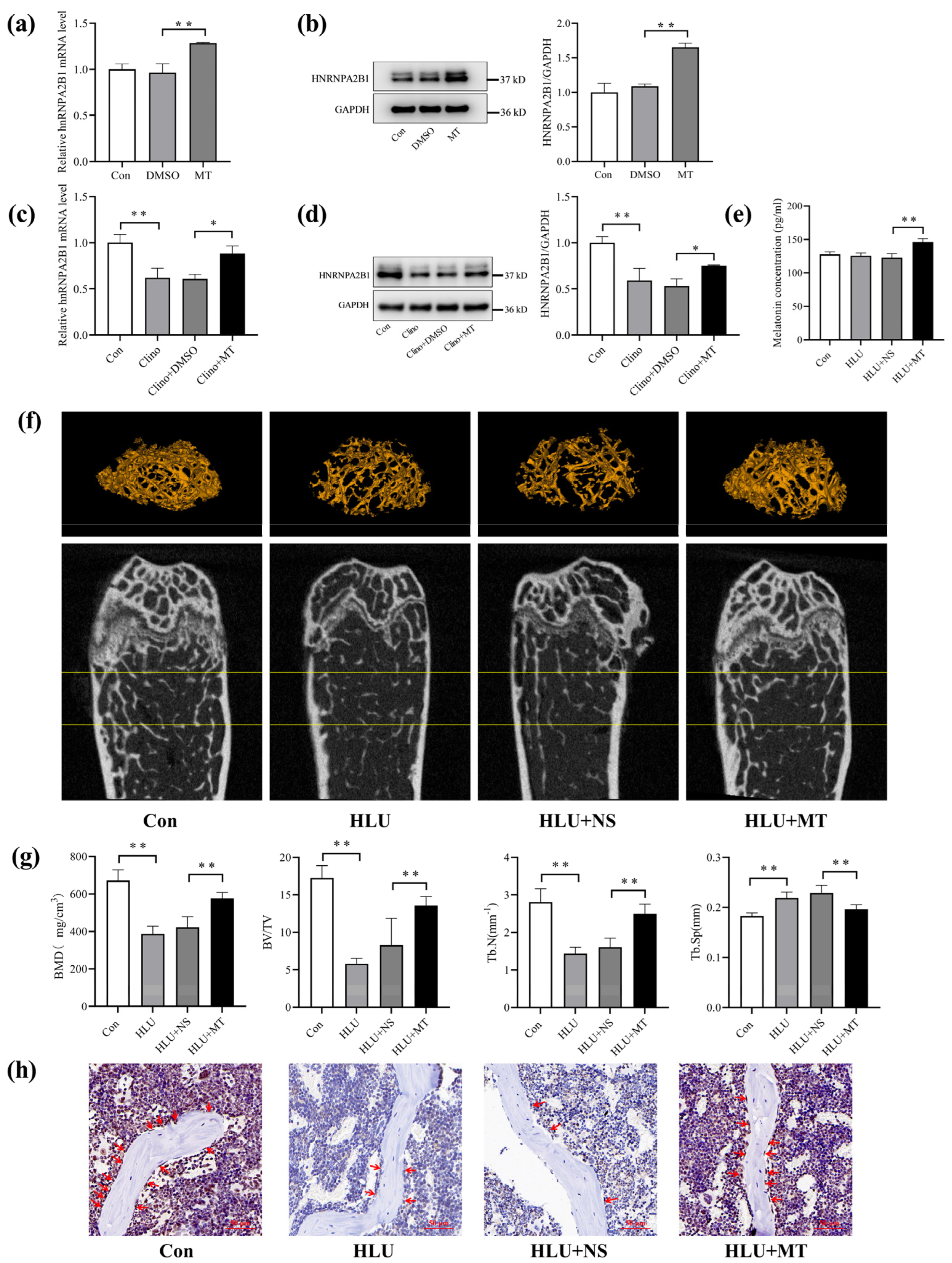
3.4. Melatonin Promotes hnRNPA2B1 Expression in Osteoblasts under Simulated Microgravity and Improves Bone Architecture in HLU Mice
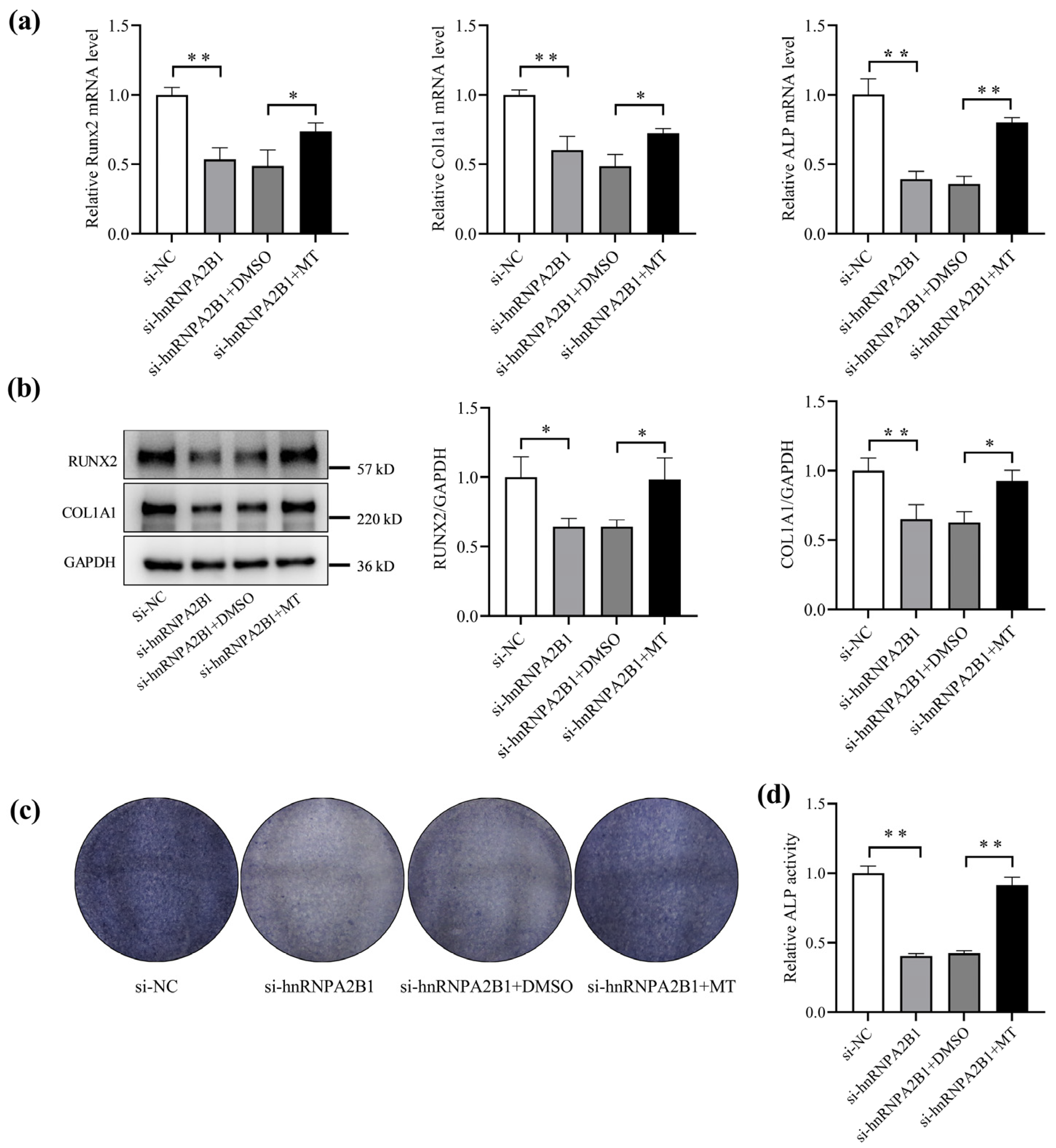
3.5. Melatonin Regulates Osteoblast Differentiation by Targeting hnRNPA2B1
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rodan, G.A.; Martin, T.J. Therapeutic approaches to bone diseases. Science 2000, 289, 1508–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baran, R.; Wehland, M.; Schulz, H.; Heer, M.; Infanger, M.; Grimm, D. Microgravity-Related Changes in Bone Density and Treatment Options: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmeliet, G.; Vico, L.; Bouillon, R. Space flight: A challenge for normal bone homeostasis. Crit. Rev. Eukaryot. Gene Expr. 2001, 11, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morey, E.R.; Baylink, D.J. Inhibition of bone formation during space flight. Science 1978, 201, 1138–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siamwala, J.H.; Rajendran, S.; Chatterjee, S. Strategies of Manipulating BMP Signaling in Microgravity to Prevent Bone Loss. Vitam. Horm. 2015, 99, 249–272. [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto, T.; Ikegame, M.; Furusawa, Y.; Tabuchi, Y.; Hatano, K.; Watanabe, K.; Kawago, U.; Hirayama, J.; Yano, S.; Sekiguchi, T.; et al. Osteoclastic and Osteoblastic Responses to Hypergravity and Microgravity: Analysis Using Goldfish Scales as a Bone Model. Zool. Sci. 2022, 39, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes-Fulford, M.; Lewis, M.L. Effects of microgravity on osteoblast growth activation. Exp. Cell Res. 1996, 224, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes-Fulford, M.; Rodenacker, K.; Jütting, U. Reduction of anabolic signals and alteration of osteoblast nuclear morphology in microgravity. J. Cell. Biochem. 2006, 99, 435–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, H.; Kumei, Y.; Morita, S.; Shimokawa, H.; Ohya, K.; Shinomiya, K. Suppression of osteoblastic phenotypes and modulation of pro- and anti-apoptotic features in normal human osteoblastic cells under a vector-averaged gravity condition. J. Med. Dent. Sci. 2003, 50, 167–176. [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar, D.; Nagaya, T.; Koga, K.; Nomura, Y.; Gruener, R.; Seo, H. Culture in vector-averaged gravity under clinostat rotation results in apoptosis of osteoblastic ROS 17/2.8 cells. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2000, 15, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumei, Y.; Shimokawa, H.; Katano, H.; Hara, E.; Akiyama, H.; Hirano, M.; Mukai, C.; Nagaoka, S.; Whitson, P.A.; Sams, C.F. Microgravity induces prostaglandin E2 and interleukin-6 production in normal rat osteoblasts: Role in bone demineralization. J. Biotechnol. 1996, 47, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhang, S.; Wu, X.Y. Effects of microgravity on the gene expression and cellular functions of osteoblasts. Space Med. Med. Eng. 2003, 16, 227–230. [Google Scholar]
- Rodionova, N.V. The dynamics of proliferation and differentiation of osteogenic cells under supportive unloading. TSitologiia I Genet. 2011, 45, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Grano, M.; Mori, G.; Minielli, V.; Barou, O.; Colucci, S.; Giannelli, G.; Alexandre, C.; Zallone, A.Z.; Vico, L. Rat hindlimb unloading by tail suspension reduces osteoblast differentiation, induces IL-6 secretion, and increases bone resorption in ex vivo cultures. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2002, 70, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Xie, Y.; He, J.; Zhou, J.; Gao, Y.; Wei, W.; Ding, N.; Ma, H.; Xian, C.J.; Chen, K.; et al. Microgravity induces inhibition of osteoblastic differentiation and mineralization through abrogating primary cilia. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malakoti, F.; Zare, F.; Zarezadeh, R.; Raei Sadigh, A.; Sadeghpour, A.; Majidinia, M.; Yousefi, B.; Alemi, F. The role of melatonin in bone regeneration: A review of involved signaling pathways. Biochimie 2022, 202, 56–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hattori, A.; Suzuki, N. Receptor-Mediated and Receptor-Independent Actions of Melatonin in Vertebrates. Zool. Sci. 2024, 41, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, J.A.; Kim, B.G.; Lin, W.L.; Cho, M.I. Melatonin promotes osteoblast differentiation and bone formation. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 22041–22047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maria, S.; Samsonraj, R.M.; Munmun, F.; Glas, J.; Silvestros, M.; Kotlarczyk, M.P.; Rylands, R.; Dudakovic, A.; van Wijnen, A.J.; Enderby, L.T.; et al. Biological effects of melatonin on osteoblast/osteoclast cocultures, bone, and quality of life: Implications of a role for MT2 melatonin receptors, MEK1/2, and MEK5 in melatonin-mediated osteoblastogenesis. J. Pineal Res. 2018, 64, e12465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, C.; Si, J.; Wang, B.; Zhang, D.; Ding, D.; Zhang, J.; Wang, H. Melatonin up-regulates bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells osteogenic action but suppresses their mediated osteoclastogenesis via MT2 -inactivated NF-κB pathway. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 177, 2106–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardeland, R. Melatonin: Signaling mechanisms of a pleiotropic agent. Biofactors 2009, 35, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K.H.; Kang, J.W.; Lee, E.M.; Kim, J.S.; Rhee, Y.H.; Kim, M.; Jeong, S.J.; Park, Y.G.; Kim, S.H. Melatonin promotes osteoblastic differentiation through the BMP/ERK/Wnt signaling pathways. J. Pineal Res. 2011, 51, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, J.H.; Cho, Y.C.; Sung, I.Y.; Kim, I.R.; Park, B.S.; Kim, Y.D. Melatonin promotes osteoblast differentiation and mineralization of MC3T3-E1 cells under hypoxic conditions through activation of PKD/p38 pathways. J. Pineal Res. 2014, 57, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Tao, L.; Qiu, S.; Shen, L.; Tian, Y.; Gong, Z.; Tao, Z.B.; Zhu, Y. Melatonin rescues glucocorticoid-induced inhibition of osteoblast differentiation in MC3T3-E1 cells via the PI3K/AKT and BMP/Smad signalling pathways. Life Sci. 2020, 257, 118044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, M.; Liu, H.; Jiang, W.; Zhou, Z.; Yao, X.; Liu, Z.; Ma, N.; Chen, B.; Yang, M. Melatonin Repairs Osteoporotic Bone Defects in Iron-Overloaded Rats through PI3K/AKT/GSK-3β/P70S6k Signaling Pathway. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2023, 2023, 7718155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Zha, K.; Tao, R.; Chen, L.; Xue, H.; Yan, C.; Lin, Z.; Endo, Y.; Cao, F.; et al. Melatonin Promotes BMSCs Osteoblastic Differentiation and Relieves Inflammation by Suppressing the NF-κB Pathways. Stem Cells Int. 2023, 2023, 7638842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Jiang, S.; Lu, C.; Yang, W.; Yang, Z.; Hu, W.; Xin, Z.; Yang, Y. Melatonin: Another avenue for treating osteoporosis. J. Pineal Res. 2019, 66, e12548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maria, S.; Witt-Enderby, P.A. Melatonin effects on bone: Potential use for the prevention and treatment for osteopenia, osteoporosis, and periodontal disease and for use in bone-grafting procedures. J. Pineal Res. 2014, 56, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munmun, F.; Witt-Enderby, P.A. Melatonin effects on bone: Implications for use as a therapy for managing bone loss. J. Pineal Res. 2021, 71, e12749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Yu, S.; Chen, G.; Zheng, W.; Peng, J.; Huang, X.; Chen, L. Insight into the roles of melatonin in bone tissue and bone-related diseases (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2021, 47, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirayama, J.; Hattori, A.; Takahashi, A.; Furusawa, Y.; Tabuchi, Y.; Shibata, M.; Nagamatsu, A.; Yano, S.; Maruyama, Y.; Matsubara, H.; et al. Physiological consequences of space flight, including abnormal bone metabolism, space radiation injury, and circadian clock dysregulation: Implications of melatonin use and regulation as a countermeasure. J. Pineal Res. 2023, 74, e12834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikegame, M.; Hattori, A.; Tabata, M.J.; Kitamura, K.I.; Tabuchi, Y.; Furusawa, Y.; Maruyama, Y.; Yamamoto, T.; Sekiguchi, T.; Matsuoka, R.; et al. Melatonin is a potential drug for the prevention of bone loss during space flight. J. Pineal Res. 2019, 67, e12594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.L.; Tan, Q.Y.; Yang, H.; Li, C.Y.; Wu, Z.; Ma, Y.F. Melatonin enhances spermatogonia activity through promoting KIAA1429-mediated m6A deposition to activate the PI3K/AKT signaling. Reprod. Biol. 2022, 22, 100681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Dong, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Dong, Y. Melatonin Alleviates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Abnormal Pregnancy through MTNR1B Regulation of m6A. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Dong, Z.; Ling, Z.; Chen, Y. The crucial mechanism and therapeutic implication of RNA methylation in bone pathophysiology. Ageing Res. Rev. 2022, 79, 101641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Hua, W.; Huang, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, G. Regulatory Role of RNA N6-Methyladenosine Modification in Bone Biology and Osteoporosis. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Guo, J.; Liu, L.; Jin, H.; Chen, X.; Zou, J. m6A demethylase FTO and osteoporosis: Potential therapeutic interventions. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 11, 1275475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.; Liu, X.; Li, X.; Li, T.; Liu, J.; Wu, L. Yth m6A RNA-Binding Protein 1 Regulates Osteogenesis of MC3T3-E1 Cells under Hypoxia via Translational Control of Thrombospondin-1. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lu, Z.; Gomez, A.; Hon, G.C.; Yue, Y.; Han, D.; Fu, Y.; Parisien, M.; Dai, Q.; Jia, G.; et al. N6-methyladenosine-dependent regulation of messenger RNA stability. Nature 2014, 505, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, B.S.; Roundtree, I.A.; Lu, Z.; Han, D.; Ma, H.; Weng, X.; Chen, K.; Shi, H.; He, C. N(6)-methyladenosine Modulates Messenger RNA Translation Efficiency. Cell 2015, 161, 1388–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarcón, C.R.; Goodarzi, H.; Lee, H.; Liu, X.; Tavazoie, S.; Tavazoie, S.F. HNRNPA2B1 Is a Mediator of m(6)A-Dependent Nuclear RNA Processing Events. Cell 2015, 162, 1299–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shigematsu, T.; Miyamoto, A.; Mukai, C.; Oshima, H.; Sekiguchi, C.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Hosoya, T. Changes in bone and calcium metabolism with space flight. Osteoporos. Int. 1997, 7 (Suppl. 3), S63–S67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomsia, M.; Cieśla, J.; Śmieszek, J.; Florek, S.; Macionga, A.; Michalczyk, K.; Stygar, D. Long-term space missions’ effects on the human organism: What we do know and what requires further research. Front. Physiol. 2024, 15, 1284644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaber, E.A.; Dvorochkin, N.; Lee, C.; Alwood, J.S.; Yousuf, R.; Pianetta, P.; Globus, R.K.; Burns, B.P.; Almeida, E.A. Microgravity induces pelvic bone loss through osteoclastic activity, osteocytic osteolysis, and osteoblastic cell cycle inhibition by CDKN1a/p21. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, K.; Hu, Z.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, L.; Wang, H.; Li, G.; Zhang, S.; Cao, X.; Shi, F. MicroRNA-139-3p regulates osteoblast differentiation and apoptosis by targeting ELK1 and interacting with long noncoding RNA ODSM. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wang, Y.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Li, G.; Dang, L.; Tan, Y.; Cao, X.; Shi, F.; Zhang, S.; et al. Bone-targeted lncRNA OGRU alleviates unloading-induced bone loss via miR-320-3p/Hoxa10 axis. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, L.; Xu, L.; Li, G.; Wang, K.; Xue, T.; Sun, Q.; Tang, H.; Cao, X.; Hu, Z.; et al. Exosomes from Microvascular Endothelial Cells under Mechanical Unloading Inhibit Osteogenic Differentiation via miR-92b-3p/ELK4 Axis. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Xu, L.; Zhang, X.; Wang, K.; Tan, Y.; Li, G.; Wang, Y.; Xue, T.; Sun, Q.; Cao, X.; et al. Methyltransferase Setdb1 Promotes Osteoblast Proliferation by Epigenetically Silencing Macrod2 with the Assistance of Atf7ip. Cells 2022, 11, 2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Clough, S.J.; Hutchinson, A.J.; Adamah-Biassi, E.B.; Popovska-Gorevski, M.; Dubocovich, M.L. MT1 and MT2 Melatonin Receptors: A Therapeutic Perspective. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2016, 56, 361–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Xu, S.; Liu, L.; Zhang, M.; Guo, J.; Yuan, Y.; Xu, J.; Chen, X.; Zou, J. m6A Methylation Regulates Osteoblastic Differentiation and Bone Remodeling. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 783322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Gu, X.; Li, D.; Cai, L.; Xu, Q. METTL3 Regulates Osteoblast Differentiation and Inflammatory Response via Smad Signaling and MAPK Signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 21, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, J.R.; Tan, Z.; Lin, W.M.; Li, Q.W.; Yuan, Q. Role of m 6A Reader YTHDC2 in Differentiation of Human Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2021, 52, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alarcón, C.R.; Lee, H.; Goodarzi, H.; Halberg, N.; Tavazoie, S.F. N6-methyladenosine marks primary microRNAs for processing. Nature 2015, 519, 482–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Su, S.; Patil, D.P.; Liu, H.; Gan, J.; Jaffrey, S.R.; Ma, J. Molecular basis for the specific and multivariant recognitions of RNA substrates by human hnRNP A2/B1. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, L.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; Jing, J.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Z.; Gao, A. The role of N6-methyladenosine modification in benzene-induced testicular damage and the protective effect of melatonin. Chemosphere 2023, 319, 138035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, Y.; Li, T.; Yang, M.; Su, L.; Zhu, Z.; Zhao, S.; Zeng, W.; Zheng, Y. Melatonin Attenuates Chromium (VI)-Induced Spermatogonial Stem Cell/Progenitor Mitophagy by Restoration of METTL3-Mediated RNA N6-Methyladenosine Modification. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 684398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Ji, X.; Wu, X.; Chen, J.; Li, X.; Jiang, H.; Fu, H.; Wang, H.; Lin, Z.; Tang, X.; et al. Melatonin antagonizes ovarian aging via YTHDF2-MAPK-NF-κB pathway. Genes. Dis. 2022, 9, 494–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.Z.; Zhu, G.Z.; Zhao, K.; Gao, J.W.; Cai, G.X.; Li, H.Z.; Huang, Y.S.; Tu, C.; Zhuang, J.S.; Huang, Z.W.; et al. Age-related decline in melatonin contributes to enhanced osteoclastogenesis via disruption of redox homeostasis. Mol. Med. 2024, 30, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.S.; Jeong, S.P.; Park, B.S.; Kim, I.R. Melatonin Attenuates RANKL-Induced Osteoclastogenesis via Inhibition of Atp6v0d2 and DC-STAMP through MAPK and NFATc1 Signaling Pathways. Molecules 2022, 27, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| RNA Oligo | Sequences (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| si-hnRNPA2B1 sense | 5′-GGUGGCUUAAGCUUUGAAATT-3′ |
| si-hnRNPA2B1 antisense | 5′-UUUCAAAGCUUAAGCCACCTT-3′ |
| si-NC sense | 5′-UUCUCCGAACGUGUCACGUTT-3′ |
| si-NC antisense | 5′-ACGUGACACGUUCGGAGAATT-3′ |
| Name of Primers | Sequences (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| hnRNPA2B1-F | 5′-GCGGAGGAAGAGGCGGTTAC-3′ |
| hnRNPA2B1-R | 5′-GTTAGAAGGCTGCTGGTTGTAGTTG-3′ |
| Runx2-F | 5′-GAACCAAGAAGGCACAGACAGA-3′ |
| Runx2-R | 5′-GGCGGGACACCTACTCTCATAC-3′ |
| Col1a1-F | 5′-GGCGGGACACCTACTCTCATAC-3′ |
| Col1a1-R | 5′-GGGACCCTTAGGCCATTGTGTA-3′ |
| ALP-F | 5′-GCAGTATGAATTGAATCGGAACAAC-3′ |
| ALP-R | 5′-ATGGCCTGGTCCATCTCCAC-3′ |
| GAPDH-F | 5′-TGTGTCCGTCGTGGATCTGA-3′ |
| GAPDH-R | 5′-TTGCTGTTGAAGTCGCAGGAG-3′ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, Q.; Xu, L.; Hu, Z.; Liu, J.; Yu, T.; Li, M.; Zhang, S.; Shi, F. Melatonin Regulates Osteoblast Differentiation through the m6A Reader hnRNPA2B1 under Simulated Microgravity. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2024, 46, 9624-9638. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46090572
Sun Q, Xu L, Hu Z, Liu J, Yu T, Li M, Zhang S, Shi F. Melatonin Regulates Osteoblast Differentiation through the m6A Reader hnRNPA2B1 under Simulated Microgravity. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2024; 46(9):9624-9638. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46090572
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Quan, Liqun Xu, Zebing Hu, Jingchun Liu, Tingfei Yu, Meng Li, Shu Zhang, and Fei Shi. 2024. "Melatonin Regulates Osteoblast Differentiation through the m6A Reader hnRNPA2B1 under Simulated Microgravity" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 46, no. 9: 9624-9638. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46090572
APA StyleSun, Q., Xu, L., Hu, Z., Liu, J., Yu, T., Li, M., Zhang, S., & Shi, F. (2024). Melatonin Regulates Osteoblast Differentiation through the m6A Reader hnRNPA2B1 under Simulated Microgravity. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 46(9), 9624-9638. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46090572






