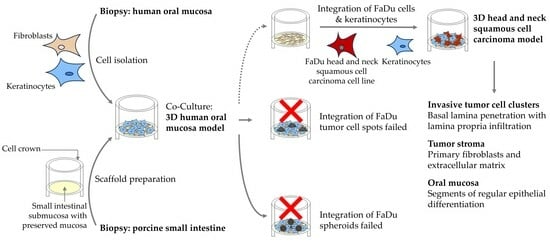
A Tissue Engineered 3D Model of Cancer Cell Invasion for Human Head and Neck Squamous-Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barsouk, A.; Aluru, J.S.; Rawla, P.; Saginala, K.; Barsouk, A. Epidemiology, Risk Factors, and Prevention of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Med. Sci. 2023, 11, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelucchi, C.; Gallus, S.; Garavello, W.; Bosetti, C.; La Vecchia, C. Cancer risk associated with alcohol and tobacco use: Focus on upper aero-digestive tract and liver. Alcohol. Res. Health 2006, 29, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Warnakulasuriya, S.; Chen, T.H.H. Areca Nut and Oral Cancer: Evidence from Studies Conducted in Humans. J. Dent. Res. 2022, 101, 1139–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashim, D.; Sartori, S.; Brennan, P.; Curado, M.P.; Wunsch-Filho, V.; Divaris, K.; Olshan, A.F.; Zevallos, J.P.; Winn, D.M.; Franceschi, S.; et al. The role of oral hygiene in head and neck cancer: Results from International Head and Neck Cancer Epidemiology (INHANCE) consortium. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 1619–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazos, J.P.; Piemonte, E.D.; Lanfranchi, H.E.; Brunotto, M.N. Characterization of Chronic Mechanical Irritation in Oral Cancer. Int. J. Dent. 2017, 2017, 6784526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borsetto, D.; Sethi, M.; Polesel, J.; Tomasoni, M.; Deganello, A.; Nicolai, P.; Bossi, P.; Fabbris, C.; Molteni, G.; Marchioni, D.; et al. The risk of recurrence in surgically treated head and neck squamous cell carcinomas: A conditional probability approach. Acta Oncol. 2021, 60, 942–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraji, F.; Cohen, E.E.W.; Guo, T.W. Evolving treatment paradigms in recurrent and metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: The emergence of immunotherapy. Transl. Cancer Res. 2023, 12, 1353–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatta, G.; Botta, L.; Sanchez, M.J.; Anderson, L.A.; Pierannunzio, D.; Licitra, L.; Group, E.W. Prognoses and improvement for head and neck cancers diagnosed in Europe in early 2000s: The EUROCARE-5 population-based study. Eur. J. Cancer 2015, 51, 2130–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapalczynska, M.; Kolenda, T.; Przybyla, W.; Zajaczkowska, M.; Teresiak, A.; Filas, V.; Ibbs, M.; Blizniak, R.; Luczewski, L.; Lamperska, K. 2D and 3D cell cultures—A comparison of different types of cancer cell cultures. Arch. Med. Sci. 2018, 14, 910–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melissaridou, S.; Wiechec, E.; Magan, M.; Jain, M.V.; Chung, M.K.; Farnebo, L.; Roberg, K. The effect of 2D and 3D cell cultures on treatment response, EMT profile and stem cell features in head and neck cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2019, 19, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loessner, D.; Stok, K.S.; Lutolf, M.P.; Hutmacher, D.W.; Clements, J.A.; Rizzi, S.C. Bioengineered 3D platform to explore cell-ECM interactions and drug resistance of epithelial ovarian cancer cells. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 8494–8506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.Q.; Kuo, J.C.; Wei, M.T.; Wu, M.C.; Yang, M.H.; Chiou, A. Fibroblast Promotes Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cell Invasion through Mechanical Barriers in 3D Collagen Microenvironments. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2020, 3, 6419–6429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickup, M.W.; Mouw, J.K.; Weaver, V.M. The extracellular matrix modulates the hallmarks of cancer. EMBO Rep. 2014, 15, 1243–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Li, P.; Du, F.; Shang, L.; Li, L. The role of organoids in cancer research. Exp. Hematol. Oncol. 2023, 12, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buskin, A.; Scott, E.; Nelson, R.; Gaughan, L.; Robson, C.N.; Heer, R.; Hepburn, A.C. Engineering prostate cancer in vitro: What does it take? Oncogene 2023, 42, 2417–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mermod, M.; Hiou-Feige, A.; Bovay, E.; Roh, V.; Sponarova, J.; Bongiovanni, M.; Vermeer, D.W.; Lee, J.H.; Petrova, T.V.; Rivals, J.P.; et al. Mouse model of postsurgical primary tumor recurrence and regional lymph node metastasis progression in HPV-related head and neck cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2018, 142, 2518–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Tian, G.; Li, J.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, K. An HNSCC syngeneic mouse model for tumor immunology research and preclinical evaluation. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2020, 46, 1501–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brand, M.; Laban, S.; Theodoraki, M.N.; Doescher, J.; Hoffmann, T.K.; Schuler, P.J.; Brunner, C. Characterization and Differentiation of the Tumor Microenvironment (TME) of Orthotopic and Subcutaneously Grown Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma (HNSCC) in Immunocompetent Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 22, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozawa, H.; Ranaweera, R.S.; Izumchenko, E.; Makarev, E.; Zhavoronkov, A.; Fertig, E.J.; Howard, J.D.; Markovic, A.; Bedi, A.; Ravi, R.; et al. SMAD4 Loss Is Associated with Cetuximab Resistance and Induction of MAPK/JNK Activation in Head and Neck Cancer Cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 5162–5175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Hu, H.; Li, Z.; Wang, D.; Zhang, W.; Qi, B.; Ye, J.; Wu, H.; et al. The histone demethylase LSD1 is a novel oncogene and therapeutic target in oral cancer. Cancer Lett. 2016, 374, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Luo, Q.; Zhang, H.; Wang, H.; Chen, W.; Meng, G.; Chen, F. The role of NLRP3 inflammasome in 5-fluorouracil resistance of oral squamous cell carcinoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 36, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mak, I.W.; Evaniew, N.; Ghert, M. Lost in translation: Animal models and clinical trials in cancer treatment. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2014, 6, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ben-David, U.; Ha, G.; Tseng, Y.Y.; Greenwald, N.F.; Oh, C.; Shih, J.; McFarland, J.M.; Wong, B.; Boehm, J.S.; Beroukhim, R.; et al. Patient-derived xenografts undergo mouse-specific tumor evolution. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 1567–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, J.; Yoshimura, K.; Sewastjanow-Silva, M.; Song, S.; Ajani, J.A. Challenges and Prospects of Patient-Derived Xenografts for Cancer Research. Cancers 2023, 15, 4352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Creighton, C.J.; Zhang, Y.; Sen, B.; Mazumdar, T.; Myers, J.N.; Lai, S.Y.; Woolfson, A.; Lorenzi, M.V.; Bell, D.; et al. Tumor grafts derived from patients with head and neck squamous carcinoma authentically maintain the molecular and histologic characteristics of human cancers. J. Transl. Med. 2013, 11, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breslin, S.; O’Driscoll, L. Three-dimensional cell culture: The missing link in drug discovery. Drug Discov. Today 2013, 18, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moharamzadeh, K.; Brook, I.M.; Van Noort, R.; Scutt, A.M.; Thornhill, M.H. Tissue-engineered oral mucosa: A review of the scientific literature. J. Dent. Res. 2007, 86, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckstead, B.L.; Pan, S.; Bhrany, A.D.; Bratt-Leal, A.M.; Ratner, B.D.; Giachelli, C.M. Esophageal epithelial cell interaction with synthetic and natural scaffolds for tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 6217–6228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertsching, H.; Walles, T.; Hofmann, M.; Schanz, J.; Knapp, W.H. Engineering of a vascularized scaffold for artificial tissue and organ generation. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 6610–6617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratmann, A.T.; Fecher, D.; Wangorsch, G.; Gottlich, C.; Walles, T.; Walles, H.; Dandekar, T.; Dandekar, G.; Nietzer, S.L. Establishment of a human 3D lung cancer model based on a biological tissue matrix combined with a Boolean in silico model. Mol. Oncol. 2014, 8, 351–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinke, M.; Gross, R.; Walles, H.; Gangnus, R.; Schutze, K.; Walles, T. An engineered 3D human airway mucosa model based on an SIS scaffold. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 7355–7362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rangan, S.R. A new human cell line (FaDu) from a hypopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer 1972, 29, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fecher, D.; Hofmann, E.; Buck, A.; Bundschuh, R.; Nietzer, S.; Dandekar, G.; Walles, T.; Walles, H.; Luckerath, K.; Steinke, M. Human Organotypic Lung Tumor Models: Suitable For Preclinical 18F-FDG PET-Imaging. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0160282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivarajan, R.; Kessie, D.K.; Oberwinkler, H.; Pallmann, N.; Walles, T.; Scherzad, A.; Hackenberg, S.; Steinke, M. Susceptibility of Human Airway Tissue Models Derived From Different Anatomical Sites to Bordetella pertussis and Its Virulence Factor Adenylate Cyclase Toxin. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 797491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonan, P.R.; Kaminagakura, E.; Pires, F.R.; Vargas, P.A.; Almeida, O.P. Cytokeratin expression in initial oral mucositis of head and neck irradiated patients. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2006, 101, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhargava, S.; Chapple, C.R.; Bullock, A.J.; Layton, C.; MacNeil, S. Tissue-engineered buccal mucosa for substitution urethroplasty. BJU Int. 2004, 93, 807–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moharamzadeh, K.; Brook, I.M.; Van Noort, R.; Scutt, A.M.; Smith, K.G.; Thornhill, M.H. Development, optimization and characterization of a full-thickness tissue engineered human oral mucosal model for biological assessment of dental biomaterials. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2008, 19, 1793–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colley, H.E.; Hearnden, V.; Jones, A.V.; Weinreb, P.H.; Violette, S.M.; Macneil, S.; Thornhill, M.H.; Murdoch, C. Development of tissue-engineered models of oral dysplasia and early invasive oral squamous cell carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2011, 105, 1582–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindberg, K.; Badylak, S.F. Porcine small intestinal submucosa (SIS): A bioscaffold supporting in vitro primary human epidermal cell differentiation and synthesis of basement membrane proteins. Burns 2001, 27, 254–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulasekara, K.K.; Lukandu, O.M.; Neppelberg, E.; Vintermyr, O.K.; Johannessen, A.C.; Costea, D.E. Cancer progression is associated with increased expression of basement membrane proteins in three-dimensional in vitro models of human oral cancer. Arch. Oral Biol. 2009, 54, 924–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.P.; Xu, K.; Cui, J.; Yuan, D.Y.; Zou, B.; Li, J.; Liu, J.L.; Li, K.Y.; Meng, Z.; Zhang, B. Cancer-associated fibroblast-derived exosomal miR-382-5p promotes the migration and invasion of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2019, 42, 1319–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bienkowska, K.J.; Hanley, C.J.; Thomas, G.J. Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts in Oral Cancer: A Current Perspective on Function and Potential for Therapeutic Targeting. Front. Oral Health 2021, 2, 686337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaballah, K.; Costea, D.E.; Hills, A.; Gollin, S.M.; Harrison, P.; Partridge, M. Tissue engineering of oral dysplasia. J. Pathol. 2008, 215, 280–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brauchle, E.; Johannsen, H.; Nolan, S.; Thude, S.; Schenke-Layland, K. Design and analysis of a squamous cell carcinoma in vitro model system. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 7401–7407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozbek, S.; Balasubramanian, P.G.; Chiquet-Ehrismann, R.; Tucker, R.P.; Adams, J.C. The evolution of extracellular matrix. Mol. Biol. Cell 2010, 21, 4300–4305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinke, M.; Dally, I.; Friedel, G.; Walles, H.; Walles, T. Host-integration of a tissue-engineered airway patch: Two-year follow-up in a single patient. Tissue Eng. Part A 2015, 21, 573–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freier, K.; Joos, S.; Flechtenmacher, C.; Devens, F.; Benner, A.; Bosch, F.X.; Lichter, P.; Hofele, C. Tissue microarray analysis reveals site-specific prevalence of oncogene amplifications in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 1179–1182. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Q.; Yu, G.P.; McCormick, S.A.; Mo, J.; Datta, B.; Mahimkar, M.; Lazarus, P.; Schaffer, A.A.; Desper, R.; Schantz, S.P. Genetic differences detected by comparative genomic hybridization in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas from different tumor sites: Construction of oncogenetic trees for tumor progression. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2002, 34, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kress, S.; Baur, J.; Otto, C.; Burkard, N.; Braspenning, J.; Walles, H.; Nickel, J.; Metzger, M. Evaluation of a Miniaturized Biologically Vascularized Scaffold in vitro and in vivo. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miserocchi, G.; Mercatali, L.; Liverani, C.; De Vita, A.; Spadazzi, C.; Pieri, F.; Bongiovanni, A.; Recine, F.; Amadori, D.; Ibrahim, T. Management and potentialities of primary cancer cultures in preclinical and translational studies. J. Transl. Med. 2017, 15, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelmann, L.; Thierauf, J.; Koerich Laureano, N.; Stark, H.J.; Prigge, E.S.; Horn, D.; Freier, K.; Grabe, N.; Rong, C.; Federspil, P.; et al. Organotypic Co-Cultures as a Novel 3D Model for Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancers 2020, 12, 2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


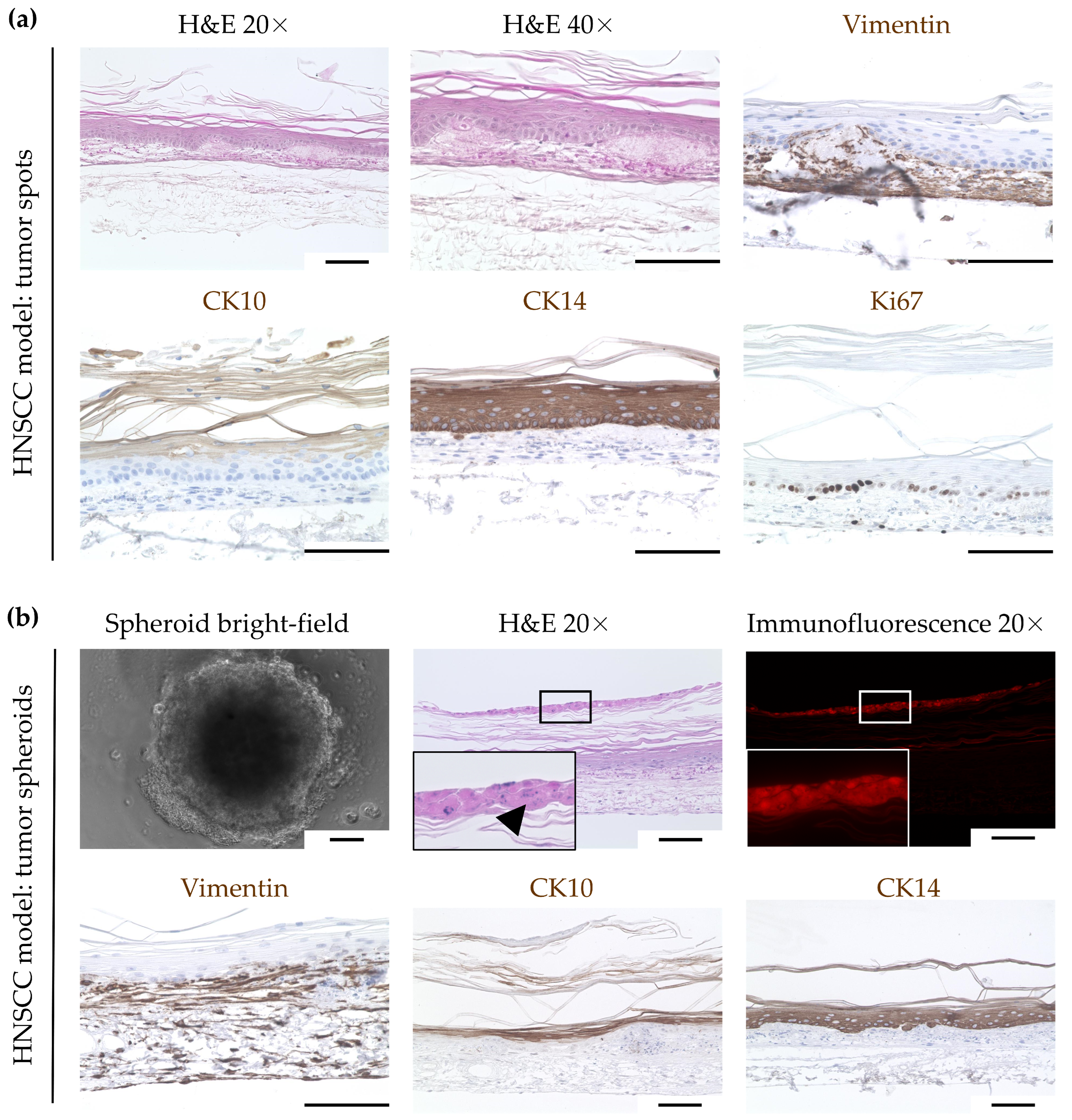

| Oral Mucosa Model | Tumor Formation | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Tumor spots | Regularly formed epithelium | No signs of malignancy or tumor formation | |
| Tumor spheroids | Regularly formed epithelium | Tumor cells located on top of stratum corneum | |
| Single tumor cells | 1:50 | Continuously formed stratum corneum, cells in the basal layers appeared irregular with nuclear pleomorphism and differences in size | Formation of tumor cell clusters; no invasion into lamina propria |
| 1:33 | Disturbed epithelial architecture | Invasive tumor growth | |
| 1:25 | No regular epithelial structure, atypical cornification | Invasive tumor growth | |
| 1:10 | No regular epithelial structure, atypical cornification | Invasive tumor growth |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stöth, M.; Mineif, A.T.; Sauer, F.; Meyer, T.J.; Mueller-Diesing, F.; Haug, L.; Scherzad, A.; Steinke, M.; Rossi, A.; Hackenberg, S. A Tissue Engineered 3D Model of Cancer Cell Invasion for Human Head and Neck Squamous-Cell Carcinoma. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2024, 46, 4049-4062. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46050250
Stöth M, Mineif AT, Sauer F, Meyer TJ, Mueller-Diesing F, Haug L, Scherzad A, Steinke M, Rossi A, Hackenberg S. A Tissue Engineered 3D Model of Cancer Cell Invasion for Human Head and Neck Squamous-Cell Carcinoma. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2024; 46(5):4049-4062. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46050250
Chicago/Turabian StyleStöth, Manuel, Anna Teresa Mineif, Fabian Sauer, Till Jasper Meyer, Flurin Mueller-Diesing, Lukas Haug, Agmal Scherzad, Maria Steinke, Angela Rossi, and Stephan Hackenberg. 2024. "A Tissue Engineered 3D Model of Cancer Cell Invasion for Human Head and Neck Squamous-Cell Carcinoma" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 46, no. 5: 4049-4062. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46050250
APA StyleStöth, M., Mineif, A. T., Sauer, F., Meyer, T. J., Mueller-Diesing, F., Haug, L., Scherzad, A., Steinke, M., Rossi, A., & Hackenberg, S. (2024). A Tissue Engineered 3D Model of Cancer Cell Invasion for Human Head and Neck Squamous-Cell Carcinoma. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 46(5), 4049-4062. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46050250