Exendin-4 Increases Scavenger Receptor Class BI Expression via Activation of AMPK/FoxO1 in Human Vascular Endothelial Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Western Blot
2.3. Real-Time PCR
2.4. Mutagenesis
2.5. Transfection and Luciferase Reporter Gene Assay
2.6. Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP) Assay
3. Results
3.1. Exendin-4 Induces the Phosphorylation of eNOS in HUVECs
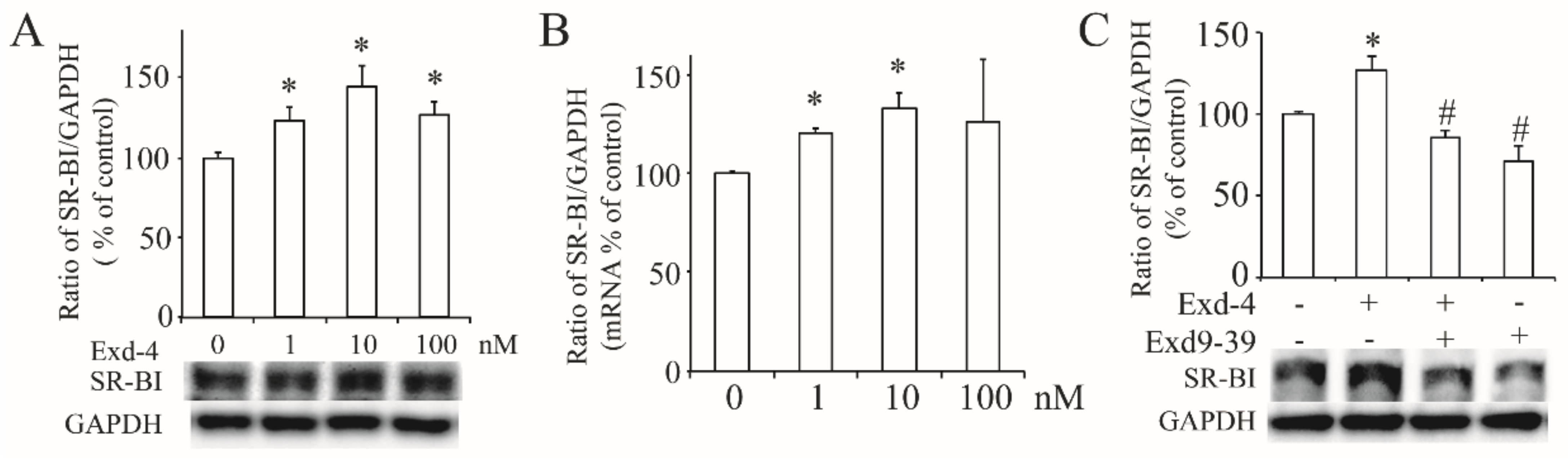
3.2. Exendin-4 Increases the Expression of hSR-BI/CLA-1 via GLP-1 Receptor in HUVECs
3.3. Exendin-4 Enhances the Promoter Activity of hSR-BI/CLA-1 via AMPK Pathway
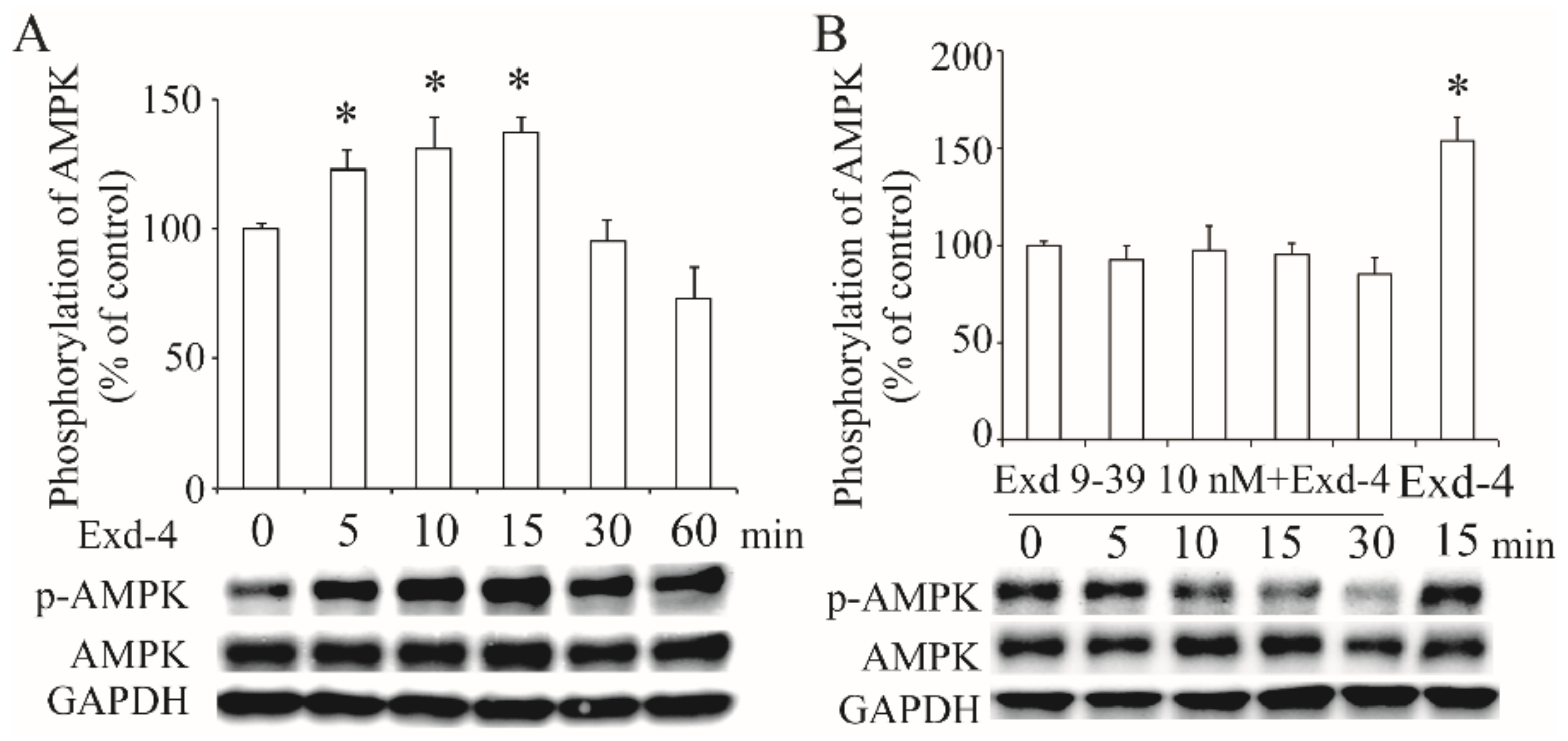
3.4. Exendin-4 Activates the AMPK via GLP-1 Receptor in HUVECs
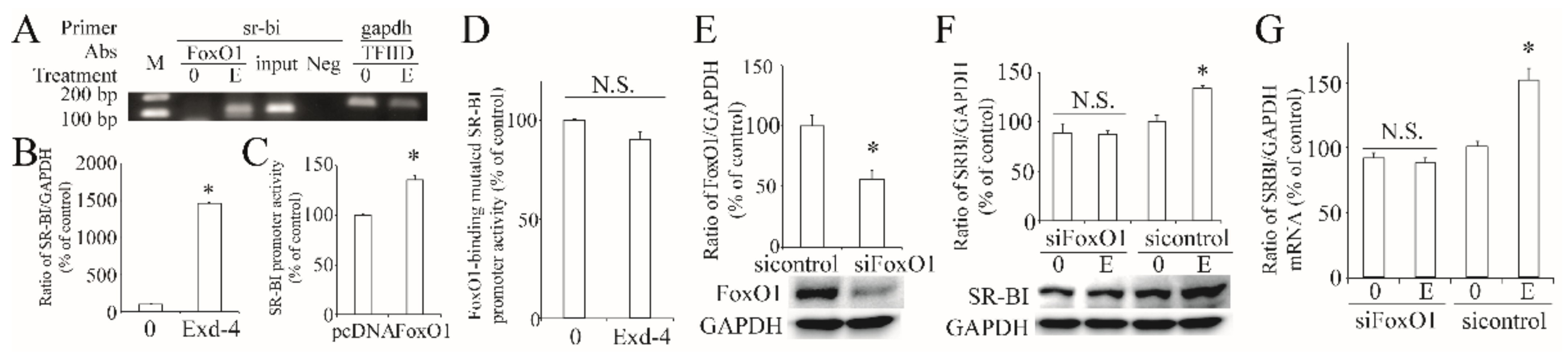
3.5. Exendin-4 Enhances the Transcription of hSR-BI/CLA-1 via FoxO1
3.6. Exendin-4 Regulates the Expression of FoxO1 via AMPK Pathway
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saeedi, P.; Petersohn, I.; Salpea, P.; Malanda, B.; Karuranga, S.; Unwin, N.; Colagiuri, S.; Guariguata, L.; Motala, A.A.; Ogurtsova, K.; et al. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9(th) edition. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2019, 157, 107843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papak, J.; Kansagara, D. Management of hyperglycemia in a hospitalized patient with diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular disease. Am. J. Cardiol. 2012, 110, 24B–31B. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deedwania, P.C. Diabetes is a vascular disease: The role of endothelial dysfunction in pathophysiology of cardiovascular disease in diabetes. Cardiol. Clin. 2004, 22, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinnen, D. Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonists for Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Spectr. 2017, 30, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, X.; She, M.; Xu, M.; Chen, H.; Li, J.; Chen, X.; Zheng, D.; Liu, J.; Chen, S.; Zhu, J.; et al. GLP-1 treatment protects endothelial cells from oxidative stress-induced autophagy and endothelial dysfunction. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 14, 1696–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Liu, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Guan, B.; Chen, Z.; Liu, L. Exendin-4 protects HUVECs from tunicamycin-induced apoptosis via inhibiting the IRE1a/JNK/caspase-3 pathway. Endocrine 2017, 55, 764–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triggle, C.R.; Ding, H. A review of endothelial dysfunction in diabetes: A focus on the contribution of a dysfunctional eNOS. J. Am. Soc. Hypertens. 2010, 4, 102–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tousoulis, D.; Kampoli, A.M.; Tentolouris, C.; Papageorgiou, N.; Stefanadis, C. The role of nitric oxide on endothelial function. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2012, 10, 4–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Zhang, J. Glucagon-like peptide-1 activates endothelial nitric oxide synthase in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2012, 33, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Chai, W.; Wang, W.; Zhao, L.; Fu, Z.; Cao, W.; Liu, Z. Protein kinase A mediates glucagon-like peptide 1-induced nitric oxide production and muscle microvascular recruitment. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 304, E222–E228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iorga, R.A.; Bacalbasa, N.; Carsote, M.; Bratu, O.G.; Stanescu, A.M.A.; Bungau, S.; Pantis, C.; Diaconu, C.C. Metabolic and cardiovascular benefits of GLP-1 agonists, besides the hypoglycemic effect (Review). Exp. Med. 2020, 20, 2396–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Olmo-Garcia, M.I.; Merino-Torres, J.F. GLP-1 Receptor Agonists and Cardiovascular Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. J. Diabetes Res. 2018, 2018, 4020492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Q.H.; Zhang, R.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.T.; Liu, J.P.; Zhang, J.; Bai, L.; Cheng, J.Q.; Fu, P.; Liu, F. Exendin-4 Ameliorates Lipotoxicity-induced Glomerular Endothelial Cell Injury by Improving ABC Transporter A1-mediated Cholesterol Efflux in Diabetic apoE Knockout Mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 26487–26501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dod, R.; Rajendran, A.; Kathrotia, M.; Clarke, A.; Dodani, S. Cardiovascular Disease in South Asian Immigrants: A Review of Dysfunctional HDL as a Potential Marker. J. Racial Ethn. Health Disparities 2022, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna-Luna, M.; Niesor, E.; Perez-Mendez, O. HDL as Bidirectional Lipid Vectors: Time for New Paradigms. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piko, P.; Kosa, Z.; Sandor, J.; Seres, I.; Paragh, G.; Adany, R. The profile of HDL-C subfractions and their association with cardiovascular risk in the Hungarian general and Roma populations. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 10915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rader, D.J.; Hovingh, G.K. HDL and cardiovascular disease. Lancet 2014, 384, 618–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murao, K.; Terpstra, V.; Green, S.R.; Kondratenko, N.; Steinberg, D.; Quehenberger, O. Characterization of CLA-1, a human homologue of rodent scavenger receptor BI, as a receptor for high density lipoprotein and apoptotic thymocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 17551–17557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnoni, M.; Andreini, D.; Pirillo, A.; Uboldi, P.; Latini, R.; Catapano, A.L.; Maggioni, A.P.; Norata, G.D.; Group, C.S. Predictive value of HDL function in patients with coronary artery disease: Relationship with coronary plaque characteristics and clinical events. Ann. Med. 2022, 54, 1036–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuhanna, I.S.; Zhu, Y.; Cox, B.E.; Hahner, L.D.; Osborne-Lawrence, S.; Lu, P.; Marcel, Y.L.; Anderson, R.G.; Mendelsohn, M.E.; Hobbs, H.H.; et al. High-density lipoprotein binding to scavenger receptor-BI activates endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Nat. Med. 2001, 7, 853–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Murao, K.; Imachi, H.; Cao, W.M.; Li, J.; Matsumoto, K.; Nishiuchi, T.; Ahmed, R.A.; Wong, N.C.; Kosaka, H.; et al. Regulation of scavenger receptor class BI gene expression by angiotensin II in vascular endothelial cells. Hypertension 2007, 49, 1378–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, J.; Fukunaga, K.; Imachi, H.; Sato, S.; Kobayashi, T.; Saheki, T.; Ibata, T.; Yoshimura, T.; Iwama, H.; Murao, K. Oxidized LDL Downregulates ABCA1 Expression via MEK/ERK/LXR Pathway in INS-1 Cells. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibata, T.; Lyu, J.; Imachi, H.; Fukunaga, K.; Sato, S.; Kobayashi, T.; Saheki, T.; Yoshimura, T.; Murao, K. Effects of 2-Methoxyestradiol, a Main Metabolite of Estradiol on Hepatic ABCA1 Expression in HepG2 Cells. Nutrients 2022, 14, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, J.; Imachi, H.; Fukunaga, K.; Sato, S.; Kobayashi, T.; Dong, T.; Saheki, T.; Matsumoto, M.; Iwama, H.; Zhang, H.; et al. Role of ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 in suppressing lipid accumulation by glucagon-like peptide-1 agonist in hepatocytes. Mol. Metab. 2020, 34, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, J.; Imachi, H.; Iwama, H.; Zhang, H.; Murao, K. Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 Regulates the Expression of ATP-Binding Cassette Transporter A1 in Pancreatic Beta Cells. Horm. Metab. Res. 2016, 48, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingvay, I.; Leiter, L.A. Use of GLP-1 RAs in Cardiovascular Disease Prevention: A Practical Guide. Circulation 2018, 137, 2200–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Wu, S.; Guo, S.; Yu, K.; Yang, Z.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Quan, X.; Ji, L.; Zhan, S. Impact of GLP-1 receptor agonists on blood pressure, heart rate and hypertension among patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2015, 110, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simo, R.; Guerci, B.; Schernthaner, G.; Gallwitz, B.; Rosas-Guzman, J.; Dotta, F.; Festa, A.; Zhou, M.; Kiljanski, J. Long-term changes in cardiovascular risk markers during administration of exenatide twice daily or glimepiride: Results from the European exenatide study. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2015, 14, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Lu, W.; Lu, Z.; Shao, X.; Hu, C.; Shi, B. Exenatide with Metformin Ameliorated Visceral Adiposity and Insulin Resistance. J. Diabetes Res. 2018, 2018, 4019248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; He, X.; Chen, Y.; Huang, Y.; Wu, L.; He, J. Exendin-4 attenuates cardiac hypertrophy via AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway activation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 468, 394–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Bu, R.; Yang, Q.; Jia, J.; Li, T.; Wang, Q.; Chen, Y. Exendin-4 Protects against Hyperglycemia-Induced Cardiomyocyte Pyroptosis via the AMPK-TXNIP Pathway. J. Diabetes Res. 2019, 2019, 8905917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdogdu, O.; Eriksson, L.; Xu, H.; Sjoholm, A.; Zhang, Q.; Nystrom, T. Exendin-4 protects endothelial cells from lipoapoptosis by PKA, PI3K, eNOS, p38 MAPK, and JNK pathways. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2013, 50, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greer, E.L.; Dowlatshahi, D.; Banko, M.R.; Villen, J.; Hoang, K.; Blanchard, D.; Gygi, S.P.; Brunet, A. An AMPK-FOXO pathway mediates longevity induced by a novel method of dietary restriction in C. elegans. Curr. Biol. 2007, 17, 1646–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.S.; Cash, A.; Hamadani, L.; Diemer, T. Oxaloacetate supplementation increases lifespan in Caenorhabditis elegans through an AMPK/FOXO-dependent pathway. Aging Cell 2009, 8, 765–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.N.; Lin, Y.N.; Gu, C.J.; Zhou, J.P.; Sun, X.W.; Cai, X.T.; Du, J.; Li, Q.Y. AMPK/FOXO1 signaling pathway is indispensable in visfatin-regulated myosin heavy chain expression in C2C12 myotubes. Life Sci. 2019, 224, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lyu, J.; Imachi, H.; Fukunaga, K.; Sato, S.; Kobayashi, T.; Saheki, T.; Japar, S.; Iwama, H.; Matsumura, Y.; Ozaki, M.; et al. Exendin-4 Increases Scavenger Receptor Class BI Expression via Activation of AMPK/FoxO1 in Human Vascular Endothelial Cells. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2022, 44, 5474-5484. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb44110370
Lyu J, Imachi H, Fukunaga K, Sato S, Kobayashi T, Saheki T, Japar S, Iwama H, Matsumura Y, Ozaki M, et al. Exendin-4 Increases Scavenger Receptor Class BI Expression via Activation of AMPK/FoxO1 in Human Vascular Endothelial Cells. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2022; 44(11):5474-5484. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb44110370
Chicago/Turabian StyleLyu, Jingya, Hitomi Imachi, Kensaku Fukunaga, Seisuke Sato, Toshihiro Kobayashi, Takanobu Saheki, Salimah Japar, Hisakazu Iwama, Yuta Matsumura, Miyo Ozaki, and et al. 2022. "Exendin-4 Increases Scavenger Receptor Class BI Expression via Activation of AMPK/FoxO1 in Human Vascular Endothelial Cells" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 44, no. 11: 5474-5484. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb44110370
APA StyleLyu, J., Imachi, H., Fukunaga, K., Sato, S., Kobayashi, T., Saheki, T., Japar, S., Iwama, H., Matsumura, Y., Ozaki, M., Yoshimura, T., & Murao, K. (2022). Exendin-4 Increases Scavenger Receptor Class BI Expression via Activation of AMPK/FoxO1 in Human Vascular Endothelial Cells. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 44(11), 5474-5484. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb44110370



