DYRK1A Overexpression in Mice Downregulates the Gonadotropic Axis and Disturbs Early Stages of Spermatogenesis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Blood Samples, Testis and Brain Tissue Collection, and Sperm Counts
2.3. Hormone Assays
2.4. Western Blotting
2.5. mRNA Extraction, Reverse Transcription, and QPCR
2.6. Immunohistochemistry Assays
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
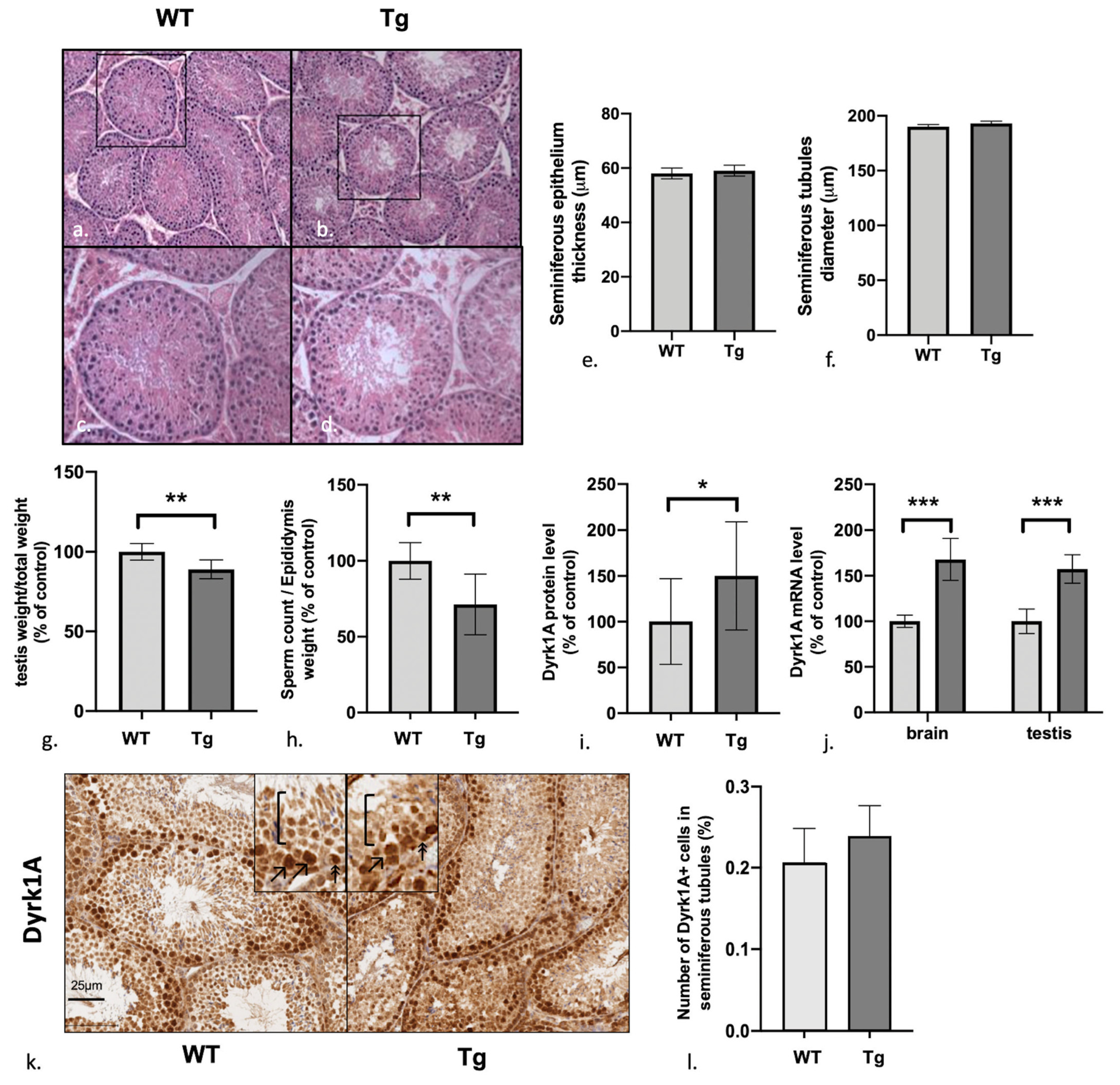
3.1. Male Mice Overexpressing Dyrk1A Have Structurally Normal But Relatively Light Testes and a Low Sperm Count
3.2. Dyrk1A (over)Expression in Tg Mice Is Predominantly Observed in the Early Stages of Spermatogenesis
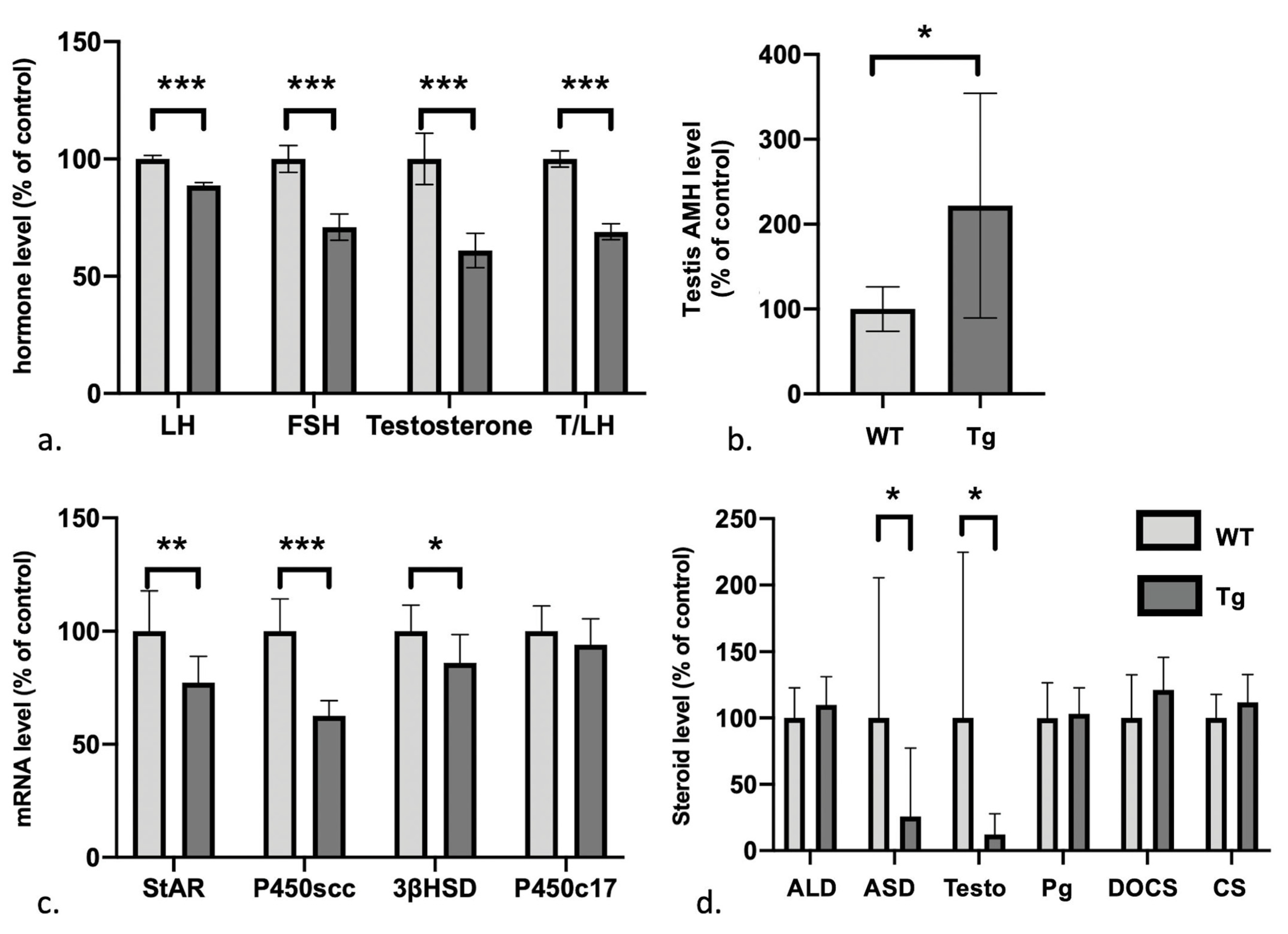
3.3. Defects in the Gonadotrophic Axis, Testosterone Levels, and Steroidogenesis But Elevated Levels of Anti-Müllerian Hormone
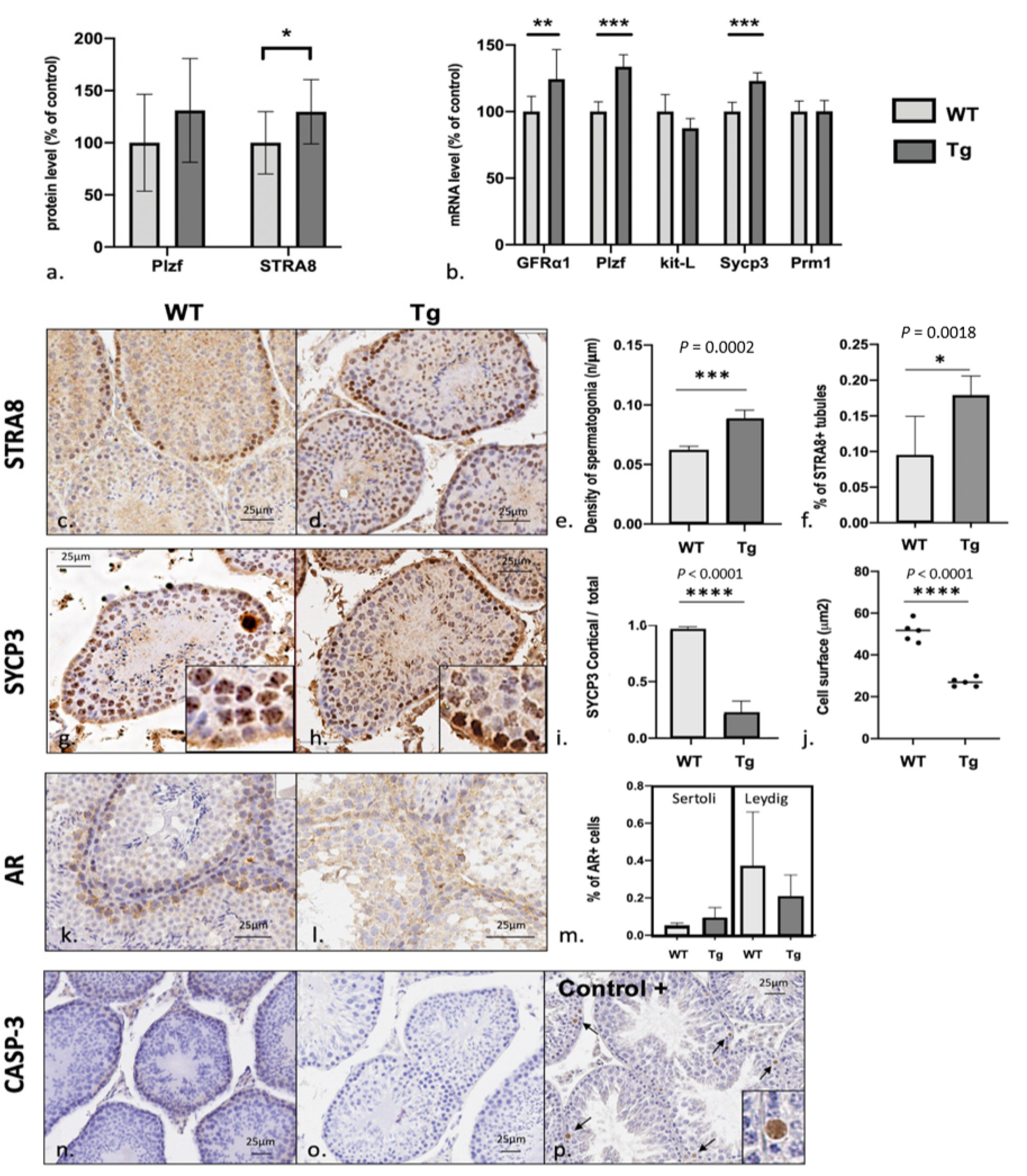
3.4. Spermatogenesis Failure in Early Stages of Meiosis with Excess Numbers of Spermatogonial Stem Cells
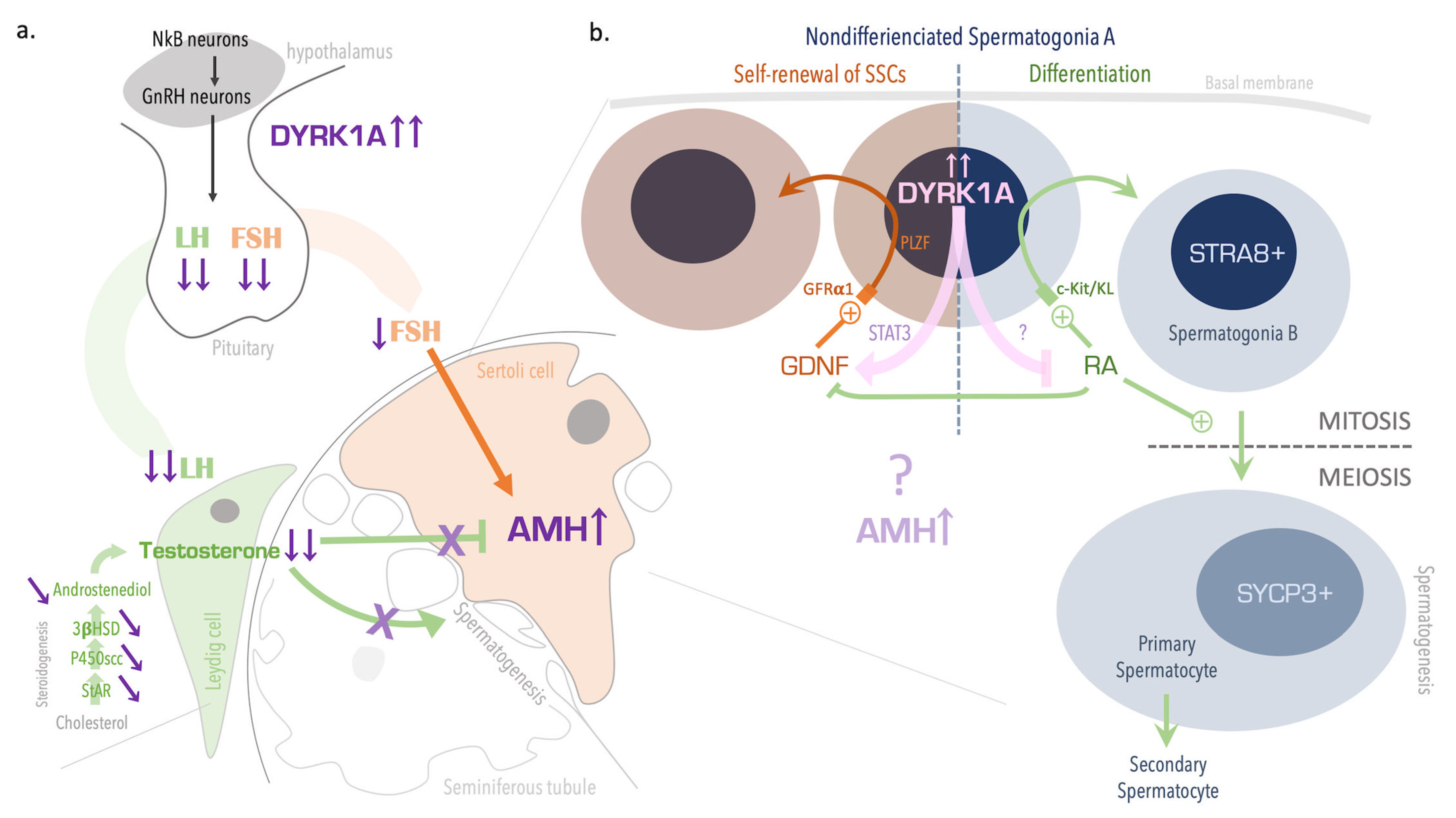
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Presson, A.P.; Partyka, G.; Jensen, K.M.; Devine, O.J.; Rasmussen, S.A.; McCabe, L.L.; McCabe, E.R.B. Current Estimate of Down Syndrome Population Prevalence in the United States. J. Pediatr. 2013, 163, 1163–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Watson, S.L.; Richards, D.A.; Miodrag, N.; Fedoroff, J.P. Sex and Genes, Part 1: Sexuality and Down, Prader–Willi, and Williams Syndromes. Intellect. Dev. Disabil. 2012, 50, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheridan, R.; Llerena, J., Jr.; Matkins, S.; Debenham, P.; Cawood, A.; Bobrow, M. Fertility in a Male with Trisomy 21. J. Med. Genet. 1989, 26, 294–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pradhan, M.; Dalal, A.; Khan, F.; Agrawal, S. Fertility in Men with Down Syndrome: A Case Report. Fertil. Steril. 2006, 86, 1765.e1–1765.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feki, A.; Hibaoui, Y. DYRK1A Protein, A Promising Therapeutic Target to Improve Cognitive Deficits in Down Syndrome. Brain Sci. 2018, 8, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laham, A.J.; Saber-Ayad, M.; El-Awady, R. DYRK1A: A down Syndrome-Related Dual Protein Kinase with a Versatile Role in Tumorigenesis. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2021, 78, 603–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Lin, Z.; Liu, M.; Wang, H.; Sun, H. Overexpression of DYRK1A, a Down Syndrome Candidate Gene, Impairs Primordial Germ Cells Maintenance and Migration in Zebrafish. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guedj, F.; Pereira, P.L.; Najas, S.; Barallobre, M.-J.; Chabert, C.; Souchet, B.; Sebrie, C.; Verney, C.; Herault, Y.; Arbones, M.; et al. DYRK1A: A Master Regulatory Protein Controlling Brain Growth. Neurobiol. Dis. 2012, 46, 190–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miura, M.; Sasagawa, I.; Suzuki, Y.; Nakada, T.; Fujii, J. Apoptosis and Expression of Apoptosis-Related Genes in the Mouse Testis Following Heat Exposure. Fertil. Steril. 2002, 77, 787–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiet, J.; Le Bouc, Y.; Guéchot, J.; Hélin, N.; Maubert, M.-A.; Farabos, D.; Lamazière, A. A Liquid Chromatography/Tandem Mass Spectometry Profile of 16 Serum Steroids, Including 21-Deoxycortisol and 21-Deoxycorticosterone, for Management of Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia. J. Endocr. Soc. 2017, 1, 186–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Souchet, B.; Guedj, F.; Sahún, I.; Duchon, A.; Daubigney, F.; Badel, A.; Yanagawa, Y.; Barallobre, M.J.; Dierssen, M.; Yu, E.; et al. Excitation/Inhibition Balance and Learning Are Modified by Dyrk1a Gene Dosage. Neurobiol. Dis. 2014, 69, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey, R.; al-Attar, L.; Louis, F.; Jaubert, F.; Barbet, P.; Nihoul-Fékété, C.; Chaussain, J.L.; Josso, N. Testicular Dysgenesis Does Not Affect Expression of Anti-Müllerian Hormone by Sertoli Cells in Premeiotic Seminiferous Tubules. Am. J. Pathol. 1996, 148, 1689–1698. [Google Scholar]
- Pfaffl, M.W.; Horgan, G.W.; Dempfle, L. Relative Expression Software Tool (REST) for Group-Wise Comparison and Statistical Analysis of Relative Expression Results in Real-Time PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, e36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, K.-J.; Jeong, H.K.; Choi, H.-S.; Ryoo, S.-R.; Kim, Y.J.; Goo, J.-S.; Choi, S.-Y.; Han, J.-S.; Ha, I.; Song, W.-J. DYRK1A BAC Transgenic Mice Show Altered Synaptic Plasticity with Learning and Memory Defects. Neurobiol. Dis. 2006, 22, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferder, I.C.; Fung, L.; Ohguchi, Y.; Zhang, X.; Lassen, K.G.; Capen, D.; Brown, D.; Xavier, R.J.; Wang, N. Meiotic Gatekeeper STRA8 Suppresses Autophagy by Repressing Nr1d1 Expression during Spermatogenesis in Mice. PLoS Genet. 2019, 15, e1008084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Griswold, M.D. Spermatogenesis: The Commitment to Meiosis. Physiol. Rev. 2016, 96, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.-L.; Ding, K.; Hu, X.; Wu, L.-W.; Zhou, D.-M.; Rao, M.-J.; Lin, N.-M.; Zhang, C. DYRK1A Inhibition Suppresses STAT3/EGFR/Met Signalling and Sensitizes EGFR Wild-Type NSCLC Cells to AZD9291. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 7427–7437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhansali, R.S.; Rammohan, M.; Lee, P.; Laurent, A.P.; Wen, Q.; Suraneni, P.; Yip, B.H.; Tsai, Y.-C.; Jenni, S.; Bornhauser, B.; et al. DYRK1A Regulates B Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia through Phosphorylation of FOXO1 and STAT3. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, 135937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, R.-H.; Xiong, J.; Liu, Y. Adenosine A2a Receptor Induces GDNF Expression by the Stat3 Signal in Vitro. Neuroreport 2012, 23, 958–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saracino, R.; Capponi, C.; Di Persio, S.; Boitani, C.; Masciarelli, S.; Fazi, F.; Fera, S.; Vicini, E. Regulation of Gdnf Expression by Retinoic Acid in Sertoli Cells. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2020, 87, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Cuevas, M.; Matunis, E.L. The Stem Cell Niche: Lessons from the Drosophila Testis. Development 2011, 138, 2861–2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oatley, J.M.; Kaucher, A.V.; Avarbock, M.R.; Brinster, R.L. Regulation of Mouse Spermatogonial Stem Cell Differentiation by STAT3 Signaling. Biol. Reprod. 2010, 83, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nagasawa, K.; Imura-Kishi, K.; Uchida, A.; Hiramatsu, R.; Kurohmaru, M.; Kanai, Y. Regionally Distinct Patterns of STAT3 Phosphorylation in the Seminiferous Epithelia of Mouse Testes. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2018, 85, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiechmann, S.; Czajkowska, H.; de Graaf, K.; Grötzinger, J.; Joost, H.-G.; Becker, W. Unusual Function of the Activation Loop in the Protein Kinase DYRK1A. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 302, 403–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-J.; Woo, H.; Lee, H.-E.; Jeon, H.; Ryu, K.-Y.; Nam, J.H.; Jeon, S.G.; Park, H.; Lee, J.-S.; Han, K.-M.; et al. The Novel DYRK1A Inhibitor KVN93 Regulates Cognitive Function, Amyloid-Beta Pathology, and Neuroinflammation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 160, 575–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tlili, A.; Noll, C.; Middendorp, S.; Duchon, A.; Jouan, M.; Benabou, E.; Hérault, Y.; Paul, J.-L.; Delabar, J.-M.; Janel, N. DYRK1A Overexpression Decreases Plasma Lecithin:Cholesterol Acyltransferase Activity and Apolipoprotein A-I Levels. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2013, 110, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Wang, L.; Chen, H.; Huang, Y.; Yang, P.; Ahmed, N.; Wang, T.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Q. Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms of Apoptosis during Dissociated Spermatogenesis. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johnson, C.; Jia, Y.; Wang, C.; Lue, Y.-H.; Swerdloff, R.S.; Zhang, X.-S.; Hu, Z.-Y.; Li, Y.-C.; Liu, Y.-X.; Hikim, A.P.S. Role of Caspase 2 in Apoptotic Signaling in Primate and Murine Germ Cells1. Biol. Reprod. 2008, 79, 806–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Young, J.; Chanson, P.; Salenave, S.; Noël, M.; Brailly, S.; O’Flaherty, M.; Schaison, G.; Rey, R. Testicular Anti-Mullerian Hormone Secretion Is Stimulated by Recombinant Human FSH in Patients with Congenital Hypogonadotropic Hypogonadism. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 90, 724–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grinspon, R.P.; Rey, R.A. Anti-Müllerian Hormone and Sertoli Cell Function in Paediatric Male Hypogonadism. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 2010, 73, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valeri, C.; Lovaisa, M.M.; Racine, C.; Edelsztein, N.Y.; Riggio, M.; Giulianelli, S.; Venara, M.; Bedecarrás, P.; Ballerini, M.G.; di Clemente, N.; et al. Molecular Mechanisms Underlying AMH Elevation in Hyperoestrogenic States in Males. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.-Y.; Zhang, H.-X.; Xiao, Z.; Qiao, J.; Li, R. Regulation of Anti-Müllerian Hormone (AMH) in Males and the Associations of Serum AMH with the Disorders of Male Fertility. Asian J. Androl. 2019, 21, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stearns, P.E.; Droulard, K.E.; Sahhar, F.H. Studies Bearing on Fertility of Male and Female Mongoloids. Am. J. Ment. Defic. 1960, 65, 37–41. [Google Scholar]
- Benda, C.E. Down’s Syndrome: Mongolism and Its Management; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvadorini, F.; Saba, P.; Galeone, F.; Tognetti, G.; Carnicelli, A.; Busoni, C.A. Studies of the dynamics of anterior pituitary gonadotropic activity in the Langdon-Down syndrome. Acta Neurol. 1975, 30, 78–83. [Google Scholar]
- Horan, R.F.; Beitins, I.Z.; Bode, H.H. LH-RH Testing in Men with Down’s Syndrome. Acta Endocrinol. 1978, 88, 594–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasen, J.; Boyar, R.M.; Shapiro, L.R. Gonadal Function in Trisomy 21. Horm. Res. 1980, 12, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagiello, G. Reproduction in Down Syndrome; University Park Press: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1981; p. 152. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, W.A.; Lowther, J.; McKenzie, I.; Price, W.H. Serum Gonadotrophins in Down’s Syndrome. J. Med. Genet. 1982, 19, 98–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hsiang, Y.H.; Berkovitz, G.D.; Bland, G.L.; Migeon, C.J.; Warren, A.C. Gonadal Function in Patients with Down Syndrome. Am. J. Med. Genet. 1987, 27, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnell, H.; Gustafsson, J.; Ivarsson, S.A.; Annerén, G. Growth and Pubertal Development in Down Syndrome. Acta Paediatr. 1996, 85, 1102–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pueschel, S.M.; Orson, J.M.; Boylan, J.M.; Pezzullo, J.C. Adolescent Development in Males with Down Syndrome. Am. J. Dis. Child 1985, 139, 236–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakadamis, A.; Angelopoulou, N.; Matziari, C.; Papameletiou, V.; Souftas, V. Bone Mass, Gonadal Function and Biochemical Assessment in Young Men with Trisomy 21. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2002, 100, 208–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attia Sexual and Reproductive Functions in Men with Down’s Syndrome. Available online: https://www.mmj.eg.net/article.asp?issn=1110-2098;year=2015;volume=28;issue=2;spage=471;epage=476;aulast=Attia (accessed on 2 July 2021).
- Sasaki, M. Meiosis in a Male with Down’s Syndrome. Chromosoma 1965, 16, 652–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finch, R.; Böök, J.A.; Finley, W.H.; Finley, S.C.; Tucker, C.C. Meiosis in Trisomic Down’s Syndrome. Ala. J. Med. Sci. 1966, 3, 117–120. [Google Scholar]
- Hungerford, D.A.; Mellman, W.J.; Balaban, G.B.; LaBadie, G.U.; Messatzzia, L.R.; Haller, G. Chromosome Structure and Function in Man. 3. Pachytene Analysis and Indentification of the Supernumerary Chromosome in a Case of Down’s Syndrome (Mongolism). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1970, 67, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hultén, M.A.; Lindsten, J. The behaviour of structural aberrations at male meiosis In lnformation from man. In Human Populations Cytogenetics; Pfizer Medical Monographs; Edinburgh University Press: Edingburgh, UK, 1970; pp. 24–61. [Google Scholar]
- Kjessler, B.; De la Chapelle, A. Meiosis and Spermatogenesis in Two Postpubertal Males with Down’s Syndrome: 47, XY, G+. Clin. Genet. 1971, 2, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schröder, J.; Lydecken, K.; De la Chapelle, A. Meiosis and Spermatogenesis in G-Trisomic Males. Humangenetik 1971, 13, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giraud, F.; Luciani, J.M.; Mattei, J.F.; Galinier, L.; Stahl, A.; Gascard, E. Clinical, mitotic and meiotic study of a trisomy 21 with diabetes in a 52 year old man. Mars Med. 1971, 108, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Johannisson, R.; Gropp, A.; Winking, H.; Coerdt, W.; Rehder, H.; Schwinger, E. Down’s Syndrome in the Male. Reproductive Pathology and Meiotic Studies. Hum. Genet. 1983, 63, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aït Yahya-Graison, E.; Aubert, J.; Dauphinot, L.; Rivals, I.; Prieur, M.; Golfier, G.; Rossier, J.; Personnaz, L.; Creau, N.; Bléhaut, H.; et al. Classification of Human Chromosome 21 Gene-Expression Variations in Down Syndrome: Impact on Disease Phenotypes. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 81, 475–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- London, J.; Rouch, C.; Bui, L.C.; Assayag, E.; Souchet, B.; Daubigney, F.; Medjaoui, H.; Luquet, S.; Magnan, C.; Delabar, J.M.; et al. Overexpression of the DYRK1A Gene (Dual-Specificity Tyrosine Phosphorylation-Regulated Kinase 1A) Induces Alterations of the Serotoninergic and Dopaminergic Processing in Murine Brain Tissues. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 3822–3831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dard, R.; Moreau, M.; Parizot, E.; Ghieh, F.; Brehier, L.; Kassis, N.; Serazin, V.; Lamaziere, A.; Racine, C.; di Clemente, N.; et al. DYRK1A Overexpression in Mice Downregulates the Gonadotropic Axis and Disturbs Early Stages of Spermatogenesis. Genes 2021, 12, 1800. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12111800
Dard R, Moreau M, Parizot E, Ghieh F, Brehier L, Kassis N, Serazin V, Lamaziere A, Racine C, di Clemente N, et al. DYRK1A Overexpression in Mice Downregulates the Gonadotropic Axis and Disturbs Early Stages of Spermatogenesis. Genes. 2021; 12(11):1800. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12111800
Chicago/Turabian StyleDard, Rodolphe, Manon Moreau, Estelle Parizot, Farah Ghieh, Leslie Brehier, Nadim Kassis, Valérie Serazin, Antonin Lamaziere, Chrystèle Racine, Nathalie di Clemente, and et al. 2021. "DYRK1A Overexpression in Mice Downregulates the Gonadotropic Axis and Disturbs Early Stages of Spermatogenesis" Genes 12, no. 11: 1800. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12111800
APA StyleDard, R., Moreau, M., Parizot, E., Ghieh, F., Brehier, L., Kassis, N., Serazin, V., Lamaziere, A., Racine, C., di Clemente, N., Vialard, F., & Janel, N. (2021). DYRK1A Overexpression in Mice Downregulates the Gonadotropic Axis and Disturbs Early Stages of Spermatogenesis. Genes, 12(11), 1800. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12111800





