Can Early Environmental Enrichment Buffer Stress from Commercial Hatchery Processing in Laying Hens?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Note
2.2. Animals and Housing
2.3. Weight
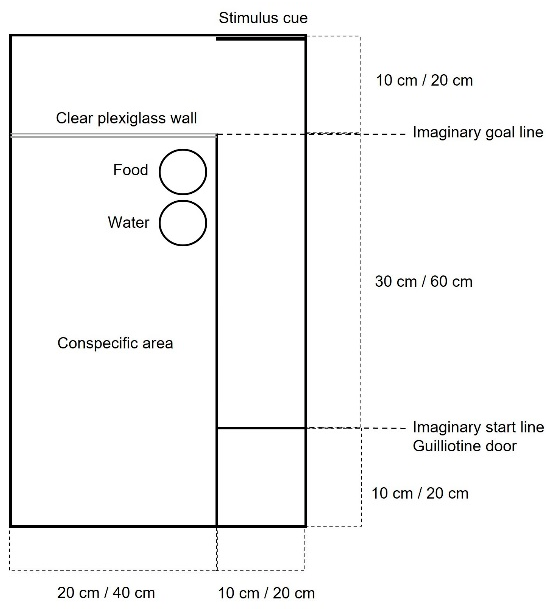
2.4. Social Isolation Test
2.5. Novel Arena Test
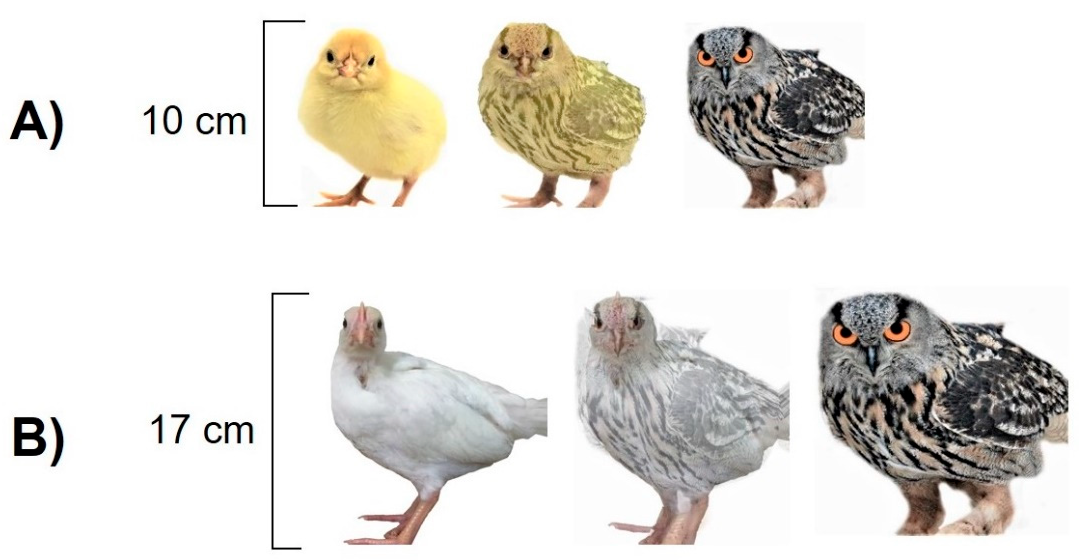
2.6. Cognitive Judgement Bias
2.7. HPA-Axis Reactivity
2.8. Statistics
3. Results
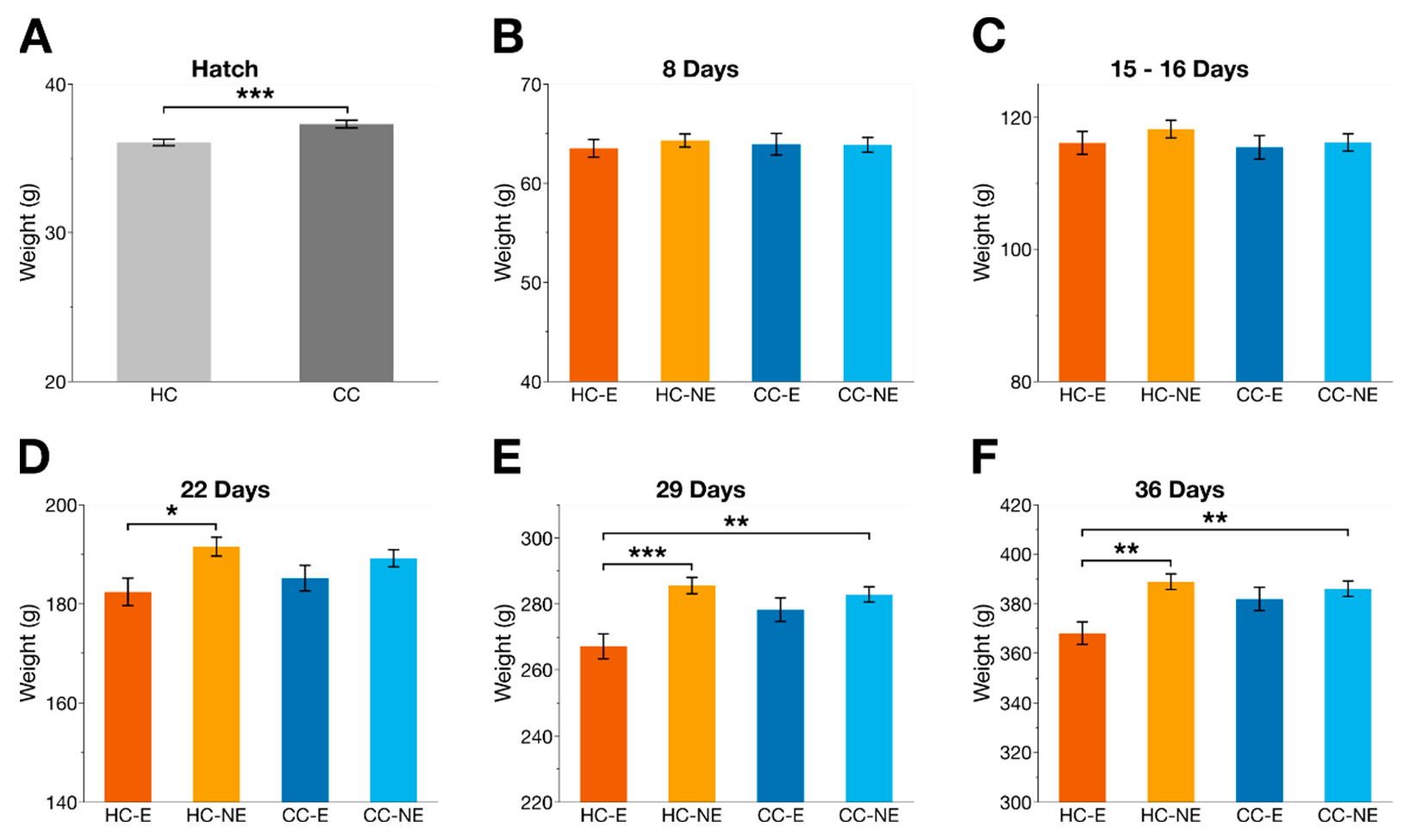
3.1. Weight
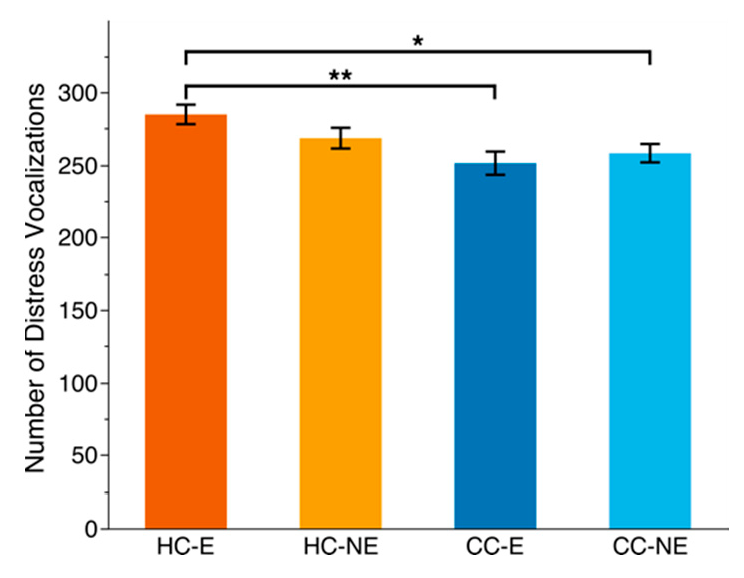
3.2. Social Isolation Test
3.3. Novel Arena Test
3.4. Cognitive Judgement Bias
3.5. HPA-Axis Reactivity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hedlund, L.; Whittle, R.; Jensen, P. Effects of commercial hatchery processing on short-and long-term stress responses in laying hens. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hedlund, L.; Jensen, P. Incubation and hatching conditions of laying hen chicks explain a large part of the stress effects from commercial large-scale hatcheries. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedlund, L.; Palazon, T.; Jensen, P. Stress during Commercial Hatchery Processing Induces Long-Time Negative Cognitive Judgement Bias in Chickens. Animals 2021, 11, 1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yahav, S.; Hurwitz, S. Induction of thermotolerance in male broiler chickens by temperature conditioning at an early age. Poult. Sci. 1996, 75, 402–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altan, O.; Altan, A.; Oguz, I.; Pabuccuoglu, A.; Konyalioglu, S. Effects of heat stress on growth, some blood variables and lipid oxidation in broilers exposed to high temperature at an early age. Br. Poult. Sci. 2000, 41, 489–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinder, D.; Luger, D.; Rusal, M.; Rzepakovsky, V.; Bresler, V.; Yahav, S. Early age cold conditioning in broiler chickens (Gallus domesticus): Thermotolerance and growth responses. J. Therm. Biol. 2002, 27, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, D.; De Haas, E.; Lee, C. A review of environmental enrichment for laying hens during rearing in relation to their behavioral and physiological development. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 9–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lupien, S.J.; McEwen, B.S.; Gunnar, M.R.; Heim, C. Effects of stress throughout the lifespan on the brain, behaviour and cognition. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2009, 10, 434–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodricks, C.L.; Miller, S.L.; Jenkin, G.; Gibbs, M.E. The role of corticosterone in prehatch-induced memory deficits in chicks. Brain Res. 2006, 1123, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, N.; Sandi, C.; Rose, S.P. Interactions of corticosterone and embryonic light deprivation on memory retention in day-old chicks. Dev. Brain Res. 1997, 101, 269–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, D.D.; Diorio, J.; Plotsky, P.M.; Meaney, M.J. Environmental enrichment reverses the effects of maternal separation on stress reactivity. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 7840–7843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashokan, A.; Hegde, A.; Mitra, R. Short-term environmental enrichment is sufficient to counter stress-induced anxiety and associated structural and molecular plasticity in basolateral amygdala. Psychoneuroendocrino 2016, 69, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douglas, C.; Bateson, M.; Walsh, C.; Bédué, A.; Edwards, S.A. Environmental enrichment induces optimistic cognitive biases in pigs. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2012, 139, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brydges, N.M.; Leach, M.; Nicol, K.; Wright, R.; Bateson, M. Environmental enrichment induces optimistic cognitive bias in rats. Anim. Behav. 2011, 81, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matheson, S.M.; Asher, L.; Bateson, M. Larger, enriched cages are associated with ‘optimistic’response biases in captive European starlings (Sturnus vulgaris). Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2008, 109, 374–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bateson, M.; Matheson, S. Performance on a categorisation task suggests that removal of environmental enrichment induces pessimism in captive European starlings (Sturnus vulgaris). Anim. Welf. 2007, 16, 33–36. [Google Scholar]
- Richter, S.H.; Schick, A.; Hoyer, C.; Lankisch, K.; Gass, P.; Vollmayr, B. A glass full of optimism: Enrichment effects on cognitive bias in a rat model of depression. Cogn. Affect. Behav. Neurosci. 2012, 12, 527–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bethell, E.J.; Koyama, N.F. Happy hamsters? Enrichment induces positive judgement bias for mildly (but not truly) ambiguous cues to reward and punishment in Mesocricetus auratus. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2015, 2, 140399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ross, M.; Rausch, Q.; Vandenberg, B.; Mason, G. Hens with benefits: Can environmental enrichment make chickens more resilient to stress? Physiol. Behav. 2020, 226, 113077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozempolska-Rucińska, I.; Kasperek, K.; Drabik, K.; Zięba, G.; Ziemiańska, A. Behavioural Variability in Chicks vs. the Pattern of Behaviour in Adult Hens. Animals 2020, 10, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, R.B.; Waddington, D. Modification of fear in domestic chicks, Gallus gallus domesticus, via regular handling and early environmental enrichment. Anim. Behav. 1992, 43, 1021–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forkman, B.; Boissy, A.; Meunier-Salaün, M.-C.; Canali, E.; Jones, R. A critical review of fear tests used on cattle, pigs, sheep, poultry and horses. Physiol. Behav. 2007, 92, 340–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sufka, K.J.; Hughes, R.A. Differential effects of handling on isolation-induced vocalizations, hypoalgesia, and hyperthermia in domestic fowl. Physiol. Behav. 1991, 50, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feltenstein, M.W.; Lambdin, L.C.; Webb, H.E.; Warnick, J.E.; Khan, S.I.; Khan, I.A.; Acevedo, E.O.; Sufka, K.J. Corticosterone response in the chick separation–stress paradigm. Physiol. Behav. 2003, 78, 489–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sufka, K.J.; Feltenstein, M.W.; Warnick, J.E.; Acevedo, E.O.; Webb, H.E.; Cartwright, C.M. Modeling the anxiety–depression continuum hypothesis in domestic fowl chicks. Behav. Pharmacol. 2006, 17, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bateson, P. The characteristics and context of imprinting. In Readings in Behavior; Van der Kloot, W., Walcott, C., Dane, B., Eds.; Holt, Rinehart and Winston, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1974; pp. 329–375. [Google Scholar]
- McCabe, B.J. Visual imprinting in birds: Behavior, models, and neural mechanisms. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riber, A.B.; Nielsen, B.L.; Ritz, C.; Forkman, B. Diurnal activity cycles and synchrony in layer hen chicks (Gallus gallus domesticus). Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2007, 108, 276–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilani, A.-M.; Knowles, T.G.; Nicol, C.J. The effect of dark brooders on feather pecking on commercial farms. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2012, 142, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riber, A.B.; Guzman, D.A. Effects of dark brooders on behavior and fearfulness in layers. Animals 2016, 6, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Riber, A.B.; Guzmán, D.A. Effects of different types of dark brooders on injurious pecking damage and production-related traits at rear and lay in layers. Poult. Sci. 2017, 96, 3529–3538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perré, Y.; Wauters, A.-M.; Richard-Yris, M.-A. Influence of mothering on emotional and social reactivity of domestic pullets. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2002, 75, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedlund, L.; Jensen, P. Effects of stress during commercial hatching on growth, egg production and feather pecking in laying hens. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0262307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peebles, E.; Zumwalt, C.; Doyle, S.; Gerard, P.; Boyle, C.; Smith, T.; Latour, M. Effects of breeder age and dietary fat source and level on broiler hatching egg characteristics. Poult. Sci. 2000, 79, 698–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silversides, F.G.; Scott, T.A. Effect of storage and layer age on quality of eggs from two lines of hens. Poult. Sci. 2001, 80, 1240–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Den Brand, H.; Parmentier, H.; Kemp, B. Effects of housing system (outdoor vs cages) and age of laying hens on egg characteristics. Br. Poult. Sci. 2004, 45, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzi, C.; Chiericato, G.M. Organic farming production. Effect of age on the productive yield and egg quality of hens of two commercial hybrid lines and two local breeds. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2005, 4, 160–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Campbell, D.L.; Gerber, P.F.; Downing, J.A.; Lee, C. Minimal Effects of Rearing Enrichments on Pullet Behaviour and Welfare. Animals 2020, 10, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nazar, N.; Skånberg, L.; McCrea, K.; Keeling, L. Start on the Right Foot: Choice in a Complex Early Environment Boosts Coping Abilities in the Domestic Fowl Chick. Res. Sq. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altan, O.; Seremet, C.; Bayraktar, H. The effects of early environmental enrichment on performance, fear and physiological responses to acute stress of broiler. Arch. Geflügelkd. 2013, 77, 23–28. [Google Scholar]
- Bailie, C.; Ball, M.; O’Connell, N. Influence of the provision of natural light and straw bales on activity levels and leg health in commercial broiler chickens. Animal 2013, 7, 618–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bailie, C.; O’Connell, N. The effect of level of straw bale provision on the behaviour and leg health of commercial broiler chickens. Animal 2014, 8, 1715–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aksit, M.; Yardim, Z.K.; Yalcin, S. Environmental enrichment influences on broiler performance and meat quality: Effect of light source and providing perches. Eur. Poult. Sci. 2017, 81, 182. [Google Scholar]
- Weldon, K.B.; Fanson, K.V.; Smith, C.L. Effects of isolation on stress responses to novel stimuli in subadult chickens (Gallus gallus). Ethology 2016, 122, 818–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumtaz, F.; Khan, M.I.; Zubair, M.; Dehpour, A.R. Neurobiology and consequences of social isolation stress in animal model—A comprehensive review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 105, 1205–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.H.; Sufka, K.J. The effects of environmental enrichment in the chick anxiety-depression model. Behav. Brain Res. 2011, 221, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salmeto, A.L.; Hymel, K.A.; Carpenter, E.C.; Brilot, B.O.; Bateson, M.; Sufka, K.J. Cognitive bias in the chick anxiety–depression model. Brain Res. 2011, 1373, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marx, G.; Leppelt, J.; Ellendorff, F. Vocalisation in chicks (Gallus gallus dom.) during stepwise social isolation. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2001, 75, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deakin, A.; Browne, W.J.; Hodge, J.J.; Paul, E.S.; Mendl, M. A screen-peck task for investigating cognitive bias in laying hens. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0158222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oluwaseun, S.I.; Beard, A.P.; Guy, J.H.; Bateson, M. Elevated levels of the stress hormone, corticosterone, cause ‘pessimistic’ judgment bias in broiler chickens. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6860. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, M.; Campbell, A.; Crump, A.; Arnott, G.; Newberry, R.; Jacobs, L. Effect of environmental complexity and stocking density on fear and anxiety in broiler chickens. Animals 2021, 11, 2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skånberg, L.; Nielsen, C.B.K.; Keeling, L.J. Litter and perch type matter already from the start: Exploring preferences and perch balance in laying hen chicks. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinchasov, Y.; Noy, Y. Comparison of post-hatch holding time and subsequent early performance of broiler chicks and turkey poults. Br. Poult. Sci. 1993, 34, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxter, M.; Bailie, C.L.; O’Connell, N. Play behaviour, fear responses and activity levels in commercial broiler chickens provided with preferred environmental enrichments. Animal 2019, 13, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roden, C.; Wechsler, B. A comparison of the behaviour of domestic chicks reared with or without a hen in enriched pens. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 1998, 55, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wauters, A.M.; Richard-Yris, M.A.; Talec, N. Maternal influences on feeding and general activity in domestic chicks. Ethology 2002, 108, 529–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

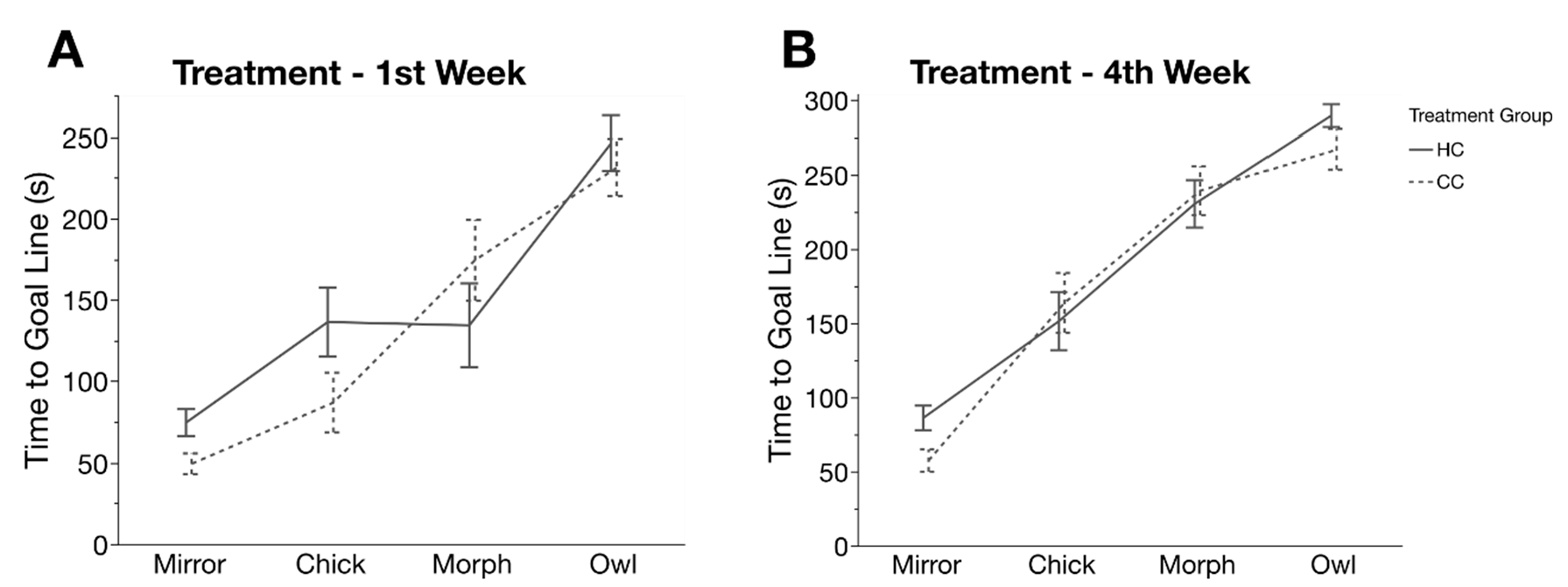
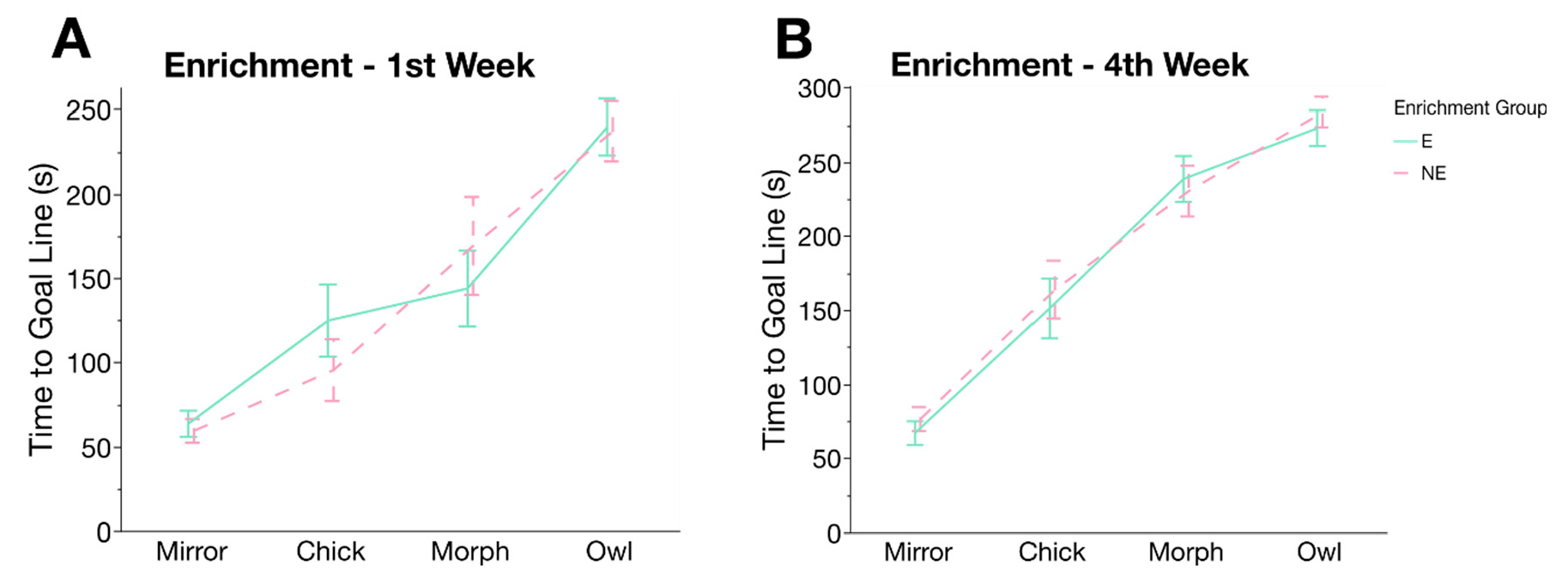
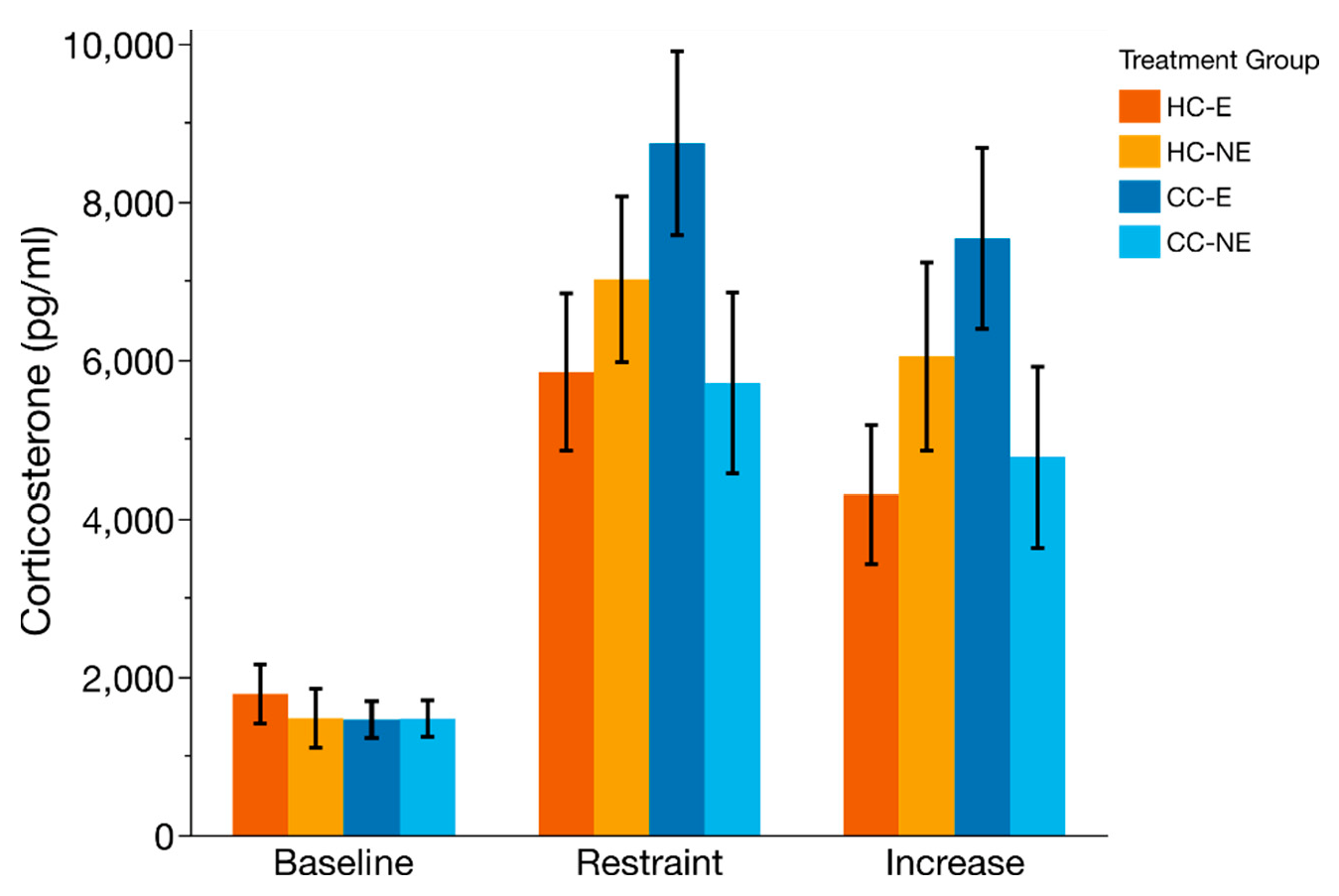
| Age (Days) | Treatment (HC/CC) | Enrichment (E/NE) | Interaction Treatment × Enrichment | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wχ2 | df | p-Value | Wχ2 | df | p-Value | Wχ2 | df | p-Value | |
| Hatch | 13.73 | 1 | <0.001 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 8 | 0.00 | 1 | 0.10 | 0.19 | 1 | 0.66 | 0.26 | 1 | 0.61 |
| 15–16 | 0.78 | 1 | 0.38 | 0.86 | 1 | 0.35 | 0.20 | 1 | 0.65 |
| 22 | <0.01 | 1 | 0.92 | 8.66 | 1 | <0.01 | 1.32 | 1 | 0.25 |
| 29 | 1.92 | 1 | 0.17 | 14.42 | 1 | <0.001 | 5.15 | 1 | 0.02 |
| 36 | 2.04 | 1 | 0.15 | 10.49 | 1 | 0.001 | 4.68 | 1 | 0.03 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hedlund, L.; Van Poucke, E.; Jensen, P. Can Early Environmental Enrichment Buffer Stress from Commercial Hatchery Processing in Laying Hens? Poultry 2022, 1, 125-137. https://doi.org/10.3390/poultry1020011
Hedlund L, Van Poucke E, Jensen P. Can Early Environmental Enrichment Buffer Stress from Commercial Hatchery Processing in Laying Hens? Poultry. 2022; 1(2):125-137. https://doi.org/10.3390/poultry1020011
Chicago/Turabian StyleHedlund, Louise, Enya Van Poucke, and Per Jensen. 2022. "Can Early Environmental Enrichment Buffer Stress from Commercial Hatchery Processing in Laying Hens?" Poultry 1, no. 2: 125-137. https://doi.org/10.3390/poultry1020011
APA StyleHedlund, L., Van Poucke, E., & Jensen, P. (2022). Can Early Environmental Enrichment Buffer Stress from Commercial Hatchery Processing in Laying Hens? Poultry, 1(2), 125-137. https://doi.org/10.3390/poultry1020011






