Bio-Remediation of Agro-Based Industries’ Wastewater and Mass Production of Spirulina (Spirulina platensis (Gomont) Geitler 1925) †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experiments
2.1. Collection of Mother Culture
2.2. Media Preparation and Inoculation
2.3. Sample Preparation
2.4. Culturing of Spirulina in Different Kinds of Wastewater
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Chemical Parameters of Various Selected Liquid Wastes
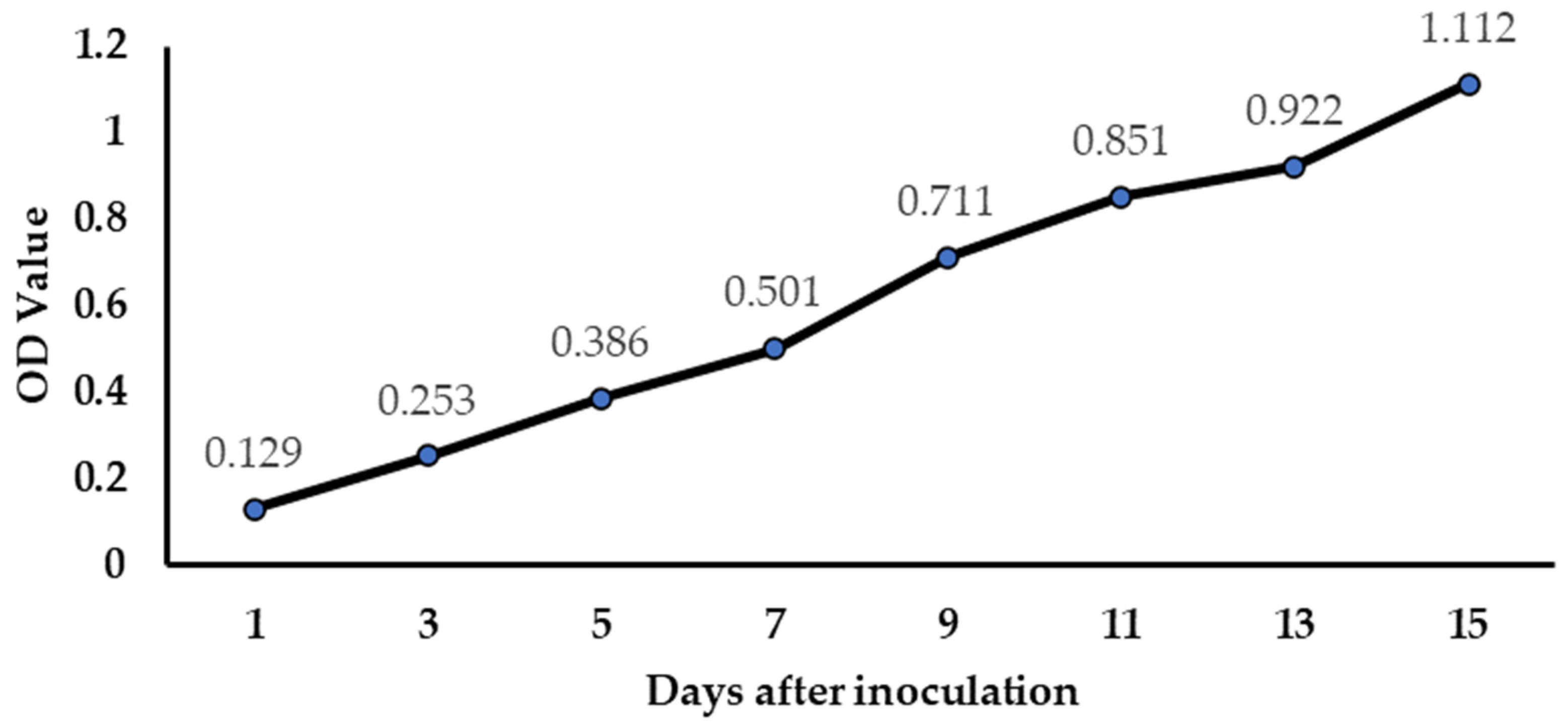
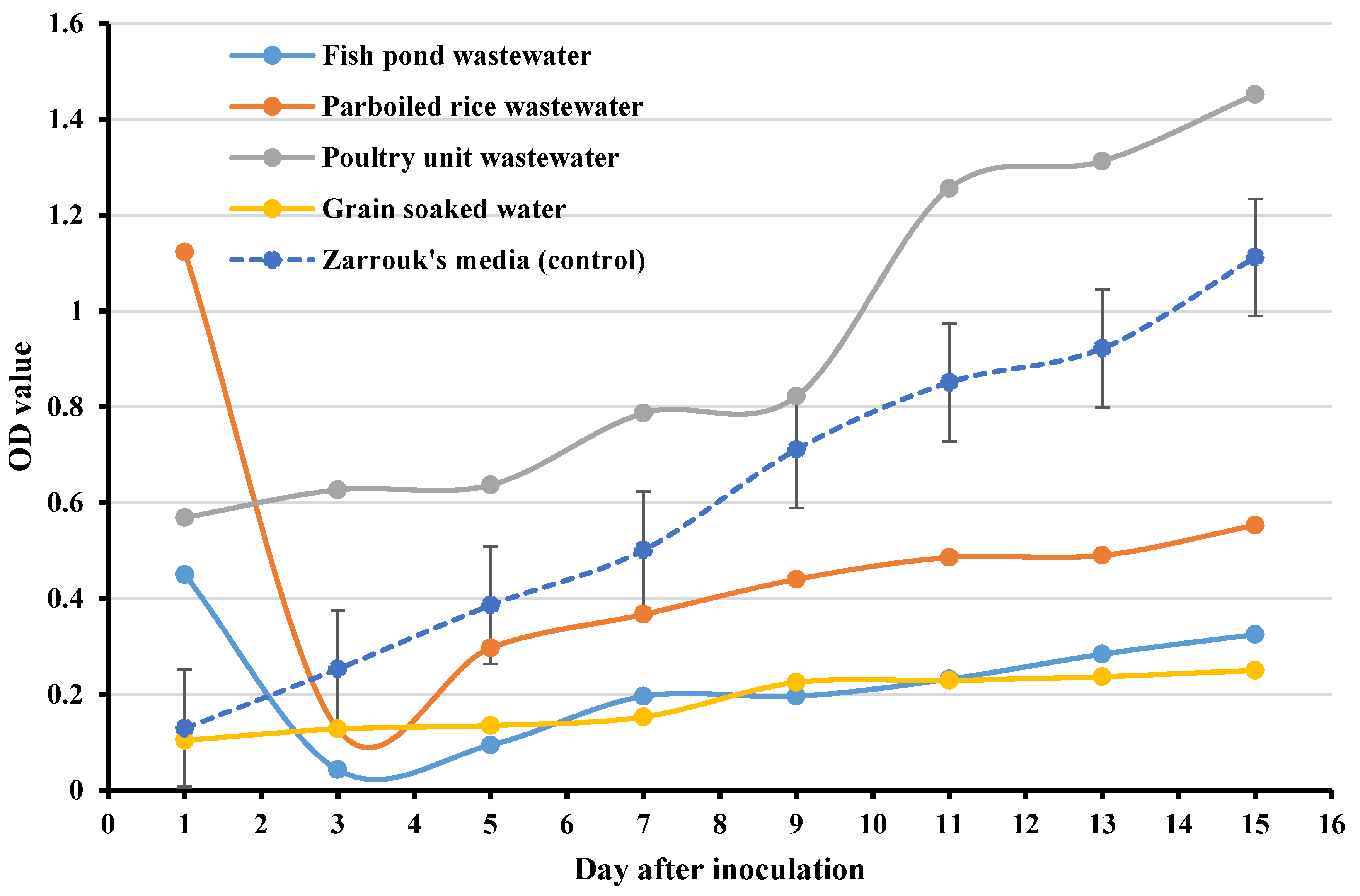
3.2. Determination of Spirulina platensis Growth in Different Wastewaters
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ariede, M.B.; Candido, T.M.; Jacome, A.L.M.; Velasco, M.V.R.; de Carvalho, J.C.M.; Baby, A.R. Cosmetic attributes of algae—A review. Algal Res. 2017, 25, 483–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolatabadi, S.; Hosseini, S.A. Wastewater treatment using Spirulina Platensis. J. Chem. Biol. Phys. Sci. 2016, 6, 1239–1246. [Google Scholar]
- Delrue, F.; Alaux, E.; Moudjaoui, L.; Gaignard, C.; Fleury, G.; Perilhou, A.; Richaud, P.; Petitjean, M.; Sassi, J.F. Optimization of Arthrospira platensis (Spirulina) growth: From laboratory scale to pilot scale. Fermentation 2017, 3, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheunbarn, S.; Peerapornpisal, Y. Cultivation of Spirulina platensis using anaerobically swine wastewater treatment effluent. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2010, 12, 586–590. Available online: https://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.1037.4007&rep=rep1&type=pdf (accessed on 3 January 2022).
- Markou, G.; Chatzipavlidis, I.; Georgakakis, D. Cultivation of Arthrospira (Spirulina) platensis in olive-oil mill wastewater treated with sodium hypochlorite. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 112, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, M.; Kaur, K.; Mishra, T.; Singh, S. To evaluate lab scale cultivation of Spirulina by using different substrates and to evaluate its chlorophyll and protein content. Int. Res. J. Biol. Sci. 2014, 3, 22–30. [Google Scholar]
- Kulkarni, S.D.; Auti, T.; Saraf, S. Bioremediation study of dairy effluent by using Spirulina platensis. Res. J. Life Sci. Bioinform. Pharm. Chem. Sci 2016, 1, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dineshkumar, R.; Narendran, R.; Sampathkumar, P. Cultivation of Spirulina platensis in different selective media. Indian J. Geo Mar. Sci. 2016, 45, 1749–1754. Available online: https://nopr.niscair.res.in/handle/123456789/40537 (accessed on 3 January 2022).
- Rajasekaran, C.; Ajeesh, C.M.; Balaji, S.; Shalini, M.; Ramamoorthy, S.I.V.A.; Ranjan, D.A.S.; Fulzele, D.P.; Kalaivani, T. Effect of modified Zarrouk’s medium on growth of different Spirulina strains. Walailak J. Sci. Technol. (WJST) 2016, 13, 67–75. Available online: https://103.58.148.28/index.php/wjst/article/view/1416 (accessed on 3 January 2022).
- Gil de los Santos, D.; Gil Turnes, C.; Rochedo Conceição, F. Bioremediation of parboiled rice effluent supplemented with biodiesel-derived glycerol using Pichia pastoris X-33. Sci. World J. 2012, 2012, 492925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mukherjee, C.; Chowdhury, R.; Sutradhar, T.; Begam, M.; Ghosh, S.M.; Basak, S.K.; Ray, K. Parboiled rice effluent: A wastewater niche for microalgae and cyanobacteria with growth coupled to comprehensive remediation and phosphorus biofertilization. Algal Res. 2016, 19, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MadkoGhofar, H.S.A.; Jahromi, M.J.; Ikhsan, F.N.M.; Samsudin, A.A. The effects of varying dilution levels of wastewater on the cultivation of Spirulina sp. Malays. J. Anim. Sci. 2019, 22, 25–33. [Google Scholar]
- ur, F.F.; Kamil, A.E.W.; Nasr, H.S. Production and nutritive value of Spirulina platensis in reduced cost media. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2012, 38, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ranjith, L.; Shukla, S.P.; Vennila, A.; Purushothaman, C.S. Growth performance of Spirulina (Arthrospira) platensis in a low cost medium: An assessment. Acta Biol. Indica 2013, 2, 335–342. Available online: https://bioscipub.com/journals/abi/pdf/335-342.pdf (accessed on 3 January 2022).
- Habib, M.A.B. A review on culture, production and use of spirulina as food for humans and feeds for domestic animals and fish. In FAO Fisheries and Aquaculture Circular; No. 1034; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2008; Volume 33, p. 14. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.S.; Lee, S.H. Quantitative analysis of Spirulina platensis growth with CO2 mixed aeration. Environ. Eng. Res. 2018, 23, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soni, R.A.; Sudhakar, K.; Rana, R.S. Comparative study on the growth performance of Spirulina platensis on modifying culture media. Energy Rep. 2019, 5, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Yuan, W.; Pei, Z.J.; Wu, Q.; Mao, E. Microalgae mass production methods. Trans. ASABE 2009, 52, 1275–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Type of Waste | Treatment | Volume of Waste | Volume of Water |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fishpond wastewater | T1 | 250 mL | 750 mL |
| T2 | 500 mL | 500 mL | |
| T3 | 750 mL | 250 mL | |
| T4 | 1000 mL | - | |
| Parboiled rice water | T1 | 250 mL | 750 mL |
| T2 | 500 mL | 500 mL | |
| T3 | 750 mL | 250 mL | |
| T4 | 1000 mL | - | |
| Poultry wastewater | T1 | 250 mL | 750 mL |
| T2 | 500 mL | 500 mL | |
| T3 | 750 mL | 250 mL | |
| T4 | 1000 mL | - | |
| Grain-soaked water | T1 | 250 mL | 750 mL |
| T2 | 500 mL | 500 mL | |
| T3 | 750 mL | 250 mL | |
| T4 | 1000 mL | - |
| Substrate | Chemical Characters at the Beginning of Culturing | Chemical Characters at the End of Culturing | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | N% | P (mg/L) | K (mg/L) | EC (mS/cm) | pH | N% | P (mg/L) | K (mg/L) | EC (mS/cm) | |
| Fishpond wastewater | 7.89 a | 1.1 b | 39.1 b | 63.7 a | 1.87 b | 6.9 b | 0.9 b | 37.1 b | 61.7 a | 9.98 a |
| Parboiled rice liquid | 5.21 a | 0.7 b | 35.9 b | 30.1 b | 1.79 a | 6.01 a | 0.6 b | 34.1 b | 30.1 b | 1.01 a |
| Poultry unit | 9.28 a | 3.2 a | 10.8 c | 36.1 b | 1.501 a | 7.5 b | 2.4 a | 8.2 c | 35.4 b | 9.11 a |
| Grain-soaked water | 8.21 a | 0.9 b | 84.2 a | 60.2 a | 1.99 a | 7.1 b | 0.7 b | 80.2 a | 59.2 a | 8.34 a |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vijayarasa, J.; Pakeerathan, K.; Thiruchchelvan, N.; Mikunthan, G. Bio-Remediation of Agro-Based Industries’ Wastewater and Mass Production of Spirulina (Spirulina platensis (Gomont) Geitler 1925). Biol. Life Sci. Forum 2021, 3, 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/IECAG2021-09716
Vijayarasa J, Pakeerathan K, Thiruchchelvan N, Mikunthan G. Bio-Remediation of Agro-Based Industries’ Wastewater and Mass Production of Spirulina (Spirulina platensis (Gomont) Geitler 1925). Biology and Life Sciences Forum. 2021; 3(1):24. https://doi.org/10.3390/IECAG2021-09716
Chicago/Turabian StyleVijayarasa, Jerentulina, Kandiah Pakeerathan, Nagarathnam Thiruchchelvan, and Gunasingham Mikunthan. 2021. "Bio-Remediation of Agro-Based Industries’ Wastewater and Mass Production of Spirulina (Spirulina platensis (Gomont) Geitler 1925)" Biology and Life Sciences Forum 3, no. 1: 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/IECAG2021-09716
APA StyleVijayarasa, J., Pakeerathan, K., Thiruchchelvan, N., & Mikunthan, G. (2021). Bio-Remediation of Agro-Based Industries’ Wastewater and Mass Production of Spirulina (Spirulina platensis (Gomont) Geitler 1925). Biology and Life Sciences Forum, 3(1), 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/IECAG2021-09716







