Abstract
The Gonipterini tribe (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) contains a number of species of economic significance, including several species of Gonipterus which are invasive pests of eucalypt plantations internationally. However, the interspecific ecosystem-level interactions and population dynamics of many species are poorly understood within their native range. This study investigated the associations of adults of two species of Oxyops and two species of Gonipterus from Central Queensland, Australia, including their phenology over the course of a year-long survey. A total of 116 adult Gonipterini weevils were found across the year, with Oxyops fasciculatus being the most abundant. Weevils were only found in 10.7% of the Eucalyptus populnea saplings surveyed; however, saplings containing weevils contained an average of 1.9 weevils. Additionally, 21% of weevils were found in close proximity to another weevil at a micro-ecosystem scale (e.g., on the same leaf). Weevil numbers peaked in March at 17.2 adults/acre, with the lowest numbers found in November (1.8 adults/acre). One of the Oxyops species (an undescribed species known only from Central Queensland) was more commonly found on the leaves, compared to Gonipterus cinnamomeus which was more commonly located on the stem or petiole. These results provide insight into the population dynamics, interactions, and spatial and temporal resource partitioning between the adults of different Gonipterini species within their native range.
1. Introduction
Within the weevil family (Coleoptera: Curculionidae), the Gonipterini tribe encompasses seven genera (Bryachus, Gonipterus, Ipterogonus, Oxyops, Pantoreites, Prophaesia and Syarbis), of which Gonipterus and Oxyops are the most economically significant. Both the larvae and adults from this tribe are generally found on eucalyptus trees, where they feed upon the leaves. Several species of Gonipterus have become international pests of Eucalyptus plantations [1,2], including in New Zealand, South America and South Africa [3]. Consequently, many studies on these genera have focused on the discovery of parasitoids for use as biocontrol agents [4], and clarifying the identification and taxonomy of cryptic species [2]. In contrast, Oxyops vitiosa has been used as a biocontrol agent for Melaleuca quinquenervia, which has become an established weed species in the Florida everglades [5].
However, despite the considerable significance of this tribe, there have been limited studies on the interactions and phenology of Gonipterini species in their natural habitat. Recent studies have investigated the phenology, trophic associations and parasitoids of Gonipterus species from Tasmania [6] and subtropical Australia [3], but did not consider Oxyops species. Consequently, this study aimed to investigate the phenology and associations between the adult weevils of two species of Oxyops and two species of Gonipterus from Central Queensland, Australia.
2. Materials and Methods
Study Area and Design
The study area was a 1.1 acre portion of open eucalypt woodland on a Central Queensland grazing property (23°46′ S, 150°21′ E) (Figure 1). The predominant eucalypt species was Eucalyptus populnea, whereas a small number of Eremophila mitchellii trees and Pittosporum spinescens shrubs were also present. The mean density of mature (>5 m height) E. populnea trees was 16 trees/acre, whereas the mean sapling density was 47 saplings/ha.

Figure 1.
A representative photograph of the survey area.
As preliminary observations indicated the highest abundance of Gonipterini weevils on E. populnea saplings, only the saplings were surveyed in this study. Twelve field surveys were conducted over the course of 2021, at approximately monthly intervals. During each survey, every E. populnea sapling in the survey area was checked for the presence of adult Gonipterini weevils, with the identity, number and location of each weevil recorded. Additionally, the length and width of each weevil was measured.
During the first three surveys (January, February and March), the height of each sapling and height of each weevil above the ground was measured. Additionally, the presence or absence of ants on the saplings was recorded throughout these three surveys, in order to investigate possible interactions between the weevil species and ants.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. General Abundance and Weevil Size
Four weevil species were found to be present in the survey area (Figure 2): Oxyops fasciculatus, Gonipterus cinnamomeus, Gonipterus sp. n. 2 and an undescribed species of Oxyops known only from this region [7], referred to throughout this paper as Oxyops sp. Over the 12 monthly surveys, a total of 116 weevils were found, with O. fasciculatus being the most abundant and Gonipterus sp. n. 2 the scarcest. The sizes of the different species are summarized in Table 1. Oxyops sp. (undescribed) was significantly longer and wider compared to O. fasciculatus and G. cinnamomeus (p < 0.05), although its length:width ratio was not significantly different (p > 0.05).

Figure 2.
The four Gonipterini species found in the survey area.

Table 1.
Number and size of the Gonipterini weevil specimens found during the survey period. Entries in the same column with different superscript letters were significantly different from one another at α = 0.05 according to a one-way ANOVA following by post hoc Tukey testing.
3.2. Height of Saplings
The mean height of E. populnea saplings containing no Gonipterini weevils was 0.69 ± 0.43 (Table 2). In contrast, the mean height of saplings containing any species of Gonipterini weevil was significantly higher (t125.35 = 3.817, p < 0.001), at 0.92 ± 0.43 m, suggesting that weevils from this species may prefer more mature saplings. A one-way ANOVA revealed significant variation in the sapling height between the different Gonipterini species. However, the height of weevils above the ground and ratio of the weevil height to total sapling height was relatively constant between the different species (Table 2).

Table 2.
Details of the sapling heights and weevil heights across the first three survey months. Entries in the same row with different superscript letters were significantly different from one another at α = 0.05 according to a one-way ANOVA following by post hoc Tukey testing.
3.3. Presence of Ants
The survey data from the first three months (Jan–Mar) revealed that ants were found on 49% of saplings which did not contain any Gonipterini weevils (Table 3). This proportion was similar to that found for Oxyops sp. (undescribed) weevils; however, ants were present on 66% of saplings containing O. fasciculatus. A chi-square test indicated no significant difference in the proportion of Gonipterini weevils found on saplings with any ants present (X21 = 0.25, p > 0.05), suggesting that the weevils did not actively avoid saplings with ants present. However, the average number of ants present in saplings with any species of Gonipterini weevil (8 ± 4 ants/sapling) was significantly lower than the number of ants found on saplings without weevils (21 ± 30 weevils/sapling; t65.16 = −3.23, p < 0.01), indicating that the weevils may purposefully avoid saplings with high numbers of ants.

Table 3.
Presence of ants on the saplings, broken down by weevil species.
3.4. Phenology
Figure 3 shows the changes in abundance of each species throughout the survey period. Weevil numbers peaked in March at 17.2 adults/acre, with the lowest numbers found in November (1.8 adults/acre). Oxyops fasciculatus was the most abundant, except for during July. The abundance of all species dropped noticeably during late autumn/early winter, with most species increasing in abundance again in late winter/early spring, before falling off in late spring. Overall, there did not appear to be significant temporal separation of the species, but rather their abundance generally rose and fell in concert.
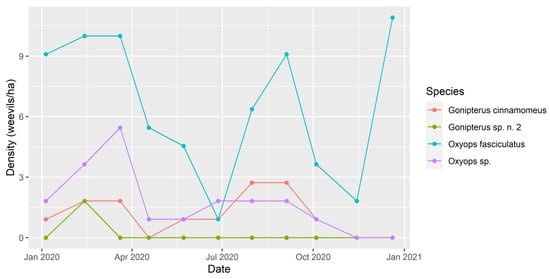
Figure 3.
Phenology of the four Gonipterini species throughout the survey period.
3.5. Within-Sapling Location
As shown in Table 4, Oxyops sp. was more commonly found on the leaves, compared to Gonipterus cinnamomeus which was more commonly located on the stem or petiole (chi-square test, X26 = 16.24, p < 0.05). Additionally, it was noted that most of the weevils on the trunk or stem of the sapling were found to be facing downwards, rather than upwards (Table 5). However, the proportion of weevils facing upward/downward did not vary significantly between the different species (chi-square test, X24 = 5.88, p > 0.05). The ecophysiological relevance of this observation is currently unknown.

Table 4.
Within-sapling locations of the various Gonipterini species.

Table 5.
Direction in which Gonipterini species on the stem or trunk were facing.
3.6. Intra- and Interspecific Interactions
Weevils were only found in 10.7% of the Eucalyptus populnea saplings surveyed; however, saplings containing weevils contained an average of 1.9 weevils, indicating clustering of the weevils into saplings with other weevils present. This was supported by detailed proximity observations (Table 6), which found that only 29% of the weevils were alone in a sapling, with the remainder found in the same tree as one or more other weevils.

Table 6.
Interactions between the Gonipterini species. Note that weevils touching another weevil also fall into the “one same leaf” category, whereas weevils on the same leaf also fall into the “in same tree” category. Values in regular font indicate weevils classified in that category only; whereas values in bold font indicate all weevils belonging to that category, regardless of whether they are also found in another category.
Furthermore, 21% of weevils were found in close proximity to another weevil at a micro-ecosystem scale (i.e., on the same leaf). A small number of weevils (13% of the total) were observed touching one another, although none were observed in copulation. Given that ~90% of the saplings within the survey area contained no weevils, these results suggest that the Gonipterini weevil species examined in this study have a strong preference for a small number of saplings in the study area. However, it is not known whether this preference is a result of these saplings providing a more suitable microhabitat compared to the other saplings, or if this results from the weevils actively seeking out saplings with other weevils present.
It was also noted that all weevils in contact with one another were always of the same species. Additionally, weevils on the same leaf were always of the same species, with two exceptions where G. cinnamomeus was found with O. fasciculatus (n = 1 observation) and Oxyops sp. (n = 1 observation). However, 60% of weevils found in the same tree as one or more weevils had at least two different weevil species found in the same tree. Overall, these results suggest that although the Gonipterini weevils may be content to share saplings with other Gonipterini species, they are moderately partitioned in space (i.e., not found on the same leaves) from other species.
4. Conclusions
This study investigated the phenology and ecosystem-level distribution and interactions of two species of Oxyops and two species of Gonipterus from Central Queensland, Australia. Oxyops fasciculatus was the most abundant species found. The number of adult weevils varied significantly throughout the year, with numbers peaking at 17.2 adults/acre in March. These results may provide insight into the population dynamics, interactions, and spatial and temporal resource partitioning that exists between different Gonipterini species within their native range.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The author wishes to thank Thomas Johnson for assistance with some of the field surveys.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
References
- Schröder, M.L.; Slippers, B.; Wingfield, M.J.; Hurley, B.P. Invasion history and management of Eucalyptus snout beetles in the Gonipterus scutellatus species complex. J. Pest Sci. 2020, 93, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mapondera, T.S.; Burgess, T.; Matsuki, M.; Oberprieler, R.G. Identification and molecular phylogenetics of the cryptic species of the Gonipterus scutellatus complex (Coleoptera: Curculionidae: Gonipterini). Aust. J. Entomol. 2012, 51, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, N.M.; Lawson, S.A.; Nahrung, H.F. Gonipterus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) in subtropical Australia: Host associations and natural enemies. Austral Entomol. 2021, 60, 588–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valente, C.; Gonçalves, C.I.; Reis, A.; Branco, M. Pre-selection and biological potential of the egg parasitoid Anaphes inexpectatus for the control of the Eucalyptus snout beetle, Gonipterus platensis. J. Pest Sci. 2017, 90, 911–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, G.S.; Massey, L.M.; Southwell, I.A. Antipredator Defense of Biological Control Agent Oxyops vitiosa Is Mediated by Plant Volatiles Sequestered from the Host Plant Melaleuca quinquenervia. J. Chem. Ecol. 2002, 28, 297–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, A.; Allen, G.R.; Oberprieler, R.G.; Ramos, A.P.; Valente, C.; Reis, A.; Franco, J.C.; Branco, M. Biological control of Gonipterus: Uncovering the associations between eucalypts, weevils and parasitoids in their native range. For. Ecol. Manag. 2019, 443, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.B. Cuticular hydrocarbon profiling reveals chemotaxonomic diversity among Gonipterini weevils (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). In Proceedings of the the 2nd International Electronic Conference on Diversity (IECD 2022)—New Insights into the Biodiversity of Plants, Animals and Microbes, Online, 15–31 March 2022. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).