Signal Correction for the Split-Hopkinson Bar Testing of Soft Materials
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The SHPB Experiment and Its Prerequisites
2.1. SHPB Setup
2.2. Specimens
| density | 1200 kg/m3 |
| ultimate strength | 3.23 MPa |
| elongation at failure | 160% |
| shore hardness | 50 A |
| wave speed c | 98 m/s |
| impedance | 0.12 kg/m2 s |
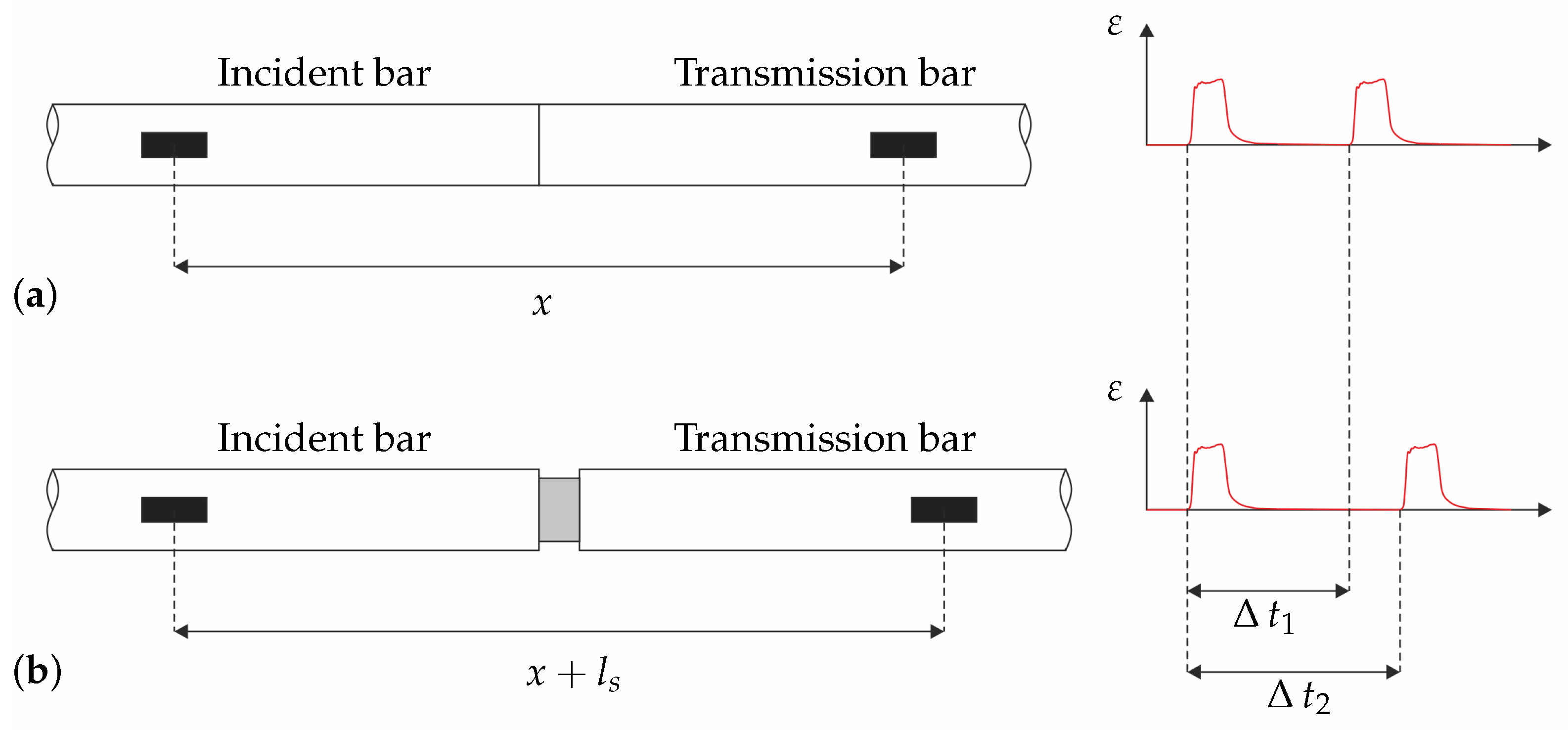
2.3. Wave Propagation Velocity
2.4. Mechanical Impedance
2.5. Reflection and Transmission Coefficients
2.6. Requirements for the SHPB Experiment
- A one-dimensional wave propagation in the bars;
- A state of equilibrium of forces in the compressed specimen, the “stress equilibrium”;
- A constant strain rate during compression of the specimen.
2.7. SHPB Equations
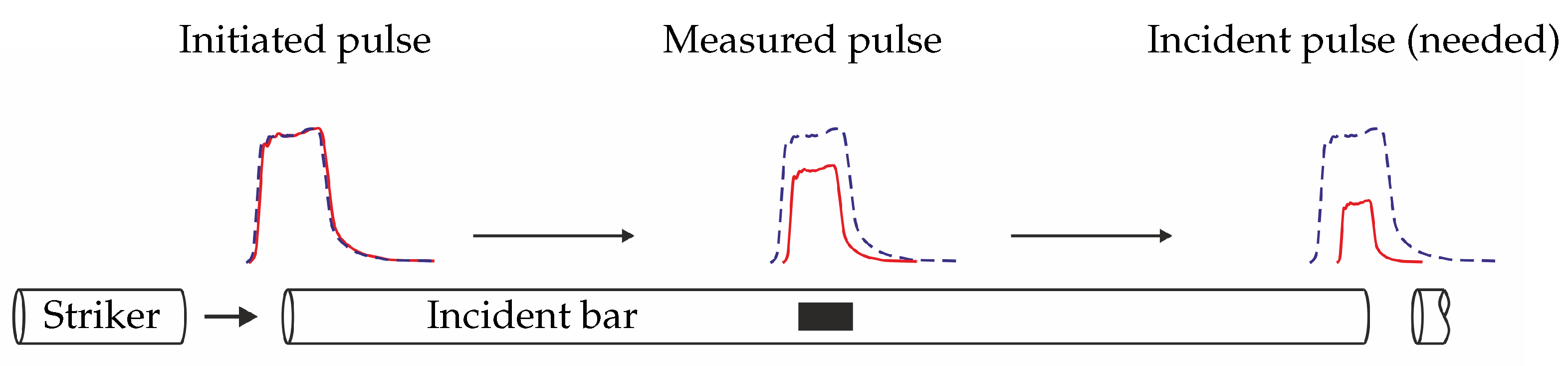
3. Signal Correction
3.1. Correction by Spectral Analysis
3.2. Validation of the Method
3.3. Signal Prediction
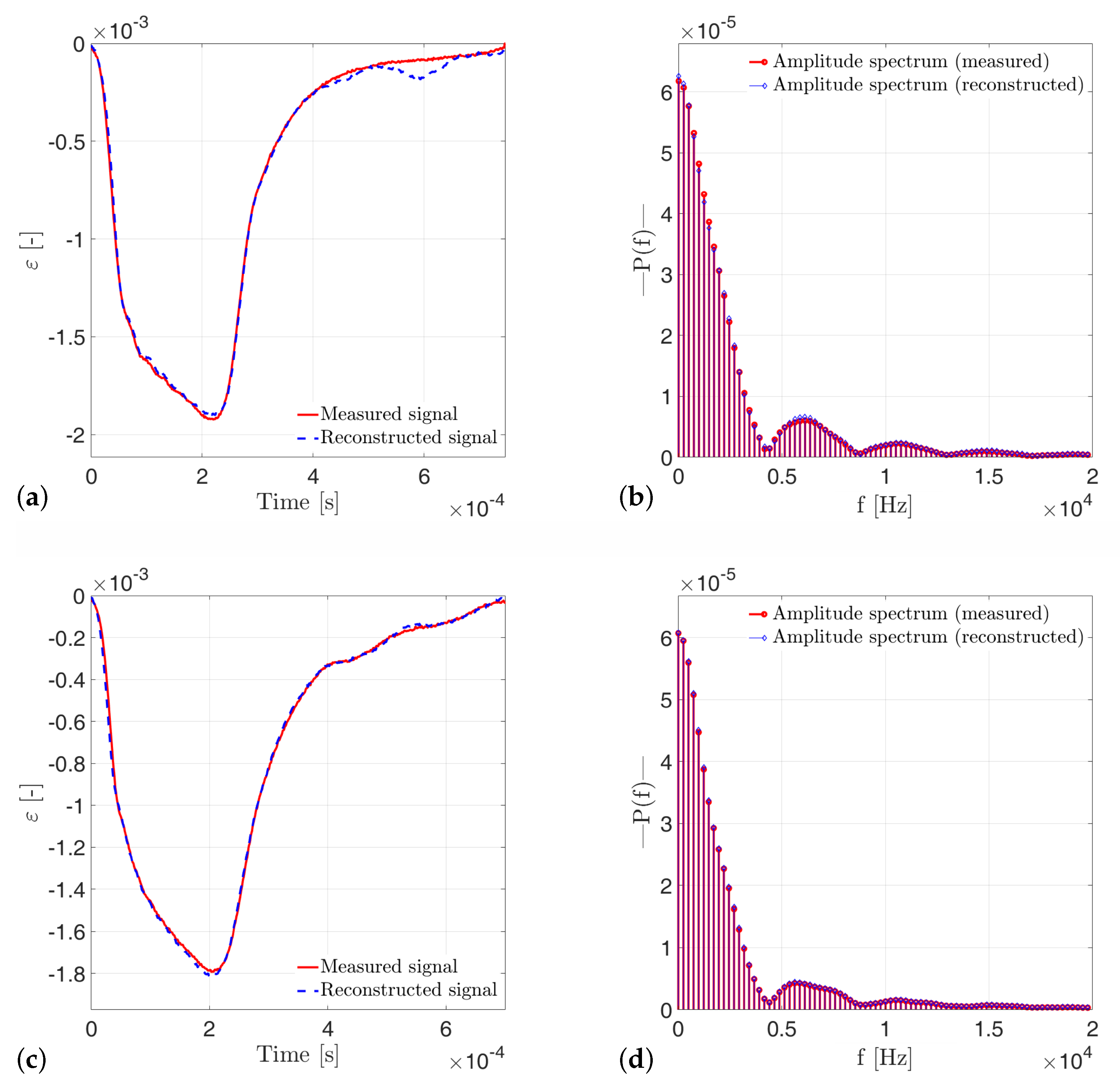
4. Experimental Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SHPB | Split Hopkinson pressure bar |
| PMMA | polymethylmethacrylate |
| PE | polyethylene |
| DLP | digital light processing |
| SLA | stereolithography |
References
- Perogamvros, N.; Mitropoulos, T.; Lampeas, G. Drop tower adaptation for medium strain rate tensile testing. Exp. Mech. 2006, 56, 419–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravani, M.; Weinberg, K. A review on split Hopkinson bar experiments on the dynamic characterisation of concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 190, 1264–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Song, B.; Frew, D.; Forrestal, M. Dynamic small strain measurements of a metal specimen with a split Hopkinson pressure bar. Exp. Mech. 2003, 43, 20–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolsky, H. An Investigation of the Mechanical Properties of Materials at very High Rates of Loading. Proc. Phys. Soc. Sect. B 1949, 62, 676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, R. The Kolsky-Hopkinson Bar Machine: Selected Topics; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hopkinson, B.X. A method of measuring the pressure produced in the detonation of high, explosives or by the impact of bullets. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Contain. Pap. A Math. Phys. Character 1914, 213, 437–456. [Google Scholar]
- Owens, A.; Tippur, H. A tensile split Hopkinson bar for testing particulate polymer composites under elevated rates of loading. Exp. Mech. 2009, 49, 799–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberg, K.; Khosravani, M.R. On the tensile resistance of UHPC at impact. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 2018, 227, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Knauss, W.; Ravichandran, G. Applicability of the time–temperature superposition principle in modeling dynamic response of a polyurea. Mech. Time-Depend. Mater. 2007, 11, 289–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, V.; Fleck, N. High strain rate compressive behaviour of aluminium alloy foams. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2000, 24, 277–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberg, K.; Khosravani, M.R.; Thimm, B.; Reppel, T.; Bogunia, L.; Aghayan, S.; Nötzel, R. Hopkinson bar experiments as a method to determine impact properties of brittle and ductile materials. GAMM-Mitteilungen 2018, 41, e201800008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieler, S.; Haller, S.; Brandt, R.; Weinberg, K. Experimental Investigation of Unidirectional Glass-Fiber-Reinforced Plastics under High Strain Rates. Appl. Mech. 2023, 4, 1127–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, S.; Schierloh, F.; Perkins, R.; Babcock, S. High-velocity deformation properties of polyurethane foams: Results of tensile and compressive tests at strain rates from 10−3 to 103 sec are presented for two kinds of polyurethane foam at various densities. Exp. Mech. 1969, 9, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, A.; Mukherjee, S.; Marathe, R.; Karthikeyan, B.; Malhotra, R. Determining strain rate dependence of human body soft tissues using a split Hopkinson pressure bar. In Proceedings of the International IRCOBI Conference on the Biomechanics of Impact, Madrid, Spain, 20–22 September 2006; pp. 20–22. [Google Scholar]
- Trexler, M.; Lennon, A.; Wickwire, A.; Harrigan, T.; Luong, Q.; Graham, J.; Maisano, A.; Roberts, J.; Merkle, A. Verification and implementation of a modified split Hopkinson pressure bar technique for characterizing biological tissue and soft biosimulant materials under dynamic shear loading. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2011, 4, 1920–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.W.; Song, B. Dynamic Characterization of Soft Materials. Dyn. Fail. Mater. Struct. 2018, 19, 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Dwyer, C.M.; Carrillo, J.G.; De la Peña, J.A.D.; Santiago, C.C.; MacDonald, E.; Rhinehart, J.; Williams, R.M.; Burhop, M.; Yelamanchi, B.; Cortes, P. Impact performance of 3D printed spatially varying elastomeric lattices. Polymers 2023, 15, 1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreide, C.; Koricho, E.; Kardel, K. Energy absorption of 3D printed multi-material elastic lattice structures. Prog. Addit. Manuf. 2024, 9, 1653–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fíla, T.; Koudelka, P.; Falta, J.; Zlámal, P.; Rada, V.; Adorna, M.; Bronder, S.; Jiroušek, O. Dynamic impact testing of cellular solids and lattice structures: Application of two-sided direct impact Hopkinson bar. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2021, 148, 103767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.G.; Gainov, R.; Heußen, D.; Bieler, S.; Sun, Z.; Weinberg, K.; Dehm, G.; Ramachandramoorthy, R. Green laser powder bed fusion based fabrication and rate-dependent mechanical properties of copper lattices. Mater. Des. 2023, 231, 112023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieler, S.; Kang, S.G.; Heußen, D.; Ramachandramoorthy, R.; Dehm, G.; Weinberg, K. Investigation of copper lattice structures using a Split Hopkinson Pressure Bar. PAMM 2021, 21, e202100155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieler, S.; Weinberg, K. Energy absorption of sustainable lattice structures under impact loading. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2412.06547. [Google Scholar]
- Iftekar, S.F.; Aabid, A.; Amir, A.; Baig, M. Advancements and limitations in 3D printing materials and technologies: A critical review. Polymers 2023, 15, 2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorham, D. Specimen inertia in high strain-rate compression. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 1989, 22, 1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray III, G.; Blumenthal, W.R.; Trujillo, C.P.; Carpenter II, R. Influence of temperature and strain rate on the mechanical behavior of Adiprene L-100. J. Phys. IV 1997, 7, C3–C523. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Deng, Q. Radial Inertia Effect of Ultra-Soft Materials from Hopkinson Bar and Solution Methodologies. Materials 2024, 17, 3793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.W.; Song, B. Split Hopkinson (Kolsky) Bar: Design, Testing and Applications; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Aghayan, S.; Bieler, S.; Weinberg, K. Determination of the high-strain rate elastic modulus of printing resins using two different split Hopkinson pressure bars. Mech. Time-Depend. Mater. 2022, 26, 761–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Formlabs: Material Properties of Elastic Resin. 2025. Available online: https://formlabs.com/materials/flexible-elastic/ (accessed on 20 January 2025).
- Graff, K.F. Wave Motion in Elastic Solids; Courier Corporation: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Zhang, B.; Forrestal, M. A split Hopkinson bar technique for low-impedance materials. Exp. Mech. 1999, 39, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Lu, F.; Frew, D.; Forrestal, M. Dynamic compression testing of soft materials. J. Appl. Mech. 2002, 69, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Lu, F.; Zhou, B. A quartz-crystal-embedded split Hopkinson pressure bar for soft materials. Exp. Mech. 2000, 40, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabo, T.L.; Wu, J. A model for longitudinal and shear wave propagation in viscoelastic media. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2000, 107, 2437–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravichandran, G.; Subhash, G. Critical Appraisal of Limiting Strain Rates for Compression Testing of Ceramics in a Split Hopkinson Pressure Bar. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1994, 77, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frew, D.; Forrestal, M.J.; Chen, W. Pulse shaping techniques for testing brittle materials with a split Hopkinson pressure bar. Exp. Mech. 2002, 42, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Sligtenhorst, C.; Cronin, D.S.; Brodland, G.W. High strain rate compressive properties of bovine muscle tissue determined using a split Hopkinson bar apparatus. J. Biomech. 2006, 39, 1852–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasso, M.; Newaz, G.; Amodio, D. Material characterization at high strain rate by Hopkinson bar tests and finite element optimization. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 487, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Wang, Z.; Kim, H.; Ma, H. Pulse shaper and dynamic compressive property investigation on ice using a large-sized modified split hopkinson pressure bar. Lat. Am. J. Solids Struct. 2016, 13, 391–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacon, C. An experimental method for considering dispersion and attenuation in a viscoelastic Hopkinson bar. Exp. Mech. 1998, 38, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Crandall, J.; Pilkey, W. Wave dispersion and attenuation in viscoelastic split Hopkinson pressure bar. Shock Vib. 1998, 5, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, J.F. Wave Propagation in Structures: An FFT-Based Spectral Analysis Methodology; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, J.; Malvern, L.; Jenkins, D. Dispersion investigation in the split Hopkinson pressure bar. Int. J. Solids Struct. 1990, 112, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecchio, K.S.; Jiang, F. Improved pulse shaping to achieve constant strain rate and stress equilibrium in split-Hopkinson pressure bar testing. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2007, 38, 2655–2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frew, D.; Forrestal, M.; Chen, W. Pulse shaping techniques for testing elastic-plastic materials with a split Hopkinson pressure bar. Exp. Mech. 2005, 45, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagar, S.K.; Sreekumar, M. Miniaturized flexible flow pump using SMA actuator. Procedia Eng. 2013, 64, 896–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN ISO 604. 2002. Available online: https://www.din.de/de/meta/suche/62730!search?query=druckeigenschaften (accessed on 20 January 2025).







| Steel Bars | Aluminum Bars | PMMA Bars | |
|---|---|---|---|
| length l | 1800 mm | 1800 mm | 3000 mm/2200 mm |
| diameter d | 20 mm | 20 mm | 20 mm |
| density | 7850 kg/m3 | 2700 kg/m3 | 1178 kg/m3 |
| elastic modulus E | 210 GPa | 70 GPa | 3.5 GPa |
| poisson number | 0.30 | 0.34 | 0.37 |
| wave speed c | 5645.2 m/s | 5071.5 m/s | 2295.9 m/s |
| impedance | 44.31 kg/m2 s | 13.69 kg/m2 s | 2.58 kg/m2 s |
| Pairing | Reflection Coefficient | Transmission Coefficient |
|---|---|---|
| Steel–EL | 0.9945 | 6.6 × 10−3 |
| Aluminum–EL | 0.9826 | 0.0174 |
| PMMA–EL | 0.91 | 0.09 |
| Bars | Striker | Specimen | Pulse Shaper | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| length [mm] | 3000/2200 | 300 | 3 | 0.3 |
| diameter [mm] | 20 | 20 | 15 | 8 |
| velocity [m/s] | - | 11.5 | - | - |
| material | PMMA | PMMA | Elastic | PE |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bieler, S.; Weinberg, K. Signal Correction for the Split-Hopkinson Bar Testing of Soft Materials. Dynamics 2025, 5, 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/dynamics5010005
Bieler S, Weinberg K. Signal Correction for the Split-Hopkinson Bar Testing of Soft Materials. Dynamics. 2025; 5(1):5. https://doi.org/10.3390/dynamics5010005
Chicago/Turabian StyleBieler, Sören, and Kerstin Weinberg. 2025. "Signal Correction for the Split-Hopkinson Bar Testing of Soft Materials" Dynamics 5, no. 1: 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/dynamics5010005
APA StyleBieler, S., & Weinberg, K. (2025). Signal Correction for the Split-Hopkinson Bar Testing of Soft Materials. Dynamics, 5(1), 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/dynamics5010005






