Urgent-Start Peritoneal Dialysis: Current State and Future Directions
Abstract
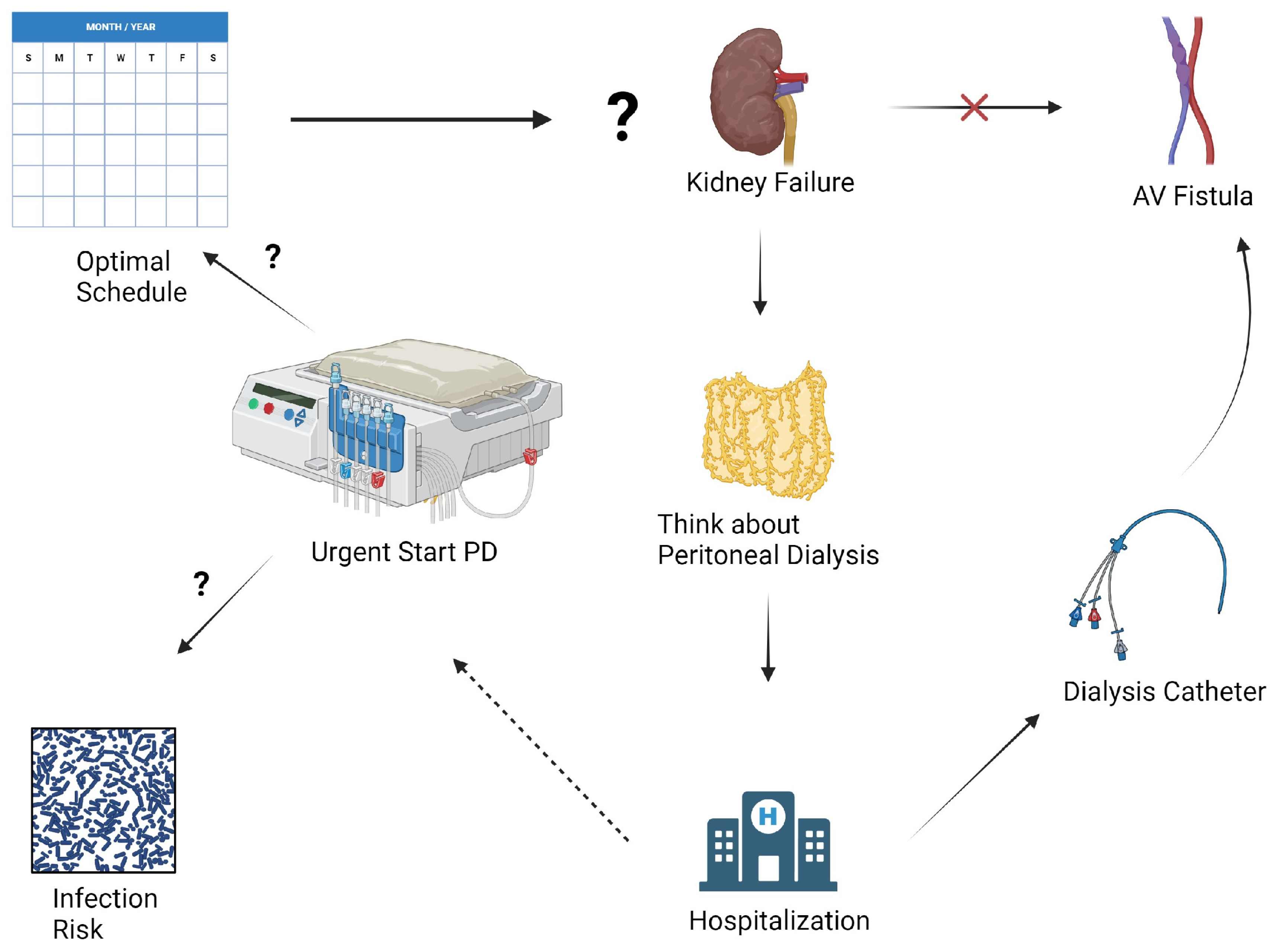
1. Introduction
2. Clinical Considerations in Urgent-Start Peritoneal Dialysis
2.1. Patient Selection Criteria for USPD
2.2. Timing of Initiation and Current Data Limitations
2.3. Catheter Insertion Techniques
2.4. Peritoneal Dialysis Prescription and Modality Choices
3. Outcomes and Efficacy of Urgent-Start Peritoneal Dialysis
3.1. Mechanical Complications and Technique Failure
3.2. Infectious Complications
3.3. Survival Rates and Patient Outcomes in USPD Compared to Other Modalities
3.4. Impact of USPD on Healthcare Utilization
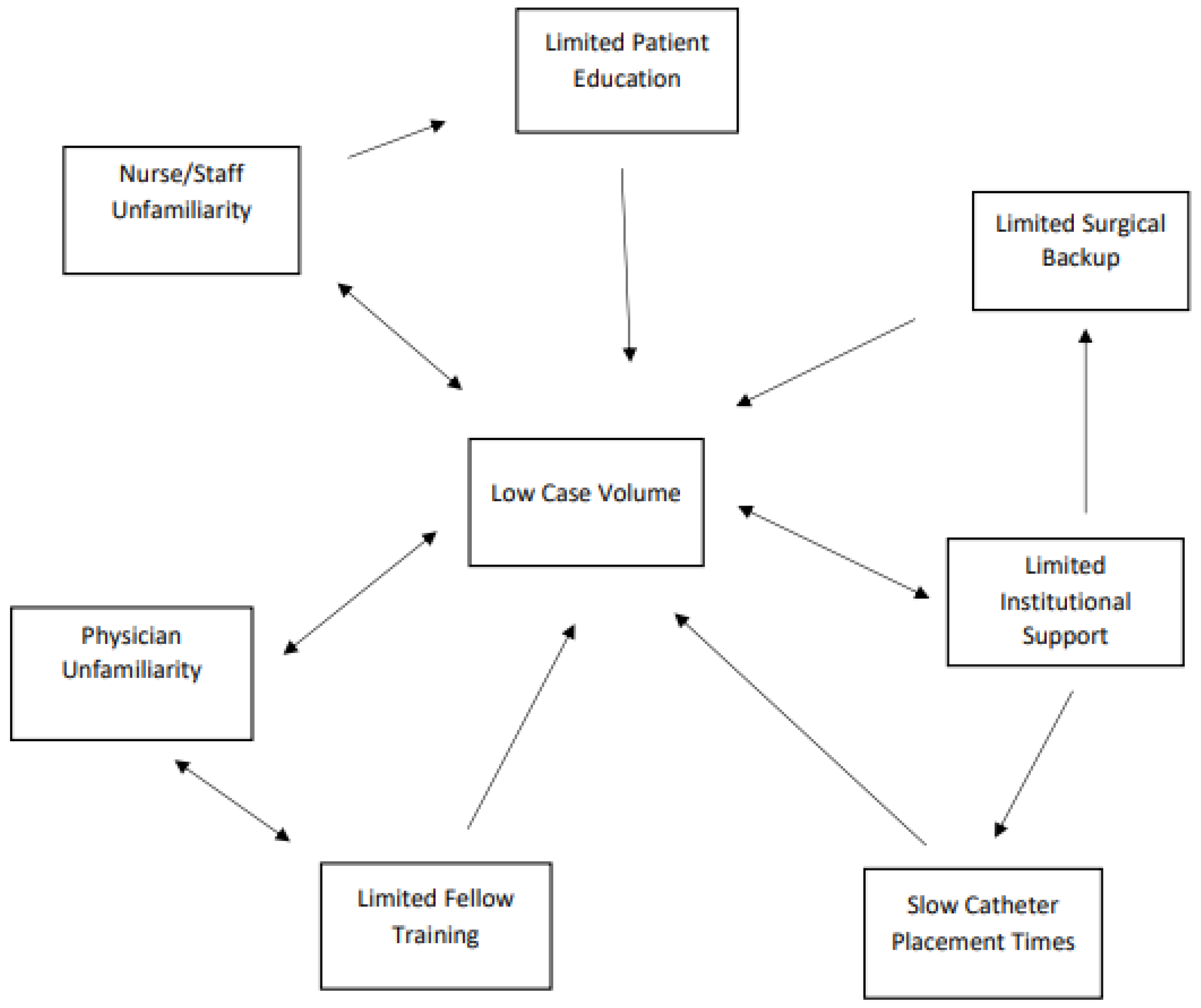
4. Barriers and Strategies to Optimize Urgent-Start Peritoneal Dialysis
4.1. Multidisciplinary Approach and Team Collaboration
4.2. Education and Training Programs for Healthcare Professionals
4.3. Patient Education
4.4. Clinical Pathways and Protocols for USPD Initiation and Follow-Up
4.5. Evidence Gaps and Areas for Future Research
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Publication | Terminology Used | Definition |
|---|---|---|
| Bittencourt, 2017 [27] | Early-start PD | PD started within 3 days |
| Kim, 2018 [18] | Urgent-start PD | Within 14 Days |
| Blake, 2018 [11] | Early-start PD and urgent-start PD | Review proposing uniform terminology: early start = within 3 days; urgent start = within 14 days |
| Sharma, 2020 [59] | Urgent Initiated PD | PD started within 3 days |
| Hu, 2022 [27] | Urgent-start PD | Within 3 days or within 14 days |
| Ng, 2022 [12] | Urgent-start PD and early-start PD | Urgent start = within 48–72 h; early start = within 14 days |
| Pilatti, 2022 [36] | Urgent-start PD | PD started within 7 days |
References
- United States Renal Data System. 2022 USRDS Annual Data Report: Epidemiology of Kidney Disease in the United States; National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Chuasuwan, A.; Pooripussarakul, S.; Thakkinstian, A.; Ingsathit, A.; Pattanaprateep, O. Comparisons of quality of life between patients underwent peritoneal dialysis and hemodialysis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2020, 18, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogt, B.; Painter, D.F.; Saad Berreta, R.; Lokhande, A.; Shah, A.D. Hospitalization in maintenance peritoneal dialysis: A review. Hosp. Pract. 2023, 51, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.X.; Gao, X.; Inglese, G.; Chuengsaman, P.; Pecoits-Filho, R.; Yu, A. A Global Overview of the Impact of Peritoneal Dialysis First or Favored Policies: An Opinion. Perit. Dial. Int. 2015, 35, 406–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briggs, V.; Davies, S.; Wilkie, M. International Variations in Peritoneal Dialysis Utilization and Implications for Practice. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2019, 74, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radhakrishnan, J.; Remuzzi, G.; Saran, R.; Williams, D.E.; Rios-Burrows, N.; Powe, N.; CDC-CKD Surveillance for the CDC-CKD Surveillance Team; Brück, K.; Wanner, C.; Stel, V.S.; et al. Taming the chronic kidney disease epidemic: A global view of surveillance efforts. Kidney Int. 2014, 86, 246–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajora, N.; Shastri, S.; Pirwani, G.; Saxena, R. How To Build a Successful Urgent-Start Peritoneal Dialysis Program. Kidney360 2020, 1, 1165–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghaffari, A.; Kumar, V.; Guest, S. Infrastructure requirements for an urgent-start peritoneal dialysis program. Perit. Dial. Int. 2013, 33, 611–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teitelbaum, I. Peritoneal Dialysis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1786–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosner, M.H. Peritoneal Dialysis Should Be Considered the First Option for Patients Requiring Urgent Start Dialysis: COMMENTARY. Kidney360 2023, 4, 141–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake, P.G.; Jain, A.K. Urgent Start Peritoneal Dialysis: Defining What It Is and Why It Matters. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. CJASN 2018, 13, 1278–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, A.K.H.; Tan, S.N.; Tay, M.E.; Van Der Straaten, J.C.; Cremere, G.; Chionh, C.Y. Comparison of planned-start, early-start and deferred-start strategies for peritoneal dialysis initiation in end-stage kidney disease. Ann. Acad. Med. Singap. 2022, 51, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Aal, A.K.; Dybbro, P.; Hathaway, P.; Guest, S.; Neuwirth, M.; Krishnamurthy, V. Best practices consensus protocol for peritoneal dialysis catheter placement by interventional radiologists. Perit. Dial. Int. 2014, 34, 481–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel Aal, A.K.; Mahmoud, K.; Moustafa, A.S.; Aboueldahab, N.A.; Souid, A.; Gunn, A.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Almehmi, A. Comparative Study on the Outcomes of Elective-Start versus Urgent-Start Peritoneal Dialysis Catheter Placement. Radiol. Res. Pract. 2020, 2020, 3751827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javaid, M.M.; Khan, B.A.; Subramanian, S. Is surgical PD catheter insertion safe for urgent-start peritoneal dialysis? Semin. Dial. 2019, 32, 225–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scalamogna, A.; Nardelli, L.; Zanoni, F.; Messa, P. Double purse-string around the inner cuff of the peritoneal catheter: A novel technique for an immediate initiation of continuous peritoneal dialysis. Int. J. Artif. Organs 2020, 43, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, M.J.; Ye, B.M.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, S.; Kim, I.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Han, M.; Rhee, H.; Song, S.H.; et al. Percutaneous peritoneal dialysis catheter implantation with no break-in period: A viable option for patients requiring unplanned urgent-start peritoneal dialysis. Kidney Res. Clin. Pract. 2020, 39, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.; Son, Y.K.; Lee, S.M.; Kim, S.E.; An, W.S. Early technical complications and long-term survival of urgent peritoneal dialysis according to break-in periods. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0206426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Htay, H.; Johnson, D.W.; Craig, J.C.; Schena, F.P.; Strippoli, G.F.; Tong, A.; Cho, Y. Catheter type, placement and insertion techniques for preventing catheter-related infections in chronic peritoneal dialysis patients. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 5, Cd004680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Fu, X.; Yang, Y.; Deng, J.; Lu, J.; Peng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.-Q.; Deng, H.-M.; Liu, H.; et al. A Comparison between Intermittent Peritoneal Dialysis and Automatic Peritoneal Dialysis on Urgent Peritoneal Dialysis. Am. J. Nephrol. 2017, 45, 540–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; He, X.; Pu, L.; Liu, X.; Zhou, X.; Wu, X.F.; Zang, Z.; Li, Z. A randomized controlled comparative study of different fluid exchange modes in urgent-start peritoneal dialysis in patients with end-stage renal disease: Automated peritoneal dialysis combined with manual fluid exchange vs. manual fluid exchange alone. Ren. Fail. 2023, 45, 2202756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhuang, X.; Zhang, M.; Wu, Y.; Liu, M.; Guan, S.; Liu, S.; Miao, L.; Cui, W. Application of automated peritoneal dialysis in urgent-start peritoneal dialysis patients during the break-in period. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2018, 50, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javaid, M.M.; Khan, B.A.; Subramanian, S. The modality of choice, manual or automated, for urgent start peritoneal dialysis. Clin. Kidney J. 2019, 12, 443–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.; Wang, H.; Li, S.; Zuo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, T.; Li, J.; Wang, L.; Feng, Z.; et al. Low-Volume Tidal Peritoneal Dialysis Is a Preferable Mode in Patients Initiating Urgent-Start Automated Peritoneal Dialysis: A Randomized, Open-Label, Prospective Control Study. Ther. Apher. Dial. 2019, 23, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scalamogna, A.; Nardelli, L.; Cicero, E.; Castellano, G. Analysis of mechanical complications in urgent-start peritoneal dialysis. J. Nephrol. 2022, 35, 1489–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- See, E.J.; Cho, Y.; Hawley, C.M.; Jaffrey, L.R.; Johnson, D.W. Early and Late Patient Outcomes in Urgent-Start Peritoneal Dialysis. Perit. Dial. Int. 2017, 37, 414–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Yang, L.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, X.; Zhou, W.; Wen, X.; Liu, S.; Cui, W. Break-in Period ≤ 24 Hours as an Option for Urgent-start Peritoneal Dialysis in Patients with Diabetes. Frontiers in endocrinology. 2022, 13, 93657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, H.; Yang, X.; Yi, C.; Guo, Q.; Li, Y.; Yang, Q.; Chen, W.; Mao, H.; Li, J.; Qiu, Y.; et al. Urgent-start peritoneal dialysis for patients with end stage renal disease: A 10-year retrospective study. BMC Nephrol. 2019, 20, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrantes, A.R.M.; Gonçalves, H.; Ferrer, F.A.D.; Lobos, A.M.V. Urgent start peritoneal dialysis: Is there room for more? Nefrologia 2021, 41, 573–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, D.B.; Mendes, M.L.; Caramori, J.T.; Falbo dos Reis, P.; Ponce, D. Urgent-start dialysis: Comparison of complications and outcomes between peritoneal dialysis and haemodialysis. Perit. Dial. Int. 2021, 41, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojtaszek, E.; Grzejszczak, A.; Grygiel, K.; Małyszko, J.; Matuszkiewicz-Rowińska, J. Urgent-Start Peritoneal Dialysis as a Bridge to Definitive Chronic Renal Replacement Therapy: Short- and Long-Term Outcomes. Front. Physiol. 2019, 9, 1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phang, C.C.; Foo, M.W.Y.; Johnson, D.W.; Wu, S.Y.; Hao, Y.; Jayaballa, M.; Koniman, R.; Chan, C.M.; Oei, E.L.; Chong, T.T.; et al. Comparison of outcomes of urgent-start and conventional-start peritoneal dialysis: A single-centre experience. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2021, 53, 583–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, J.V.C.; Ponce, D. Infectious and mechanical complications in planned-start vs. urgent-start peritoneal dialysis: A cohort study. Braz. J. Nephrol. 2023, 45, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, K.S.; Subhramanyam, S.V.; Pavankumar, N.; Antony, S.; Sarfaraz Khan, M.A. Emergent Start Peritoneal Dialysis for End-Stage Renal Disease: Outcomes and Advantages. Blood Purif. 2018, 45, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, X.; Yang, L.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, X.; Zhou, W.; Hu, X.; Liu, S.; Luo, P.; Cui, W. Feasibility of a break-in period of less than 24 hours for urgent start peritoneal dialysis: A multicenter study. Ren. Fail. 2022, 44, 450–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilatti, M.; Theodorovitz, V.C.; Hille, D.; Sevignani, G.; Ferreira, H.C.; Vieira, M.A.; Calice-Silva, V.; de França, P.H.C. Urgent vs. planned peritoneal dialysis initiation: Complications and outcomes in the first year of therapy. Braz. J. Nephrol. 2022, 44, 482–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bitencourt Dias, D.; Mendes, M.L.; Burgugi Banin, V.; Barretti, P.; Ponce, D. Urgent-Start Peritoneal Dialysis: The First Year of Brazilian Experience. Blood Purif. 2017, 44, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhalla, N.M.; Arora, N.; Darbinian, J.A.; Zheng, S. Urgent Start Peritoneal Dialysis: A Population-Based Cohort Study. Kidney Med. 2022, 4, 100414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, M.; Kohnle, M.; Trapp, R.; Haastert, B.; Rump, L.C.; Aker, S. Comparable outcome of acute unplanned peritoneal dialysis and haemodialysis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2012, 27, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Fang, W.; Zhu, M.; Yu, Z.; Fang, Y.; Yan, H.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Q.; Che, X.; Xie, Y.; et al. Urgent-Start Peritoneal Dialysis and Hemodialysis in ESRD Patients: Complications and Outcomes. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Htay, H.; Johnson, D.W.; Craig, J.C.; Teixeira-Pinto, A.; Hawley, C.M.; Cho, Y. Urgent-start peritoneal dialysis versus haemodialysis for people with chronic kidney disease. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2021, 2021, CD012899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Ni, Z.; Mou, S.; Lu, R.; Fang, W.; Huang, J.; Hu, C.; Zhang, H.; Yan, H.; Li, Z.; et al. Feasibility of Urgent-Start Peritoneal Dialysis in Older Patients with End-Stage Renal Disease: A Single-Center Experience. Perit. Dial. Int. 2018, 38, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zang, X.; Du, X.; Li, L.; Mei, C. Complications and outcomes of urgent-start peritoneal dialysis in elderly patients with end-stage renal disease in China: A retrospective cohort study. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e032849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parapiboon, W.; Sangsuk, J.; Nopsopon, T.; Pitsawong, W.; Tatiyanupanwong, S.; Kanjanabuch, T.; Johnson, D.W. Randomized Study of Urgent-Start Peritoneal Dialysis Versus Urgent-Start Temporary Hemodialysis in Patients Transitioning to Kidney Failure. Kidney Int. Rep. 2022, 7, 1866–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.; Ni, Z.; Che, X.; Gu, L.; Zhu, M.; Yuan, J.; Huang, J.; Gu, A.; Jin, Y.; Yan, H.; et al. Peritoneal Dialysis as an Option for Unplanned Dialysis Initiation in Patients with End-Stage Renal Disease and Diabetes Mellitus. Blood Purif. 2019, 47, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.X.; Ghaffari, A.; Dhatt, H.; Kumar, V.; Balsera, C.; Wallace, E.; Khairullah, Q.; Lesher, B.; Gao, X.; Henderson, H.; et al. Economic evaluation of urgent-start peritoneal dialysis versus urgent-start hemodialysis in the United States. Medicine 2014, 93, e293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.; Lu, R.; Lv, S.; Wang, L.; Mou, S.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Q.; Pang, H.; Yan, H.; Li, Z.; et al. Automated peritoneal dialysis as a cost-effective urgent-start dialysis option for ESRD patients: A prospective cohort study. Int. J. Artif. Organs 2022, 45, 672–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dean, D.; Cruz, D.N. We Use Permcaths Instead of Peritoneal Catheters for Acute Kidney Injury and Urgent-Start Dialysis. Semin. Dial. 2016, 29, 260–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javaid, M.M.; Khan, B.A.; Yeo, E.X.; Teo, B.W.; Subramanian, S. Sustained Increase in Peritoneal Dialysis Prevalence through a Structured PD Initiation Service. Perit. Dial. Int. 2018, 38, 374–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.; Taber-Hight, E.B.; Miller, B.W. Perceptions of Home Dialysis Training and Experience Among US Nephrology Fellows. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2021, 77, 713–718.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javaid, M.M.; Lee, E.; Khan, B.A.; Subramanian, S. Description of an Urgent-Start Peritoneal Dialysis Program in Singapore. Perit. Dial. Int. 2017, 37, 500–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machowska, A.; Alscher, M.D.; Vanga, S.R.; Koch, M.; Aarup, M.; Qureshi, A.R.; Lindholm, B.; Rutherford, P. Offering Patients Therapy Options in Unplanned Start (OPTiONS): Implementation of an educational program is feasible and effective. BMC Nephrol. 2017, 18, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schanz, M.; Ketteler, M.; Heck, M.; Dippon, J.; Alscher, M.D.; Kimmel, M. Impact of an in-Hospital Patient Education Program on Choice of Renal Replacement Modality in Unplanned Dialysis Initiation. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2017, 42, 865–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Baharani, J. Dialysis education and options for late presenters—An ongoing dilemma. Hemodial. Int. 2023, 27, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakurada, T.; Koitabashi, K.; Murasawa, M.; Kohatsu, K.; Kojima, S.; Shibagaki, Y. Effects of one-hour discussion on the choice of dialysis modality at the outpatient clinic: A retrospective cohort study using propensity score matching. Ther. Apher. Dial. 2023, 27, 442–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaikishen, A.; Lick, A.; Owen, J.G.; Naljayan, M.V. Louisiana State University Nephrology: Initiation of a Multicenter Urgent-Start Peritoneal Dialysis Program. Adv. Perit. Dial. 2016, 32, 11–14. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sourial, M.Y.; Sourial, M.H.; Dalsan, R.; Graham, J.; Ross, M.; Chen, W.; Golestaneh, L. Urgent Peritoneal Dialysis in Patients With COVID-19 and Acute Kidney Injury: A Single-Center Experience in a Time of Crisis in the United States. Am. J. Kidney 2020, 76, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akomeah, J.; Apostol, A.; Barnes, E.; Charytan, C.; Enriquez, U.; Katikaneni, M.; Liu, F.; Messina, A.; Neelakantappa, K.; Radhakrishnan, J.; et al. Optimizing Kidney Replacement Therapy During the COVID-19 Pandemic Across a Complex Healthcare System. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 604182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, M.; Parry, M.; Alam, S.; Mahanta, P.; Doley, P.; Mazumder, M.A.; Jeelani, H.; Dange, S. A Comparable Study on the Outcomes of Urgent Initiated Peritoneal Dialysis Versus Conventional Start, A Single Centre Study from North-East India. Iran J. Kidney Dis. 2020, 14, 488–493. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vogt, B.; Shah, A.D. Urgent-Start Peritoneal Dialysis: Current State and Future Directions. Kidney Dial. 2024, 4, 15-26. https://doi.org/10.3390/kidneydial4010002
Vogt B, Shah AD. Urgent-Start Peritoneal Dialysis: Current State and Future Directions. Kidney and Dialysis. 2024; 4(1):15-26. https://doi.org/10.3390/kidneydial4010002
Chicago/Turabian StyleVogt, Braden, and Ankur D. Shah. 2024. "Urgent-Start Peritoneal Dialysis: Current State and Future Directions" Kidney and Dialysis 4, no. 1: 15-26. https://doi.org/10.3390/kidneydial4010002
APA StyleVogt, B., & Shah, A. D. (2024). Urgent-Start Peritoneal Dialysis: Current State and Future Directions. Kidney and Dialysis, 4(1), 15-26. https://doi.org/10.3390/kidneydial4010002






