Benchmarking RNA Editing Detection Tools
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Computational Environment
2.2. RNA-Seq Dataset
2.3. Reference Genome and Annotations
2.4. Reads Processing and Mapping
2.5. Analysis with RNA Editing Detection Tools
3. Results
3.1. Availability of RNA Editing Detection Tools
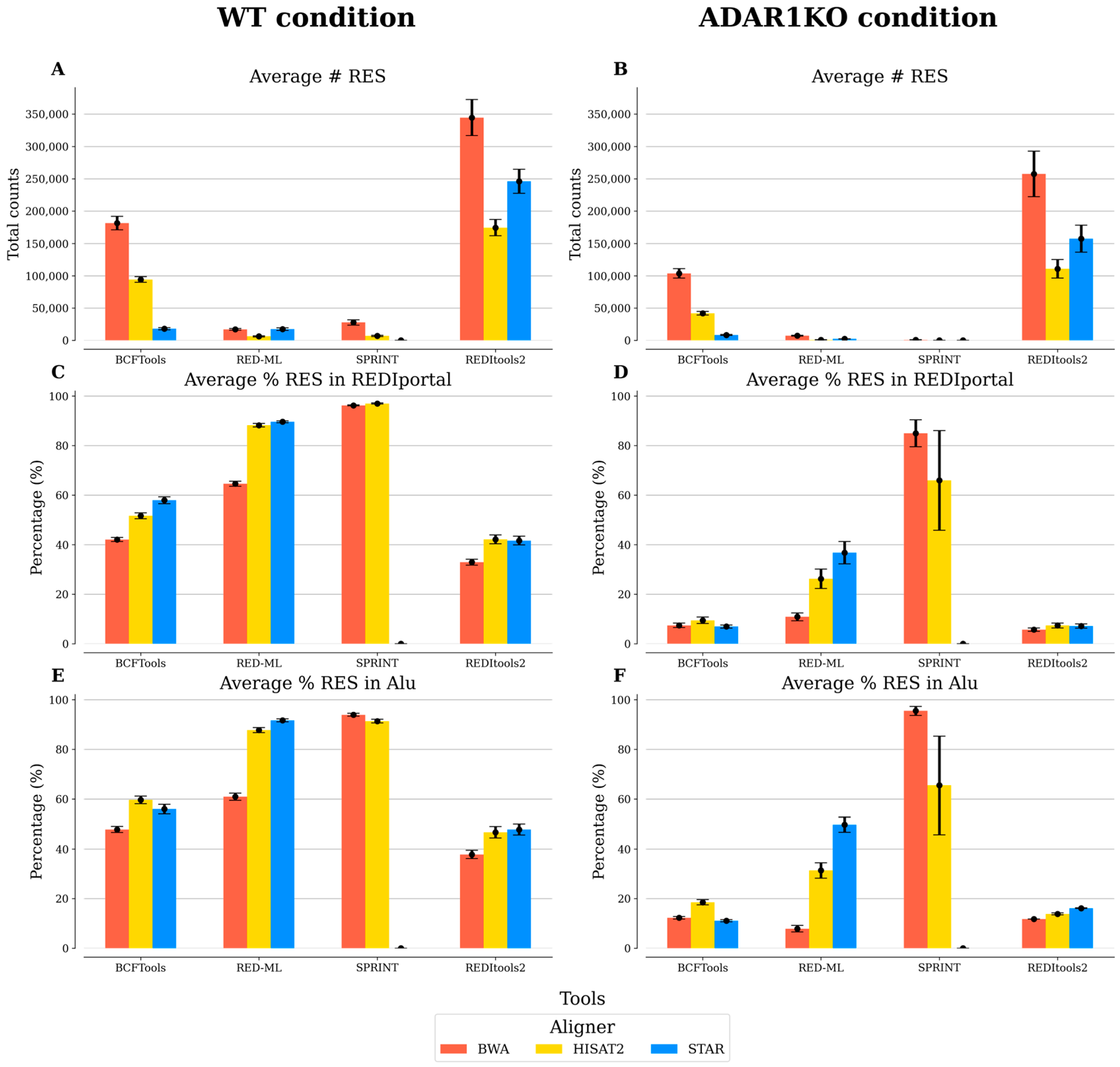
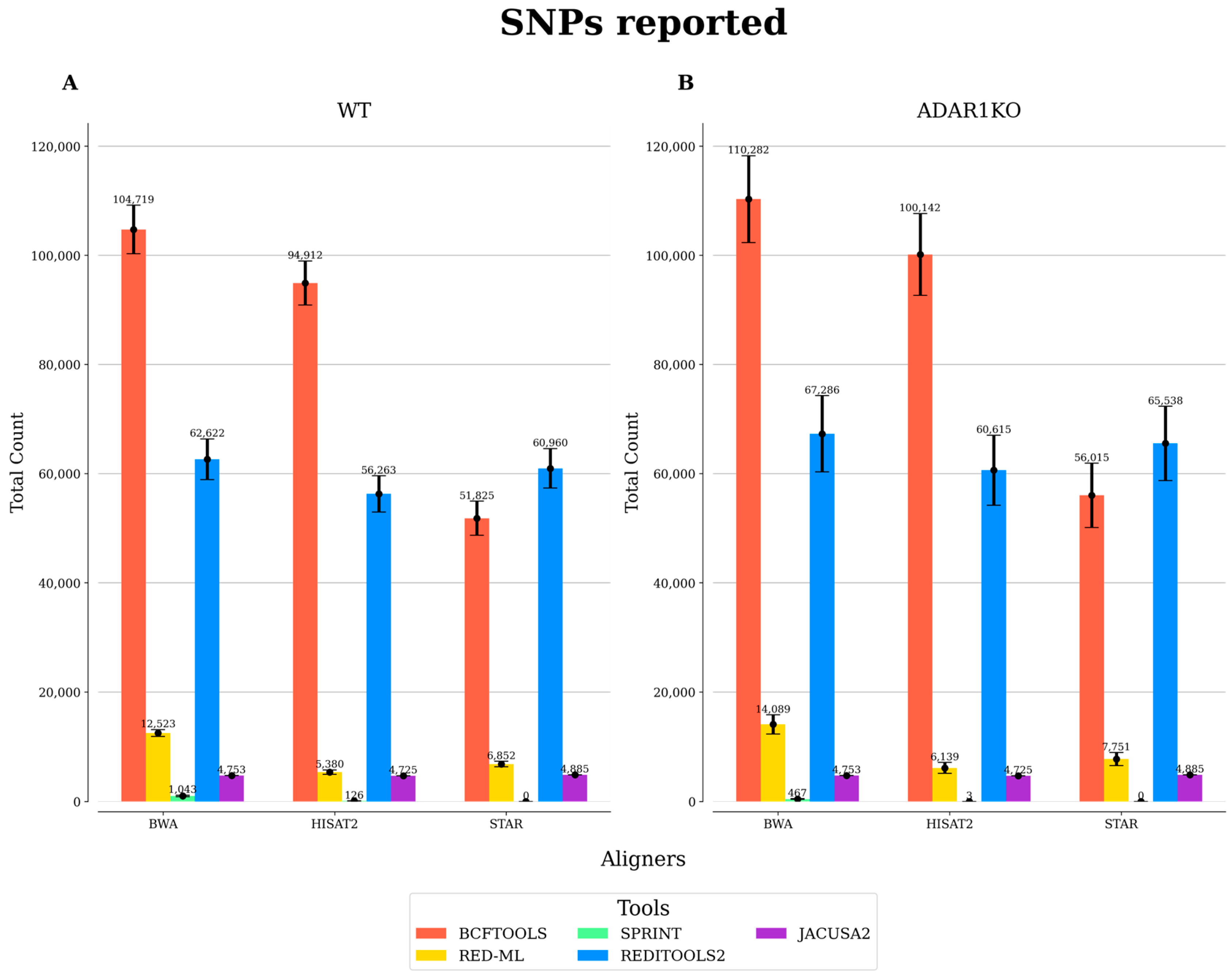
3.2. Comparison of Benchmarked RNA Editing Detection Tools
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brennicke, A.; Marchfelder, A.; Binder, S. RNA editing. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 1999, 23, 297–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikura, K. Functions and regulation of RNA editing by ADAR deaminases. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2010, 79, 321–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.X.; Cho, D.S.; Wang, Q.; Lai, F.; Carter, K.C.; Nishikura, K. A third member of the RNA-specific adenosine deaminase gene family, ADAR3, contains both single- and double-stranded RNA binding domains. RNA 2000, 6, 755–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takenaka, M.; Zehrmann, A.; Verbitskiy, D.; Hartel, B.; Brennicke, A. RNA editing in plants and its evolution. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2013, 47, 335–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boccaletto, P.; Stefaniak, F.; Ray, A.; Cappannini, A.; Mukherjee, S.; Purta, E.; Kurkowska, M.; Shirvanizadeh, N.; Destefanis, E.; Groza, P.; et al. MODOMICS: A database of RNA modification pathways. 2021 update. Nucleic. Acids Res. 2022, 50, D231–D235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Yang, Y.; Sun, B.F.; Chen, Y.S.; Xu, J.W.; Lai, W.Y.; Li, A.; Wang, X.; Bhattarai, D.P.; Xiao, W.; et al. 5-methylcytosine promotes mRNA export—NSUN2 as the methyltransferase and ALYREF as an m(5)C reader. Cell Res. 2017, 27, 606–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, M. RNA 5-Methylcytosine Analysis by Bisulfite Sequencing. Methods Enzymol. 2015, 560, 297–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dominissini, D.; Moshitch-Moshkovitz, S.; Salmon-Divon, M.; Amariglio, N.; Rechavi, G. Transcriptome-wide mapping of N(6)-methyladenosine by m(6)A-seq based on immunocapturing and massively parallel sequencing. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 176–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Wang, I.X.; Li, Y.; Bruzel, A.; Richards, A.L.; Toung, J.M.; Cheung, V.G. Widespread RNA and DNA sequence differences in the human transcriptome. Science 2011, 333, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahn, J.H.; Lee, J.H.; Li, G.; Greer, C.; Peng, G.; Xiao, X. Accurate identification of A-to-I RNA editing in human by transcriptome sequencing. Genome Res. 2012, 22, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, D.; Weirick, T.; Dimmeler, S.; Uchida, S. RNAEditor: Easy detection of RNA editing events and the introduction of editing islands. Brief. Bioinform. 2017, 18, 993–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Chen, H.; Shao, J.; Zhang, H.; Wu, K.; Liu, C. Identification of Symmetrical RNA Editing Events in the Mitochondria of Salvia miltiorrhiza by Strand-specific RNA Sequencing. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parkhomchuk, D.; Borodina, T.; Amstislavskiy, V.; Banaru, M.; Hallen, L.; Krobitsch, S.; Lehrach, H.; Soldatov, A. Transcriptome analysis by strand-specific sequencing of complementary DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, e123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazak, L.; Haviv, A.; Barak, M.; Jacob-Hirsch, J.; Deng, P.; Zhang, R.; Isaacs, F.J.; Rechavi, G.; Li, J.B.; Eisenberg, E.; et al. A-to-I RNA editing occurs at over a hundred million genomic sites, located in a majority of human genes. Genome Res. 2014, 24, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, J.B.t.; Sadri, G.; Fischer, A.G.; Weirick, T.; Militello, G.; Wysoczynski, M.; Gumpert, A.M.; Braun, T.; Uchida, S. The A-to-I RNA Editing Enzyme Adar1 Is Essential for Normal Embryonic Cardiac Growth and Development. Circ. Res. 2020, 127, 550–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Miyakoda, M.; Yang, W.; Khillan, J.; Stachura, D.L.; Weiss, M.J.; Nishikura, K. Stress-induced apoptosis associated with null mutation of ADAR1 RNA editing deaminase gene. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 4952–4961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Samuel, C.E. Editing of glutamate receptor subunit B pre-mRNA by splice-site variants of interferon-inducible double-stranded RNA-specific adenosine deaminase ADAR1. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 5070–5077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, F.; Chen, C.X.; Carter, K.C.; Nishikura, K. Editing of glutamate receptor B subunit ion channel RNAs by four alternatively spliced DRADA2 double-stranded RNA adenosine deaminases. Mol. Cell Biol. 1997, 17, 2413–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, S.H.; Danan-Gotthold, M.; Ben-Izhak, M.; Rechavi, G.; Cohen, C.J.; Louzoun, Y.; Levanon, E.Y. Increased RNA Editing May Provide a Source for Autoantigens in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Cell Rep. 2018, 23, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.H.; Luo, X.; Nie, Y.; Su, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Kabir, K.; Zhang, D.; Rabinovici, R. Widespread inosine-containing mRNA in lymphocytes regulated by ADAR1 in response to inflammation. Immunology 2003, 109, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liddicoat, B.J.; Piskol, R.; Chalk, A.M.; Ramaswami, G.; Higuchi, M.; Hartner, J.C.; Li, J.B.; Seeburg, P.H.; Walkley, C.R. RNA editing by ADAR1 prevents MDA5 sensing of endogenous dsRNA as nonself. Science 2015, 349, 1115–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez Morales, D.; Ilieva, M.; Rennie, S.; Uchida, S. Potential usages of A-to-I RNA editing patterns as diagnostic biomarkers. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2023, 324, C837–C842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, H.; Calis, J.J.A.; Wu, X.; Sun, T.; Yu, Y.; Sarbanes, S.L.; Dao Thi, V.L.; Shilvock, A.R.; Hoffmann, H.H.; Rosenberg, B.R.; et al. Human ADAR1 Prevents Endogenous RNA from Triggering Translational Shutdown. Cell 2018, 172, 811–824 e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.; Liu, D.; Li, Q.; Lei, M.; Xu, L.; Wu, L.; Wang, Z.; Ren, S.; Li, W.; Xia, M.; et al. RED-ML: A novel, effective RNA editing detection method based on machine learning. GigaScience 2017, 6, gix012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Lu, Y.; Yan, S.; Xing, Q.; Tian, W. SPRINT: An SNP-free toolkit for identifying RNA editing sites. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 3538–3548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flati, T.; Gioiosa, S.; Spallanzani, N.; Tagliaferri, I.; Diroma, M.A.; Pesole, G.; Chillemi, G.; Picardi, E.; Castrignano, T. HPC-REDItools: A novel HPC-aware tool for improved large scale RNA-editing analysis. BMC Bioinform. 2020, 21, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piechotta, M.; Naarmann-de Vries, I.S.; Wang, Q.; Altmuller, J.; Dieterich, C. RNA modification mapping with JACUSA2. Genome Biol. 2022, 23, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danecek, P.; Bonfield, J.K.; Liddle, J.; Marshall, J.; Ohan, V.; Pollard, M.O.; Whitwham, A.; Keane, T.; McCarthy, S.A.; Davies, R.M.; et al. Twelve years of SAMtools and BCFtools. GigaScience 2021, 10, giab008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankish, A.; Diekhans, M.; Jungreis, I.; Lagarde, J.; Loveland, J.E.; Mudge, J.M.; Sisu, C.; Wright, J.C.; Armstrong, J.; Barnes, I.; et al. Gencode 2021. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D916–D923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannon, G.J. FASTX-Toolkit. Available online: http://hannonlab.cshl.edu/fastx_toolkit (accessed on 5 February 2023).
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Paggi, J.M.; Park, C.; Bennett, C.; Salzberg, S.L. Graph-based genome alignment and genotyping with HISAT2 and HISAT-genotype. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 907–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobin, A.; Davis, C.A.; Schlesinger, F.; Drenkow, J.; Zaleski, C.; Jha, S.; Batut, P.; Chaisson, M.; Gingeras, T.R. STAR: Ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramaswami, G.; Lin, W.; Piskol, R.; Tan, M.H.; Davis, C.; Li, J.B. Accurate identification of human Alu and non-Alu RNA editing sites. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 579–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butterfield, Y.S.; Kreitzman, M.; Thiessen, N.; Corbett, R.D.; Li, Y.; Pang, J.; Ma, Y.P.; Jones, S.J.; Birol, I. JAGuaR: Junction alignments to genome for RNA-seq reads. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e102398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broad Institute. Picard Toolkit. 2014. Available online: https://sourceforge.net/projects/picard/files/picard-tools/1.119/ (accessed on 5 February 2023).
- Lin, Y.C.; Boone, M.; Meuris, L.; Lemmens, I.; Van Roy, N.; Soete, A.; Reumers, J.; Moisse, M.; Plaisance, S.; Drmanac, R.; et al. Genome dynamics of the human embryonic kidney 293 lineage in response to cell biology manipulations. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picardi, E.; D’Erchia, A.M.; Lo Giudice, C.; Pesole, G. REDIportal: A comprehensive database of A-to-I RNA editing events in humans. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D750–D757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picardi, E.; Pesole, G. REDItools: High-throughput RNA editing detection made easy. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 1813–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q. Analysis of RNA Editing Sites from RNA-Seq Data Using GIREMI. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1751, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, A. Allelic association: Linkage disequilibrium structure and gene mapping. Mol. Biotechnol. 2009, 41, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherry, S.T.; Ward, M.; Sirotkin, K. dbSNP-database for single nucleotide polymorphisms and other classes of minor genetic variation. Genome Res. 1999, 9, 677–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Quinones-Valdez, G.; Fu, T.; Choudhury, M.; Reese, F.; Mortazavi, A.; Xiao, X. L-GIREMI uncovers RNA editing sites in long-read RNA-seq. Genome Biol. 2023, 24, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Lian, J.; Li, Q.; Zhang, P.; Zhou, Y.; Zhan, X.; Zhang, G. RES-Scanner: A software package for genome-wide identification of RNA-editing sites. GigaScience 2016, 5, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmi, S.; Borukhov, I.; Levanon, E.Y. Identification of widespread ultra-edited human RNAs. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1002317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.D.; Kim, T.T.; Walsh, T.; Kobayashi, Y.; Matise, T.C.; Buyske, S.; Gabriel, A. Widespread RNA editing of embedded alu elements in the human transcriptome. Genome Res. 2004, 14, 1719–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKenna, A.; Hanna, M.; Banks, E.; Sivachenko, A.; Cibulskis, K.; Kernytsky, A.; Garimella, K.; Altshuler, D.; Gabriel, S.; Daly, M.; et al. The Genome Analysis Toolkit: A MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res. 2010, 20, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genomes Project, C.; Auton, A.; Brooks, L.D.; Durbin, R.M.; Garrison, E.P.; Kang, H.M.; Korbel, J.O.; Marchini, J.L.; McCarthy, S.; McVean, G.A.; et al. A global reference for human genetic variation. Nature 2015, 526, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International HapMap, C. The International HapMap Project. Nature 2003, 426, 789–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piechotta, M.; Wyler, E.; Ohler, U.; Landthaler, M.; Dieterich, C. JACUSA: Site-specific identification of RNA editing events from replicate sequencing data. BMC Bioinform. 2017, 18, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.I.; Clark, W.C.; Pan, D.W.; Eckwahl, M.J.; Dai, Q.; Pan, T. Pseudouridines have context-dependent mutation and stop rates in high-throughput sequencing. RNA Biol. 2018, 15, 892–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Light, D.; Haas, R.; Yazbak, M.; Elfand, T.; Blau, T.; Lamm, A.T. RESIC: A Tool for Comprehensive Adenosine to Inosine RNA Editing Site Identification and Classification. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 686851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmead, B.; Trapnell, C.; Pop, M.; Salzberg, S.L. Ultrafast and memory-efficient alignment of short DNA sequences to the human genome. Genome Biol. 2009, 10, R25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.S.; Hur, B.; Kim, S. RDDpred: A condition-specific RNA-editing prediction model from RNA-seq data. BMC Genom. 2016, 17 (Suppl. S1), 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramaswami, G.; Li, J.B. RADAR: A rigorously annotated database of A-to-I RNA editing. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D109–D113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiran, A.; Baranov, P.V. DARNED: A DAtabase of RNa EDiting in humans. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 1772–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Tan, B.C.; Kang, L.; Tian, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Liang, Y.; Hu, X.; Tan, X.; et al. Comprehensive analysis of RNA-Seq data reveals extensive RNA editing in a human transcriptome. Nat. Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witten, I.H.; Frank, E.; Hall, M.A.; Pal, C.J. Data Mining: Practical Machine Learning Tools and Techniques; Morgan Kaufmann: Amsterdam, The Netherlands; London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Barnett, D.W.; Garrison, E.K.; Quinlan, A.R.; Stromberg, M.P.; Marth, G.T. BamTools: A C++ API and toolkit for analyzing and managing BAM files. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 1691–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, Z.; Liu, F.; Zhao, C.; Ren, C.; An, G.; Mei, C.; Bo, X.; Shu, W. Accurate identification of RNA editing sites from primitive sequence with deep neural networks. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alon, S.; Erew, M.; Eisenberg, E. DREAM: A webserver for the identification of editing sites in mature miRNAs using deep sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 2568–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nigita, G.; Alaimo, S.; Ferro, A.; Giugno, R.; Pulvirenti, A. Knowledge in the Investigation of A-to-I RNA Editing Signals. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2015, 3, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Wang, H.; Song, Y.; Dai, Z.; Yu, H.; Yin, M.; Wang, D.; Yang, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, T.; et al. Large-scale prediction of ADAR-mediated effective human A-to-I RNA editing. Brief. Bioinform. 2019, 20, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo Giudice, C.; Pesole, G.; Picardi, E. REDIdb 3.0: A Comprehensive Collection of RNA Editing Events in Plant Organellar Genomes. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Xia, L.; Zhang, Y.; Niu, G.; Li, M.; Wang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Sang, J.; Zou, D.; Hu, S.; et al. Plant editosome database: A curated database of RNA editosome in plants. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D170–D174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, G.; Zou, D.; Li, M.; Zhang, Y.; Sang, J.; Xia, L.; Li, M.; Liu, L.; Cao, J.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Editome Disease Knowledgebase (EDK): A curated knowledgebase of editome-disease associations in human. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D78–D83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.H.; Chen, S.C. The Cancer Editome Atlas: A Resource for Exploratory Analysis of the Adenosine-to-Inosine RNA Editome in Cancer. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 3001–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Pertea, G.; Trapnell, C.; Pimentel, H.; Kelley, R.; Salzberg, S.L. TopHat2: Accurate alignment of transcriptomes in the presence of insertions, deletions and gene fusions. Genome Biol. 2013, 14, R36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baruzzo, G.; Hayer, K.E.; Kim, E.J.; Di Camillo, B.; FitzGerald, G.A.; Grant, G.R. Simulation-based comprehensive benchmarking of RNA-seq aligners. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmid, C.W.; Deininger, P.L. Sequence organization of the human genome. Cell 1975, 6, 345–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diroma, M.A.; Ciaccia, L.; Pesole, G.; Picardi, E. Elucidating the editome: Bioinformatics approaches for RNA editing detection. Brief. Bioinform. 2019, 20, 436–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engstrom, P.G.; Steijger, T.; Sipos, B.; Grant, G.R.; Kahles, A.; Ratsch, G.; Goldman, N.; Hubbard, T.J.; Harrow, J.; Guigo, R.; et al. Systematic evaluation of spliced alignment programs for RNA-seq data. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 1185–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, J.H.; Ko, Y.H.; Kang, K. RNA variant identification discrepancy among splice-aware alignment algorithms. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0201822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bass, B.L. RNA editing by adenosine deaminases that act on RNA. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2002, 71, 817–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchida, S.; Jones, S.P. RNA Editing: Unexplored Opportunities in the Cardiovascular System. Circ. Res. 2018, 122, 399–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, H.E.; Ilieva, M.; Bishop, A.J.R.; Uchida, S. Current Status of Epitranscriptomic Marks Affecting lncRNA Structures and Functions. Noncoding RNA 2022, 8, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Tool | Real Run Time (h) | CPU % | Maximum RSS (GB) |
|---|---|---|---|
| BCFtools | 9.83 | 105 | 1.06 |
| RED-ML | 63.77 | 99 | 12.42 |
| SPRINT | 23.33 | 98 | 12.17 |
| JACUSA2 | 3.70 | 559 | 32.57 |
| REDItools2 | 215.18 | 99 | 1.29 |
| Sample Condition | Aligner | Tool | # RES | % (ADAR1KO/WT) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WT | BWA | RED-ML | 17,110 | |
| ADAR1KO | BWA | RED-ML | 7228 | 42.24 |
| WT | HISAT2 | RED-ML | 6158 | |
| ADAR1KO | HISAT2 | RED-ML | 918 | 14.91 |
| WT | STAR | RED-ML | 17,309 | |
| ADAR1KO | STAR | RED-ML | 2267 | 13.10 |
| WT | BWA | REDItools2 | 344,646 | |
| ADAR1KO | BWA | REDItools2 | 257,445 | 74.70 |
| WT | HISAT2 | REDItools2 | 174,481 | |
| ADAR1KO | HISAT2 | REDItools2 | 110,643 | 63.41 |
| WT | STAR | REDItools2 | 246,040 | |
| ADAR1KO | STAR | REDItools2 | 157,254 | 63.91 |
| WT | BWA | SPRINT | 27,707 | |
| ADAR1KO | BWA | SPRINT | 919 | 3.32 |
| WT | HISAT2 | SPRINT | 6903 | |
| ADAR1KO | HISAT2 | SPRINT | 58 | 0.84 |
| WT | STAR | SPRINT | N/A | |
| ADAR1KO | STAR | SPRINT | N/A | N/A |
| WT | BWA | JACUSA2 | 27,388 | |
| ADAR1KO | BWA | JACUSA2 | 18,606 | 67.93 |
| WT | HISAT2 | JACUSA2 | 13,252 | |
| ADAR1KO | HISAT2 | JACUSA2 | 7739 | 58.40 |
| WT | STAR | JACUSA2 | 20,455 | |
| ADAR1KO | STAR | JACUSA2 | 12,431 | 60.77 |
| Sample Condition | Aligner | Tool | # RES | % (ADAR1KO/WT) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WT | BWA | RED-ML | 3949 | |
| ADAR1KO | BWA | RED-ML | 962 | 24 |
| WT | HISAT2 | RED-ML | 1976 | |
| ADAR1KO | HISAT2 | RED-ML | 206 | 10 |
| WT | STAR | RED-ML | 4262 | |
| ADAR1KO | STAR | RED-ML | 396 | 9 |
| WT | BWA | REDItools2 | 42,891 | |
| ADAR1KO | BWA | REDItools2 | 33,648 | 78 |
| WT | HISAT2 | REDItools2 | 15,083 | |
| ADAR1KO | HISAT2 | REDItools2 | 8234 | 55 |
| WT | STAR | REDItools2 | 21,734 | |
| ADAR1KO | STAR | REDItools2 | 11,651 | 54 |
| WT | BWA | SPRINT | 1358 | |
| ADAR1KO | BWA | SPRINT | 50 | 4 |
| WT | HISAT2 | SPRINT | 415 | |
| ADAR1KO | HISAT2 | SPRINT | 3 | 1 |
| WT | STAR | SPRINT | N/A | |
| ADAR1KO | STAR | SPRINT | N/A | N/A |
| WT | BWA | JACUSA2 | 20,048 | |
| ADAR1KO | BWA | JACUSA2 | 14,941 | 75 |
| WT | HISAT2 | JACUSA2 | 9642 | |
| ADAR1KO | HISAT2 | JACUSA2 | 6342 | 66 |
| WT | STAR | JACUSA2 | 14,681 | |
| ADAR1KO | STAR | JACUSA2 | 10,029 | 68 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Morales, D.R.; Rennie, S.; Uchida, S. Benchmarking RNA Editing Detection Tools. BioTech 2023, 12, 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/biotech12030056
Morales DR, Rennie S, Uchida S. Benchmarking RNA Editing Detection Tools. BioTech. 2023; 12(3):56. https://doi.org/10.3390/biotech12030056
Chicago/Turabian StyleMorales, David Rodríguez, Sarah Rennie, and Shizuka Uchida. 2023. "Benchmarking RNA Editing Detection Tools" BioTech 12, no. 3: 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/biotech12030056
APA StyleMorales, D. R., Rennie, S., & Uchida, S. (2023). Benchmarking RNA Editing Detection Tools. BioTech, 12(3), 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/biotech12030056








