In Silico Characterization of Inflammatory and Anti-Inflammatory Modulation in Diabetic Nephropathy: The Construction of a Genetic Panel
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Systematic Review
2.2. Meta-Analysis
2.3. Protein–Protein Interaction and Network Analysis
2.4. Microarray Data and Data Processing
3. Results
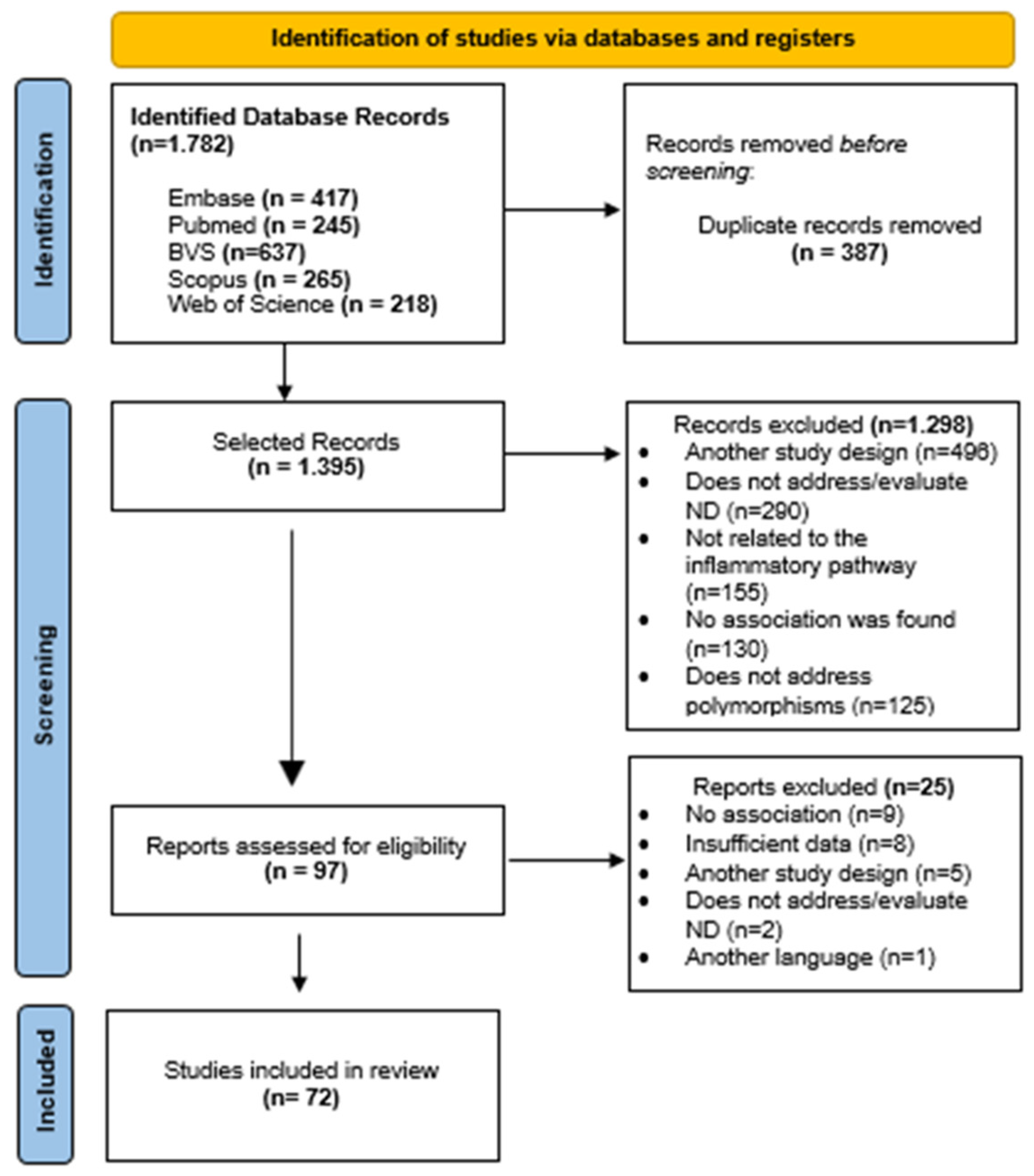
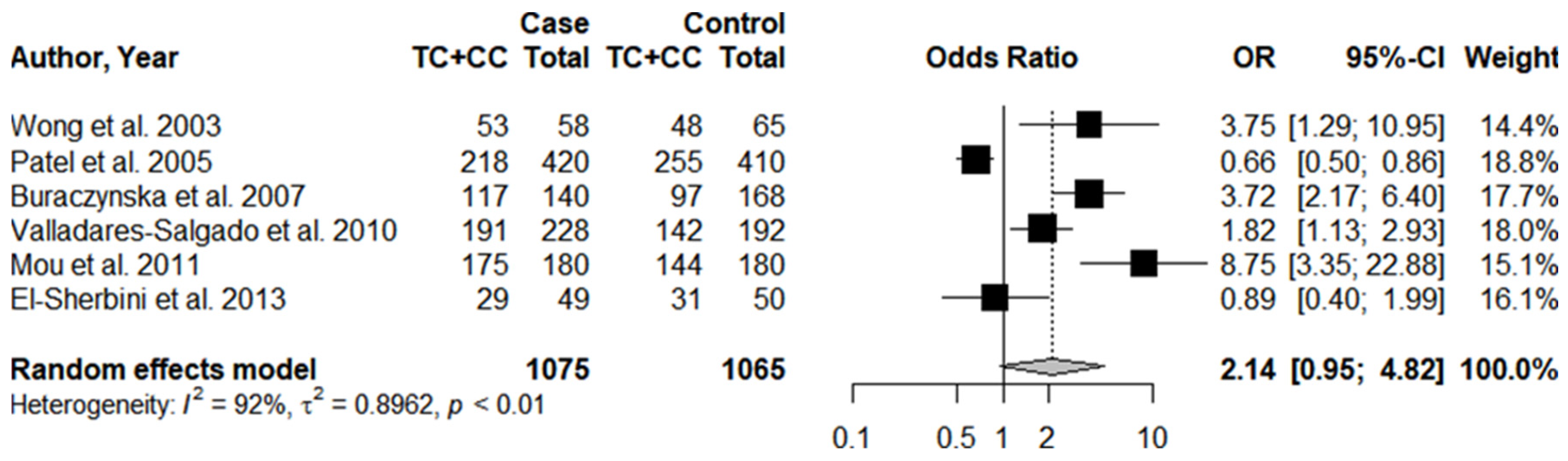
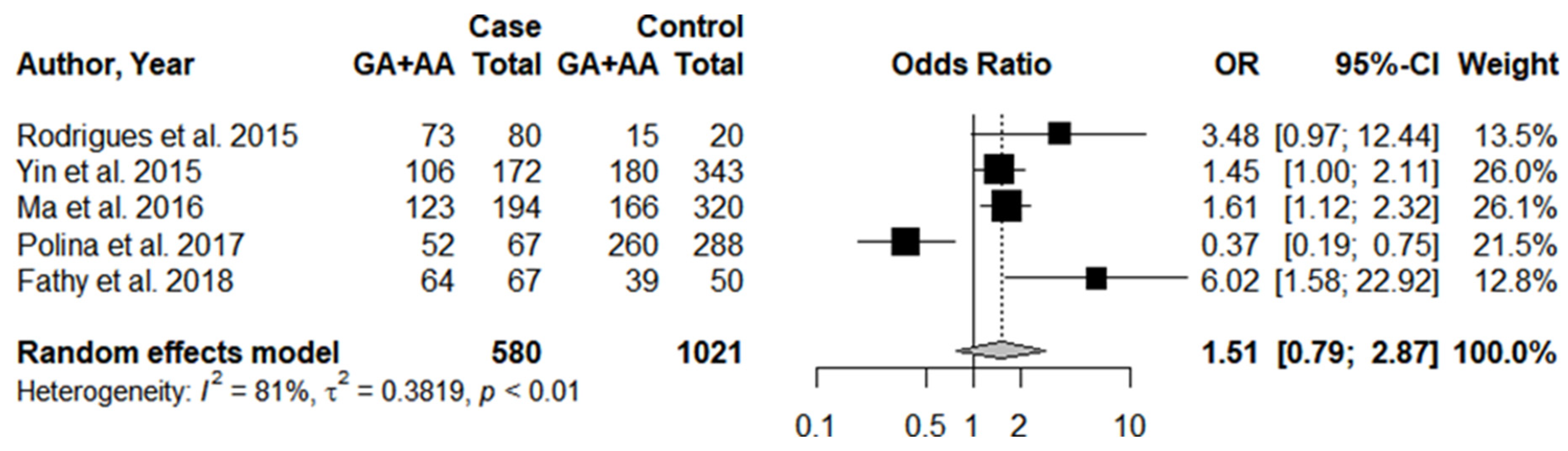
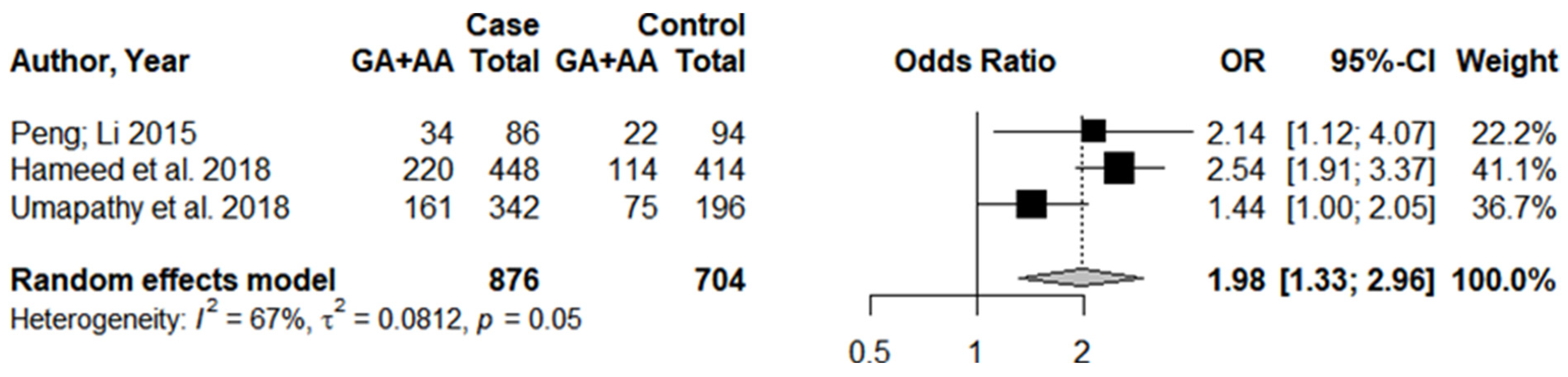
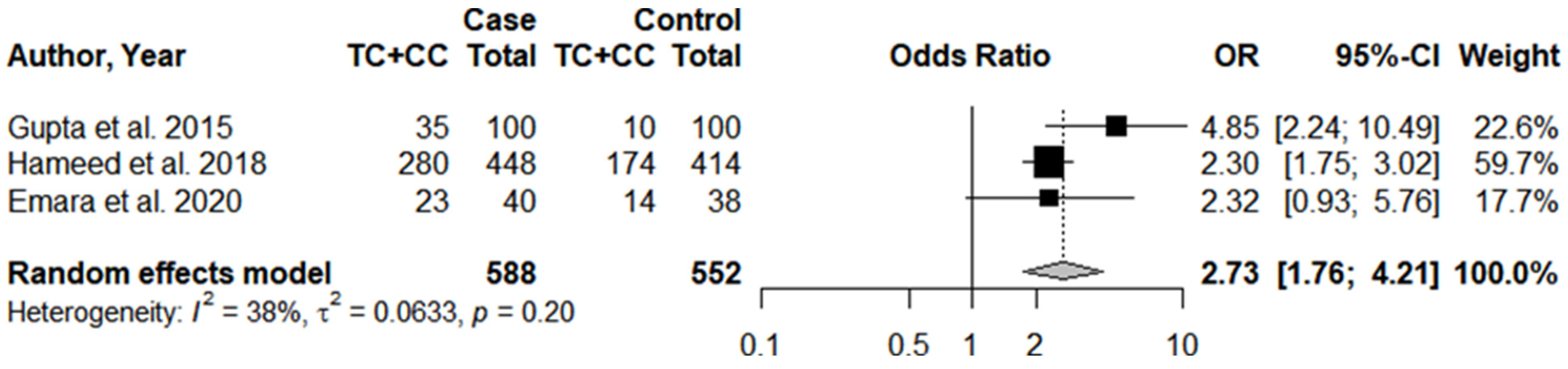
3.1. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
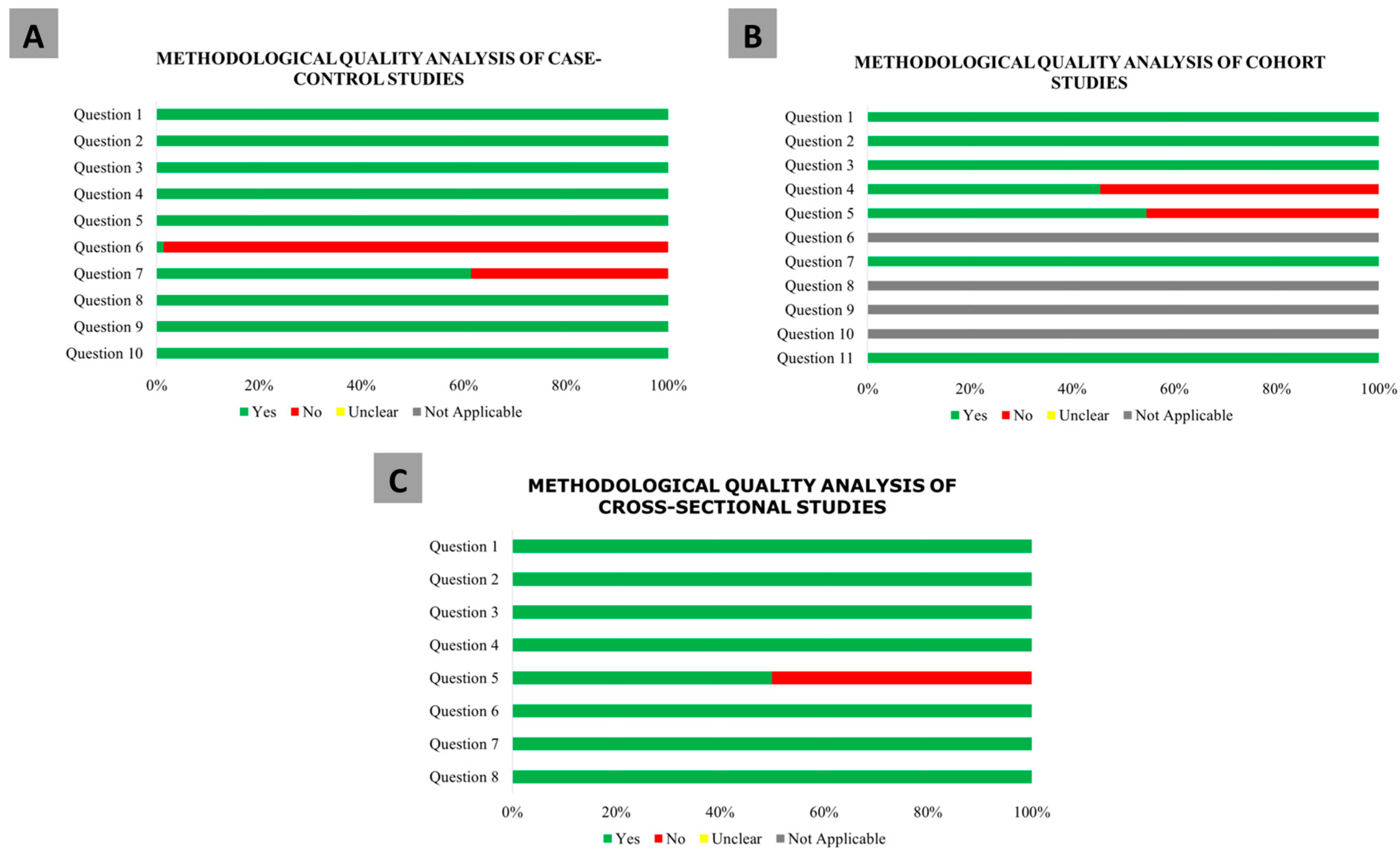
3.2. Methodological Quality Analysis
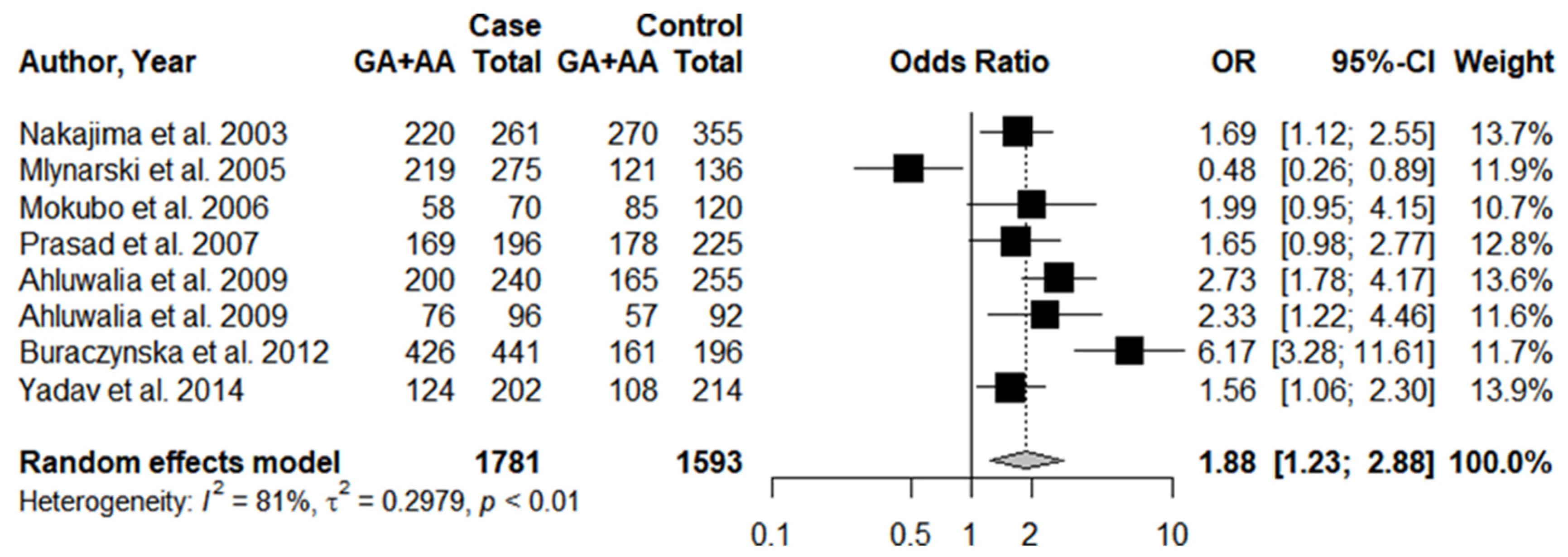
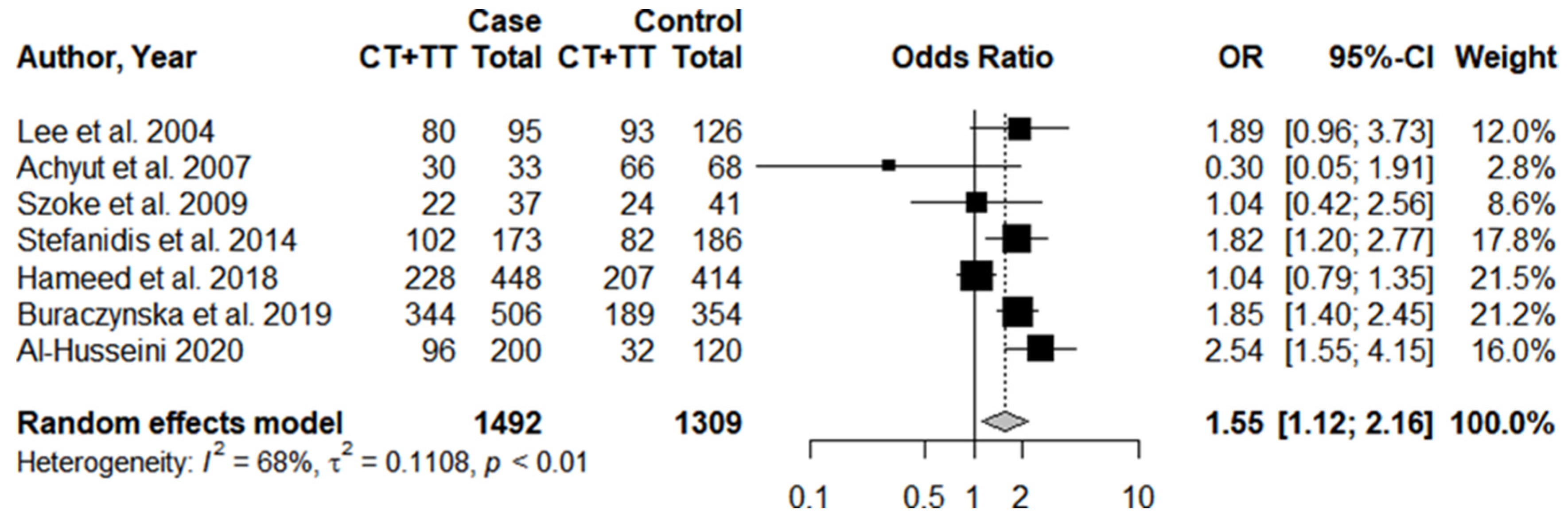
3.3. Individual Results
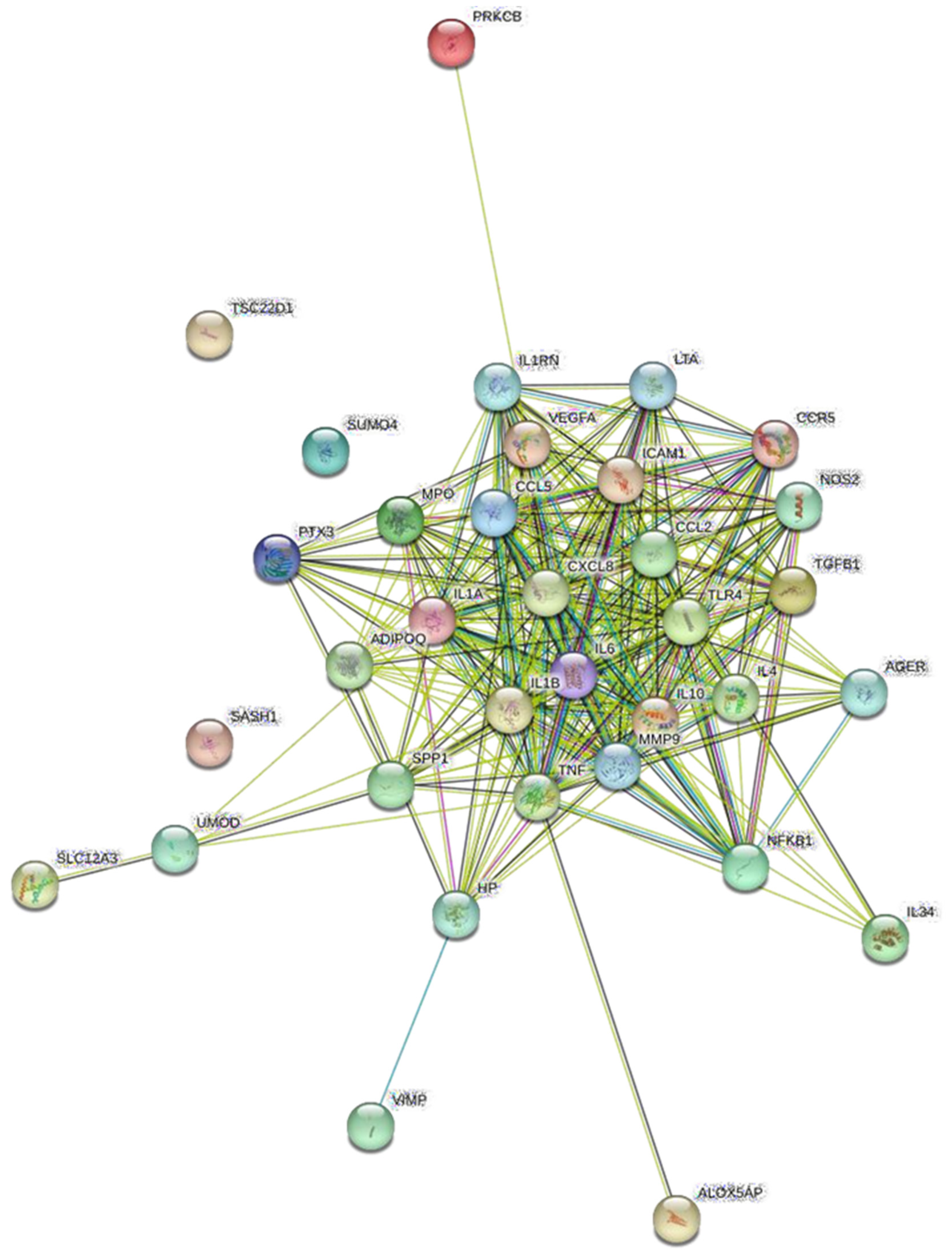
3.4. Protein Network Analysis and Identification of Hub Genes
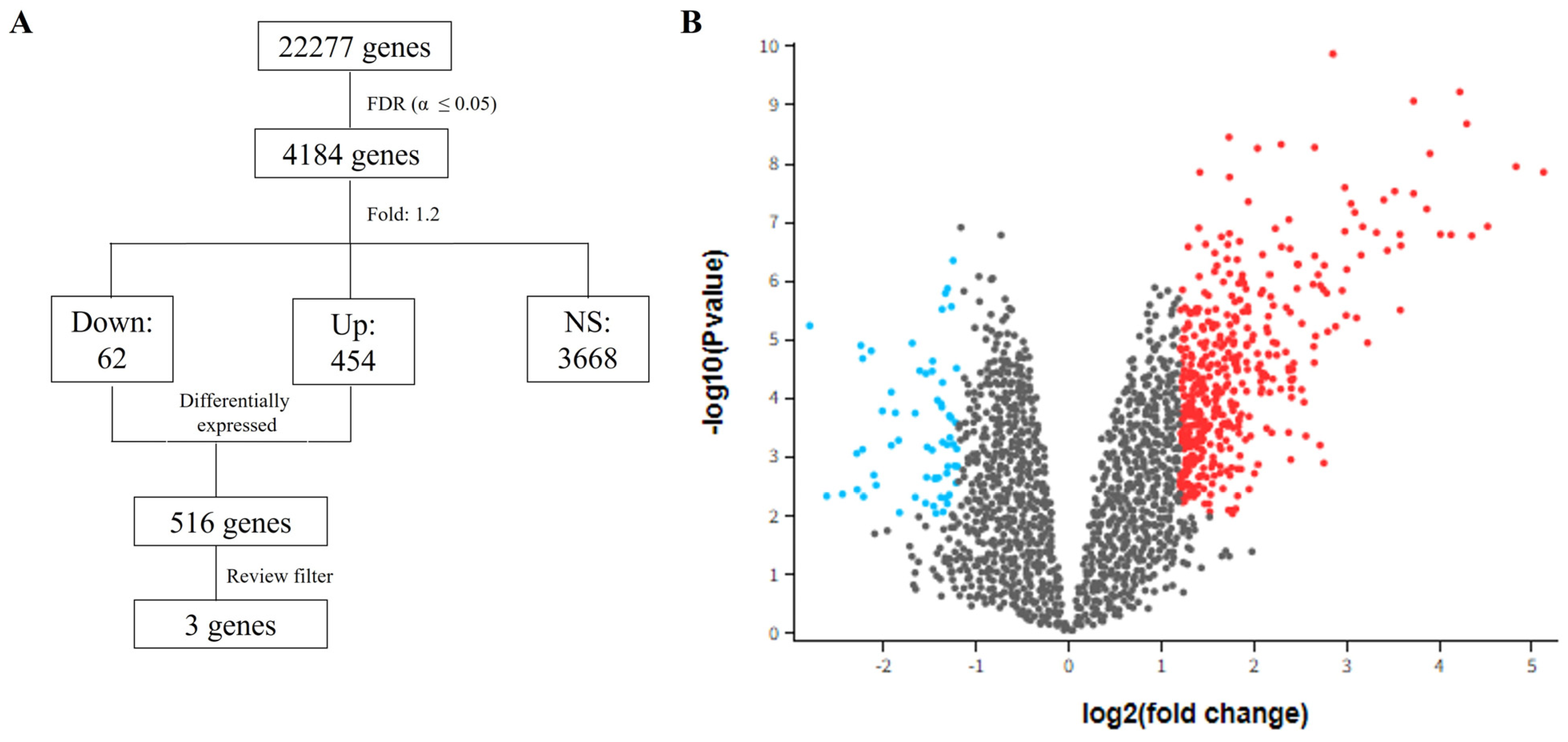
3.5. Differential Expression Analysis—GSE30529
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hintsa, S.; Dube, L.; Abay, M.; Angesom, T.; Workicho, A. Determinants of diabetic nephropathy in Ayder Referral Hospital, northern Ethiopia: A case-control study. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0173566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Lima, R.M.; Dos Anjos, L.R.B.; Alves, T.B.; Coelho, A.S.G.; Pedrino, G.R.; da Silva Santos Cruz, A.H.S.; Reis, A.A.S. Do GST polymorphisms influence in the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy? Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2018, 478, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, S.; Ali, A.; Katare, R. Molecular complexities underlying the vascular complications of diabetes mellitus—A comprehensive review. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2020, 34, 107613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pichler, R.; Afkarian, M.; Dieter, B.P.; Tuttle, K.R. Immunity and inflammation in diabetic kidney disease: Translating mechanisms to biomarkers and treatment targets. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2017, 312, F716–F731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayego-Mateos, S.; Morgado-Pascual, J.L.; Opazo-Ríos, L.; Guerrero-Hue, M.; García-Caballero, C.; Vázquez-Carballo, C.; Mas, S.; Sanz, A.B.; Herencia, C.; Mezzano, S.; et al. Pathogenic pathways and therapeutic approaches targeting inflammation in diabetic nephropathy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agere, S.A.; Kim, E.Y.; Akhtar, N.; Ahmed, S. Syndecans in chronic inflammatory and autoimmune diseases: Pathological insights and therapeutic opportunities. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 6346–6358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, J.A.; Moreno, S.; Rubio-Navarro, A.; Gómez-Guerrero, C.; Ortiz, A.; Egido, J. Role of chemokines in proteinuric kidney disorders. Expert. Rev. Mol. Med. 2014, 16, e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, F.; Rossing, P. Diagnosis of diabetic kidney disease: State of the art and future perspective. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2018, 8, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, R.; Gui, D.; Zheng, L.; Zhai, R.; Wang, F.; Wang, N. Mechanistic insight and management of diabetic nephropathy: Recent progress and future perspective. J. Diabetes Res. 2017, 2017, e1839809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, J.B.; Florez, J.C. Genetics of diabetes mellitus and diabetes complications. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2020, 16, 377–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouzzani, M.; Hammady, H.; Fedorowicz, Z.; Elmagarmid, A. Rayyan—A web and mobile app for systematic reviews. Syst. Ver. 2016, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egger, M.; Smith, G.D.; Schneider, M.; Minder, C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ 1997, 315, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egger, M.; Smith, G.D. Meta-analysis: Potentials and promise. BMJ 1997, 315, 1371–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Ma, J.; Brismar, K.; Efendic, S.; Gu, H.F. A single nucleotide polymorphism alters the sequence of SP1 binding site in the adiponectin promoter region and is associated with diabetic nephropathy among type 1 diabetic patients in the Genetics of Kidneys in Diabetes Study. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2009, 23, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaziri, R.; Aubert, R.; Roussel, R.; Emery, N.; Maimaitiming, S.; Bellili, N.; Miot, A.; Saulnier, P.J.; Travert, F.; Hadjadj, S.; et al. Association of ADIPOQ genetic variants and plasma adiponectin isoforms with the risk of incident renal events in type 2 diabetes. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2010, 25, 2231–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Cilenšek, I.; Šeruga, M.; Makuc, J.; Završnik, M.; Petrovič, D. The ALOXA5AP gene (rs38022789) is associated with diabetic nephropathy in Slovenian patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Gene 2020, 741, 144551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahluwalia, T.S.; Khullar, M.; Ahuja, M.; Kohli, H.S.; Bhansali, A.; Mohan, V.; Venkatesan, R.; Rai, T.S.; Sud, K.; Singal, P.K. Common variants of inflammatory cytokine genes are associated with risk of nephropathy in type 2 diabetes among Asian Indians. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, J.-Y. Association of polymorphisms in monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 promoter with diabetic kidney failure in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2007, 22, 810–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raina, P.; Matharoo, K.; Bhanwer, A.J.S. Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) g.-2518A4G polymorphism and susceptibility to type 2 diabetes (T2D) and end stage renal disease (ESRD) in the North-West Indian population of Punjab. Ann. Hum. Biol. 2015, 42, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, K.; Tanaka, Y.; Nomiyama, T.; Ogihara, T.; Ikeda, F.; Kanno, R.; Iwashita, N.; Sakai, K.; Watada, H.; Onuma, T.; et al. RANTES promoter genotype is associated with diabetic nephropathy in type 2 diabetic subjects. Diabetes Care 2003, 26, 892–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mlynarski, W.M.; Placha, G.P.; Wolkow, P.P.; Bochenski, J.P.; Warram, J.H.; Krolewski, A.S. Risk of diabetic nephropathy in type 1 diabetes is associated with functional polymorphisms in RANTES receptor gene (CCR5): A sex-specific effect. Diabetes 2005, 54, 3331–3335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokubo, A.; Tanaka, Y.; Nakajima, K.; Watada, H.; Hirose, T.; Kawasumi, M.; Sakai, K.; Kanazawa, A.; Maeda, S.; Hosokawa, K.; et al. Chemotactic cytokine receptor 5 (CCR5) gene promoter polymorphism (59029A/G) is associated with diabetic nephropathy in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes: A 10-year longitudinal study. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2006, 73, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, P.; Tiwari, A.K.; Kumar, K.P.; Ammini, A.C.; Gupta, A.; Gupta, R.; Thelma, B.K. Association of TGFβ1, TNFα, CCR2 and CCR5 gene polymorphisms in type-2 diabetes and renal insufficiency among Asian Indians. BMC Med. Genet. 2007, 8, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buraczynska, M.; Zukowski, P.; Wacinski, P.; Berger-Smyka, B.; Dragan, M.; Mozul, S. Chemotactic cytokine receptor 5 gene polymorphism: Relevance to microvascular complications in type 2 diabetes. Cytokine 2012, 58, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.K.; Kumar, V.; Dutta, P.; Bhansali, A.; Jha, V. Variations in CCR5, but not HFE, ELMO1, or SLC12A3, are associated with susceptibility to kidney disease in north Indian individuals with type 2 diabetes. J. Diabetes 2014, 6, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessa, S.S.; Hamdy, S.M.; Ali, E.M. Haptoglobin gene polymorphism in type 2 diabetic patients with and without nephropathy: An Egyptian study. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2007, 18, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, B.R.; Savage, D.A.; Brady, H.R.; Maxwell, A.P. Association between haptoglobin gene variants and diabetic nephropathy: Haptoglobin polymorphism in nephropathy susceptibility. Nephron Exp. Nephrol. 2007, 105, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seman, N.A.; Anderstam, B.; Mohamud, W.N.W.; Östenson, C.G.; Brismar, K.; Gu, H.F. Genetic, epigenetic and protein analyses of intercellular adhesion molecule 1 in Malaysian subjects with type 2 diabetes and diabetic nephropathy. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2015, 29, 1234–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabhi, B.; Mistry, K.N. Oxidative stress and its association with TNF-α-308 G/C and IL-1α-889 C/T gene polymorphisms in patients with diabetes and diabetic nephropathy. Gene 2015, 562, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Ihm, C.-G.; Sohn, S.D.; Lee, T.W.; Kim, M.J.; Koh, G.; Oh, S.J.; Woo, J.-T.; Kim, S.W.; Kim, J.W.; et al. Polymorphisms in interleukin-1ß and interleukin-1 receptor antagonist genes are associated with kidney failure in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Am. J. Nephrol. 2004, 24, 410–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achyut, B.R.; Srivastava, A.; Bhattacharya, S.; Mittal, B. Genetic association of interleukin-1β (-511C/T) and interleukin-1 receptor antagonist (86 bp repeat) polymorphisms with Type 2 diabetes mellitus in North Indians. Clin. Chim. Acta 2007, 377, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szoke, D.; Molnar, B.; Solymosi, N.; Racz, K.; Gergics, P.; Blasko, B.; Vasarhelyi, B.; Vannay, A.; Mandy, Y.; Klausz, G.; et al. Polymorphisms of the ApoE, HSD3B1, IL-1beta and p53 genes are associated with the development of early uremic complications in diabetic patients: Results of a DNA resequencing array study. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2009, 23, 217–227. [Google Scholar]
- Stefanidis, I.; Kreuer, K.; Dardiotis, E.; Arampatzis, S.; Eleftheriadis, T.; Hadjigeorgiou, G.M.; Zintzaras, E.; Mertens, P.-R. Association between the interleukin-1b gene (IL1B) C-511T polymorphism and the risk of diabetic nephropathy in type 2 diabetes: A candidate-gene association study. DNA Cell Biol. 2014, 33, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, I.; Masoodi, S.R.; Malik, P.A.; Mir, S.A.; Ghazanfar, K.; Ganai, B.A. Genetic variations in key inflammatory cytokines exacerbate the risk of diabetic nephropathy by influencing the gene expression. Gene 2018, 661, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buraczynska, M.; Ksiazek, K.; Wacinski, P.; Zaluska, W. Interleukin-1β gene (IL1B) polymorphism and risk of developing diabetic nephropathy. Immunol. Investig. 2019, 48, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Husseini, R.M.A.H. Impact of interleukin-1 beta gene allelic polymorphisms in diabetic and non-diabetic hemodialysis Iraqi patients. Syst. Rev. Pharm. 2020, 11, 63–69. [Google Scholar]
- Blakemore, A.I.F. Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist allele (IL1RN*2) associated with nephropathy in diabetes mellitus. Hum. Genet. 1996, 97, 369–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Shabrawi, M.M.; Bayoumy, N.M.; Hassan, H.H. Interleukin-4 polymorphism in Egyptian patients with type-2 diabetic nephropathy. Life Sci. J. 2011, 8, 577–582. [Google Scholar]
- Neelofar, K.; Ahmad, J.; Ahmad, A.; Alam, K. Study of IL4-590C/T and IL6-174G/C gene polymorphisms in type 2 diabetic patients with chronic kidney disease in North Indian population. J. Cell Biochem. 2017, 118, 1803–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamura, A.; Hasegawa, G.; Obayashi, H.; Kamiuchi, K.; Ishii, M.; Yano, M.; Tanaka, T.; Yamaguchi, M.; Shigeta, H.; Ogata, M.; et al. Interleukin-6 polymorphism (-634C/G) in the promoter region and the progression of diabetic nephropathy in Type 2 diabetes. Diabet. Med. 2002, 19, 1000–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.-T.; Huang, M.-C.; Chung, H.-F.; Chiu, Y.-F.; Chen, P.-S.; Chen, F.-P.; Lee, C.-Y.; Shin, S.-J.; Hwang, S.-J.; Huang, Y.-F.; et al. Interleukin-6 gene polymorphisms correlate with the progression of nephropathy in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes: A prospective cohort study. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pr. 2016, 120, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitamura, A.; Hasegawa, G.; Obayashi, H.; Kamiuchi, K.; Ishii, M.; Yano, M.; Tanaka, T.; Yamaguchi, M.; Shigeta, H.; Ogata, M.; et al. Association of interleukin-6 polymorphism (-634C/G) in the promoter region with diabetic nephropathy in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Bangladesh J. Med. Sci. 2019, 18, 741–747. [Google Scholar]
- Ng, D.P.; Nurbaya, S.; Sandra, H.J.; Krolewski, A.S. An IL-6 haplotype on human chromosome 7p21 confers risk for impaired renal function in type 2 diabetic patients. Kidney Int. 2008, 74, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmuganathan, R.; Ramanathan, K.; Padmanabhan, G.; Vijayaraghavan, B. Evaluation of Interleukin 8 gene polymorphism for predicting inflammation in Indian chronic kidney disease and peritoneal dialysis patients. Alex. J. Med. 2016, 53, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rodrigues, K.F.; Pietrani, N.T.; Sandrim, V.C.; Vieira, C.M.A.F.; Fernandes, A.P.; Bosco, A.A.; Gomes, K.B. Association of a large panel of cytokine gene polymorphisms with complications and comorbidities in type 2 diabetes patients. J. Diabetes Res. 2015, 2015, 605965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Q.; Zhai, Q.; Wang, D.; Hai, J.; Cao, M.; Wang, J.; Wang, T. Investigation on the association between interleukin-10 -592C/A, 819C/T and -1082A/G gene polymorphisms and development of diabetic nephropathy. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 15216–15221. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, D.H.; Xu, Q.Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhai, Q.Q.; Guo, M.H. Association between interleukin-10 gene polymorphisms and susceptibility to diabetic nephropathy in a Chinese population. Genet. Mol. Res. 2016, 15, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polina, E.R.; da Silva Pereira, B.L.; Crispim, D.; Sbruzzi, R.C.; Canani, L.H.; Dos Santos, K.G. Association of -1082A>G polymorphism in the interleukin-10 gene with estimated glomerular filtration rate in type 2 diabetes. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2017, 42, 1164–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathy, S.A.; Mohamed, M.R.; Ali, M.A.; El-Helaly, A.E.; Alattar, A.T. Influence of IL-6, IL-10, IFN-γ, and TNF-α genetic variants on susceptibility to diabetic kidney disease in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. Biomarkers 2019, 24, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kung, W.J.; Lin, C.C.; Liu, S.H.; Chaung, H.C. Association of interleukin-10 polymorphisms with cytokines in type 2 diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2010, 12, 809–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, L.-N.; Chen, C.-C.; Wu, F.-Y.; Lin, C.-C.; Hsiao, J.-H.; Chang, C.-T.; Kardia, S.L.R.; Li, T.-C.; Tsai, F.-J. Identified single-nucleotide polymorphisms and haplotypes at 16q22.1 increase diabetic nephropathy risk in Han Chinese population. BMC Genet. 2014, 15, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Luk, A.O.Y.; Ma, R.C.W.; So, W.-Y.; Tam, C.H.T.; Ng, M.C.Y.; Yang, X.; Lam, V.; Tong, P.C.Y.; Chan, J.C.N. Predictive role of multilocus genetic polymorphisms in cardiovascular disease and inflammation-related genes on chronic kidney disease in Type 2 diabetes—An 8-year prospective cohort analysis of 1163 patients. Nephrol Dial Transpl. 2012, 27, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albert, C.; Kube, J.; Albert, A.; Schanze, D.; Zenker, M.; Mertens, P.R. Cubilin single nucleotide polymorphism variants are associated with macroangiopathy while a matrix metalloproteinase-9 single nucleotide polymorphism flip-flop may indicate susceptibility of diabetic nephropathy in type-2 diabetic patients. Nephron 2019, 141, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buraczynska, K.; Koziol-Montewka, M.; Majdan, M.; Tokarz, A.; Ksiazek, A. Genetic determination of TNF and myeloperoxidase production in dialyzed patients with diabetic nephropathy. Ren. Fail. 2004, 26, 633–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katakami, N.; Kume, S.; Kaneto, H.; Uzu, T.; Kashiwagi, A.; Yamasaki, Y.; Maegawa, H.; Shimomura, I. Association of myeloperoxidase G-463A gene polymorphism with diabetic nephropathy in Japanese type 2 diabetic subjects. Endocr. J. 2013, 60, 457–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, A.; Gupta, S.; Mehndiratta, M.; Sharma, M.; Singh, K.; Kalra, O.P.; Agarwal, S.; Gambhir, J.K. Association of NFKB1 gene polymorphism (rs28362491) with levels of inflammatory biomarkers and susceptibility to diabetic nephropathy in Asian Indians. World J. Diabetes 2017, 8, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Li, Y.M.; Yang, L.Q.; Zhong, C.G.; Zhuang, Z.X. Association of NOS2 and NOS3 gene polymorphisms with susceptibility to type 2 diabetes mellitus and diabetic nephropathy in the Chinese Han population. IUBMB Life 2016, 68, 516–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheema, B.S.; Iyengar, S.; Ahluwalia, T.S.; Kohli, H.S.; Sharma, R.; Shah, V.N.; Bhansali, A.; Sakhuja, V.; Khullar, M. Association of an osteopontin gene promoter polymorphism with susceptibility to diabetic nephropathy in Asian Indians. Clin. Chim. Acta 2012, 413, 1600–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zheng, T.; Wang, F.; Wang, N.; Song, Y.; Li, M.; Li, L.; Jiang, J.; Zhao, W. Pro12Ala polymorphism in the PPARG gene contributes to the development of diabetic nephropathy in Chinese type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Lei, T. Rs12976445 polymorphism is associated with risk of diabetic nephropathy through modulating expression of MicroRNA-125 and Interleukin-6R. Med. Sci. Monit. 2015, 21, 3490–3497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araki, S.-I.; Ng, D.P.K.; Krolewski, B.; Wyrwicz, L.; Rogus, J.J.; Canani, L.; Makita, Y.; Haneda, M.; Warram, J.H.; Krolewski, A.S. Identification of a common risk haplotype for diabetic nephropathy at the Protein Kinase C-β1 (PRKCB1) gene locus. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2003, 14, 2015–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Yu, W.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, H.; Bi, Y.; Zhu, D. Association of Pentraxin 3 gene polymorphisms with susceptibility to diabetic nephropathy. Med. Sci. Monit. 2017, 23, 428–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Naidany, S.S.; Zahran, E.; Abd El Gayed, E.M. Association of Pentraxin 3 rs2305619 (A/G) gene polymorphism and its serum level with the risk of nephropathy in type II diabetic patients. Gene Rep. 2020, 20, 100670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindholm, E.; Bakhtadze, E.; Sjögren, M.; Cilio, C.M.; Agardh, E.; Groop, L.; Agardh, C.D. The -374 T/A polymorphism in the gene encoding RAGE is associated with diabetic nephropathy and retinopathy in type 1 diabetic patients. Diabetologia 2006, 49, 2745–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, W.; Li, J.; Xu, J.-X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Xiao, J.-R.; Zhu, L.-Y.; Liu, J.-Y. Association of 2184AG polymorphism in the RAGE gene with diabetic nephropathy in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes. J. Diabetes Res. 2015, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonough, C.W.; Palmer, N.D.; Hicks, P.J.; Roh, B.H.; An, S.S.; Cooke, J.N.; Hester, J.M.; Wing, M.R.; Bostrom, M.A.; Rudock, M.E.; et al. A genome-wide association study for diabetic nephropathy genes in African Americans. Kidney Int. 2011, 79, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Mao, A.; Fu, X.; She, Y.; Wei, X. Correlation between SEPS1 gene polymorphism and type 2 diabetes mellitus: A preliminary study. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2019, 33, e22967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodhini, D.; Chidambaram, M.; Liju, S.; Revathi, B.; Laasya, D.; Sathish, N.; Kanthimathi, S.; Ghosh, S.; Anjana, R.M.; Mohan, V.; et al. Association of rs11643718 SLC12A3 and rs741301 ELMO1 variants with diabetic nephropathy in South Indian population. Ann. Hum. Genet. 2016, 80, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, N.; Yadav, A.K.; Kumar, V.; Dutta, P.; Bhansali, A.; Jha, V. SUMO4 163 G>A variation is associated with kidney disease in Indian subjects with type 2 diabetes. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2016, 43, 345–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.; Hibberd, M.L.; Millward, B.A.; Demaine, A.G. Chromosome 7q35 and susceptibility to diabetic microvascular complications. J. Diabetes Complicat. 1996, 10, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, T.Y.H.; Poon, P.; Chow, K.M.; Szeto, C.C.; Cheung, M.K.; Li, P.K.T. Association of transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) T869C (Leu 10Pro) gene polymorphisms with type 2 diabetic nephropathy in Chinese. Kidney Int. 2003, 63, 1831–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Patel, A.; Scott, W.R.; Lympany, P.A.; Rippin, J.D.; Gill, G.V.; Barnett, A.H.; Bain, S.C.; Warren 3/UK GoKind Study Group. The TGF-β1 gene codon 10 polymorphism contributes to the genetic predisposition to nephropathy in Type 1 diabetes. Diabet. Med. 2005, 22, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buraczynska, M.; Baranowicz-Gaszczyk, I.; Borowicz, E.; Ksiazek, A. TGF-β1 and TSC-22 gene polymorphisms and susceptibility to microvascular complications in type 2 diabetes. Nephron Physiol. 2007, 106, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valladares-Salgado, A.; Angeles-Martínez, J.; Rosas, M.; García-Mena, J.; Utrera-Barillas, D.; Gómez-Díaz, R.; Escobedo-de la Peña, J.; Parra, E.J.; Cruz, M. Association of polymorphisms within the transforming growth factor-b1 gene with diabetic nephropathy and serum cholesterol and triglyceride concentrations. Nephrology 2010, 15, 644–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mou, X.; Liu, W.-h.; Zhou, D.-y.; Liu, Y.-h.; Hu, Y.-b.; Ma, G.-l.; Shou, C.-m.; Chen, J.-w.; Zhao, J.-x. Association of Chinese Medicine Constitution Susceptibility to Diabetic Nephropathy and Transforming Growth Factor-β1 (T869C) Gene Polymorphism. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 2011, 17, 680–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Sherbini, S.M.; Shahen, S.M.; Mosaad, Y.M.; Abdelgawad, M.S.; Talaat, R.M. Gene polymorphism of transforming growth factor-b1 in Egyptian patients with type 2 diabetes and diabetic nephropathy. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2013, 45, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Abbas, S.A.; Raza, S.T.; Mir, S.S.; Siddiqi, Z.; Zaidi, A.; Zaidi, Z.H.; Mahdi, F. Role of variants rs5030717 and rs5030718 of TLR4 in the risk prediction of nephropathy, hypertension and dyslipidemia in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Br. J. Biomed. Sci. 2018, 75, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Mehndiratta, M.; Kalra, S.; Kalra, O.P.; Shukla, R.; Gambhir, J.K. Association of Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF) promoter polymorphisms with plasma TNF-α levels and susceptibility to diabetic nephropathy in North Indian population. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2015, 29, 338–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emara, M.; El-Edel, R.; Fathy, W.M.; Aboelkhair, N.T.; Watany, M.M.; Abou-Elela, D.H. Study the Association of Tumor Necrosis Factor Promoter Polymorphism with Type 2 Diabetic Nephropathy. Mediat. Inflamm. 2020, 2020, 1498278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Li, L.J. TNF-α-308G/A polymorphism associated with TNF-α protein expression in patients with diabetic nephropathy. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 3127–3131. [Google Scholar]
- Umapathy, D.; Krishnamoorthy, E.; Mariappanadar, V.; Viswanathan, V.; Ramkumar, K.M. Increased levels of circulating TNF-α is associated with (-308G/A) promoter polymorphism of TNF-α gene in Diabetic Nephropathy. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 107, 2113–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V.; Yadav, A.K.; Kumar, V.; Bhansali, A.; Jha, V. Uromodulin rs4293393 T>C variation is associated with kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes. Indian. J. Med. Res. 2017, 146, 15–21. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.; Cross, D.F.; Ollerenshaw, M.; Millward, B.A.; Demaine, A.G. Polymorphisms of the vascular endothelial growth factor and susceptibility to diabetic microvascular complications in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2003, 17, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matoba, K.; Takeda, Y.; Nagai, Y.; Kawanami, D.; Utsunomiya, K.; Nishimura, R. Unraveling the Role of Inflammation in the Pathogenesis of Diabetic Kidney Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zandi-Nejad, K.; Eddy, A.A.; Glassock, R.J.; Brenner, B.M. Why is proteinuria an ominous biomarker of progressive kidney disease? Kidney Int. 2004, 66, S76–S89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kany, S.; Vollrath, J.T.; Relja, B. Cytokines in inflammatory disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myśliwska, J.; Zorena, K.; Semetkowska-Jurkiewicz, E.; Rachoń, D.; Suchanek, H.; Myśliwski, A. High levels of circulating interleukin-10 in diabetic nephropathy patients. Eur. Cytokine Netw. 2005, 16, 117–122. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues, K.F.; Pietrani, N.T.; Bosco, A.A.; Campos, F.M.F.; Sandrim, V.C.; Gomes, K.B. IL-6, TNF-α, and IL-10 levels/polymorphisms and their association with type 2 diabetes mellitus and obesity in Brazilian individuals. Arch. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 61, 438–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.-W.; Hu, A.-M.; Sun, Q.-Q.; Zhang, B.-B.; Liu, H.-L.; Wang, Q.; Zeng, Y.-H.; Xu, R.-J.; Zhang, S.-J.; Shi, L.-B. Association between interleukin 10 gene -1082 A/G polymorphism and the risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis of 4250 subjects. Cytokine 2013, 62, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziyadeh, F.N. Different roles for TGF-beta and VEGF in the pathogenesis of the cardinal features of diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pr. 2008, 82, S38–S41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesch, G.H. MCP-1/CCL2, A new diagnostic marker and therapeutic target for progressive renal injury in diabetic nephropathy. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2008, 294, F697–F701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Mesallamy, H.O.; Ahmed, H.H.; Bassyouni, A.A.; Ahmed, A.S. Clinical significance of inflammatory and fibrogenic cytokines in diabetic nephropathy. Clin. Biochem. 2012, 45, 646–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mezzano, S.; Aros, C.; Droguett, A.; Burgos, M.E.; Ardiles, L.; Flores, C.; Schneider, H.; Ruiz-Ortega, M.; Egido, J. NF-κB activation and overexpression of regulated genes in human diabetic nephropathy. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2004, 19, 2505–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro-González, J.F.; Mora-Fernández, C.; Fuentes, M.M.; García-Pérez, J. Inflammatory molecules and pathways in the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2011, 7, 327–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.T.; Yang, Y.; Yang, J.F.; Gao, Y.M.; Cao, J.Y.; Li, Z.L.; Tang, T.T.; Lv, L.L.; Wang, B.; Wen, Y.; et al. Urinary sediment CCL5 messenger RNA as a potential prognostic biomarker of diabetic nephropathy. Clin. Kidney J. 2021, 15, 534–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barutta, F.; Bellini, S.; Gruden, G. Mechanisms of podocyte injury and implications for diabetic nephropathy. Clin. Sci. 2022, 136, 493–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, R.; Ma, N.; Liu, L.; Shi, R.; Zhang, B.; Lin, N.; Tian, Y. Potential role and expression level of urinary CXCL8 in different stages of incipient diabetic nephropathy with undiminished creatinine clearance: A pilot study. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2023, 16, 1783–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Thompson, S.G.; Deeks, J.J.; Altman, D.G. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ. 2003, 327, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Paresh, C.; Hongbo, Y.; Anna, P.F.; Jing, Z.; Ernest, H.L.; Eric, Q.W.; Ruixuan, J.; Raafat, S. Healthcare resource use, costs, and disease progression associated with diabetic nephropathy in adults with type 2 diabetes: A retrospective observational study. Diabetes Ther. 2017, 8, 555–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuseppe, N.; Cinzia, C.; Paola, B.; Marisa, P.A.; Eric, A. Genetic tests and genomic biomarkers: Regulation, qualification and validation. Clin. Cases Min. Bone Metab. 2008, 5, 149–154. [Google Scholar]
- Matthew, J.S.; Maheswari, S.; Nathan, R.W. Making Meaningful Clinical Use of Biomarkers. Biomark. Insights 2017, 12, 1177271917715236. [Google Scholar]



| Acronym | Description |
|---|---|
| P (Population) | Individuals with diabetes mellitus (types 1 and 2) who developed Diabetic Nephropathy as a complication. |
| E (Exposure | Presence of genetic polymorphisms associated with inflammation in the population. |
| O (Outcome) | Outcome of interest related to the development of Diabetic Nephropathy. |
| Databases | Search Strategy |
|---|---|
| Pubmed | (((‘Diabetic Nephropathies’) OR (Nephropathies, Diabetic) OR (Nephropathy, Diabetic) OR (‘Diabetic Nephropathy’) OR (‘Diabetic Kidney Disease’) OR (‘Diabetic Kidney Diseases’) OR (Kidney Disease *, Diabetic) OR (‘Diabetic Glomerulosclerosis’) OR (Glomerulosclerosis, Diabetic) OR (‘Intracapillary Glomerulosclerosis’) OR (‘Nodular Glomerulosclerosis’) OR (Glomerulosclerosis, Nodular) OR (‘Kimmelstiel-Wilson Syndrome’) OR (‘Kimmelstiel Wilson Syndrome’) OR (Syndrome, Kimmelstiel-Wilson) OR (‘Kimmelstiel-Wilson Disease’) OR (‘Kimmelstiel Wilson Disease’)) AND ((Polymorphism *, Genetic) OR (‘Genetic Polymorphism’) OR (‘Genetic Polymorphisms’) OR (‘Gene Polymorphism’) OR (‘Gene Polymorphisms’) OR (Polymorphism *, Gene) OR (Polymorphism * (Genetics)) OR (‘Genetic Susceptibility’) OR (‘Genetic Susceptibilities’) OR (Susceptibilit *, Genetic) OR (‘Genetic Predisposition’) OR (‘Genetic Predispositions’) OR (Predisposition *, Genetic)) AND ((Inflammation *) OR (‘Innate Inflammatory Response’) OR (‘Innate Inflammatory Responses’) OR (Inflammatory Response, Innate) OR (‘Inflammation Mediators’) OR (Mediators, Inflammation) OR (‘Mediators of Inflammation’))) |
| SCOPUS | (TITLE-ABS-KEY (“Diabetic Nephropath *”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY (Nephropath *, Diabetic) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY (“Diabetic Kidney Disease *”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY (Kidney Disease *, Diabetic) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY (“Diabetic Glomerulosclerosis”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY (Glomerulosclerosis, Diabetic) OR-TITLE-ABS-KEY (“Intracapillary Glomerulosclerosis”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY (“Nodular Glomerulosclerosis”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY (Glomerulosclerosis, Nodular) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY (“Kimelstiel$Wilson Syndrome”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY (Syndrome, Kimmelstiel-Wilson) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY (“Kimmelstiel$Wilson Disease”) AND TITLE-ABS-KEY (Polymorphism *, Genetic) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY (“Genetic Polymorphism *”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY (“Gene Polymorphism *”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY (“Polymorphism, Gene”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY (“Polymorphism (Genetics)”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY (“Genetic Susceptibilit *”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY (Susceptibilit *, Genetic) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY (“Genetic Predisposition *”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY (“Predisposition, Genetic”) AND TITLE-ABS-KEY (Inflammat *) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY (“Innate Inflammatory Response”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY (Inflammatory Response, Innate) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY (“Inflammation Mediators”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY (Mediators, Inflammation) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY (“Mediators of Inflammation”)) |
| BVS | (‘Diabetic Nephropathies’) OR (Nephropath *, Diabetic) OR (‘Diabetic Nephropathy’) OR (‘Diabetic Kidney Disease’) OR (‘Diabetic Kidney Diseases’) OR (Kidney Disease *, Diabetic) OR (‘Diabetic Glomerulosclerosis’) OR (Glomerulosclerosis, Diabetic) OR (‘Intracapillary Glomerulosclerosis’) OR (‘Nodular Glomerulosclerosis’) OR (Glomerulosclerosis, Nodular) OR (‘Kimmelstiel-Wilson Syndrome’) OR (‘Kimmelstiel Wilson Syndrome’) OR (Syndrome, Kimmelstiel-Wilson) OR (‘Kimmelstiel- Wilson Disease’) OR (‘Kimmelstiel Wilson Disease’) AND (Polymorphism *, Genetic) OR (‘Genetic Polymorphism’) OR (‘Genetic Polymorphisms’) OR (‘Gene Polymorphism’) OR (‘Gene Polymorphisms’) OR (Polymorphism *, Gene) OR (Polymorphism * (Genetics)) OR (‘Genetic Susceptibility’) OR (‘Genetic Susceptibilities’) OR (Susceptibilit *, Genetic) OR (‘Genetic Predisposition’) OR (‘Genetic Predispositions’) OR (Predisposition *, Genetic) AND (Inflammat *) OR (‘Innate Inflammatory Response’) OR (Inflammatory Response, Innate) OR (‘Innate Inflammatory Responses’) OR (‘Inflammation Mediators’) OR (Mediators, Inflammation) OR (‘Mediators of Inflammation’) |
| Web of Science | TS = (((“Diabetic Nephropathies”) OR (Nephropathies, Diabetic) OR (Nephropathy, Diabetic) OR (“Diabetic Nephropathy”) OR (“Diabetic Kidney Disease$”) OR (Kidney Disease$, Diabetic) OR (“Diabetic Glomerulosclerosis”) OR (Glomerulosclerosis, Diabetic) OR (“Intracapillary Glomerulosclerosis”) OR (“Nodular Glomerulosclerosis”) OR (Glomerulosclerosis, Nodular) OR (“Kimmelstiel-Wilson Syndrome”) OR (“Kimmelstiel Wilson Syndrome”) OR (Syndrome, Kimmelstiel-Wilson) OR (“Kimmelstiel-Wilson Disease”) OR (“Kimmelstiel Wilson Disease”)) AND ((Polymorphism *, Genetic) OR (“Genetic Polymorphism$”) OR (“Gene Polymorphism$”) OR (Polymorphism$, Gene) OR (Polymorphism$ (Genetics)) OR (“Genetic Susceptibilit *”) OR (Susceptibilit *, Genetic) OR (“Genetic Predisposition$”) OR (Predisposition$, Genetic)) AND ((Inflammat *) OR (“Innate Inflammatory Response$”) OR (Inflammatory Response, Innate) OR (“Inflammation Mediators”) OR (Mediators, Inflammation) OR (“Mediators of Inflammation”))) |
| EMBASE | (‘diabetic glomerulopathy’ OR ‘diabetic glomerulosclerosis’ OR ‘diabetic intercapillary glomerulosclerosis’ OR ‘diabetic kidney disease’ OR ‘diabetic nephropathies’ OR ‘glomerulonecrosis, intercapillary’ OR ‘glomerulosclerosis, diabetic’ OR ‘glomerulosclerosis, intercapillary’ OR ‘intercapillary glomerulosclerosis’ OR ‘diabetic nephropathy’ OR ‘kimmelstiel wilson nephropathy’ OR ‘kimmelstiel wilson syndrome’ OR ‘nephropathy, diabetic’ OR ‘kidney disease’ OR ‘diabetic complication’) AND (‘genetic polymorphism’ OR ‘polymorphism (genetics)’ OR ‘polymorphism, genetic’ OR ‘genetic susceptibility’ OR ‘genetic predisposition’) AND (inflammation OR ‘acute inflammation’ OR ‘inflammation reaction’ OR ‘inflammation response’ OR ‘inflammatory condition’ OR ‘inflammatory lesion’ OR ‘inflammatory process’ OR ‘inflammatory reaction’ OR ‘inflammatory response’ OR ‘reaction, inflammation’ OR ‘response, inflammatory’ OR ‘innate immunity’ OR ‘autacoid’ OR ‘inflammation mediators’) |
| Gene | Gene Location | Gene Function in the Inflammatory Pathway | Evaluated Polymorphism | Type of Polymorphism | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADIPOQ | 3q27.3 | It encodes an anti-inflammatory adipocytokine that antagonizes TNF-alpha by negatively regulating its expression in various tissues and organs and neutralizing its effects. It prevents NF-kappa-B endothelial signaling through a cAMP-dependent pathway. | rs266729 (−11377 C/G) | SNP | [14] |
| rs17300539 (−11391 G/A) | [15] | ||||
| rs2241766 (45 T/G) | |||||
| ALOXA5AP | 13q12.3 | It encodes a protein, that when associated with 5-lipoxygenase, performs the synthesis of leukotrienes (LTs). Leukotrienes are a family of lipid mediators that act as pro-inflammatory mediators. | rs3803278 (8733 T/C) | SNP | [16] |
| CCL2 (MCP-1) | 17q12 | Encodes a chemokine member of the CC subfamily involved in immunoregulatory and inflammatory processes. Displays chemotactic activity for monocytes and basophils, but not for neutrophils or eosinophils. | rs3917887 (int1del554-567) | Indel | [17] |
| rs1024611 (−2518 A/G) | SNP | [18,19] | |||
| CCR5 | 3p21.31 | Chemokine CC receptors (CCRs) predominantly recognize inflammatory CC chemokines, such as CCL3, CCL4, and RANTES. They may play a role in controlling the proliferation or differentiation of the granulocytic lineage and participate in the migration of T lymphocytes to the site of infection, acting as a chemotactic receptor. | rs1799987 (59029 G/A) | SNP | [17,20,21,22,23,24,25] |
| rs333 (Delta 32) | Indel | [17,21] | |||
| Hp | 16q22.2 | Haptoglobin (Hp) captures hemoglobin and combines it with free plasma, enabling hepatic recycling of heme iron and preventing renal damage. It also acts as an antioxidant, antibacterial agent, and plays a role in modulating the acute-phase inflammatory response. | Hp1/Hp2 | Codominant alleles | [26,27] |
| ICAM1 | 19p13.2 | Encodes a cell surface glycoprotein that is particularly expressed in endothelial cells and the immune system. It binds to integrins of the CD11a/CD18 or CD11b/CD18 type. | rs5498 (K469E; 1462 A/G) | SNP | [28] |
| IL1α | 2q14.1 | Encodes a member of the interleukin-1 cytokine family. It is pleiotropic and related to various immune responses, inflammatory processes, and hematopoiesis. This cytokine is produced by monocytes and macrophages as a pro-protein, which is proteolytically processed and released in response to cellular injury, leading to apoptosis. | rs1800587 (−889 C/T) | SNP | [29] |
| IL1β | 2q14.1 | Encodes a member of the interleukin-1 cytokine family. This cytokine is produced by activated macrophages as a pro-protein, which is proteolytically processed to its active form by Caspase 1. It is an important mediator of the inflammatory response and is related to various cellular activities, including cell proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis. | rs16944 (−511 C/T) | SNP | [30,31,32,33,34,35,36] |
| IL1RN | 2q14.1 | Encodes a member of the interleukin-1 cytokine family. This protein inhibits the activities of IL-1α and IL-1β and modulates various immune and inflammatory responses related to interleukin-1, particularly during the acute phase of infection and inflammation. | (VNTR 86 bp) | Variable number tandem repeat (VNTR) | [30,31,37] |
| IL4 | 5q31.1 | Encodes a pleiotropic cytokine produced by activated T cells. IL-4, a type 2 cytokine, is considered important for tissue repair, counteracting the effects of pro-inflammatory type 1 cytokines. Additionally, it intervenes and regulates various responses in the human host, such as acute inflammation. | rs2243250 (−590 C/T) | SNP | [38,39] |
| IL6 | 7p15.3 | Encodes a cytokine that acts on inflammation and the maturation of B cells. This cytokine is primarily produced in sites of acute and chronic inflammation, where it is secreted into the serum and induces a transcriptional inflammatory response through the interleukin-6 alpha receptor. | rs1800796 (−634 C/G) | SNP | [40,41,42] |
| rs1800795 (−174 G/C) | [43] | ||||
| rs2069837 (A/G) | [41] | ||||
| rs1524107 (T/C) | |||||
| (−176 G/C) | [39] | ||||
| IL8 (CXCL8) | 4q13.3 | Encodes a protein that is a member of the CXC chemokine family; one of the main mediators of the inflammatory response. IL-8 acts as a chemotactic factor, directing neutrophils to the site of infection. It also participates, along with other cytokines, in the pro-inflammatory signaling cascade. | rs4073 (−251 T/A) | SNP | [17] |
| rs2227306 (+781 C/T) | [44] | ||||
| IL10 | 1q32.1 | Encodes a cytokine primarily produced by monocytes and to a lesser extent by lymphocytes. This cytokine has pleiotropic effects on immunoregulation and inflammation, and negatively regulates the expression of Th1 cytokines, MHC class II molecules, etc. It can block NF-kappa B activity and is related to the regulation of the JAK-STAT signaling pathway. | rs1800896 (−1082 G/A) | SNP | [45,46,47,48,49] |
| rs1800872 (−592 C/A) | [50] | ||||
| IL34 | 16q22.1 | Encodes a cytokine that promotes the differentiation and viability of monocytes and macrophages through the colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor (CSF1R). | rs6499323 (G/A) | SNP | [51] |
| LTA | 6p21.33 | Encodes a protein member of the tumor necrosis factor family; a cytokine produced by lymphocytes. This protein also intervenes in various inflammatory, immune-stimulatory, and antiviral responses. | rs1041981 (Thr26Asn; 804 C/A) | SNP | [52] |
| rs909253 (Ala252Gly; A/G) | |||||
| MMP9 | 20q13.12 | Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) act on pro-inflammatory mediators, regulating various aspects of inflammation, and can function as a switch in acute and chronic inflammation. Therefore, MMP9 is considered a pro-inflammatory cytokine. | rs17576 (Arg 279Gln, G/A) | SNP | [17,53] |
| MPO | 17q22 | Myeloperoxidase (MPO) is a heme protein produced during myeloid differentiation, constituting an essential component of the azurophilic granules in neutrophils. This enzyme provides essential hypohalous acids for the microbicidal activity of neutrophils. | rs2333227 (−463 G/A) | SNP | [54,55] |
| NFKB1 | 4q24 | NF-κB is a transcription regulator activated by various intra- and extra-cellular stimuli, such as cytokines, free radicals, etc. When activated, it translocates to the nucleus and stimulates the expression of genes involved in various biological functions, such as cell growth and immune cell development. | rs28362491 (−94 ATTG) | Indel | [56] |
| NOS2 | 17q11.2 | Encodes the protein Nitric Oxide Synthase 2, which increases the synthesis of pro-inflammatory mediators, such as IL6 and IL8. | rs2779248 (T/C) | SNP | [57] |
| rs1137933 (G/A) | |||||
| OPN (SPP1) | 4q22.1 | Encodes a cytokine involved in increasing the production of interferon-gamma and interleukin-12 and reducing interleukin-10. This cytokine is essential in the pathway leading to type I immunity. | rs11730582 (−443 C/T) | SNP | [58] |
| PPARγ | 3p25.2 | Encodes a member of the nuclear receptor subfamily of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR). PPAR-γ can inhibit the expression of pro-inflammatory genes, suppressing responses mediated by NF-kappa-B. | rs1801282 (Pro12Ala; C/G) | SNP | [59] |
| pri-miR-125a | 19q13.41 | Encodes a miRNA considered a potential regulator of IL-6R. Li; Lei (2015) report that the expression level of the IL-6R protein was significantly decreased by the introduction of miR-125a mimetics. | rs12976445 (C/T) | SNP | [60] |
| PRKCB1 | 16p12.2-p12.1 | Protein kinase Cs (PKCs) are a family of serine/threonine-specific protein kinases that plays an important role in B-cell activation by regulating B-cell receptor (BCR)-mediated NF-kappa-B activation. | rs3760106 (−1504 C/T) | SNP | [61] |
| rs2575390 (−546 C/G) | |||||
| PTX3 | 3q25.32 | The expression of the protein produced by this gene is induced by inflammatory cytokines in response to inflammatory stimuli in various types of mesenchymal and epithelial cells. It promotes fibrocyte differentiation and is involved in the regulation of inflammation and complement activation. | rs2305619 (281 A/G) | SNP | [62,63] |
| RAGE (AGER) | 14q32.31 | Encodes a protein considered an intracellular signal transducer or pro-inflammatory peptide. It acts as a mediator of acute and chronic vascular inflammation, regulating the production/expression of TNF-alpha, oxidative stress, and endothelial dysfunction in type 2 diabetes. | rs1800624 (−374 T/A) | SNP | [64] |
| rs3134940 (2184 A/G) | [65] | ||||
| RANTES (CCL5) | 17q12 | Produces a protein chemotactic for blood monocytes, memory helper T cells, and eosinophils. Additionally, it can activate various chemokine receptors, including CCR1, CCR3, CCR4, and CCR5. | rs2280788 (−28 C/G) | SNP | [20] |
| SASH1 | 6q24.3-q25.1 | Encodes a scaffold protein related to the TLR4 signaling pathway that can induce cytokine production and migration of endothelial cells in response to invading pathogens. | rs6930576 (G/A) | SNP | [66] |
| SEPS1 (SELENOS) | 15q26.3 | Encodes a transmembrane protein located in the endoplasmic reticulum. It is involved in the process of degrading misfolded proteins and may play a role in inflammation control, acting as an anti-inflammatory and antioxidant protein. | rs4975814 (G/T) | SNP | [67] |
| SLC12A3 | 16q13 | Encodes an electroneutral sodium and chloride ion cotransporter. It is a receptor for the pro-inflammatory cytokine IL18 and contributes to IL18-induced cytokine production, including IFNG, IL6, IL18, and CCL2. | rs11643718 (Arg913Gln; 78 G/A) | SNP | [68] |
| SUMO4 | 6q25.1 | Encodes small ubiquitin-related modifiers. The protein encoded by this gene particularly modifies IKBA, causing negative regulation of NF-kappa-B-dependent transcription of the IL12B gene. | rs237025 (M55V; c.163 G/A) | SNP | [69] |
| TCRBC (TRB) | 7q34 | Encodes T cell receptors that recognize processed foreign antigens as small peptides bound to major histocompatibility complex molecules on the surface of antigen-presenting cells. | (9.2;10.0 kb) | Not identified | [70] |
| TGFβ1 | 19q13.2 | Encodes a secreted ligand of the TGF-beta protein superfamily. This protein regulates cell proliferation, differentiation, and growth, and may modulate the expression and activation of other growth factors, such as interferon-gamma and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. | rs1800470 (869 T/C) | SNP | [71,72,73,74,75,76] |
| rs1800471 (915 G/C) | [74] | ||||
| TLR4 | 9q33.1 | Encodes a protein member of the Toll-like receptor (TLR) family that plays a fundamental role in pathogen recognition and activation of innate immunity. They recognize molecular patterns associated with pathogens and are involved in the production of cytokines necessary for effective immunity. | rs5030718 (14367 G/A) | SNP | [77] |
| TNFα | 6p21.33 | Encodes a multifunctional pro-inflammatory cytokine belonging to the tumor necrosis factor superfamily. This cytokine is primarily secreted by macrophages and is involved in the regulation of various biological processes, such as cell proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, lipid metabolism, and coagulation. | rs1799964 (−1031 T/C) | SNP | [34,78,79] |
| rs1800629 (−308 G/A) | [34,80,81] | ||||
| rs361525 (−238 G/A) | [34] | ||||
| TSC22 (TSC22D1) | 13q14.11 | Encodes a leucine zipper protein expressed in many tissues and involved in the signaling of TGF-1. | (−396 A/G) | SNP | [73] |
| UMOD | 16p12.3 | Encodes a protein that can bind to immunoglobulin G, complement 1q, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), signaling a role in innate immunity. It can also act as a receptor for the binding and endocytosis of cytokines (IL-1 and IL-2) and TNF. | rs4293393 (T/C) | SNP | [82] |
| VEGF-A | 6p21.1 | Encodes a protein that acts as a pro-inflammatory cytokine, increasing the permeability of endothelial cells and inducing the expression of endothelial cell adhesion molecules through its ability to act as a chemotactic agent for monocytes. | rs35569394 (−2549 D/I) | Indel | [83] |
| Ranking | Gene | Full Gene Name | Score |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | TNF | Tumor Necrosis Factor | 54.0 |
| 2 | IL1B | Interleukin 1 Beta | 52.0 |
| 3 | IL6 | Interleukin 6 | 50.0 |
| 3 | IL10 | Interleukin 10 | 50.0 |
| 6 | ICAM1 | Intercellular Adhesion Molecule 1 | 48.0 |
| 6 | CXCL8 (IL8) | Chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 8 | 48.0 |
| 6 | MMP9 | Matrix Metallopeptidase 9 | 48.0 |
| 6 | TLR4 | Toll-like receptor 4 | 48.0 |
| 6 | VEGFA | Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A | 48.0 |
| 11 | IL4 | Interleukin 4 | 46.0 |
| 12 | IL1A | Interleukin 1 Alpha | 44.0 |
| 13 | CCL5 | Chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 5 | 42.0 |
| 14 | MPO | Myeloperoxidase | 38.0 |
| 14 | ADIPOQ | Adiponectin, C1Q and Collagen Domain Containing | 38.0 |
| 14 | TGFB1 | Transforming Growth Factor Beta 1 | 38.0 |
| 17 | LTA | Lymphotoxin Alpha | 36.0 |
| 18 | SPP1 | Secreted Phosphoprotein 1 | 34.0 |
| 18 | IL1RN | Interleukin 1 Receptor Antagonist | 34.0 |
| 920 | NOS2 | Nitric Oxide Synthase 2 | 32.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Costa, C.C.P.d.; Assunção, L.d.P.; Santos, K.d.F.; Silva, L.d.; Santos, R.d.S.; Reis, A.A.d.S. In Silico Characterization of Inflammatory and Anti-Inflammatory Modulation in Diabetic Nephropathy: The Construction of a Genetic Panel. J. Mol. Pathol. 2024, 5, 335-359. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmp5030024
Costa CCPd, Assunção LdP, Santos KdF, Silva Ld, Santos RdS, Reis AAdS. In Silico Characterization of Inflammatory and Anti-Inflammatory Modulation in Diabetic Nephropathy: The Construction of a Genetic Panel. Journal of Molecular Pathology. 2024; 5(3):335-359. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmp5030024
Chicago/Turabian StyleCosta, Caroline Christine Pincela da, Leandro do Prado Assunção, Kamilla de Faria Santos, Laura da Silva, Rodrigo da Silva Santos, and Angela Adamski da Silva Reis. 2024. "In Silico Characterization of Inflammatory and Anti-Inflammatory Modulation in Diabetic Nephropathy: The Construction of a Genetic Panel" Journal of Molecular Pathology 5, no. 3: 335-359. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmp5030024
APA StyleCosta, C. C. P. d., Assunção, L. d. P., Santos, K. d. F., Silva, L. d., Santos, R. d. S., & Reis, A. A. d. S. (2024). In Silico Characterization of Inflammatory and Anti-Inflammatory Modulation in Diabetic Nephropathy: The Construction of a Genetic Panel. Journal of Molecular Pathology, 5(3), 335-359. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmp5030024






