A Real-World Study Reporting the Use of Foundation Medicine® Testing in Portugal
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Foundation Medicine® Testing
2.3. Statistical Analysis
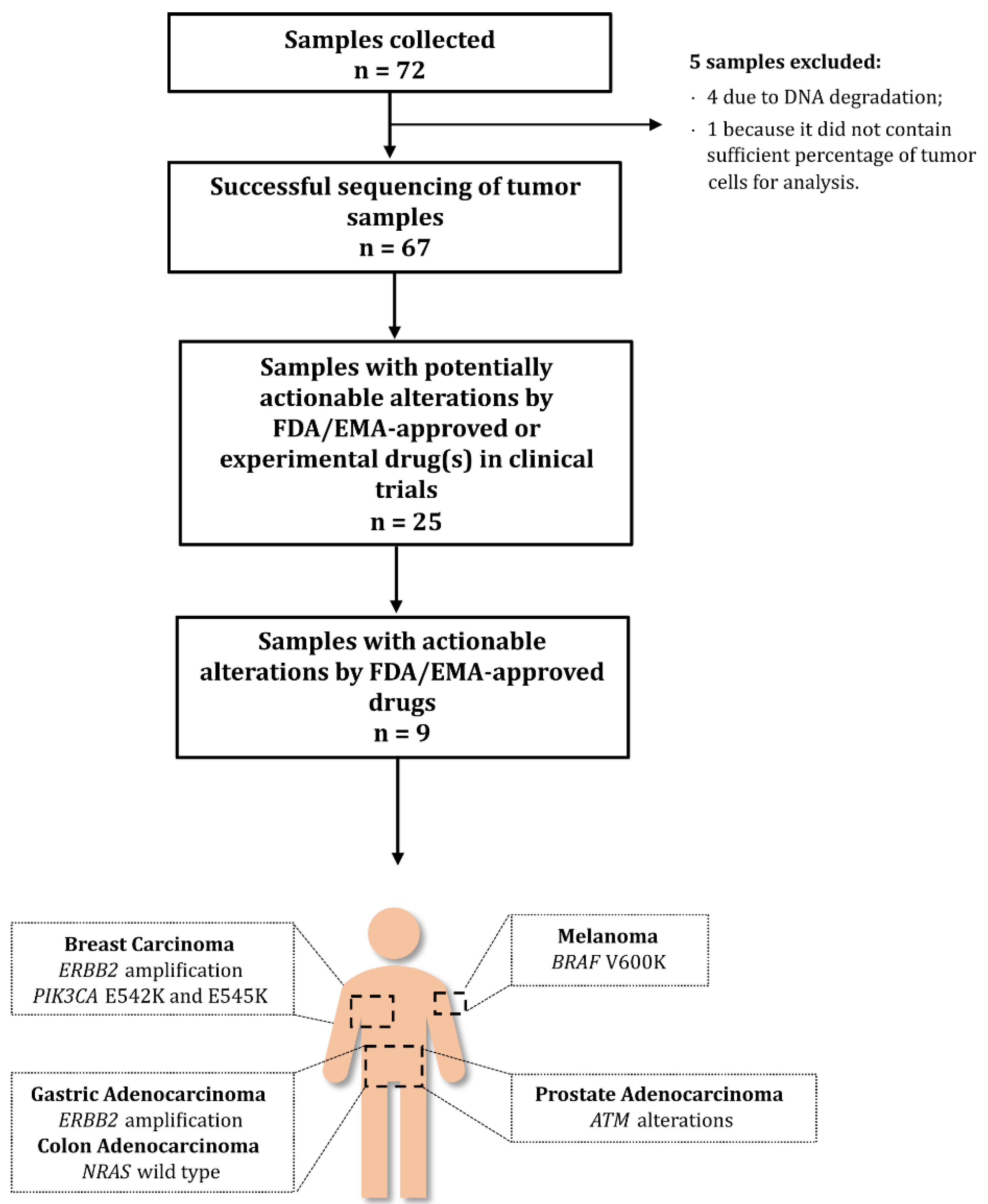
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Tumour Histology
3.3. Characteristics of Foundation Medicine® Testing
3.4. Frequency of Genomic Alterations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Avila, M.; Meric-Bernstam, F. Next-generation sequencing for the general cancer patient. Clin. Adv. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 17, 447–454. [Google Scholar]
- Mockus, S.M.; Patterson, S.E.; Statz, C.; Bult, C.J.; Tsongalis, G.J. Clinical Trials in Precision Oncology. Clin. Chem. 2016, 62, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radovich, M.; Kiel, P.J.; Nance, S.M.; Niland, E.E.; Parsley, M.E.; Ferguson, M.E.; Jiang, G.; Ammakkanavar, N.R.; Einhorn, L.H.; Cheng, L.; et al. Clinical benefit of a precision medicine based approach for guiding treatment of refractory cancers. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 56491–56500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodhouse, R.; Li, M.; Hughes, J.; Delfosse, D.; Skoletsky, J.; Ma, P.; Meng, W.; Dewal, N.; Milbury, C.; Clark, T.; et al. Clinical and analytical validation of FoundationOne Liquid CDx, a novel 324-Gene cfDNA-based comprehensive genomic profiling assay for cancers of solid tumor origin. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0237802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouaid, C.; Dujon, C.; Do, P.; Monnet, I.; Madroszyk, A.; Le Caer, H.; Auliac, J.B.; Berard, H.; Thomas, P.; Lena, H.; et al. Feasibility and clinical impact of re-biopsy in advanced non small-cell lung cancer: A prospective multicenter study in a real-world setting (GFPC study 12-01). Lung Cancer 2014, 86, 170–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwaederle, M.C.; Patel, S.P.; Husain, H.; Ikeda, M.; Lanman, R.B.; Banks, K.C.; Talasaz, A.; Bazhenova, L.; Kurzrock, R. Utility of Genomic Assessment of Blood-Derived Circulating Tumor DNA (ctDNA) in Patients with Advanced Lung Adenocarcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 5101–5111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frampton, G.M.; Fichtenholtz, A.; Otto, G.A.; Wang, K.; Downing, S.R.; He, J.; Schnall-Levin, M.; White, J.; Sanford, E.M.; An, P.; et al. Development and validation of a clinical cancer genomic profiling test based on massively parallel DNA sequencing. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 1023–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karol, D.; McKinnon, M.; Mukhtar, L.; Awan, A.; Lo, B.; Wheatley-Price, P. The Impact of Foundation Medicine Testing on Cancer Patients: A Single Academic Centre Experience. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 687730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foundation Medicine. FoundationOne® CDx Technical Information. Available online: https://www.rochefoundationmedicine.com/f1cdxtech (accessed on 7 February 2022).
- Foundation Medicine. FoundationOne® Liquid CDx Technical Information. Available online: https://info.foundationmedicine.com/hubfs/FMI%20Labels/FoundationOne_Liquid_CDx_Label_Technical_Info.pdf (accessed on 7 February 2022).
- Foundation Medicine. FoundationOne® Heme Technical Specifications. Available online: https://assets.ctfassets.net/w98cd481qyp0/42r1cTE8VR4137CaHrsaen/a7e4b78c5ee67503ede12ef0c3507de3/FoundationOne_Heme_Technical_Specifications.pdf (accessed on 7 February 2022).
- Ali, S.M.; Palma, N.A.; Wang, K.; Ross, J.S.; Stephens, P.J.; Yelensky, R.; Palmer, G.A.; Lipson, D.; Miller, V.A. Clinical next generation sequencing (NGS) to reveal high frequency of alterations to guide targeted therapy in lung cancer patients. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 8020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boland, P.M.; Skarbnik, A.P.; Cristofanilli, M.; Alpaugh, R.K.; Olszanski, A.J. Application of next-generation sequencing (NGS) for evaluation of advanced epithelial cancers: A single institution experience. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 11092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Patel, M.; Phillip, I.; Bailey, M.; Berman, E.; Park, J.H.; Shukla, N.N.; Chung, S.S.; Castro-Malaspina, H.; Douer, D.; et al. Clinical Relevant Alterations Identified By Comprehensive Genomic Profiling Can Potentially Improve Therapeutic Option and Change Prognosis in Hematologic Malignancies. Blood 2016, 128, 5109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrondo, R.D.; Mariotti, V.; Gonzalez Velez, M.; Leslie, L.A. Clinical implications of genomic-directed therapies by comprehensive genomic profiling in breast cancer patients at a large academic cancer center. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, e12037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gullo, I.; Marques, A.; Pinto, R.; Cirnes, L.; Schmitt, F. Morphological control for molecular testing: A practical approach. J. Clin. Pathol. 2021, 74, 331–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoyagi, Y.; Kano, Y.; Tohyama, K.; Matsudera, S.; Kumaki, Y.; Takahashi, K.; Mitsumura, T.; Harada, Y.; Sato, A.; Nakamura, H.; et al. Clinical utility of comprehensive genomic profiling in Japan: Result of PROFILE-F study. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0266112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinet, S.; Durand, S.; Perani, A.; Darnaud, L.; Amadjikpe, F.; Yon, M.; Darbas, T.; Vergnenegre, A.; Egenod, T.; Simonneau, Y.; et al. Clinical management of molecular alterations identified by high throughput sequencing in patients with advanced solid tumors in treatment failure: Real-world data from a French hospital. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1104659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teuwen, L.A.; Roets, E.; D’Hoore, P.; Pauwels, P.; Prenen, H. Comprehensive Genomic Profiling and Therapeutic Implications for Patients with Advanced Cancers: The Experience of an Academic Hospital. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, M.; Takahama, T.; Sakai, K.; Shimizu, S.; Watanabe, S.; Kawakami, H.; Tanaka, K.; Sato, C.; Hayashi, H.; Nonagase, Y.; et al. Clinical Application of the FoundationOne CDx Assay to Therapeutic Decision-Making for Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors. Oncologist 2021, 26, e588–e596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Falco, V.A.-O.; Poliero, L.; Vitello, P.P.; Ciardiello, D.; Vitale, P.; Zanaletti, N.; Giunta, E.F.; Terminiello, M.; Caputo, V.; Carlino, F.; et al. Feasibility of next-generation sequencing in clinical practice: Results of a pilot study in the Department of Precision Medicine at the University of Campania ‘Luigi Vanvitelli’. ESMO Open 2020, 5, e000675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, D.; Zhang, D.; Chen, K.; Lu, J.; Wu, J.; Cao, X.; Ying, L.; Jin, Q.; Ye, Y.; Xie, Z.; et al. High performance of targeted next generation sequencing on variance detection in clinical tumor specimens in comparison with current conventional methods. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 36, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baugh, E.H.; Ke, H.; Levine, A.J.; Bonneau, R.A.; Chan, C.S. Why are there hotspot mutations in the TP53 gene in human cancers? Cell Death Differ. 2018, 25, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirshfield, K.M.; Tolkunov, D.; Zhong, H.; Ali, S.M.; Stein, M.N.; Murphy, S.; Vig, H.; Vazquez, A.; Glod, J.; Moss, R.A.; et al. Clinical Actionability of Comprehensive Genomic Profiling for Management of Rare or Refractory Cancers. Oncologist 2016, 21, 1315–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, R.; Ohtsuka, T.; Kubo, M.; Kajihara, A.; Fujii, A.; Watanabe, Y.; Mori, Y.; Ikenaga, N.; Nakata, K.; Shindo, K.; et al. FoundationOne(R) CDx gene profiling in Japanese pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma patients: A single-institution experience. Surg. Today 2021, 51, 619–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marabelle, A.; Fakih, M.; Lopez, J.; Shah, M.; Shapira-Frommer, R.; Nakagawa, K.; Chung, H.C.; Kindler, H.L.; Lopez-Martin, J.A.; Miller, W.H., Jr.; et al. Association of tumour mutational burden with outcomes in patients with advanced solid tumours treated with pembrolizumab: Prospective biomarker analysis of the multicohort, open-label, phase 2 KEYNOTE-158 study. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 1353–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, R.S.P.; Haberberger, J.; Severson, E.; Duncan, D.L.; Hemmerich, A.; Edgerly, C.; Ferguson, N.L.; Williams, E.; Elvin, J.; Vergilio, J.A.; et al. A pan-cancer analysis of PD-L1 immunohistochemistry and gene amplification, tumor mutation burden and microsatellite instability in 48,782 cases. Mod. Pathol. 2021, 34, 252–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sha, D.; Jin, Z.; Budczies, J.; Kluck, K.; Stenzinger, A.; Sinicrope, F.A. Tumor Mutational Burden as a Predictive Biomarker in Solid Tumors. Cancer Discov. 2020, 10, 1808–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fancello, L.; Gandini, S.; Pelicci, P.G.; Mazzarella, L. Tumor mutational burden quantification from targeted gene panels: Major advancements and challenges. J. Immunother. Cancer 2019, 7, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenzinger, A.; Allen, J.D.; Maas, J.; Stewart, M.D.; Merino, D.M.; Wempe, M.M.; Dietel, M. Tumor mutational burden standardization initiatives: Recommendations for consistent tumor mutational burden assessment in clinical samples to guide immunotherapy treatment decisions. Genes. Chromosomes Cancer 2019, 58, 578–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ott, P.A.; Bang, Y.J.; Piha-Paul, S.A.; Razak, A.R.A.; Bennouna, J.; Soria, J.C.; Rugo, H.S.; Cohen, R.B.; O’Neil, B.H.; Mehnert, J.M.; et al. T-Cell-Inflamed Gene-Expression Profile, Programmed Death Ligand 1 Expression, and Tumor Mutational Burden Predict Efficacy in Patients Treated With Pembrolizumab Across 20 Cancers: KEYNOTE-028. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarchoan, M.; Hopkins, A.; Jaffee, E.M. Tumor Mutational Burden and Response Rate to PD-1 Inhibition. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 2500–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalmers, Z.R.; Connelly, C.F.; Fabrizio, D.; Gay, L.; Ali, S.M.; Ennis, R.; Schrock, A.; Campbell, B.; Shlien, A.; Chmielecki, J.; et al. Analysis of 100,000 human cancer genomes reveals the landscape of tumor mutational burden. Genome Med. 2017, 9, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, A.M.; Sokol, E.S.; Frampton, G.M.; Lippman, S.M.; Kurzrock, R. Microsatellite-Stable Tumors with High Mutational Burden Benefit from Immunotherapy. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2019, 7, 1570–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dror, C.M.; Wyatt, A.W.; Chi, K.N. Olaparib for the treatment of metastatic prostate cancer. Future Oncol. 2021, 17, 2413–2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grieb, B.C.; Agarwal, R. HER2-Directed Therapy in Advanced Gastric and Gastroesophageal Adenocarcinoma: Triumphs and Troubles. Curr. Treat. Options Oncol. 2021, 22, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, H.A. Sotorasib: First Approval. Drugs 2021, 81, 1573–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paz-Ares, L.; Gondos, A.; Saldana, D.; Thomas, M.; Mascaux, C.; Bubendorf, L.; Barlesi, F. Genomic testing among patients with newly diagnosed advanced non-small cell lung cancer in the United States: A contemporary clinical practice patterns study. Lung Cancer 2022, 167, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Age, median (min–max) | 60.5 (27–82) |
| Sex, female, n (%) | 41 (56.9) |
| Stage, n (%) * | |
| I | 0 (0.0) |
| II | 2 (2.8) |
| III | 3 (4.2) |
| IV | 44 (61.1) |
| Unknown | 23 (31.9) |
| Type of Foundation Medicine® testing, n (%) | |
| FoundationOne CDX | 63 (87.5) |
| FoundationOne Liquid CDX | 6 (8.3) |
| FoundationOne Heme | 3 (4.2) |
| Tumour Type | Frequency | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Breast carcinoma | 14 | 19.4 |
| Unknown primary | 8 | 11.1 |
| Prostate adenocarcinoma | 8 | 11.1 |
| Gastric adenocarcinoma | 8 | 11.1 |
| Colon adenocarcinoma | 5 | 6.9 |
| Glioblastoma | 4 | 5.6 |
| Melanoma | 4 | 5.6 |
| Ovarian carcinoma | 3 | 4.2 |
| Foundation Medicine® Test | Turnaround Time, Median Calendar Days (Min–Max) | Percentage of Tumour Cells, Median (Min–Max) |
|---|---|---|
| FoundationOne CDX (n = 63) | 16 (5–48) | 40 (10–90) |
| FoundationOne Liquid (n = 6) | 15 (12–24) | N/A |
| FoundationOne Heme (n = 3) | 30 (22–40) | 60 (30–70) |
| Altered Gene | SNV | CNV | Rearrangement | Frequency | Percentage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FoundationOne CDx | |||||
| TP53 | 36 | 0 | 0 | 36 | 23% |
| CDKN2A/B | 4 | 12 | 0 | 16 | 10% |
| KRAS | 13 | 2 | 0 | 15 | 10% |
| APC | 13 | 0 | 0 | 13 | 8% |
| PTEN | 9 | 3 | 0 | 12 | 8% |
| TERT | 7 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 4% |
| MYC | 0 | 7 | 0 | 7 | 4% |
| MTAP | 0 | 6 | 0 | 6 | 4% |
| PIK3CA | 6 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 4% |
| FGFR1 | 1 | 4 | 0 | 5 | 3% |
| TMPRSS2-ERG | 0 | 0 | 4 | 4 | 3% |
| ZNF703 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 4 | 3% |
| ERBB2 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 4 | 3% |
| FBXW7 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 3% |
| MCL1 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 4 | 3% |
| ATM | 3 | 1 | 0 | 4 | 3% |
| RB1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 1% |
| FoundationOne Liquid CDx | |||||
| KRAS | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1% |
| PIK3CA | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1% |
| RB1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1% |
| FoundationOne Heme | |||||
| TP53 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1% |
| ZNF703 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1% |
| RB1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1% |
| Total | |||||
| 105 | 47 | 4 | 156 | 100% | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pinto, R.; Schmitt, F. A Real-World Study Reporting the Use of Foundation Medicine® Testing in Portugal. J. Mol. Pathol. 2023, 4, 156-165. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmp4030014
Pinto R, Schmitt F. A Real-World Study Reporting the Use of Foundation Medicine® Testing in Portugal. Journal of Molecular Pathology. 2023; 4(3):156-165. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmp4030014
Chicago/Turabian StylePinto, Regina, and Fernando Schmitt. 2023. "A Real-World Study Reporting the Use of Foundation Medicine® Testing in Portugal" Journal of Molecular Pathology 4, no. 3: 156-165. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmp4030014
APA StylePinto, R., & Schmitt, F. (2023). A Real-World Study Reporting the Use of Foundation Medicine® Testing in Portugal. Journal of Molecular Pathology, 4(3), 156-165. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmp4030014








