Comprehensive Review of Metastatic Breast Carcinoma in Cytology Specimens
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Metastatic Breast Carcinoma Patterns
3. Fine-Needle Aspiration Cytology for Metastatic Breast Carcinoma
4. Touch-Imprints for Regional Metastatic Breast Carcinoma
5. Exfoliative Cytology for Metastatic Breast Carcinoma
6. Cytomorphology of Metastatic Breast Carcinoma in FNA Specimens
7. Cytomorphology of Metastatic Breast Carcinoma in Effusion Specimens
8. Cytomorphology of Metastatic Breast Carcinoma in CSF Specimens
9. Immunocytochemistry for the Diagnosis of MBC
10. Biomarker Analysis in Cytology Specimens
11. Molecular Analysis of MBC
12. Newer Techniques
13. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cancer.Net. Breast Cancer—Metastatic: Statistics. Available online: https://www.cancer.net/cancer-types/breast-cancer-metastatic/statistics#:~:text=Breast%20cancer%20is%20the%20most%20common%20cancer%20in,non-metastatic%20breast%20cancer%20later%20develop%20metastatic%20breast%20cancer (accessed on 8 October 2022).
- Chen, M.T.; Sun, H.F.; Zhao, Y.; Fu, W.Y.; Yang, L.P.; Gao, S.P.; Li, L.D.; Jiang, H.L.; Jin, W. Comparison of patterns and prognosis among distant metastatic breast cancer patients by age groups: A SEER population-based analysis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Liu, X.; Wei, B.; Liu, N.; Li, Q.; Su, X. Mucinous breast carcinoma metastatic to thyroid gland: Report of a case diagnosed by fine-needle aspiration cytology. Diagn. Cytopathol. 2020, 48, 475–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Jalali, M.; Staerkel, G. Fine needle aspiration cytology of a thyroid metastasis of metaplastic breast carcinoma: A case report. Acta Cytol. 2005, 49, 327–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauvanaud, C.; Sergent, F.; Long, J.A.; Pasquier, D.; Saada-Sebag, G.; Descotes, J.L.; Rambeaud, J.J. The urinary bladder is an uncommon site of metastasis from breast cancer. Gynecol. Obstet. Fertil. 2014, 42, 813–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.R.; Boon, A.P. Metastatic breast cancer presenting as an ovarian cyst: Diagnosis by fine needle aspiration cytology. Cytopathology 1992, 3, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borst, M.J.; Ingold, J.A. Metastatic patterns of invasive lobular versus invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast. Surgery 1993, 114, 637–641; discussion 641–642. [Google Scholar]
- Soni, A.; Ren, Z.; Hameed, O.; Chanda, D.; Morgan, C.J.; Siegal, G.P.; Wei, S. Breast cancer subtypes predispose the site of distant metastases. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2015, 143, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vona-Davis, L.; Rose, D.P.; Gadiyaram, V.; Ducatman, B.; Hobbs, G.; Hazard, H.; Kurian, S.; Abraham, J. Breast cancer pathology, receptor status, and patterns of metastasis in a rural appalachian population. J. Cancer Epidemiol. 2014, 2014, 170634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerratana, L.; Fanotto, V.; Bonotto, M.; Bolzonello, S.; Minisini, A.M.; Fasola, G.; Puglisi, F. Pattern of metastasis and outcome in patients with breast cancer. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2015, 32, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashton, P.R.; Hollingsworth, A.S., Jr.; Johnston, W.W. The cytopathology of metastatic breast cancer. Acta Cytol. 1975, 19, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Gipponi, M.; Fregatti, P.; Garlaschi, A.; Murelli, F.; Margarino, C.; Depaoli, F.; Baccini, P.; Gallo, M.; Friedman, D. Axillary ultrasound and Fine-Needle Aspiration Cytology in the preoperative staging of axillary node metastasis in breast cancer patients. Breast 2016, 30, 146–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Leary, D.P.; O’Brien, O.; Relihan, N.; McCarthy, J.; Ryan, M.; Barry, J.; Kelly, L.M.; Redmond, H.P. Rapid on-site evaluation of axillary fine-needle aspiration cytology in breast cancer. Br. J. Surg. 2012, 99, 807–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kane, G.; Fleming, C.; Heneghan, H.; McCartan, D.; James, P.; Trueick, R.; Harrington, L.; Nally, F.; Quinn, C.; O’Doherty, A.; et al. False-negative rate of ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration cytology for identifying axillary lymph node metastasis in breast cancer patients. Breast J. 2019, 25, 848–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkuwari, E.; Auger, M. Accuracy of fine-needle aspiration cytology of axillary lymph nodes in breast cancer patients: A study of 115 cases with cytologic-histologic correlation. Cancer 2008, 114, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Heiden-van der Loo, M.; Schaapveld, M.; Ho, V.K.; Siesling, S.; Rutgers, E.J.; Peeters, P.H. Outcomes of a population-based series of early breast cancer patients with micrometastases and isolated tumour cells in axillary lymph nodes. Ann. Oncol. 2013, 24, 2794–2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, D.; Beca, F.; Schmitt, F. Metastatic breast cancer: Mechanisms and opportunities for cytology. Cytopathology 2014, 25, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darvishian, F.; Singh, B.; Krauter, S.; Chiriboga, L.; Gangi, M.D.; Melamed, J. Impact of decalcification on receptor status in breast cancer. Breast J. 2011, 17, 689–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caudle, A.S.; Kuerer, H.M.; Krishnamurthy, S.; Shin, K.; Hobbs, B.P.; Ma, J.; Mittendorf, E.A.; Washington, A.C.; DeSnyder, S.M.; Black, D.M.; et al. Feasibility of fine-needle aspiration for assessing responses to chemotherapy in metastatic nodes marked with clips in breast cancer: A prospective registry study. Cancer 2019, 125, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobel, J.M.; Lai, R.; Mallery, S.; Levy, M.J.; Wiersema, M.J.; Greenwald, B.D.; Gunaratnam, N.T. The utility of EUS-guided FNA in the diagnosis of metastatic breast cancer to the esophagus and the mediastinum. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2005, 61, 416–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creager, A.J.; Geisinger, K.R.; Shiver, S.A.; Perrier, N.D.; Shen, P.; Ann Shaw, J.; Young, P.R.; Levine, E.A. Intraoperative evaluation of sentinel lymph nodes for metastatic breast carcinoma by imprint cytology. Mod. Pathol. 2002, 15, 1140–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, R.; Hoda, S.A.; Marcus, A.; Hoda, R.S. Metastatic Breast Carcinoma in Cerebrospinal Fluid: A Cytopathological Review of 15 Cases. Breast J. 2017, 23, 456–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, I.M.; Alath, P.; George, S.S.; Jaragh, M.; Al Jassar, A.; Kapila, K. Metastatic breast carcinoma in pleural fluid: Correlation of receptor and HER2 status with the primary carcinoma-a pilot study. Diagn. Cytopathol. 2016, 44, 980–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shabaik, A.; Lin, G.; Peterson, M.; Hasteh, F.; Tipps, A.; Datnow, B.; Weidner, N. Reliability of Her2/neu, estrogen receptor, and progesterone receptor testing by immunohistochemistry on cell block of FNA and serous effusions from patients with primary and metastatic breast carcinoma. Diagn. Cytopathol. 2011, 39, 328–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, P. Urine cytology of metastatic breast lobular carcinoma. Diagn. Cytopathol. 2019, 47, 738–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radio, S.J.; Rennard, S.I.; Kessinger, A.; Vaughan, W.P.; Linder, J. Breast carcinoma in bronchoalveolar lavage. A cytologic and immunocytochemical study. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 1989, 113, 333–336. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, L.; Oshilaja, O.; Sierk, A.; Zhang, G.; Booth, C.N.; Brainard, J.; Dyhdalo, K.S. Metastatic breast cancer diagnosed on cervical cytology. Cytopathology 2021, 32, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Gupta, M.K.; Gupta, R.; Mishra, R.S. Breast metastasis of cervical carcinoma diagnosed by fine needle aspiration cytology. A case report. Acta Cytol. 1998, 42, 959–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rau, A.R.; Saldanha, P.; Raghuveer, C.V. Metastatic lobular mammary carcinoma diagnosed in cervicovaginal smears: A case report. Diagn. Cytopathol. 2003, 29, 300–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, K.M.; Turyan, H.V.; Jones, J.B.; Hoda, R.S. Metastatic lobular carcinoma in a ThinPrep Pap test: Cytomorphology and differential diagnosis. Diagn. Cytopathol. 2005, 33, 58–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, R.; Rana, D.; Gupta, L.; Singh, M.; Jain, S.; Rathi, A.K. Mucinous breast carcinoma metastatic to parotid gland: Report of a case diagnosed by fine needle aspiration. Cytopathology 2019, 30, 128–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khurana, K.K.; Wilbur, D.; Dawson, A.E. Fine needle aspiration cytology of invasive micropapillary carcinoma of the breast. A report of two cases. Acta Cytol. 1997, 41, 1394–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, W.K.; Poon, C.S.; Kong, J.H. Fine needle aspiration cytology of invasive micropapillary carcinoma of the breast: Review of cases in a three-year period. Acta Cytol. 2001, 45, 973–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catroppo, J.F.; Lara, J.F. Metastatic metaplastic carcinoma of the breast (MCB): An uncharacteristic pattern of presentation with clinicopathologic correlation. Diagn. Cytopathol. 2001, 25, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.N.; Kawamoto, S.; Cimino-Mathews, A.; Illei, P.B.; Rosenthal, D.L.; VandenBussche, C.J. Metastatic metaplastic breast carcinoma mimicking pulmonary squamous cell carcinoma on fine-needle aspiration. Diagn. Cytopathol. 2015, 43, 844–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shidham, V.B. Metastatic Carcinoma in Effusions. CytoJournal 2022, 19, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, T.C.; Saad, R.S.; Liu, Y.; Silverman, J.F. The diagnosis of malignancy in effusion cytology: A pattern recognition approach. Adv. Anat. Pathol. 2006, 13, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallonee, M.M.; Lin, F.; Hassanein, R. A morphologic analysis of the cells of ductal carcinoma of the breast and of adenocarcinoma of the ovary in pleural and abdominal effusions. Acta Cytol. 1987, 31, 441–447. [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhuri, S.R.; Fetsch, P.; Squires, J.; Kohn, E.; Filie, A.C. Adenocarcinoma cells in effusion cytology as a diagnostic pitfall with potential impact on clinical management: A case report with brief review of immunomarkers. Diagn. Cytopathol. 2014, 42, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cibas, E.; Ducatman, B. Cytology: Diagnostic Principles and Clinical Correlates, 5th ed.; Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Camillo, N.D.; Dos Santos, G.T.; Prolla, J.C.; Flores, E.R.; Introini, G.O.; Brackmann, R.L.; da Cruz, I.B.; Bica, C.G. Impact of cell arrangement of pleural effusion in survival of patients with breast cancer. Acta Cytol. 2014, 58, 446–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieterich, M.; Goodman, S.N.; Rojas-Corona, R.R.; Emralino, A.B.; Jimenez-Joseph, D.; Sherman, M.E. Multivariate analysis of prognostic features in malignant pleural effusions from breast cancer patients. Acta Cytol. 1994, 38, 945–952. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Antic, T.; Gong, Y.; Sneige, N. Tumor type and single-cell/mesothelial-like cell pattern of breast carcinoma metastases in pleural and peritoneal effusions. Diagn. Cytopathol. 2012, 40, 311–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monaco, S.E.; Dabbs, D.J.; Kanbour-Shakir, A. Pleomorphic lobular carcinoma in pleural fluid: Diagnostic pitfall for atypical mesothelial cells. Diagn. Cytopathol. 2008, 36, 657–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugli, A.; Forster, Y.; Haas, P.; Nocito, A.; Bucher, C.; Bissig, H.; Mirlacher, M.; Storz, M.; Mihatsch, M.J.; Sauter, G. Calretinin expression in human normal and neoplastic tissues: A tissue microarray analysis on 5233 tissue samples. Hum. Pathol. 2003, 34, 994–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, R.M.; Bigner, S.H.; Johnston, W.W. Metastatic breast carcinoma in cerebrospinal fluid. A cytomorphometric study. Acta Cytol. 1982, 26, 787–792. [Google Scholar]
- Silverman, J.; Ujevich, B.; Adjapong, O.; Xie, J. Metastatic Carcinoma in Cerebrospinal Fluid Cytology: The Significance of Cytoplasmic Blebs. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2016, 146 (Suppl. S1), 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sardana, R.; Parwani, A.V.; Cui, X.; Balakrishna, J. Unusual cerebrospinal fluid finding of intracytoplasmic granules in metaplastic carcinoma of the breast with acinar differentiation. Diagn. Cytopathol. 2021, 49, E152–E155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shield, P.W.; Papadimos, D.J.; Walsh, M.D. GATA3: A promising marker for metastatic breast carcinoma in serous effusion specimens. Cancer Cytopathol. 2014, 122, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braxton, D.R.; Cohen, C.; Siddiqui, M.T. Utility of GATA3 immunohistochemistry for diagnosis of metastatic breast carcinoma in cytology specimens. Diagn. Cytopathol. 2015, 43, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, B.; Guo, M.; Zhao, J.; Gong, Y. Utility and pitfalls of GATA3 immunocytochemistry for diagnosis of metastatic breast carcinoma and urothelial carcinoma on cytology specimens. J. Am. Soc. Cytopathol. 2017, 6, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Adeniran, A.J. Clinicopathological Review of Micropapillary Urothelial Carcinoma. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2022, 24, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, E.C.; Wang, G.; Parkinson, B.; Huo, L.; Peng, Y.; Wang, J.; Salisbury, T.; Wu, Y.; Chen, H.; Albarracin, C.T.; et al. TRPS1, GATA3, and SOX10 expression in triple-negative breast carcinoma. Hum. Pathol. 2022, 125, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gown, A.M.; Fulton, R.S.; Kandalaft, P.L. Markers of metastatic carcinoma of breast origin. Histopathology 2016, 68, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelwahed, M.; Yurtsever, N.; Savant, D.; Karam, P.; Gimenez, C.; Das, K.; Sheikh-Fayyaz, S.; Khutti, S. Utility of TRPS-1 immunohistochemistry in diagnosis of metastatic breast carcinoma in cytology specimens. J. Am. Soc. Cytopathol. 2022, 11, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Stendahl, K.; Cai, G.; Adeniran, A.; Harigopal, M.; Gilani, S.M. Evaluation of TRPS1 Expression in Pleural Effusion Cytology Specimens With Metastatic Breast Carcinoma. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2022, 158, 416–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, B.; Dong, H.P.; Holth, A.; Berner, A.; Risberg, B. Flow cytometric immunophenotyping of cancer cells in effusion specimens: Diagnostic and research applications. Diagn. Cytopathol. 2007, 35, 568–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amir, E.; Miller, N.; Geddie, W.; Freedman, O.; Kassam, F.; Simmons, C.; Oldfield, M.; Dranitsaris, G.; Tomlinson, G.; Laupacis, A.; et al. Prospective study evaluating the impact of tissue confirmation of metastatic disease in patients with breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 587–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilking, U.; Karlsson, E.; Skoog, L.; Hatschek, T.; Lidbrink, E.; Elmberger, G.; Johansson, H.; Lindstrom, L.; Bergh, J. HER2 status in a population-derived breast cancer cohort: Discordances during tumor progression. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2011, 125, 553–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, F.; Harbeck, N.; Fallowfield, L.; Kyriakides, S.; Senkus, E.; Group, E.G.W. Locally recurrent or metastatic breast cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2012, 23 (Suppl. S7), vii11–vii19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, M.E. ASCO-CAP guidelines for breast predictive factor testing: An update. Appl. Immunohistochem. Mol. Morphol. 2011, 19, 499–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, K.H.; Hammond, M.E.H.; Dowsett, M.; McKernin, S.E.; Carey, L.A.; Fitzgibbons, P.L.; Hayes, D.F.; Lakhani, S.R.; Chavez-MacGregor, M.; Perlmutter, J.; et al. Estrogen and Progesterone Receptor Testing in Breast Cancer: ASCO/CAP Guideline Update. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 1346–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, J.W.; Lee, K.; Chung, Y.R.; Jang, M.H.; Ahn, S.; Park, S.Y. The updated 2018 American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists guideline on human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 interpretation in breast cancer: Comparison with previous guidelines and clinical significance of the proposed in situ hybridization groups. Hum. Pathol. 2020, 98, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pareja, F.; Murray, M.P.; Jean, R.D.; Konno, F.; Friedlander, M.; Lin, O.; Edelweiss, M. Cytologic assessment of estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, and HER2 status in metastatic breast carcinoma. J. Am. Soc. Cytopathol. 2017, 6, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vohra, P.; Buelow, B.; Chen, Y.Y.; Serrano, M.; Vohra, M.S.; Berry, A.; Ljung, B.M. Estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 expression in breast cancer FNA cell blocks and paired histologic specimens: A large retrospective study. Cancer Cytopathol. 2016, 124, 828–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domanski, A.M.; Monsef, N.; Domanski, H.A.; Grabau, D.; Ferno, M. Comparison of the oestrogen and progesterone receptor status in primary breast carcinomas as evaluated by immunohistochemistry and immunocytochemistry: A consecutive series of 267 patients. Cytopathology 2013, 24, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srebotnik Kirbis, I.; Us Krasovec, M.; Pogacnik, A.; Strojan Flezar, M. Optimization and validation of immunocytochemical detection of oestrogen receptors on cytospins prepared from fine needle aspiration (FNA) samples of breast cancer. Cytopathology 2015, 26, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinsek, Z.P.; Nolde, N.; Kardum-Skelin, I.; Nizzoli, R.; Onal, B.; Rezanko, T.; Tani, E.; Ostovic, K.T.; Vielh, P.; Schmitt, F.; et al. Multinational study of oestrogen and progesterone receptor immunocytochemistry on breast carcinoma fine needle aspirates. Cytopathology 2013, 24, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.K.; Gupta, N.; Rajwanshi, A.; Joshi, K.; Singh, G. Immunochemistry for oestrogen receptor, progesterone receptor and HER2 on cell blocks in primary breast carcinoma. Cytopathology 2012, 23, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, Y.; Nakagomi, H.; Omori, M.; Inoue, M.; Takahashi, K.; Maruyama, M.; Takano, A.; Furuya, K.; Amemiya, K.; Ishii, E.; et al. Benefits of using the cell block method to determine the discordance of the HR/HER2 expression in patients with metastatic breast cancer. Breast Cancer 2016, 23, 633–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doxtader, E.E.; Calhoun, B.C.; Sturgis, C.D.; Booth, C.N. HER2 FISH concordance in breast cancer patients with both cytology and surgical pathology specimens. J. Am. Soc. Cytopathol. 2018, 7, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Shen, R.; Chaudhary, S.; Gao, F.; Li, Z. Correlation of Expression of Breast Biomarkers in Primary and Metastatic Breast Carcinomas: A Single-Institution Experience. Acta Cytol. 2016, 60, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cytopathology: Massive parallel sequencing to assess the mutational landscape of fine needle aspirate samples: A pilot study. Lab. Investig. 2013, 93, 81–110. [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Joh, D.Y.; Heggestad, J.T.; Zhang, S.; Anderson, G.R.; Bhattacharyya, J.; Wardell, S.E.; Wall, S.A.; Cheng, A.B.; Albarghouthi, F.; Liu, J.; et al. Author Correction: Cellphone enabled point-of-care assessment of breast tumor cytology and molecular HER2 expression from fine-needle aspirates. NPJ Breast Cancer 2021, 7, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modi, S.; Jacot, W.; Yamashita, T.; Sohn, J.; Vidal, M.; Tokunaga, E.; Tsurutani, J.; Ueno, N.T.; Prat, A.; Chae, Y.S.; et al. Trastuzumab Deruxtecan in Previously Treated HER2-Low Advanced Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
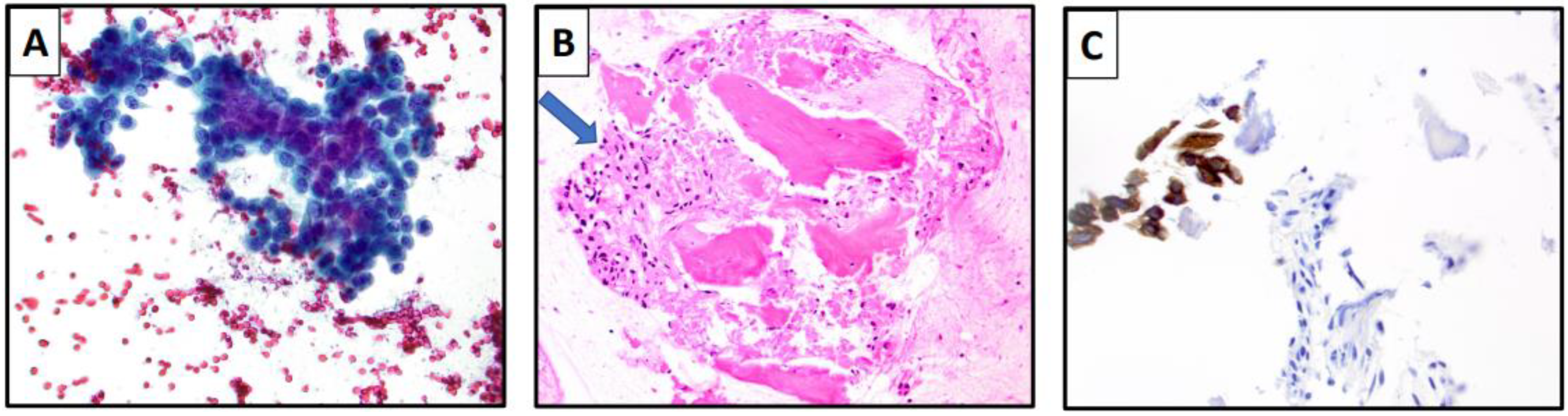
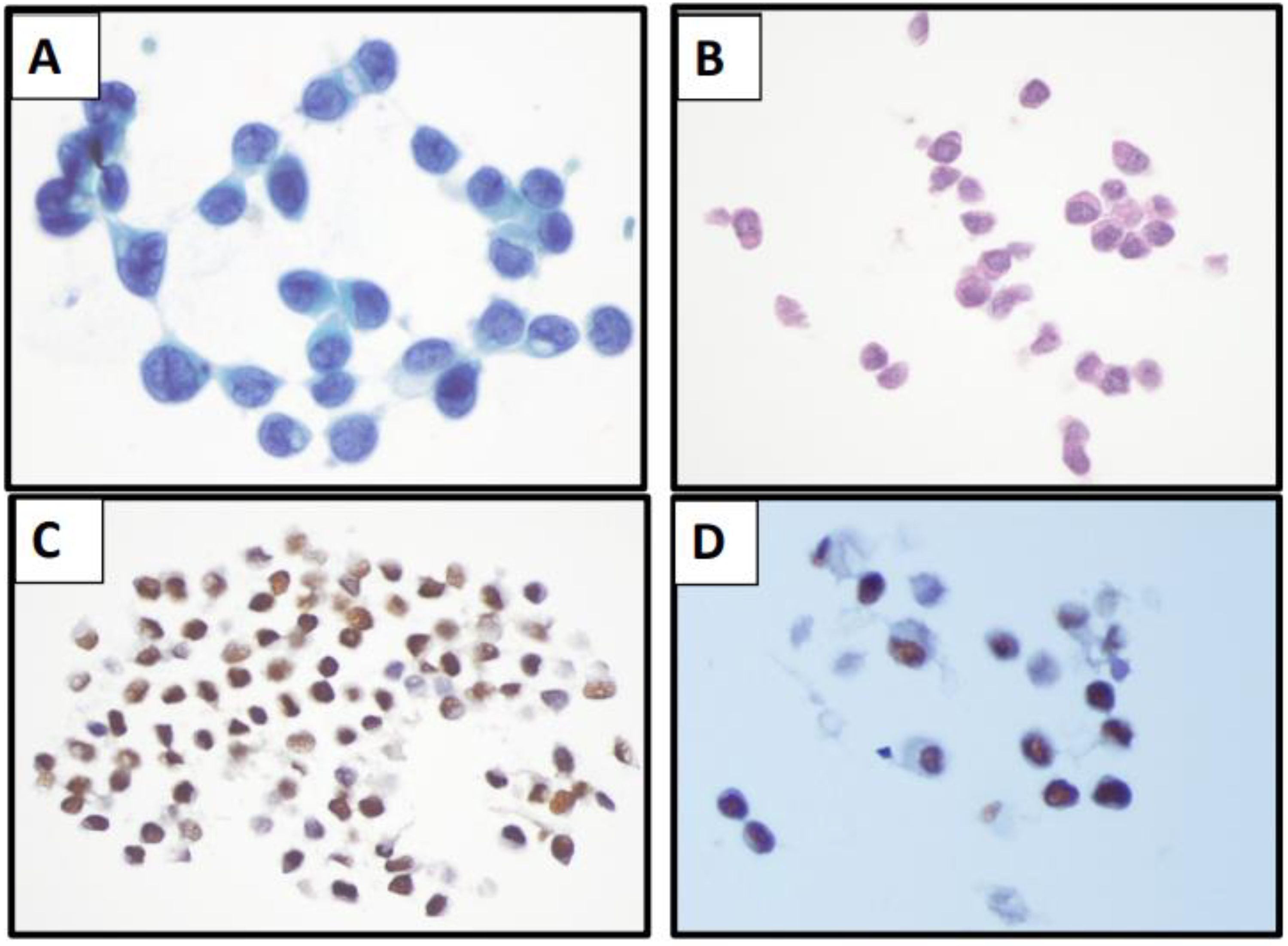



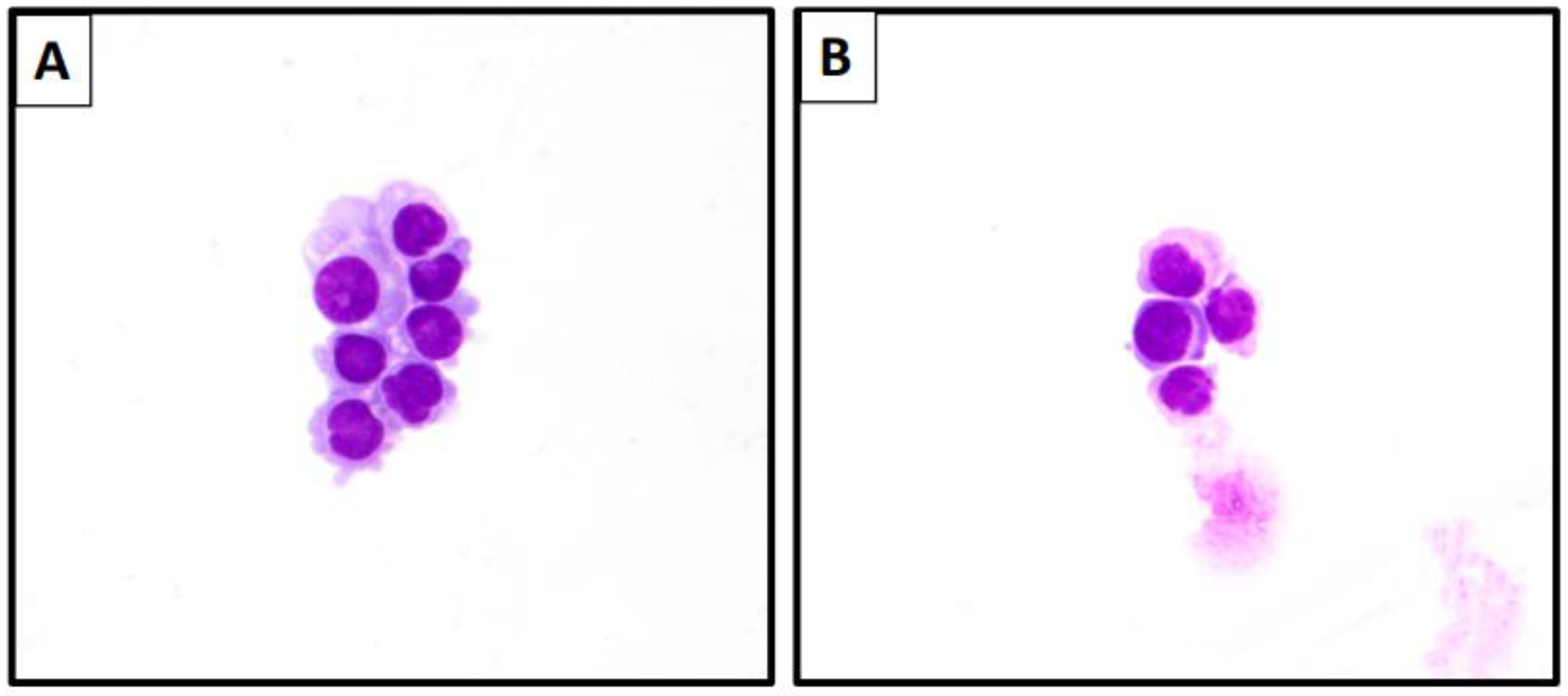
| Specimen Type | Characteristic Cytomorphologic Features |
|---|---|
| Fine Needle Aspiration | Invasive breast carcinoma of no special type Well-circumscribed tissue fragments with round to oval cells with focal acinar formation Lobular Carcinoma Single cells or small loose clusters or single file arrangement Monotonous nuclei with high N:C ratio Scant to moderate cytoplasm Intracytoplasmic lumens/vacuoles |
| Effusion Specimens | Invasive breast carcinoma of no special type Three dimensional tightly packed groups (cannonball-like clusters) Hollow clusters on cell block preparation Lobular Carcinoma Single cell, signet ring cells Mesothelial-like cell pattern Single files Mildly atypical cells Moderately abundant cytoplasm |
| Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) | Invasive breast carcinoma of no special type Single cells, rarely cannon ball-like arrangements Large cells, prominent nucleolus Occasional binucleation Highly variable in size Cytoplasmic blebs Lobular Carcinoma Isolated, medium sized cells Signet ring morphology |
| Key Points Regarding Breast Biomarkers |
|---|
|
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baskota, S.U.; Qazi, D.; Chandra, A.; Vohra, P. Comprehensive Review of Metastatic Breast Carcinoma in Cytology Specimens. J. Mol. Pathol. 2022, 3, 293-306. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmp3040025
Baskota SU, Qazi D, Chandra A, Vohra P. Comprehensive Review of Metastatic Breast Carcinoma in Cytology Specimens. Journal of Molecular Pathology. 2022; 3(4):293-306. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmp3040025
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaskota, Swikrity U., Daniel Qazi, Ashish Chandra, and Poonam Vohra. 2022. "Comprehensive Review of Metastatic Breast Carcinoma in Cytology Specimens" Journal of Molecular Pathology 3, no. 4: 293-306. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmp3040025
APA StyleBaskota, S. U., Qazi, D., Chandra, A., & Vohra, P. (2022). Comprehensive Review of Metastatic Breast Carcinoma in Cytology Specimens. Journal of Molecular Pathology, 3(4), 293-306. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmp3040025







