Abstract
Introduction: Consanguinity has been associated with adverse health outcomes. The objective of the present study was to assess the association between parental consanguinity and risk of infection with human immunodeficiency virus type-1 (HIV-1). Methods: Data were collected from 333 HIV-1 infected individuals referred to a local health center in Shiraz (southern Iran). A total of 999 healthy individuals frequency matched with the cases according to their sex and age were also studied, as a control group. Results: Prevalence of parental consanguineous marriage was 23.7% and 32.8% among patients and controls, respectively (Chi2=9.880, df=1, p=0.007). The mean inbreeding coefficient was 0.0110 and 0.0156 among patients and controls, respectively. The risk of infection with HIV-1 decreased as a function of inbreeding coefficient (Chi2=7.531, p=0.006). Conclusions: The present finding indicates a negative association between the susceptibility of HIV-1 infection and the inbreeding coefficient.
Introduction
It is suggested that consanguineous marriage, the marriage between relatives, has been a long- standing social habit among populations [1]. Prevalence of consanguinity depends on several factors, including demographic, religious, cultural and socio-economic factors [1,2].
This type of marriage has received a great deal of attention as a potential risk factor for many adverse health outcomes [2]. It has been reported that in populations where consanguineous marriages are common, inbred individuals are more common among infected cases for tuberculosis and hepatitis [3]. Consanguineous unions are common in many Asian and African countries [2].
For countries where the consanguineous marriage is common [4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12], the association between consanguinity and susceptibility to human immunodeficiency virus type-1 (HIV-1) is highly important.
To the best of our knowledge, there is no study concerning the association between susceptibility to HIV-1 and parental consanguineous marriages. Therefore, the present case-control study was carried out.
Methods
Participants
Data were collected from 333 HIV-1-infected individuals (48 females, 285 males) referred to a local health center in Shiraz (Fars province, southern Iran). A total of 999 healthy individuals (144 females, 855 males) frequency matched with the cases according to their sex and age were also studied, as a control group.
Collected data covered socio-demographic characteristics such as, history of incarceration, injection drug abuse, risky sexual behaviors, blood transfusion, HIV-1 infection status of the mother and consanguinity marriages of parents. All participants provided informed consent. This research was approved by the institutional review board of the Shiraz University.
Coefficient of Inbreeding
The coefficient of inbreeding (F) is the probability that an individual has received both alleles of a pair from an identical ancestral source, or the proportion of loci at which he is homozygous.
Consanguineous marriages were classified by the degree of relatedness between parents: first cousins (F=1/16), first cousins once removed (F=1/32), second cousins (F=1/64), and beyond second cousins (F<1/64). The coefficient of inbreeding (F) for offspring of first cousins, first cousins once removed, second cousins, and beyond second cousins was 1/16, 1/32, 1/64, and <1/64, respectively. The mean inbreeding coefficient (alpha) was calculated for the sample. Considering the low prevalence of first cousin once removed, second cousin, and beyond second cousin marriages among parents of the patients, we classified parental marriages into three categories as follows: first cousin marriages, other related marriages, and unrelated marriages.
Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using the Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) (version 11.5). A probability of p<0.05 considered statistically significant difference.
Results
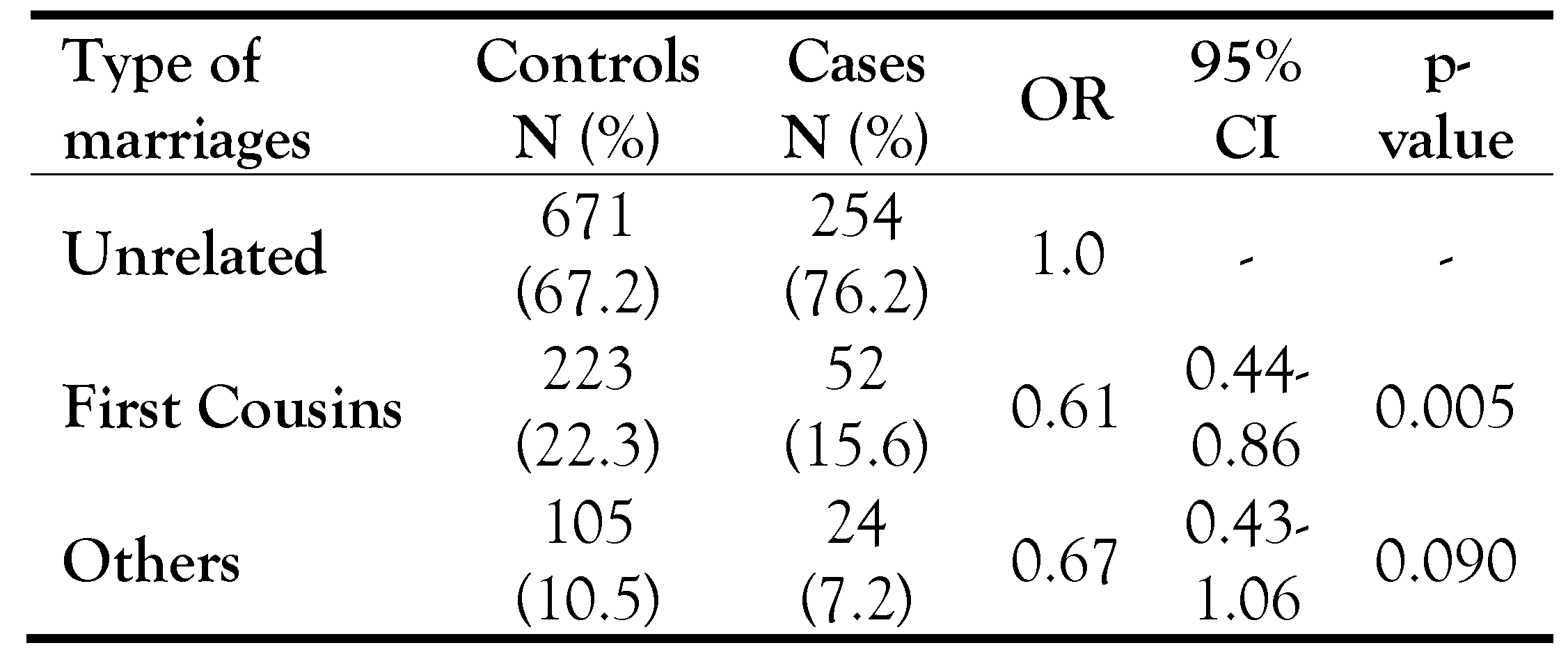
Overall the proportion of parental consanguineous marriages was 23.7 and 32.8 percent among patient and control groups, respectively (Table 1). There was a significant difference between cases and controls for the type of marriages among parents of patient and control groups (Chi2=9.880, df=1, p=0.007). The equivalent mean inbreeding coefficient (alpha) was 0.0110 and 0.0156 among patient and control groups, respectively.

Table 1.
Association between parental marriages and risk of HIV-1 infection in offspring.
As shown in Table 1, the first cousin marriages were the commonest type of all matings in parents of patients (15.6%) and controls (22.3%). This type of marriage has significantly decreased the risk of infection with HIV-1 in the offspring (OR=0.61, 95% CI: 0.44-0.86, p=0.005). Other types of consanguinity were 8.1 and 10.5 percent among parents of HIV-1- infected patients and controls, respectively, indicating that although the risk of infection decreased, the observed alteration is not statistically significant (OR=0.67, 95% CI: 0.43-1.06, p=0.090).
In this study, the inbreeding coefficient was higher in the HIV-negative control group, the present data suggesting that the risk of HIV-1 infection decreased as a function of inbreeding coefficient (Chi2=7.531, p=0.006).
It should be noted that there was no significant difference between types of marriages and selected risk factor for HIV-1 infection such as: history of incarceration (Chi2=3.269, df=2, p=0.195), injection drug abuse (Chi2=2.464, df=2, p=0.292), risky sexual behaviors (Chi2=0.001, df=2, p=0.999), blood transfusion (Chi2=0.089, df=2, p=0.956) and child of infected mother (Chi2=1.90, df=2, p=0.387).
Discussion
Several studies indicate that parental consanguinity is correlated with an increased risk of infection in the offspring [3]. Based on the data released by the World Health Organization (WHO) in 2013, the prevalence of HIV infection in Iran was estimated at 129 per 100,000 people. Therefore the present finding indicating a negative association between the susceptibility of infection with HIV-1 and inbreeding coefficient is an unexpected association.
It is shown that some individuals remain uninfected by HIV-1 despite repeated exposure to the virus. A molecular basis for such HIV-1 resistance has been reported [13,14,15,16]. Variants of the CCR-5 (MIM: 601373) gene may be responsible for relative or absolute resistance to HIV-1 infection. A 32 base pair deletion (delta32), resulting in a defective CCR-5 protein, was identified as reducing the risk of HIV-1 infection in the homozygous state and offering partial resistance to infection in the heterozygote genotype [13,14,15,16]. Therefore, the resistance against HIV-1 infection may increase as a function of number of the delta32 alleles.
The global distribution of the delta32 allele among various human populations is widely variable [17,18,19]. The delta32 allele is more prevalent in European and European-derived populations (about 10-20 percent) but almost absent or extremely rare among African and East Asian ethnic origins. Based on a previously published study, this allele has a prevalence of about 2.5 percent in the Iranian healthy population [19].
If parents were not related to each other, based on the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, the prevalence of homozygote for the delta32 allele of CCR-5 is equal to q2. However, in consanguineous marriages, the prevalence of this genotype becomes equal to q2 + Fpq. Where p and q are frequencies of wild type and the variant alleles, and F is the inbreeding coefficient. Assuming q=0.025 and F=0.0625, the homozygote for the delta32 allele (resistant against HIV-1 infection) increased about 3.43- fold in offspring of consanguineous marriages compared with unrelated marriages. Therefore theoretically, individuals who are resistant against infection with HIV-1 increased among offspring of consanguineous marriages compared with offspring of unrelated marriages. This point supports our present finding.
It is well established that there are several other genes (such as SDF-1, SCYA5, KIR3, etc) involved in susceptibility to HIV-1 infection [20,21,22]. Considering that variants of these loci associated with resistance to HIV-infection have a relatively low prevalence in the population (about 0.02–0.20), the frequency of individuals who are resistant to HIV-infection is increased among the offspring of consanguineous marriages compared with unrelated marriages. Taken together, the observed association between parental consanguinity and a lower risk for HIV-1 infection might be interpreted.
It should be noted that other studies on different ethnic groups are necessary to evaluate the generalization of the present results and our suggestion on risk of infection with HIV-1.
Author Contributions
MR: data collection and writing; MS: idea, statistical analysis and writing.
Funding
This study was supported by the Shiraz University.
Acknowledgments
The authors are indebted to the participants for their close cooperation. The authors are indebted to Dr. Ali Reza Hassan Abadi, Dr. Hassan Joolaei, Mrs. Mahnaz Nozarian (Shiraz University of Medical Sciences) for their contribution for sampling. The authors are indebted to Dr. Maryam Ansari-Lari for critical reading of the manuscript and for her contribution in discussion.
Conflicts of interest
All authors – none to declare.
References
- Saadat, M. Consanguineous marriages in Iranian folktales. Community Genet. 2007, 10, 38–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bittles, A.H. Consanguinity and its relevance to clinical genetics. Clin Genet. 2001, 60, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, E.J.; Frodsham, A.J.; Zhang, L.; Hill, A.V.; Amos, W. Consanguinity and susceptibility to infectious diseases in humans. Biol Lett. 2009, 5, 574–6. [Google Scholar]
- Khoury, S.A.; Massad, D. Consanguineous marriage in Jordan. Am J Med Genet. 1992, 43, 769–75. [Google Scholar]
- Rajab, A.; Patton, M.A. A study of consanguinity in the Sultanate of Oman. Ann Hum Biol. 2000, 27, 321–6. [Google Scholar]
- Saadat, M.; Ansari-Lari, M.; Farhud, D.D. Consanguineous marriage in Iran. Ann Hum Biol. 2004, 31, 263–9. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Othman, H.; Saadat, M. Prevalence of consanguineous marriages in Syria. J Biosoc Sci. 2009, 41, 685–92. [Google Scholar]
- Tadmouri, G.O.; Nair, P.; Obeid, T.; Al Ali, M.T.; Al Khaja, N.; Hamamy, H.A. Consanguinity and reproductive health among Arabs. Reprod Health. 2009, 6, 17. [Google Scholar]
- Rafiee, L.; Saadat, M. Prevalence of consanguineous marriages among Iranian Georgians. J Biosoc Sci 2011, 43, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Saify, K.; Saadat, M. Consanguineous marriages in Afghanistan. J Biosoc Sci. 2012, 44, 73–81. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, M.M. Effects of consanguineous marriage on reproductive behaviour, adverse pregnancy outcomes and offspring mortality in Oman. Ann Hum Biol. 2013, 40, 243–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Kheshen, G.; Saadat, M. Prevalence of consanguineous marriages among shi'a populations of Lebanon. J Biosoc Sci. 2013, 45, 675–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, M.; Carrington, M.; Winkler, C.; et al. Genetic restriction of HIV-1 infection and progression to AIDS by a deletion allele of the CKR5 structural gene. Hemophilia Growth and Development Study, Multicenter AIDS Cohort Study, Multicenter Hemophilia Cohort Study, San Francisco City Cohort, ALIVE Study. Science. 1996, 273, 1856–62. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Paxton, W.A.; Wolinsky, S.M.; et al. The role of a mutant CCR5 allele in HIV-1 transmission and disease progression. Nat Med 1996, 2, 1240–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Paxton, W.A.; Choe, S.; et al. Homozygous defect in HIV-1 coreceptor accounts for resistance of some multiply-exposed individuals to HIV-1 infection. Cell. 1996, 86, 367–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samson, M.; Libert, F.; Doranz, B.J.; et al. Resistance to HIV-1 infection in Caucasian individuals bearing mutantalleles of the CCR-5 chemokine receptor gene. Nature. 1996, 382, 722–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinson, J.J.; Chapman, N.H.; Rees, D.C.; Liu, Y.T.; Clegg, J.B. Global distribution of the CCR5 gene 32-basepair deletion. Nature Genet. 1997, 16, 100–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, P.A.; Buckler-White, A.; Alkhatib, G.; et al. Inherited resistance to HIV-1 conferred by an inactivating mutation in CC chemokine receptor 5, studies in populations with contrasting clinical phenotypes, defined racial background, and quantified risk. Mol Med. 1997, 3, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voevodin, A.; Samilchuk, E.; Dashti, S. A survey for 32 nucleotide deletion in the CCR-5 chemokine receptor gene (deltaccr-5) conferring resistance to human immunodeficiency virus type 1 in different ethnic groups and in chimpanzees. J Med Virol. 1998, 55, 147–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, E.; Dhanda, R.; Bamshad, M.; et al. Global survey of genetic variation in CCR5, RANTES, and MIP- 1alpha: impact on the epidemiology of the HIV-1 pandemic. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2001, 98, 5199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioannidis, J.P.; Rosenberg, P.S.; Goedert, J.J.; et al. Effects of CCR5-Delta32, CCR2-64I, and SDF-1 3'A alleles on HIV-1 disease progression: An international meta- analysis of individual-patient data. Ann Intern Med. 2001, 135, 782–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boulet, S.; Sharafi, S.; Simic, N.; et al. Increased proportion of KIR3DS1 homozygotes in HIV-exposed uninfected individuals. AIDS. 2008, 22, 595–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© GERMS 2013.