Abstract
Introduction: Enterococcus casseliflavus is a rare pathogen in human infections, despite being widely distributed in natural environments. This systematic review aims to evaluate the evidence related to endophthalmitis caused by E. casseliflavus. Methods: A thorough search of PubMed, PubMed Central, and Scopus databases was conducted, covering the period up to October 2022. Results: A total of 53 records were identified, with 8 studies reporting a total of 21 cases meeting the inclusion criteria. Among these studies, 7 described isolated case reports, while 1 study described 14 cases. The overall quality of the reports was good, as all articles were determined to have low risk of bias. Vancomycin susceptibility was reported in only one case of isolated case reports, while the remaining cases were all vancomycin resistant. With regard to management, in most cases intravenous ampicillin and linezolid were administered, while only one study reported administration of vancomycin. Conclusions: Ophthalmologists should be aware of the potential for E. casseliflavus to cause endophthalmitis infections and the challenges associated with its intrinsic resistance to vancomycin.
Introduction
Enterococci cause serious infections, including urinary tract and intra-abdominal infections, bacteremia, endocarditis, as well as meningitis.[1] Enterococcus casseliflavus, a motile member of the Enterococcus species, was first described in 1968 by Mundt and Graham in samples obtained by a variety of plants.[2] E. casseliflavus has emerged as a species that frequently exhibits resistance to vancomycin and is mostly reported in chronically ill and immunosuppressed patients.31
Indeed, among Enterococcus strains, E. casseliflavus stands out as a rare vancomycinresistant variant not belonging to the faecium or faecalis groups.[3] This strain is widespread in nature, inhabiting soil, animals, and plants. While it typically benignly colonizes the human gastrointestinal tract, it can infrequently cause clinically significant infections in immunocompromised patients. Notably, the biliary tract is the usual entry route for those infections.
Endophthalmitis is considered a rare presentation.[1] Indeed, endogenous endophthalmitis, a rare and potentially sightthreatening ocular infection, arises through hematogenous spread from a distant primary source. Well-defined risk factors include immunosuppression, intravenous drug abuse, and invasive medical procedures.[4]
The occurrence of endophthalmitis varies across different clinical settings, with the most common instances being acute-onset cases following cataract surgery, delayed-onset blebrelated endophthalmitis, and episodes of trauma.[4] In the context of postoperative endophthalmitis, enterococci were responsible for 2.2% of culture-confirmed cases after cataract surgery or secondary to intraocular lens implantation, as reported in the Endophthalmitis Vitrectomy Study.[4] Despite appropriate intervention, Enterococcus endophthalmitis often leads to a poor visual outcome. The rising resistance of Enterococcus infections to commonly used antibiotics is currently a cause for concern.[3]
Herein, we systematically assess through a literature search all the relevant evidence regarding E. casseliflavus endophthalmitis infections.
Methods
Study design
The aim of this systematic review is to comprehensively assess and enhance our understanding of the pathogenic potential of this uncommon microorganism. We therefore performed a qualitative synthesis of published articles reporting endophthalmitis infection from E. casseliflavus in humans.
Search strategy
An extensive bibliographic search of PubMed, PubMed Central and Scopus databases was conducted from inception until the 23rd of October 2022. No language restriction was applied. The search terms used were: “Enterococcus casseliflavus” AND “Endophthalmitis” and the search was expanded by investigating all the references presented separately.
Eligibility criteria and data extraction
Eligibility criteria for this systematic review included articles reporting at least one case of E. casseliflavus-induced endophthalmitis in humans. Studies that met these inclusion criteria were independently reviewed by two investigators (SAK and APA), with study characteristics being extracted. In the event of any discrepancies between the two investigators, a consensus was reached through discussion and agreement. Data extraction was performed with adherence to the 2020 Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analysis (PRISMA).[5] Due to the study design, no institutional review board (IRB) approval was obtained.
Risk of bias assessment
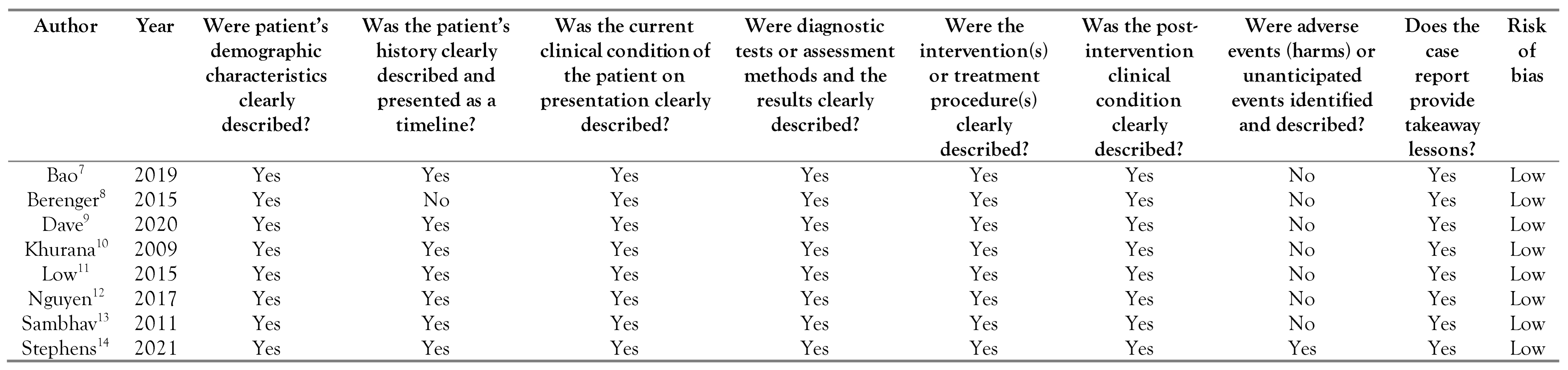
Risk-of-bias assessment was performed independently by 2 reviewers (SAK, APA); disagreements were resolved by consensus. We used the Joanna Briggs Institute (JBI) critical appraisal checklist for case reports.[6] Each of the studies was assessed according to the following items: patient demographic characteristics, history, current clinical condition, diagnostic tests or assessment methods and their results, the intervention(s) or treatment procedure(s), postintervention clinical condition, adverse events (harms) or unanticipated events, takeaway lessons. In line with the JBI tool for assessing case reports, a judgment of “yes” indicated low risk of bias, while a judgement of “no” to any of the included questions negatively impacted the overall quality of the case report. Labelling an item as “unclear” indicated an unclear or unknown risk of bias.
Results
Study selection
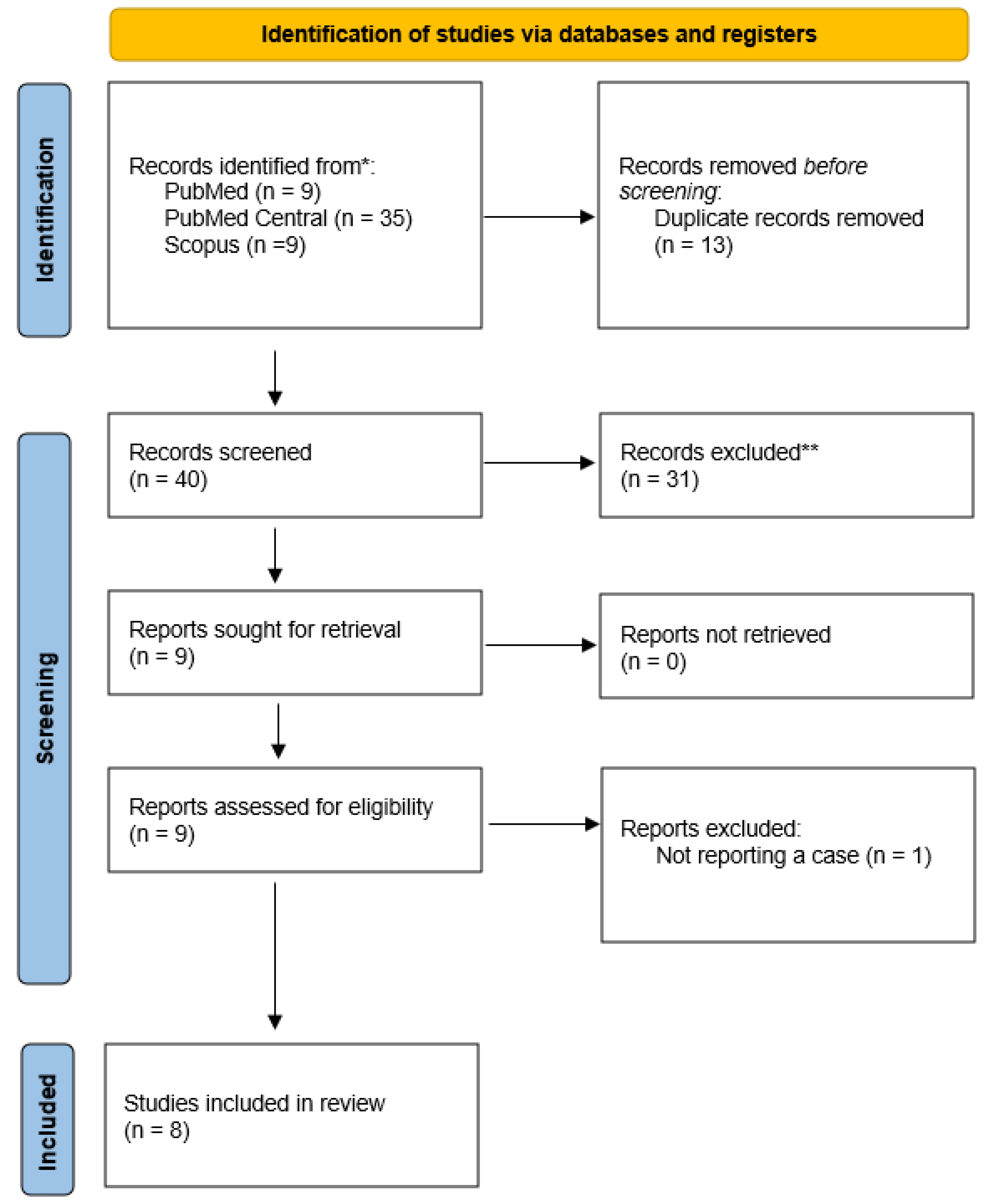
In Figure 1, the PRISMA flow chart reveals the selection process of included studies. With the above-mentioned search terms, we identified 9 records on Medline via PubMed, 35 records on PubMed Central and 9 records on Scopus. After removing duplicates, 40 articles remained, among which 31 were initially excluded because of study design. Subsequently, we examined in detail the remaining 9 articles. Among them, one study was excluded as it did not meet selection criteria (not reporting a case).[1] Finally, our systematic review included 8 studies with a total of 21 cases (patients with E. casseliflavus endophthalmitis).[7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14]
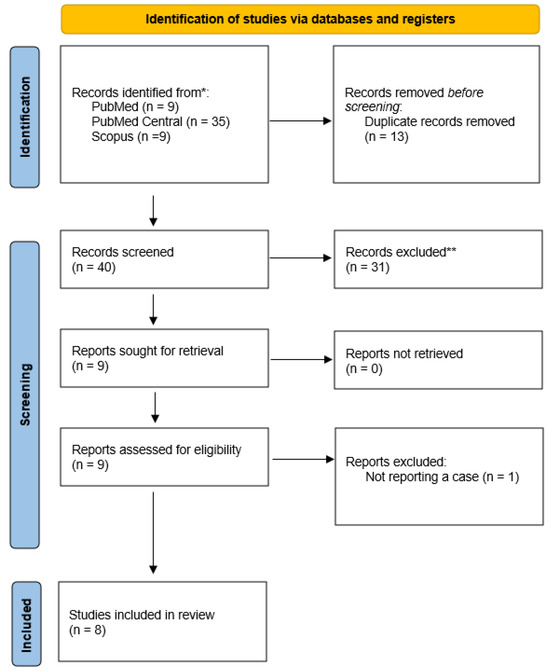
Figure 1.
PRISMA flow diagram of articles related to Enterococcus casseliflavus endophthalmitis case reports.
Study characteristics
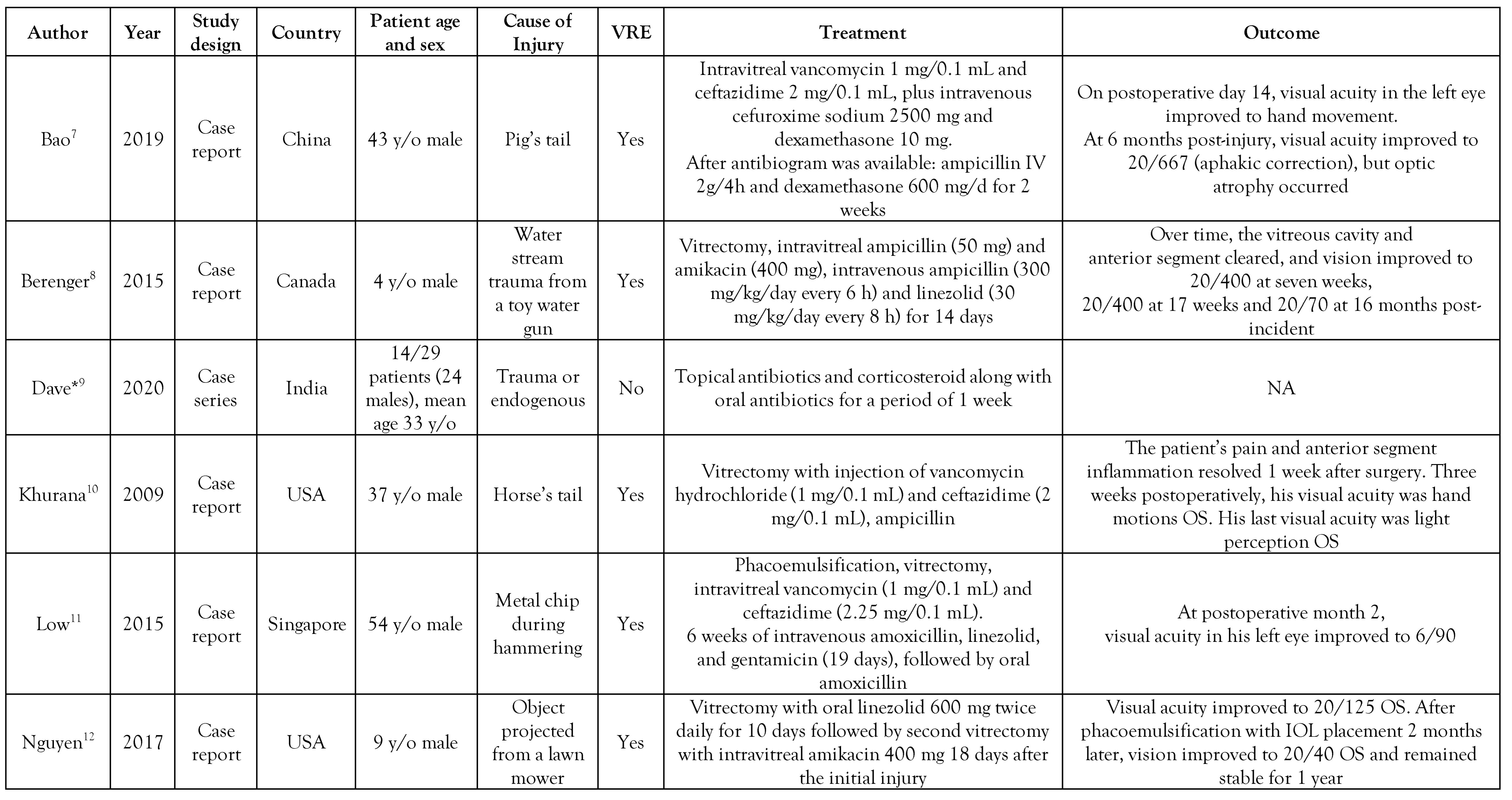
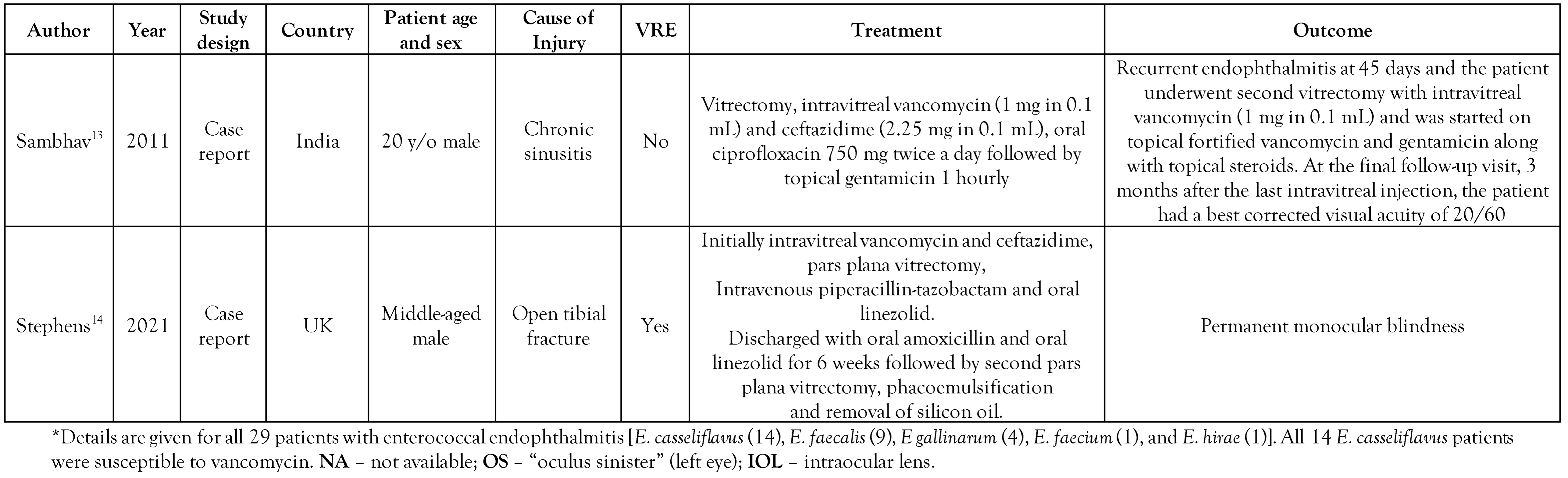
All included studies were written in English and were published between 2009 and 2021 (Table 1). Seven studies described isolated case reports.[7,8,10,11,12,13,14] while one study described 14 cases.[9] The latter were reported in India. Regarding the isolated case reports, 2 were from the USA, while the remaining 5 cases were each reported in Canada, Singapore, UK, China, and India, respectively. In the isolated cases, the mean patient age was 28 years old (4-54 years) and all of them were male. In most cases, injury preceded the infection. As far as the case series study is concerned, the mean patient age was 33 years old.

Table 1.
Study (case reports) characteristics of Enterococcus casseliflavus endophthalmitis infections reported in the literature.
Among all isolated case reports, susceptibility to vancomycin was reported only in one case,[13] while the rest of the isolated case reports all reported vancomycin resistance. In the case series study, all 14 isolated strains of E. casseliflavus were reported as susceptible to vancomycin by using the Kirby Bauer disc diffusion method.[9] With regard to management, in most cases intravenous ampicillin and linezolid were administered, while only one study reported administration of vancomycin.[8]
Quality appraisal
The overall quality of the cases was good, as all articles were determined to have low risk of bias. These results are included in Table 2.

Table 2.
Reported cases of E. casseliflavus and their risk of bias according to the Joanna Briggs Institute (JBI) Critical Appraisal Checklist for Case Reports [6].
Discussion
This systematic review aimed to comprehensively evaluate the existing literature on endophthalmitis infections in humans, caused by E. casseliflavus. To our knowledge, this is the first systematic review conducted on this uncommon microorganism as a causative agent of ocular infections.
E. casseliflavus has been isolated from vegetables and farm animals,[15,16,17] and can also colonize the gastrointestinal tract of both nonhospitalized and hospitalized individuals.[18,19] It rarely causes invasive infections in humans, mainly in patients with serious comorbidities, such as receipt of organ transplant, hematologic malignancy, diabetes mellitus, renal failure, and immunosuppressive treatment.[20,21,22] However, the clinical epidemiology of E. casseliflavus is largely unknown due to limitations in microbiological detection and identification.[23]
There are several pathogenic determinants that enhance Enterococcus spp. colonizing ability and virulence in humans, thus increasing its ability to cause disease. These determinants are associated with surface proteins, capsule formation, secreted proteins and peptides, aggregation substances, and biofilm formation.[24,25] However, significant interspecies differences have been observed regarding the pathogenic potential of enterococci. In general, E. casseliflavus is considered less virulent than E. faecium and E. faecalis and is associated with lower mortality rates.[3,26]
Microbiological confirmation of the clinical diagnosis of infectious endophthalmitis in general is crucial, not only for the identification of the pathogenic microorganism but also to appropriately guide treatment based on isolated species and susceptibility profile. The use of standard culture methods has a low yield, with false negative results up to 30%.[27] Many factors contribute to this low rate, such as the sample type, the low concentration of the microbe, or the use of antibiotics before specimen collection.
Typically, cultured samples are aqueous humor or vitreous humor, collected via needle aspiration or posterior vitrectomy. In order to increase sensitivity, automated identification methods, such as matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time of flight (MALDITOF), and new molecular techniques, such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and sequencing, are combined in addition to conventional microbiological diagnostics (direct microscopy, Gram stain, and culture on growth media).
Combining conventional methods with PCR, especially multiplex or panbacterial, and sequencing, can improve sensitivity by 20% to up to 50%, respectively.[28,29] Use of MALDI-TOF can also decrease time to identification up to 24 hours, providing valuable and accurate information earlier and with low cost.[30] Furthermore, conventional microbiological methods may underestimate the burden and clinical impact of E. casseliflavus, which is intrinsically resistant to several antibiotics, including vancomycin.[31] Regarding vancomycin, E. casseliflavus should be always reported as resistant. Misidentification of E. casseliflavus or reporting it as vancomycin-susceptible may lead to empirical treatment failure and worse patient outcomes.
E. casseliflavus resistance to vancomycin is non-transferable and low-level, denoted as VanC phenotype.[31] This phenotype is derived from a chromosomal cluster of genes encoding a modified pathway of the peptidoglycan biosynthesis, which may be inducible or constitutive. It leads to replacement of the terminal D-Ala of peptidoglycan precursors with D-Ser, which decreases the binding affinity of vancomycin to these precursors, thus blocking its antimicrobial mechanism of action.[32] While enterococci possessing the VanC phenotype are considered in vitro susceptible to teicoplanin,[32] and may also be considered susceptible to telavancin, oritavancin and dalbavancin,[33] limited data exist regarding the in vivo susceptibility of E. casseliflavus against these antibiotics, thus avoiding them may be prudent. Linezolid, daptomycin and the synergistic combination of anti-enterococcal beta-lactam with aminoglycoside whenever feasible and based on susceptibility results, are among the treatment options for severe infections by E. casseliflavus.[1]
The optimal therapeutic approach and the prognosis are difficult to determine due to the low number of endophthalmitis cases caused by E. casseliflavus. The main surgical outcome remains retention of the globe. Concerning visual acuity, the role of early vitrectomy in combination with guided antimicrobial treatment remains crucial.
In the retrospective study by Dave et al., improvement in visual acuity was evident in 34.8% of cases that were managed urgently with vitrectomy and intravitreal treatment (vancomycin + ceftazidime ± dexamethasone).[9] Interestingly, in this study, E. casseliflavus was reported to be susceptible to vancomycin. Although intravitreal vancomycin remains standard protocol in cases of endophthalmitis, in the majority of the studies included in our systematic review, E. casseliflavus was resistant to vancomycin, which could explain observed differences in outcomes.[34,35] It could also be suggested that in injuries inflicted by animals, where there is high risk of E. casseliflavus-related endophthalmitis, an alternative antibiotic intravitreal regimen that covers E. casseliflavus may be considered.
Nevertheless, cases with good visual outcomes have been described. In 3 case reports included in our systematic review, patients ended up with visual acuity 20/70, 20/40 and 20/60, respectively.[8,12,13] It is important to mention that in all 3 cases, after initial vitrectomy and vitreous sampling analysis, a second vitrectomy was performed, with addition of appropriate antibiotics based on the antibiogram. Intravitreal antibiotics of choice included amikacin (0.4 mg/0.1 mL) or combination of ampicillin (5 mg/0.1mL) and amikacin.
The intrinsic vancomycin resistance of E. casseliflavus has important clinical implications that impact treatment decisions, namely the duration of treatment and the need for close postoperative follow-up. Clinicians must ensure that the selected alternative antibiotics, either intraocular or systemic, are administered for an adequate duration to achieve complete resolution of the infection. Additionally, frequent monitoring and follow-up are crucial to assess the patient's response to treatment and to detect any signs of relapse or complications. Clinicians must be vigilant in selecting alternative antibiotics based on susceptibility testing as well, and a multidisciplinary approach involving infectious disease specialists and microbiologists is often crucial in managing infections caused by this resistant pathogen.
One limitation of our systematic review is represented by the relatively small number of cases that were identified, a fact that could be attributed to potential publication bias. Furthermore, since our final selection was limited to case reports and case series, we were unable to perform a meta-analysis. As a result, our conclusions may be less robust. Nonetheless, we attempted to mitigate the risk of bias and enhance the quality of our analysis by employing the JBI critical appraisal checklist for each included case report.
Conclusions
In conclusion, the goal of this systematic review was to raise awareness among clinicians regarding E. casseliflavus as a potential cause of infectious endophthalmitis, which can be a vision-threatening infection if not treated promptly and adequately. The inherent resistance of E. casseliflavus to vancomycin renders management of such infections challenging, necessitating further clinical studies to define optimal antimicrobial treatment strategies.
Author Contributions
SAK and APA performed conceptualization and study design, data collection, interpretation, and table preparation. SAK and APA wrote the initial manuscript and approved the final manuscript as submitted. NS, MM and CT reviewed and did necessary revisions of the manuscript. IG conceptualized and approved the final manuscript. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Funding
None to declare.
Conflicts of Interest
All authors – none to declare.
References
- Monticelli, J.; Knezevich, A.; Luzzati, R.; Di Bella, S. Clinical management of non-faecium non-faecalis vancomycinresistant enterococci infection. Focus on Enterococcus gallinarum and Enterococcus casseliflavus/flavescens. J. Infect. Chemother. 2018, 24, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mundt, J.O.; Graham, W.F. Streptococcus faecium var. casselifavus, nov. var. J. Bacteriol. 1968, 95, 2005–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Britt, N.S.; Potter, E.M. Clinical epidemiology of vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus gallinarum and Enterococcus casseliflavus bloodstream infections. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2016, 5, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, D.P.; Wisniewski, S.R.; Wilson, L.A.; et al. Spectrum and susceptibilities of microbiologic isolates in the Endophthalmitis Vitrectomy Study. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 1996, 122, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moola, S.; Munn, Z.; Tufanaru, C.; et al. Systematic reviews of etiology and risk. In Joanna Briggs Institute Reviewer's Manual; Aromataris, E., Munn, Z., Eds.; The Joanna Briggs Institute: Adelaide, South Australia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, Q.D.; Liu, T.X.; Xie, M.; Tian, X. Exogenous endophthalmitis caused by Enterococcus casseliflavus: A case report. World J. Clin. Cases. 2019, 7, 3904–3911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berenger, B.M.; Kulkarni, S.; Hinz, B.J.; Forgie, S.E. Exogenous endophthalmitis caused by Enterococcus casseliflavus: A case report and discussion regarding treatment of intraocular infection with vancomycinresistant enterococci. Can. J. Infect. Dis. Med. Microbiol. 2015, 26, 330–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dave, V.P.; Pathengay, A.; Braimah, I.Z.; et al. Enterococcus endophthalmitis: Clinical settings, antimicrobial susceptibility, and management outcomes. Retina 2020, 40, 898–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurana, R.N.; Leder, H.A.; Nguyen, Q.D.; Do, D.V. Enterococcus casseliflavus endophthalmitis associated with a horse tail injury. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2009, 127, 1551–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, J.R.; Teoh, C.S.; Chien, J.M.; Huang, E.H. Enterococcus casseliflavus endophthalmitis due to metallic intraocular foreign body. Eye 2015, 29, 840–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, J.; Hartnett, M.E. Successful management of posttraumatic vancomycin-resistant enterococcus endophthalmitis. Am. J. Ophthalmol. Case Rep. 2017, 5, 117–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sambhav, K.; Mathai, A.; Reddy, A.K.; Reddy, B.V.; Bhatia, K.; Balne, P.K. Endogenous endophthalmitis caused by Enterococcus casseliflavus. J. Med. Microbiol. 2011, 60, 670–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephens, A.; Sivapathasuntharam, C.; James, H.K. Monocular loss of vision following an open tibial fracture: A case of Enterococcus casseliflavus endogenous endophthalmitis. BMJ Case Rep. 2021, 14, e241292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Kharousi, Z.S.; Guizani, N.; Al-Sadi, A.M.; Al-Bulushi, I.M.; Shaharoona, B. Hiding in fresh fruits and vegetables: Opportunistic pathogens may cross geographical barriers. Int. J. Microbiol. 2016, 2016, 4292417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graves, A.; Weaver, R.W.; Entry, J. Characterization of enterococci populations in livestock manure using BIOLOG. Microbiol. Res. 2009, 164, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thal, L.A.; Chow, J.W.; Mahayni, R.; et al. Characterization of antimicrobial resistance in enterococci of animal origin. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1995, 39, 2112–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toye, B.; Shymanski, J.; Bobrowska, M.; Woods, W.; Ramotar, K. Clinical and epidemiological significance of enterococci intrinsically resistant to vancomycin (possessing the vanC genotype). J. Clin. Microbiol. 1997, 35, 3166–3170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordts, B.; Van Landuyt, H.; Ieven, M.; Vandamme, P.; Goossens, H. Vancomycin-resistant enterococci colonizing the intestinal tracts of hospitalized patients. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1995, 33, 2842–2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, K.C.; Cockerill, I.I.I.F.R.; Patel, R. Clinical and epidemiological features of Enterococcus casseliflavus/flavescens and Enterococcus gallinarum bacteremia: A report of 20 cases. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2001, 32, 1540–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasilakopoulou, A.; Vourli, S.; Siafakas, N.; Kavatha, D.; Tziolos, N.; Pournaras, S. Enterococcus casseliflavus bacteraemia in a patient with chronic renal disease. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2020, 12, 70–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iaria, C.; Stassi, G.; Costa, G.B.; Di Leo, R.; Toscano, A.; Cascio, A. Enterococcal meningitis caused by Enterococcus casseliflavus. First case report. BMC Infect. Dis. 2005, 5, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prakash, V.P.; Rao, S.R.; Parija, S.C. Emergence of unusual species of enterococci causing infections, South India. BMC Infect. Dis. 2005, 5, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arias, C.A.; Murray, B.E. The rise of the Enterococcus: Beyond vancomycin resistance. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 10, 266–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abril, A.G.; Quintela-Baluja, M.; Villa, T.G.; Calo-Mata, P.; Barros-Velazquez, J.; Carrera, M. Proteomic characterization of virulence factors and related proteins in Enterococcus strains from dairy and fermented food products. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.H.; Lee, S.O.; Kim, T.H.; et al. Clinical features and outcomes of bacteremia caused by Enterococcus casseliflavus and Enterococcus gallinarum: Analysis of 56 cases. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2004, 38, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durand, M.L. Endophthalmitis. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2013, 19, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seal, D.; Reischl, U.; Behr, A.; et al. Laboratory diagnosis of endophthalmitis: Comparison of microbiology and molecular methods in the European Society of Cataract & Refractive Surgeons multicenter study and susceptibility testing. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2008, 34, 1439–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Fu, A.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, W.; Cheng, Y. Microbiological diagnosis of endophthalmitis using nanopore targeted sequencing. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2021, 49, 1060–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mailhac, A.; Durand, H.; Boisset, S.; et al. MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry for rapid diagnosis of postoperative endophthalmitis. J. Proteom. 2017, 152, 150–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courvalin, P. Resistance of enterococci to glycopeptides. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1990, 34, 2291–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cetinkaya, Y.; Falk, P.; Mayhall, C.G. Vancomycin-resistant enterococci. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2000, 13, 686–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klinker, K.P.; Borgert, S.J. Beyond vancomycin: The tail of the lipoglycopeptides. Clin. Ther. 2015, 37, 2619–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Results of the Endophthalmitis Vitrectomy Study. A randomized trial of immediate vitrectomy and of intravenous antibiotics for the treatment of postoperative bacterial endophthalmitis. Endophthalmitis Vitrectomy Study Group. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1995, 113, 1479–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandarakis, S.A.; Doumazos, L.; Mitsopoulou, D.; et al. A review on pathogens and necessary diagnostic work for bleb-related infections (BRIs). Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandarakis, S.A.; Spernovasilis, N.; Georgalas, I.; Mendris, M.; Tsioutis, C.; Agouridis, A.P. Endophthalmitis caused by Enterococcus casseliflavus: A systematic review of literature. GERMS 2023, 13, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© GERMS 2023.