Endophthalmitis Caused by Enterococcus casseliflavus: A Systematic Review of Literature
Abstract
Introduction
Methods
Study design
Search strategy
Eligibility criteria and data extraction
Risk of bias assessment
Results
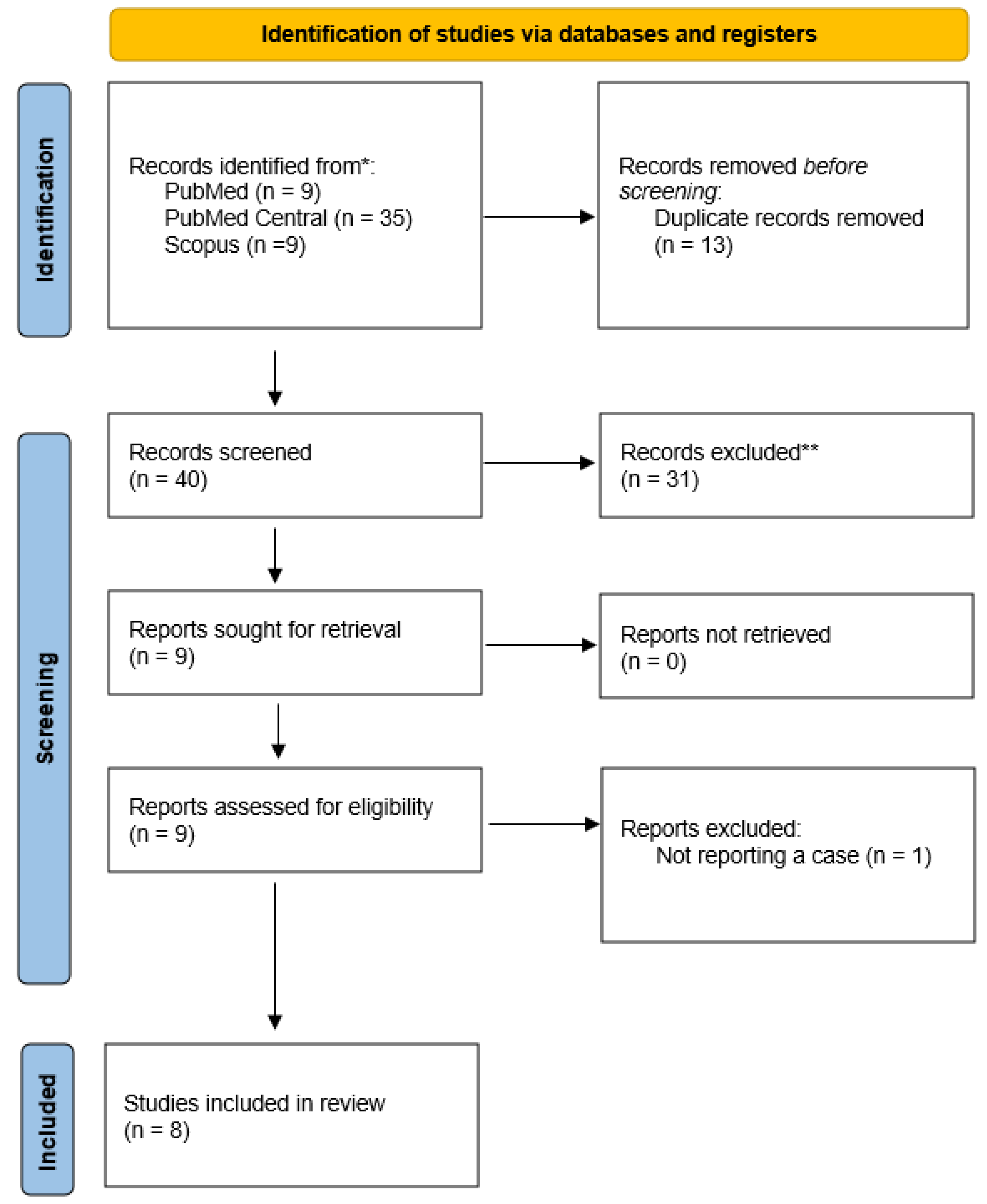
Study selection
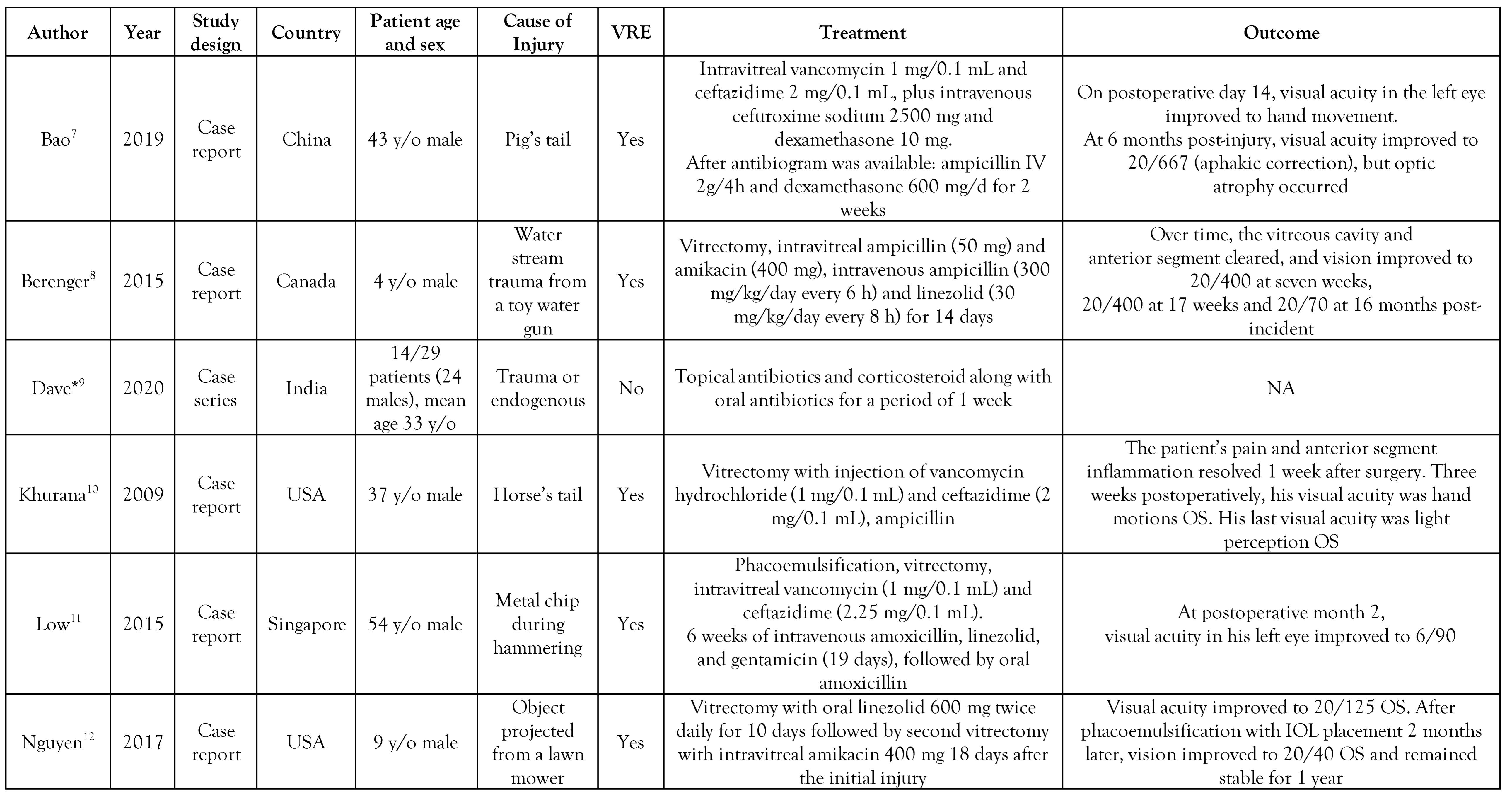
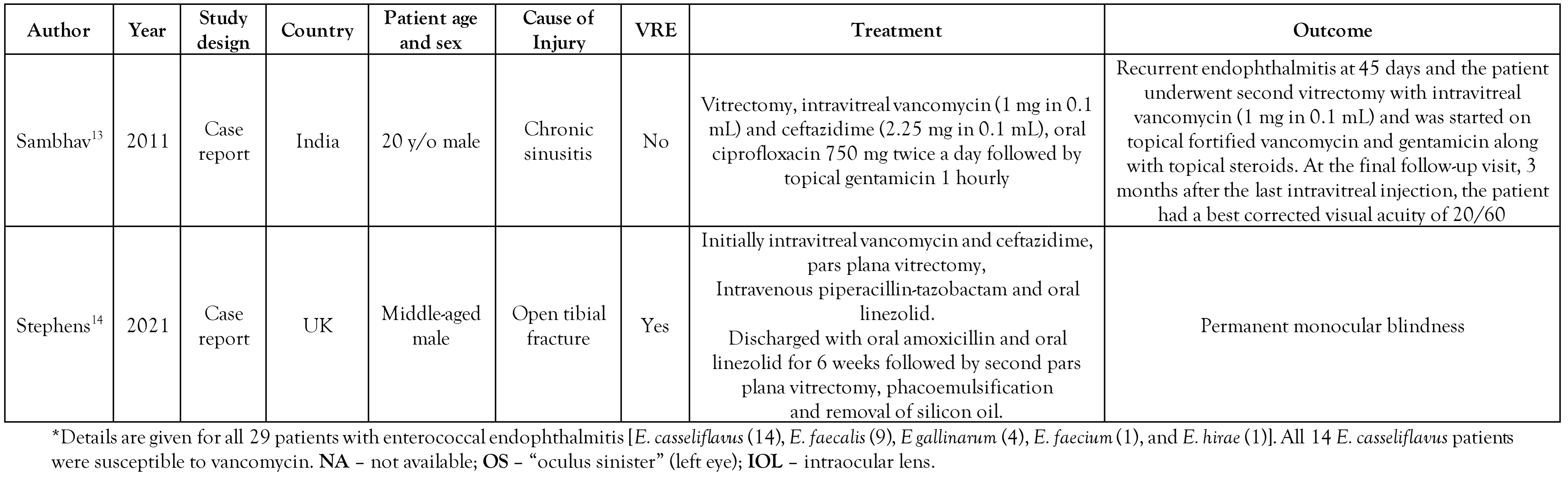
Study characteristics
Quality appraisal
Discussion
Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Monticelli, J.; Knezevich, A.; Luzzati, R.; Di Bella, S. Clinical management of non-faecium non-faecalis vancomycinresistant enterococci infection. Focus on Enterococcus gallinarum and Enterococcus casseliflavus/flavescens. J. Infect. Chemother. 2018, 24, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mundt, J.O.; Graham, W.F. Streptococcus faecium var. casselifavus, nov. var. J. Bacteriol. 1968, 95, 2005–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Britt, N.S.; Potter, E.M. Clinical epidemiology of vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus gallinarum and Enterococcus casseliflavus bloodstream infections. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2016, 5, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, D.P.; Wisniewski, S.R.; Wilson, L.A.; et al. Spectrum and susceptibilities of microbiologic isolates in the Endophthalmitis Vitrectomy Study. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 1996, 122, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moola, S.; Munn, Z.; Tufanaru, C.; et al. Systematic reviews of etiology and risk. In Joanna Briggs Institute Reviewer's Manual; Aromataris, E., Munn, Z., Eds.; The Joanna Briggs Institute: Adelaide, South Australia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, Q.D.; Liu, T.X.; Xie, M.; Tian, X. Exogenous endophthalmitis caused by Enterococcus casseliflavus: A case report. World J. Clin. Cases. 2019, 7, 3904–3911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berenger, B.M.; Kulkarni, S.; Hinz, B.J.; Forgie, S.E. Exogenous endophthalmitis caused by Enterococcus casseliflavus: A case report and discussion regarding treatment of intraocular infection with vancomycinresistant enterococci. Can. J. Infect. Dis. Med. Microbiol. 2015, 26, 330–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dave, V.P.; Pathengay, A.; Braimah, I.Z.; et al. Enterococcus endophthalmitis: Clinical settings, antimicrobial susceptibility, and management outcomes. Retina 2020, 40, 898–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurana, R.N.; Leder, H.A.; Nguyen, Q.D.; Do, D.V. Enterococcus casseliflavus endophthalmitis associated with a horse tail injury. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2009, 127, 1551–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, J.R.; Teoh, C.S.; Chien, J.M.; Huang, E.H. Enterococcus casseliflavus endophthalmitis due to metallic intraocular foreign body. Eye 2015, 29, 840–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, J.; Hartnett, M.E. Successful management of posttraumatic vancomycin-resistant enterococcus endophthalmitis. Am. J. Ophthalmol. Case Rep. 2017, 5, 117–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sambhav, K.; Mathai, A.; Reddy, A.K.; Reddy, B.V.; Bhatia, K.; Balne, P.K. Endogenous endophthalmitis caused by Enterococcus casseliflavus. J. Med. Microbiol. 2011, 60, 670–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephens, A.; Sivapathasuntharam, C.; James, H.K. Monocular loss of vision following an open tibial fracture: A case of Enterococcus casseliflavus endogenous endophthalmitis. BMJ Case Rep. 2021, 14, e241292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Kharousi, Z.S.; Guizani, N.; Al-Sadi, A.M.; Al-Bulushi, I.M.; Shaharoona, B. Hiding in fresh fruits and vegetables: Opportunistic pathogens may cross geographical barriers. Int. J. Microbiol. 2016, 2016, 4292417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graves, A.; Weaver, R.W.; Entry, J. Characterization of enterococci populations in livestock manure using BIOLOG. Microbiol. Res. 2009, 164, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thal, L.A.; Chow, J.W.; Mahayni, R.; et al. Characterization of antimicrobial resistance in enterococci of animal origin. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1995, 39, 2112–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toye, B.; Shymanski, J.; Bobrowska, M.; Woods, W.; Ramotar, K. Clinical and epidemiological significance of enterococci intrinsically resistant to vancomycin (possessing the vanC genotype). J. Clin. Microbiol. 1997, 35, 3166–3170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordts, B.; Van Landuyt, H.; Ieven, M.; Vandamme, P.; Goossens, H. Vancomycin-resistant enterococci colonizing the intestinal tracts of hospitalized patients. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1995, 33, 2842–2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, K.C.; Cockerill, I.I.I.F.R.; Patel, R. Clinical and epidemiological features of Enterococcus casseliflavus/flavescens and Enterococcus gallinarum bacteremia: A report of 20 cases. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2001, 32, 1540–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasilakopoulou, A.; Vourli, S.; Siafakas, N.; Kavatha, D.; Tziolos, N.; Pournaras, S. Enterococcus casseliflavus bacteraemia in a patient with chronic renal disease. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2020, 12, 70–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iaria, C.; Stassi, G.; Costa, G.B.; Di Leo, R.; Toscano, A.; Cascio, A. Enterococcal meningitis caused by Enterococcus casseliflavus. First case report. BMC Infect. Dis. 2005, 5, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prakash, V.P.; Rao, S.R.; Parija, S.C. Emergence of unusual species of enterococci causing infections, South India. BMC Infect. Dis. 2005, 5, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arias, C.A.; Murray, B.E. The rise of the Enterococcus: Beyond vancomycin resistance. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 10, 266–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abril, A.G.; Quintela-Baluja, M.; Villa, T.G.; Calo-Mata, P.; Barros-Velazquez, J.; Carrera, M. Proteomic characterization of virulence factors and related proteins in Enterococcus strains from dairy and fermented food products. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.H.; Lee, S.O.; Kim, T.H.; et al. Clinical features and outcomes of bacteremia caused by Enterococcus casseliflavus and Enterococcus gallinarum: Analysis of 56 cases. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2004, 38, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durand, M.L. Endophthalmitis. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2013, 19, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seal, D.; Reischl, U.; Behr, A.; et al. Laboratory diagnosis of endophthalmitis: Comparison of microbiology and molecular methods in the European Society of Cataract & Refractive Surgeons multicenter study and susceptibility testing. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2008, 34, 1439–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Fu, A.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, W.; Cheng, Y. Microbiological diagnosis of endophthalmitis using nanopore targeted sequencing. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2021, 49, 1060–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mailhac, A.; Durand, H.; Boisset, S.; et al. MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry for rapid diagnosis of postoperative endophthalmitis. J. Proteom. 2017, 152, 150–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courvalin, P. Resistance of enterococci to glycopeptides. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1990, 34, 2291–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cetinkaya, Y.; Falk, P.; Mayhall, C.G. Vancomycin-resistant enterococci. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2000, 13, 686–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klinker, K.P.; Borgert, S.J. Beyond vancomycin: The tail of the lipoglycopeptides. Clin. Ther. 2015, 37, 2619–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Results of the Endophthalmitis Vitrectomy Study. A randomized trial of immediate vitrectomy and of intravenous antibiotics for the treatment of postoperative bacterial endophthalmitis. Endophthalmitis Vitrectomy Study Group. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1995, 113, 1479–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandarakis, S.A.; Doumazos, L.; Mitsopoulou, D.; et al. A review on pathogens and necessary diagnostic work for bleb-related infections (BRIs). Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandarakis, S.A.; Spernovasilis, N.; Georgalas, I.; Mendris, M.; Tsioutis, C.; Agouridis, A.P. Endophthalmitis caused by Enterococcus casseliflavus: A systematic review of literature. GERMS 2023, 13, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
  |
 |
© GERMS 2023.
Share and Cite
Kandarakis, S.A.; Spernovasilis, N.; Georgalas, I.; Mendris, M.; Tsioutis, C.; Agouridis, A.P. Endophthalmitis Caused by Enterococcus casseliflavus: A Systematic Review of Literature. Germs 2023, 13, 343-351. https://doi.org/10.18683/germs.2023.1404
Kandarakis SA, Spernovasilis N, Georgalas I, Mendris M, Tsioutis C, Agouridis AP. Endophthalmitis Caused by Enterococcus casseliflavus: A Systematic Review of Literature. Germs. 2023; 13(4):343-351. https://doi.org/10.18683/germs.2023.1404
Chicago/Turabian StyleKandarakis, Stylianos A., Nikolaos Spernovasilis, Ilias Georgalas, Michalis Mendris, Constantinos Tsioutis, and Aris P. Agouridis. 2023. "Endophthalmitis Caused by Enterococcus casseliflavus: A Systematic Review of Literature" Germs 13, no. 4: 343-351. https://doi.org/10.18683/germs.2023.1404
APA StyleKandarakis, S. A., Spernovasilis, N., Georgalas, I., Mendris, M., Tsioutis, C., & Agouridis, A. P. (2023). Endophthalmitis Caused by Enterococcus casseliflavus: A Systematic Review of Literature. Germs, 13(4), 343-351. https://doi.org/10.18683/germs.2023.1404




