Albendazole Exhibits Anti-Neoplastic Actions against Gastric Cancer Cells by Affecting STAT3 and STAT5 Activation by Pleiotropic Mechanism(s)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Cell Lines and Culture Conditions
2.3. MTT Assay
2.4. Western Blot Analysis
2.5. EMSA
2.6. Immunocytochemistry
2.7. Transfection with SHP-1 siRNA
2.8. Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR)
2.9. GSH/GSSG Assay
2.10. Cell Cycle Analysis
2.11. Annexin V Assay
2.12. TUNEL Assay
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
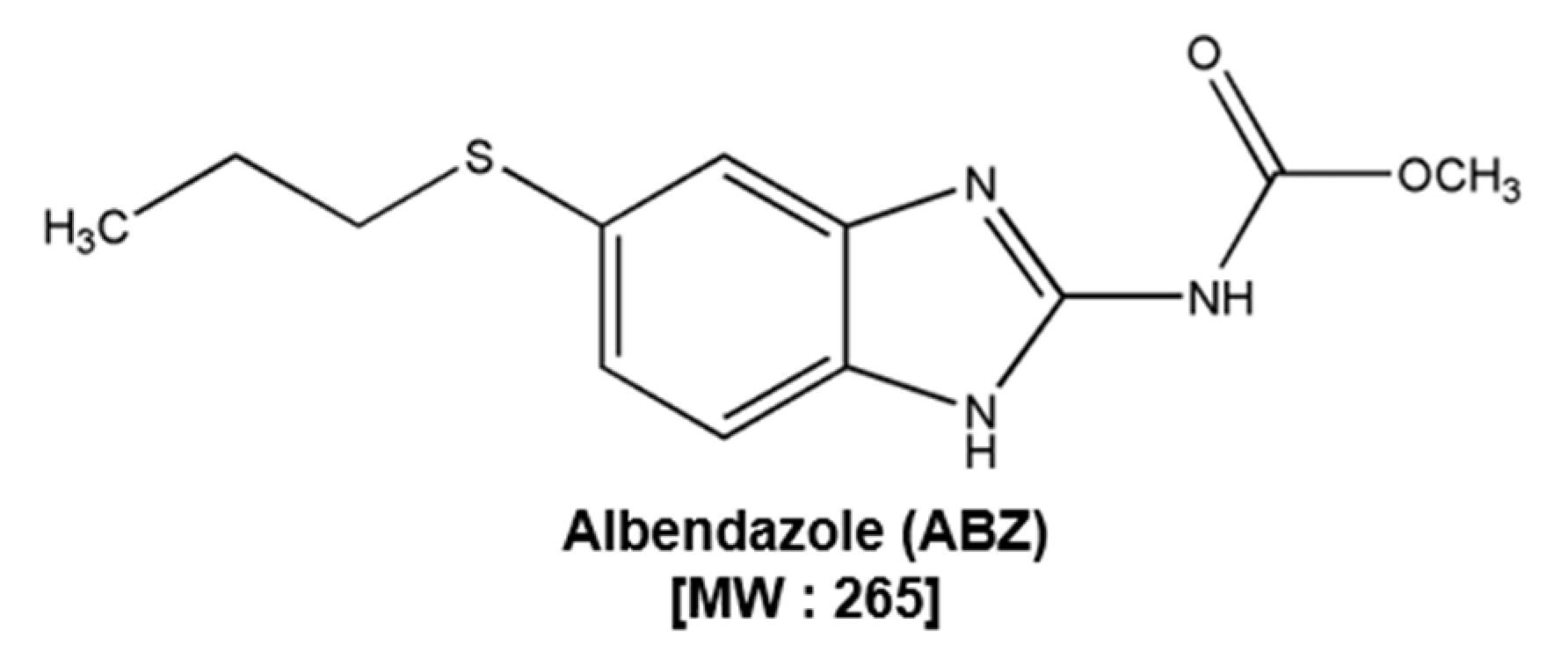
3.1. ABZ Suppresses the Cell Viability
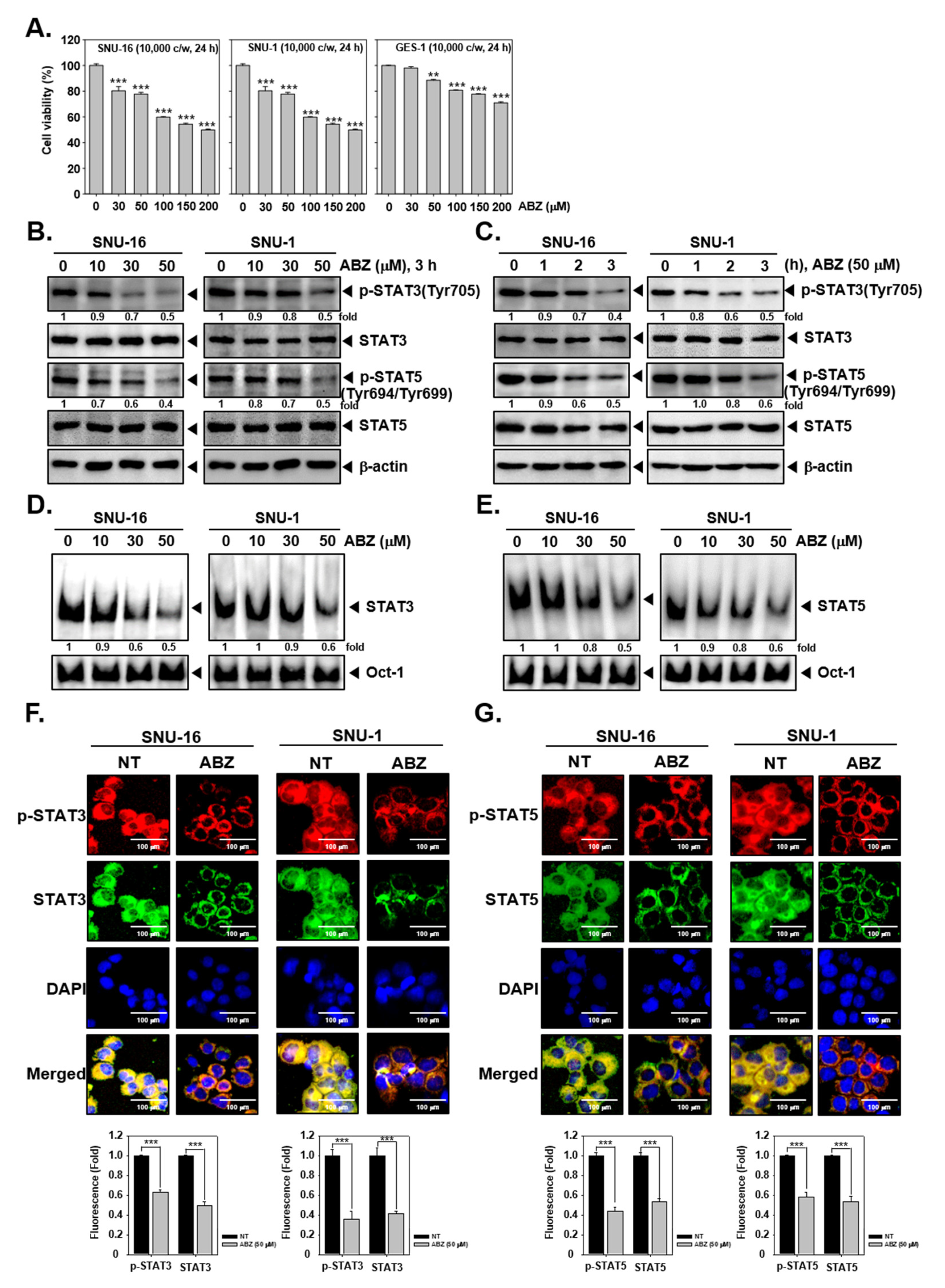
3.2. ABZ Substantially Affected STAT3 and STAT5 Phosphorylation
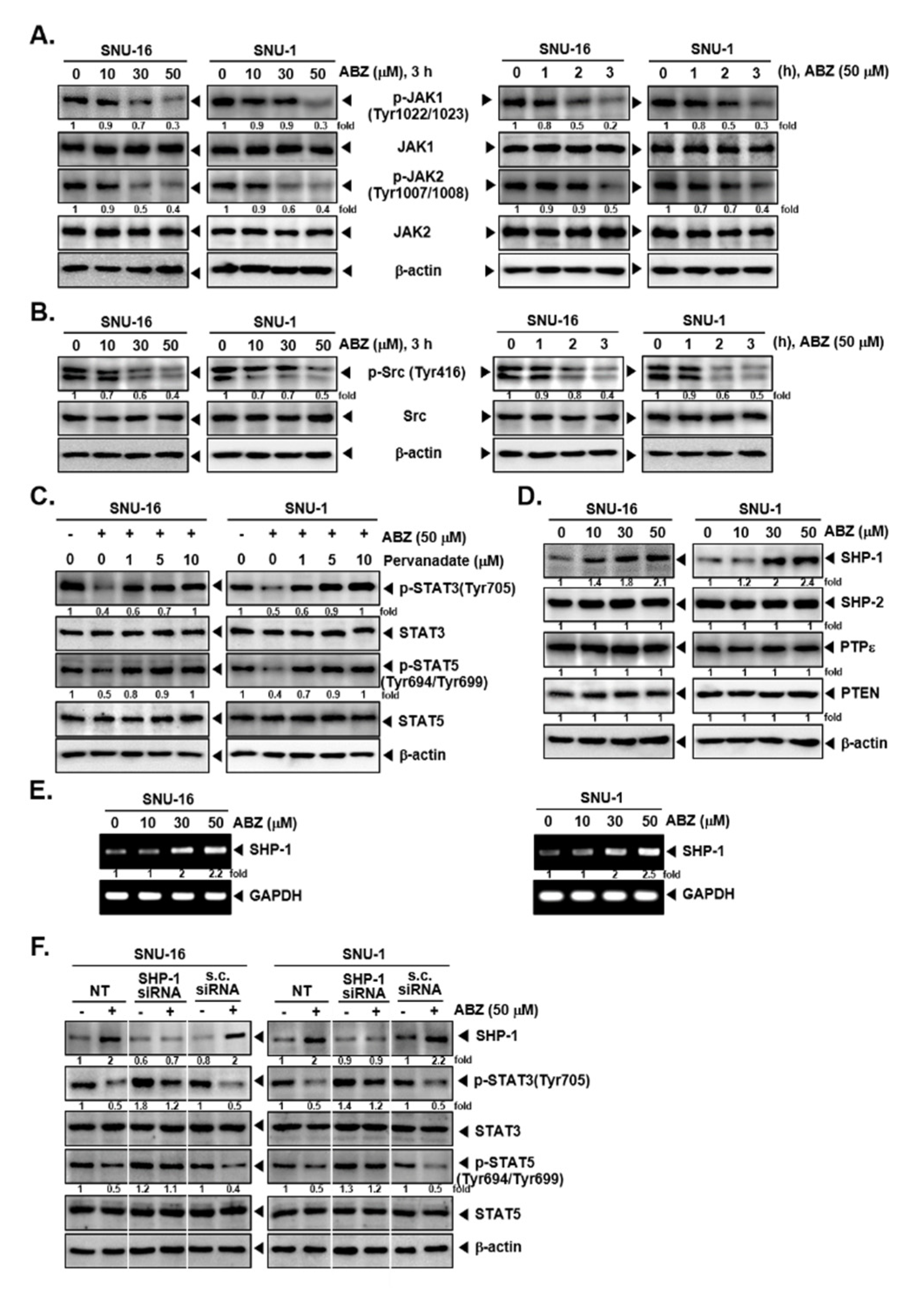
3.3. ABZ Alters Phosphorylation of JAK1/2 and Src Kinases
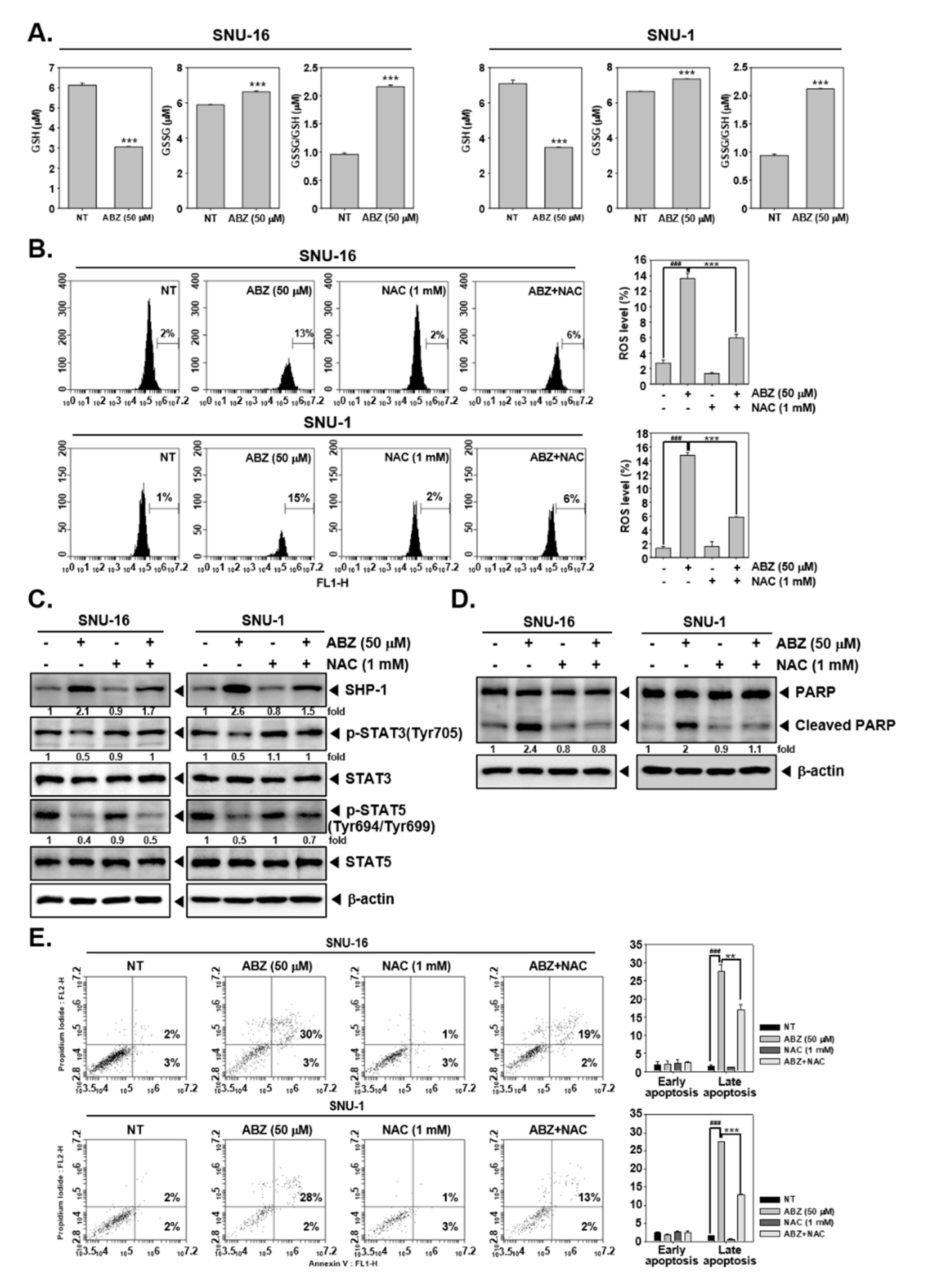
3.4. Tyrosine Phosphatases Affect STAT3/5 Modulatory Actions of ABZ
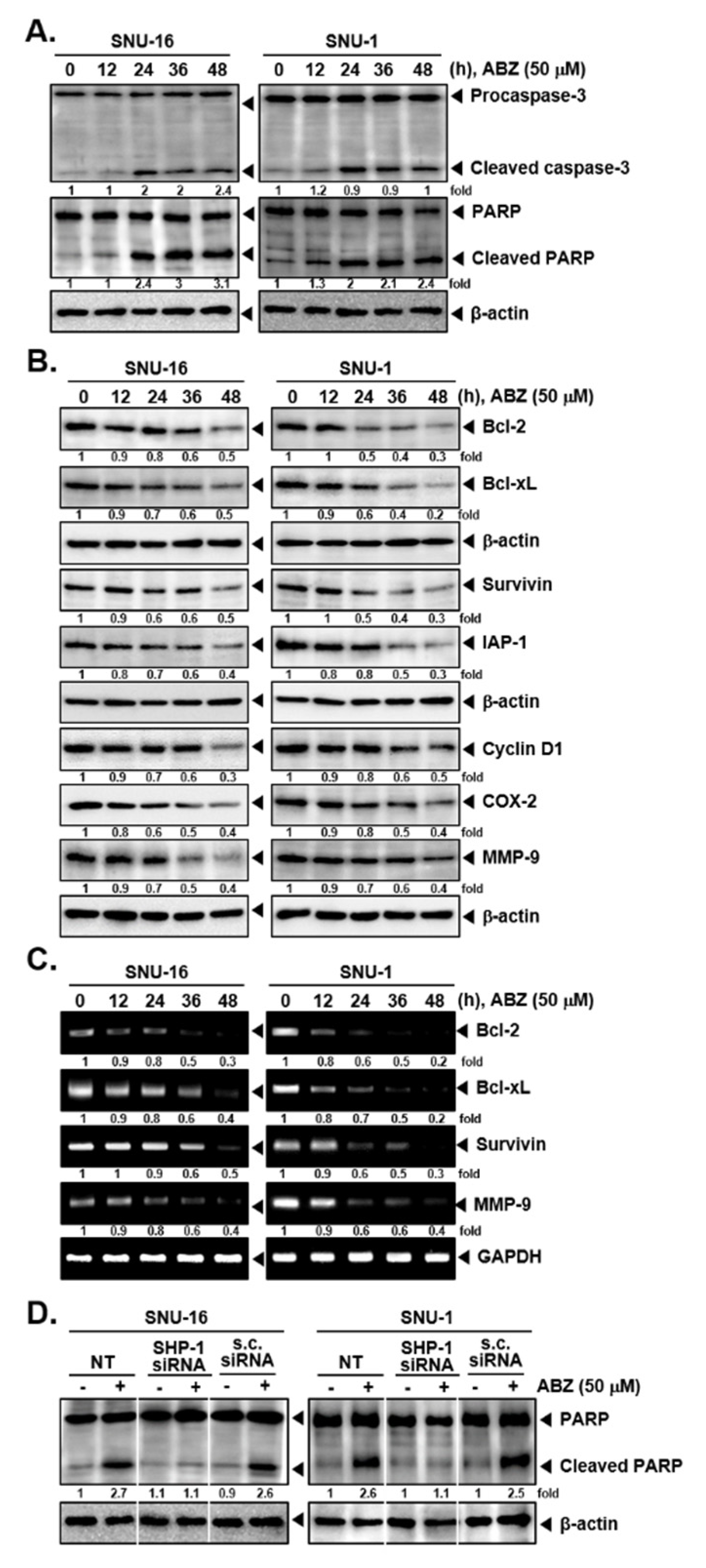
3.5. ABZ Alters the Levels of Various Oncogenic Proteins and Caused Apoptosis
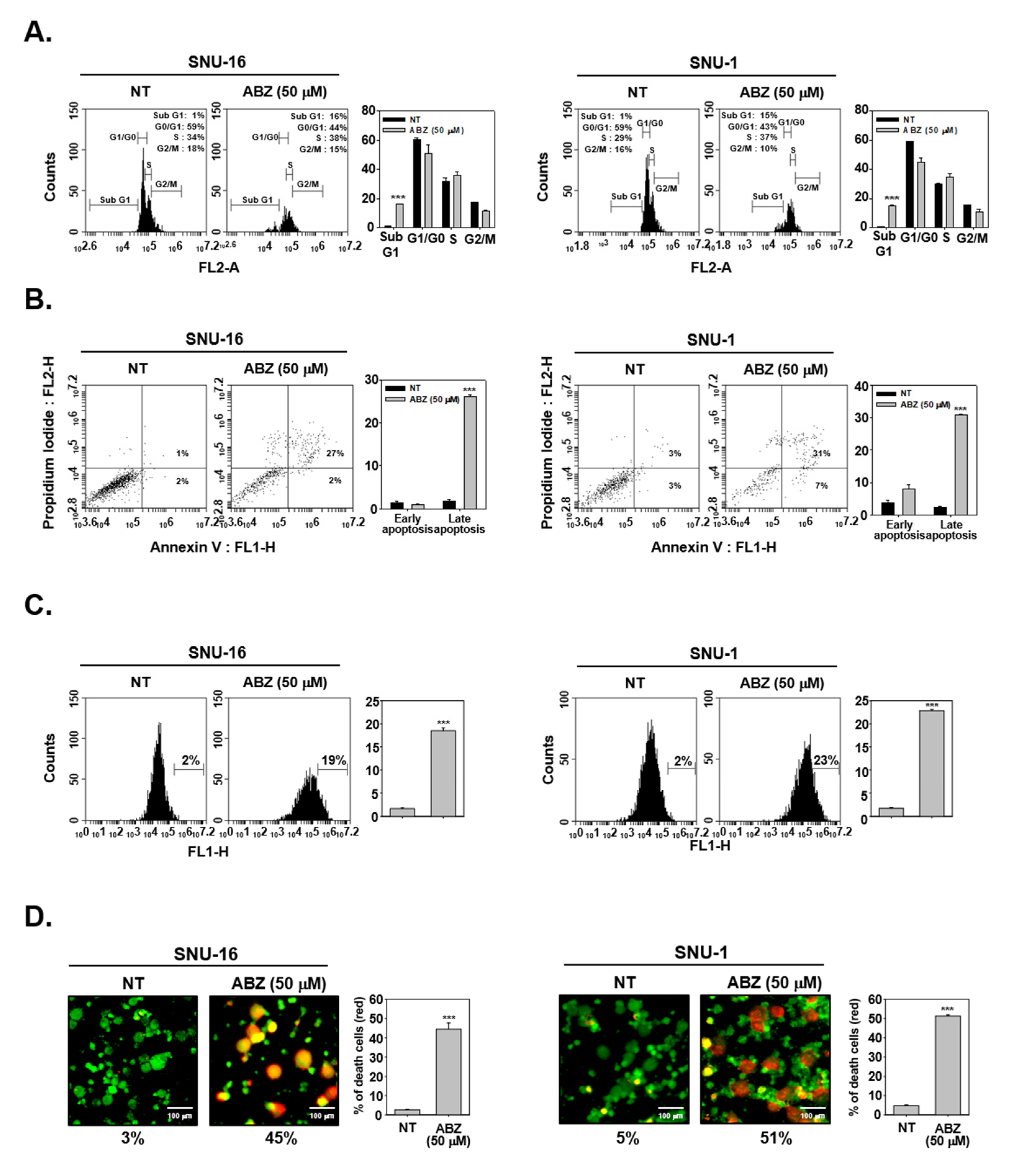
3.6. ABZ Induces Apoptotic Cell Death in Gastric Cancer Cells
3.7. ABZ Exhibits Anti-Neoplastic Effect through ROS-Mediated Events
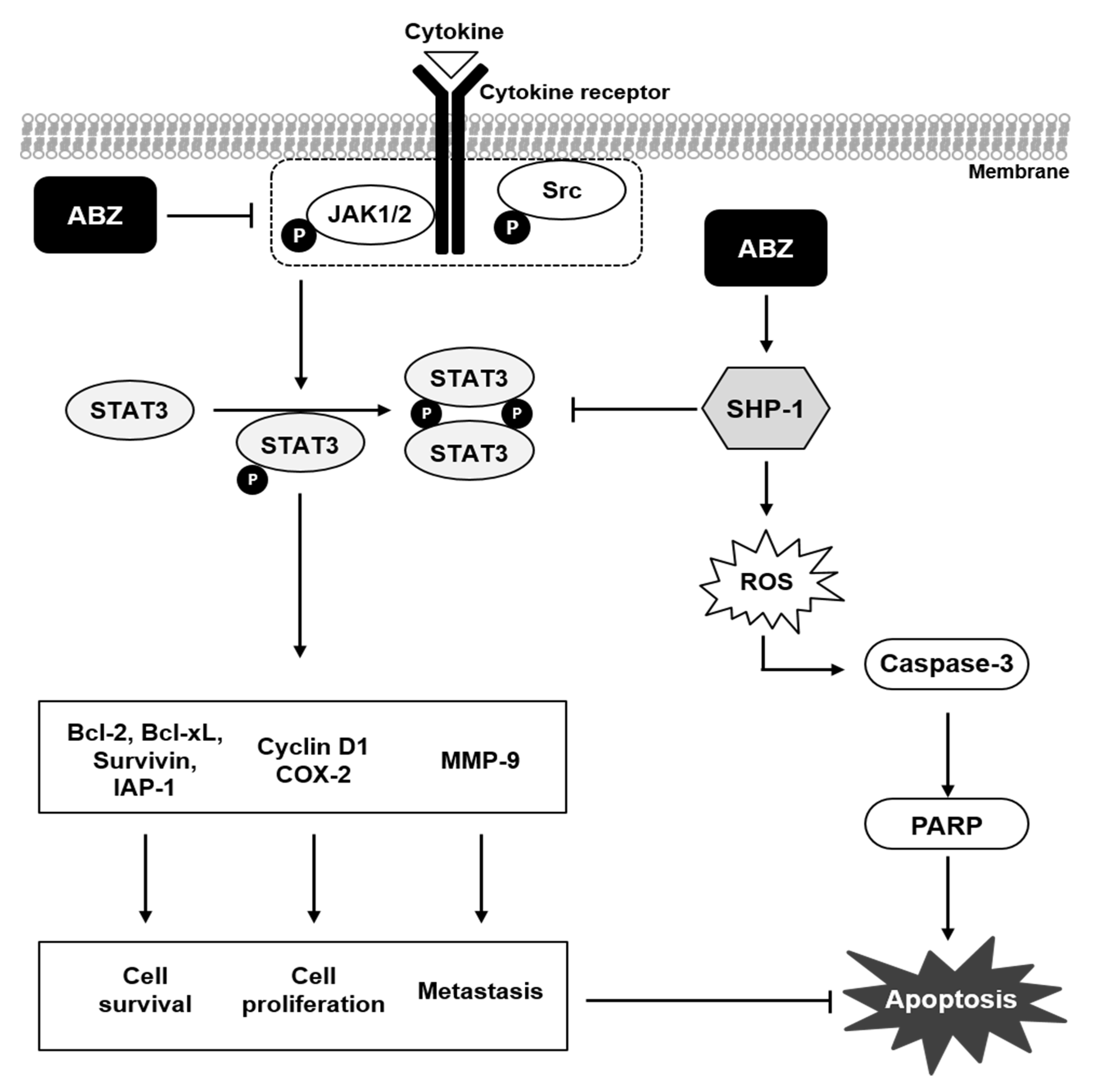
4. Discussions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ihle, J.N. STATs: Signal Transducers and Activators of Transcription. Cell 1996, 84, 331–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, M.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Bhardwaj, V.; Goel, A.; Gupta, R.; Sharma, A.; Baligar, P.; Kumar, A.P.; Goh, B.C.; Wang, L.; et al. The pleiotropic role of transcription factor STAT3 in oncogenesis and its targeting through natural products for cancer prevention and therapy. Med. Res. Rev. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Jove, R. The STATs of cancer—New molecular targets come of age. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, E.Z.P.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Arfuso, F.; Dharmarajan, A.; Wang, C.; Kumar, A.P.; Samy, R.P.; Lim, L.H.; Wang, L.; Goh, B.C.; et al. Targeting transcription factor STAT3 for cancer prevention and therapy. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 162, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furqan, M.; Mukhi, N.; Lee, B.; Liu, D. Dysregulation of JAK-STAT pathway in hematological malignancies and JAK inhibitors for clinical application. Biomark. Res. 2013, 1, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, A.L.; Hirpara, J.L.; Pervaiz, S.; Eu, J.-Q.; Sethi, G.; Goh, B.-C. Do STAT3 inhibitors have potential in the future for cancer therapy? Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2017, 26, 883–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashrafizadeh, M.; Ahmadi, Z.; Kotla, N.G.; Afshar, E.G.; Samarghandian, S.; Mandegary, A.; Pardakhty, A.; Mohammadinejad, R.; Sethi, G. Nanoparticles Targeting STATs in Cancer Therapy. Cells 2019, 8, 1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Lee, S.G.; Yang, W.M.; Arfuso, F.; Um, J.Y.; Kumar, A.P.; Bianc, J.; Kwang, G.S.; Ahnet, S. Formononetin-induced oxidative stress abrogates the activation of STAT3/5 signaling axis and suppresses the tumor growth in multiple myeloma preclinical model. Cancer Lett. 2018, 431, 123–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.T.; Um, J.-Y.; Chinnathambi, A.; Alharbi, S.A.; Narula, A.S.; Namjoshi, O.A.; Blough, B.E.; Ahn, K.S. Evodiamine Mitigates Cellular Growth and Promotes Apoptosis by Targeting the c-Met Pathway in Prostate Cancer Cells. Molecules 2020, 25, 1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Baek, S.H.; Um, J.Y.; Shim, B.S.; Ahn, K.S. Resveratrol attenuates constitutive STAT3 and STAT5 activation through induction of PTPepsilon and SHP-2 tyrosine phosphatases and potentiates sorafenib-induced apoptosis in renal cell carcinoma. BMC Nephrol. 2016, 17, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, A.; Sexl, V.; Valent, P.; Moriggl, R. Inhibition of STAT5: A therapeutic option in BCR-ABL1-driven leukemia. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 9564–9576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, A.; Murphy, J.J. STAT5 in Cancer and Immunity. J. Interf. Cytokine Res. 2016, 36, 226–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.H.; Jung, S.H.; Chinnathambi, A.; Alahmadi, T.A.; Alharbi, S.A.; Sethi, G.; Ahn, K.S. Attenuation of STAT3 Signaling Cascade by Daidzin Can Enhance the Apoptotic Potential of Bortezomib against Multiple Myeloma. Biomolecules 2019, 10, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Schaefer, T.S. ErbB-2 Activates Stat3α in a Src- and JAK2-dependent Manner. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 38486–38493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S.J.; A Snowden, J.; Zeidler, M.P.; Danson, S. The role of JAK/STAT signalling in the pathogenesis, prognosis and treatment of solid tumours. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 113, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loh, C.-Y.; Arya, A.; Naema, A.F.; Wong, W.F.; Sethi, G.; Looi, C.Y. Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription (STATs) Proteins in Cancer and Inflammation: Functions and Therapeutic Implication. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, Y.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Nam, D.; Narula, A.S.; Namjoshi, O.A.; Blough, B.E.; Um, J.-Y.; Sethi, G.; Ahn, K.S. Anti-myeloma Effects of Icariin Are Mediated Through the Attenuation of JAK/STAT3-Dependent Signaling Cascade. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Crowe, P.J.; Goldstein, D.; Yang, J.L. STAT3 inhibition, a novel approach to enhancing targeted therapy in human cancers (review). Int. J. Oncol. 2012, 41, 1181–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, S.H.; Lee, J.H.; Ko, J.-H.; Lee, H.; Nam, D.; Lee, S.G.; Yang, W.M.; Um, J.-Y.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.-H.; et al. Ginkgetin Blocks Constitutive STAT3 Activation and Induces Apoptosis through Induction of SHP-1 and PTEN Tyrosine Phosphatases. Phytotherapy Res. 2016, 30, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.-M.; Lee, J.H.; Sethi, G.; Kim, C.; Baek, S.H.; Nam, D.; Chung, W.-S.; Shim, B.S.; Ahn, K.S. Bergamottin, a natural furanocoumarin obtained from grapefruit juice induces chemosensitization and apoptosis through the inhibition of STAT3 signaling pathway in tumor cells. Cancer Lett. 2014, 354, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Amin, H.M.; Franko, B.; Frantz, C.; Shi, X.; Lai, R. Loss of SHP1 enhances JAK3/STAT3 signaling and decreases proteosome degradation of JAK3 and NPM-ALK in ALK+ anaplastic large-cell lymphoma. Blood 2006, 108, 2796–2803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Mohan, C.D.; Deivasigamani, A.; Jung, Y.Y.; Rangappa, S.; Basappa, S.; Chinnathambi, A.; Alahmadi, T.A.; Alharbi, S.A.; Garg, M.; et al. Brusatol suppresses STAT3-driven metastasis by downregulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Adv. Res. 2020, 26, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Mohan, C.D.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Rangappa, S.; Sethi, G.; Siveen, K.S.; Chinnathambi, A.; Alahmadi, T.A.; Alharbi, S.A.; Basappa, S.; et al. Vitexin abrogates invasion and survival of hepatocellular carcinoma cells through targeting STAT3 signaling pathway. Biochimie 2020, 175, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, Y.Y.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Narula, A.S.; Kim, C.; Lee, J.H.; Namjoshi, O.A.; Blough, B.E.; Sethi, G.; Ahn, K.S. Oxymatrine Attenuates Tumor Growth and Deactivates STAT5 Signaling in a Lung Cancer Xenograft Model. Cancers 2019, 11, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, S.T.; Kim, C.; Lee, J.H.; Chinnathambi, A.; Alharbi, S.A.; Shair, O.H.; Sethi, G.; Ahn, K.S. Cycloastragenol can negate constitutive STAT3 activation and promote paclitaxel-induced apoptosis in human gastric cancer cells. Phytomedicine 2019, 59, 152907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, C.D.; Rangappa, S.; Preetham, H.D.; Nayaka, S.C.; Gupta, V.K.; Basappa, S.; Sethi, G.; Rangappa, K.S. Targeting STAT3 signaling pathway in cancer by agents derived from Mother Nature. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Dikshit, R.; Eser, S.; Mathers, C.; Rebelo, M.; Parkin, D.M.; Forman, D.; Bray, F. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 136, E359–E386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonelli, P.; Borrelli, A.; Tuccillo, F.M.; Silvestro, L.; Palaia, R.; Buonaguro, F.M. Precision medicine in gastric cancer. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2019, 11, 804–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, S.C.; Kamangar, F.; Kim, M.P.; Hammoud, S.; Haque, R.; Maitra, A.; Montgomery, E.; Heitmiller, R.E.; Choti, M.A.; Lillemoe, K.D.; et al. Survival After Gastric Adenocarcinoma Resection: Eighteen-Year Experience at a Single Institution. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2005, 9, 718–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartgrink, H.H.; Jansen, E.P.; van Grieken, N.C.; van de Velde, C.J. Gastric cancer. Lancet 2009, 374, 477–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manu, K.A.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Ramachandran, L.; Li, F.; Siveen, K.S.; Chinnathambi, A.; Zayed, M.E.; Alharbib, S.A.; Alan, F.A.; Kumaret, P.; et al. Isorhamnetin augments the anti-tumor effect of capecitabine through the negative regulation of NF-kappaB signaling cascade in gastric cancer. Cancer Lett. 2015, 363, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, D.; Allum, W.H.; Stenning, S.P.; Thompson, J.N.; Van De Velde, C.J.; Nicolson, M.; Scarffe, J.H.; Lofts, F.J.; Falk, S.J.; Iveson, T.J.; et al. Perioperative Chemotherapy versus Surgery Alone for Resectable Gastroesophageal Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 355, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manu, K.A.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Li, F.; Chen, L.; Siveen, K.S.; Ahn, K.S.; Kumar, A.P.; Sethi, G. Simvastatin sensitizes human gastric cancer xenograft in nude mice to capecitabine by suppressing nuclear factor-kappa B-regulated gene products. J. Mol. Med. 2014, 92, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manu, K.A.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Ramachandran, L.; Li, F.; Fong, C.W.; Kumar, A.P.; Tan, P.; Sethi, G. First evidence that gamma-tocotrienol inhibits the growth of human gastric cancer and chemosensitizes it to capecitabine in a xenograft mouse model through the modulation of NF-kappaB pathway. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 2220–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.S.; Yap, W.N.; Arfuso, F.; Kar, S.; Wang, C.; Cai, W.; Dharmarajan, A.M.; Sethi, G.; Kumar, A.P. Targeting the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in gastric carcinoma: A reality for personalized medicine? World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 12261–12273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macdonald, J.S.; Smalley, S.R.; Benedetti, J.; Hundahl, S.A.; Estes, N.C.; Stemmermann, G.N.; Haller, D.G.; Ajani, J.A.; Gunderson, L.L.; Jessup, J.M.; et al. Chemoradiotherapy after Surgery Compared with Surgery Alone for Adenocarcinoma of the Stomach or Gastroesophageal Junction. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 345, 725–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siveen, K.S.; Sikka, S.; Surana, R.; Dai, X.; Zhang, J.; Kumar, A.P.; Tan, B.K.; Sethi, G.; Bishayee, A. Targeting the STAT3 signaling pathway in cancer: Role of synthetic and natural inhibitors. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Bioenerg. 2014, 1845, 136–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, Y.-S.; Yang, S.-F.; Sethi, G.; Shun-Fa, Y. Natural Bioactives in Cancer Treatment and Prevention. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 182835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Ho, P.C.-L.; Wong, F.C.; Sethi, G.; Wang, L.Z.; Goh, B.C. Garcinol: Current status of its anti-oxidative, anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer effects. Cancer Lett. 2015, 362, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tewari, D.; Nabavi, S.F.; Nabavi, S.M.; Sureda, A.; Farooqi, A.A.; Atanasov, A.G.; Vacca, R.A.; Sethi, G.; Bishayee, A. Targeting activator protein 1 signaling pathway by bioactive natural agents: Possible therapeutic strategy for cancer prevention and intervention. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 128, 366–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugam, M.K.; Ong, T.H.; Kumar, A.P.; Lun, C.K.; Ho, P.C.; Wong, P.T.H.; Hui, K.M.; Sethi, G. Ursolic Acid Inhibits the Initiation, Progression of Prostate Cancer and Prolongs the Survival of TRAMP Mice by Modulating Pro-Inflammatory Pathways. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e32476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upcroft, P.; Upcroft, J.A. Drug Targets and Mechanisms of Resistance in the Anaerobic Protozoa. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2001, 14, 150–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küster, T.; Stadelmann, B.; Aeschbacher, D.; Hemphill, A. Activities of fenbendazole in comparison with albendazole against Echinococcus multilocularis metacestodes in vitro and in a murine infection model. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2014, 43, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayan, A. Albendazole, mebendazole and praziquantel. Review of non-clinical toxicity and pharmacokinetics. Acta Trop. 2003, 86, 141–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourgholami, M.; Woon, L.; Almajd, R.; Akhter, J.; Bowery, P.; Morris, D. In vitro and in vivo suppression of growth of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by albendazole. Cancer Lett. 2001, 165, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourgholami, M.H.; Akhter, J.; Wang, L.; Lu, Y.; Morris, D.L. Antitumor activity of albendazole against the human colorectal cancer cell line HT-29: In vitro and in a xenograft model of peritoneal carcinomatosis. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2004, 55, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Du, J.; Wang, J. Albendazole inhibits HIF-1α-dependent glycolysis and VEGF expression in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2017, 428, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.-L.; Lian, D.-D.; Zhu, M.J.; Li, X.M.; Lee, J.K.; Yoon, T.-J.; Lee, J.-H.; Jiang, R.-H.; Kim, C.D. Antitumor Effect of Albendazole on Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC) Cells. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.-J.; Lee, Y.-C.; Huang, C.-H.; Shi, Y.-J.; Chen, Y.-J.; Pei, S.-N.; Chou, Y.-W.; Chang, L.-S. Non-mitotic effect of albendazole triggers apoptosis of human leukemia cells via SIRT3/ROS/p38 MAPK/TTP axis-mediated TNF-α upregulation. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2019, 162, 154–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, C.; Baek, S.H.; Ko, J.-H.; Lee, S.G.; Yang, W.M.; Um, J.-Y.; Sethi, G.; Ahn, K.S. Capsazepine inhibits JAK/STAT3 signaling, tumor growth, and cell survival in prostate cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 8, 17700–17711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, Y.Y.; Um, J.-Y.; Narula, A.S.; Namjoshi, O.A.; Blough, B.E.; Kumar, A.P.; Ahn, K.S. Identification of Matrine as a Novel Regulator of the CXCR4 Signaling Axis in Tumor Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.; Cho, S.K.; Kapoor, S.; Kumar, A.; Vali, S.; Abbasi, T.; Hoon Kim, S.-H.; Sethi, G.; Ahn, K.S. beta-Caryophyllene oxide inhibits constitutive and inducible STAT3 signaling pathway through induction of the SHP-1 protein tyrosine phosphatase. Mol. Carcinog. 2014, 53, 793–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, C.; Kim, S.-H.; Sethi, G.; Ahn, K.S. Farnesol inhibits tumor growth and enhances the anticancer effects of bortezomib in multiple myeloma xenograft mouse model through the modulation of STAT3 signaling pathway. Cancer Lett. 2015, 360, 280–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.H.; Baek, S.H.; Um, J.-Y.; Ahn, K.S. Anti-neoplastic Effect of Ginkgolide C through Modulating c-Met Phosphorylation in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, C.; Sethi, G.; Ahn, K.S. Brassinin inhibits STAT3 signaling pathway through modulation of PIAS-3 and SOCS-3 expression and sensitizes human lung cancer xenograft in nude mice to paclitaxel. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 6386–6405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Mohan, C.D.; Basappa, S.; Rangappa, S.; Chinnathambi, A.; Alahmadi, T.A.; Alharbi, S.A.; Kumar, A.P.; Sethi, G.; Ahn, K.S.; et al. The IkappaB Kinase Inhibitor ACHP Targets the STAT3 Signaling Pathway in Human Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma Cells. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.; A Doudican, N.; Schiff, P.B.; Orlow, S.J. Albendazole sensitizes cancer cells to ionizing radiation. Radiat. Oncol. 2011, 6, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, A.; Borghouts, C.; Brendel, C.; Moriggl, R.; Delis, N.; Brill, B.; Vafaizadeh, V.; Groner, B. The Inhibition of Stat5 by a Peptide Aptamer Ligand Specific for the DNA Binding Domain Prevents Target Gene Transactivation and the Growth of Breast and Prostate Tumor Cells. Pharmaceuticals 2013, 6, 960–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furtek, S.L.; Backos, D.S.; Matheson, C.J.; Reigan, P. Strategies and Approaches of Targeting STAT3 for Cancer Treatment. ACS Chem. Biol. 2016, 11, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, R.; Bowman, T.L.; Niu, G.; Yu, H.; Minton, S.; A Muro-Cacho, C.; E Cox, C.; Falcone, R.; Fairclough, R.; Parsons, S.; et al. Constitutive activation of Stat3 by the Src and JAK tyrosine kinases participates in growth regulation of human breast carcinoma cells. Oncogene 2001, 20, 2499–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenev, T.; Böhmer, S.A.; Kaufmann, R.; Frese, S.; Bittorf, T.; Beckers, T.; Böhmer, F.D. Perinuclear localization of the protein-tyrosine phosphatase SHP-1 and inhibition of epidermal growth factor-stimulated STAT1/3 activation in A431 cells. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2000, 79, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Baumann, H. Dual Signaling Role of the Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase SHP-2 in Regulating Expression of Acute-Phase Plasma Proteins by Interleukin-6 Cytokine Receptors in Hepatic Cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1999, 19, 5326–5338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.; Steinberg, B.M. PTEN is a negative regulator of STAT3 activation in human papillomavirus-infected cells. J. Gen. Virol. 2002, 83, 1651–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, S.H.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, C.; Ko, J.-H.; Ryu, S.-H.; Lee, S.-G.; Yang, W.M.; Um, J.-Y.; Chinnathambi, A.; Alharbi, S.A.; et al. Ginkgolic Acid C 17:1, Derived from Ginkgo biloba Leaves, Suppresses Constitutive and Inducible STAT3 Activation through Induction of PTEN and SHP-1 Tyrosine Phosphatase. Molecules 2017, 22, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Chiang, S.Y.; Nam, D.; Chung, W.S.; Lee, J.; Na, Y.S.; Sethi, G.; Ahn, K.S. Capillarisin inhibits constitutive and inducible STAT3 activation through induction of SHP-1 and SHP-2 tyrosine phosphatases. Cancer Lett. 2014, 345, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Weng, Z.; Xu, C. Albendazole suppresses cell proliferation and migration and induces apoptosis in human pancreatic cancer cells. Anti-Cancer Drugs 2020, 31, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirtonia, A.; Sethi, G.; Garg, M. The multifaceted role of reactive oxygen species in tumorigenesis. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2020, 77, 4459–4483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.C.; Hevia, D.; Patchva, S.; Park, B.; Koh, W.; Aggarwal, B.B. Upsides and Downsides of Reactive Oxygen Species for Cancer: The Roles of Reactive Oxygen Species in Tumorigenesis, Prevention, and Therapy. Antioxidants Redox Signal. 2012, 16, 1295–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryter, S.W.; Kim, H.P.; Hoetzel, A.; Park, J.W.; Nakahira, K.; Wang, X.; Choi, A.M.K. Mechanisms of Cell Death in Oxidative Stress. Antioxidants Redox Signal. 2007, 9, 49–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, C.; Lee, S.-G.; Sethi, G.; Ahn, K.S. Ophiopogonin D, a Steroidal Glycoside Abrogates STAT3 Signaling Cascade and Exhibits Anti-Cancer Activity by Causing GSH/GSSG Imbalance in Lung Carcinoma. Cancers 2018, 10, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruber, R.C.; LaRocca, D.; Minchenberg, S.B.; Christophi, G.P.; Hudson, C.A.; Ray, A.K.; Shafit-Zagardo, B.; Massa, P.T. The control of reactive oxygen species production by SHP-1 in oligodendrocytes. Glia 2015, 63, 1753–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krötz, F.; Engelbrecht, B.; Buerkle, M.A.; Bassermann, F.; Bridell, H.; Gloe, T.; Duyster, J.; Pohl, U.; Sohn, H.-Y. The Tyrosine Phosphatase, SHP-1, Is a Negative Regulator of Endothelial Superoxide Formation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2005, 45, 1700–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, M.H.; Ha, I.J.; Um, J.-Y.; Ahn, K.S. Albendazole Exhibits Anti-Neoplastic Actions against Gastric Cancer Cells by Affecting STAT3 and STAT5 Activation by Pleiotropic Mechanism(s). Biomedicines 2021, 9, 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9040362
Yang MH, Ha IJ, Um J-Y, Ahn KS. Albendazole Exhibits Anti-Neoplastic Actions against Gastric Cancer Cells by Affecting STAT3 and STAT5 Activation by Pleiotropic Mechanism(s). Biomedicines. 2021; 9(4):362. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9040362
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Min Hee, In Jin Ha, Jae-Young Um, and Kwang Seok Ahn. 2021. "Albendazole Exhibits Anti-Neoplastic Actions against Gastric Cancer Cells by Affecting STAT3 and STAT5 Activation by Pleiotropic Mechanism(s)" Biomedicines 9, no. 4: 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9040362
APA StyleYang, M. H., Ha, I. J., Um, J.-Y., & Ahn, K. S. (2021). Albendazole Exhibits Anti-Neoplastic Actions against Gastric Cancer Cells by Affecting STAT3 and STAT5 Activation by Pleiotropic Mechanism(s). Biomedicines, 9(4), 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9040362







