Typical Pediatric Brain Tumors Occurring in Adults—Differences in Management and Outcome
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Medulloblastoma
2.1. Incidence and Classification
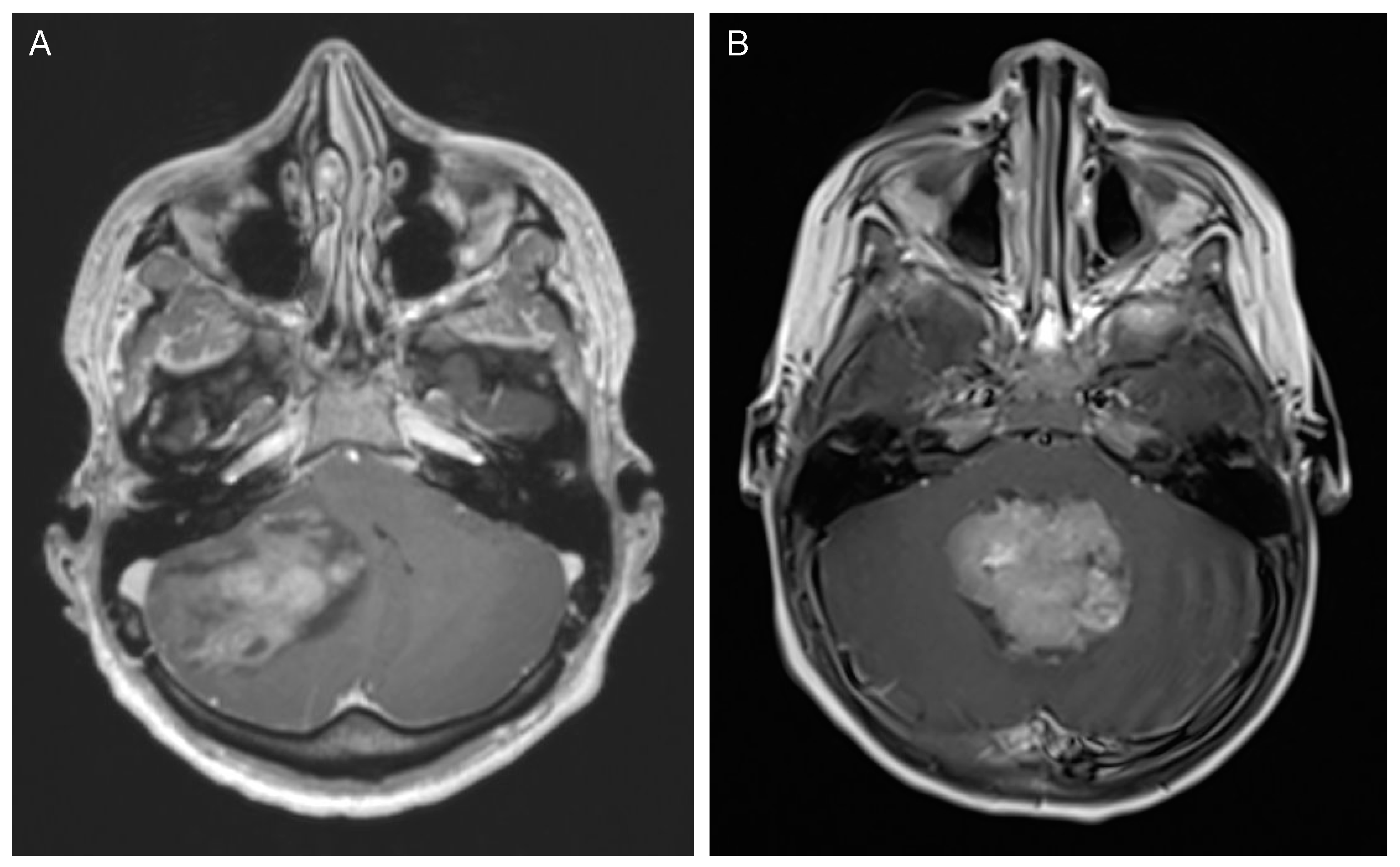
2.2. Clinical Presentation and Diagnostic Tools
2.3. Management and Outcome
3. Pilocytic Astrocytoma
3.1. Incidence and Classification
3.2. Clinical Presentation
3.3. Management and Outcome
4. Craniopharyngioma
4.1. Incidence and Classification
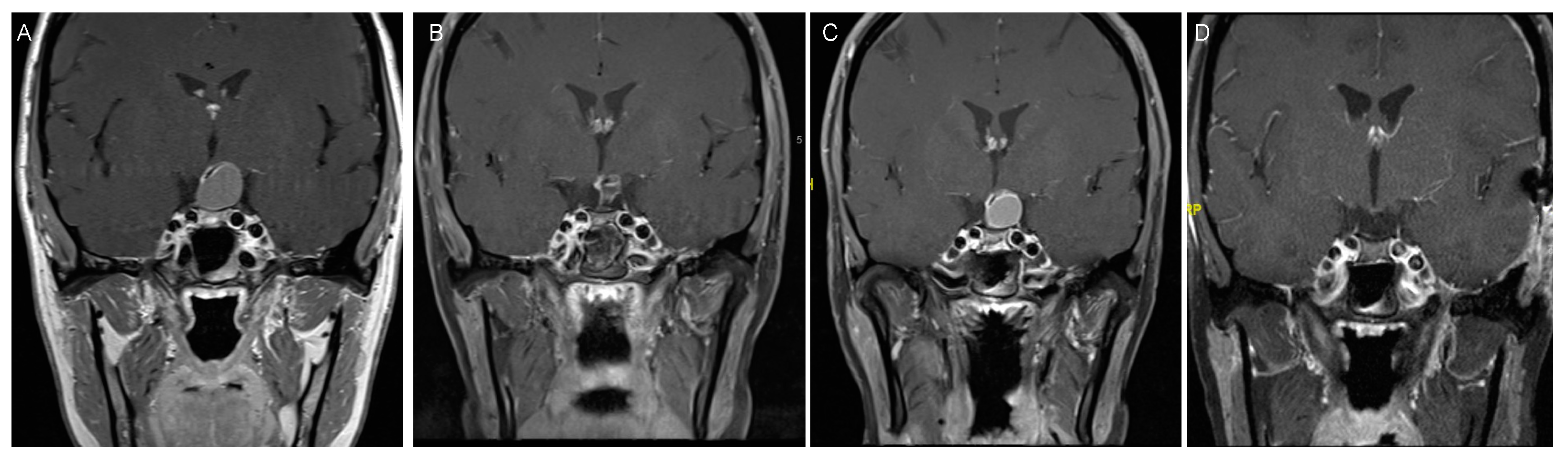
4.2. Clinical Presentation
4.3. Treatment Strategies and Outcome
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Gittleman, H.; Truitt, G.; Boscia, A.; Kruchko, C.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S. CBTRUS Statistical Report: Primary Brain and Other Central Nervous System Tumors Diagnosed in the United States in 2011–2015. Neuro-Oncology 2018, 20, iv1–iv86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franceschi, E.; Hofer, S.; Brandes, A.A.; Frappaz, D.; Kortmann, R.-D.; Bromberg, J.; Dangouloff-Ros, V.; Boddaert, N.; Hattingen, E.; Wiestler, B.; et al. EANO–EURACAN Clinical Practice Guideline for Diagnosis, Treatment, and Follow-up of Post-Pubertal and Adult Patients with Medulloblastoma. Lancet Oncol 2019, 20, e715–e728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, T.; Trippel, M.; Tacke, U.; van Velthoven, V.; Gumpp, V.; Bartelt, S.; Ostertag, C.; Nikkhah, G. Neurosurgical Treatment Strategies in Childhood Craniopharyngiomas: Is Less More? Child’s Nerv Syst 2009, 25, 1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calaminus, G.; Frappaz, D.; Kortmann, R.D.; Krefeld, B.; Saran, F.; Pietsch, T.; Vasiljevic, A.; Garre, M.L.; Ricardi, U.; Mann, J.R.; et al. Outcome of Patients with Intracranial Non-Germinomatous Germ Cell Tumors—Lessons from the SIOP-CNS-GCT-96 Trial. Neuro-oncology 2017, 19, 1661–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabash, M.A. Characteristics, Survival and Incidence Rates and Trends of Pilocytic Astrocytoma in Children in the United States; SEER-Based Analysis. J. Neurol. Sci. 2019, 400, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, D.R.; Brown, P.D.; Galanis, E.; Hammack, J.E. Pilocytic Astrocytoma Survival in Adults: Analysis of the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program of the National Cancer Institute. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2012, 108, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juraschka, K.; Taylor, M.D. Medulloblastoma in the Age of Molecular Subgroups: A Review: JNSPG 75th Anniversary Invited Review Article. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2019, 24, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carta, R.; Del Baldo, G.; Miele, E.; Po, A.; Besharat, Z.M.; Nazio, F.; Colafati, G.S.; Piccirilli, E.; Agolini, E.; Rinelli, M.; et al. Cancer Predisposition Syndromes and Medulloblastoma in the Molecular Era. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 566822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, R.M.; Richardson, S.; Schwalbe, E.C.; Hicks, D.; Lindsey, J.C.; Crosier, S.; Rafiee, G.; Grabovska, Y.; Wharton, S.B.; Jacques, T.S.; et al. Time, Pattern, and Outcome of Medulloblastoma Relapse and Their Association with Tumour Biology at Diagnosis and Therapy: A Multicentre Cohort Study. Lancet Child Adolesc. Health 2020, 4, 865–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.H.; Housepian, E.M.; Herbert, C. An Operative Staging System and a Megavoltage Radiotherapeutic Technic for Cerebellar Medulloblastomas. Radiology 1969, 93, 1351–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padovani, L.; Sunyach, M.-P.; Perol, D.; Mercier, C.; Alapetite, C.; Haie-Meder, C.; Hoffstetter, S.; Muracciole, X.; Kerr, C.; Wagner, J.-P.; et al. Common Strategy for Adult and Pediatric Medulloblastoma: A Multicenter Series of 253 Adults. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2007, 68, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandes, A.A.; Franceschi, E.; Tosoni, A.; Blatt, V.; Ermani, M. Long-term Results of a Prospective Study on the Treatment of Medulloblastoma in Adults. Cancer 2007, 110, 2035–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Reifenberger, G.; von Deimling, A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Cavenee, W.K.; Ohgaki, H.; Wiestler, O.D.; Kleihues, P.; Ellison, D.W. The 2016 World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A Summary. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 131, 803–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giangaspero, F.; Perilongo, G.; Fondelli, M.P.; Brisigotti, M.; Carollo, C.; Burnelli, R.; Burger, P.C.; Garrè, M.L. Medulloblastoma with Extensive Nodularity: A Variant with Favorable Prognosis. J.Neurosurg. 1999, 91, 971–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orr, B.A. Pathology, Diagnostics, and Classification of Medulloblastoma. Brain Pathol. 2020, 30, 664–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louis, D.N.; Ohgaki, H.; Wiestler, O.D.; Cavenee, W.K.; Burger, P.C.; Jouvet, A.; Scheithauer, B.W.; Kleihues, P. The 2007 WHO Classification of Tumours of the Central Nervous System. Acta Neuropathol. 2007, 114, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capozza, M.A.; Trombatore, G.; Triarico, S.; Mastrangelo, S.; Attinà, G.; Maurizi, P.; Ruggiero, A. Adult Medulloblastoma: An Overview on Current and Future Strategies of Treatment. Expert Opin. Orphan D 2019, 7, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramaswamy, V.; Remke, M.; Bouffet, E.; Bailey, S.; Clifford, S.C.; Doz, F.; Kool, M.; Dufour, C.; Vassal, G.; Milde, T.; et al. Risk Stratification of Childhood Medulloblastoma in the Molecular Era: The Current Consensus. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 131, 821–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, T.; Schwalbe, E.C.; Williamson, D.; Sill, M.; Hovestadt, V.; Mynarek, M.; Rutkowski, S.; Robinson, G.W.; Gajjar, A.; Cavalli, F.; et al. Second-Generation Molecular Subgrouping of Medulloblastoma: An International Meta-Analysis of Group 3 and Group 4 Subtypes. Acta Neuropathol. 2019, 138, 309–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Arcy, C.E.; Nobre, L.F.; Arnaldo, A.; Ramaswamy, V.; Taylor, M.D.; Naz-Hazrati, L.; Hawkins, C.E. Immunohistochemical and NanoString-Based Subgrouping of Clinical Medulloblastoma Samples. J Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2020, 79, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellison, D.W.; Dalton, J.; Kocak, M.; Nicholson, S.L.; Fraga, C.; Neale, G.; Kenney, A.M.; Brat, D.J.; Perry, A.; Yong, W.H.; et al. Medulloblastoma: Clinicopathological Correlates of SHH, WNT, and Non-SHH/WNT Molecular Subgroups. Acta Neuropathol. 2011, 121, 381–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, F.; Ohgaki, H.; Xu, L.; Giangaspero, F.; Li, C.; Li, P.; Yang, Z.; Wang, B.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; et al. Molecular Subgroups of Adult Medulloblastoma: A Long-Term Single-Institution Study. Neuro-Oncology 2016, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remke, M.; Hielscher, T.; Northcott, P.A.; Witt, H.; Ryzhova, M.; Wittmann, A.; Benner, A.; von Deimling, A.; Scheurlen, W.; Perry, A.; et al. Adult Medulloblastoma Comprises Three Major Molecular Variants. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 2717–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, G.C.-H.; Li, K.K.-W.; Wang, W.-W.; Liu, A.P.-Y.; Huang, Q.J.; Chan, A.K.-Y.; Poon, M.F.-M.; Chung, N.Y.-F.; Wong, Q.H.-W.; Chen, H.; et al. Clinical and Mutational Profiles of Adult Medulloblastoma Groups. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2020, 8, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kool, M.; Korshunov, A.; Pfister, S.M. Update on Molecular and Genetic Alterations in Adult Medulloblastoma. MEMO Mag. Eur. Med. Oncol. 2012, 5, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Northcott, P.A.; Korshunov, A.; Witt, H.; Hielscher, T.; Eberhart, C.G.; Mack, S.; Bouffet, E.; Clifford, S.C.; Hawkins, C.E.; French, P.; et al. Medulloblastoma Comprises Four Distinct Molecular Variants. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 29, 1408–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franceschi, E.; Minichillo, S.; Mura, A.; Tosoni, A.; Mascarin, M.; Tomasello, C.; Bartolini, S.; Brandes, A.A. Adjuvant Chemotherapy in Average-Risk Adult Medulloblastoma Patients Improves Survival: A Long Term Study. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Bueren, A.O.; Friedrich, C.; von Hoff, K.; Kwiecien, R.; Müller, K.; Pietsch, T.; Warmuth-Metz, M.; Hau, P.; Benesch, M.; Kuehl, J.; et al. Metastatic Medulloblastoma in Adults: Outcome of Patients Treated According to the HIT2000 Protocol. Eur. J. Cancer 2015, 51, 2434–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabori, U.; Sung, L.; Hukin, J.; Laperriere, N.; Crooks, B.; Carret, A.-S.; Silva, M.; Odame, I.; Mpofu, C.; Strother, D.; et al. Medulloblastoma in the Second Decade of Life: A Specific Group with Respect to Toxicity and Management. Cancer 2005, 103, 1874–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Song, Q.; Day, B.W. Phase I and Phase II Sonidegib and Vismodegib Clinical Trials for the Treatment of Paediatric and Adult MB Patients: A Systemic Review and Meta-Analysis. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2019, 7, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packer, R.J.; Sutton, L.N.; Goldwein, J.W.; Perilongo, G.; Bunin, G.; Ryan, J.; Cohen, B.H.; D’Angio, G.; Kramer, E.D.; Zimmerman, R.A.; et al. Improved Survival with the Use of Adjuvant Chemotherapy in the Treatment of Medulloblastoma. J. Neurosurg. 1991, 74, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Bueren, A.O.; von Hoff, K.; Pietsch, T.; Gerber, N.U.; Warmuth-Metz, M.; Deinlein, F.; Zwiener, I.; Faldum, A.; Fleischhack, G.; Benesch, M.; et al. Treatment of Young Children with Localized Medulloblastoma by Chemotherapy Alone: Results of the Prospective, Multicenter Trial HIT 2000 Confirming the Prognostic Impact of Histology. Neuro-Oncology 2011, 13, 669–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ang, C.; Hauerstock, D.; Guiot, M.; Kasymjanova, G.; Roberge, D.; Kavan, P.; Muanza, T. Characteristics and Outcomes of Medulloblastoma in Adults. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2008, 51, 603–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brasme, J.-F.; Chalumeau, M.; Doz, F.; Lacour, B.; Valteau-Couanet, D.; Gaillard, S.; Delalande, O.; Aghakhani, N.; Sainte-Rose, C.; Puget, S.; et al. Interval between Onset of Symptoms and Diagnosis of Medulloblastoma in Children: Distribution and Determinants in a Population-Based Study. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2012, 171, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunschner, L.J.; Kuttesch, J.; Hess, K.; Yung, W.K.A. Survival and Recurrence Factors in Adult Medulloblastoma: The M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Experience from 1978 to 1998. Neuro-Oncology 2001, 3, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fattal-Valevski, A.; Nissan, N.; Kramer, U.; Constantini, S. Seizures as the Clinical Presenting Symptom in Children with Brain Tumors. J. Child Neurol. 2012, 28, 292–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majd, N.; Penas-Prado, M. Updates on Management of Adult Medulloblastoma. Curr. Treat. Option Oncol. 2019, 20, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, K.E.; Vezina, G.; Poussaint, T.Y.; Warmuth-Metz, M.; Chamberlain, M.C.; Packer, R.J.; Brandes, A.A.; Reiss, M.; Goldman, S.; Fisher, M.J.; et al. Response Assessment in Medulloblastoma and Leptomeningeal Seeding Tumors: Recommendations from the Response Assessment in Pediatric Neuro-Oncology Committee. Neuro-Oncology 2017, 20, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, C.; Ramaswamy, V.; Kulkarni, A.V.; Rutka, J.T.; Remke, M.; Tabori, U.; Hawkins, C.; Bouffet, E.; Taylor, M.D. Clinical Implications of Medulloblastoma Subgroups: Incidence of CSF Diversion Surgery. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2015, 15, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangubat, E.Z.; Chan, M.; Ruland, S.; Roitberg, B.Z. Hydrocephalus in Posterior Fossa Lesions: Ventriculostomy and Permanent Shunt Rates by Diagnosis. Neurol. Res. 2009, 31, 668–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, S.-Y.; Dubinski, D.; Behmanesh, B.; Bernstock, J.D.; Seifert, V.; Konczalla, J.; Tritt, S.; Senft, C.; Gessler, F. Management of Hydrocephalus after Resection of Posterior Fossa Lesions in Pediatric and Adult Patients—Predictors for Development of Hydrocephalus. Neurosurg. Rev. 2020, 43, 1143–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riva-Cambrin, J.; Detsky, A.S.; Lamberti-Pasculli, M.; Sargent, M.A.; Armstrong, D.; Moineddin, R.; Cochrane, D.D.; Drake, J.M. Predicting Postresection Hydrocephalus in Pediatric Patients with Posterior Fossa Tumors. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. PED 2009, 3, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, E.M.; Hielscher, T.; Bouffet, E.; Remke, M.; Luu, B.; Gururangan, S.; McLendon, R.E.; Bigner, D.D.; Lipp, E.S.; Perreault, S.; et al. Prognostic Value of Medulloblastoma Extent of Resection after Accounting for Molecular Subgroup: A Retrospective Integrated Clinical and Molecular Analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 484–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wibroe, M.; Rochat, P.; Juhler, M. Cerebellar Mutism Syndrome and Other Complications After Surgery in the Posterior Fossa in Adults: A Prospective Study. World Neurosurg. 2018, 110, e738–e746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmahmann, J.D. Pediatric Post-Operative Cerebellar Mutism Syndrome, Cerebellar Cognitive Affective Syndrome, and Posterior Fossa Syndrome: Historical Review and Proposed Resolution to Guide Future Study. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2020, 36, 1205–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buglione, M.; Ghirardelli, P.; Triggiani, L.; Pedretti, S.; Pasinetti, N.; De Bari, B.; Tonoli, S.; Borghetti, P.; Spiazzi, L.; Magrini, S.M. Radiotherapy for Adult Medulloblastoma: Long Term Result from a Single Institution. A Review of Prognostic Factors and Why We Do Need a Multi-Institutional Cooperative Program. Rep. Pract. Oncol. Radiother. 2015, 20, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, C. Treatment of Adult Nonmetastatic Medulloblastoma Patients According to the Paediatric HIT 2000 Protocol: A Prospective Observational Multicentre Study. Eur. J. Cancer 2013, 49, 893–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacDonald, T.J.; Aguilera, D.; Castellino, R.C. The Rationale for Targeted Therapies in Medulloblastoma. Neuro-Oncology 2014, 16, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Garancher, A.; Ramaswamy, V.; Wechsler-Reya, R.J. Medulloblastoma: From Molecular Subgroups to Molecular Targeted Therapies. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2015, 41, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieran, M.W.; Chisholm, J.; Casanova, M.; Brandes, A.A.; Aerts, I.; Bouffet, E.; Bailey, S.; Leary, S.; MacDonald, T.J.; Mechinaud, F.; et al. Phase I Study of Oral Sonidegib (LDE225) in Pediatric Brain and Solid Tumors and a Phase II Study in Children and Adults with Relapsed Medulloblastoma. Neuro-Oncology 2017, 19, 1542–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, G.W.; Orr, B.A.; Wu, G.; Gururangan, S.; Lin, T.; Qaddoumi, I.; Packer, R.J.; Goldman, S.; Prados, M.D.; Desjardins, A.; et al. Vismodegib Exerts Targeted Efficacy Against Recurrent Sonic Hedgehog–Subgroup Medulloblastoma: Results From Phase II Pediatric Brain Tumor Consortium Studies PBTC-025B and PBTC-032. JCO 2015, 33, 2646–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segal, D.; Karajannis, M.A. Pediatric Brain Tumors: An Update. Curr. Probl. Pediatr. Adolesc. Health Care 2016, 46, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobbous, M.; Bernstock, J.D.; Coffee, E.; Friedman, G.K.; Metrock, L.K.; Chagoya, G.; Elsayed, G.; Nakano, I.; Hackney, J.R.; Korf, B.R.; et al. An Update on Neurofibromatosis Type 1-Associated Gliomas. Cancers 2020, 12, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Angelo, F.; Ceccarelli, M.; Tala; Garofano, L.; Zhang, J.; Frattini, V.; Caruso, F.P.; Lewis, G.; Alfaro, K.D.; Bauchet, L.; et al. The Molecular Landscape of Glioma in Patients with Neurofibromatosis 1. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkhard, C.; Patre, P.-L.D.; Schüler, D.; Schüler, G.; Yaşargil, M.G.; Yonekawa, Y.; Lütolf, U.M.; Kleihues, P.; Ohgaki, H. A Population-Based Study of the Incidence and Survival Rates in Patients with Pilocytic Astrocytoma. J. Neurosurg. 2003, 98, 1170–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theeler, B.J.; Ellezam, B.; Sadighi, Z.S.; Mehta, V.; Tran, M.D.; Adesina, A.M.; Bruner, J.M.; Puduvalli, V.K. Adult Pilocytic Astrocytomas: Clinical Features and Molecular Analysis. Neuro-Oncology 2014, 16, 841–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salles, D.; Laviola, G. Pilocytic Astrocytoma: A Review of General, Clinical, and Molecular Characteristics. J. Child Neurol. 2020, 35, 852–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soleman, J.; Kozyrev, D.A.; Ben-Sira, L.; Constantini, S.; Roth, J. Management of Incidental Brain Tumors in Children: A Systematic Review. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2020, 36, 1607–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleman, J.; Roth, J.; Ram, Z.; Yalon, M.; Constantini, S. Malignant Transformation of a Conservatively Managed Incidental Childhood Cerebral Mass Lesion: Controversy Regarding Management Paradigm. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2017, 33, 2169–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, V.P.; Jones, D.T.W.; Giannini, C. Pilocytic Astrocytoma: Pathology, Molecular Mechanisms and Markers. Acta Neuropathol. 2015, 129, 775–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, F.J.; Scheithauer, B.W.; Burger, P.C.; Jenkins, S.; Giannini, C. Anaplasia in Pilocytic Astrocytoma Predicts Aggressive Behavior. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2010, 34, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinhardt, A.; Stichel, D.; Schrimpf, D.; Sahm, F.; Korshunov, A.; Reuss, D.E.; Koelsche, C.; Huang, K.; Wefers, A.K.; Hovestadt, V.; et al. Anaplastic Astrocytoma with Piloid Features, a Novel Molecular Class of IDH Wildtype Glioma with Recurrent MAPK Pathway, CDKN2A/B and ATRX Alterations. Acta Neuropathol. 2018, 136, 273–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, D.T.W.; Kocialkowski, S.; Liu, L.; Pearson, D.M.; Bäcklund, L.M.; Ichimura, K.; Collins, V.P. Tandem Duplication Producing a Novel Oncogenic BRAF Fusion Gene Defines the Majority of Pilocytic Astrocytomas. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 8673–8677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horbinski, C. To BRAF or Not to BRAF: Is That Even a Question Anymore? J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2013, 72, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollack, I.F.; Agnihotri, S.; Broniscer, A. Childhood Brain Tumors: Current Management, Biological Insights, and Future Directions: JNSPG 75th Anniversary Invited Review Article. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2019, 23, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, P.; Kumar, A.; Jha, P.; Purkait, S.; Faruq, M.; Suri, A.; Suri, V.; Sharma, M.C.; Sarkar, C. Genetic Alterations Related to BRAF-FGFR Genes and Dysregulated MAPK/ERK/MTOR Signaling in Adult Pilocytic Astrocytoma. Brain Pathol. 2017, 27, 580–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristiansen, I.; Strinnholm, M.; Strömberg, B.; Frisk, P. Clinical Characteristics, Long-Term Complications and Health-Related Quality of Life (HRQoL) in Children and Young Adults Treated for Low-Grade Astrocytoma in the Posterior Fossa in Childhood. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2019, 142, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horger, M.; Beschorner, R.; Nägele, T.; Danz, S.; Ernemann, U. Pilozytisches Astrozytom: Bildgebende Diagnostik. Röfo - Fortschritte Auf Dem Gebiet Der Röntgenstrahlen Und Der Bildgebenden Verfahren 2009, 181, 1109–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- She, D.; Lu, Y.; Xiong, J.; Geng, D.; Yin, B. MR Imaging Features of Spinal Pilocytic Astrocytoma. BMC Med. Imaging 2019, 19, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.J.; Marchan, E.; Peterson, J.; Harrell, A.C.; Quinones-Hinojosa, A.; Brown, P.D.; Trifiletti, D.M. Management and Survival of Adult Patients with Pilocytic Astrocytoma in the National Cancer Database. World Neurosurg. 2018, 112, e881–e887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beni-Adani, L.; Gomori, M.; Spektor, S.; Constantini, S. Cyst Wall Enhancement in Pilocytic Astrocytoma: Neoplastic or Reactive Phenomena. Pediatr. Neurosurg. 2000, 32, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wade, A.; Hayhurst, C.; Amato-Watkins, A.; Lammie, A.; Leach, P. Cerebellar Pilocytic Astrocytoma in Adults: A Management Paradigm for a Rare Tumour. Acta Neurochir. 2013, 155, 1431–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stüer, C.; Vilz, B.; Majores, M.; Becker, A.; Schramm, J.; Simon, M. Frequent Recurrence and Progression in Pilocytic Astrocytoma in Adults. Cancer 2007, 110, 2799–2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kano, H.; Kondziolka, D.; Niranjan, A.; Flickinger, J.C.; Lunsford, L.D. Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Pilocytic Astrocytomas Part 1: Outcomes in Adult Patients. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2009, 95, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, M.W.; Whipple, N.S.; Poppe, M.M.; Mendez, J.S.; Cannon, D.M.; Burt, L.M. The Use and Efficacy of Chemotherapy and Radiotherapy in Children and Adults with Pilocytic Astrocytoma. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2021, 151, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lassaletta, A.; Scheinemann, K.; Zelcer, S.M.; Hukin, J.; Wilson, B.A.; Jabado, N.; Carret, A.S.; Lafay-Cousin, L.; Larouche, V.; Hawkins, C.E.; et al. Phase II Weekly Vinblastine for Chemotherapy-Naïve Children With Progressive Low-Grade Glioma: A Canadian Pediatric Brain Tumor Consortium Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 3537–3543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreck, K.C.; Grossman, S.A.; Pratilas, C.A. BRAF Mutations and the Utility of RAF and MEK Inhibitors in Primary Brain Tumors. Cancers 2019, 11, 1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fangusaro, J.; Onar-Thomas, A.; Poussaint, T.Y.; Wu, S.; Ligon, A.H.; Lindeman, N.; Banerjee, A.; Packer, R.J.; Kilburn, L.B.; Goldman, S.; et al. Selumetinib in Paediatric Patients with BRAF-Aberrant or Neurofibromatosis Type 1-Associated Recurrent, Refractory, or Progressive Low-Grade Glioma: A Multicentre, Phase 2 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 1011–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunin, G.R.; Surawicz, T.S.; Witman, P.A.; Preston-Martin, S.; Davis, D.F.; Bruner, J.M. The Descriptive Epidemiology of Craniopharyngioma. J. Neurosurg. 1998, 89, 547–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momin, A.A.; Recinos, M.A.; Cioffi, G.; Patil, N.; Soni, P.; Almeida, J.P.; Kruchko, C.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S.; Recinos, P.F.; Kshettry, V.R. Descriptive Epidemiology of Craniopharyngiomas in the United States. Pituitary 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, E.H.; Feldt-Rasmussen, U.; Poulsgaard, L.; Kristensen, L.Ø.; Astrup, J.; Jørgensen, J.O.; Bjerre, P.; Andersen, M.; Andersen, C.; Jørgensen, J.; et al. Incidence of Craniopharyngioma in Denmark (n = 189) and Estimated World Incidence of Craniopharyngioma in Children and Adults. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2011, 104, 755–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouanneau, E.; Raverot, G. Adult Craniopharyngiomas, Differences and Lessons from Paediatrics; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubuulwa, J.; Lei, T. Pathological and Topographical Classification of Craniopharyngiomas: A Literature Review. J. Neurol. Surg. Rep. 2016, 77, e121–e127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karavitaki, N.; Brufani, C.; Warner, J.T.; Adams, C.B.T.; Richards, P.; Ansorge, O.; Shine, B.; Turner, H.E.; Wass, J.A.H. Craniopharyngiomas in Children and Adults: Systematic Analysis of 121 Cases with Long-term Follow-up. Clin. Endocrinol. 2005, 62, 397–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, H.L. Craniopharyngioma. Endocr. Rev. 2014, 35, 513–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brastianos, P.K.; Taylor-Weiner, A.; Manley, P.E.; Jones, R.T.; Dias-Santagata, D.; Thorner, A.R.; Lawrence, M.S.; Rodriguez, F.J.; Bernardo, L.A.; Schubert, L.; et al. Exome Sequencing Identifies BRAF Mutations in Papillary Craniopharyngiomas. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirollos, R.W.; Helmy, A.; Thomson, S.; Hutchinson, P.J. Oxford Textbook of Neurological Surgery, 1st ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2019; ISBN 978-0-19-874670-6. [Google Scholar]
- Hölsken, A.; Sill, M.; Merkle, J.; Schweizer, L.; Buchfelder, M.; Flitsch, J.; Fahlbusch, R.; Metzler, M.; Kool, M.; Pfister, S.M.; et al. Adamantinomatous and Papillary Craniopharyngiomas Are Characterized by Distinct Epigenomic as Well as Mutational and Transcriptomic Profiles. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2016, 4, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puget, S.; Grill, J.; Zerah, M.; Pierre-Kahn, A. Pediatric Craniopharyngiomas: Classification and Treatment According to the Degree of Hypothalamic Involvement. J. Neurosurg. 2007, 106, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Serna, R.; Gómez-Amador, J.L.; Barges-Coll, J.; Nathal-Vera, E.; Revuelta-Gutiérrez, R.; Alonso-Vanegas, M.; Ramos-Peek, M.; Portocarrero-Ortiz, L. Treatment of Craniopharyngioma in Adults: Systematic Analysis of a 25-Year Experience. Arch. Med. Res. 2012, 43, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensterle, M.; Jazbinsek, S.; Bosnjak, R.; Popovic, M.; Zaletel, L.Z.; Vesnaver, T.V.; Kotnik, B.F.; Kotnik, P. Advances in the Management of Craniopharyngioma in Children and Adults. Radiol. Oncol. 2019, 53, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jazbinšek, S.; Kolenc, D.; Bošnjak, R.; Faganel Kotnik, B.; Zadravec Zaletel, L.; Jenko Bizjan, B.; Vipotnik Vesnaver, T.; Battelino, T.; Janež, A.; Jensterle, M.; et al. Prevalence of Endocrine and Metabolic Comorbidities in a National Cohort of Patients with Craniopharyngioma. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 2020, 93, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, H.L. Childhood Craniopharyngioma. Pituitary 2013, 16, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, H.L.; Bruhnken, G.; Emser, A.; Faldum, A.; Etavard-Gorris, N.; Gebhardt, U.; Kolb, R.; Sörensen, N. Longitudinal Study on Quality of Life in 102 Survivors of Childhood Craniopharyngioma. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2005, 21, 975–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogusz, A.; Boekhoff, S.; Warmuth-Metz, M.; Calaminus, G.; Eveslage, M.; Müller, H.L. Posterior Hypothalamus-Sparing Surgery Improves Outcome after Childhood Craniopharyngioma. Endocr. Connect. 2019, 8, 481–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, T.-Y.; Jung, S.; Moon, K.-S.; Kim, I.-Y.; Kang, S.-S.; Kim, J.-H. Endocrinological Outcomes of Pediatric Craniopharyngiomas with Anatomical Pituitary Stalk Preservation: Preliminary Study. Pediatr. Neurosurg. 2010, 46, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Fan, Y.; Cen, B. Effect of Preserving the Pituitary Stalk During Resection of Craniopharyngioma in Children on the Diabetes Insipidus and Relapse Rates and Long-Term Outcomes. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2017, 28, e591–e595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Lu, X.; Yang, N.; Zheng, J.; Huang, B.; Li, L. Association of Pituitary Stalk Management with Endocrine Outcomes and Recurrence in Microsurgery of Craniopharyngiomas: A Meta-Analysis. Clin. Neurol. Neurosur. 2015, 136, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albright, A.L.; Hadjipanayis, C.G.; Lunsford, L.D.; Kondziolka, D.; Pollack, I.F.; Adelson, P.D. Individualized Treatment of Pediatric Craniopharyngiomas. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2005, 21, 649–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MG, Y.; M, C.; M, K.; G, S.; PJ, T.; P, R. Total Removal of Craniopharyngiomas. Approaches and Long-Term Results in 144 Patients. J. Neurosurg. 1990, 73, 3–11. [Google Scholar]
- Fouda, M.A.; Karsten, M.; Staffa, S.J.; Scott, R.M.; Marcus, K.J.; Baird, L.C. Management Strategies for Recurrent Pediatric Craniopharyngioma: New Recommendations. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2021, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Effenterre, R.V.; Boch, A.-L. Craniopharyngioma in Adults and Children: A Study of 122 Surgical Cases. J. Neurosurg. 2002, 97, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajithkumar, T.; Mazhari, A.-L.; Stickan-Verfürth, M.; Kramer, P.-H.; Fuentes, C.-S.; Lambert, J.; Thomas, H.; Müller, H.; Fleischhack, G.; Timmermann, B. Proton Therapy for Craniopharyngioma—An Early Report from a Single European Centre. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 30, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, V.S.; Thamboo, A.; Quon, J.; Nayak, J.V.; Hwang, P.H.; Edwards, M.; Patel, Z.M. Outcomes After Endoscopic Endonasal Resection of Craniopharyngiomas in the Pediatric Population. World Neurosurg 2017, 108, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatreau, J.R.; Patel, M.R.; Shah, R.N.; McKinney, K.A.; Wheless, S.A.; Senior, B.A.; Ewend, M.G.; Germanwala, A.V.; Ebert, C.S.; Zanation, A.M. Anatomical Considerations for Endoscopic Endonasal Skull Base Surgery in Pediatric Patients. Laryngoscope 2010, 120, 1730–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komotar, R.J.; Starke, R.M.; Raper, D.M.S.; Anand, V.K.; Schwartz, T.H. Endoscopic Endonasal Compared with Microscopic Transsphenoidal and Open Transcranial Resection of Craniopharyngiomas. World Neurosurg. 2012, 77, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahlbusch, R.; Honegger, J.; Paulus, W.; Huk, W.; Buchfelder, M. Surgical Treatment of Craniopharyngiomas: Experience with 168 Patients. J. Neurosurg. 1999, 90, 237–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoicas, F.; Schöfl, C. Craniopharyngioma in Adults. Front. Endocrinol. 2012, 3, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boehling, N.S.; Grosshans, D.R.; Bluett, J.B.; Palmer, M.T.; Song, X.; Amos, R.A.; Sahoo, N.; Meyer, J.J.; Mahajan, A.; Woo, S.Y. Dosimetric Comparison of Three-Dimensional Conformal Proton Radiotherapy, Intensity-Modulated Proton Therapy, and Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy for Treatment of Pediatric Craniopharyngiomas. Int. J. Radiation Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2012, 82, 643–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, H.L. The Diagnosis and Treatment of Craniopharyngioma. Neuroendocrinology 2020, 110, 753–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Bi, W.L.; Giantini Larsen, A.; Al-Abdulmohsen, S.; Abedalthagafi, M.; Dunn, I.F. Craniopharyngioma: A Roadmap for Scientific Translation. Neurosurg. Focus 2018, 44, E12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.; Allen, J.; Zagzag, D.; Wisoff, J.; Radmanesh, A.; Gindin, T.; Nicolaides, T. Radiologic Response to MEK Inhibition in a Patient with a WNT-activated Craniopharyngioma. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2021, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hengartner, A.C.; Prince, E.; Vijmasi, T.; Hankinson, T.C. Adamantinomatous Craniopharyngioma: Moving toward Targeted Therapies. Neurosurg. Focus 2020, 48, E7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Adults | Children | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subgroup | SHH | WNT | Group 3 | Group 4 | SHH | WNT | Group 3 | Group 4 |
| % of cases | 60–65% | 10–15% | 5% | 20% | 20–25% | 10–15% | 20–25% | 40% |
| Gender Ratio (m:f) | 2:1 | 1:1 | 2:1 | 4:1 | 2:1 | 1:1 | 2:1 | 1:1 |
| Location | Cerebellar hemisphere/ CPA | Cerebellar hemisphere/ CPA | Midline, 4th ventricle | Midline, 4th ventricle | Cerebellar hemisphere | Cerebellar hemisphere | Midline, 4th ventricle | Midline, 4th ventricle |
| Histology | Nodular-desmoplastic | Classic | Classic | Classic/ Anaplastic | Classic/ Nodular- desmoplastic/ Anaplastic | Classic | Classic/ Anaplastic | Classic/ Anaplastic |
| Metastasis (%) | <10, local | <10, local | 10–15, distant | 20, distant | 10–15, Local | <10, Local | 40, Distant | 35, Distant |
| Molecular/Genetic alterations | TP53 (poor prognosis) | TP53 | MYC N * | MYC * | TP53 (poor prognosis) MYC N | - | MYC N | MYC |
| Prognosis | Intermediate, Poor with TP53 | Good | Poor | Intermediate | Intermediate, Poor with TP53, Infants better | Excellent | Poor | Intermediate |
| 5-year OS (%) | 81% TP53: 41% | 82% | 25% | 39% | 75–90%, TP53: 40–50% | >90% | 55%, MYC N: <50% | 75–90% |
| Characteristics | Adults | Children |
|---|---|---|
| Incidence per 106 persons | 0.6 | 5–6 |
| Location (most common) | Cerebellar hemisphere | Midline, 4th ventricle |
| Presenting Symptom | 60% gait ataxia, 40% vestibular syndrome, >80% hydrocephalus | >80% vomiting, hydrocephalus |
| Associated Syndromes | - | Li-Fraumeni, Gorlin, Turcot |
| Molecular alterations | Depending on subtype | Depending on subtype |
| Metastasis | Depending on subtype | Depending on subtype |
| Primary Treatment | Surgery | Surgery |
| Additional Therapy | Chemotherapy (Packer regiment), CSI | Chemotherapy (HIT 2000 regiment), CSI (>3 years) |
| Posterior Fossa Syndrome postoperative (%) | 16 | 8–39 |
| Shunt Dependency (%) | 7–21 | 20–40 |
| Prognostic Factors | Depending on subtype | Depending on subtype |
| 5-year OS (%) | 25–82% | 50–90% |
| Characteristics | Adults | Children |
|---|---|---|
| Location (most common) | supratentorial (35–45%), cerebellar (35–40%), brain stem, optic pathway (5–10%), spinal (2–5%) | cerebellar (70%), brain stem, optic pathway (10–20%), spinal (2–5%) |
| Associated Syndromes | - | NF-1, Tuberous Sclerosis Complex |
| Molecular alterations | BRAF: 20% | BRAF: 70% |
| Primary Treatment | Surgery | Surgery |
| Additional Therapy | Chemotherapy (temozolomide, carboplatin, etoposide), Radiation for deep-seated lesions, recurrence | Chemotherapy (cisplatin, vincristine, or vinblastine), Radiation (>3 years) for deep-seated lesions or recurrence, MEK inhibitor for BRAF mutation |
| Prognostic Factors | GTR (good) | Cerebellar location, GTR (good) |
| 5-year OS (%) | 83–87% | >90% |
| Characteristics | Adults | Children |
|---|---|---|
| Age Distribution (years) | 50–70 | 5–14 |
| Frequency (%) | 2–5 | 4–9 |
| Histology | Adamantinomatous & Papillary CP | Adamantinomatous CP |
| Molecular alterations | CTNNB1 (aCP), BRAF (pCP) | CTNNB1 |
| Presenting Symptom | Visual field deficit | Endocrine disturbances |
| Endocrine Deficits at Presentation (%) | 30% | 60% |
| Primary Treatment | GTR if possible, radiotherapy, BRAF targeted therapy | Tumor reduction/cyst drainage, proton beam therapy, local chemotherapy(controversial) |
| Endocrine Postoperative Complications | 70% diabetes insipidus, 15% growth hormone deficiency | 75% growth hormone deficiency, 20% diabetes insipidus |
| Visual Field Complications | 7–14% visual field deficits, good postoperative recovery in 60% | 8–20% visual field deficits, good postoperative recovery in 50% |
| 5-year OS (%) | ~90% | ~90% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Greuter, L.; Guzman, R.; Soleman, J. Typical Pediatric Brain Tumors Occurring in Adults—Differences in Management and Outcome. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 356. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9040356
Greuter L, Guzman R, Soleman J. Typical Pediatric Brain Tumors Occurring in Adults—Differences in Management and Outcome. Biomedicines. 2021; 9(4):356. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9040356
Chicago/Turabian StyleGreuter, Ladina, Raphael Guzman, and Jehuda Soleman. 2021. "Typical Pediatric Brain Tumors Occurring in Adults—Differences in Management and Outcome" Biomedicines 9, no. 4: 356. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9040356
APA StyleGreuter, L., Guzman, R., & Soleman, J. (2021). Typical Pediatric Brain Tumors Occurring in Adults—Differences in Management and Outcome. Biomedicines, 9(4), 356. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9040356







