Extracellular Vesicle miR-200c Enhances Gefitinib Sensitivity in Heterogeneous EGFR-Mutant NSCLC
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Lines and Culture
2.2. The Ultrafiltration (UF) Method
2.3. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.4. Size Distribution Measured by Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis
2.5. Cell/EV Lysis and Western Blot Analysis
2.6. EV Staining, Immunofluorescent Images, and Live Imaging
2.7. DNA Quantification and Droplet Digital PCR Analysis
2.8. Combination Treatment with Gefitinib and EVs and MTT Assays
2.9. The Coculture System, GW4869 Treatment, and MTT Assays
2.10. MicroRNA Transfection into Cells and EV and MTT Assays
2.11. Animal Model
2.12. Patient and Sample Processing
2.13. EGFR-Mutation Abundance Evaluation Using Real-Time PCR and Immunohistochemistry Staining
2.14. EV RNA Isolation from Blood and Micro-RNA Profiling
2.15. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of Extracellular Vesicles Released from EGFR-Mutant Cells and Their Transfer to EGFR Wild-Type Cells
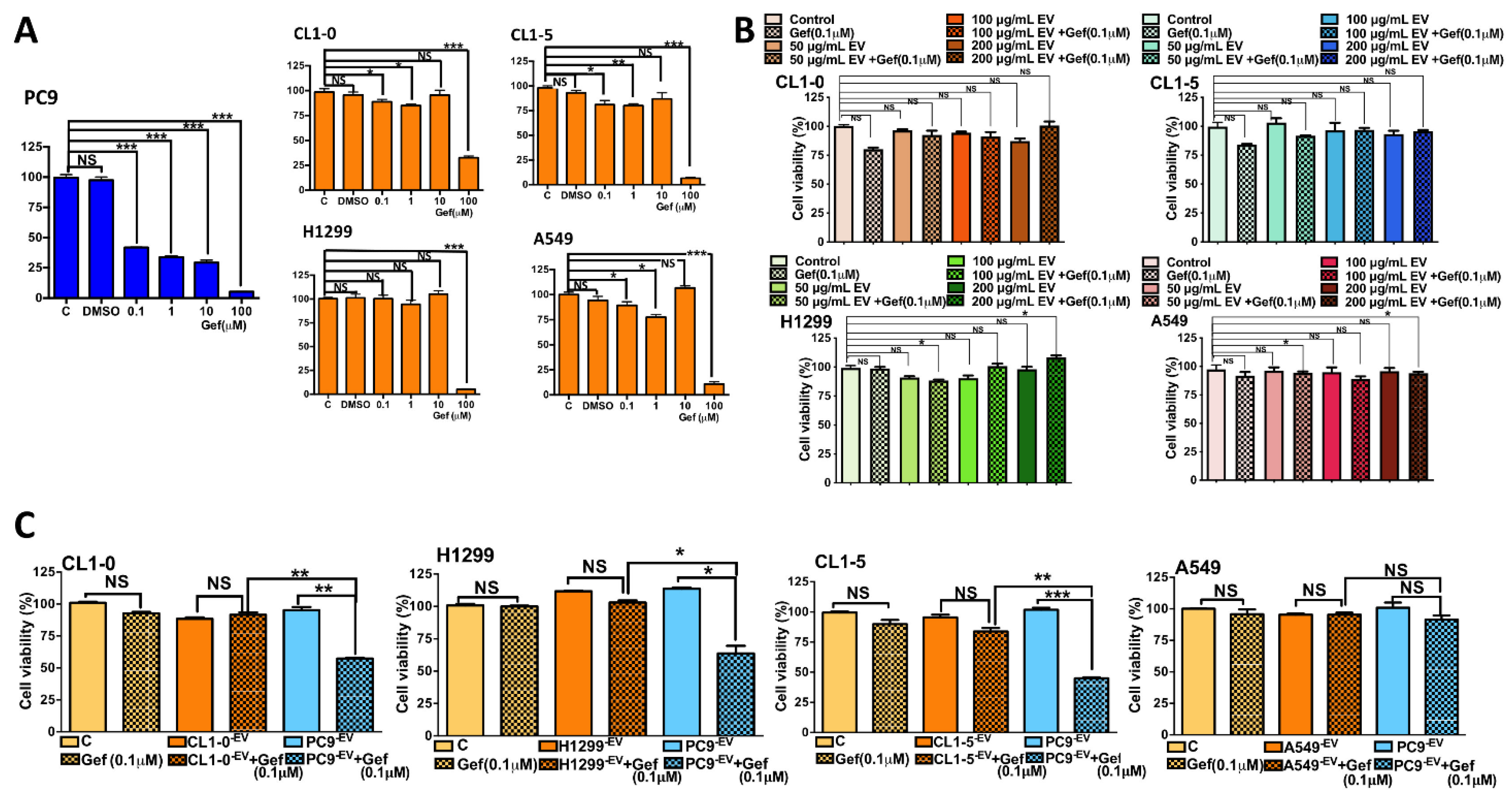
3.2. The Uptake of PC9 EVs Affects the Sensitivity of Wild-Type EGFR to Gefitinib
3.3. Coculture with PC9 Cells Sensitizes EGFR Wild-Type Cells to Gefitinib, and Inhibition of Exosome Secretion Reverses This Effect
3.4. EVs Derived from EGFR-Mutant Cells Inhibit EGFR Wild-Type Tumor Growth In Vivo
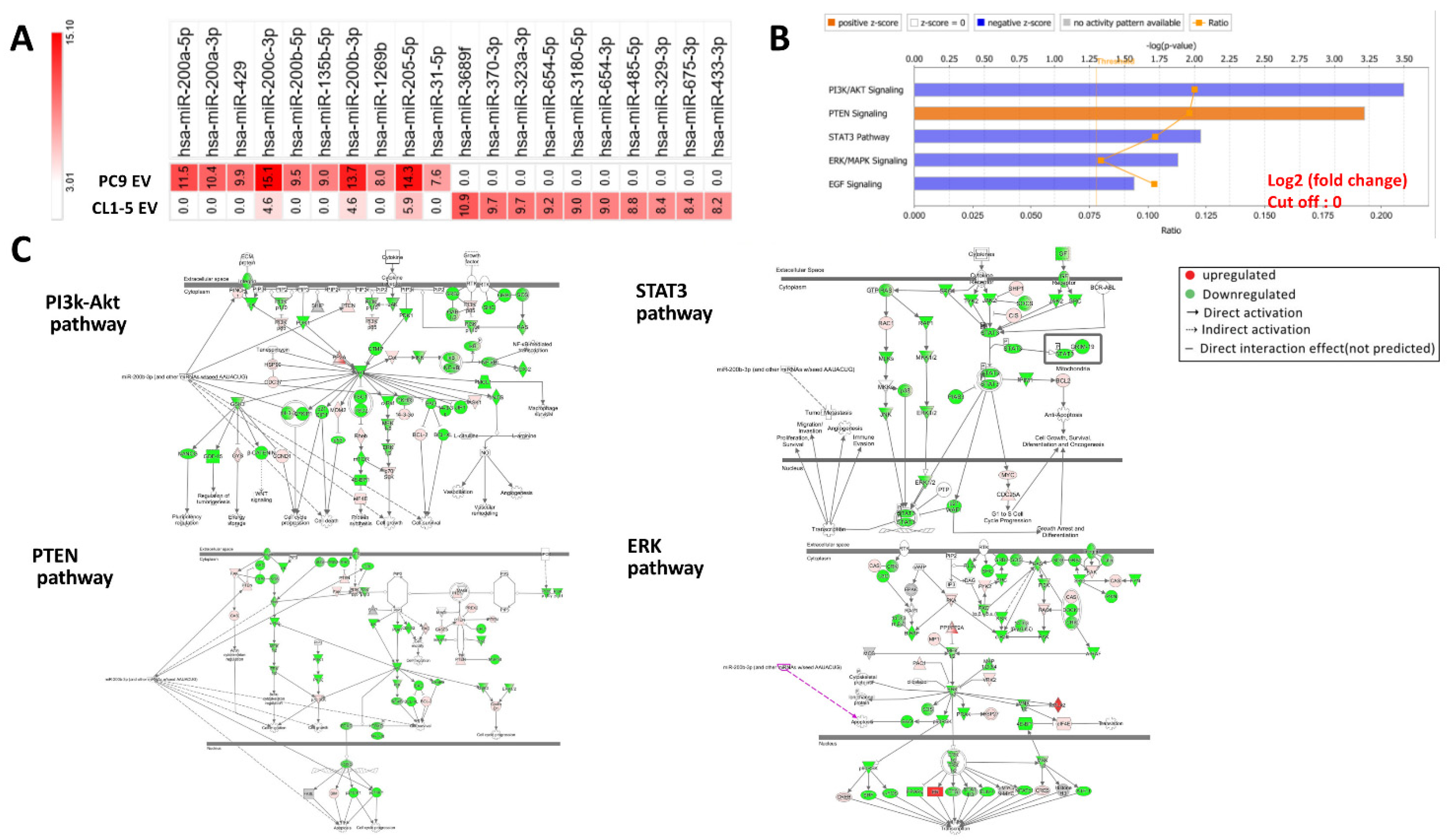
3.5. Micro-RNA Expression Profiles Are Significantly Different between EVs from EGFR-Mutant Cells and EVs from EGFR Wild-Type Cells
3.6. The miRNA Profiles of Circulating EVs Are Significantly Different between EGFR-TKI Good Responders and Poor Responders and Similar to the miRNA Profiles Identified in PC9 EVs
3.7. Transfection of miR-200c Inhibits Downstream Signaling Pathways of EGFR and Enhances Gefitinib Sensitivity of EGFR Wild-Type Cells
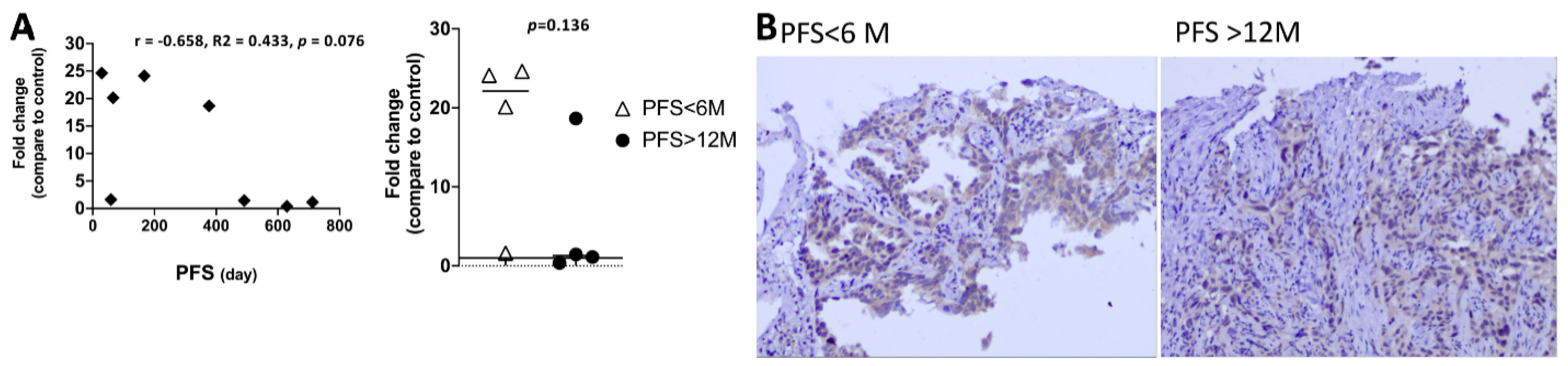
3.8. The EGFR-Mutation Abundance Is Not Associated with Clinical Outcome
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, Z.-Y.; Zhong, W.-Z.; Zhang, X.-C.; Su, J.; Yang, X.-N.; Chen, Z.-H.; Yang, J.-J.; Zhou, Q.; Yan, H.-H.; An, S.-J.; et al. EGFR mutation heterogeneity and the mixed response to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors of lung adenocarcinomas. Oncologist 2012, 17, 978–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Biase, D.; Genestreti, G.; Visani, M.; Acquaviva, G.; Di Battista, M.; Cavallo, G.; Paccapelo, A.; Cancellieri, A.; Trisolini, R.; Degli Esposti, R.; et al. The percentage of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR)-mutated neoplastic cells correlates to response to tyrosine kinase inhibitors in lung adenocarcinoma. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Zhang, X.C.; Chen, Z.H.; Yin, X.L.; Yang, J.J.; Xu, C.R.; Yan, H.H.; Chen, H.J.; Su, J.; Zhong, W.Z.; et al. Relative abundance of EGFR mutations predicts benefit from gefitinib treatment for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 3316–3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zomer, A.; van Rheenen, J. Implications of Extracellular Vesicle Transfer on Cellular Heterogeneity in Cancer: What Are the Potential Clinical Ramifications? Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 2071–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, Y.-L.; Chu, P.-Y.; Lee, B.-H.; Chen, K.-C.; Yang, C.-Y.; Kuo, W.-H.; Shen, T.-L. Basics and applications of tumor-derived extracellular vesicles. J. Biomed. Sci. 2019, 26, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valadi, H.; Ekstrom, K.; Bossios, A.; Sjostrand, M.; Lee, J.J.; Lotvall, J.O. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zomer, A.; Maynard, C.; Verweij, F.J.; Kamermans, A.; Schafer, R.; Beerling, E.; Schiffelers, R.M.; de Wit, E.; Berenguer, J.; Ellenbroek, S.I.J.; et al. In vivo imaging reveals extracellular vesicle-mediated phenocopying of metastatic behavior. Cell 2015, 161, 1046–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinbichler, T.B.; Dudás, J.; Skvortsov, S.; Ganswindt, U.; Riechelmann, H.; Skvortsova, I.-I. Therapy resistance mediated by exosomes. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Q.; Liu, J.T.; Fan, L.L.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, L.; Wang, F.; Yu, H.Q.; Gao, J.; Wei, W.; Wang, H.; et al. Exosomes derived from gefitinib-treated EGFR-mutant lung cancer cells alter cisplatin sensitivity via up-regulating autophagy. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 24585–24595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, D.Y.; You, S.; Jung, J.H.; Lee, J.C.; Rho, J.K.; Lee, K.Y.; Freeman, M.R.; Kim, K.P.; Kim, J. Extracellular vesicles shed from gefitinib-resistant nonsmall cell lung cancer regulate the tumor microenvironment. Proteomics 2014, 14, 1845–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheruvanky, A.; Zhou, H.; Pisitkun, T.; Kopp, J.B.; Knepper, M.A.; Yuen, P.S.; Star, R.A. Rapid isolation of urinary exosomal biomarkers using a nanomembrane ultrafiltration concentrator. Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol. 2007, 292, F1657–F1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oxnard, G.R.; Paweletz, C.P.; Kuang, Y.; Mach, S.L.; O’Connell, A.; Messineo, M.M.; Luke, J.J.; Butaney, M.; Kirschmeier, P.; Jackman, D.M.; et al. Noninvasive detection of response and resistance in EGFR-mutant lung cancer using quantitative next-generation genotyping of cell-free plasma DNA. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 1698–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, H.; Shien, K.; Tomida, S.; Okayasu, K.; Suzawa, K.; Hashida, S.; Torigoe, H.; Watanabe, M.; Yamamoto, H.; Soh, J.; et al. Targeting the miR-200c/LIN28B axis in acquired EGFR-TKI resistance non-small cell lung cancer cells harboring EMT features. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, P.-L.; Wu, Y.-L.; Chang, W.-Y.; Ho, C.-L.; Tseng, Y.-L.; Lai, W.-W.; Su, W.-C.; Lin, C.-C.; Yang, S.-C. Preventing and treating brain metastases with three first-line EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitors in patients with EGFR mutation-positive advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2018, 10, 1758835918797589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peraldo-Neia, C.; Migliardi, G.; Mello-Grand, M.; Montemurro, F.; Segir, R.; Pignochino, Y.; Cavalloni, G.; Torchio, B.; Mosso, L.; Chiorino, G.; et al. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) mutation analysis, gene expression profiling and EGFR protein expression in primary prostate cancer. BMC Cancer 2011, 11, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakur, B.K.; Zhang, H.; Becker, A.; Matei, I.; Huang, Y.; Costa-Silva, B.; Zheng, Y.; Hoshino, A.; Brazier, H.; Xiang, J.; et al. Double-stranded DNA in exosomes: A novel biomarker in cancer detection. Cell Res. 2014, 24, 766–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Li, L.; Zhu, Y.; Huang, C.; Qin, Y.; Liu, H.; Ren-Heidenreich, L.; Shi, B.; Ren, H.; Chu, X.; et al. Coexistence of EGFR with KRAS, or BRAF, or PIK3CA somatic mutations in lung cancer: A comprehensive mutation profiling from 5125 Chinese cohorts. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 110, 2812–2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuyama, K.; Sun, H.; Mitsutake, S.; Igarashi, Y. Sphingolipid-modulated exosome secretion promotes clearance of amyloid-beta by microglia. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 10977–10989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, M.C.; Wu, M.Y.; Hwang, M.H.; Chang, Y.T.; Huang, H.J.; Lin, A.M.; Yang, J.C. Chloroquine enhances gefitinib cytotoxicity in gefitinib-resistant nonsmall cell lung cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, G.; Zheng, G.; Ge, M.; Wang, J.; Huang, R.; Shu, Q.; Xu, J. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles affect disease outcomes via transfer of microRNAs. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2018, 9, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godlewski, J.; Ferrer-Luna, R.; Rooj, A.K.; Mineo, M.; Ricklefs, F.; Takeda, Y.S.; Nowicki, M.O.; Salińska, E.; Nakano, I.; Lee, H.; et al. MicroRNA signatures and molecular subtypes of glioblastoma: The role of extracellular transfer. Stem Cell Rep. 2017, 8, 1497–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirsh, V. Turning EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer into a chronic disease: Optimal sequential therapy with EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2018, 10, 1758834017753338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tirkes, T.; Hollar, M.A.; Tann, M.; Kohli, M.D.; Akisik, F.; Sandrasegaran, K. Response criteria in oncologic imaging: Review of traditional and new criteria. Radiographics 2013, 33, 1323–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotow, J.; Bivona, T.G. Understanding and targeting resistance mechanisms in NSCLC. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 637–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, Y.; Peled, N.; Wynes, M.W.; Yoshida, K.; Pardo, M.; Mascaux, C.; Ohira, T.; Tsuboi, M.; Matsubayashi, J.; Nagao, T.; et al. Novel epidermal growth factor receptor mutation-specific antibodies for non-small cell lung cancer: Immunohistochemistry as a possible screening method for epidermal growth factor receptor mutations. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2010, 5, 1551–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.K.; Jella, K.K.; Nasti, T.; Li, Z.; Lawson, D.H.; Ahmed, R.; Dynan, W. Identification of radiation induced exosomes as a potential in situ vaccine for melanoma growth delay. J. Clinl. Oncol. 2018, 36, e21535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitai, Y.; Kawasaki, T.; Sueyoshi, T.; Kobiyama, K.; Ishii, K.J.; Zou, J.; Akira, S.; Matsuda, T.; Kawai, T. DNA-containing exosomes derived from cancer cells treated with topotecan activate a STING-dependent pathway and reinforce antitumor immunity. J. Immunol. 2017, 198, 1649–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koga, Y.; Yasunaga, M.; Moriya, Y.; Akasu, T.; Fujita, S.; Yamamoto, S.; Matsumura, Y. Exosome can prevent RNase from degrading microRNA in feces. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2011, 2, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanlikilicer, P.; Rashed, M.H.; Bayraktar, R.; Mitra, R.; Ivan, C.; Aslan, B.; Zhang, X.; Filant, J.; Silva, A.M.; Rodriguez-Aguayo, C.; et al. Ubiquitous release of exosomal tumor suppressor miR-6126 from ovarian cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 7194–7207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosell, R.; Karachaliou, N. Lung cancer in 2014: Optimizing lung cancer treatment approaches. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 12, 75–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.Q.; Cen, W.L.; Cen, J.M.; Cen, W.N.; Li, J.Y.; Li, M.W.; Gan, T.Q.; Hu, X.H.; Chen, G. Clinical significance of miR-210 and its prospective signaling pathways in non-small cell lung cancer: Evidence from gene expression omnibus and the cancer genome atlas data mining with 2763 samples and validation via real-time quantitative PCR. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 46, 925–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, G.-H.; Lu, Y.-Y.; Xie, J.-L.; Gao, Z.-K.; Wu, X.-B.; Yao, W.-S.; Gu, W.-G. Overexpression of miR-758 inhibited proliferation, migration, invasion, and promoted apoptosis of non-small cell lung cancer cells by negatively regulating HMGB. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, BSR20180855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhen, Q.; Liu, J.; Gao, L.; Liu, J.; Wang, R.; Chu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Tan, G.; Zhao, X.; Lv, B. MicroRNA-200a targets EGFR and c-Met to inhibit migration, invasion, and gefitinib resistance in non-small cell lung cancer. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2015, 146, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceppi, P.; Mudduluru, G.; Kumarswamy, R.; Rapa, I.; Scagliotti, G.V.; Papotti, M.; Allgayer, H. Loss of miR-200c expression induces an aggressive, invasive, and chemoresistant phenotype in non-small cell lung cancer. Mol. Cancer Res. 2010, 8, 1207–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejero, R.; Navarro, A.; Campayo, M.; Vinolas, N.; Marrades, R.M.; Cordeiro, A.; Ruiz-Martinez, M.; Santasusagna, S.; Molins, L.; Ramirez, J.; et al. miR-141 and miR-200c as markers of overall survival in early stage non-small cell lung cancer adenocarcinoma. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.K.; Jung, S.B.; Kim, J.S.; Roh, M.S.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, E.H.; Lee, H.W. Expression of microRNA miR-126 and miR-200c is associated with prognosis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Virchows Arch. 2014, 465, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Fu, L. Mechanisms of resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2015, 5, 390–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezquita, L.; Varga, A.; Planchard, D. Safety of osimertinib in EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2018, 17, 1239–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.J.; Rho, J.K.; Jeon, B.-S.; Choi, S.J.; Park, S.C.; Lee, S.S.; Kim, H.-R.; Kim, C.H.; Lee, J.C. Combined inhibition of IGFR enhances the effects of gefitinib in H1650: A lung cancer cell line with EGFR mutation and primary resistance to EGFR-TK inhibitors. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2009, 66, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endzelins, E.; Berger, A.; Melne, V.; Bajo-Santos, C.; Sobolevska, K.; Abols, A.; Rodriguez, M.; Santare, D.; Rudnickiha, A.; Lietuvietis, V.; et al. Detection of circulating miRNAs: Comparative analysis of extracellular vesicle-incorporated miRNAs and cell-free miRNAs in whole plasma of prostate cancer patients. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Lu, J.; Bai, Y.; Xie, X.; Lu, Z. miRNA in plasma exosome is stable under different storage conditions. Molecules 2014, 19, 1568–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Patient/Age Sex/Smoking | ECOG 1 | PFS 2 | Mutation | Stage | PD Location | Best Response | EKI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1/59/M/− | 0 | 2.2 | L858R | T3N3M1b | MPE 3 | PD 4 | Erlotinib |
| 2/75/F/− | 1 | 5.2 | 19Del | T4N3M1a | lung | SD | Erlotinib |
| 3/82/M/− | 0 | 4.9 | L858R | T3N2 M1a | lung | SD | Afatinib |
| 4/56/M/+ | 0 | 2.0 | L858R | T4N3M1b | intestine | PD | Erlotinib |
| 5/53/M/+ | 1 | 1.0 | L858R | T4N3M1b | lung | PD | Afatinib |
| 6/53/F/− | 1 | 28.8 | L858R | T3N2 M1a | lung | SD | Gefitinib |
| 7/58/M/+ | 0 | 19.8 | L858R | T1N3M1b | brain | PR | Erlotinib |
| 8/80/M/+ | 1 | 16.0 | 19Del | T4N3M1b | liver | PR | Gefitinib |
| 9/64/M/+ | 1 | 12.6 | 19Del | T4N3M1b | brain | PR | Erlotinib |
| 10/73/F/− | 1 | 17.5 | L858R | T4N3M1b | MPE | PR | Erlotinib |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, C.-C.; Wu, C.-Y.; Tseng, J.T.-C.; Hung, C.-H.; Wu, S.-Y.; Huang, Y.-T.; Chang, W.-Y.; Su, P.-L.; Su, W.-C. Extracellular Vesicle miR-200c Enhances Gefitinib Sensitivity in Heterogeneous EGFR-Mutant NSCLC. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9030243
Lin C-C, Wu C-Y, Tseng JT-C, Hung C-H, Wu S-Y, Huang Y-T, Chang W-Y, Su P-L, Su W-C. Extracellular Vesicle miR-200c Enhances Gefitinib Sensitivity in Heterogeneous EGFR-Mutant NSCLC. Biomedicines. 2021; 9(3):243. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9030243
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Chien-Chung, Chin-You Wu, Joseph Ta-Chien Tseng, Chun-Hua Hung, Shang-Yin Wu, Yu-Ting Huang, Wei-Yuan Chang, Po-Lan Su, and Wu-Chou Su. 2021. "Extracellular Vesicle miR-200c Enhances Gefitinib Sensitivity in Heterogeneous EGFR-Mutant NSCLC" Biomedicines 9, no. 3: 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9030243
APA StyleLin, C.-C., Wu, C.-Y., Tseng, J. T.-C., Hung, C.-H., Wu, S.-Y., Huang, Y.-T., Chang, W.-Y., Su, P.-L., & Su, W.-C. (2021). Extracellular Vesicle miR-200c Enhances Gefitinib Sensitivity in Heterogeneous EGFR-Mutant NSCLC. Biomedicines, 9(3), 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9030243








