WPK5, a Novel Kunitz-Type Peptide from the Leech Whitmania pigra Inhibiting Factor XIa, and Its Loop-Replaced Mutant to Improve Potency
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Animals
2.3. Screening of Kunitz-Type Peptides
2.4. Clone, Expression and Purification of Kunitz-Type Peptides
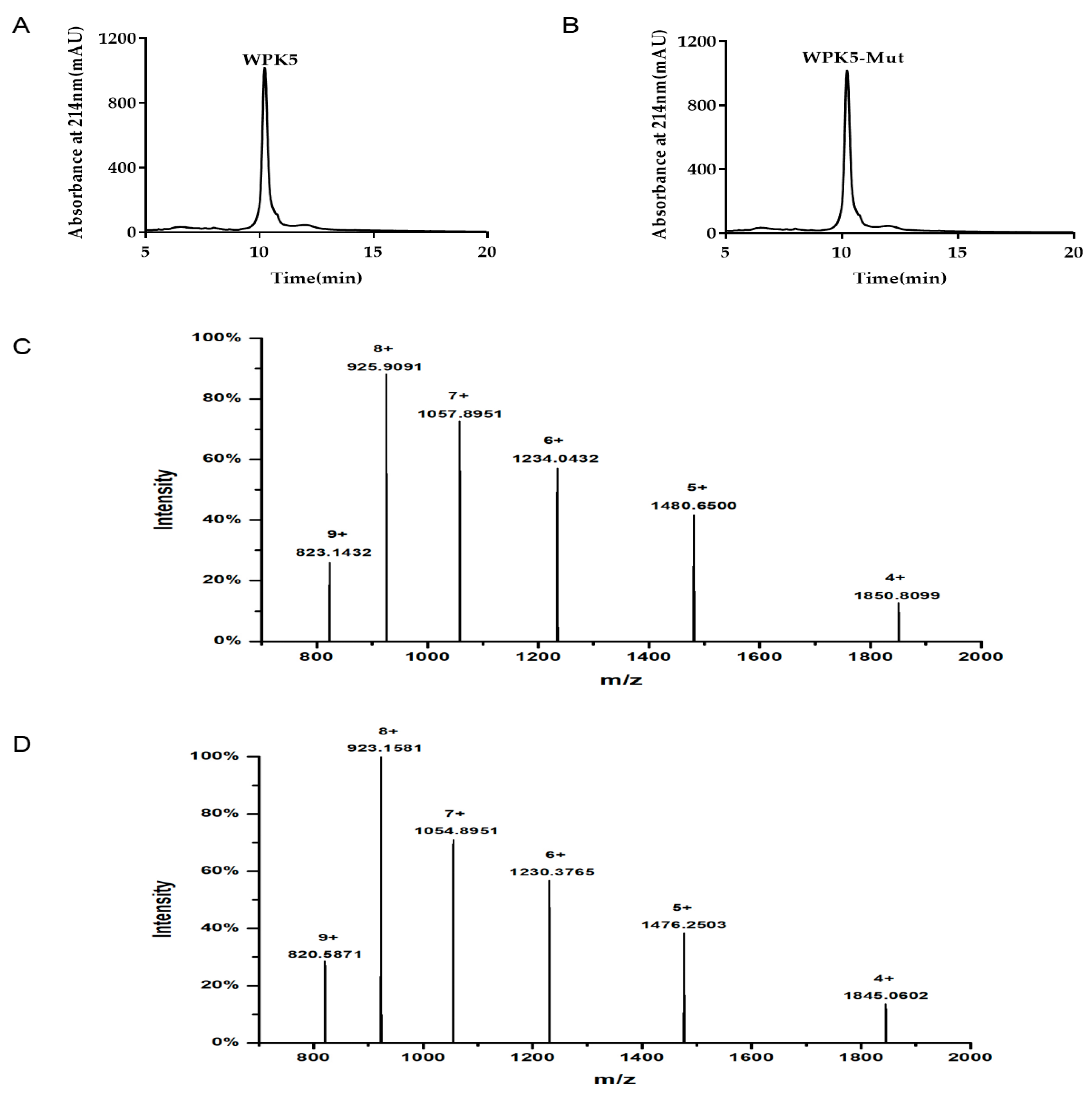
2.5. HPLC and LC-Q-TOF-MS Analysis
2.6. FXIa Inhibitory Activity Test of Kunitz-Type Peptides
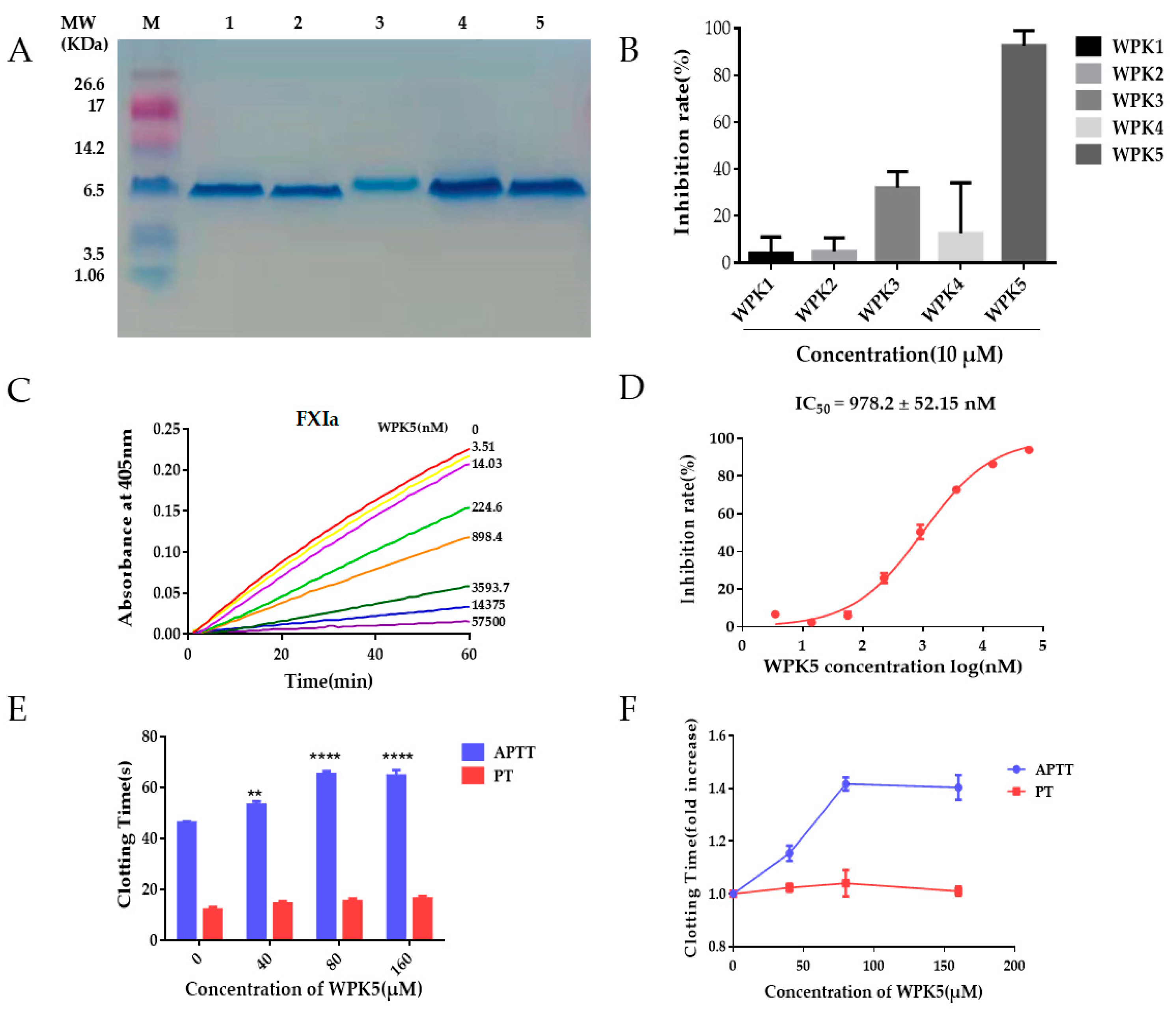
2.7. Protease Selectivity Assay
2.8. APTT and PT Assay
2.9. Antithrombotic Activity Assay
2.10. Tail Bleeding Time Assay
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
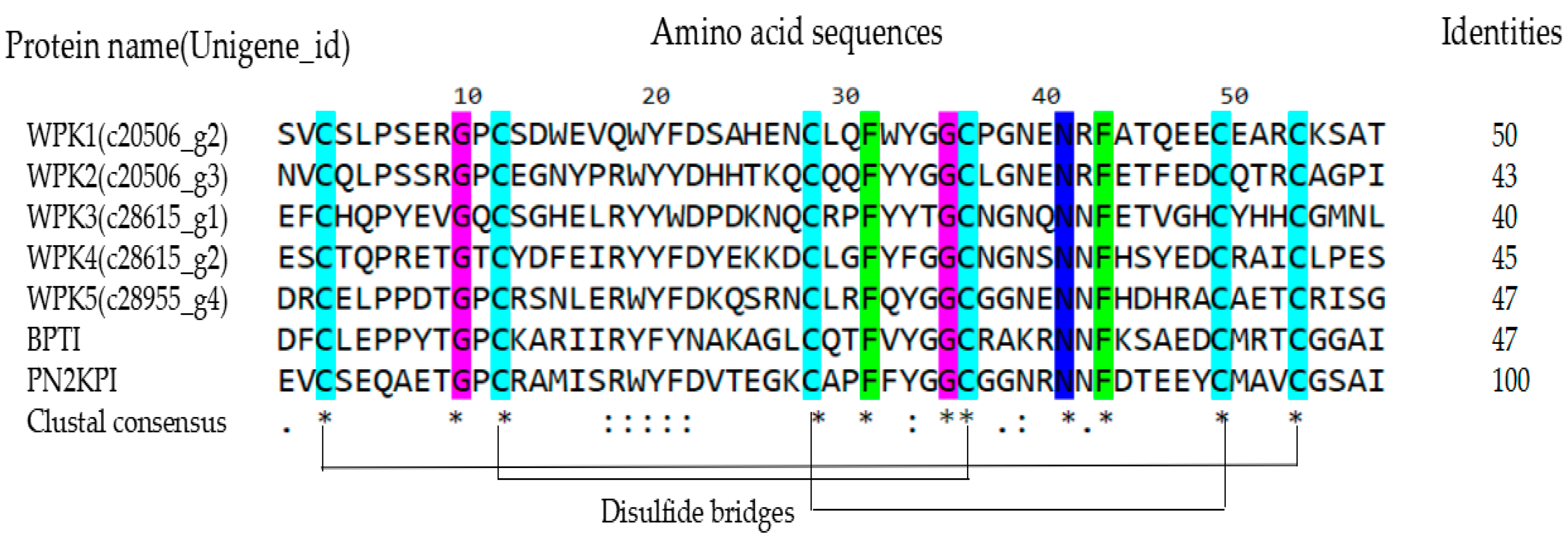
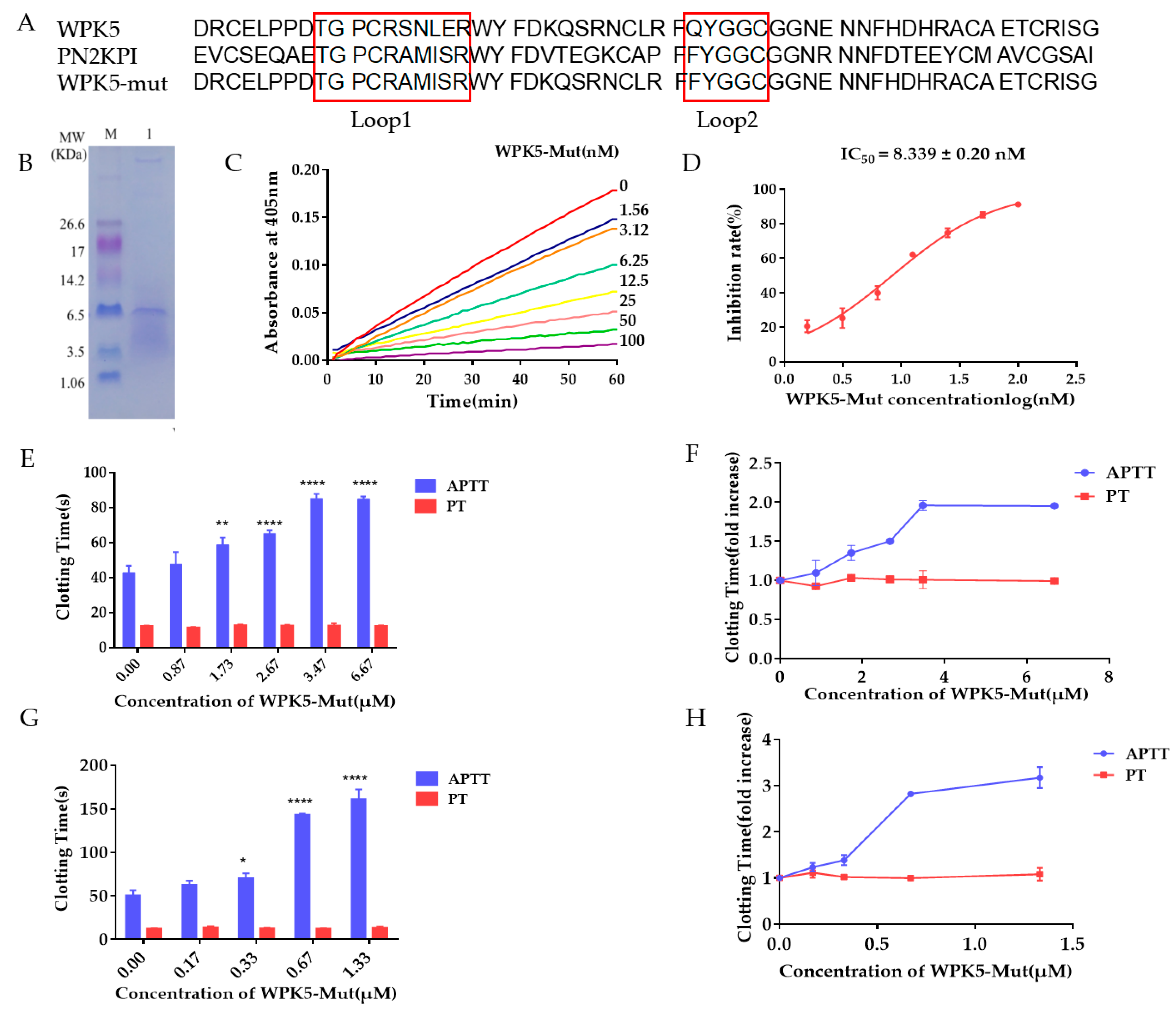
3.1. Five Kunitz-Type Peptides Were Identified from the Salivary Gland of the Leech Whitmania Pigra
3.2. Clone, Expression, and Purification of WPK1-WPK5 and WPK5-Mut
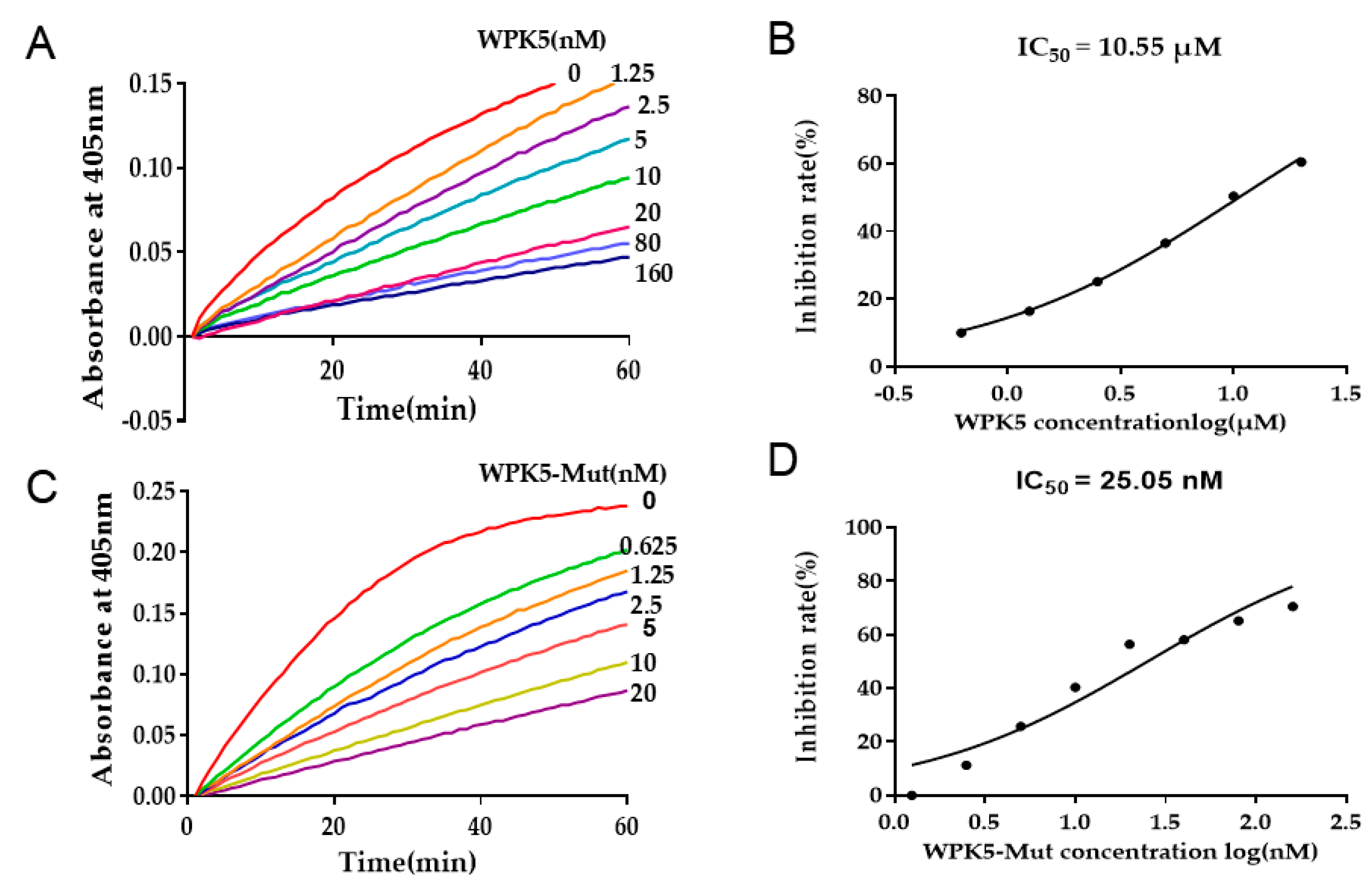
3.3. WPK5 Is a FXIa Inhibitor
3.4. Improve WPK5 Potency by Loop Replacement
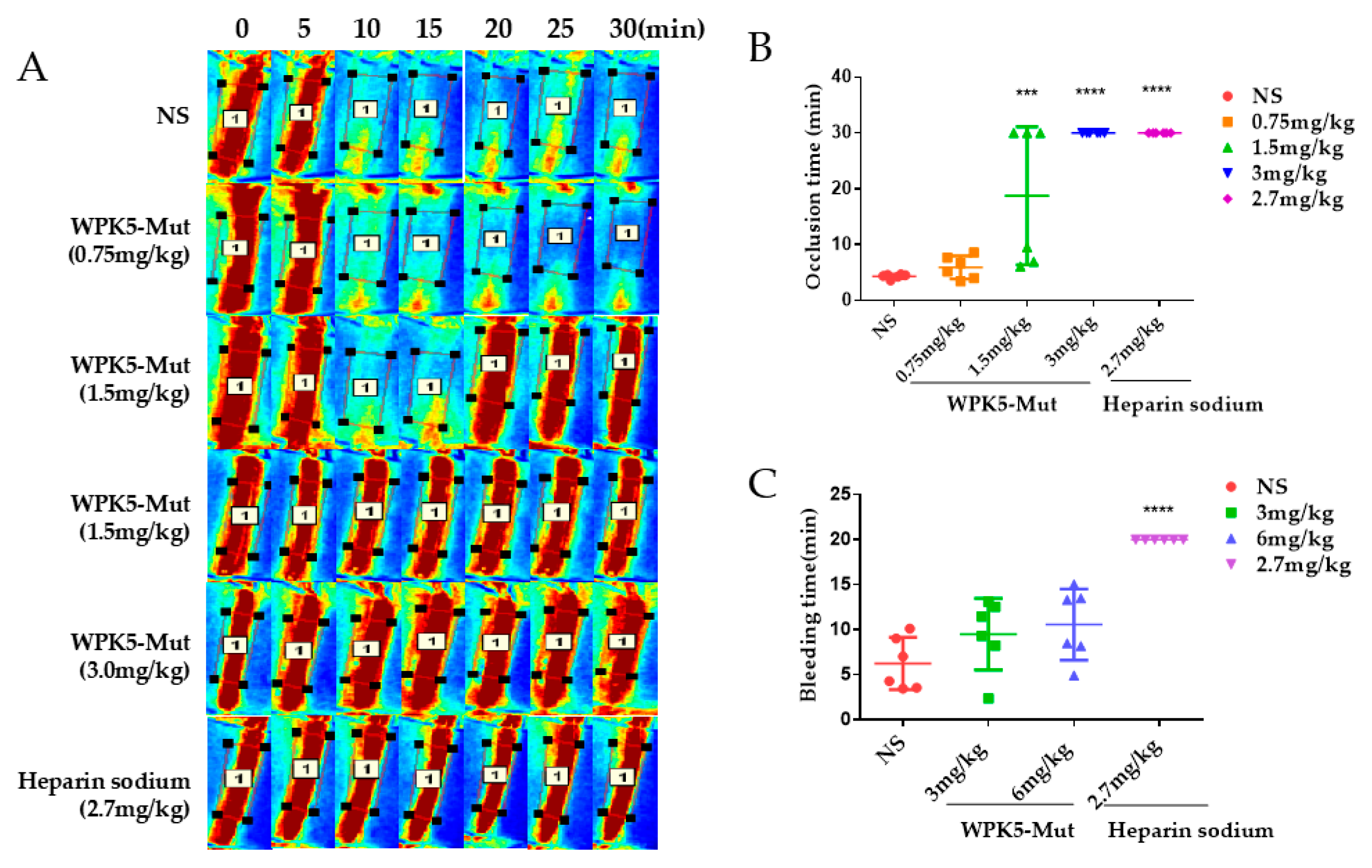
3.5. WPK5-Mut Prevent FeCl3-Induced Carotid Artery Thrombosis in Mice
3.6. WPK5-Mut Did Not Show Bleeding Risk in Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Ranasinghe, S.; McManus, D.P. Structure and function of invertebrate Kunitz serine protease inhibitors. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2013, 39, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, M. Evolutionary Aspects of the Structural Convergence and Functional Diversification of Kunitz-Domain Inhibitors. J. Mol. Evol. 2020, 88, 537–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, C.F.R.; Oliveira, C.T.; Taveira, G.B.; de Oliveira Mello, E.; Gomes, V.M.; Macedo, M.L.R. Characterization of a Kunitz trypsin inhibitor from Enterolobium timbouva with activity against Candida species. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 119, 645–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Q.; Li, S.; Siu, S.; Yang, B.; Huang, C.; Chan, J.Y.; Morlighem, J.; Wong, C.; Radis-Baptista, G.; Lee, S.M. Novel Kunitz-like Peptides Discovered in the Zoanthid Palythoa caribaeorum through Transcriptome Sequencing. J. Proteome Res. 2018, 17, 891–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shigetomi, H.; Onogi, A.; Kajiwara, H.; Yoshida, S.; Furukawa, N.; Haruta, S.; Tanase, Y.; Kanayama, S.; Noguchi, T.; Yamada, Y.; et al. Anti-inflammatory actions of serine protease inhibitors containing the Kunitz domain. Inflamm. Res. 2010, 59, 679–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsujimoto, H.; Kotsyfakis, M.; Francischetti, I.M.; Eum, J.H.; Strand, M.R.; Champagne, D.E. Simukunin from the salivary glands of the black fly Simulium vittatum inhibits enzymes that regulate clotting and inflammatory responses. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e29964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corral-Rodriguez, M.A.; Macedo-Ribeiro, S.; Barbosa, P.P.; Fuentes-Prior, P. Tick-derived Kunitz-type inhibitors as antihemostatic factors. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2009, 39, 579–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gailani, D.; Smith, S.B. Structural and functional features of factor XI. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2009, 7, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gailani, D.; Renne, T. Intrinsic pathway of coagulation and arterial thrombosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2007, 27, 2507–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, B.M.; Matafonov, A.; Ivanov, I.; Sun, M.F.; Cheng, Q.; Dickeson, S.K.; Li, C.; Sun, D.; Verhamme, I.M.; Emsley, J.; et al. An update on factor XI structure and function. Thromb. Res. 2018, 161, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomon, O.; Steinberg, D.M.; Zucker, M.; Varon, D.; Zivelin, A.; Seligsohn, U. Patients with severe factor XI deficiency have a reduced incidence of deep-vein thrombosis. Thromb. Haemost. 2011, 105, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salomon, O.; Steinberg, D.M.; Koren-Morag, N.; Tanne, D.; Seligsohn, U. Reduced incidence of ischemic stroke in patients with severe factor XI deficiency. Blood 2008, 111, 4113–4117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meijers, J.C.; Tekelenburg, W.L.; Bouma, B.N.; Bertina, R.M.; Rosendaal, F.R. High levels of coagulation factor XI as a risk factor for venous thrombosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 342, 696–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.T.; Flanders, M.M.; Kim, H.; Rodgers, G.M. Elevated factor XI activity levels are associated with an increased odds ratio for cerebrovascular events. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2006, 126, 411–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suri, M.F.; Yamagishi, K.; Aleksic, N.; Hannan, P.J.; Folsom, A.R. Novel hemostatic factor levels and risk of ischemic stroke: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2010, 29, 497–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegerink, B.; Govers-Riemslag, J.W.; Rosendaal, F.R.; Ten, C.H.; Algra, A. Intrinsic coagulation activation and the risk of arterial thrombosis in young women: Results from the Risk of Arterial Thrombosis in relation to Oral contraceptives (RATIO) case-control study. Circulation 2010, 122, 1854–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doggen, C.J.; Rosendaal, F.R.; Meijers, J.C. Levels of intrinsic coagulation factors and the risk of myocardial infarction among men: Opposite and synergistic effects of factors XI and XII. Blood 2006, 108, 4045–4051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berliner, J.I.; Rybicki, A.C.; Kaplan, R.C.; Monrad, E.S.; Freeman, R.; Billett, H.H. Elevated levels of Factor XI are associated with cardiovascular disease in women. Thromb. Res. 2002, 107, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, E.D.; Gailani, D.; Castellino, F.J. FXI is essential for thrombus formation following FeCl3-induced injury of the carotid artery in the mouse. Thromb. Haemost. 2002, 87, 774–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Cheng, Q.; Xu, L.; Feuerstein, G.Z.; Hsu, M.Y.; Smith, P.L.; Seiffert, D.A.; Schumacher, W.A.; Ogletree, M.L.; Gailani, D. Effects of factor IX or factor XI deficiency on ferric chloride-induced carotid artery occlusion in mice. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2005, 3, 695–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Smith, P.L.; Hsu, M.Y.; Gailani, D.; Schumacher, W.A.; Ogletree, M.L.; Seiffert, D.A. Effects of factor XI deficiency on ferric chloride-induced vena cava thrombosis in mice. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2006, 4, 1982–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gailani, D.; Lasky, N.M.; Broze, G.J. A murine model of factor XI deficiency. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 1997, 8, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumacher, W.A.; Seiler, S.E.; Steinbacher, T.E.; Stewart, A.B.; Bostwick, J.S.; Hartl, K.S.; Liu, E.C.; Ogletree, M.L. Antithrombotic and hemostatic effects of a small molecule factor XIa inhibitor in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 570, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, A.; Nishihira, K.; Kitazawa, T.; Yoshihashi, K.; Soeda, T.; Esaki, K.; Imamura, T.; Hattori, K.; Asada, Y. Factor XI contributes to thrombus propagation on injured neointima of the rabbit iliac artery. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2006, 4, 1496–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruber, A.; Hanson, S.R. Factor XI-dependence of surface- and tissue factor-initiated thrombus propagation in primates. Blood 2003, 102, 953–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tucker, E.I.; Marzec, U.M.; White, T.C.; Hurst, S.; Rugonyi, S.; McCarty, O.J.; Gailani, D.; Gruber, A.; Hanson, S.R. Prevention of vascular graft occlusion and thrombus-associated thrombin generation by inhibition of factor XI. Blood 2009, 113, 936–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Horani, R.A.; Afosah, D.K. Recent advances in the discovery and development of factor XI/XIa inhibitors. Med. Res. Rev. 2018, 38, 1974–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navaneetham, D.; Jin, L.; Pandey, P.; Strickler, J.E.; Babine, R.E.; Abdel-Meguid, S.S.; Walsh, P.N. Structural and mutational analyses of the molecular interactions between the catalytic domain of factor XIa and the Kunitz protease inhibitor domain of protease nexin 2. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 36165–36175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Carvalho, L.P.; Chan, M.Y.; Kini, R.M.; Kang, T.S. Fasxiator, a novel factor XIa inhibitor from snake venom, and its site-specific mutagenesis to improve potency and selectivity. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2015, 13, 248–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, D.; Mizurini, D.M.; Assumpcao, T.C.; Li, Y.; Qi, Y.; Kotsyfakis, M.; Ribeiro, J.M.; Monteiro, R.Q.; Francischetti, I.M. Desmolaris, a novel factor XIa anticoagulant from the salivary gland of the vampire bat (Desmodus rotundus) inhibits inflammation and thrombosis in vivo. Blood 2013, 122, 4094–4106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, G.X. Inhibition of thrombin: Relevance to anti-thrombosis strategy. Front. Biosci. 2006, 11, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Strube, K.H.; Kroger, B.; Bialojan, S.; Otte, M.; Dodt, J. Isolation, sequence analysis, and cloning of haemadin. An anticoagulant peptide from the Indian leech. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 8590–8595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salzet, M.; Chopin, V.; Baert, J.; Matias, I.; Malecha, J. Theromin, a novel leech thrombin inhibitor. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 30774–30780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chopin, V.; Salzet, M.; Baert, J.; Vandenbulcke, F.; Sautiere, P.E.; Kerckaert, J.P.; Malecha, J. Therostasin, a novel clotting factor Xa inhibitor from the rhynchobdellid leech, Theromyzon tessulatum. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 32701–32707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, H.J.; Park, J.S.; Medina, J.B.; Park, S.C.; Cho, S.J. Spatiotemporal Expression of Anticoagulation Factor Antistasin in Freshwater Leeches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faria, F.; Kelen, E.M.; Sampaio, C.A.; Bon, C.; Duval, N.; Chudzinski-Tavassi, A.M. A new factor Xa inhibitor (lefaxin) from the Haementeria depressa leech. Thromb. Haemost. 1999, 82, 1469–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munro, R.; Jones, C.P.; Sawyer, R.T. Calin—A platelet adhesion inhibitor from the saliva of the medicinal leech. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 1991, 2, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connolly, T.M.; Jacobs, J.W.; Condra, C. An inhibitor of collagen-stimulated platelet activation from the salivary glands of the Haementeria officinalis leech. I. Identification, isolation, and characterization. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 6893–6898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seymour, J.L.; Henzel, W.J.; Nevins, B.; Stults, J.T.; Lazarus, R.A. Decorsin. A potent glycoprotein IIb-IIIa antagonist and platelet aggregation inhibitor from the leech Macrobdella decora. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 10143–10147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazur, P.; Henzel, W.J.; Seymour, J.L.; Lazarus, R.A. Ornatins: Potent glycoprotein IIb-IIIa antagonists and platelet aggregation inhibitors from the leech Placobdella ornata. Eur. J. Biochem. 1991, 202, 1073–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.H.; Liu, Z.J.; Cao, Y.; Hua, Y.; Chen, C.; Guo, W.; Kong, Y. A novel protease-activated receptor 1 inhibitor from the leech Whitmania pigra. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2019, 17, 591–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Ye, X.; Ming, X.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Su, X.; Su, W.; Kong, Y. A Novel Direct Factor Xa Inhibitory Peptide with Anti-Platelet Aggregation Activity from Agkistrodon acutus Venom Hydrolysates. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.; Chen, M.; Duan, Z.; Mwangi, J.; Li, P.; Lai, R. Isolation and Characterization of Poecistasin, an Anti-Thrombotic Antistasin-Type Serine Protease Inhibitor from Leech Poecilobdella manillensis. Toxins 2018, 10, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwatsuki, Y.; Kawasaki, T.; Hayashi, K.; Moritani, Y.; Nii, T.; Miyata, K. Combined effects of a factor Xa inhibitor YM466 and a GPIIb/IIIa antagonist YM128 on thrombosis and neointima formation in mice. Thromb. Haemost. 2004, 92, 1221–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bennett, J.A.; Mastrangelo, M.A.; Ture, S.K.; Smith, C.O.; Loelius, S.G.; Berg, R.A.; Shi, X.; Burke, R.M.; Spinelli, S.L.; Cameron, S.J.; et al. The choline transporter Slc44a2 controls platelet activation and thrombosis by regulating mitochondrial function. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emsley, J.; McEwan, P.A.; Gailani, D. Structure and function of factor XI. Blood 2010, 115, 2569–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Li, H.; Navaneetham, D.; Reichenbach, Z.W.; Tuma, R.F.; Walsh, P.N. The kunitz protease inhibitor domain of protease nexin-2 inhibits factor XIa and murine carotid artery and middle cerebral artery thrombosis. Blood 2012, 120, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Oltersdorf, T.; Fritz, L.C.; Schenk, D.B.; Lieberburg, I.; Johnson-Wood, K.L.; Beattie, E.C.; Ward, P.J.; Blacher, R.W.; Dovey, H.F.; Sinha, S. The secreted form of the Alzheimer’s amyloid precursor protein with the Kunitz domain is protease nexin-II. Nature 1989, 341, 144–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deist, B.R.; Rausch, M.A.; Fernandez-Luna, M.T.; Adang, M.J.; Bonning, B.C. Bt toxin modification for enhanced efficacy. Toxins 2014, 6, 3005–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Liu, Y.; Ji, X.; Zheng, Y.; Li, Z.; Jiang, S.; Li, H.; Kong, Y. DAKS1, a Kunitz Scaffold Peptide from the Venom Gland of Deinagkistrodon acutus Prevents Carotid-Artery and Middle-Cerebral-Artery Thrombosis via Targeting Factor XIa. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Enzyme | Inhibition (9.782 µM) | Inhibition (97.82 µM) |
|---|---|---|
| FXa | 5.54% | 4.88% |
| FXIIa | 17.31% | 42.16% |
| Kallikrein | 57.26% | 85.25% |
| Thrombin | 0% | 23.07% |
| Trypsin | 44.40% | 85.24% |
| Inhibtor | Molar Ratio | Inhibition, % |
|---|---|---|
| WPK5-Mut | 50:1, inhibitor:FXIa | 86.21 |
| WPK5-Mut | 775:1, inhibitor:FXa | 28.25 |
| WPK5-Mut | 1550:1, inhibitor:Thrombin | −38.00 |
| WPK5-Mut | 775:1, inhibitor:Kallikrein | 25.25 |
| WPK5-Mut | 39:1, inhibitor:Trypsin | 85.20 |
| WPK5-Mut | 775:1, inhibitor:FXIIa | 21.50 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, Y.-Z.; Ji, X.-R.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Jiang, S.; Yu, X.-Y.; Jia, Z.-P.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, J.-Q.; Zhang, J.-L.; Kong, Y. WPK5, a Novel Kunitz-Type Peptide from the Leech Whitmania pigra Inhibiting Factor XIa, and Its Loop-Replaced Mutant to Improve Potency. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1745. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9121745
Zheng Y-Z, Ji X-R, Liu Y-Y, Jiang S, Yu X-Y, Jia Z-P, Zhao Y, Zhang J-Q, Zhang J-L, Kong Y. WPK5, a Novel Kunitz-Type Peptide from the Leech Whitmania pigra Inhibiting Factor XIa, and Its Loop-Replaced Mutant to Improve Potency. Biomedicines. 2021; 9(12):1745. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9121745
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Yi-Zheng, Xiao-Ru Ji, Yun-Yang Liu, Shuai Jiang, Xiang-Ying Yu, Zhi-Ping Jia, Yue Zhao, Jun-Qiao Zhang, Jia-Li Zhang, and Yi Kong. 2021. "WPK5, a Novel Kunitz-Type Peptide from the Leech Whitmania pigra Inhibiting Factor XIa, and Its Loop-Replaced Mutant to Improve Potency" Biomedicines 9, no. 12: 1745. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9121745
APA StyleZheng, Y.-Z., Ji, X.-R., Liu, Y.-Y., Jiang, S., Yu, X.-Y., Jia, Z.-P., Zhao, Y., Zhang, J.-Q., Zhang, J.-L., & Kong, Y. (2021). WPK5, a Novel Kunitz-Type Peptide from the Leech Whitmania pigra Inhibiting Factor XIa, and Its Loop-Replaced Mutant to Improve Potency. Biomedicines, 9(12), 1745. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9121745






