The Role of Circulating MicroRNAs in Patients with Early-Stage Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
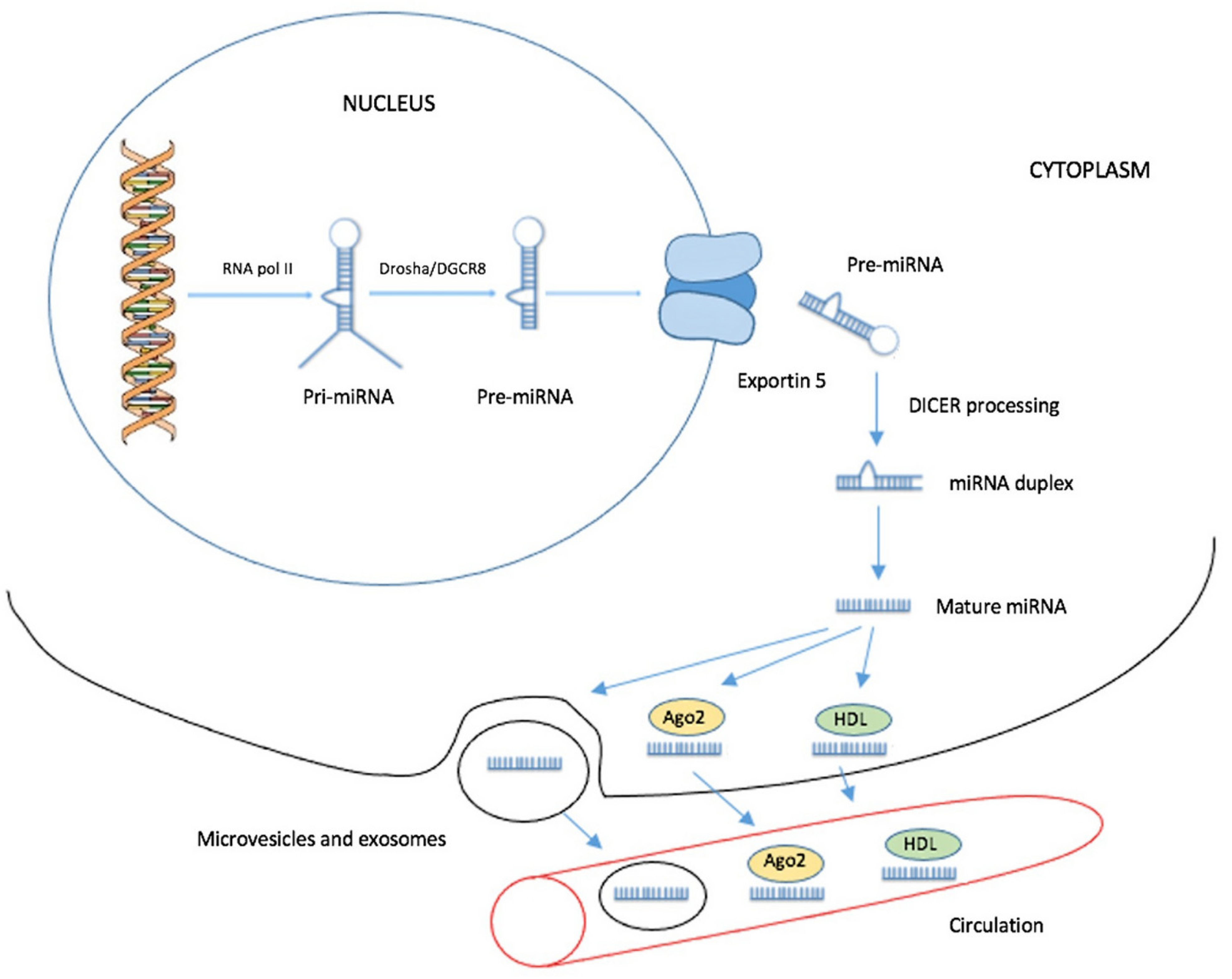
2. Biogenesis of Circulating miRNAs
3. Methods for Detection of Circulating miRNAs
4. Circulating miRNAs and Their Diagnostic Significance in Early-Stage PDAC
4.1. Characteristics of the Most Studied miRNAs with Diagnostic Potential
4.1.1. miR-21-5p
4.1.2. miR-25-3p
4.1.3. miR-182-5p
4.1.4. miR-221-3p
4.1.5. miR-483-3p
4.1.6. miR-10b-5p
5. Circulating miRNAs and Their Prognostic Significance in Early-Stage PDAC
5.1. Characteristics of the Most Studied miRNAs with Prognostic Value
5.1.1. miR-21-5p
5.1.2. miR-375-3p
5.1.3. miR-365a-3p and miR-99a-5p
5.1.4. miR-182-5p
5.1.5. miR-196a-5p
5.1.6. miR-221-3p
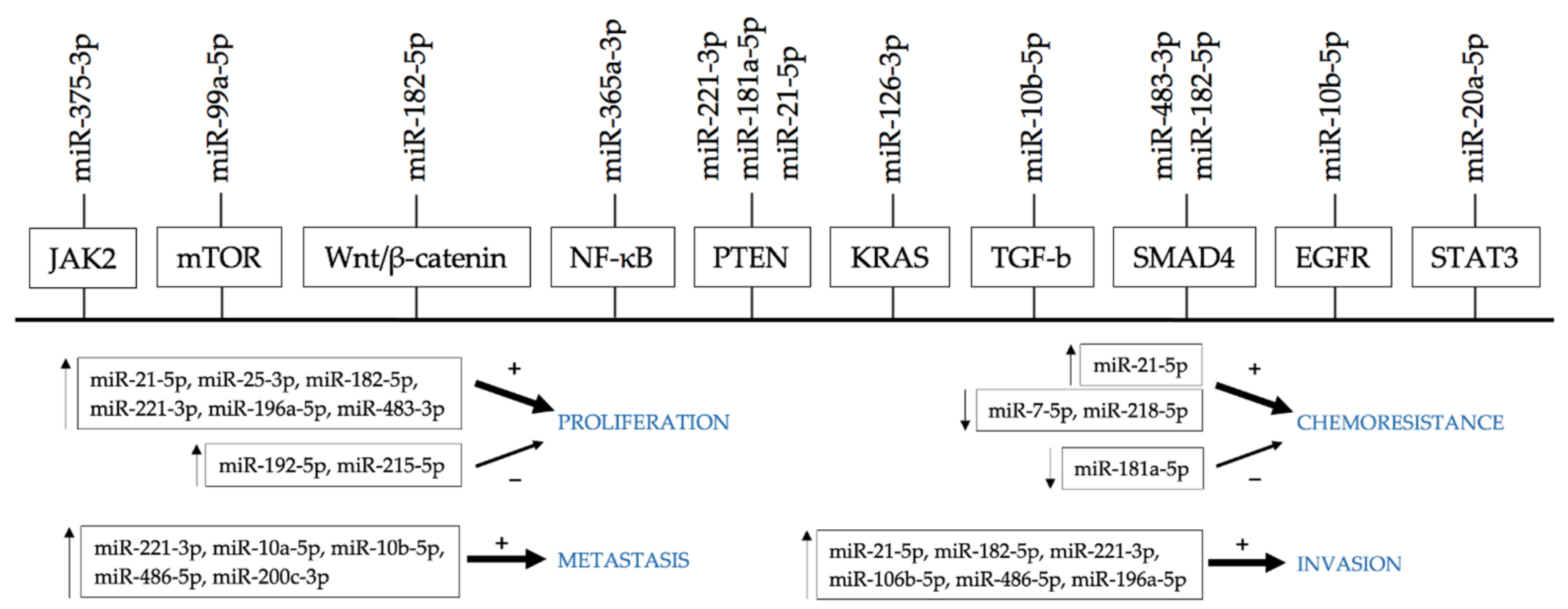
6. miRNAs as a Marker of Chemoresistance
7. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cascinu, S.; Falconi, M.; Valentini, V.; Jelic, S.; Group, E.G.W. Pancreatic cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2010, 21 (Suppl. 5), v55–v58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardini, B.; Primavesi, F.; Maglione, M.; Oberschmied, J.; Guschlbauer, L.; Gasteiger, S.; Kuscher, S.; Resch, T.; Oberhuber, R.; Margreiter, C.; et al. Outcomes following pancreatic resections—Results and challenges of an Austrian university hospital compared to nationwide data and international centres. Eur. Surg. 2019, 51, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labori, K.J.; Katz, M.H.; Tzeng, C.W.; Bjornbeth, B.A.; Cvancarova, M.; Edwin, B.; Kure, E.H.; Eide, T.J.; Dueland, S.; Buanes, T.; et al. Impact of early disease progression and surgical complications on adjuvant chemotherapy completion rates and survival in patients undergoing the surgery first approach for resectable pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma—A population-based cohort study. Acta Oncol. 2016, 55, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.E.; Lee, K.T.; Lee, J.K.; Paik, S.W.; Rhee, J.C.; Choi, K.W. Clinical usefulness of carbohydrate antigen 19-9 as a screening test for pancreatic cancer in an asymptomatic population. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2004, 19, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenner, B.; Chari, S.T.; Kelsen, D.; Klimstra, D.S.; Pandol, S.J.; Rosenthal, M.; Rustgi, A.K.; Taylor, J.A.; Yala, A.; Abul-Husn, N.; et al. Artificial Intelligence and Early Detection of Pancreatic Cancer: 2020 Summative Review. Pancreas 2021, 50, 251–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dell’Aquila, E.; Fulgenzi, C.A.M.; Minelli, A.; Citarella, F.; Stellato, M.; Pantano, F.; Russano, M.; Cursano, M.C.; Napolitano, A.; Zeppola, T.; et al. Prognostic and predictive factors in pancreatic cancer. Oncotarget 2020, 11, 924–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Nakeeb, A.; El Shobary, M.; El Dosoky, M.; Nabeh, A.; El Sorogy, M.; El Eneen, A.A.; abu Zeid, M.; Elwahab, M.A. Prognostic factors affecting survival after pancreaticoduodenectomy for pancreatic adenocarcinoma (single center experience). Hepatogastroenterology 2014, 61, 1426–1438. [Google Scholar]
- Artemaki, P.I.; Letsos, P.A.; Zoupa, I.C.; Katsaraki, K.; Karousi, P.; Papageorgiou, S.G.; Pappa, V.; Scorilas, A.; Kontos, C.K. The Multifaceted Role and Utility of MicroRNAs in Indolent B-Cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsaraki, K.; Karousi, P.; Artemaki, P.I.; Scorilas, A.; Pappa, V.; Kontos, C.K.; Papageorgiou, S.G. MicroRNAs: Tiny Regulators of Gene Expression with Pivotal Roles in Normal B-Cell Development and B-Cell Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Cancers 2021, 13, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papanota, A.M.; Karousi, P.; Kontos, C.K.; Ntanasis-Stathopoulos, I.; Scorilas, A.; Terpos, E. Multiple Myeloma Bone Disease: Implication of MicroRNAs in Its Molecular Background. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redis, R.S.; Calin, S.; Yang, Y.; You, M.J.; Calin, G.A. Cell-to-cell miRNA transfer: From body homeostasis to therapy. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 136, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, B.D.; Kasinski, A.L.; Slack, F.J. Aberrant regulation and function of microRNAs in cancer. Curr. Biol. 2014, 24, R762–R776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daoud, A.Z.; Mulholland, E.J.; Cole, G.; McCarthy, H.O. MicroRNAs in Pancreatic Cancer: Biomarkers, prognostic, and therapeutic modulators. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.Q.; Zou, C.L.; Chen, H.B.; Jiang, M.J.; Mei, Z.; Gu, D.N. MicroRNA-7 as a Potential Biomarker for Prognosis in Pancreatic Cancer. Dis. Markers 2020, 2020, 2782101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berindan-Neagoe, I.; Calin, G.A. Molecular pathways: microRNAs, cancer cells, and microenvironment. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 6247–6253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rupaimoole, R.; Calin, G.A.; Lopez-Berestein, G.; Sood, A.K. miRNA Deregulation in Cancer Cells and the Tumor Microenvironment. Cancer Discov. 2016, 6, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwagami, Y.; Eguchi, H.; Nagano, H.; Akita, H.; Hama, N.; Wada, H.; Kawamoto, K.; Kobayashi, S.; Tomokuni, A.; Tomimaru, Y.; et al. miR-320c regulates gemcitabine-resistance in pancreatic cancer via SMARCC1. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 109, 502–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gablo, N.; Trachtova, K.; Prochazka, V.; Hlavsa, J.; Grolich, T.; Kiss, I.; Srovnal, J.; Rehulkova, A.; Lovecek, M.; Skalicky, P.; et al. Identification and Validation of Circulating Micrornas as Prognostic Biomarkers in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Patients Undergoing Surgical Resection. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rie, D.; Abugessaisa, I.; Alam, T.; Arner, E.; Arner, P.; Ashoor, H.; Astrom, G.; Babina, M.; Bertin, N.; Burroughs, A.M.; et al. An integrated expression atlas of miRNAs and their promoters in human and mouse. Nat. Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 872–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, H.K.; Griffiths-Jones, S.; Enright, A.J. Genomic ana.alysis of human microRNA transcripts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 17719–17724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, X.; Hagedorn, C.H.; Cullen, B.R. Human microRNAs are processed from capped, polyadenylated transcripts that can also function as mRNAs. RNA 2004, 10, 1957–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Kim, M.; Han, J.; Yeom, K.H.; Lee, S.; Baek, S.H.; Kim, V.N. MicroRNA genes are transcribed by RNA polymerase II. EMBO J. 2004, 23, 4051–4060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.L.; Miller, J.D.; Ying, S.Y. Intronic microRNA (miRNA). J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2006, 2006, 26818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garajova, I.; Le Large, T.Y.; Frampton, A.E.; Rolfo, C.; Voortman, J.; Giovannetti, E. Molecular mechanisms underlying the role of microRNAs in the chemoresistance of pancreatic cancer. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 678401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Ahn, C.; Han, J.; Choi, H.; Kim, J.; Yim, J.; Lee, J.; Provost, P.; Radmark, O.; Kim, S.; et al. The nuclear RNase III Drosha initiates microRNA processing. Nature 2003, 425, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.C.; Chen, T.H.; Huang, Y.M.; Wei, P.L.; Lin, J.C. Involvement of microRNA in Solid Cancer: Role and Regulatory Mechanisms. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, J.; Hayder, H.; Zayed, Y.; Peng, C. Overview of MicroRNA Biogenesis, Mechanisms of Actions, and Circulation. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forman, J.J.; Legesse-Miller, A.; Coller, H.A. A search for conserved sequences in coding regions reveals that the let-7 microRNA targets Dicer within its coding sequence. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 14879–14884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; San Lucas, A.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y. Identifying microRNA targets in different gene regions. BMC Bioinform. 2014, 15 (Suppl. 7), S4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhou, W.; Liu, Y.; Liu, T.; Li, C.; Wang, L. Oncogenic role of microRNA-532-5p in human colorectal cancer via targeting of the 5’UTR of RUNX3. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 7215–7220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huntzinger, E.; Izaurralde, E. Gene silencing by microRNAs: Contributions of translational repression and mRNA decay. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2011, 12, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, K.; Zhang, X.; Lin, T.; Liu, T.; Wang, Z.; Liu, S.; Zhou, L.; Wei, J.; Chang, H.; Li, K.; et al. Circulating miRNA-21-5p as a diagnostic biomarker for pancreatic cancer: Evidence from comprehensive miRNA expression profiling analysis and clinical validation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalluri, R.; LeBleu, V.S. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science 2020, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arroyo, J.D.; Chevillet, J.R.; Kroh, E.M.; Ruf, I.K.; Pritchard, C.C.; Gibson, D.F.; Mitchell, P.S.; Bennett, C.F.; Pogosova-Agadjanyan, E.L.; Stirewalt, D.L.; et al. Argonaute2 complexes carry a population of circulating microRNAs independent of vesicles in human plasma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 5003–5008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turchinovich, A.; Samatov, T.R.; Tonevitsky, A.G.; Burwinkel, B. Circulating miRNAs: Cell-cell communication function? Front. Genet. 2013, 4, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turchinovich, A.; Weiz, L.; Langheinz, A.; Burwinkel, B. Characterization of extracellular circulating microRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 7223–7233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vickers, K.C.; Palmisano, B.T.; Shoucri, B.M.; Shamburek, R.D.; Remaley, A.T. MicroRNAs are transported in plasma and delivered to recipient cells by high-density lipoproteins. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011, 13, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, J.A.; Baxter, D.H.; Zhang, S.; Huang, D.Y.; Huang, K.H.; Lee, M.J.; Galas, D.J.; Wang, K. The microRNA spectrum in 12 body fluids. Clin. Chem. 2010, 56, 1733–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halkova, T.; Cuperkova, R.; Minarik, M.; Benesova, L. MicroRNAs in Pancreatic Cancer: Involvement in Carcinogenesis and Potential Use for Diagnosis and Prognosis. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2015, 2015, 892903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eloubeidi, M.A.; Jhala, D.; Chhieng, D.C.; Chen, V.K.; Eltoum, I.; Vickers, S.; Mel Wilcox, C.; Jhala, N. Yield of endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration biopsy in patients with suspected pancreatic carcinoma. Cancer 2003, 99, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilad, S.; Meiri, E.; Yogev, Y.; Benjamin, S.; Lebanony, D.; Yerushalmi, N.; Benjamin, H.; Kushnir, M.; Cholakh, H.; Melamed, N.; et al. Serum microRNAs are promising novel biomarkers. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kroh, E.M.; Parkin, R.K.; Mitchell, P.S.; Tewari, M. Analysis of circulating microRNA biomarkers in plasma and serum using quantitative reverse transcription-PCR (qRT-PCR). Methods 2010, 50, 298–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Kowdley, K.V. Method for microRNA isolation from clinical serum samples. Anal. Biochem. 2012, 431, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, J.S.; Milosevic, D.; Reddi, H.V.; Grebe, S.K.; Algeciras-Schimnich, A. Analysis of circulating microRNA: Preanalytical and analytical challenges. Clin. Chem. 2011, 57, 833–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trakunram, K.; Champoochana, N.; Chaniad, P.; Thongsuksai, P.; Raungrut, P. MicroRNA Isolation by Trizol-Based Method and Its Stability in Stored Serum and cDNA Derivatives. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2019, 20, 1641–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mitchell, P.S.; Parkin, R.K.; Kroh, E.M.; Fritz, B.R.; Wyman, S.K.; Pogosova-Agadjanyan, E.L.; Peterson, A.; Noteboom, J.; O’Briant, K.C.; Allen, A.; et al. Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based markers for cancer detection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 10513–10518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaguchi, T.; Komatsu, S.; Ichikawa, D.; Morimura, R.; Tsujiura, M.; Konishi, H.; Takeshita, H.; Nagata, H.; Arita, T.; Hirajima, S.; et al. Clinical impact of circulating miR-221 in plasma of patients with pancreatic cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 108, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimura, R.; Komatsu, S.; Ichikawa, D.; Takeshita, H.; Tsujiura, M.; Nagata, H.; Konishi, H.; Shiozaki, A.; Ikoma, H.; Okamoto, K.; et al. Novel diagnostic value of circulating miR-18a in plasma of patients with pancreatic cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2011, 105, 1733–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ideozu, J.E.; Zhang, X.; Rangaraj, V.; McColley, S.; Levy, H. Microarray profiling identifies extracellular circulating miRNAs dysregulated in cystic fibrosis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, Z.B.; Bartak, B.K.; Kalmar, A.; Galamb, O.; Wichmann, B.; Dank, M.; Igaz, P.; Tulassay, Z.; Molnar, B. Comparison of Circulating miRNAs Expression Alterations in Matched Tissue and Plasma Samples During Colorectal Cancer Progression. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2019, 25, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, A.; Kwee, L.C.; Grass, E.; Neely, M.L.; Gregory, S.G.; Fox, K.A.A.; Armstrong, P.W.; White, H.D.; Ohman, E.M.; Roe, M.T.; et al. Whole blood sequencing reveals circulating microRNA associations with high-risk traits in non-ST-segment elevation acute coronary syndrome. Atherosclerosis 2017, 261, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawat, M.; Kadian, K.; Gupta, Y.; Kumar, A.; Chain, P.S.G.; Kovbasnjuk, O.; Kumar, S.; Parasher, G. MicroRNA in Pancreatic Cancer: From Biology to Therapeutic Potential. Genes 2019, 10, 752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shams, R.; Saberi, S.; Zali, M.; Sadeghi, A.; Ghafouri-Fard, S.; Aghdaei, H.A. Identification of potential microRNA panels for pancreatic cancer diagnosis using microarray datasets and bioinformatics methods. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duell, E.J.; Lujan-Barroso, L.; Sala, N.; Deitz McElyea, S.; Overvad, K.; Tjonneland, A.; Olsen, A.; Weiderpass, E.; Busund, L.T.; Moi, L.; et al. Plasma microRNAs as biomarkers of pancreatic cancer risk in a prospective cohort study. Int. J. Cancer 2017, 141, 905–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, J.; Jia, E.; Ren, N.; Lindsay, A.; Yu, H. Circulating microRNAs as promising diagnostic biomarkers for pancreatic cancer: A systematic review. Onco Targets Ther. 2019, 12, 6665–6684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, N.A.; Kholy, Z.A.; Anwar, M.M.; Ahmad, M.A.; Ahmad, S.M. Plasma miR-22-3p, miR-642b-3p and miR-885-5p as diagnostic biomarkers for pancreatic cancer. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 143, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, X.; Wang, M.; McElyea, S.D.; Sherman, S.; House, M.; Korc, M. A microRNA signature in circulating exosomes is superior to exosomal glypican-1 levels for diagnosing pancreatic cancer. Cancer Lett. 2017, 393, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slater, E.P.; Strauch, K.; Rospleszcz, S.; Ramaswamy, A.; Esposito, I.; Kloppel, G.; Matthai, E.; Heeger, K.; Fendrich, V.; Langer, P.; et al. MicroRNA-196a and -196b as Potential Biomarkers for the Early Detection of Familial Pancreatic Cancer. Transl. Oncol. 2014, 7, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Chen, X.; Du, Y.; Yao, W.; Shen, L.; Wang, C.; Hu, Z.; Zhuang, R.; Ning, G.; Zhang, C.; et al. Serum microRNA expression profile as a biomarker in the diagnosis and prognosis of pancreatic cancer. Clin. Chem. 2012, 58, 610–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganepola, G.A.; Rutledge, J.R.; Suman, P.; Yiengpruksawan, A.; Chang, D.H. Novel blood-based microRNA biomarker panel for early diagnosis of pancreatic cancer. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2014, 6, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Cao, Z.; Liu, W.; You, L.; Zhou, L.; Wang, C.; Lou, W.; Sun, B.; Miao, Y.; Liu, X.; et al. Plasma miRNAs Effectively Distinguish Patients With Pancreatic Cancer From Controls: A Multicenter Study. Ann. Surg. 2016, 263, 1173–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, I.A.; Rashid, S.; Singh, N.; Rashid, S.; Singh, V.; Gunjan, D.; Das, P.; Dash, N.R.; Pandey, R.M.; Chauhan, S.S.; et al. Panel of serum miRNAs as potential non-invasive biomarkers for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iorio, M.V.; Croce, C.M. MicroRNAs in cancer: Small molecules with a huge impact. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 5848–5856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagao, Y.; Hisaoka, M.; Matsuyama, A.; Kanemitsu, S.; Hamada, T.; Fukuyama, T.; Nakano, R.; Uchiyama, A.; Kawamoto, M.; Yamaguchi, K.; et al. Association of microRNA-21 expression with its targets, PDCD4 and TIMP3, in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Mod. Pathol. 2012, 25, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Bart, J.; Tan, L.P.; Platteel, I.; Sluis, T.; Huitema, S.; Harms, G.; Fu, L.; Hollema, H.; Berg, A. Expression of miR-21 and its targets (PTEN, PDCD4, TM1) in flat epithelial atypia of the breast in relation to ductal carcinoma in situ and invasive carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2009, 9, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.H.; Tsao, C.J. Emerging role of microRNA-21 in cancer. Biomed. Rep. 2016, 5, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.; Zhou, X.; Dang, Y.; Yan, J.; Zhang, G. Potential Role of Circulating MiR-21 in the Diagnosis and Prognosis of Digestive System Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Medicine 2015, 94, e2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frampton, A.E.; Krell, J.; Jamieson, N.B.; Gall, T.M.; Giovannetti, E.; Funel, N.; Mato Prado, M.; Krell, D.; Habib, N.A.; Castellano, L.; et al. microRNAs with prognostic significance in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: A meta-analysis. Eur. J. Cancer 2015, 51, 1389–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hruban, R.H.; Adsay, N.V.; Albores-Saavedra, J.; Compton, C.; Garrett, E.S.; Goodman, S.N.; Kern, S.E.; Klimstra, D.S.; Kloppel, G.; Longnecker, D.S.; et al. Pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia: A new nomenclature and classification system for pancreatic duct lesions. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2001, 25, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hruban, R.H.; Takaori, K.; Klimstra, D.S.; Adsay, N.V.; Albores-Saavedra, J.; Biankin, A.V.; Biankin, S.A.; Compton, C.; Fukushima, N.; Furukawa, T.; et al. An illustrated consensus on the classification of pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia and intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2004, 28, 977–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaConti, J.J.; Shivapurkar, N.; Preet, A.; Deslattes Mays, A.; Peran, I.; Kim, S.E.; Marshall, J.L.; Riegel, A.T.; Wellstein, A. Tissue and serum microRNAs in the Kras(G12D) transgenic animal model and in patients with pancreatic cancer. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Li, A.; Hong, S.M.; Hruban, R.H.; Goggins, M. MicroRNA alterations of pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasias. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 981–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caponi, S.; Funel, N.; Frampton, A.E.; Mosca, F.; Santarpia, L.; Van der Velde, A.G.; Jiao, L.R.; De Lio, N.; Falcone, A.; Kazemier, G.; et al. The good, the bad and the ugly: A tale of miR-101, miR-21 and miR-155 in pancreatic intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms. Ann. Oncol. 2013, 24, 734–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, L.R.; Frampton, A.E.; Jacob, J.; Pellegrino, L.; Krell, J.; Giamas, G.; Tsim, N.; Vlavianos, P.; Cohen, P.; Ahmad, R.; et al. MicroRNAs targeting oncogenes are down-regulated in pancreatic malignant transformation from benign tumors. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e32068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abue, M.; Yokoyama, M.; Shibuya, R.; Tamai, K.; Yamaguchi, K.; Sato, I.; Tanaka, N.; Hamada, S.; Shimosegawa, T.; Sugamura, K.; et al. Circulating miR-483-3p and miR-21 is highly expressed in plasma of pancreatic cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 46, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Bai, R.; Li, M.; Ye, H.; Wu, C.; Wang, C.; Li, S.; Tan, L.; Mai, D.; Li, G.; et al. Excessive miR-25-3p maturation via N(6)-methyladenosine stimulated by cigarette smoke promotes pancreatic cancer progression. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Tong, Y.; Zhong, A.; Wang, Y.; Lu, R.; Guo, L. Identification of Serum microRNA-25 as a novel biomarker for pancreatic cancer. Medicine 2020, 99, e23863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artemaki, P.I.; Scorilas, A.; Kontos, C.K. Circular RNAs: A New Piece in the Colorectal Cancer Puzzle. Cancers 2020, 12, 2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verheyen, E.M.; Gottardi, C.J. Regulation of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling by protein kinases. Dev. Dyn. 2010, 239, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papatsirou, M.; Artemaki, P.I.; Karousi, P.; Scorilas, A.; Kontos, C.K. Circular RNAs: Emerging Regulators of the Major Signaling Pathways Involved in Cancer Progression. Cancers 2021, 13, 2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Ji, J.; Song, J.; Li, X.; Han, S.; Lian, W.; Cao, C.; Zhang, X.; Li, M. MicroRNA-182 promotes pancreatic cancer cell proliferation and migration by targeting beta-TrCP2. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2016, 48, 1085–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Yang, L.; Xiao, Y.; Zhu, J.; Li, Z. Circulating microRNA-182 in plasma and its potential diagnostic and prognostic value for pancreatic cancer. Med. Oncol. 2014, 31, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S.; Dubaybo, H.; Ali, S.; Goncalves, P.; Kollepara, S.L.; Sethi, S.; Philip, P.A.; Li, Y.W. Down-regulation of miR-221 inhibits proliferation of pancreatic cancer cells through up-regulation of PTEN, p27(kip1), p57(kip2), and PUMA. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2013, 3, 465–477. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Q.H.; Li, P.; Chen, X.; Zong, L.; Jiang, Z.D.; Nan, L.G.; Lei, J.J.; Duan, W.X.; Zhang, D.; Li, X.Q.; et al. miR-221/222 induces pancreatic cancer progression through the regulation of matrix metalloproteinases. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 14153–14164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, Y.; Hu, X.; Shao, C. MicroRNA 483-3p suppresses the expression of DPC4/Smad4 in pancreatic cancer. FEBS Lett. 2011, 585, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilentz, R.E.; Iacobuzio-Donahue, C.A.; Argani, P.; McCarthy, D.M.; Parsons, J.L.; Yeo, C.J.; Kern, S.E.; Hruban, R.H. Loss of expression of Dpc4 in pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia: Evidence that DPC4 inactivation occurs late in neoplastic progression. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 2002–2006. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bloomston, M.; Frankel, W.L.; Petrocca, F.; Volinia, S.; Alder, H.; Hagan, J.P.; Liu, C.G.; Bhatt, D.; Taccioli, C.; Croce, C.M. MicroRNA expression patterns to differentiate pancreatic adenocarcinoma from normal pancreas and chronic pancreatitis. JAMA 2007, 297, 1901–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, H.; Gore, J.; Deitz, S.; Korc, M. microRNA-10b enhances pancreatic cancer cell invasion by suppressing TIP30 expression and promoting EGF and TGF-beta actions. Oncogene 2014, 33, 4664–4674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira-Cunha, M.; Newman, W.G.; Siriwardena, A.K. Epidermal growth factor receptor in pancreatic cancer. Cancers 2011, 3, 1513–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strobel, O.; Hank, T.; Hinz, U.; Bergmann, F.; Schneider, L.; Springfeld, C.; Jager, D.; Schirmacher, P.; Hackert, T.; Buchler, M.W. Pancreatic Cancer Surgery: The New R-status Counts. Ann. Surg. 2017, 265, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Q.; Hao, X.; Zhang, M.; Tang, W.; Yang, M.; Li, L.; Xiang, D.; Desano, J.T.; Bommer, G.T.; Fan, D.; et al. MicroRNA miR-34 inhibits human pancreatic cancer tumor-initiating cells. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e6816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhayat, S.A.; Abdeen, B.; Kohler, G.; Senninger, N.; Haier, J.; Mardin, W.A. MicroRNA-100 and microRNA-21 as markers of survival and chemotherapy response in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma UICC stage II. Clin. Epigenetics 2015, 7, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovannetti, E.; Funel, N.; Peters, G.J.; Del Chiaro, M.; Erozenci, L.A.; Vasile, E.; Leon, L.G.; Pollina, L.E.; Groen, A.; Falcone, A.; et al. MicroRNA-21 in pancreatic cancer: Correlation with clinical outcome and pharmacologic aspects underlying its role in the modulation of gemcitabine activity. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 4528–4538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.H.; Voortman, J.; Giovannetti, E.; Steinberg, S.M.; Leon, L.G.; Kim, Y.T.; Funel, N.; Park, J.K.; Kim, M.A.; Kang, G.H.; et al. Identification of microRNA-21 as a biomarker for chemoresistance and clinical outcome following adjuvant therapy in resectable pancreatic cancer. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamieson, N.B.; Morran, D.C.; Morton, J.P.; Ali, A.; Dickson, E.J.; Carter, C.R.; Sansom, O.J.; Evans, T.R.; McKay, C.J.; Oien, K.A. MicroRNA molecular profiles associated with diagnosis, clinicopathologic criteria, and overall survival in patients with resectable pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 534–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, M.Z.; Kong, X.; Weng, M.Z.; Cheng, K.; Gong, W.; Quan, Z.W.; Peng, C.H. Candidate microRNA biomarkers of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: Meta-analysis, experimental validation and clinical significance. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 32, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaconstantinou, I.G.; Manta, A.; Gazouli, M.; Lyberopoulou, A.; Lykoudis, P.M.; Polymeneas, G.; Voros, D. Expression of microRNAs in patients with pancreatic cancer and its prognostic significance. Pancreas 2013, 42, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Zhuang, L.; Zhang, J.; Fan, J.; Luo, J.; Chen, H.; Wang, K.; Liu, L.; Chen, Z.; Meng, Z. The serum miR-21 level serves as a predictor for the chemosensitivity of advanced pancreatic cancer, and miR-21 expression confers chemoresistance by targeting FasL. Mol. Oncol. 2013, 7, 334–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dillhoff, M.; Liu, J.; Frankel, W.; Croce, C.; Bloomston, M. MicroRNA-21 is overexpressed in pancreatic cancer and a potential predictor of survival. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2008, 12, 2171–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadera, B.E.; Li, L.; Toste, P.A.; Wu, N.; Adams, C.; Dawson, D.W.; Donahue, T.R. MicroRNA-21 in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma tumor-associated fibroblasts promotes metastasis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, K.; Cunningham, D.; Peckitt, C.; Barton, S.; Tait, D.; Hawkins, M.; Watkins, D.; Starling, N.; Rao, S.; Begum, R.; et al. miR-21 expression and clinical outcome in locally advanced pancreatic cancer: Exploratory analysis of the pancreatic cancer Erbitux, radiotherapy and UFT (PERU) trial. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 12672–12681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.Y.; Tao, F.; Wang, W.; Ji, K.W. Prognostic value of microRNA-21 in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: A meta-analysis. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2016, 14, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karasek, P.; Gablo, N.; Hlavsa, J.; Kiss, I.; Vychytilova-Faltejskova, P.; Hermanova, M.; Kala, Z.; Slaby, O.; Prochazka, V. Pre-operative Plasma miR-21-5p Is a Sensitive Biomarker and Independent Prognostic Factor in Patients with Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Undergoing Surgical Resection. Cancer Genom. Proteom. 2018, 15, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Du, Y.; Wang, G.; Gao, J.; Gong, Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, J.; Jing, Q.; Qin, Y.; et al. Detection of differentially expressed microRNAs in serum of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma patients: miR-196a could be a potential marker for poor prognosis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2011, 56, 602–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.-W.; Lin, J.-S.; He, X.-X. The emerging role of miR-375 in cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 135, 1011–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Li, X.; Cao, W.; Qi, Y.; Yang, X. Antagonism of microRNA-99a promotes cell invasion and down-regulates E-cadherin expression in pancreatic cancer cells by regulating mammalian target of rapamycin. Acta Histochem. 2014, 116, 723–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costello, E.; Greenhalf, W.; Neoptolemos, J.P. New biomarkers and targets in pancreatic cancer and their application to treatment. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 9, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giovannetti, E.; Erozenci, A.; Smit, J.; Danesi, R.; Peters, G.J. Molecular mechanisms underlying the role of microRNAs (miRNAs) in anticancer drug resistance and implications for clinical practice. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2012, 81, 103–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Gu, J.; Li, J. Mechanisms of drug resistance of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma at different levels. Biosci. Rep. 2020, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahreddine, H.; Borden, K. Mechanisms and insights into drug resistance in cancer. Front. Pharmacol. 2013, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garofalo, M.; Croce, C.M. MicroRNAs as therapeutic targets in chemoresistance. Drug Resist. Update 2013, 16, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gisel, A.; Valvano, M.; El Idrissi, I.G.; Nardulli, P.; Azzariti, A.; Carrieri, A.; Contino, M.; Colabufo, N.A. miRNAs for the detection of multidrug resistance: Overview and perspectives. Molecules 2014, 19, 5611–5623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijer, L.L.; Garajova, I.; Caparello, C.; Le Large, T.Y.S.; Frampton, A.E.; Vasile, E.; Funel, N.; Kazemier, G.; Giovannetti, E. Plasma miR-181a-5p Downregulation Predicts Response and Improved Survival After FOLFIRINOX in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Ann. Surg. 2020, 271, 1137–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boni, V.; Bitarte, N.; Cristobal, I.; Zarate, R.; Rodriguez, J.; Maiello, E.; Garcia-Foncillas, J.; Bandres, E. miR-192/miR-215 influence 5-fluorouracil resistance through cell cycle-mediated mechanisms complementary to its post-transcriptional thymidilate synthase regulation. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2010, 9, 2265–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paik, W.H.; Kim, H.R.; Park, J.K.; Song, B.J.; Lee, S.H.; Hwang, J.H. Chemosensitivity induced by down-regulation of microRNA-21 in gemcitabine-resistant pancreatic cancer cells by indole-3-carbinol. Anticancer Res. 2013, 33, 1473–1481. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, X.; Wang, W.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, M.; Wang, F.; Yu, J.; Ma, Y.; Sun, G. MicroRNA-21 induces 5-fluorouracil resistance in human pancreatic cancer cells by regulating PTEN and PDCD4. Cancer Med. 2016, 5, 693–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.K.; Lee, E.J.; Esau, C.; Schmittgen, T.D. Antisense inhibition of microRNA-21 or -221 arrests cell cycle, induces apoptosis, and sensitizes the effects of gemcitabine in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Pancreas 2009, 38, e190–e199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papatsirou, M.; Artemaki, P.I.; Scorilas, A.; Kontos, C.K. The role of circular RNAs in therapy resistance of patients with solid tumors. Pers. Med. 2020, 17, 469–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krutzfeldt, J.; Rajewsky, N.; Braich, R.; Rajeev, K.G.; Tuschl, T.; Manoharan, M.; Stoffel, M. Silencing of microRNAs in vivo with ‘antagomirs’. Nature 2005, 438, 685–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhao, L.; Ischenko, I.; Bao, Q.; Schwarz, B.; Niess, H.; Wang, Y.; Renner, A.; Mysliwietz, J.; Jauch, K.W.; et al. Antisense inhibition of microRNA-21 and microRNA-221 in tumor-initiating stem-like cells modulates tumorigenesis, metastasis, and chemotherapy resistance in pancreatic cancer. Target. Oncol. 2015, 10, 535–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| miRNAs with Promising Diagnostic Utility (as Standalone or in Panels) | Source | Control | Number of PDAC Patients: All Stages (Stages I and II) vs. Controls | Regulation in PDAC Samples | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-21-5p, miR-30c-5p, miR-10b-5p | Plasma | NC | 225 (N/A) vs. 225 | Upregulation | [55] |
| miR-10b-5p, miR-21-5p, miR-30c-5p, miR-181a-5p, let-7a-5p | Plasma/exosomes | CP/NC | 29 (27) vs. 17 | Upregulation (downregulation: let-7a-5p) | [58] |
| miR-22-3p, miR-642b-3p, miR-885-5p | Plasma | NC | 35 (33) vs. 15 | Upregulation | [57] |
| miR-196a-5p, miR-196b-5p | Serum | pNET/CP/PanIN1/NC | 19 (9) vs. 35 | Upregulation | [59] |
| miR-20a-5p, miR-21-5p, miR-24-3p, miR-25-3p, miR-99a-5p, miR-185-5p, miR-191-5p | Serum | CP/NC | 197 (74) vs. 240 | Upregulation | [60] |
| miR-642b-3p, miR-885-5p, miR-22-3p | Plasma | NC | 11 (11) vs. 22 | Upregulation | [61] |
| miR-486-5p, miR-126-3p, miR-938 | Plasma | NC | 156 (113) vs. 65 | Upregulation | [62] |
| miR-126-3p, miR-26b-3p, miR-938, miR-19b-3p | Plasma | pNET | 156 (113) vs. 27 | Upregulation | [62] |
| miR-486-5p, miR-126-3p, miR-938, miR-663b, miR-19b-3p | Plasma | CP | 156 (113) vs. 57 | Upregulation (downregulation: miR-663b) | [62] |
| miR-215-5p, miR-122-5p, miR-192-5p, miR-30b-5p, miR-320b | Serum | CP/NC | 50 (15) vs. 75 | Upregulation (downregulation: miR-30b-5p and miR-320b) | [63] |
| miR-21-5p | Plasma | NC | 32 (N/A) vs. 42 | Upregulation | [76] |
| miR-483-3p | Plasma | IPMN/NC | 32 (N/A) vs. 42 | Upregulation | [76] |
| miR-25-3p | Serum | NC | 80 (42) vs. 91 | Upregulation | [78] |
| miR-182-5p | Plasma | CP/NC | 109 (38) vs. 88 | Upregulation | [83] |
| miR-221-3p | Plasma | NC | 42 PDAC + 5 other pancreatic cancers (16 at stage I-IIA) vs. 30 | Upregulation | [48] |
| miR-10b-5p | Plasma | CP/NC | 17 (N/A) vs. 25 | Upregulation | [89] |
| miRNA | Tumor Stage | Source | Prognosis | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-365a-3p | Resectable | Plasma | Good | [19] |
| miR-99a-5p | Resectable | Plasma | Good | [19] |
| miR-200c-3p | Resectable | Plasma | Poor | [19] |
| miR-21-5p | All | Plasma/serum | Poor | [76,103] |
| Resectable | Plasma | Poor | [104] | |
| miR-182-5p | Resectable | Plasma | Poor | [83] |
| miR-221-3p | All | Plasma | Poor | [48] |
| miR-375-3p | Resectable | Plasma | Poor | [104] |
| miR-196a-5p | All | Serum | Poor | [105] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Eid, M.; Karousi, P.; Kunovský, L.; Tuček, Š.; Brančíková, D.; Kala, Z.; Slabý, O.; Mayer, J.; Kontos, C.K.; Trna, J. The Role of Circulating MicroRNAs in Patients with Early-Stage Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1468. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9101468
Eid M, Karousi P, Kunovský L, Tuček Š, Brančíková D, Kala Z, Slabý O, Mayer J, Kontos CK, Trna J. The Role of Circulating MicroRNAs in Patients with Early-Stage Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. Biomedicines. 2021; 9(10):1468. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9101468
Chicago/Turabian StyleEid, Michal, Paraskevi Karousi, Lumír Kunovský, Štěpán Tuček, Dagmar Brančíková, Zdeněk Kala, Ondřej Slabý, Jiří Mayer, Christos K. Kontos, and Jan Trna. 2021. "The Role of Circulating MicroRNAs in Patients with Early-Stage Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma" Biomedicines 9, no. 10: 1468. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9101468
APA StyleEid, M., Karousi, P., Kunovský, L., Tuček, Š., Brančíková, D., Kala, Z., Slabý, O., Mayer, J., Kontos, C. K., & Trna, J. (2021). The Role of Circulating MicroRNAs in Patients with Early-Stage Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. Biomedicines, 9(10), 1468. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9101468









