The Persistence of Hepatitis C Virus Infection in Hepatocytes Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression by Pro-Inflammatory Interluekin-8 Expression
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and HCV Viral Infection
2.2. Distinguishing Intracellular HCV via Fluorescence-Activated Cell Sorting (FACS)
2.3. Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS)
2.4. Relative Fold Change Expression
2.5. Data Analysis Tools
2.6. Western Blotting
2.7. Cohort Collection
2.8. Real-Time PCR
2.9. Chemokine Assays
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
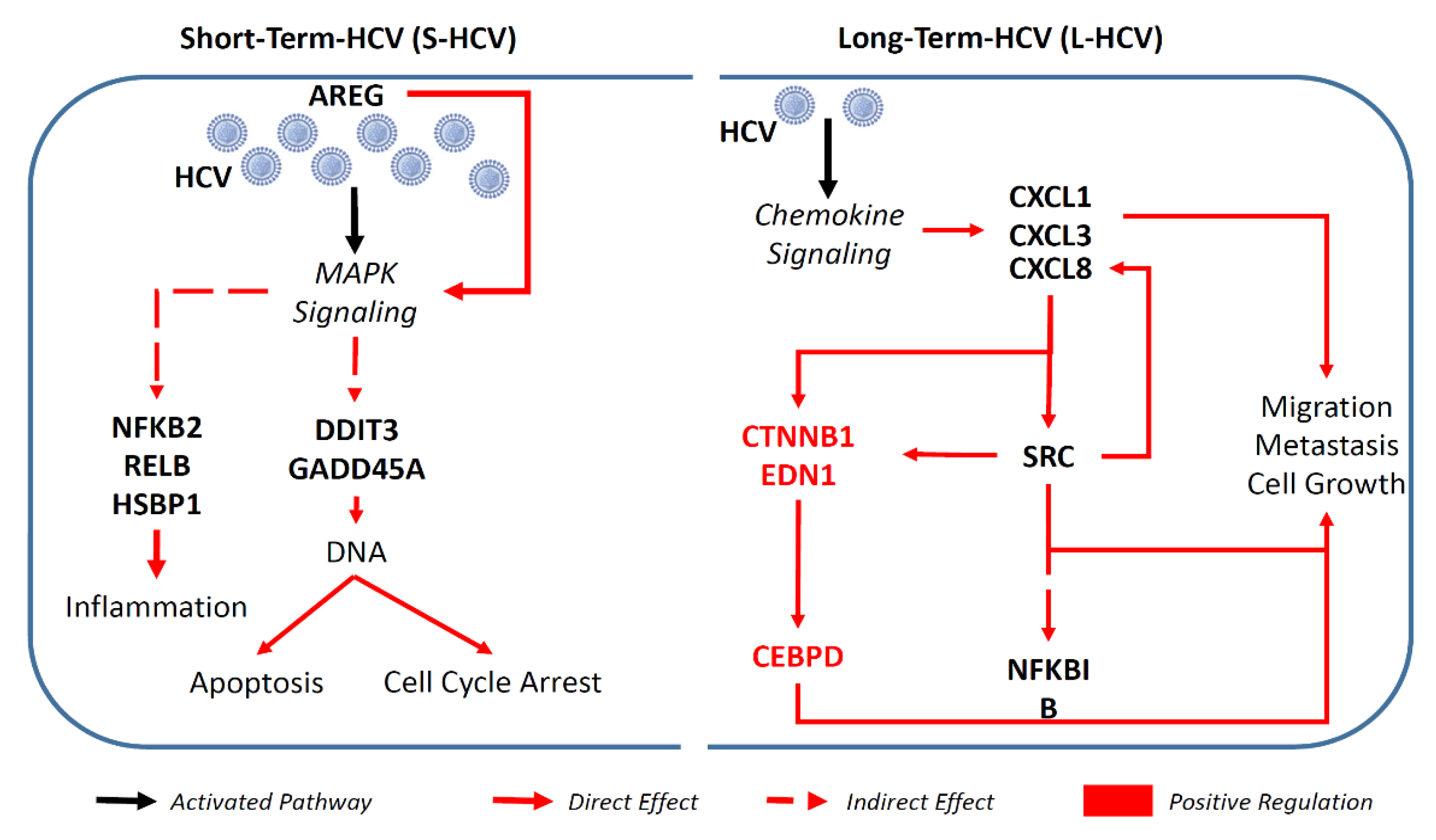
3.1. S-HCV Is Implicated in Cell Death and Survival Network, Whereas L-HCV Is Implicated in Cellular Movement, Cell-To-Cell Signalling, and the Cancer Network
3.2. S-HCV Is Driven towards Cell Death and an Inflammatory Response
3.3. L-HCV Promotes Migration and Metastasis via the Chemokine Signaling Pathway
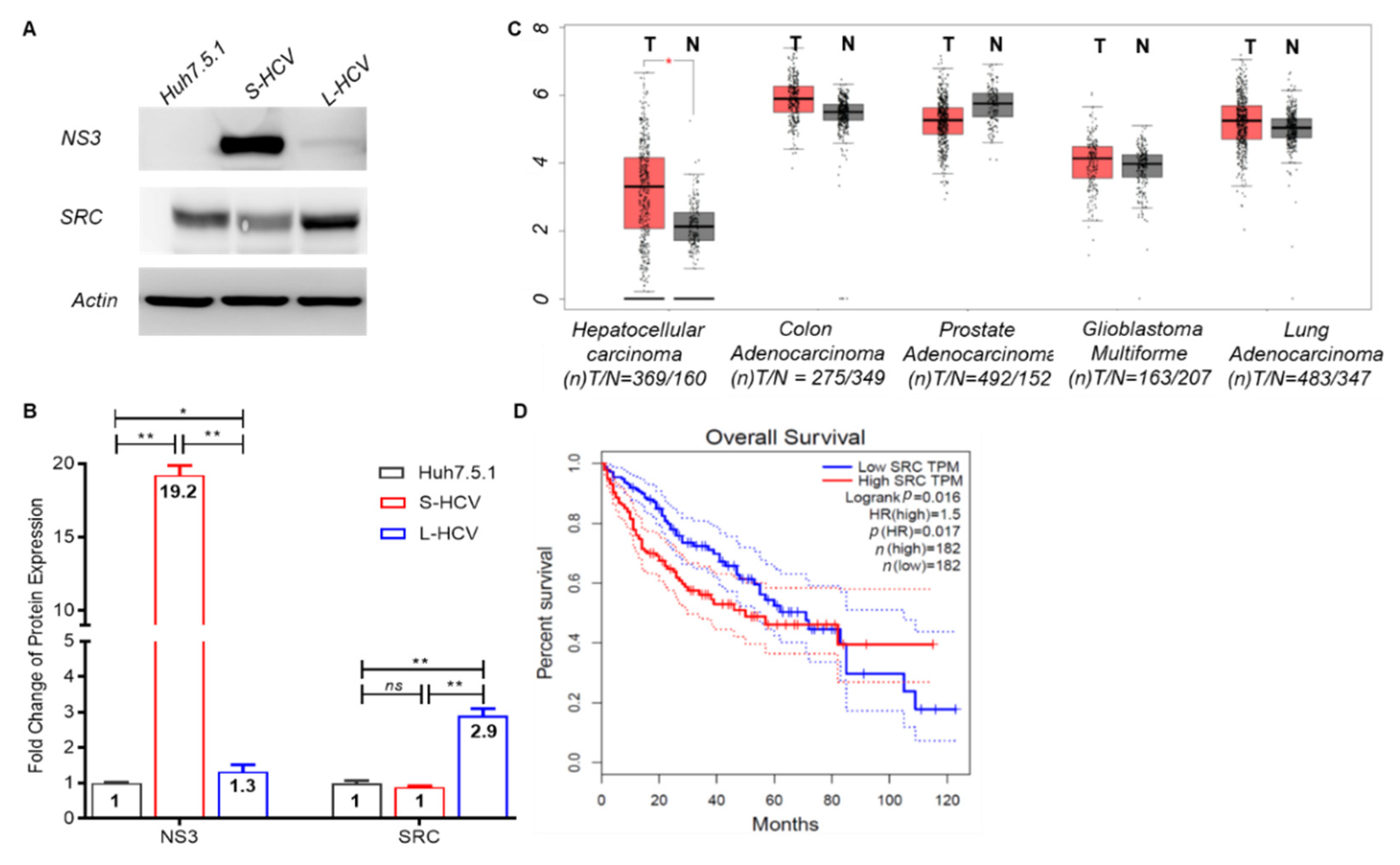
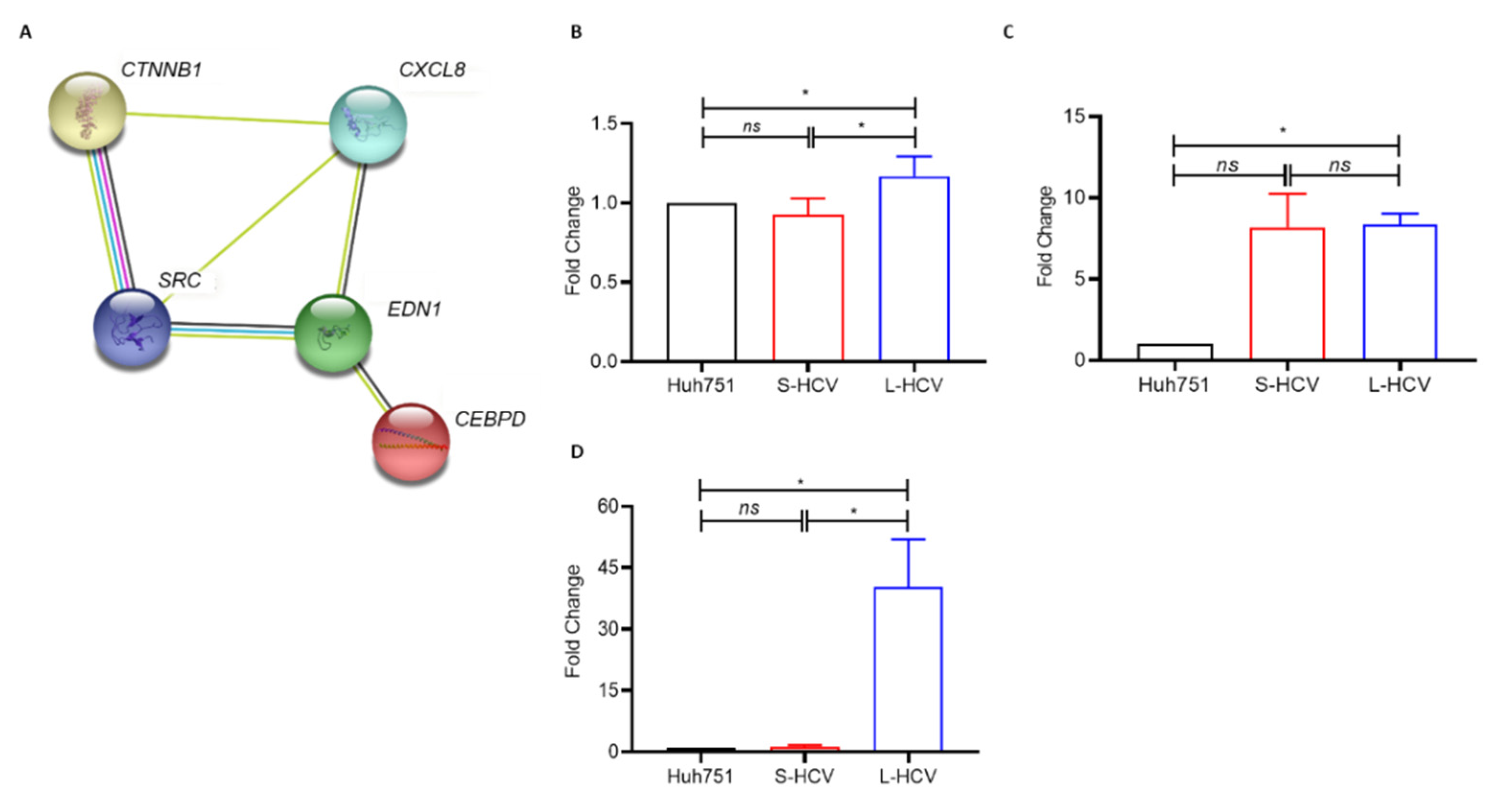
3.4. Persistent HCV Infection Induced CXCL8 Expression and Activation of Oncogene SRC in Liver Hepatocellular Carcinoma (LIHC)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ireland, G.; Mandal, S.; Hickman, M.; Ramsay, M.; Harris, R.; Simmons, R. Mortality rates among individuals diagnosed with hepatitis C virus (HCV); an observational cohort study, England, 2008 to 2016. Euro. Surveill. 2019, 24, 1800695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, E.; Bajpai, M.; Choudhary, A. Hepatitis C virus: Screening, diagnosis, and interpretation of laboratory assays. Asian J. Transfus. Sci. 2014, 8, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Serag, H.B. Epidemiology of viral hepatitis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2012, 142, 1264–1273.e1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holmberg, S.D.; Spradling, P.R.; Moorman, A.C.; Denniston, M.M. Hepatitis C in the United States. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 1859–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wyles, D.; Mangia, A.; Cheng, W.; Shafran, S.; Schwabe, C.; Ouyang, W.; Hedskog, C.; McNally, J.; Brainard, D.M.; Doehle, B.P.; et al. Long-term persistence of HCV NS5A resistance-associated substitutions after treatment with the HCV NS5A inhibitor, ledipasvir, without sofosbuvir. Antivir. Ther. 2018, 23, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, A.Y.; Hoare, M.; Shankar, A.N.; Allison, M.; Alexander, G.J.M.; Michalak, T.I. Persistence of Hepatitis C Virus Traces after Spontaneous Resolution of Hepatitis C. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinaldi, L.; Nevola, R.; Franci, G.; Perrella, A.; Corvino, G.; Marrone, A.; Berretta, M.; Morone, M.V.; Galdiero, M.; Giordano, M.; et al. Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma after HCV Clearance by Direct-Acting Antivirals Treatment Predictive Factors and Role of Epigenetics. Cancers 2020, 12, 1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamontagne, R.J.; Bagga, S.; Bouchard, M.J. Hepatitis B virus molecular biology and pathogenesis. Hepatoma Res. 2016, 2, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradpour, D.; Penin, F. Hepatitis C virus proteins: From structure to function. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2013, 369, 113–142. [Google Scholar]
- Manns, M.P.; Buti, M.; Gane, E.; Pawlotsky, J.-M.; Razavi, H.; Terrault, N.; Younossi, Z. Hepatitis C virus infection. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdane, N.; Jühling, F.; Crouchet, E.; El Saghire, H.; Thumann, C.; Oudot, M.A.; Bandiera, S.; Saviano, A.; Ponsolles, C.; Roca Suarez, A.A.; et al. HCV-Induced Epigenetic Changes Associated With Liver Cancer Risk Persist After Sustained Virologic Response. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 2313–2329.e2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kato, T.; Date, T.; Miyamoto, M.; Furusaka, A.; Tokushige, K.; Mizokami, M.; Wakita, T. Efficient replication of the genotype 2a hepatitis C virus subgenomic replicon. Gastroenterology 2003, 125, 1808–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindenbach, B.D.; Evans, M.J.; Syder, A.J.; Wölk, B.; Tellinghuisen, T.L.; Liu, C.C.; Maruyama, T.; Hynes, R.O.; Burton, D.R.; McKeating, J.A.; et al. Complete Replication of Hepatitis C Virus in Cell Culture. Science 2005, 309, 623–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhong, J.; Gastaminza, P.; Cheng, G.; Kapadia, S.; Kato, T.; Burton, D.R.; Wieland, S.F.; Uprichard, S.L.; Wakita, T.; Chisari, F.V. Robust hepatitis C virus infection in vitro. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 9294–9299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anticoli, S.; Amatore, D.; Matarrese, P.; De Angelis, M.; Palamara, A.T.; Nencioni, L.; Ruggieri, A. Counteraction of HCV-Induced Oxidative Stress Concurs to Establish Chronic Infection in Liver Cell Cultures. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 6452390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-C.; Yang, J.-F.; Wang, C.-L.; Huang, C.-F.; Lin, Y.-Y.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Lo, C.-T.; Lee, P.-Y.; Wu, K.-T.; Lin, C.-I.; et al. Distinct subpopulations of hepatitis C virus infectious cells with different levels of intracellular hepatitis C virus core protein. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2016, 32, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.-H.; Zhao, L.-F.; Lin, P.; Su, X.-R.; Chen, S.-J.; Huang, L.-Q.; Wang, H.-F.; Zhang, H.; Hu, Z.-F.; Yao, K.-T.; et al. GenCLiP 2.0: A web server for functional clustering of genes and construction of molecular networks based on free terms. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2534–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, S.X.; Jung, D.; Yao, R. ShinyGO: A graphical gene-set enrichment tool for animals and plants. Bioinformatics 2019, 36, 2628–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Gable, A.L.; Lyon, D.; Junge, A.; Wyder, S.; Huerta-Cepas, J.; Simonovic, M.; Doncheva, N.T.; Morris, J.H.; Bork, P.; et al. STRING v11: Protein–protein association networks with increased coverage, supporting functional discovery in genome-wide experimental datasets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 47, D607–D613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, Z.; Li, C.; Kang, B.; Gao, G.; Li, C.; Zhang, Z. GEPIA: A web server for cancer and normal gene expression profiling and interactive analyses. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, W98–W102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scheuer, P.J. Classification of chronic viral hepatitis: A need for reassessment. J. Hepatol. 1991, 13, 372–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-F.; Yeh, M.-L.; Tsai, P.-C.; Hsieh, M.-H.; Yang, H.-L.; Hsieh, M.-Y.; Yang, J.-F.; Lin, Z.-Y.; Chen, S.-C.; Wang, L.-Y.; et al. Baseline gamma-glutamyl transferase levels strongly correlate with hepatocellular carcinoma development in non-cirrhotic patients with successful hepatitis C virus eradication. J. Hepatol. 2014, 61, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omata, M.; Lesmana, L.A.; Tateishi, R.; Chen, P.-J.; Lin, S.-M.; Yoshida, H.; Kudo, M.; Lee, J.M.; Choi, B.I.; Poon, R.T.P.; et al. Asian Pacific Association for the Study of the Liver consensus recommendations on hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol. Int. 2010, 4, 439–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bruix, J.; Sherman, M. Management of hepatocellular carcinoma: An update. Hepatology 2011, 53, 1020–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Moliner, L.; Pontisso, P.; De Salvo, G.L.; Cavalletto, L.; Chemello, L.; Alberti, A. Serum and liver HCV RNA levels in patients with chronic hepatitis C: Correlation with clinical and histological features. Gut 1998, 42, 856–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colussi, G.; Donnini, D.; Brizzi, R.F.; Maier, S.; Valenti, L.; Catena, C.; Cavarape, A.; Sechi, L.A.; Soardo, G. Sustained virologic response to direct-acting antiviral agents predicts better outcomes in hepatitis C virus-infected patients: A retrospective study. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 6094–6106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshida, Y.; Fuchs, B.C.; Bardeesy, N.; Baumert, T.F.; Chung, R.T. Pathogenesis and prevention of hepatitis C virus-induced hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2014, 61, S79–S90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cardoso, A.C.; Moucari, R.; Figueiredo-Mendes, C.; Ripault, M.P.; Giuily, N.; Castelnau, C.; Boyer, N.; Asselah, T.; Martinot-Peignoux, M.; Maylin, S.; et al. Impact of peginterferon and ribavirin therapy on hepatocellular carcinoma: Incidence and survival in hepatitis C patients with advanced fibrosis. J. Hepatol. 2010, 52, 652–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Wang, J.; Xiao, H.; Wu, W.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X. MAPK signaling pathways regulate mitochondrial-mediated apoptosis induced by isoorientin in human hepatoblastoma cancer cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 53, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelain, S.; Schnuriger, A.; Francois, C.; Nguyen-Khac, E.; Fournier, C.; Schmit, J.L.; Capron, D.; Dubuisson, J.; Wychowski, C.; Thibault, V.; et al. Low levels of hepatitis C virus (HCV) neutralizing antibodies in patients coinfected with HCV and human immunodeficiency virus. J. Infect. Dis. 2008, 198, 332–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mitchell, J.K.; Lemon, S.M.; McGivern, D.R. How do persistent infections with hepatitis C virus cause liver cancer? Curr. Opin. Virol. 2015, 14, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bartsch, H.; Nair, J. Chronic inflammation and oxidative stress in the genesis and perpetuation of cancer: Role of lipid peroxidation, DNA damage, and repair. Langenbeck’s Arch. Surg. 2006, 391, 499–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radziwill, G.; Weiss, A.; Heinrich, J.; Baumgartner, M.; Boisguerin, P.; Owada, K.; Moelling, K. Regulation of c-Src by binding to the PDZ domain of AF-6. EMBO J. 2007, 26, 2633–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Feniger-Barish, R.; Yron, I.; Meshel, T.; Matityahu, E.; Ben-Baruch, A. IL-8-induced migratory responses through CXCR1 and CXCR2: Association with phosphorylation and cellular redistribution of focal adhesion kinase. Biochemistry 2003, 42, 2874–2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Wu, Y.; Wang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Kong, D.; Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Wang, G.; Jin, Y.; Jin, X.; et al. Elevated Src expression associated with hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis in northern Chinese patients. Oncol. Lett. 2015, 10, 3026–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Ning, Z.; Hu, Z.; Yu, Q.; He, B.; Hu, G. High interleukin-8 and/or extracellular signal-regulated kinase 2 expression predicts poor prognosis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 18, 5215–5224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lu, J.W.; Liao, C.Y.; Yang, W.Y.; Lin, Y.M.; Jin, S.L.; Wang, H.D.; Yuh, C.H. Overexpression of endothelin 1 triggers hepatocarcinogenesis in zebrafish and promotes cell proliferation and migration through the AKT pathway. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e85318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.X.; Li, D.Q.; He, A.R.; Motwani, M.; Vasiliou, V.; Eswaran, J.; Mishra, L.; Kumar, R. Synergistic inhibition of hepatocellular carcinoma growth by cotargeting chromatin modifying enzymes and poly (ADP-ribose) polymerases. Hepatology 2012, 55, 1840–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perez, S.; Kaspi, A.; Domovitz, T.; Davidovich, A.; Lavi-Itzkovitz, A.; Meirson, T.; Alison Holmes, J.; Dai, C.-Y.; Huang, C.-F.; Chung, R.T.; et al. Hepatitis C virus leaves an epigenetic signature post cure of infection by direct-acting antivirals. PLoS Genet. 2019, 15, e1008181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackham, S.; Baillie, A.; Al-Hababi, F.; Remlinger, K.; You, S.; Hamatake, R.; McGarvey, M.J. Gene Expression Profiling Indicates the Roles of Host Oxidative Stress, Apoptosis, Lipid Metabolism, and Intracellular Transport Genes in the Replication of Hepatitis C Virus. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 5404–5414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sheshadri, N.; Sharan, S.; Sterneck, E. CEBPD is an early endoplasmic reticulum stress response gene implicated in breast cancer cell survival. FASEB J. 2017, 31, 758.2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.M.; Ji, S.; Li, Y.; Fu, L.Y.; Jiang, T.; Meng, F.D. beta-Catenin promotes cell proliferation, migration, and invasion but induces apoptosis in renal cell carcinoma. Onco. Targets Ther. 2017, 10, 711–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, V.H.L.; Hough, R.; Bernaudo, S.; Peng, C. Wnt/beta-catenin signalling in ovarian cancer: Insights into its hyperactivation and function in tumorigenesis. J. Ovarian. Res. 2019, 12, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brass, A.; Brenndörfer, E.D. The role of chemokines in hepatitis C virus-mediated liver disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 4747–4779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fahey, S.; Dempsey, E.; Long, A. The role of chemokines in acute and chronic hepatitis C infection. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2014, 11, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fierro, N.A.; González-Aldaco, K.; Torres-Valadez, R.; Trujillo-Trujillo, M.E.; Roman, S.; Trujillo-Ochoa, J.L.; Panduro, A. Spontaneous hepatitis C viral clearance and hepatitis C chronic infection are associated with distinct cytokine profiles in Mexican patients. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo. Cruz. 2015, 110, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, Z.-Q.; Huang, T.; Deng, Y.-Z.; Zhu, G.-Z. Expression profile and kinetics of cytokines and chemokines in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 17995–18003. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kadoya, H.; Nagano-Fujii, M.; Deng, L.; Nakazono, N.; Hotta, H. Nonstructural Proteins 4A and 4B of Hepatitis C Virus Transactivate the Interleukin 8 Promoter. Microbiol. Immunol. 2005, 49, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, T.N.Q.; Lin, D.M.H.; Mulrooney-Cousins, P.M.; Churchill, N.D.; Kowala-Piaskowska, A.; Mozer-Lisewska, I.; Machaj, A.; Pazgan-Simon, M.; Zalewska, M.; Simon, K.; et al. Hepatitis C virus load and expression of a unique subset of cellular genes in circulating lymphoid cells differentiate non-responders from responders to pegylated interferon alpha–ribavirin treatment. J. Med. Virol. 2013, 85, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes, G.R. The nonstructural NS5A protein of hepatitis C virus: An expanding, multifunctional role in enhancing hepatitis C virus pathogenesis. J. Biomed. Sci. 2002, 9, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goto, K.; Roca Suarez, A.A.; Wrensch, F.; Baumert, T.F.; Lupberger, J. Hepatitis C Virus and Hepatocellular Carcinoma: When the Host Loses Its Grip. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, D.; Zheng, Y.; Wen, J.; Han, J.; Tuo, H.; Liu, Y.; Peng, Y. Role of chemokines in hepatocellular carcinoma (Review). Oncol. Rep. 2021, 45, 809–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
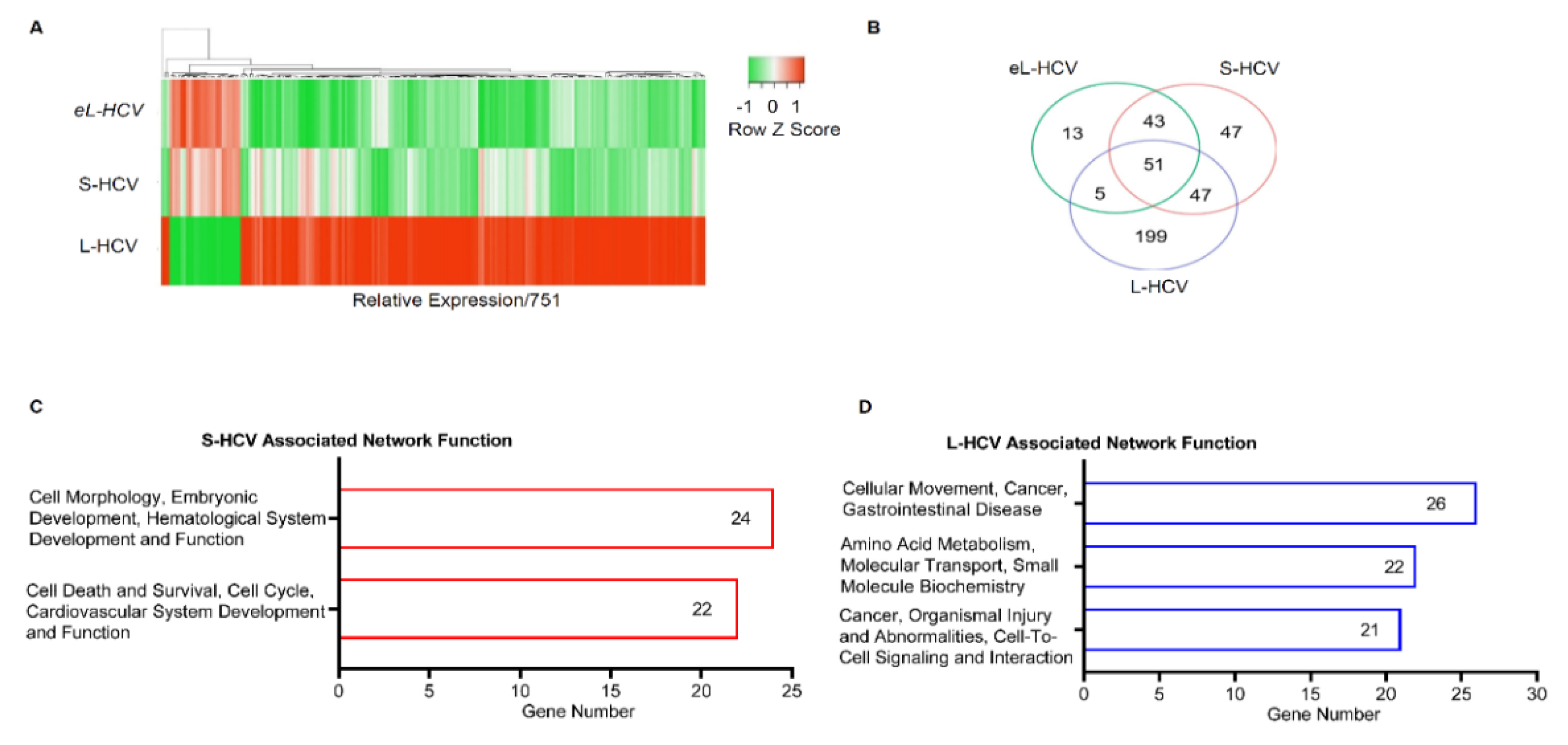
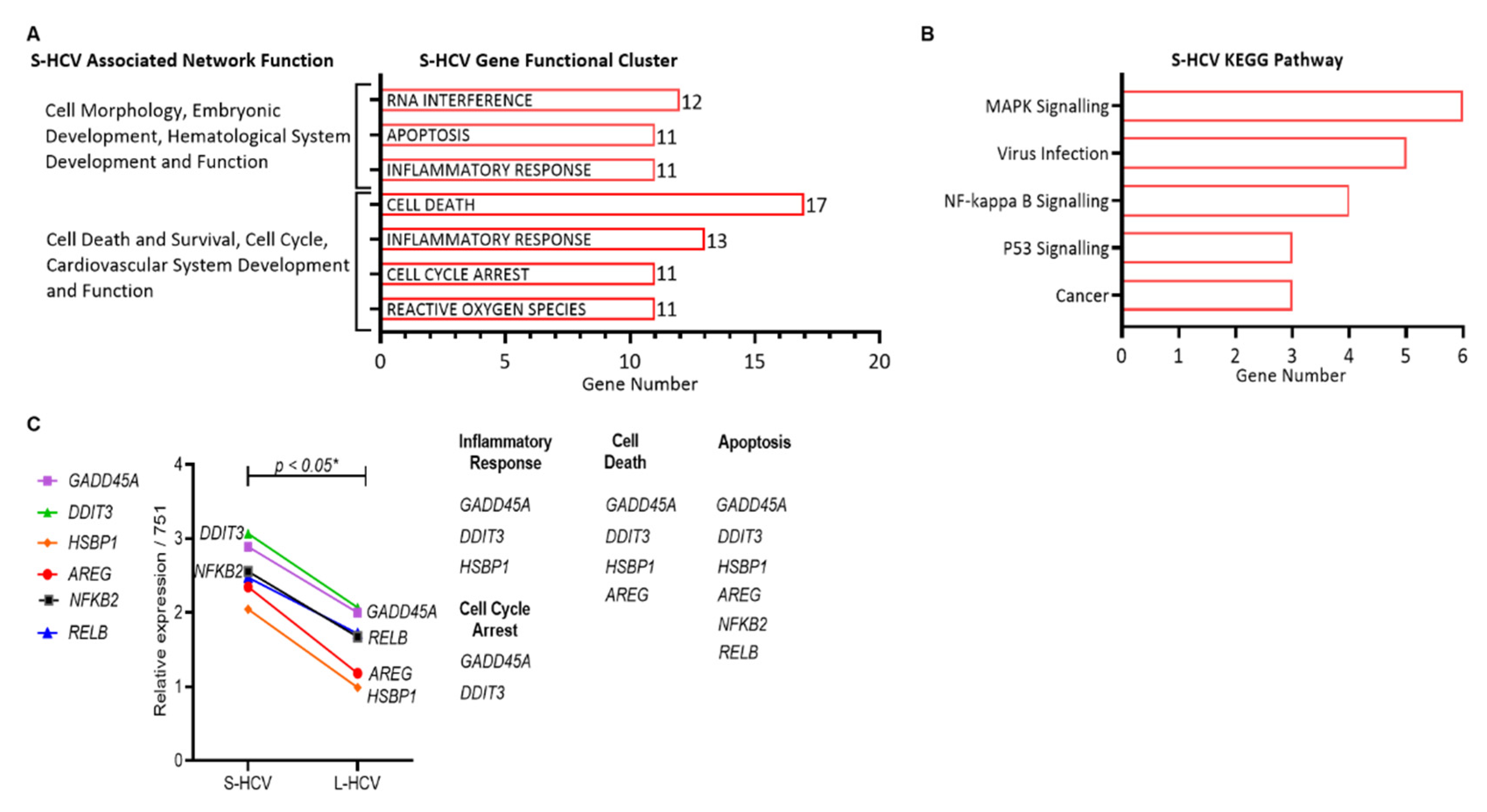
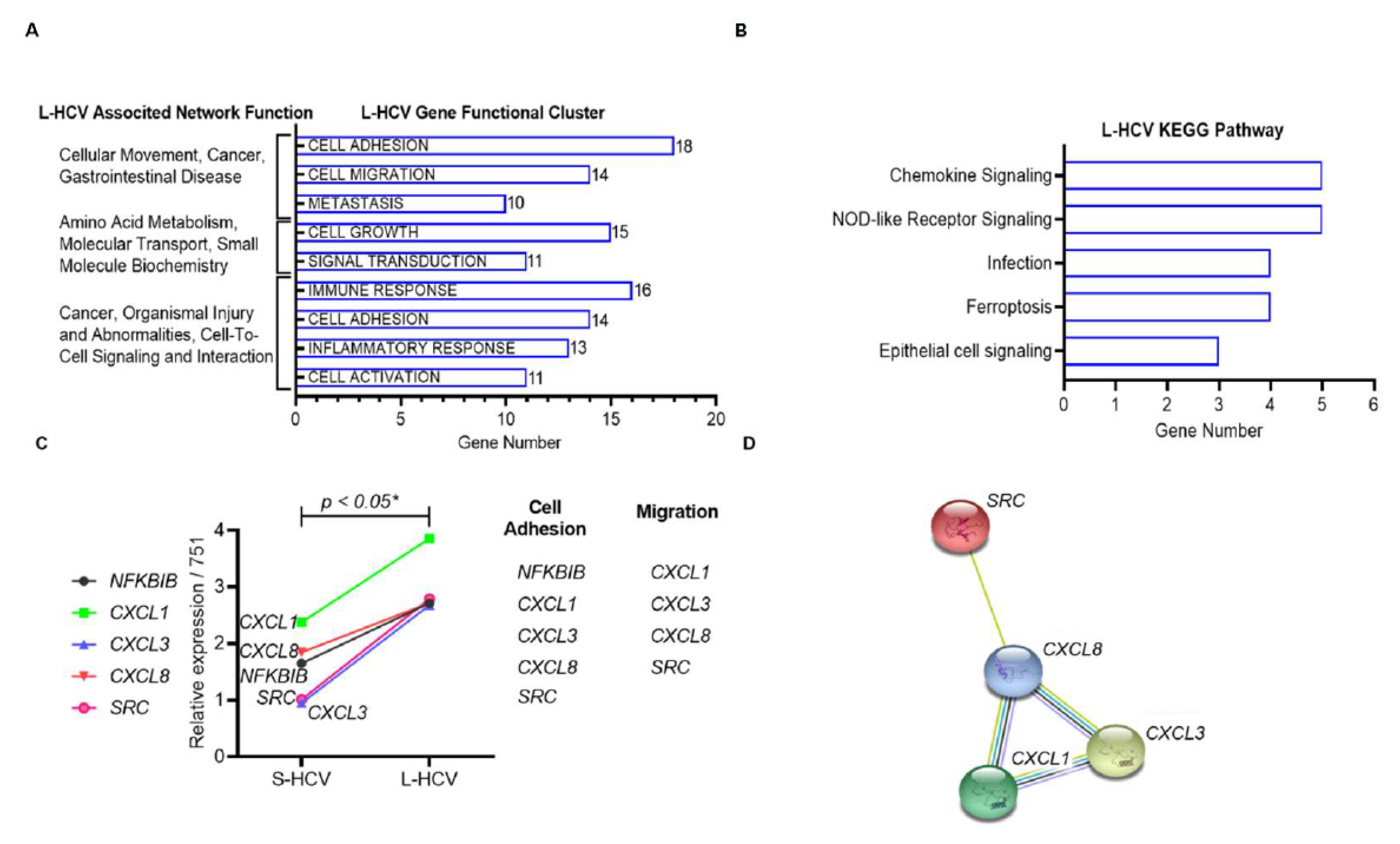
| ID | Associated Network Functions | Score | Molecules | Gene List |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Cell Morphology, Embryonic Development, Hematological System Development and Function | 47 | 24 | AGR2, HDAC9, PPARGC1A, ANKRD1, ISG15, RASD1, AREG, ISG20, RELB, BBC3, MIR17HG, SESN2, BTG2, MT-ND2, SLC1A5, CREB5, NFKB2, TNFRSF12A, DUSP10, NFKBIE, TUBA1A, EPB41L4A-AS1, NUPR1, UCA1 |
| 2 | Cell Death and Survival, Cell Cycle, Cardiovascular System Development and Function | 42 | 22 | ASNS, ERK, DDIT3, ATF3, GADD45A, DDIT4, BEX2, GDF15, EIF1, BHLHE40, HSPB1, ELF3, CTH, JUNB, STC2, CXCL2, KLF10, TNFAIP3, KLF6, MAFF, TRIB3, SH3BP2 |
| ID | Associated Network Functions | Score | Focus Molecules | Gene List |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Cellular Movement, Cancer, Gastrointestinal Disease. | 43 | 26 | AJUBA, H2AC18/H2AC19, CTNND2, ANXA3, HOXB7, EIF4EBP1, CD55, LASP1, EPCAM, CD9, LIMA1, GPX2, CDH1, MT2A, ZFAS1, CDH17, OCLN, TFF3, CDH2, RCN1, TINAGL1, CLDN7, SEMA3C, TRIM31, TSPAN8, VTN |
| 2 | Amino Acid Metabolism, Molecular Transport, Small Molecule Biochemistry. | 34 | 22 | APOC3, KLF5, EDN1, BMF, PARP9, EPS8L2, C9orf72, PDCD4, GSTA2, CCR6, PMAIP1, HLA-E, CEBPD, S100A11, SLC3A2, CHMP4C, S100A6, SLC7A11, CYP1A1, SAT1, SOCS2, SPINT1 |
| 3 | Cancer, Organismal Injury and Abnormalities, Cell-to-Cell Signaling and Interaction. | 32 | 21 | ANXA1, IL18, CXCL8, BLVRA, IL32, F2RL1, CAV1, KYNU, G0S2, CXCL1, MARVELD3, HMOX1, CXCL3, MDK, HOXB9, NFKBIB, OPTN, TSC22D3, NUB1, SRC, UBD |
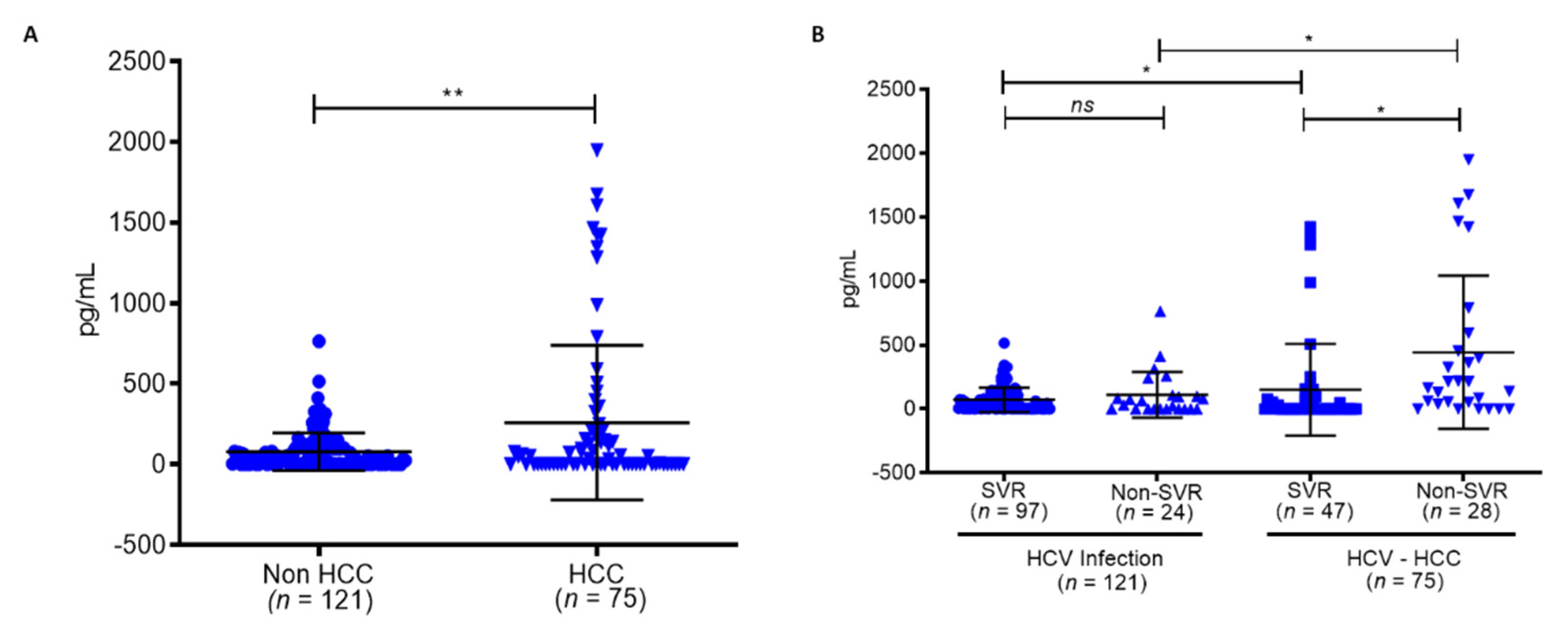
| Clinical Factors | HCV Infection (n = 121) | HCV-HCC (n = 75) | p-Value | HCV Infection (n = 121) | HCV-HCC (n = 75) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SVR (n = 97) | Non-SVR (n = 24) | p-Value | SVR (n = 47) | Non-SVR (n = 28) | p-Value | ||||
| Age | 49.29 ± 11.14 | 58.6 ± 8.18 | 0.0001 * | 48.74 ± 11.20 | 51.50 ± 10.56 | 0.646 | 60.15 ± 7. 72 | 56.00 ± 8.40 | 0.0152 * |
| Sex (F/M) | 58/63 | 29/46 | 0.8331 | 45/52 | 13/11 | 0.357 | 14/33 | 15/13 | 0.0149 * |
| AFP (IU/L) | 10.99 ± 15.69 | 36.53 ± 96.70 | 0.0001 * | 10.66 ± 16.49 | 12.31 ± 10.89 | 0.8975 | 21.09 ± 31.18 | 62.45 ± 151.19 | 0.9945 |
| BMI (Kg/m2) | 40.57 ± 5.55 | 41.61 ± 6.20 | 0.9461 | 40.59 ± 5.43 | 40.52 ± 5.90 | 0.7201 | 41.90 ± 7.06 | 41.12 ± 4.49 | 0.2522 |
| Cirrhosis (N) | 28/121 | 50/75 | 0.002 * | 21/97 | 7/24 | 0.25 | 27/47 | 23/28 | 0.0829 |
| GOT (IU/L) | 94.45 ± 63.40 | 111.17 ± 64.93 | 0.9441 | 96.48 ± 66.42 | 86.21 ± 46.76 | 0.239 | 108.72 ± 71.23 | 115.21 ± 53.69 | 0.7221 |
| GPT (IU/L) | 153.71 ± 120.65 | 145.88 ± 95.24 | 0.2069 | 159.89 ± 125.90 | 128.75 ± 89. 11 | 0.1308 | 149.17 ± 109.99 | 140.35 ± 64.78 | 0.4912 |
| GGT (IU/L) | 58.72 ± 54.13 | 95.65 ± 72.80 | 0.9996 | 60.18 ± 58.31 | 52.74 ± 30.06 | 0.2893 | 83.42 ± 63.40 | 116.03 ± 83.74 | 0.5529 |
| PLT (103/µL) | 178.86 ± 62.49 | 123.67 ± 40.47 | <0.001 * | 185.61 ± 61.57 | 151.58 ± 57.23 | 0.059 | 129.12 ± 38.06 | 114.50 ± 43.37 | 0.0919 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shabangu, C.S.; Siphepho, P.Y.; Li, C.-Y.; Cheng, W.-C.; Lu, M.-Y.; Huang, C.-F.; Yeh, M.-L.; Dai, C.-Y.; Huang, J.-F.; Chuang, W.-L.; et al. The Persistence of Hepatitis C Virus Infection in Hepatocytes Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression by Pro-Inflammatory Interluekin-8 Expression. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1446. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9101446
Shabangu CS, Siphepho PY, Li C-Y, Cheng W-C, Lu M-Y, Huang C-F, Yeh M-L, Dai C-Y, Huang J-F, Chuang W-L, et al. The Persistence of Hepatitis C Virus Infection in Hepatocytes Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression by Pro-Inflammatory Interluekin-8 Expression. Biomedicines. 2021; 9(10):1446. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9101446
Chicago/Turabian StyleShabangu, Ciniso Sylvester, Phumelele Yvonne Siphepho, Chia-Yang Li, Wei-Chung Cheng, Ming-Ying Lu, Chung-Feng Huang, Ming-Lun Yeh, Chia-Yen Dai, Jee-Fu Huang, Wan-Long Chuang, and et al. 2021. "The Persistence of Hepatitis C Virus Infection in Hepatocytes Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression by Pro-Inflammatory Interluekin-8 Expression" Biomedicines 9, no. 10: 1446. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9101446
APA StyleShabangu, C. S., Siphepho, P. Y., Li, C.-Y., Cheng, W.-C., Lu, M.-Y., Huang, C.-F., Yeh, M.-L., Dai, C.-Y., Huang, J.-F., Chuang, W.-L., Lin, Z.-Y., Yu, M.-L., & Wang, S.-C. (2021). The Persistence of Hepatitis C Virus Infection in Hepatocytes Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression by Pro-Inflammatory Interluekin-8 Expression. Biomedicines, 9(10), 1446. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9101446








