Defining Parallels between the Salivary Glands and Pancreas to Better Understand Pancreatic Carcinogenesis
Abstract
1. Introduction
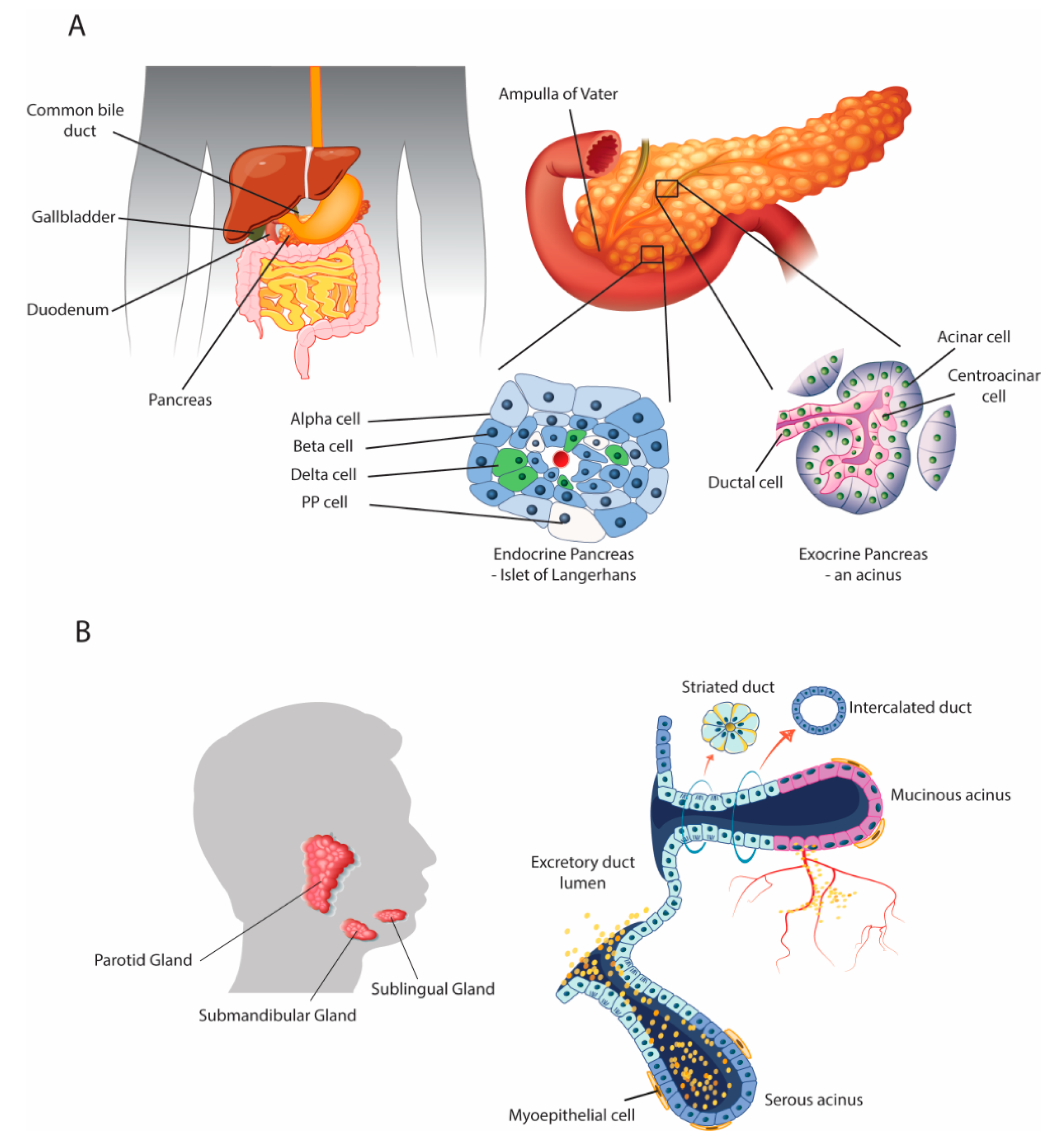
2. Parallels with the Salivary Glands
2.1. Anatomical and Physiological Parallels
2.2. Interaction between the Organs: The Role of the Growth Factor EGF
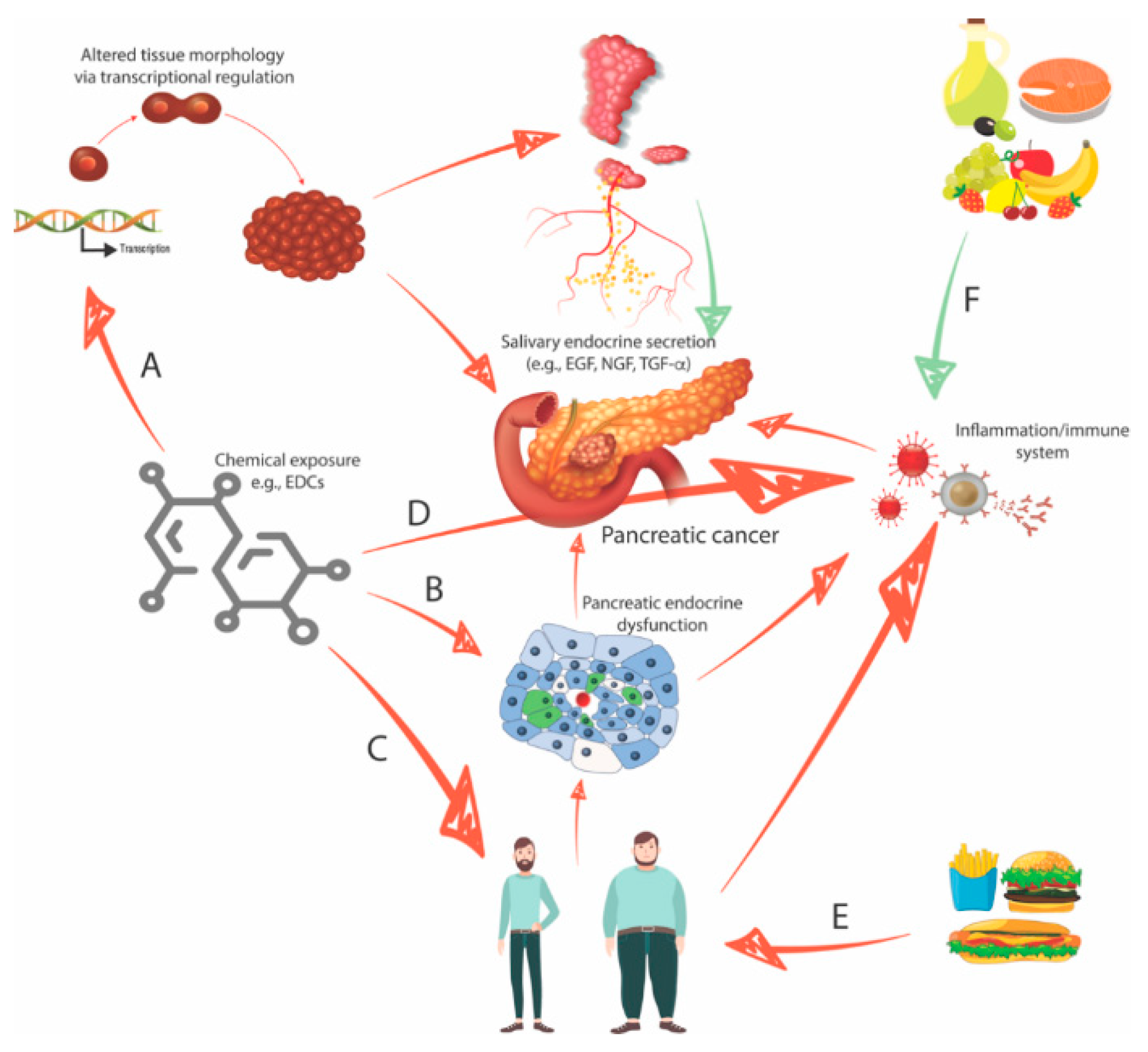
2.3. Endocrine-Disrupting Compounds Perturb Organ Morphology and Function
2.4. Endocrine-Disrupting Compounds Contribute to the Development of Type II Diabetes and Obesity
2.5. Four Interconnected Risk Factors for Pancreatic Cancer: Chemical Exposure, Diabetes, Obesity, and Eating Behavior
3. Urgent Need for Early Diagnosis: Identification of Salivary Biomarkers and Development of Screening Tools
4. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PDAC | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma |
| USA | United States of America |
| FOLFIRINOX | Folinic acid, 5-fluorouracil, irinotecan, and oxaliplatin |
| EGF | Epidermal growth factor |
| NGF | Nerve growth factor |
| TGF-α | Transforming growth factor alpha |
| TGF-β | Transforming growth factor bêta |
| HGF | Hepatocyte growth factor |
| IGF-I | Insulin-like growth factor 1 |
| IGF-II | Insulin-like growth factor 2 |
| bFGF | Basic fibroblast growth factor |
| EDC | Endocrine-disrupting chemical |
| AR | Androgen receptor |
| PR | Progesterone receptor |
| NP | Nonylphenol |
| BPA | Bisphenol A |
| ERα | Estrogen receptor alpha |
| CDK4 | Cyclin-dependent kinase 4 |
| IL-6 | Interleukin 6 |
| IL-1 | Interleukin 1 |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| VEGF | Vascular endothelial growth factor |
| IDDM | Insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus |
| NIDDM | Non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus |
References
- Harbuzariu, A.; Oprea-Ilies, G.; Gonzalez-Perez, R.R. Pancreatic cancer, leptin, and chemoresistance: Current challenges. In Advances in Pancreatic Cancer; Rodrigo, L., Ed.; Intech Open: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuigan, A.; Kelly, P.; Turkington, R.C.; Jones, C.; Coleman, H.G.; McCain, R.S. Pancreatic cancer: A review of clinical diagnosis, epidemiology, treatment and outcomes. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 4846–4861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demir, I.E.; Friess, H. Pancreatic cancer—Lessons from the past decade. Indian J. Med. Paediatr. Oncol. 2015, 36, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.; Ma, J.; Zou, Z.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2014, 64, 9–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahib, L.; Smith, B.D.; Aizenberg, R.; Rosenzweig, A.B.; Fleshman, J.M.; Matrisian, L.M. Projecting cancer incidence and deaths to 2030: The unexpected burden of thyroid, liver, and pancreas cancers in the United States. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 2913–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mace, T.A.; Shakya, R.; Pitarresi, J.R.; Swanson, B.; McQuinn, C.W.; Loftus, S.; Nordquist, E.; Cruz-Monserrate, Z.; Yu, L.; Young, G.; et al. IL-6 and PD-L1 antibody blockade combination therapy reduces tumour progression in murine models of pancreatic cancer. Gut 2018, 67, 320–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conroy, T.; Desseigne, F.; Ychou, M.; Bouché, O.; Guimbaud, R.; Bécouarn, Y.; Adenis, A.; Raoul, J.L.; Gourgou-Bourgade, S.; de la Fouchardière, C.; et al. Groupe Tumeurs Digestives of Unicancer; PRODIGE Intergroup. FOLFINIROX versus gemcitabine for metastatic pancreatic cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 1817–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Hoff, D.D.; Ervin, T.; Arena, F.P.; Chiorean, E.G.; Infante, J.; Moore, M.; Seay, T.; Tjulandin, S.A.; Ma, W.W.; Saleh, M.N.; et al. Increased survival in pancreatic cancer with nab-paclitaxel plus gemcitabine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 1691–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducreux, M.; Cuhna, A.S.; Caramella, C.; Hollebecque, A.; Burtin, P.; Goéré, D.; Seufferlein, T.; Haustermans, K.; van Laethem, J.L.; Conroy, T.; et al. ESMO guidelines committee. cancer of the pancreas: ESMO clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, v56–v68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.Y.; Shi, S.; Liang, C.; Meng, Q.C.; Hua, J.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, B.; Xu, J.; Yu, X.J. The microbiota and microbiome in pancreatic cancer: More influential than expected. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, D.; Lowenfels, A.B. The epidemiology of pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer. Gastroenterology 2013, 144, 1252–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iodice, S.; Gandini, S.; Maisonneuve, P.; Lowenfels, A.B. Tobacco and the risk of pancreatic cancer: A review and meta-analysis. Langenbecks Arch. Surg. 2008, 393, 535–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chari, S.T.; Leibson, C.L.; Rabe, K.G.; Timmons, L.J.; Ransom, J.; de Andrade, M.; Petersen, G.M. Pancreatic cancer-associated diabetes mellitus: Prevalence and temporal association with diagnosis of cancer. Gastroenterology 2008, 134, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Gonzalez, A.B.; Sweetland, S.; Spencer, E. A meta-analysis of obesity and the risk of pancreatic cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2003, 89, 519–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soto, A.M.; Sonnenschein, C. Environmental causes of cancer: Endocrine disruptors as carcinogens. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2010, 6, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Jonathan, N. Endocrine disrupting chemicals and breast cancer: The saga of bisphenol, A. In Estrogen Receptor and Breast Cancer. Cancer Drug Discovery and Development; Zhang, X., Ed.; Humana Press: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 343–377. [Google Scholar]
- Bachelet, D.; Verner, M.A.; Neri, M.; Duverger, É.C.; Charlier, C.; Arveux, P.; Haddad, S.; Guénel, P. Breast cancer and exposure to organochlorines in the CECILE Study: Associations with plasma levels measured at the time of diagnosis and estimated during adolescence. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouidhi, W.; Bergès, R.; Tiffon, C.; Desmetz, C.; El May, M.; Auger, J.; Canivenc-Lavier, M. Perinatal xenohormone exposure impacts sweet preference and submandibular development in male rats. Oral. Dis. 2013, 19, 812–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathison, R. Submandibular Salivary Gland Endocrine Secretions and Systemic Pathophysiological Responses. Open Inflamm. J. 2009, 2, 9–21. [Google Scholar]
- Mathison, R. The submandibular glands: A role in homeostasis and allostasis. Biomed. Rev. 1995, 4, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.G.; Ohana, E.; Park, H.W.; Yang, D.; Muallem, S. Molecular mechanism of pancreatic and salivary gland fluid and HCO3 secretion. Physiol. Rev. 2012, 92, 39–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamisawa, T.; Tu, Y.; Egawa, N.; Sakaki, N.; Inokuma, S.; Kamata, N. Salivary gland involvement in chronic pancreatitis of various etiologies. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2003, 98, 323–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagatelian, M.A.; Fravel, J.; Gallo, S.H.; Makk, L.J.; Looney, S.W.; Wright, R.A. Do parotid duct abnormalities occur in patients with chronic alcoholic pancreatitis? Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1998, 93, 197–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gittes, G.K. Developmental biology of the pancreas: A comprehensive review. Dev. Biol. 2009, 326, 4–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakonczay, Z., Jr.; Vág, J.; Földes, A.; Nagy, K.; Nagy, Á.; Hegyi, P.; Varga, G. Chronic inflammation in the pancreas and salivary glands--lessons from similarities and differences in pathophysiology and treatment modalities. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2014, 20, 1104–1120. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jennings, R.E.; Berry, A.A.; Strutt, J.P.; Gerrard, D.T.; Hanley, N.A. Human pancreas development. Development 2015, 142, 3126–3137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Som, P.M.; Miletich, I. The embryology of the salivary glands: An Update. Neurographics 2015, 5, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, R. Role of saliva in the maintenance of taste sensitivity. Crit. Rev. Oral. Biol. Med. 2000, 11, 216–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neyraud, E. Role of saliva in oral food perception. Monogr. Oral. Sci. 2014, 24, 61–70. [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen, A.M.; Bardow, A.; Jensen, S.B.; Nauntofte, B. Saliva and gastrointestinal functions of taste, mastication, swallowing and digestion. Oral. Dis. 2002, 8, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marti, U.; Burwen, S.J.; Jones, A.L. Biological effects of epidermal growth factor, with emphasis on the gastrointestinal tract and liver: An update. Hepatology 1989, 9, 126–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, F.; Harris, R.C. Epidermal growth factor, from gene organization to bedside. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol 2014, 28, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouidhi, W.; Desmetz, C.; Nahdi, A.; Bergès, R.; Cravedi, J.P.; Auger, J.; May, M.E.; Canivenc-Lavier, M.C. In utero and lactational exposure to low-dose genistein-vinclozolin mixture affects the development and growth factor mRNA expression of the submandibular salivary gland in immature female rats. Toxicol. Pathol. 2012, 40, 593–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Yu, J.; Wang, P.; Luo, Y.; Yang, X.F.; Yang, X.S.; Li, W.M.; Xu, J. The adverse effects of perinatal exposure to nonylphenol on carbohydrate metabolism in male offspring rats. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2017, 27, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabriel, F.L.; Routledge, E.J.; Heidlberger, A.; Rentsch, D.; Guenther, K.; Giger, W.; Sumpter, J.P.; Kohler, H.P. Isomer-specific degradation and endocrine disrupting activity of nonylphenols. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 6399–6408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, A.; Guieysse, B.; Jefferson, B.; Cartmell, E.; Lester, J.N. Nonylphenol in the environment: A critical review on occurrence, fate, toxicity and treatment in wastewaters. Environ. Int. 2008, 34, 1033–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vivacqua, A.; Recchia, A.G.; Fasanella, G.; Gabriele, S.; Carpino, A.; Rago, V.; di Gioia, M.L.; Leggio, A.; Bonofiglio, D.; Liguori, A.; et al. The food contaminants bisphenol A and 4-nonylphenol act as agonists for estrogen receptor alpha in MCF7 breast cancer cells. Endocrine 2003, 22, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Magdalena, P.; García-Arévalo, M.; Quesada, I.; Nadal, Á. Bisphenol-A treatment during pregnancy in mice: A new window of susceptibility for the development of diabetes in mothers later in life. Endocrinology 2015, 156, 1659–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grün, F.; Blumberg, B. Endocrine disrupters as obesogens. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2009, 304, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuo, Y.; Morita, M.; Oka, S.; Ishido, M. Motor hyperactivity caused by a deficit in dopaminergic neurons and the effects of endocrine disruptors: A study inspired by the physiological roles of PACAP in the brain. Regul. Pept. 2004, 123, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakata, I.; Tanaka, T.; Yamazaki, M.; Tanizaki, T.; Zheng, Z.; Sakai, T. Gastric estrogen directly induces ghrelin expression and production in the rat stomach. J. Endocrinol. 2006, 190, 749–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.S.; Yoon, C.Y.; Jang, P.G.; Park, Y.J.; Shin, C.S.; Park, H.S.; Ryu, J.W.; Pak, Y.K.; Park, J.Y.; Lee, K.U.; et al. The mitogenic and antiapoptotic actions of ghrelin in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Mol. Endocrinol. 2004, 18, 2291–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jubendradass, R.; D’Cruz, S.C.; Mathur, P.P. Long-term exposure to nonylphenol affects insulin signaling in the liver of adult male rats. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2012, 31, 868–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiffon, C. Non-hereditary risk factors associated with pancreatic cancer: A focus on obesity and diabetes. Integr. Cancer Sci. Ther. 2020, 7, 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Cascetta, P.; Cavaliere, A.; Piro, G.; Torroni, L.; Santoro, R.; Tortora, G.; Melisi, D.; Carbone, C. Pancreatic cancer and obesity: Molecular mechanisms of cell transformation and chemoresistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Incio, J.; Ligibel, J.A.; McManus, D.T.; Suboj, P.; Jung, K.; Kawaguchi, K.; Pinter, M.; Babykutty, S.; Chin, S.M.; Vardam, T.D.; et al. Obesity promotes resistance to anti-VEGF therapy in breast cancer by up-regulating IL-6 and potentially FGF-2. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, eaag0945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furmli, S.; Elmasry, R.; Ramos, M.; Fung, J. Therapeutic use of intermittent fasting for people with type 2 diabetes as an alternative to insulin. BMJ Case Rep. 2018, 2018, bcr-2017-221854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovannucci, E.; Harlan, D.M.; Archer, M.C.; Bergenstal, R.M.; Gapstur, S.M.; Habel, L.A.; Pollak, M.; Regensteiner, J.G.; Yee, D. Diabetes and cancer: A consensus report. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 1674–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coussens, L.M.; Werb, Z. Inflammation and cancer. Nature 2002, 420, 860–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, I.; Masoodi, S.R.; Mir, S.A.; Nabi, M.; Ghazanfar, K.; Ganai, B.A. Type 2 diabetes mellitus: From a metabolic disorder to an inflammatory condition. World J. Diabetes 2015, 6, 598–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsalamandris, S.; Antonopoulos, A.S.; Oikonomou, E.; Papamikroulis, G.A.; Vogiatzi, G.; Papaioannou, S.; Deftereos, S.; Tousoulis, D. The role of inflammation in diabetes: Current concepts and future perspectives. Eur. Cardiol. 2019, 14, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gore, A.C.; Chappell, V.A.; Fenton, S.E.; Flaws, J.A.; Nadal, A.; Prins, G.S.; Toppari, J.; Zoeller, R.T. EDC-2: The endocrine society’s second scientific statement on endocrine-disrupting chemicals. Endocr. Rev. 2015, 36, E1–E150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, K.; Jabłońska, E.; Ratajczak-Wrona, W. Immunomodulatory effects of synthetic endocrine disrupting chemicals on the development and functions of human immune cells. Environ. Int. 2019, 125, 350–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casanova-Nakayama, A.; Wenger, M.; Burki, R.; Eppler, E.; Krasnov, A.; Segner, H. Endocrine disrupting compounds: Can they target the immune system of fish? Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 63, 412–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, C.H.; Yang, S.N.; Kuo, P.L.; Hung, C.H. Immunomodulatory effects of environmental endocrine disrupting chemicals. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2012, 28, S37–S42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Csaba, G. Lifelong impact of perinatal endocrine disruptor exposures (faulty hormonal imprinting). IJPAES 2019, 9, 94–102. [Google Scholar]
- Kirkegård, J.; Cronin-Fenton, D.; Heide-Jørgensen, U.; Mortensen, F.V. Acute pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer risk: A nationwide matched-cohort study in Denmark. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 1729–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkegård, J.; Mortensen, F.V.; Cronin-Fenton, D. Chronic pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 112, 1366–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.K.; Yadav, D.; Garg, P.K. Diagnosis and management of chronic pancreatitis: A Review. JAMA 2019, 322, 2422–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magruder, J.T.; Elahi, D.; Andersen, D.K. Diabetes and pancreatic cancer: Chicken or egg? Pancreas 2011, 40, 339–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.H.; Wong, D.T. Saliva: An emerging biofluid for early detection of diseases. Am. J. Dent. 2009, 22, 241–248. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Xiao, H.; Karlan, S.; Zhou, H.; Gross, J.; Elashoff, D.; Akin, D.; Yan, X.; Chia, D.; Karlan, B.; et al. Discovery and preclinical validation of salivary transcriptomic and proteomic biomarkers for the non-invasive detection of breast cancer. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e15573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsiougiannis, S.; Wong, D.T. The Proteomics of Saliva in Sjögren’s Syndrome. Rheum. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2016, 42, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maciejczyk, M.; Szulimowska, J.; Skutnik, A.; Taranta-Janusz, K.; Wasilewska, A.; Wiśniewska, N.; Zalewska, A. Salivary biomarkers of oxidative stress in children with chronic kidney disease. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maciejczyk, M.; Skutnik-Radziszewska, A.; Zieniewska, I.; Matczuk, J.; Domel, E.; Waszkiel, D.; Żendzian-Piotrowska, M.; Szarmach, I.; Zalewska, A. Antioxidant defense, oxidative modification, and salivary gland function in an early phase of cerulein pancreatitis. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 8403578-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawczuk, B.; Maciejczyk, M.; Sawczuk-Siemieniuk, M.; Posmyk, R.; Zalewska, A.; Car, H. Salivary gland function, antioxidant defence and oxidative damage in the saliva of patients with breast cancer: Does the BRCA1 mutation disturb the salivary redox profile? Cancers (Basel) 2019, 11, 1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaczor-Urbanowicz, K.E.; Trivedi, H.M.; Lima, P.O.; Camargo, P.M.; Giannobile, W.V.; Grogan, T.R.; Gleber-Netto, F.O.; Whiteman, Y.; Li, F.; Lee, H.J.; et al. Salivary exRNA biomarkers to detect gingivitis and monitor disease regression. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2018, 45, 806–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczor-Urbanowicz, K.E.; Carreras-Presas, C.M.; Aro, K.; Tu, M.; Garcia-Godoy, F.; Wong, D.T. Saliva diagnostics—Current views and directions. Exp. Biol. Med. (Maywood) 2017, 242, 459–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Nonaka, T.; Wong, D.T.W. Salivary exosomes as nanocarriers for cancer biomarker delivery. Materials (Basel) 2019, 12, 654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, D.T.W. Salivaomics. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 2012, 143, 19S–24S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonaka, T.; Wong, D.T.W. Saliva-exosomics in cancer: Molecular characterization of cancer-derived exosomes in saliva. Enzymes 2017, 42, 125–151. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Farrell, J.J.; Zhou, H.; Elashoff, D.; Akin, D.; Park, N.H.; Chia, D.; Wong, D.T. Salivary transcriptomic biomarkers for detection of resectable pancreatic cancer. Gastroenterology 2010, 138, 949–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Kaczor-Urbanowicz, K.E.; Sun, J.; Majem, B.; Lo, H.C.; Kim, Y.; Koyano, K.; Rao, S.L.; Kang, S.Y.; Kim, S.M.; et al. Characterization of human salivary extracellular RNA by next-generation sequencing. Clin. Chem. 2018, 64, 1085–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meleti, M.; Cassi, D.; Vescovi, P.; Setti, G.; Pertinhez, T.A.; Pezzi, M.E. Salivary microRNA for diagnosis of systemic diseases and malignant tumors: A systematic review. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cirugía Bucal 2020, 25, e299. [Google Scholar]
- Setti, G.; Pezzi, M.E.; Viani, M.V.; Pertinhez, T.A.; Cassi, D.; Magnoni, C.; Bellini, P.; Musolino, A.; Vescovi, P.; Meleti, M. Salivary MicroRNA for diagnosis of cancer and systemic diseases: A systematic review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Z.; Yin, X.; Gong, B.; Nie, W.; Wu, B.; Zhang, X.; Huang, J.; Zhang, P.; Zhou, Z.; Li, Z. Salivary microRNAs show potential as a noninvasive biomarker for detecting resectable pancreatic cancer. Cancer Prev. Res. (Phila) 2015, 8, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrell, J.J.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, H.; Chia, D.; Elashoff, D.; Akin, D.; Paster, B.J.; Joshipura, K.; Wong, D.T.W. Variations of oral microbiota are associated with pancreatic diseases including pancreatic cancer. Gut 2012, 61, 582–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, C.; Kim, Y.; Chia, D.; Spielmann, N.; Eibl, G.; Elashoff, D.; Wei, F.; Lin, Y.L.; Moro, A.; Grogan, T.; et al. Role of pancreatic cancer-derived exosomes in salivary biomarker development. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 26888–26897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tiffon, C. Defining Parallels between the Salivary Glands and Pancreas to Better Understand Pancreatic Carcinogenesis. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 178. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8060178
Tiffon C. Defining Parallels between the Salivary Glands and Pancreas to Better Understand Pancreatic Carcinogenesis. Biomedicines. 2020; 8(6):178. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8060178
Chicago/Turabian StyleTiffon, Céline. 2020. "Defining Parallels between the Salivary Glands and Pancreas to Better Understand Pancreatic Carcinogenesis" Biomedicines 8, no. 6: 178. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8060178
APA StyleTiffon, C. (2020). Defining Parallels between the Salivary Glands and Pancreas to Better Understand Pancreatic Carcinogenesis. Biomedicines, 8(6), 178. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8060178



