Discovery, Pharmacological Characterisation and NMR Structure of the Novel µ-Conotoxin SxIIIC, a Potent and Irreversible NaV Channel Inhibitor
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Chemicals
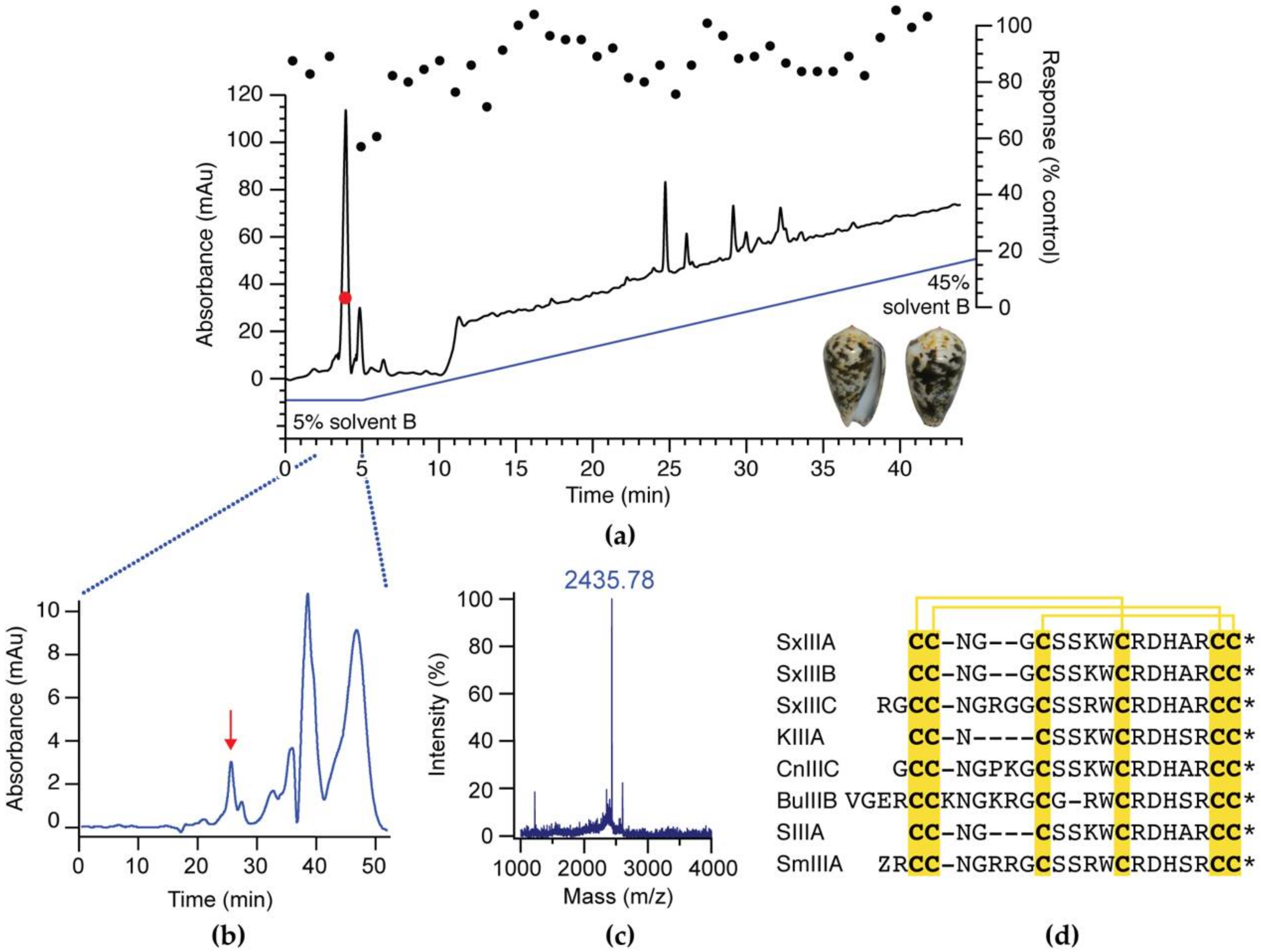
2.2. Activity-Guided Isolation of SxIIIC
2.3. Peptide Sequencing
2.4. Peptide Synthesis
2.5. Oxidation
2.6. Whole-Cell Patch-Clamp Electrophysiology
2.7. NMR Experiments
2.8. NMR Structure Calculations
3. Results
3.1. Activity-Guided Isolation of SxIIIC from Conus striolatus
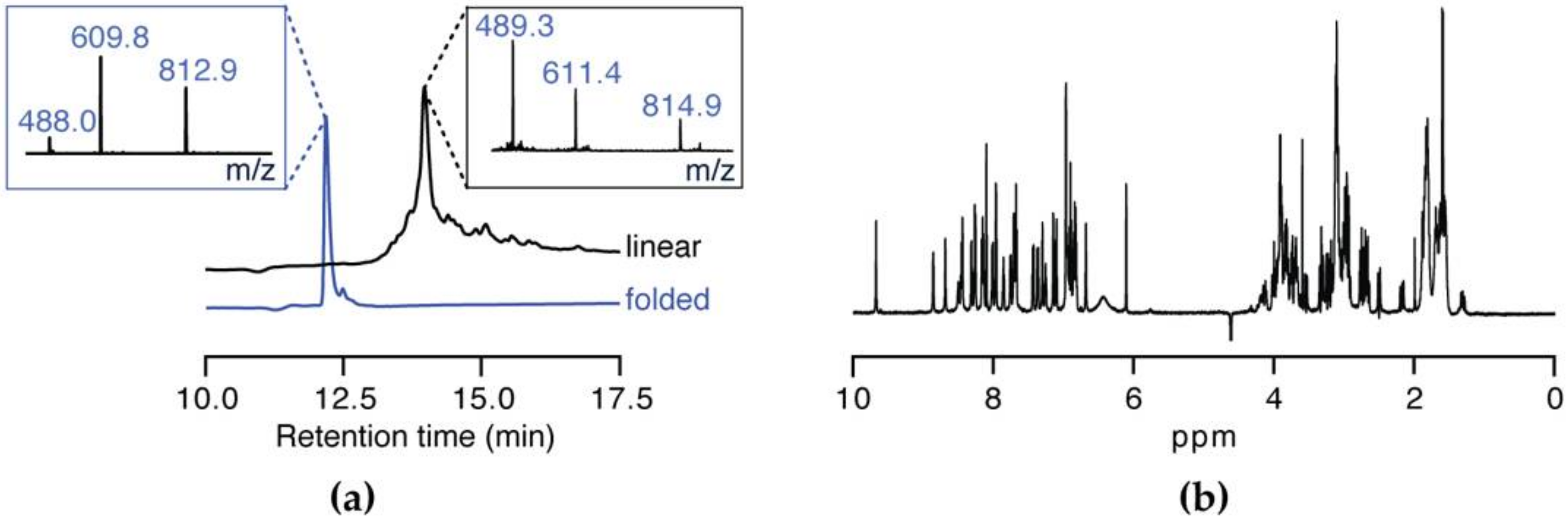
3.2. Peptide Synthesis of SxIIIC
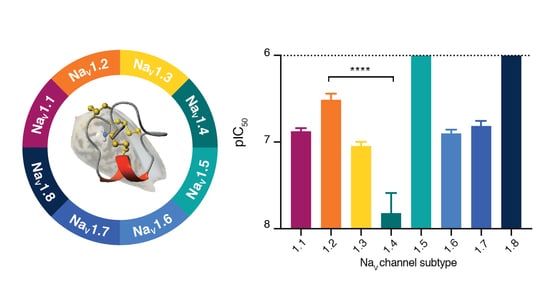
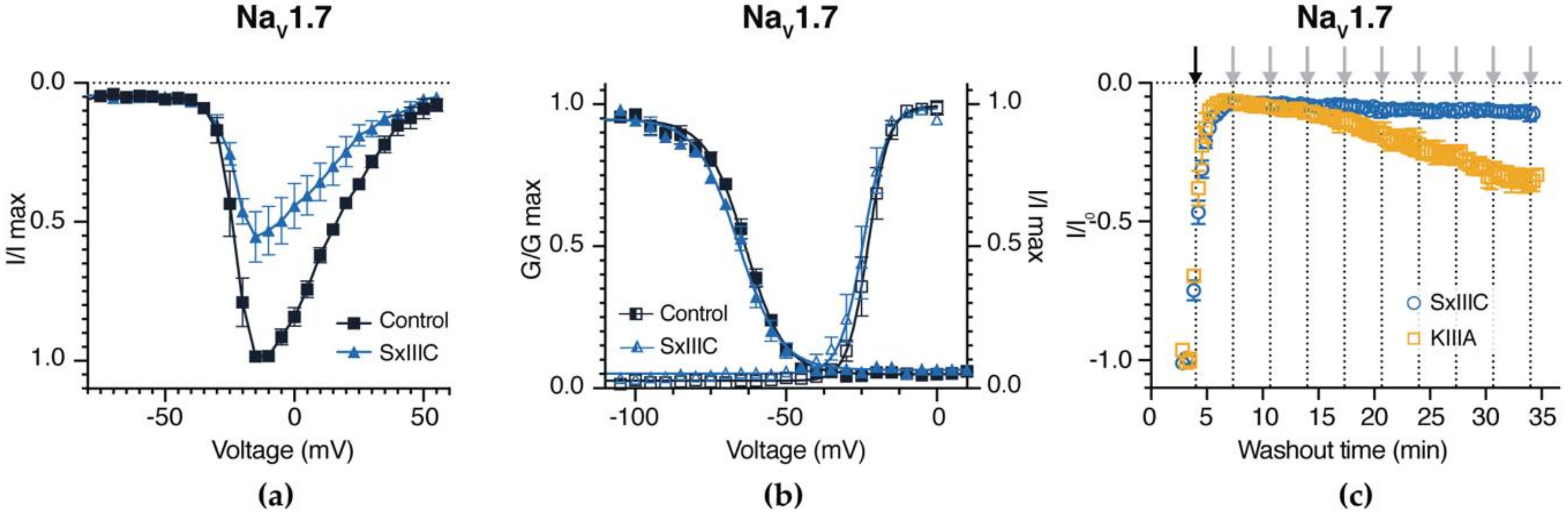
3.3. SxIIIC Displays a Unique NaV Channel Subtype Selectivity Profile
3.4. SxIIIC Is an Irreversible Presumptive Pore Blocker of NaV1.7
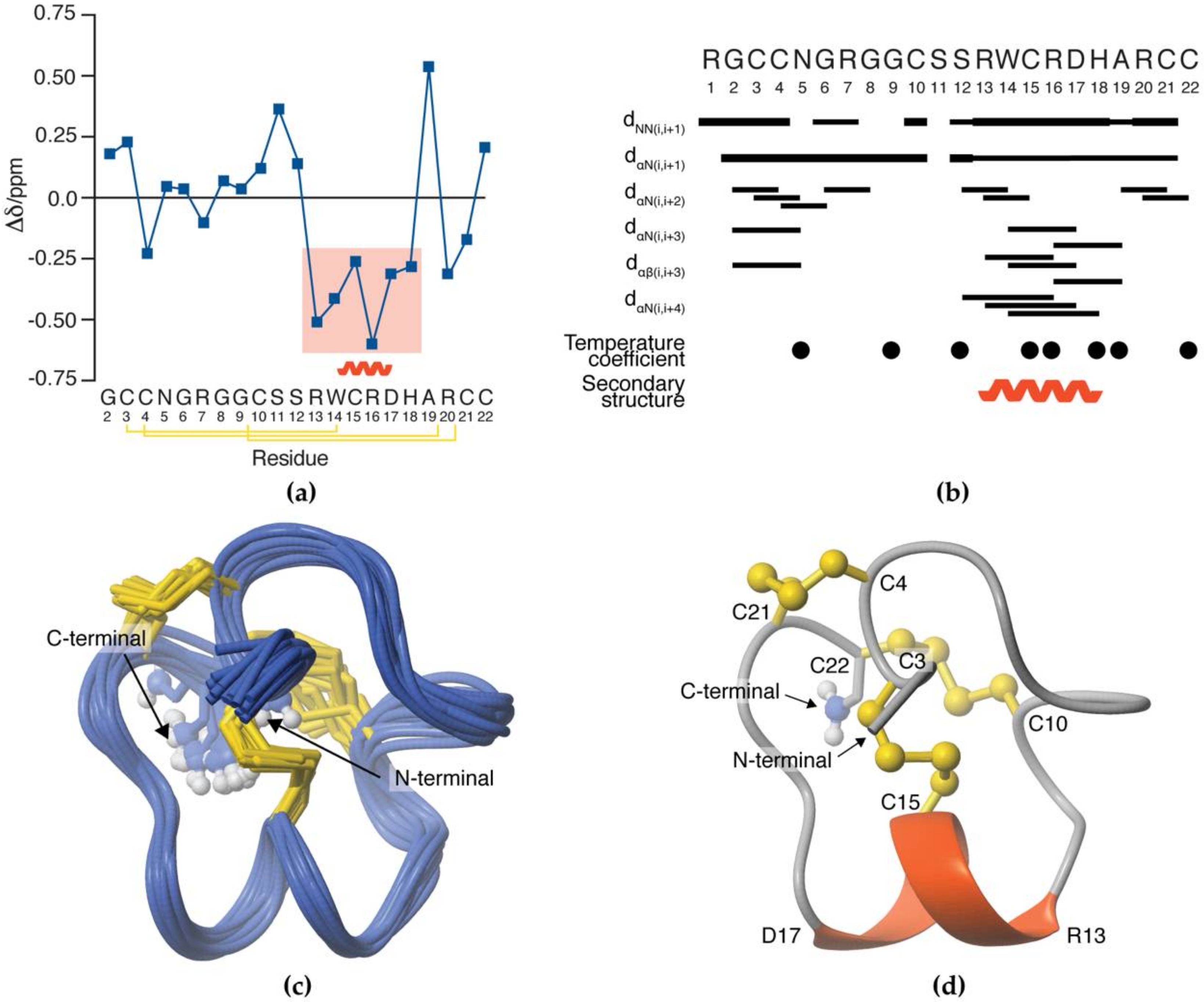
3.5. NMR Solution Structure of SxIIIC
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Armstrong, C.M. Ionic pores, gates, and gating currents. Q. Rev. Biophys. 1974, 7, 179–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catterall, W.A. Voltage-gated sodium channels at 60: Structure, function and pathophysiology. J. Physiol. 2012, 590, 2577–2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catterall, W.A.; Goldin, A.L.; Waxman, S.G. International Union of Pharmacology. XLVII. Nomenclature and structure-function relationships of voltage-gated sodium channels. Pharmacol. Rev. 2005, 57, 397–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catterall, W.A.; Kalume, F.; Oakley, J.C. NaV1.1 channels and epilepsy. J. Physiol. 2010, 588, 1849–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lossin, C.; Nam, T.S.; Shahangian, S.; Rogawski, M.A.; Choi, S.Y.; Kim, M.K.; Sunwoo, I.N. Altered fast and slow inactivation of the N440K NaV1.4 mutant in a periodic paralysis syndrome. Neurology 2012, 79, 1033–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.L.; Bink-Boelkens, M.T.; Bezzina, C.R.; Viswanathan, P.C.; Beaufort-Krol, G.C.; van Tintelen, P.J.; van den Berg, M.P.; Wilde, A.A.; Balser, J.R. A sodium-channel mutation causes isolated cardiac conduction disease. Nature 2001, 409, 1043–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dib-Hajj, S.D.; Yang, Y.; Black, J.A.; Waxman, S.G. The NaV1.7 sodium channel: From molecule to man. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2013, 14, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dib-Hajj, S.D.; Waxman, S.G. Sodium channels in human pain disorders: Genetics and pharmacogenomics. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2019, 42, 87–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetter, I.; Deuis, J.R.; Mueller, A.; Israel, M.R.; Starobova, H.; Zhang, A.; Rash, L.D.; Mobli, M. NaV1.7 as a pain target—From gene to pharmacology. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 172, 73–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilchrist, J.; Bosmans, F. Animal toxins can alter the function of NaV1.8 and NaV1.9. Toxins 2012, 4, 620–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikhonov, D.B.; Zhorov, B.S. Predicting structural details of the sodium channel pore basing on animal toxin studies. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 880–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terlau, H.; Olivera, B.M. Conus venoms: A rich source of novel ion channel-targeted peptides. Physiol. Rev. 2004, 84, 41–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.A.; Ennis, I.L.; French, R.J.; Dudley, S.C.; Tomaselli, G.F., Jr.; Marban, E. Clockwise domain arrangement of the sodium channel revealed by µ-conotoxin (GIIIA) docking orientation. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 11072–11077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, X.; Li, Z.; Huang, X.; Huang, G.; Gao, S.; Shen, H.; Liu, L.; Lei, J.; Yan, N. Molecular basis for pore blockade of human Na+ channel NaV1.2 by the µ-conotoxin KIIIA. Science 2019, 363, 1309–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erak, M.; Bellmann-Sickert, K.; Els-Heindl, S.; Beck-Sickinger, A.G. Peptide chemistry toolbox—Transforming natural peptides into peptide therapeutics. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 2759–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikhonov, D.B.; Bruhova, I.; Zhorov, B.S. Atomic determinants of state-dependent block of sodium channels by charged local anesthetics and benzocaine. FEBS Lett. 2006, 580, 6027–6032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tosti, E.; Boni, R.; Gallo, A. µ-Conotoxins modulating sodium currents in pain perception and transmission: A therapeutic potential. Mar. Drugs. 2017, 15, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, Z.; Zhang, M.M.; Gupta, K.; Gajewiak, J.; Gulyas, J.; Balaram, P.; Rivier, J.E.; Olivera, B.M.; Yoshikami, D.; Bulaj, G.; et al. Mammalian neuronal sodium channel blocker µ-conotoxin BuIIIB has a structured N-terminus that influences potency. ACS Chem. Biol. 2013, 8, 1344–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McArthur, J.R.; Singh, G.; McMaster, D.; Winkfein, R.; Tieleman, D.P.; French, R.J. Interactions of key charged residues contributing to selective block of neuronal sodium channels by µ-conotoxin KIIIA. Mol. Pharmacol. 2011, 80, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markgraf, R.; Leipold, E.; Schirmeyer, J.; Paolini-Bertrand, M.; Hartley, O.; Heinemann, S.H. Mechanism and molecular basis for the sodium channel subtype specificity of micro-conopeptide CnIIIC. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 167, 576–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walewska, A.; Skalicky, J.J.; Davis, D.R.; Zhang, M.M.; Lopez-Vera, E.; Watkins, M.; Han, T.S.; Yoshikami, D.; Olivera, B.M.; Bulaj, G. NMR-based mapping of disulfide bridges in cysteine-rich peptides: Application to the µ-conotoxin SxIIIA. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 14280–14286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetter, I.; Lewis, R.J. Characterization of endogenous calcium responses in neuronal cell lines. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2010, 79, 908–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.N.T.; Tran, P.; Deuis, J.R.; Agwa, A.J.; Zhang, A.H.; Vetter, I.; Schroeder, C.I. Enzymatic ligation of a pore blocker toxin and a gating modifier toxin: Creating double-knotted peptides with improved sodium channel NaV1.7 inhibition. Bioconjug. Chem. 2020, 31, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vranken, W.F.; Boucher, W.; Stevens, T.J.; Fogh, R.H.; Pajon, A.; Llinas, M.; Ulrich, E.L.; Markley, J.L.; Ionides, J.; Laue, E.D. The CCPN data model for NMR spectroscopy: Development of a software pipeline. Proteins 2005, 59, 687–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wishart, D.S.; Bigam, C.G.; Holm, A.; Hodges, R.S.; Sykes, B.D. 1H, 13C and 15N random coil NMR chemical shifts of the common amino acids. I. Investigations of nearest-neighbor effects. J. Biomol. NMR 1995, 5, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Bax, A. Protein backbone and sidechain torsion angles predicted from NMR chemical shifts using artificial neural networks. J. Biomol. NMR 2013, 56, 227–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, D.A.; Kaas, Q.; Rosengren, K.J. Prediction of disulfide dihedral angles using chemical shifts. Chem. Sci. 2018, 9, 6548–6556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guntert, P.; Buchner, L. Combined automated NOE assignment and structure calculation with CYANA. J. Biomol. NMR 2015, 62, 453–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baxter, N.J.; Williamson, M.P. Temperature dependence of 1H chemical shifts in proteins. J. Biomol. NMR 1997, 9, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nederveen, A.J.; Doreleijers, J.F.; Vranken, W.; Miller, Z.; Spronk, C.A.; Nabuurs, S.B.; Guntert, P.; Livny, M.; Markley, J.L.; Nilges, M.; et al. RECOORD: A recalculated coordinate database of 500+ proteins from the PDB using restraints from the BioMagResBank. Proteins 2005, 59, 662–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, C.J.; Headd, J.J.; Moriarty, N.W.; Prisant, M.G.; Videau, L.L.; Deis, L.N.; Verma, V.; Keedy, D.A.; Hintze, B.J.; Chen, V.B.; et al. MolProbity: More and better reference data for improved all-atom structure validation. Protein Sci. 2018, 27, 293–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vetter, I. Development and optimization of FLIPR high throughput calcium assays for ion channels and GPCRs. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2012, 740, 45–82. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jacob, R.B.; McDougal, O.M. The M-superfamily of conotoxins: A review. Cell. Mol. Life. Sci. 2010, 67, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, R.J.; Schroeder, C.I.; Ekberg, J.; Nielsen, K.J.; Loughnan, M.; Thomas, L.; Adams, D.A.; Drinkwater, R.; Adams, D.J.; Alewood, P.F. Isolation and structure-activity of µ-conotoxin TIIIA, a potent inhibitor of tetrodotoxin-sensitive voltage-gated sodium channels. Mol. Pharmacol. 2007, 71, 676–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroeder, C.I.; Ekberg, J.; Nielsen, K.J.; Adams, D.; Loughnan, M.L.; Thomas, L.; Adams, D.J.; Alewood, P.F.; Lewis, R.J. Neuronally µ-conotoxins from Conus striatus utilize an alpha-helical motif to target mammalian sodium channels. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 21621–21628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leipold, E.; Markgraf, R.; Miloslavina, A.; Kijas, M.; Schirmeyer, J.; Imhof, D.; Heinemann, S.H. Molecular determinants for the subtype specificity of µ-conotoxin SIIIA targeting neuronal voltage-gated sodium channels. Neuropharmacology 2011, 61, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, M.J.; Yoshikami, D.; Azam, L.; Gajewiak, J.; Olivera, B.M.; Bulaj, G.; Zhang, M.M. µ-Conotoxins that differentially block sodium channels NaV1.1 through 1.8 identify those responsible for action potentials in sciatic nerve. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 10302–10307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.M.; Green, B.R.; Catlin, P.; Fiedler, B.; Azam, L.; Chadwick, A.; Terlau, H.; McArthur, J.R.; French, R.J.; Gulyas, J.; et al. Structure/function characterization of µ-conotoxin KIIIA, an analgesic, nearly irreversible blocker of mammalian neuronal sodium channels. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 30699–30706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koradi, R.; Billeter, M.; Wuthrich, K. MOLMOL: A program for display and analysis of macromolecular structures. J. Mol. Graph. 1996, 14, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himaya, S.W.A.; Rai, S.K.; Pamfili, G.; Jin, A.-H.; Alewood, P.F.; Lewis, R.J. Venomic interrogation reveals the complexity of Conus striolatus venom. Aust. J. Chem. 2020, 73, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivera, B.M.; Seger, J.; Horvath, M.P.; Fedosov, A.E. Prey-capture strategies of fish-hunting cone snails: Behavior, neurobiology and evolution. Brain Behav. Evol. 2015, 86, 58–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivera, B.M.; Gray, W.R.; Zeikus, R.; McIntosh, J.M.; Varga, J.; Rivier, J.; de Santos, V.; Cruz, L.J. Peptide neurotoxins from fish-hunting cone snails. Science 1985, 230, 1338–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, H.Z.; Liu, D.L.; Wu, K.; Lei, J.L.; Yan, N. Structures of human NaV1.7 channel in complex with auxiliary subunits and animal toxins. Science 2019, 363, 1303–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoo, K.K.; Feng, Z.P.; Smith, B.J.; Zhang, M.M.; Yoshikami, D.; Olivera, B.M.; Bulaj, G.; Norton, R.S. Structure of the analgesic µ-conotoxin KIIIA and effects on the structure and function of disulfide deletion. Biochemistry 2009, 48, 1210–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Haegen, A.; Peigneur, S.; Tytgat, J. Importance of position 8 in µ-conotoxin KIIIA for voltage-gated sodium channel selectivity. FEBS J. 2011, 278, 3408–3418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, C.I.; Adams, D.; Thomas, L.; Alewood, P.F.; Lewis, R.J. N- and C-terminal extensions of µ-conotoxins increase potency and selectivity for neuronal sodium channels. Biopolymers 2012, 98, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
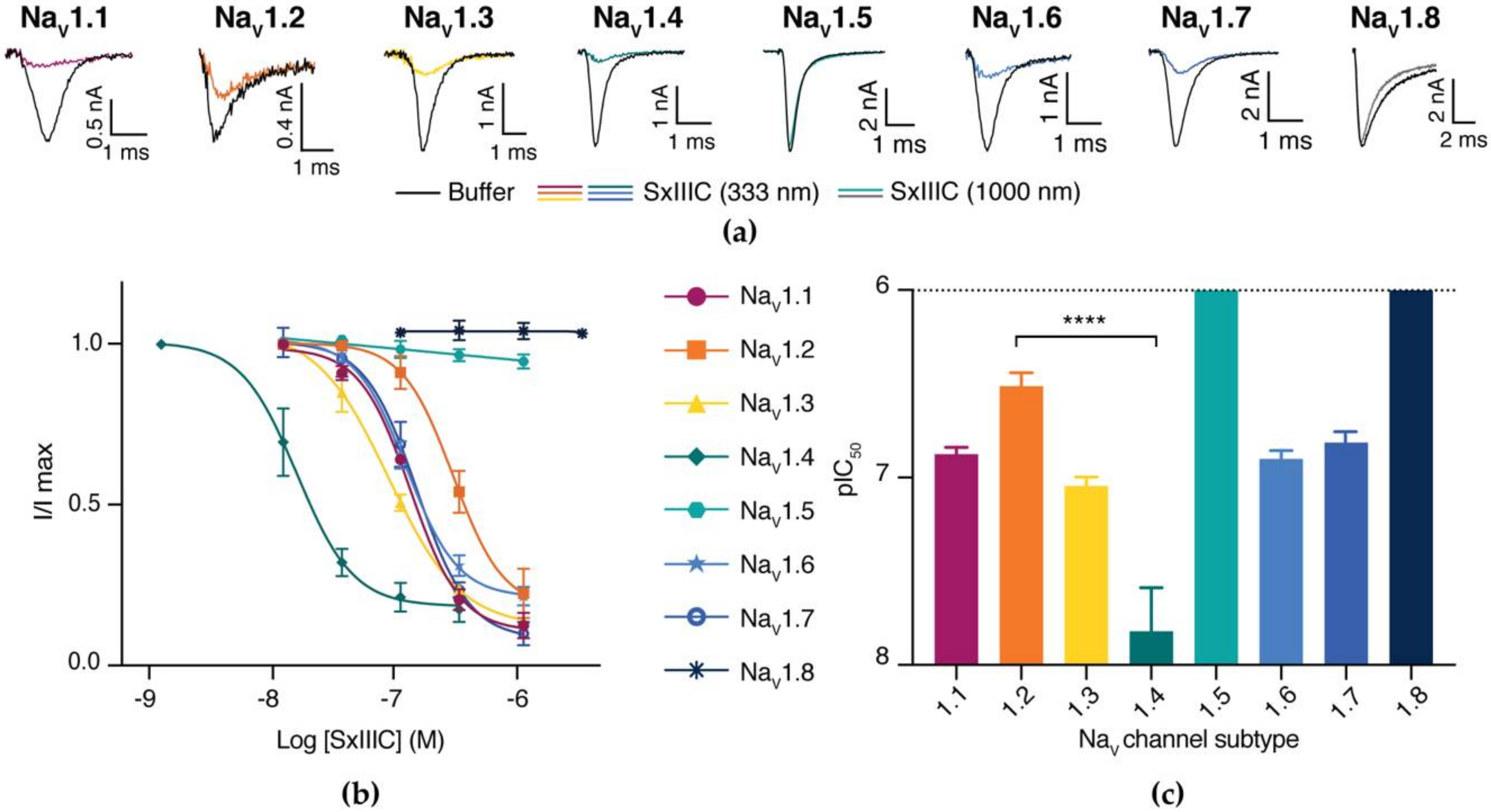
| Subtype | IC50 ± SEM (nM) | n |
|---|---|---|
| NaV1.1 | 132.0 ± 11.6 | 5 |
| NaV1.2 | 363.8 ± 53.8 | 5 |
| NaV1.3 | 89.4 ± 11.1 | 3 |
| NaV1.4 | 15.11 ± 10.7 | 10 |
| NaV1.5 | >5000 | 4 |
| NaV1.6 | 124.9 ± 11.1 | 4 |
| NaV1.7 | 152.2 ± 21.8 | 4 |
| NaV1.8 | >5000 | 3 |
| Distance Restraints | |
| Intraresidue (i − j = 0) | 77 |
| Sequential (|i − j| = 1) | 58 |
| Medium range (|i − j| < 5) | 24 |
| Long range (|i − j| > 5) | 7 |
| Hydrogen bonds 1 | 6 |
| Total | 172 |
| Dihedral angle restraints | |
| Φ | 12 |
| Φ | 10 |
| χ1 | 4 |
| χ2 | 2 |
| Total | 28 |
| Structure Statistics | |
| Energies (kcal/mol, mean ± SD) | |
| Overall | −465.4 ± 17.8 |
| Bonds | 8.8 ± 0.9 |
| Angles | 33.4 ± 2.5 |
| Improper | 16.2 ± 2.8 |
| Dihedral | 96.6 ± 1.3 |
| Van de Waals | −73.1 ± 6.3 |
| Electrostatic | −547.7 ± 19.5 |
| NOE (exp.) | 0.1 ± 0.0 |
| Constrained dihedrals (exp.) | 0.1 ± 0.1 |
| Atomic RMSD (Å) | |
| Mean global backbone (1–22) | 0.76 ± 0.17 |
| Mean global heavy (1–22) | 1.94 ± 0.39 |
| MolProbity Statistics | |
| Clash score, all atoms 2 | 14.8 ± 6.6 |
| Poor rotamers | 0.0 ± 0.0 |
| Ramachandran outliers (%) | 0.0 ± 0.0 |
| Ramachandran favoured (%) | 80.0 ± 10.0 |
| MolProbity score | 2.4 ± 0.3 |
| MolProbity percentile 3 | 54.0 ± 13.6 |
| Violations | |
| Distance constraints (>0.2 Å) | 0 |
| Dihedral-angle constraints (>2°) | 0 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
McMahon, K.L.; Tran, H.N.T.; Deuis, J.R.; Lewis, R.J.; Vetter, I.; Schroeder, C.I. Discovery, Pharmacological Characterisation and NMR Structure of the Novel µ-Conotoxin SxIIIC, a Potent and Irreversible NaV Channel Inhibitor. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 391. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8100391
McMahon KL, Tran HNT, Deuis JR, Lewis RJ, Vetter I, Schroeder CI. Discovery, Pharmacological Characterisation and NMR Structure of the Novel µ-Conotoxin SxIIIC, a Potent and Irreversible NaV Channel Inhibitor. Biomedicines. 2020; 8(10):391. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8100391
Chicago/Turabian StyleMcMahon, Kirsten L., Hue N.T. Tran, Jennifer R. Deuis, Richard J. Lewis, Irina Vetter, and Christina I. Schroeder. 2020. "Discovery, Pharmacological Characterisation and NMR Structure of the Novel µ-Conotoxin SxIIIC, a Potent and Irreversible NaV Channel Inhibitor" Biomedicines 8, no. 10: 391. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8100391
APA StyleMcMahon, K. L., Tran, H. N. T., Deuis, J. R., Lewis, R. J., Vetter, I., & Schroeder, C. I. (2020). Discovery, Pharmacological Characterisation and NMR Structure of the Novel µ-Conotoxin SxIIIC, a Potent and Irreversible NaV Channel Inhibitor. Biomedicines, 8(10), 391. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8100391