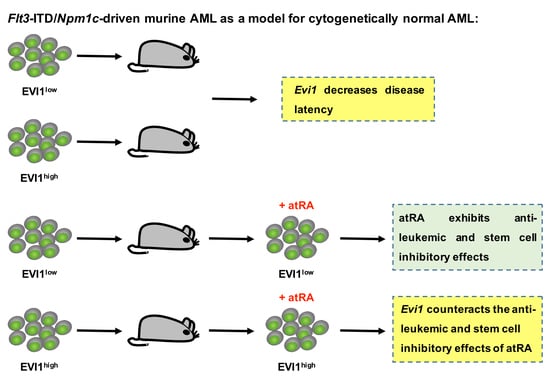
Evi1 Counteracts Anti-Leukemic and Stem Cell Inhibitory Effects of All-Trans Retinoic Acid on Flt3-ITD/Npm1c-Driven Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Ethics Approval
2.2. Ex Vivo Culture of Cells from Flt3-ITD/Npm1c-Driven Murine AML and Evi1 Overexpression
2.3. Drug Treatment, Cell Viability (Metabolic Activity), and Apoptosis Assays
2.4. Determination of Myeloid Differentiation by Flow Cytometry
2.5. Serial Replating Assays
2.6. Quantitative RT-PCR
2.7. Immunoblot Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analyses of Experimental Data
3. Results
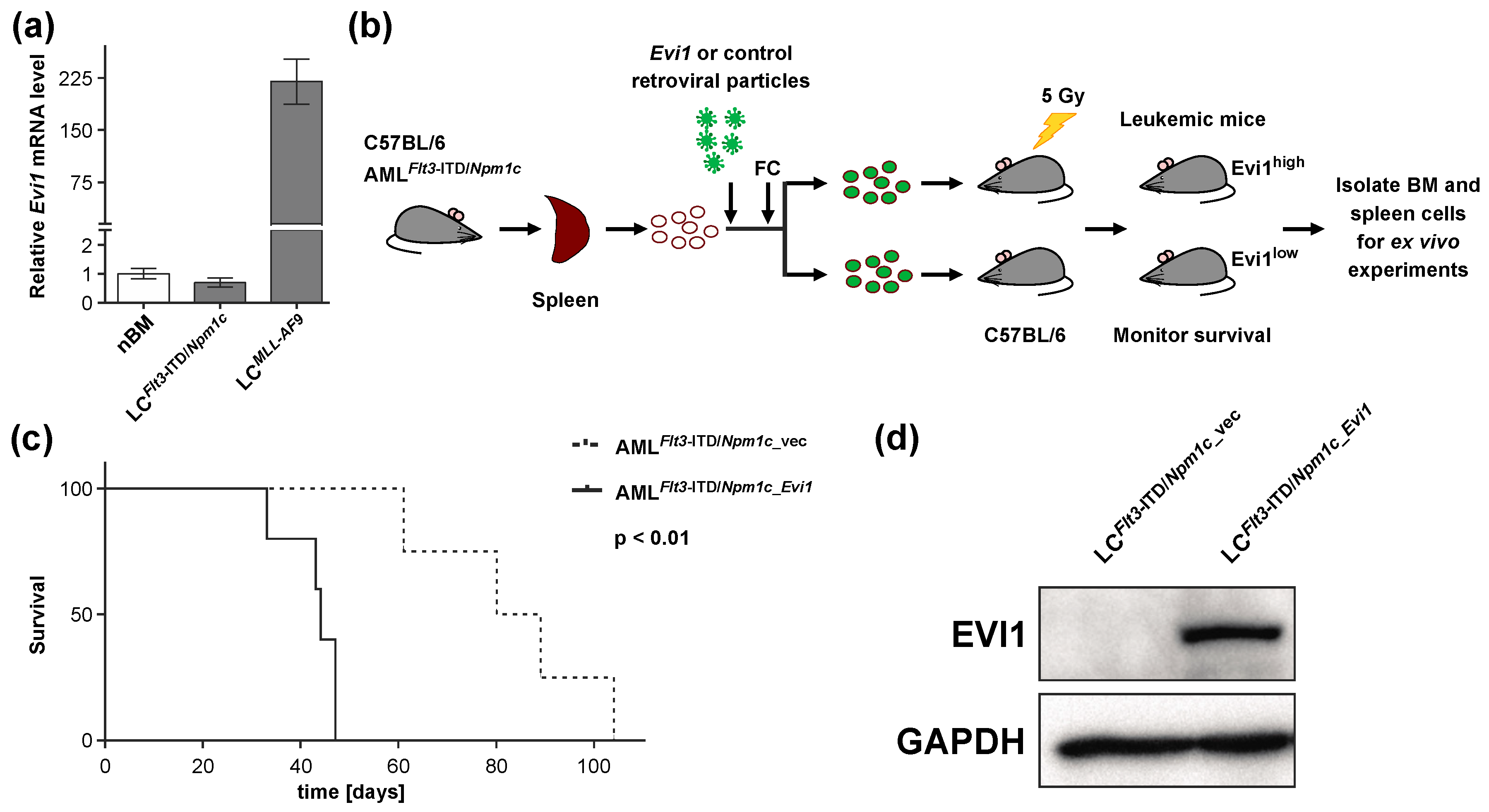
3.1. Experimental Expression of Evi1 in Flt3-ITD/Npm1c-Driven Murine AML Decreases Disease Latency
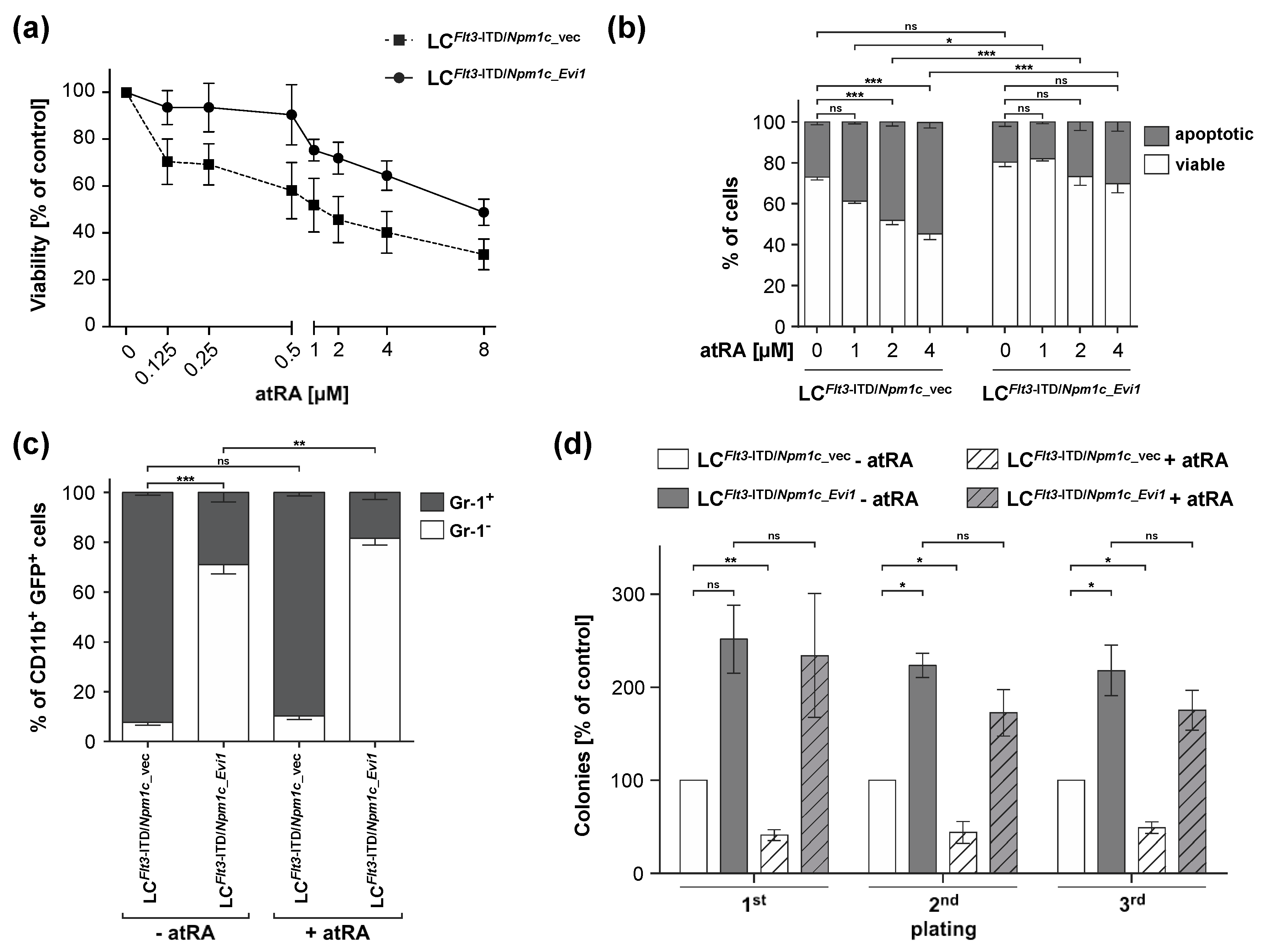
3.2. atRA Reduces Viability and Stem Cell Related Properties in LCs from Flt3-ITD/Npm1c-Driven AML, but Experimental Expression of Evi1 Counteracts These Effects
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Almeida, A.; Ramos, F. Acute myeloid leukemia in the older adults. Leuk. Res. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sanford, D.; Ravandi, F. Management of Newly Diagnosed Acute Myeloid Leukemia in the Elderly: Current Strategies and Future Directions. Drugs Aging 2015, 32, 983–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrence, M.; Stojanov, P.; Polak, P.; Kryukov, G.; Cibulskis, K.; Sivachenko, A.; Carter, S.; Stewart, C.; Mermel, C.; Roberts, S.; et al. Mutational heterogeneity in cancer and the search for new cancer-associated genes. Nature 2013, 499, 214–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Network, C.G.A.R. Genomic and epigenomic landscapes of adult de novo acute myeloid leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 2059–2074. [Google Scholar]
- Grimwade, D.; Ivey, A.; Huntly, B. Molecular landscape of acute myeloid leukemia in younger adults and its clinical relevance. Blood 2016, 127, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Papaemmanuil, E.; Gerstung, M.; Bullinger, L.; Gaidzik, V.; Paschka, P.; Roberts, N.; Potter, N.; Heuser, M.; Thol, F.; Bolli, N.; et al. Genomic Classification and Prognosis in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 2209–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, S.; Mitchell, A.; Kennedy, J.; Chen, W.; McLeod, J.; Ibrahimova, N.; Arruda, A.; Popescu, A.; Gupta, V.; Schimmer, A.; et al. A 17-gene stemness score for rapid determination of risk in acute leukaemia. Nature 2016, 540, 433–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackl, H.; Astanina, K.; Wieser, R. Molecular and genetic alterations associated with therapy resistance and relapse of acute myeloid leukemia. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2017, 10, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gough, S.; Slape, C.; Aplan, P. NUP98 gene fusions and hematopoietic malignancies: Common themes and new biologic insights. Blood 2011, 118, 6247–6257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meyer, C.; Hofmann, J.; Burmeister, T.; Groger, D.; Park, T.; Emerenciano, M.; Pombo de Oliveira, M.; Renneville, A.; Villarese, P.; Macintyre, E.; et al. The MLL recombinome of acute leukemias in 2013. Leukemia 2013, 27, 2165–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieser, R. The oncogene and developmental regulator EVI1: Expression, biochemical properties, and biological functions. Gene 2007, 396, 346–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haas, K.; Kundi, M.; Sperr, W.; Esterbauer, H.; Ludwig, W.; Ratei, R.; Koller, E.; Gruener, H.; Sauerland, C.; Fonatsch, C.; et al. Expression and prognostic significance of different mRNA 5’-end variants of the oncogene EVI1 in 266 patients with de novo AML: EVI1 and MDS1/EVI1 overexpression both predict short remission duration. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2008, 47, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groschel, S.; Lugthart, S.; Schlenk, R.; Valk, P.; Eiwen, K.; Goudswaard, C.; van Putten, W.; Kayser, S.; Verdonck, L.; Lubbert, M.; et al. High EVI1 expression predicts outcome in younger adult patients with acute myeloid leukemia and is associated with distinct cytogenetic abnormalities. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 2101–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohl, S.; Bullinger, L.; Rucker, F. New Targeted Agents in Acute Myeloid Leukemia: New Hope on the Rise. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ablain, J.; de The, H. Retinoic acid signaling in cancer: The parable of acute promyelocytic leukemia. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 135, 2262–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testa, U.; Lo-Coco, F. Targeting of leukemia-initiating cells in acute promyelocytic leukemia. Stem Cell Investig. 2015, 2, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Sanz, M.; Fenaux, P.; Tallman, M.; Estey, E.; Lowenberg, B.; Naoe, T.; Lengfelder, E.; Dohner, H.; Burnett, A.; Chen, S.; et al. Management of acute promyelocytic leukemia: Updated recommendations from an expert panel of the European LeukemiaNet. Blood 2019, 133, 1630–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lishner, M.; Curtis, J.; Minkin, S.; McCulloch, E. Interaction between retinoic acid and cytosine arabinoside affecting the blast cells of acute myeloblastic leukemia. Leukemia 1989, 3, 784–788. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, G.; Minden, M.; McCulloch, E. Regulation by retinoic acid and hydrocortisone of the anthracycline sensitivity of blast cells of acute myeloblastic leukemia. Leukemia 1994, 8, 2065–2075. [Google Scholar]
- Heuser, M.; Argiropoulos, B.; Kuchenbauer, F.; Yung, E.; Piper, J.; Fung, S.; Schlenk, R.; Dohner, K.; Hinrichsen, T.; Rudolph, C.; et al. MN1 overexpression induces acute myeloid leukemia in mice and predicts ATRA resistance in patients with AML. Blood 2007, 110, 1639–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chee, L.; Hendy, J.; Purton, L.; McArthur, G. ATRA and the specific RARalpha agonist, NRX195183, have opposing effects on the clonogenicity of pre-leukemic murine AML1-ETO bone marrow cells. Leukemia 2013, 27, 1369–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Steinmetz, B.; Hackl, H.; Slabáková, E.; Schwarzinger, I.; Smějová, M.; Spittler, A.; Arbesu, I.; Shehata, M.; Souček, K.; Wieser, R. The oncogene EVI1 enhances transcriptional and biological responses of human myeloid cells to all-trans retinoic acid. Cell Cycle 2014, 13, 2931–2943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- El Hajj, H.; Dassouki, Z.; Berthier, C.; Raffoux, E.; Ades, L.; Legrand, O.; Hleihel, R.; Sahin, U.; Tawil, N.; Salameh, A.; et al. Retinoic acid and arsenic trioxide trigger degradation of mutated NPM1, resulting in apoptosis of AML cells. Blood 2015, 125, 3447–3454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martelli, M.; Gionfriddo, I.; Mezzasoma, F.; Milano, F.; Pierangeli, S.; Mulas, F.; Pacini, R.; Tabarrini, A.; Pettirossi, V.; Rossi, R.; et al. Arsenic trioxide and all-trans retinoic acid target NPM1 mutant oncoprotein levels and induce apoptosis in NPM1-mutated AML cells. Blood 2015, 125, 3455–3465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boutzen, H.; Saland, E.; Larrue, C.; de Toni, F.; Gales, L.; Castelli, F.; Cathebas, M.; Zaghdoudi, S.; Stuani, L.; Kaoma, T.; et al. Isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 mutations prime the all-trans retinoic acid myeloid differentiation pathway in acute myeloid leukemia. J. Exp. Med. 2016, 213, 483–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhagen, H.; Smit, M.; Rutten, A.; Denkers, F.; Poddighe, P.; Merle, P.; Ossenkoppele, G.; Smit, L. Primary acute myeloid leukemia cells with overexpression of EVI-1 are sensitive to all-trans retinoic acid. Blood 2016, 127, 458–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, C.; Grandits, A.; Purton, L.; Sill, H.; Wieser, R. All-trans retinoic acid in non-promyelocytic acute myeloid leukemia: Driver lesion dependent effects on leukemic stem cells. Cell Cycle 2020, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlenk, R.; Frohling, S.; Hartmann, F.; Fischer, J.; Glasmacher, A.; del Valle, F.; Grimminger, W.; Gotze, K.; Waterhouse, C.; Schoch, R.; et al. Phase III study of all-trans retinoic acid in previously untreated patients 61 years or older with acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2004, 18, 1798–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burnett, A.; Hills, R.; Green, C.; Jenkinson, S.; Koo, K.; Patel, Y.; Guy, C.; Gilkes, A.; Milligan, D.; Goldstone, A.; et al. The impact on outcome of the addition of all-trans retinoic acid to intensive chemotherapy in younger patients with nonacute promyelocytic acute myeloid leukemia: Overall results and results in genotypic subgroups defined by mutations in NPM1, FLT3, and CEBPA. Blood 2010, 115, 948–956. [Google Scholar]
- Schlenk, R.; Lubbert, M.; Benner, A.; Lamparter, A.; Krauter, J.; Herr, W.; Martin, H.; Salih, H.; Kundgen, A.; Horst, H.; et al. All-trans retinoic acid as adjunct to intensive treatment in younger adult patients with acute myeloid leukemia: Results of the randomized AMLSG 07-04 study. Ann. Hematol. 2016, 95, 1931–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuley-Bagheri, Y.; Kreuzer, K.; Monsef, I.; Lubbert, M.; Skoetz, N. Effects of all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) in addition to chemotherapy for adults with acute myeloid leukaemia (AML) (non-acute promyelocytic leukaemia (non-APL)). Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 8, CD011960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlenk, R.; Dohner, K.; Kneba, M.; Gotze, K.; Hartmann, F.; Del Valle, F.; Kirchen, H.; Koller, E.; Fischer, J.; Bullinger, L.; et al. Gene mutations and response to treatment with all-trans retinoic acid in elderly patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Results from the AMLSG Trial AML HD98B. Haematologica 2009, 94, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stahl, M.; Kim, T.; Zeidan, A. Update on acute myeloid leukemia stem cells: New discoveries and therapeutic opportunities. World J. Stem Cells 2016, 8, 316–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haas, S.; Trumpp, A.; Milsom, M. Causes and Consequences of Hematopoietic Stem Cell Heterogeneity. Cell Stem Cell 2018, 22, 627–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pinho, S.; Frenette, P. Haematopoietic stem cell activity and interactions with the niche. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2019, 20, 303–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Greenblatt, S.; Shirley, C.; Duffield, A.; Bruner, J.; Li, L.; Nguyen, B.; Jung, E.; Aplan, P.; Ghiaur, G.; et al. All-trans retinoic acid synergizes with FLT3 inhibition to eliminate FLT3/ITD+ leukemia stem cells in vitro and in vivo. Blood 2016, 127, 2867–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, C.; Bauer, K.; Hackl, H.; Schlerka, A.; Koller, E.; Hladik, A.; Stoiber, D.; Zuber, J.; Staber, P.; Hoelbl-Kovacic, A.; et al. All-trans retinoic acid enhances, and a pan-RAR antagonist counteracts, the stem cell promoting activity of EVI1 in acute myeloid leukemia. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mupo, A.; Celani, L.; Dovey, O.; Cooper, J.; Grove, C.; Rad, R.; Sportoletti, P.; Falini, B.; Bradley, A.; Vassiliou, G. A powerful molecular synergy between mutant Nucleophosmin and Flt3-ITD drives acute myeloid leukemia in mice. Leukemia 2013, 27, 1917–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Livak, K.; Schmittgen, T. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzeler, K.; Hummel, M.; Bloomfield, C.; Spiekermann, K.; Braess, J.; Sauerland, M.; Heinecke, A.; Radmacher, M.; Marcucci, G.; Whitman, S.; et al. An 86-probe-set gene-expression signature predicts survival in cytogenetically normal acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2008, 112, 4193–4201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, G.; Yamazaki, Y.; Takuwa, M.; Takahara, T.; Kaneko, K.; Kuwata, T.; Miyata, S.; Nakamura, T. Trib1 and Evi1 cooperate with Hoxa and Meis1 in myeloid leukemogenesis. Blood 2007, 109, 3998–4005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe-Okochi, N.; Yoshimi, A.; Sato, T.; Ikeda, T.; Kumano, K.; Taoka, K.; Satoh, Y.; Shinohara, A.; Tsuruta, T.; Masuda, A.; et al. The shortest isoform of C/EBPbeta, liver inhibitory protein (LIP), collaborates with Evi1 to induce AML in a mouse BMT model. Blood 2013, 121, 4142–4155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lubbert, M.; Grishina, O.; Schmoor, C.; Schlenk, R.; Jost, E.; Crysandt, M.; Heuser, M.; Thol, F.; Salih, H.; Schittenhelm, M.; et al. Valproate and Retinoic Acid in Combination With Decitabine in Elderly Nonfit Patients With Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Results of a Multicenter, Randomized, 2 × 2, Phase II Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wass, M.; Gollner, S.; Besenbeck, B.; Schlenk, R.; Mundmann, P.; Gothert, J.; Noppeney, R.; Schliemann, C.; Mikesch, J.; Lenz, G.; et al. A proof of concept phase I/II pilot trial of LSD1 inhibition by tranylcypromine combined with ATRA in refractory/relapsed AML patients not eligible for intensive therapy. Leukemia 2020, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bindels, E.; Havermans, M.; Lugthart, S.; Erpelinck, C.; Wocjtowicz, E.; Krivtsov, A.; Rombouts, E.; Armstrong, S.; Taskesen, E.; Haanstra, J.; et al. EVI1 is critical for the pathogenesis of a subset of MLL-AF9-rearranged AMLs. Blood 2012, 119, 5838–5849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groschel, S.; Schlenk, R.; Engelmann, J.; Rockova, V.; Teleanu, V.; Kuhn, M.; Eiwen, K.; Erpelinck, C.; Havermans, M.; Lubbert, M.; et al. Deregulated expression of EVI1 defines a poor prognostic subset of MLL-rearranged acute myeloid leukemias: A study of the German-Austrian Acute Myeloid Leukemia Study Group and the Dutch-Belgian-Swiss HOVON/SAKK Cooperative Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krivtsov, A.; Figueroa, M.; Sinha, A.; Stubbs, M.; Feng, Z.; Valk, P.; Delwel, R.; Dohner, K.; Bullinger, L.; Kung, A.; et al. Cell of origin determines clinically relevant subtypes of MLL-rearranged AML. Leukemia 2013, 27, 852–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esnault, C.; Rahme, R.; Rice, K.; Berthier, C.; Gaillard, C.; Quentin, S.; Maubert, A.; Kogan, S.; de The, H. FLT3-ITD impedes retinoic acid, but not arsenic, responses in murine acute promyelocytic leukemias. Blood 2019, 133, 1495–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purton, L.; Bernstein, I.; Collins, S. All-trans retinoic acid delays the differentiation of primitive hematopoietic precursors (lin(−)c-kit(+)Sca-1(+)) while enhancing the terminal maturation of committed granulocyte monocyte progenitors. Blood 1999, 94, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purton, L.; Bernstein, I.; Collins, S. All-trans retinoic acid enhances the long-term repopulating activity of cultured hematopoietic stem cells. Blood 2000, 95, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purton, L.; Dworkin, S.; Olsen, G.; Walkley, C.; Fabb, S.; Collins, S.; Chambon, P. RARgamma is critical for maintaining a balance between hematopoietic stem cell self-renewal and differentiation. J. Exp. Med. 2006, 203, 1283–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabezas-Wallscheid, N.; Buettner, F.; Sommerkamp, P.; Klimmeck, D.; Ladel, L.; Thalheimer, F.; Pastor-Flores, D.; Roma, L.; Renders, S.; Zeisberger, P.; et al. Vitamin A-Retinoic Acid Signaling Regulates Hematopoietic Stem Cell Dormancy. Cell 2017, 169, 807–823.e819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hernandez, D.; Palau, L.; Norsworthy, K.; Anders, N.; Alonso, S.; Su, M.; Petkovich, M.; Chandraratna, R.; Rudek, M.; Smith, B.; et al. Overcoming microenvironment-mediated protection from ATRA using CYP26-resistant retinoids. Leukemia 2020, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nguyen, C.H.; Grandits, A.M.; Vassiliou, G.S.; Staber, P.B.; Heller, G.; Wieser, R. Evi1 Counteracts Anti-Leukemic and Stem Cell Inhibitory Effects of All-Trans Retinoic Acid on Flt3-ITD/Npm1c-Driven Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 385. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8100385
Nguyen CH, Grandits AM, Vassiliou GS, Staber PB, Heller G, Wieser R. Evi1 Counteracts Anti-Leukemic and Stem Cell Inhibitory Effects of All-Trans Retinoic Acid on Flt3-ITD/Npm1c-Driven Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells. Biomedicines. 2020; 8(10):385. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8100385
Chicago/Turabian StyleNguyen, Chi Huu, Alexander M. Grandits, George S. Vassiliou, Philipp B. Staber, Gerwin Heller, and Rotraud Wieser. 2020. "Evi1 Counteracts Anti-Leukemic and Stem Cell Inhibitory Effects of All-Trans Retinoic Acid on Flt3-ITD/Npm1c-Driven Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells" Biomedicines 8, no. 10: 385. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8100385
APA StyleNguyen, C. H., Grandits, A. M., Vassiliou, G. S., Staber, P. B., Heller, G., & Wieser, R. (2020). Evi1 Counteracts Anti-Leukemic and Stem Cell Inhibitory Effects of All-Trans Retinoic Acid on Flt3-ITD/Npm1c-Driven Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells. Biomedicines, 8(10), 385. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8100385