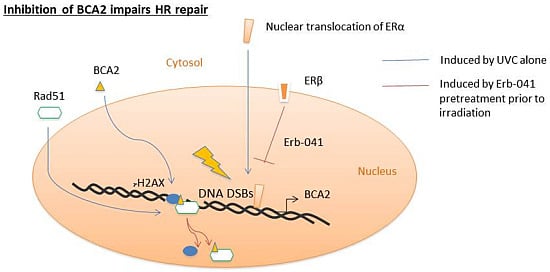
Regulation of DNA Damage Response by Estrogen Receptor β-Mediated Inhibition of Breast Cancer Associated Gene 2
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Cell Irradiation
2.3. Antibodies and Drugs
2.4. Plasmids, siRNAs and Transfection
2.5. Protein Extraction and Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate−Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE)
2.6. Immunoprecipitation Assay
2.7. Quantitative Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction
2.8. Clonogenic Assay
2.9. Cell Cycle Analysis with Fluorescent-Activated Cell Sorting (FACS)
2.10. Immunofluorescence Staining and Confocal Microscopy
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Erb-041 Decreased Estrogen Receptor α (ERα) Signaling While Inhibiting Breast Cancer Associated-Gene 2 (BCA2) Transcription
3.2. Erb-041 Induced the Accumulation of Cells in S Phase and Potentiated DNA Synthesis, Reducing the Repair of Ultraviolet-Induced DNA Damage
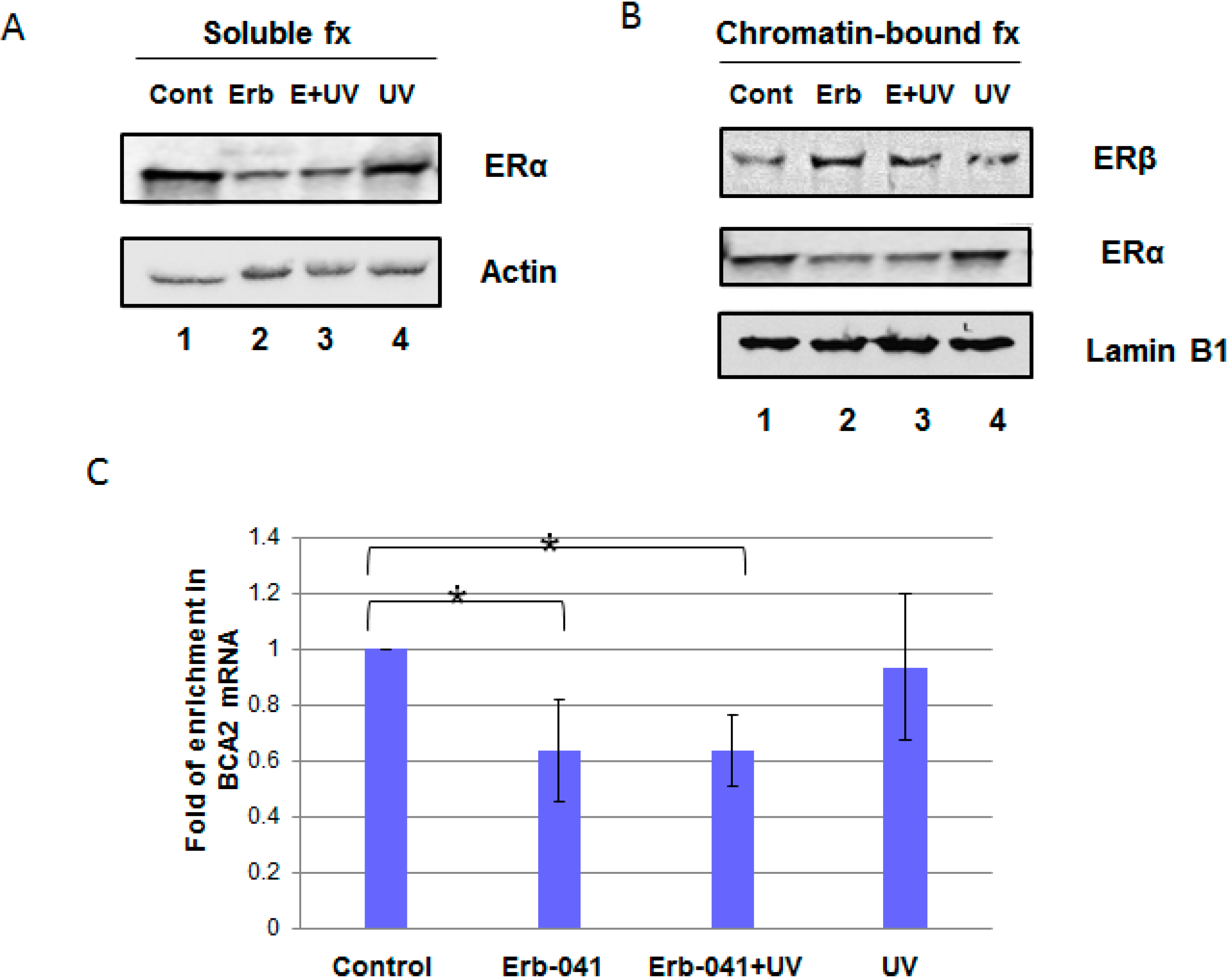
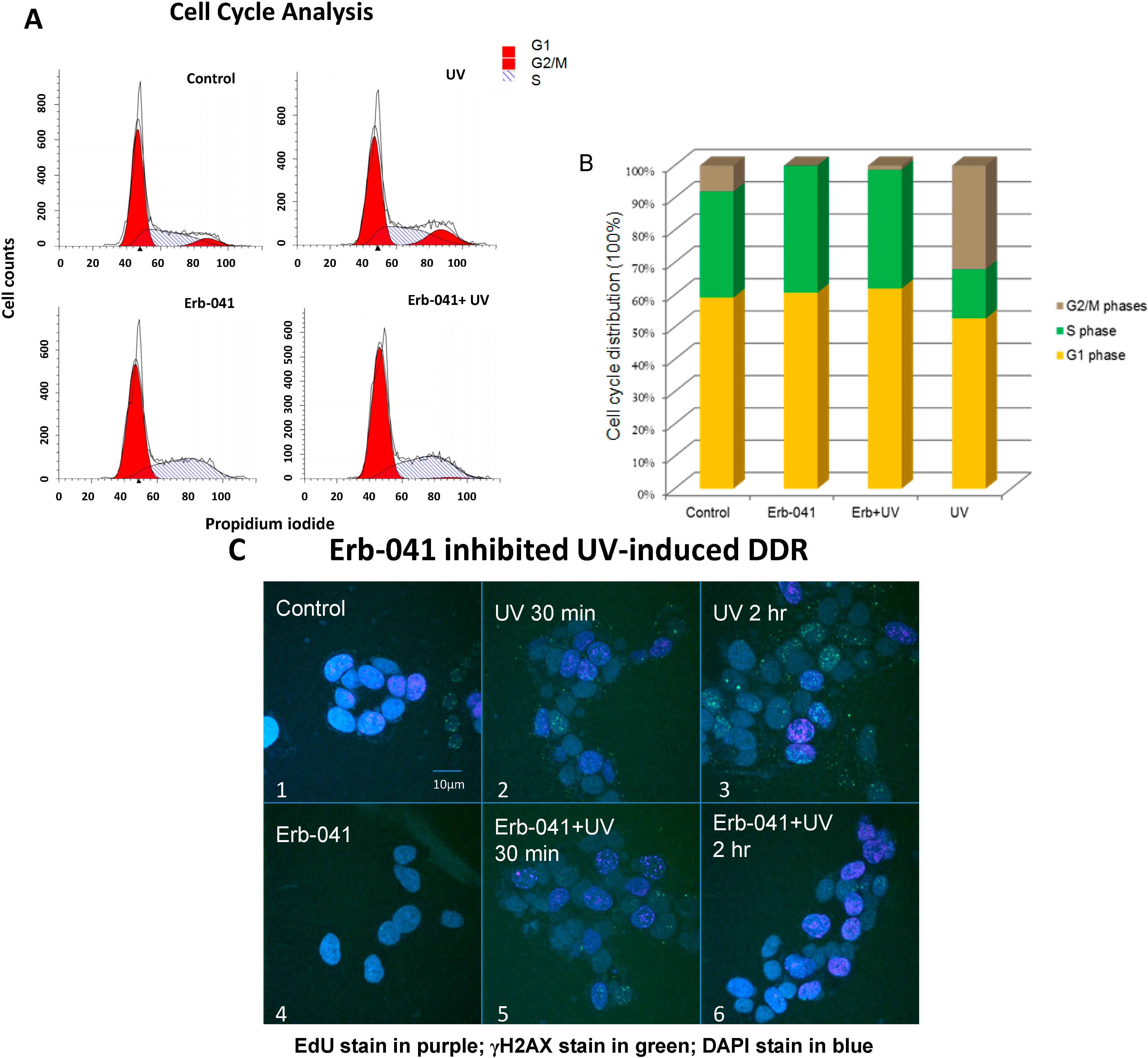
3.3. Erb-041 Exacerbated UV-induced DNA Damage through Reduction of BCA2 Expression and Mitigation of DNA Damage Response
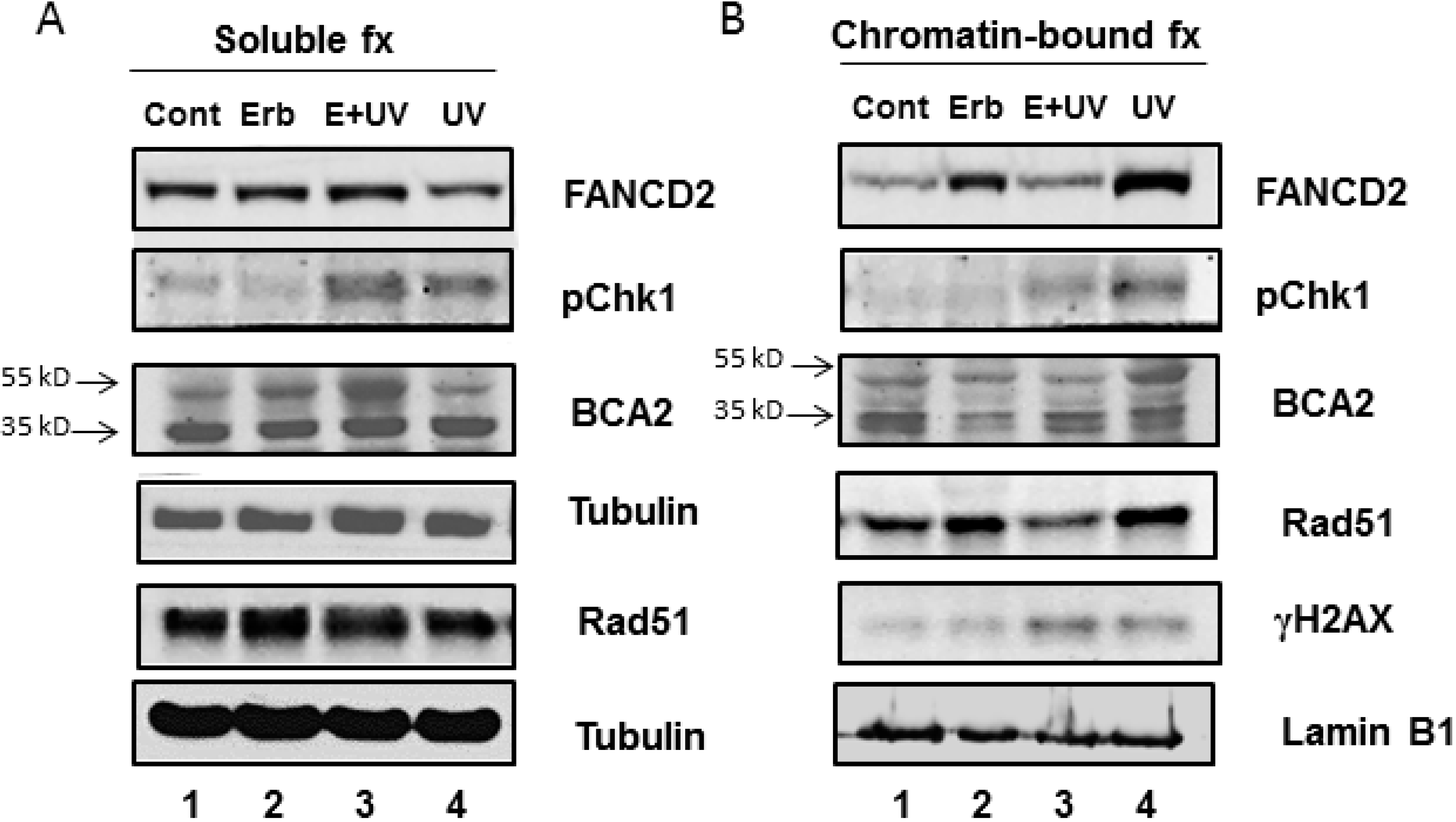
3.4. BCA2 Knockdown Intrinsically Induced DNA Damage Response and Impeded the Repair of UV-Induced DNA Damage

3.5. BCA2 Endogenously Interacted with γH2AX and Rad51 in Association with Ubiquitin-Mediated Degradation

3.6. Rad51 Protein Degradation May Be Preceded by the Nuclear Co-Localization of BCA2 and Rad51 Under Co-Treatment with Erb-041 and UVC
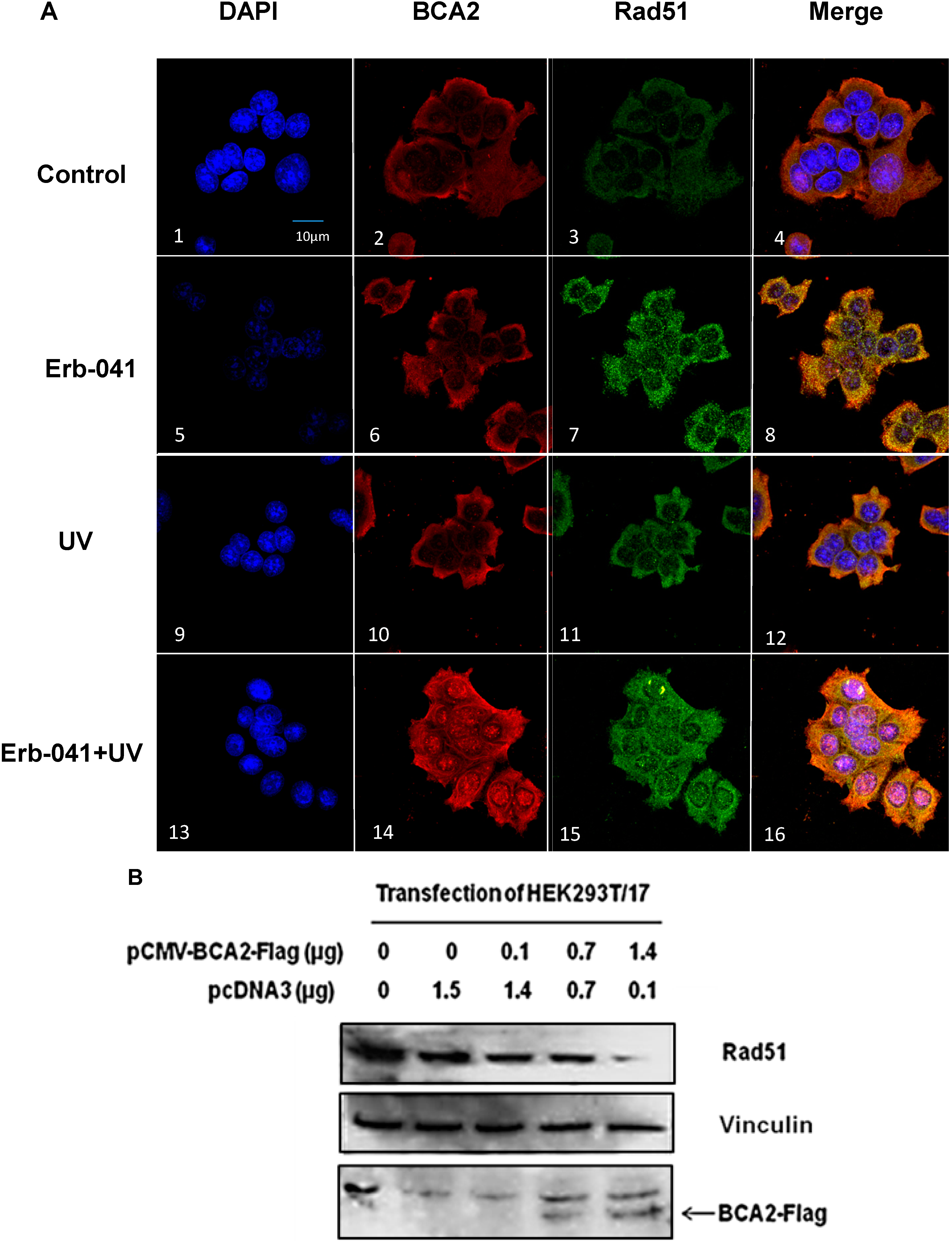
4. Discussion

5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Abbreviations
| BCA2 | breast cancer-associated gene 2 |
| DDR | DNA damage response |
| DSB | double-stranded break |
| ER | estrogen receptor |
| ERα | estrogen receptor α |
| HR | homologous recombination |
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Evers, N.M.; Wang, S.; van den Berg, J.H.J.; Houtman, R.; Melchers, D.; de Haan, L.H.; Ederveen, A.G.J.; Groten, J.P.; Rietjens, I.M. Identification of coregulators influenced by estrogen receptor subtype specific binding of the ER antagonists 4-hydroxytamoxifen and fulvestrant. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2014, 220C, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caldon, C.E. Estrogen signaling and the DNA damage response in hormone dependent breast cancers. Front. Oncol. 2014, 4, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guirouilh-Barbat, J.; Wilhelm, T.; Lopez, B.S. AKT1/BRCA1 in the control of homologous recombination and genetic stability: The missing link between hereditary and sporadic breast cancers. Oncotarget 2010, 1, 691–199. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chaudhary, S.C.; Tripti Singh, S.S.; Talwelkar, R.K.; Srivastava, A.; Arumugam, Z.; Weng, C.A.; Elmets, F.; Afaq, L.K.; Athar, M. Erb-041, an Estrogen Receptor-Β agonist, inhibits skin photocarcinogenesis in SKH-1 hairless mice by downregulating the WNT signaling pathway. Cancer Prev. Res. 2014, 7, 186–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, K. Estrogen and DNA damage: The silent source of breast cancer? JNCI 2013, 95, 100–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Santi, A.; Cernera, G.; Migliaccio, A.; Perillo, B. Analysis of histone posttranslational modifications in the control of chromatin plasticity observed at estrogen-responsive sites in human breast cancer cells. Methods Mol. Biol. 2014, 1204, 59–69. [Google Scholar]
- Monroe, D.G.; Secreto, F.J.; Subramaniam, M.; Getz, B.J.; Khosla, S.; Spelsberg, T.C. Estrogen receptor alpha and beta heterodimers exert unique effects on estrogen- and tamoxifen-dependent gene expression in human U2OS osteosarcoma Cells. Mol. Endocrinol. 2005, 19, 1555–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powell, E.; Xu, W. Intermolecular interactions identify ligand-selective activity of estrogen receptor alpha/beta dimers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 19012–19017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Protein Marker Associated with Positive Outcome in Invasive Breast Cancer. Available online: http://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/ 2005/11/051126141009.htm (accessed on 3 September 2014).
- Kona, F.R.; Stark, K.; Bisoski, L.; Buac, D.; Cui, Q.; Dou, Q.P. Transcriptional activation of breast cancer-associated gene 2 by estrogen receptor. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2012, 135, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burger, A.M.; Gao, Y.; Amemiya, Y.; Kahn, H.J.; Kitching, R.; Yang, Y.; Sun, P.; Narod, S.A.; Hanna, W.M.; Seth, A.K. A novel RING-type ubiquitin ligase breast cancer-associated gene 2 correlates with outcome in invasive breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 10401–10412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burger, A.M.; Kona, F.; Amemiya, Y.; Gao, Y.; Bacopulos, S.; Seth, A.K. Role of the BCA2 ubiquitin E3 ligase in hormone responsive breast cancer. Open Cancer J. 2010, 3, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Nie, Z.; Chen, W.; Zhou, Z.; Kong, Q.; Seth, A.K.; Liu, R.; Chen, C. RNF115/BCA2 E3 ubiquitin ligase promotes breast cancer cell proliferation through targeting p21Waf1/Cip1 for ubiquitin-mediated degradation. Neoplasia 2013, 15, 1028–1035. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mizuno, K.; Kitamur, A.; Sasaki, T. Rabring7, a novel Rab7 target protein with a RING finger motif. Mol. Biol. Cell 2003, 14, 3741–3752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Zhang, M.; Ma, Z.; Guo, K.; Tergaonkar, V.; Zeng, Q.; Hong, W. A role of Rab7 in stabilizing EGFR-Her2 and in sustaining Akt survival signal. J. Cell. Physiol. 2012, 227, 2788–2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urbanska, K.; Pannizzo, P.; Lassak, A.; Gualco, E.; Surmacz, E.; Croul, S.; Del Valle, L.; Khalili, K.; Reiss, K. Estrogen receptor beta-mediated nuclear interaction between IRS-1 and Rad51 Inhibits homologous recombination directed DNA repair in medulloblastoma. J. Cell. Physiol. 2009, 219, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbano, R.; Copetti, M.; Perrone, G.; Pazienza, V.; Muscarella, L.A.; Balsamo, T.; Storlazzi, C.T.; Ripoli, M.; Rinaldi, M.; Valori, V.M.; et al. High RAD51 mRNA expression characterize estrogen receptor-positive/progesteron receptor-negative breast cancer and is associated with patient’s outcome. Int. J. Cancer 2011, 129, 536–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belcher, S.M.; Ma, X.; Le, H.H. Blockade of estrogen receptor signaling inhibits growth and migration of medulloblastoma. Endocrinology 2009, 150, 1112–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, P.; Robberson, D.L. DNA strand exchange mediated by a RAD51–ssDNA nucleoprotein filament with polarity opposite to that of RecA. Cell 1995, 82, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Jacobs, S.A.; West, S.C.; Ogawa, T.; Egelman, E.H. Domain structure and dynamics in the helical filaments formed by RecA and Rad51 on DNA. In Links between Recombination and Replication: Vital Roles of Recombination; National Academies Press: Irvine, CA, USA, 2002; Volume 98, Issue 15, pp. 8392–8393. [Google Scholar]
- Powell, S.N.; Willers, H.; Xia, F. BRCA2 keeps Rad51 in line: High-fidelity homologous recombination prevents breast and ovarian cancer? Mol. Cell 2002, 10, 1262–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galkin, V.E.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, X.-P.; Qian, X.; He, Y.; Yu, X.; Heyer, W.-D.; Luo, Y.; Egelman, E.H. The Rad51/RadA N-terminal domain activates nucleoprotein filament ATPase activity. Structure 2006, 14, 983–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sisci, D.; Morelli, C.; Cascio, S.; Lanzino, M.; Garofalo, C.; Reiss, K.; Garcia, M.; Russo, A.; Andò, S.; Surmacz, E. The estrogen receptor alpha:insulin receptor substrate 1 complex in breast cancer: Structure–function relationships. Ann. Oncol. 2007, 18, vi81–vi85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ERB 041. Available online: http://www.tocris.com/ dispprod.php?ItemId=298648 (accessed on 10 October 2014).
- Lattrich, C.; Schüler, S.; Häring, J.; Skrzypczak, M.; Ortmann, O.; Treeck, O. Effects of a combined treatment with tamoxifen and estrogen receptor β agonists on human breast cancer cell lines. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2014, 289, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catley, M.C.; Birrell, M.A.; Hardaker, E.L.; de Alba, J.; Farrow, S.; Haj-Yahia, S.; Belvisi, M.G. Estrogen receptor Β: Expression profile and possible anti-inflammatory role in disease. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2008, 326, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sareddy, G.R.; Nair, B.C.; Gonugunta, V.K.; Zhang, Q.; Brenner, A.; Brann, D.W.; Tekmal, R.R.; Vadlamudi, R.K. Therapeutic significance of estrogen receptor Β agonists in gliomas. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2012, 11, 1174–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amemiya, Y.; Azmi, P.; Seth, A. Autoubiquitination of BCA2 RING E3 ligase regulates its own stability and affects cell migration. Mol. Cancer Res. 2008, 6, 1385–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandal, S.; Davie, J.R. Estrogen regulated expression of the p21Waf1/Cip1 gene in estrogen receptor positive human breast cancer cell. J. Cell Physiol. 2010, 224, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stewart, Z.A.; Leach, S.D.; Pietenpol, J.A. p21Waf1/Cip1 inhibition of cyclin E/Cdk2 activity prevents endoreduplication after mitotic spindle disruption. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1999, 19, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ferrándiz, N.; Caraballo, J.M.; García-Gutierrez, L.; Devgan, V.; Rodriguez-Paredes, M.; Lafita, M.C.; Bretones, G. p21 as a transcriptional co-repressor of S-phase and mitotic control genes. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rastogi, R.P.; Richa; Kumar, A.; Tyagi, M.B.; Sinha, R.P. Molecular mechanisms of ultraviolet radiation-induced DNA damage and repair. J. Nucleic Acids 2010, 2010, e592980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldovan, G.-L.; D’Andrea, A.D. How the fanconi anemia pathway guards the genome. Annu. Rev. Genomics 2009, 43, 223–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, S.P.; Durocher, D. Regulation of DNA damage responses by ubiquitin and SUMO. Mol. Cell 2013, 49, 795–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yajima, H.; Lee, K.-J.; Zhang, S.; Kobayashi, J.; Chen, B.P.C. DNA double-strand break formation upon UV-induced replication stress activates ATM and DNA-PKcs kinases. J. Mol. Biol. 2009, 385, 800–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burma, S.; Chen, B.P.; Murphy, M.; Kurimasa, A.; Chen, D.J. ATM phosphorylates histone H2AX in response to DNA double-strand breaks. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 42462–42467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, M.-R.; Peng, G.; Hung, W.-C.; Lin, S.-Y. Monoubiquitination of H2AX protein regulates DNA damage response signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 28599–28607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.-H.; Sun, Y.; Glickman, R.D. Ursolic acid-regulated energy metabolism—Reliever or propeller of ultraviolet-induced oxidative stress and DNA damage? Proteomes 2014, 2, 399–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chargari, C.; Toillon, R.A.; Macdermed, D.; Castadot, P.; Magné, N. Concurrent hormone and radiation therapy in patients with breast cancer: What is the rationale? Lancet. Oncol. 2009, 10, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mobley, J.A.; Brueggemeier, R.W. Estrogen receptor-mediated regulation of oxidative stress and DNA damage in breast cancer. Carcinogenesis 2004, 25, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, Y.-H.; Sun, Y.; Gerweck, L.E.; Glickman, R.D. Regulation of DNA Damage Response by Estrogen Receptor β-Mediated Inhibition of Breast Cancer Associated Gene 2. Biomedicines 2015, 3, 182-200. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines3020182
Lee Y-H, Sun Y, Gerweck LE, Glickman RD. Regulation of DNA Damage Response by Estrogen Receptor β-Mediated Inhibition of Breast Cancer Associated Gene 2. Biomedicines. 2015; 3(2):182-200. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines3020182
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Yuan-Hao, Youping Sun, Leo E. Gerweck, and Randolph D. Glickman. 2015. "Regulation of DNA Damage Response by Estrogen Receptor β-Mediated Inhibition of Breast Cancer Associated Gene 2" Biomedicines 3, no. 2: 182-200. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines3020182
APA StyleLee, Y.-H., Sun, Y., Gerweck, L. E., & Glickman, R. D. (2015). Regulation of DNA Damage Response by Estrogen Receptor β-Mediated Inhibition of Breast Cancer Associated Gene 2. Biomedicines, 3(2), 182-200. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines3020182