Abstract
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is a major global health concern, particularly in Western countries where there is high consumption of processed food. Gut microbiota, intestinal inflammation, and autophagy play pivotal roles in CRC initiation and progression. Probiotics and probiotic metabolites (particularly short-chain fatty acids) have emerged as potential preventive and adjuvant therapeutics by restoring a balanced gut microbiota, dampening inflammation, stimulating immune response, and improving barrier integrity and intestinal epithelial homeostasis by modulating autophagy. This narrative review discusses the current evidence supporting the anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory, and pro-autophagy effects of probiotics and their metabolites and explores their potential preventive and therapeutic applications in CRC management.
1. Introduction
1.1. Colorectal Cancer: Epidemiology, Risk Factors, Prevention, and Therapy at a Glance
Worldwide statistics indicate that colorectal cancer (CRC) incidence ranks third and mortality second (after lung) in 2022, being now the first-leading and second-leading cause of cancer death in men and women, respectively [1]. The most significant risk factors for developing CRC are genetic predisposition (inherited mutations in relevant genes), a family history of CRC, and chronic inflammatory conditions of the gastrointestinal tract [2,3]. Additional factors associated with an increased risk of developing sporadic CRC include age over 50, male sex, obesity, and a sedentary lifestyle [4].
Surgery remains the gold standard treatment for CRC, although, in most cases, it is preceded or followed by adjuvant chemotherapy and radiotherapy to shrink or stabilize the tumor [5,6]. Standard chemotherapy protocols include monotherapy with 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) and multi-drug therapy combining 5-FU with leucovorin and oxaliplatin or with leucovorin and irinotecan [5]. More recently, novel strategies such as target therapy, gene therapy, and immunotherapy have been introduced to treat CRC [7]. Early detection of CRC through colonoscopy and modification of lifestyle risk factors are crucial for prevention and reducing the risk of developing the tumor [8]. The highest incidence rates are reported in high-income and well-developed regions, including Europe, Australia, North America, and Eastern Asia, suggesting a link with lifestyle and dietary factors [8,9,10]. Having an impact on gut microbiota, alcohol consumption, and dietary choices constitute the most important modifiable risk factors for CRC [11,12,13].
The gut microbiota plays a crucial role in maintaining intestinal homeostasis through numerous functions, including the breakdown of non-digestible dietary components, the renewal of epithelial cells, the maintenance of intestinal mucosal integrity, immune system modulation, and the secretion of antimicrobial substances. It also protects against infections by competing with pathogenic organisms for nutrients and receptors while promoting overall health through the synthesis of vitamins, regulation of fat reserves, and energy storage [14]. The state of eubiosis, which refers to the balance between the host and its microbiota, is essential for proper gut function and overall health [15]. Gut microbiota is highly sensitive to environmental factors such as dietary macro- and micronutrients, infections, and lifestyle, which can lead to alterations in its composition and function, a condition known as dysbiosis [16,17]. Gut dysbiosis is often associated with intestinal inflammation, which may evolve into IBD and CRC [18]. Specifically, a reduction in the abundance of beneficial bacteria or an overgrowth of pathogenic organisms such as Bacteroides, Prevotella, Proteobacteria, Eubacterium, Fusobacterium, Proteobacteria, Escherichia coli, Clostriudium, and Salmonella spp. can disrupt the balance of microbiota, creating an environment that promotes inflammation and tumorigenesis [19,20].
Recently, prebiotics, probiotics, and postbiotics capable of restoring eubiosis have emerged as potent dietary supplements for the prevention and post-surgery adjuvant therapy of CRC [21]. The most important metabolites released by the intestinal microbiota with beneficial effects on human health are short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), including acetate, butyrate, and propionate. These postbiotics are produced during the fermentation of non-digestible plant fibers (prebiotics) in the diet. Butyrate is by far the most abundant one and serves as the primary energy source for intestinal cells [22]. Butyrate has a wide range of beneficial effects on health. By interacting with its receptors, it modulates immune system activity, promotes the release of anti-inflammatory cytokines, and exhibits various anti-tumor properties, including inducing autophagy and apoptosis and reducing the proliferation of neoplastic cells. Additionally, butyrate plays a crucial role in reducing oxidative stress and reinforcing the intestinal barrier, preserving gut integrity [23,24].
This narrative review presents the most recent knowledge on the role of autophagy and inflammation in CRC and how probiotics and their metabolites modulate these processes to prevent and cure CRC. To prepare this review, we searched for scientific publications in public databases using appropriate combinations of keywords, including probiotics, postbiotics, microbiota, microbiome, colorectal cancer, inflammation, autophagy, immunity, engineered microorganisms, etc. The relevant literature was selected according to four main criteria: 1. reputation of the journal and expertise of the authors; 2. quality of methodology, description of mechanisms, and translational significance of the results; 3. discussion of controversial issues where applicable; 4. most recent publications were given priority.
1.2. Microbiota and Colorectal Cancerogenesis: The Role of Genetics and Epigenetics
Most cases of CRC are sporadic and develop from polyps through the adenoma–carcinoma sequence following a characteristic sequential accumulation of genetic and epigenetic mutations in well-defined oncogenes, tumor suppressor genes, and DNA repair genes in 10 years or more [25,26]. CRC hereditary predisposition is linked to germline inherited monoallelic mutations in tumor suppressor or DNA repair genes [2,27]. Inactivation (by mutation or epigenetic silencing) of the second allele creates the conditions for the initiation step of tumorigenesis, which can be followed by additional mutations or epimutations in oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes that eventually lead to frank carcinoma.
Around 80% of CRCs are associated with mutations in the Wnt/β-Catenin signaling pathway [28], which is involved in key processes such as adult tissue renewal and homeostasis, hematopoietic stem cell maintenance, and regulation of cell proliferation, migration, and differentiation [29]. Loss-of-function mutations in the oncosuppressor APC, mutations in CTNNB1 (β-Catenin gene), and the excessive presence of Wnt ligands in the tumor microenvironment (TME) disrupt these regulatory mechanisms, resulting in uncontrolled tumor growth [30,31]. The APC mutation specifically initiates the formation of adenomas or intestinal polyps, some of which progress to adenocarcinomas due to the accumulation of additional mutations, including those in KRAS, DCC, TP53, and SMAD4 [32].
Genetic and epigenetic mutations in genes relevant to colorectal carcinogenesis are influenced by and interact with environmental factors, such as diet, lifestyle, therapy, and gut microbiota, thereby accelerating the development and progression of the disease [33]. The following findings exemplify how gut microbes can influence gene function and, consequently, the development of colorectal cancer.
Genotoxic pks+ Escherichia coli strain and Bacteroides fragilis have been shown to cause DNA mutations through the production of free radicals and of genotoxins (namely, colibactin), thus contributing to oncogenic activation and CRC development [34,35]. Similarly, Enterococcus faecalis has been shown to cause chromosomal instability and aneuploidy in enterocytes through oxidative stress [36].
Dysbiosis may contribute to CRC development also via epigenome changes [37]. For instance, antibiotic therapy-induced and diet-dependent depletion of SCFA-producing bacteria in the intestine may influence chromatin accessibility and transcription in a way that promotes CRC progression [38,39,40,41]. Similarly, genotoxins produced by Bacteroides fragilis have been shown to modulate the methylation and chromatin accessibility of genes involved in CRC development [42]. The microbe composition also influences the intestine epithelial cell expression of long non-coding RNAs and of microRNAs that have an impact on intestine homeostasis, although their mechanistic role in CRC development and progression remains to be elucidated [43].
On the contrary, eubiosis can prevent mutagenic and epimutagenic events, thus protecting from CRC development. In vitro studies have shown that certain Lactobacillus strains possess anti-genotoxic and anti-mutagenic properties, effectively reducing mutagen levels and thereby lowering the risk of CRC initiation [44,45]. In a mice model of colorectal carcinogenesis, the supplementation with probiotic strains of Bifidobacterium bifidum and Lactobacillus acidophilus reduced the expression of the oncomiRNAs miR-135b and miR-155 while increasing the expression of miR-26b and miR-18a, and these changes were associated with downregulation of the oncogene K-Ras and the upregulation of the tumor suppressors APC and PTEN [46]. In this same line, the supplementation with Bifidiobacterium longum inhibited colorectal carcinogenesis in mice via downregulation of miR-155 and miR-21a and up-regulation of the tumor suppressive miRNAs miR-145 and miR-15a [47].
Finally, the inhibition of cell proliferation and induction of cell death in CRC cells by butyrate has been (at least partly) attributed to its capability to modulate the expression of pro-apoptotic and cell cycle genes via HDAC inhibition [48].
1.3. Colorectal Cancerogenesis: The Role of Autophagy
Autophagy is a catabolic process highly conserved in eukaryotic cells that maintains cell homeostasis through the lysosome-mediated degradation of damaged (unfolded, oxidized), aged, or redundant cellular components, as well as the destruction of intracellular pathogens. Based on the mechanism that directs the degrading material (cargo) to the lysosome, autophagy is classified into three types: (i) macroautophagy (where the cargo is sequestered within the autophagosomes), (ii) microautophagy (small portion of the cytoplasm is internalized by invagination of the lysosome membrane), and (iii) chaperon-mediated autophagy (internalization of selected proteins is mediated by HSC73) [49]. A more in-depth description of the autophagy machinery and its biochemical regulation by extracellular signals and by genetics and epigenetics can be found in excellent reviews [49,50,51]. Here, we will only give a glance at macroautophagy (simply referred to as autophagy) since this pathway plays a major role in macromolecular degradation and turnover. This process is characterized by the sequestration of the cargo within autophagosomes (double-membrane organelles) that subsequently fuse with endosomes and lysosomes, forming the autolysosomes in which the cargo is fully degraded, and the substrates are exported in the cytosol for reutilization [40]. Autophagy is repressed by growth signals and an abundance of nutrients (glucose, amino acids) through the activation of mTORC1, while it is induced in conditions of nutrient depletion and reduced oxidative phosphorylation through the activation of AMPK [49]. Autophagy is a pro-survival pathway that opposes apoptosis, yet when hyper-induced because of overwhelming cellular toxicity it can precipitate autophagic cell death [49]. This is reflected in cancer, where autophagy may play two opposite roles: (i) as anti-cancer, it can prevent carcinogenesis by eliminating damaged subcellular structure and protecting the genome by contrasting cell mass growth and inhibiting cell proliferation and cell migration and by promoting cancer cell dormancy, whereas (ii) as pro-cancer, it can favor survival in floating metastatic cells and can protect the cancer cell from chemo- and radio-induced damages [52]. Autophagy also plays a role in reshaping the TME by reducing angiogenesis and inflammation, relieving immune suppression, favoring tumor dormancy, and promoting the reversal of the phenoconversion of cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) into normal fibroblasts [53,54,55]. Stimulation of autophagy also re-educates M2 tumor-associated macrophages [56].
The involvement of autophagy in CRC is suggested by the finding of microsatellite instability and frameshift mutations in the autophagy-related genes ATG2B, ATG5, and ATG9B [57]. The role of autophagy in colorectal carcinogenesis is multifaceted and apparently controversial, as it is likely stage- and context-dependent [58,59]. For instance, in a small cohort of CRC patients, it was found that the expression of ATG10 was positively associated with metastasis and poor prognosis [60], yet another study proved that downregulation of ATG10 in CRC was associated with EMT and liver metastasization [61]. Upregulation of autophagy genes or proteins in cancer cells could reflect a stress response rather than the cause of malignancy. For instance, knock-down of autophagy was reported to improve 5-FU chemotherapy toxicity in CRC [62].
Particularly when assessing the expression of autophagy genes or proteins in pathological specimens, it is important to also consider the tumor microenvironment since autophagy is differentially dysregulated in the cell depending on the surrounding conditions. For instance, in the hypoxic niche, autophagy is induced to promote the survival and proliferation of colorectal cancer stem cells [63]. Another important caveat in assigning a role for autophagy in cancer is related to the methods used to assess it. Older studies using chloroquine (which alkalinizes lysosomal pH) or 3-methyladenine (a PI3K inhibitor) should be treated with caution because of their nonspecific effects. The role of autophagy in cancer is better appreciated in models where it is genetically manipulated, although we cannot ignore the possibility of off-target effects, especially when using miRNAs. In Apc+/− mice genetically predisposed to CRC, the conditional ATG7 knock-down in enterocytes prevented CRC development by improving T-cytotoxic immune response and was associated with altered microbiota [64]. However, in this same Apc+/− CRC model, the heterozygous deletion of ATG5 led to an increased tumor burden [65]. Additionally, autophagy could protect Apc+/− mice from E. coli colibactin-induced colorectal carcinogenesis [66].
In several in vitro and in vivo CRC models, the post-transcriptional silencing of autophagy-related genes was found to inhibit chemoresistance, cancer growth and invasiveness, and metastasis [67,68,69].
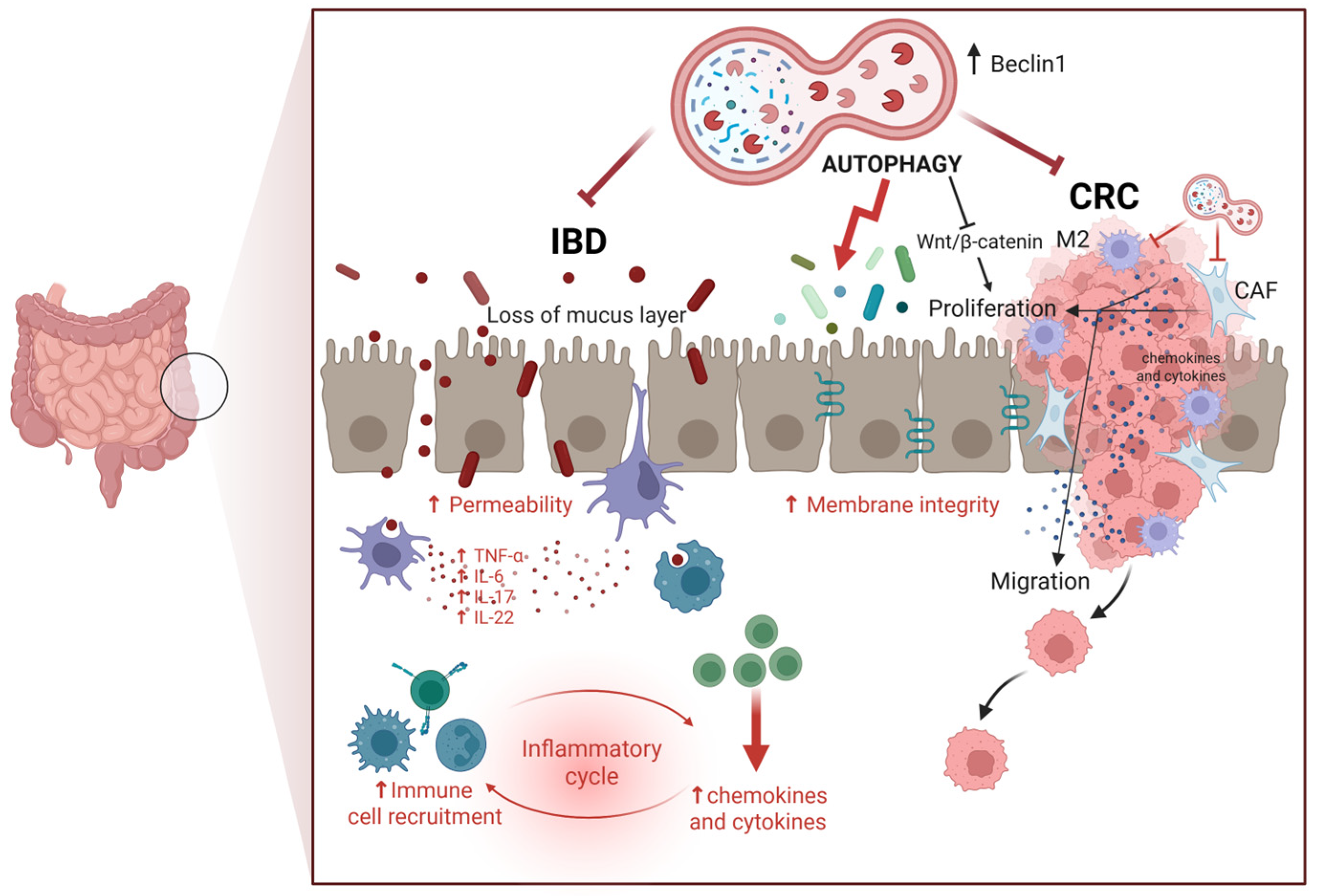
On the other hand, there is evidence that supports the anti-cancer role of autophagy in inhibiting CRC growth, progression, and metastasis [70,71]. For instance, pharmacologic inhibition of mTORC1 and mTORC2 suppressed CRC growth in an autophagy-dependent manner [72]. Consistent with the latter, increased expression of the autophagy-related tumor suppressor gene BECLIN-1 is associated with better overall survival in CRC patients undergoing chemotherapy [73]. In several in vitro and in vivo CRC settings, the miRNA-mediated knock-down of autophagy was associated with increased resistance to therapy, tumor growth, invasiveness, metastasization, and poor prognosis, such as was the case with MiR-338-5p silencing of PI3KC3 [74] and miR-183-5p silencing of ATG5 [75]. Further, autophagy stimulates the immune system functions, improves pathogen clearance, and downmodulates the production of inflammatory cytokines, thus preventing the onset of intestinal inflammatory diseases that could evolve in CRC [76,77,78,79]. Connected with this, autophagy has been shown to improve the intestinal barrier, enhancing the cell-to-cell tight junction [80,81]. To be noted, TNFα induces intestinal permeability through inhibition of autophagy [82]. Figure 1 schematizes the beneficial roles of autophagy in preventing CRC.
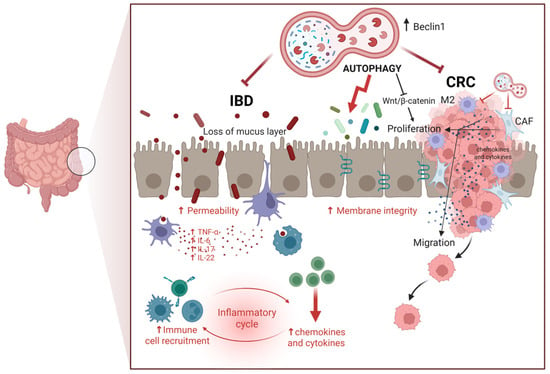
Figure 1.
Role of autophagy in regulating intestinal homeostasis. Autophagy counteracts colorectal cancer (CRC) by limiting cell proliferation and migration, mainly through inhibition of the Wnt/β-Catenin pathway) while also mitigating inflammation associated with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), a condition that can progress to CRC. Autophagy in epithelial cells is also important for maintaining cell-to-cell adhesion and producing mucus, which prevents colonization by pathogenic bacteria. These activities highlight the dual protective role of autophagy in maintaining intestinal integrity and preventing tumorigenesis (Created in BioRender. Isidoro, C. (2025) https://BioRender.com/pzq0dhg).
As a final note, in transgenic mice knock-down for ATG5 in enterocytes, the intestinal microbiota was dramatically changed, with a prevalence of bacteria promoting inflammatory diseases [83].
1.4. Colorectal Cancerogenesis: The Role of Inflammation and Its Interplay with Immune Cells
Chronic inflammation is a crucial hallmark of cancers [84]. Inflammatory immune cells and the associated cytokines in the TME are thought to play a double-faced role in the initiation and progression of CRC [85]. Inflammation starts as a defensive response of the immune system to pathogens or tissue damage. In response to intestine-localized inflammation, cytokines produced by gut immune cells (TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6) stimulate the crosstalk among the gut microenvironment cells [85]. However, the persistent activation of the inflammatory response leads to an excess release of cytokines, chemokines, and growth factors that eventually contribute to malignant transformation, cancer growth, and progression [86]. The sequential phases of induction of inflammation, stimulation of proliferation, and tumorigenesis following microbial dysbiosis and metabolic alterations have been clearly elucidated in animal models of colitis-associated colorectal cancer (CAC) [87].
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is associated with oxidative stress and DNA damage, resulting in genetic alterations that cause dysplasia and stimulate the proliferation of epithelial cells, eventually leading to tumor development [88]. Accordingly, IBD patients have approximately a two- to three-fold increased risk of developing CRC compared to the general population [89,90].
In CRC, a complex interplay exists between intestinal microbes, epithelial cancer cells, and stromal cells (including CAFs, tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs), and immune cells) that dynamically change their composition and phenotype (and behavior) within the TME according to the availability of nutrients, growth factors, cytokines, and probiotic metabolites. The latter alters the cellular composition of the TME by recruiting and reprogramming stromal cells, and this reflects in a dynamic change from suppressive to permissive TME in the different areas of the tumor, which, in turn, will determine the behavior of CRC cells in terms of growth, metastasization, dormancy, or chemoresistance. Reciprocally, cancer cells and stromal cells release a plethora of inflammatory cytokines that ultimately affect the microbiota, further contributing to the creation of a permissive TME for the growth and metastasization of CRC [91]. IL-6 is a master inflammatory cytokine, along with TNF-α, IL-17, and IL-22, promoting the development and progression of CRC [92,93]. IL-6 secreted by CRC-associated fibroblasts stimulates angiogenesis, inhibits CRC cell death, and induces CRC cell proliferation and motility [94,95]. Further, IL-6 induces the release of TGF-β, thus promoting EMT (Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition), activates the proliferation pathways (such as ERK/MAPK, PI3K, and Wnt/β-Catenin), promotes M2 TAM polarization, and suppresses the immune response [95,96]. The serum levels of IL-6 increase during the progression from colorectal adenoma to carcinoma, and, consistently, CAC and CRC patients with high serum levels of IL-6 present with tumors of large size, relapse, and shorter overall survival [97]. Macrophages are key players in the TME, where they can dynamically change their phenotype from M1-like to M2-like depending on the extracellular stimuli. M1-like macrophages, identified by the expression of CD80 and CD86, show glycolytic metabolism and dialogue with TH1 and exert a pro-inflammatory and anti-tumor function, while M2-like macrophages (and their subtypes), identified by the expression of CD206 and CD163, show phosphorylation oxidative metabolism and dialogue with TH2 and exert an anti-inflammatory, immune-suppressive, and pro-tumorigenic function [98,99]. Macrophages reprogram their metabolism and phenotype in response to the extracellular signals. In the tumor niche, the crosstalk between cancer cells and macrophages determines the fate of CRC. Mimicking this situation in vitro, CRC cells co-cultured with CD68, CD204, and CD206-positive M2-like macrophages showed an increased rate of proliferation and colony formation [56]. Interestingly, this effect was abrogated when the M2-like macrophages were pre-exposed to rapamycin to induce autophagy, highlighting the strict interplay between autophagy and inflammation in colorectal carcinogenesis [56]. As stated above, another layer of complexity is due to the ability of microbiota and its metabolites to modulate the phenotype of macrophages within the TME [100,101]. In the gut of CRC patients, Bacteroides and Bacillus faecalis are associated with an increased infiltration of Tregs and consequent M2-TAM accumulation in the TME [102]. Indeed, in a colitis murine model, propionate and butyrate were shown to promote the accumulation of anti-inflammatory M2-like macrophages through the induction of Treg [103]. Summing up, M1-mediated inflammation starts as a first line of defense against colorectal cancer, stimulating TH1-mediated immune response, yet with time, cancer cells secrete cytokines that reprogram the macrophages into M2-type that are anti-inflammatory but, at the same time, immune-suppressive and supportive of tumor growth. These M2-TAMs also recruit fibroblasts that, in the TME, become CAF-releasing IL-6 and other inflammatory cytokines. This scenario resembles that of a wound that never heals, as brilliantly defined by Harold F. Dvorak in 1986 [104]. In this context, probiotics and their metabolites may promote “healing” by turning off excess inflammation in the intestinal TME (see Section 1.6).
1.5. Dysbiosis and Colorectal Cancerogenesis: The Role of Diet and Microbiota
CRC incidence is strongly associated with dietary habits [105]. The Western diet, characterized by a high intake of red and processed meats, saturated fats, alcohol, and sugar, is associated with an increased risk of CRC [13,106]. This is linked to the oxidative metabolism of foods that typically make up the Western diet [107]. A fat-rich diet associates with inflammatory adipose tissue and contributes to colorectal carcinogenesis [108]. In contrast, diets rich in low-fat dairy products such as fruits, vegetables, legumes, fiber, whole grains, and fish, combined with moderate alcohol intake, have been shown to have a protective effect against CRC. This protective effect is attributed to their content in prebiotics and specific micronutrients, such as calcium and magnesium, vitamins like vitamin D and vitamin B6, and polyphenols [12].
The gut microbiota is a dynamic community of several types of microbes, including archaea, eukaryotes, bacteria, viruses, and parasites, that have evolved to grow and survive in the gastrointestinal tract. Within the microbial community, bacteria are the most abundant group, comprising approximately 100 trillion individuals [109]. These bacteria belong to several phyla, including Firmicutes, Bacteroidetes, Actinobacteria, Fusobacteria, Proteobacteria, Verrucomicrobia, and Cyanobacteria, with Firmicutes and Bacteroidetes constituting 90% of the total bacterial population [110]. Throughout life, the composition of the gut microbiota changes since it is influenced by age, sex, and lifestyle factors such as physical exercise, sedentary behavior, smoking, diet, and the use of antibiotics, creating a unique microbial profile for each individual [16,17,19]. Interestingly, all these factors impact autophagy modulation, and it has been shown that impaired autophagy in intestinal cells alters the microbiome composition [83].
The microbiome of CRC patients is altered, with a reduction in Bacteroides, Firmicutes, and Lactobacillus, along with a remarkable increase in Fusobacterium species, among others [111,112]. This imbalance results in mucosal permeability, triggers inflammation, and promotes the activation of the Wnt/β-Catenin mitogenic pathway.
The bacteria in the gastrointestinal tract can ferment non-digestible carbohydrates, generating SCFAs. The main SCFAs are acetate, propionate, and butyrate. SCFAs exhibit various beneficial effects, such as maintaining intestinal barrier integrity, regulating immune function, providing protection against pathogens, and promoting anti-inflammatory responses [76,113]. SCFAs also display anti-tumor properties by inducing apoptosis, reducing the proliferation of neoplastic cells, and mitigating oxidative stress [114]. The homeostatic effects of SCFAs on the colonic epithelium are mediated by SCFA-specific transporters. Specifically, MCT1 is located on both the apical and basolateral membranes, MCT4 is found on the basolateral membrane, and SMCT1 and SMCT2 are located on the apical region of intestinal cells [115].
Dysbiosis is a common feature of intestinal diseases, including IBD, CAC, and CRC [116]. Consistently, patients with CRC exhibit low microbial biodiversity, with specific bacteria, such as Fusobacterium nucleatum, Escherichia coli, Enterococcus faecalis, Streptococcus gallolyticus, and Bacteroides fragilis present in higher abundance in their gut [20,117,118].
Below, we detail the mechanisms through which the main pathogenic bacteria may promote colorectal cancerogenesis.
Fusobacterium nucleatum invades the intestinal epithelium through the expression of the adhesion protein FadA. This protein forms a complex with E-cadherin, increasing intestinal barrier permeability [101] and enhancing β-Catenin activity [119], which promotes cancer cell growth. Additionally, F. nucleatum suppresses immune cell activity by binding specific inhibitory receptors on natural killer (NK) cells and T cells [103]. An increase in tumor-promoting cytokines, including IL-17 and TNF-α, in CRC is associated with the activation of the NF-κB pathway by F. nucleatum [120].
A similar role is attributed to Bacteroides fragilis, which produces a metalloprotease that cleaves E-cadherin, disrupting the intestinal barrier [121]. It also induces the nuclear translocation of β-Catenin [122] and stimulates the production of IL-8 and IL-17, triggering an aberrant immune response and promoting tumorigenesis [123].
Additionally, Salmonella, Clostridium difficile, and Prevotella are also linked to CRC pathogenesis through the activation of the β-Catenin [124,125].
Streptococcus gallolyticus drives CRC carcinogenesis by inducing inflammation through IL-1, COX-2, and IL-8 pathways [115], as well as by increasing the levels of β-Catenin and C-MYC [126].
The intestinal dysbiosis is also accompanied by a reduction in butyrate-producing bacteria, such as Eubacterium, Roseburia, and Faecalibacterium, further creating a microenvironment favorable to CRC development and progression [127] (Figure 2).
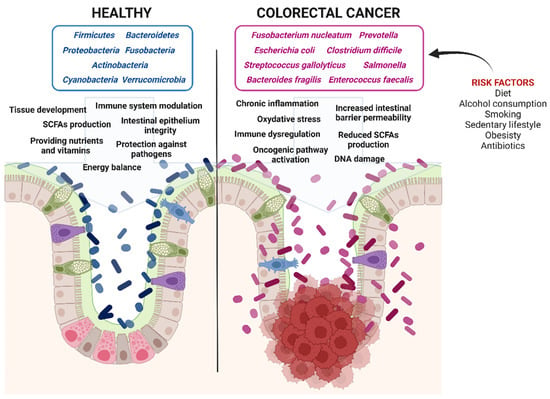
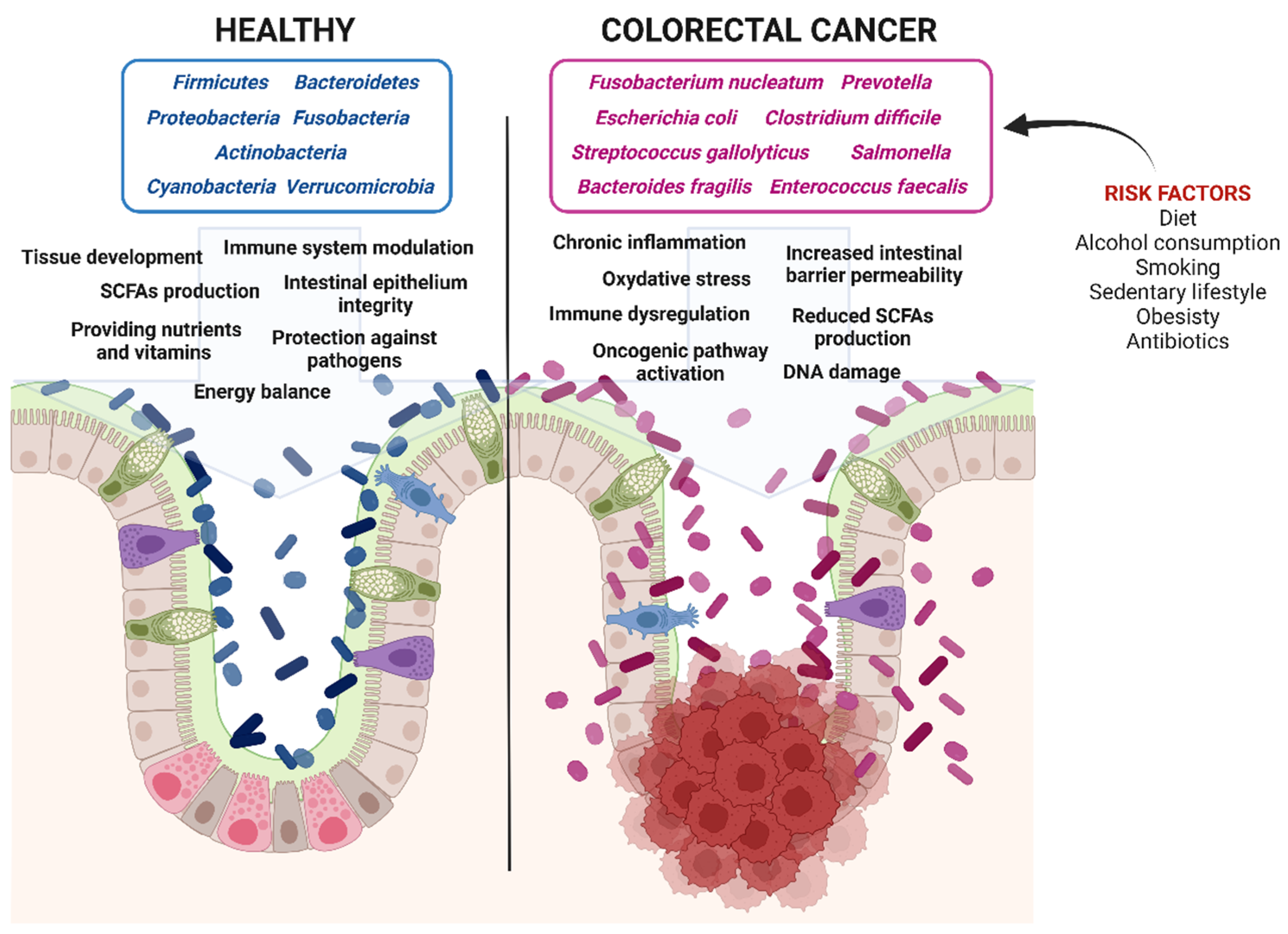
Figure 2.
Impact of gut microbiota on colorectal cancer progression. Healthy gut microbiota maintains epithelial integrity and energy balance, prevents inflammation, provides essential nutrients and vitamins, produces short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), and protects against pathogen invasion. In contrast, dysbiotic gut microbiota increases intestinal permeability, promotes chronic inflammation and oxidative stress, induces DNA damage, activates oncogenic pathways, and reduces SCFA production, all of which contribute to colorectal cancer development (Created in BioRender. Isidoro, C. (2025) https://BioRender.com/pzq0dhg).
1.6. Beneficial Effects of Probiotics and Postbiotics in Colorectal Cancer: Impact on Inflammation and Autophagy
Probiotics are living bacteria that elicit beneficial health effects by restoring eubiosis. Probiotics and their metabolites (postbiotics) exhibit anti-cancer properties through various mechanisms, such as altering gut microbiota composition, reducing intestinal pH levels, neutralizing mutagens or carcinogens, enhancing immune responses while dampening inflammation, and promoting autophagy, apoptosis, and cell differentiation processes [128,129,130]. Further, probiotics enhance the activity of antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase, catalase, and glutathione peroxidase, which counteract oxidative stress and provide additional protection against CRC development [130]. Here, we will emphasize the impact on the immune–inflammation response and autophagy.
One of the ways probiotics combat inflammation is through the interaction of bacterial products with Toll-like receptors (TLRs) expressed on dendritic cells, CD4+ T cells, and macrophages. TLR2 (that engages with peptidoglycan from Gram-positive bacteria), TLR4 (that engages with Lipopolysaccharide from Gram-negative bacteria), and TLR5 (that engages with flagellin) signal to immune cells and discriminate the presence of commensal or pathogenic bacteria that should be tolerated or rejected, respectively [131]. Excess stimulation of TLR4 versus TLR2 has been associated with a higher risk of CRC [132,133]. For instance, through these interactions, Lactobacillus rhamnosus and Lactobacillus reuteri trigger the differentiation of naïve CD4+ T cells into Treg cells, which produce IL-10 and reduce the production of TNF-α [134]. Polysaccharide A from Bacteroides fragilis could dampen inflammation (while inducing tolerance) through direct interaction with TLR2 on Treg (not on dendritic cells) to induce the secretion of IL-10 that, in turn, suppressed the pro-inflammatory T17 [135]. Furthermore, probiotic strains of Lactobacillus acidophilus, helveticus, and plantarum inhibited the activation of NF-κB by interacting with TLR4 on macrophages, thereby reducing the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 [136]. Additionally, probiotics promote the differentiation of B cells into IgA-producing plasma cells, enhancing mucus production and preventing the adhesion of microorganisms to intestinal epithelial cells, thereby reducing the risk of pathogen penetration [130,137,138]. Another beneficial anti-cancer effect of certain probiotics is the induction of autophagy [128]. The expression of the autophagy genes ATG7, ATG5, and ATG16 increased in CRC cells incubated with a mixture of sonicated Bifidobacterium bifidum, longum, and infantis [139]. Soluble metabolites of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum OC01 were found to reduce cell proliferation and migration of CRC cells cultivated as 2D- or 3D-spheroids, even in the presence of the inflammatory cytokine IL-6, an effect linked to induction of autophagy and β-Catenin degradation [140]. Additionally, these metabolites changed the secretome of CRC cells, reducing the release of cytokines (particularly TGF-β) so that tumor-promoting M2-like macrophages were reverted into an anti-tumor M1-like phenotype [141].
Figure 3 illustrates (in a simplified manner) how probiotics and postbiotics influence the immune–inflammatory response and the crosstalk between different types of immune cells. A more detailed description of the mechanistic interaction between probiotics and intestinal immune cells can be found in [138,142], and a more in-depth discussion of the anti-inflammatory mechanisms of probiotics and postbiotics in the gut can be found in [76,138]. It is to be stressed that the crosstalk between immune cells in the lamina propria differs in healthy, inflammatory diseases and colorectal cancer. As an additional layer of complexity, the interplay between the microbiota (and probiotics with their postbiotics) and the cancer cells change with time dynamically and spatially, thus leading to a continuous rearrangement of the cellular composition in the stroma.
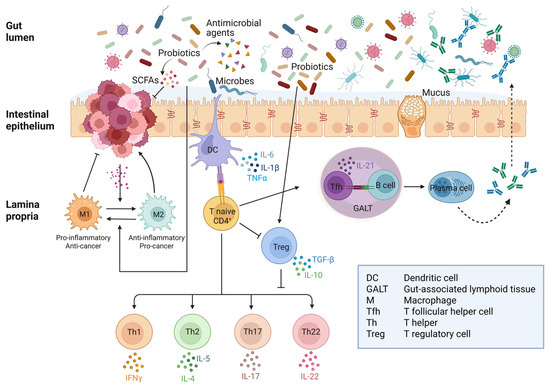
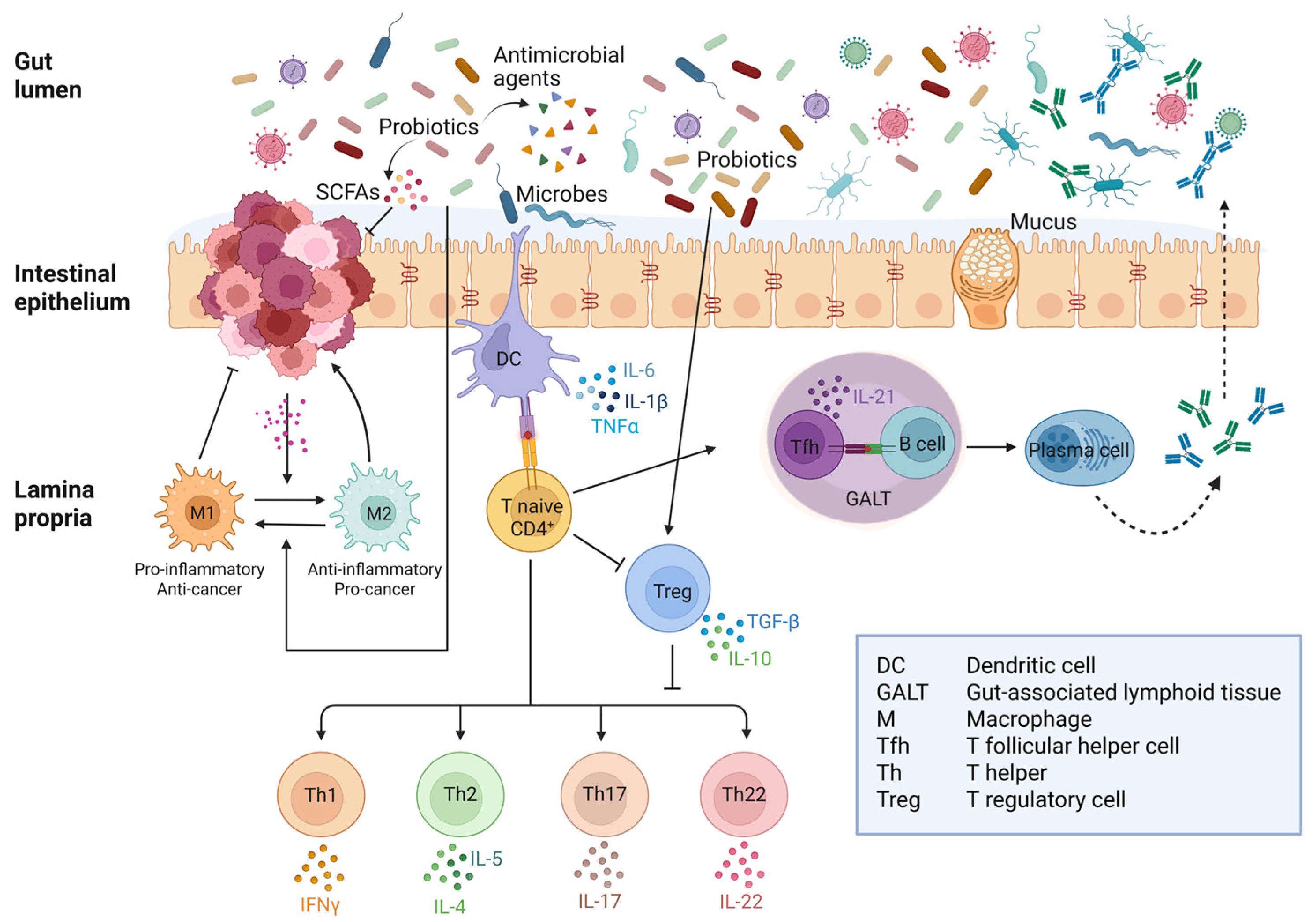
Figure 3.
Crosstalk between immune and inflammatory responses to gut microbiota in healthy intestine and colorectal cancer. In the presence of pathogenic bacteria, dendritic cells trigger an immune response through Th cells while inhibiting Treg differentiation. On the other hand, commensal bacteria are tolerated by promoting Treg and suppressing Th response. Colorectal cancer cells release soluble factors that promote the phenoconversion of macrophages into M2-type TAMs, which release factors that support tumor growth. Probiotics and their postbiotics downregulate the inflammatory response by activating Treg cells, which then suppress Th17 and Th22. Moreover, SCFAs can revert M2-type into M1-type TAMs with anti-tumor activity (Created in BioRender. Ferraresi, A. (2025) https://BioRender.com/5tjh823).
In this context, the picture is further complicated by the fact that autophagy in epithelial intestinal cells influences the microbiota, limiting the growth of pathogenic bacteria that induce inflammation and intestinal permeability [83]. However, autophagy is dysregulated and differentially modulated in CRC cells, depending on the availability of oxygen, nutrients, growth factors, and cytokines, which implies different scenarios in different niches.
The anti-carcinogenic effects of probiotics are also attributed to the production of SCFAs, which can act on both epithelial and immune cells [143]. Butyrate is the primary SCFA absorbed by the intestinal epithelium and serves as the main energy source for colonocytes, while acetate and propionate mainly reach the liver [22]. Butyrate promotes the integrity of the gut barrier by regulating the genes that encode for the tight junction proteins, such as claudin-1, zonula occludens-1, and occludin [144]. Furthermore, by enhancing the expression of Mucin 2, butyrate reinforces the mucus layer of the gut epithelium, which is essential for protection against pathogens and immune response regulation [145]. SCFAs, particularly butyrate, negatively regulate the inflammatory signaling pathway mediated by the inflammasome complex NLRP3, thereby inhibiting macrophage activation [56]. In M2-type macrophages, butyrate promotes the production of the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 while reducing the production of inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, MCP-1, and IL-6 through the activation of GPR43 (G-protein coupled receptor 43) [146].
Butyrate has been shown to prevent the activation of CD4+ T cells isolated from normal gut lamina propria through inhibition of HDAC in a dose-dependent manner, and this decreased the formation and the cytokine production of Th1, Th17, and Th22 cells [147].
The beneficial effects of SCFAs extend to the epithelial cells. As mentioned above, dysregulation of autophagy in intestinal epithelium may lead to impaired bacteria clearance and pathogen invasion and overall gut microbiota dysbiosis and exacerbated chronic inflammation that ultimately increases the risk of CRC [76,83]. Butyrate was shown to stimulate autophagy in CRC cells through the activation of the LKB1-AMPK pathway [148]. Of relevance, in colorectal cancer cells, there is a crucial interplay between the Wnt pathway and autophagy. Activation of the Wnt/β-Catenin signaling pathway has been shown to inhibit autophagy while promoting CRC growth [149]. Butyrate was reported to downregulate the Wnt/β-Catenin pathway, thus counteracting the early stages of CRC development. In resting epithelial cells, β-Catenin is bound to E-Cadherin and to the APC destruction complex that directs its ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation so that its accumulation in the cell and translocation in the nucleus is prevented. Proteolytic degradation of E-Cadherin by metalloproteases secreted by Bacteroides fragilis frees β-Catenin [122]. Further, most CRCs have mutations in APC and/or CTNB1 that impair the degradation of β-Catenin [150,151]. By inducing autophagy as an alternative mechanism to the proteasomal degradation, which is ineffective in APC- and β-Catenin-mutated CRC, butyrate promoted the autophagic sequestration and degradation of β-Catenin, and this inhibited the proliferation and migration of CRC cells [152].
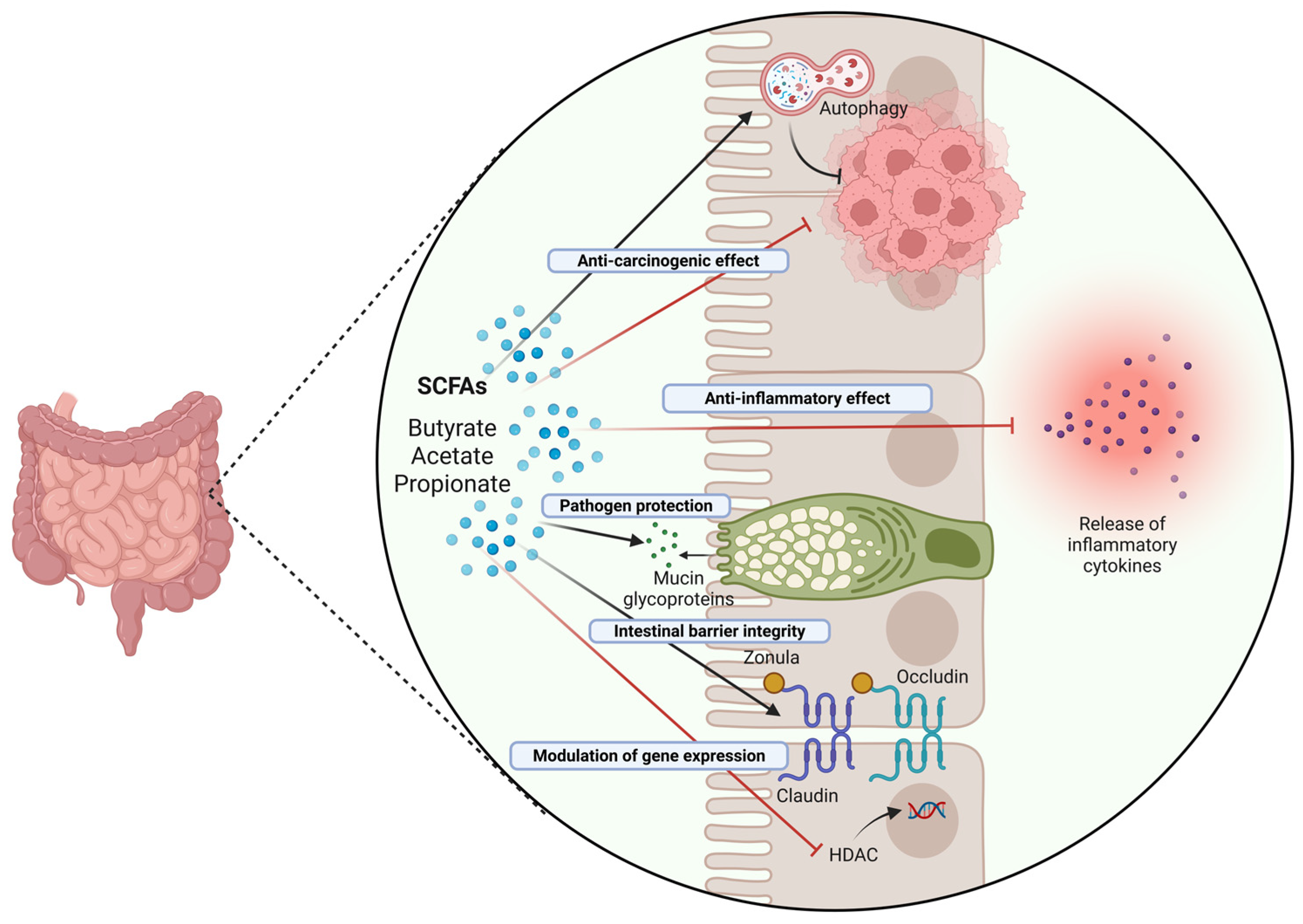
Figure 4 schematizes the mechanisms of protective action of butyrate on the intestinal mucosa.
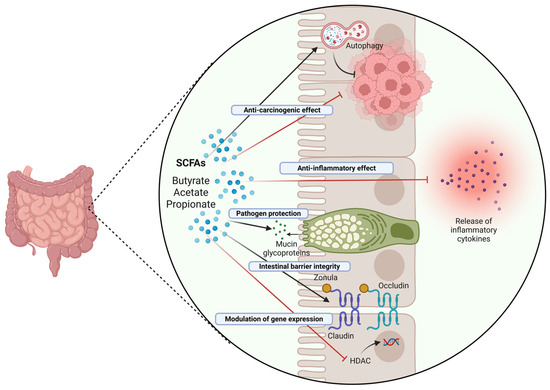
Figure 4.
Role and mechanisms of action of SCFAs in the intestinal epithelium. SCFAs, particularly butyrate, exhibit anti-carcinogenic effects in the intestine through a range of mechanisms, including induction of protective autophagy (and correlated downregulation of the Wnt/β-Catenin pathway), immunomodulation of the inflammatory response, epigenetic modulation of gene expression, and stabilization of intestinal barrier integrity (Created in BioRender. Isidoro, C. (2025) https://BioRender.com/pzq0dhg).
1.7. Challenges in Probiotic-Based Therapy and Future Directions
The previous paragraphs have illustrated how probiotics and postbiotics help reshape gut microbiota by promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria, improving the inflammatory and immune responses, and stimulating protective autophagy, overall reducing the risk of CRC development. Several preclinical and clinical evidence support the preventive, therapeutic, and adjuvant perioperative efficacy of probiotics and their soluble metabolites in CRC [153,154].
Below are some examples to give an idea of the preventive and therapeutic potential of this approach. In animal models, the treatment with probiotics of the Lactobacillus genus decreased the formation of tumors, reduced the growth of aerobic bacteria in the intestine, and restored the correct host immune functions [155,156,157]. A mixture of Lactobacillus species (namely two strains of L. plantarum and one strain each of L. reuteri, L. brevis, and L. rhamnosus) was found to inhibit the in vitro proliferation of human CRC cell lines and the in vivo growth of CRC in mice through modulation of the expression of APC (which was increased) and of β-Catenin (which was decreased) [158]. In CAC models, the administration of VSL#3, a probiotic mixture containing Bifidobacterium breve, B. infantis, B. longum, Lactobacillus acidophilus, L. bulgaricus, L. casei, L. plantarum, and Streptococcus thermophilus, reduced the incidence of high-grade dysplasia and prevented the development of CRC. These probiotic strains contrasted colorectal carcinogenesis in mouse models of Dextran Sulfate Sodium (DSS)- and Azoxymethane (AOM)-induced colitis, reducing the activation of STAT3 and the expression of BCL-2 and IL-6 [159,160].
In patients with CRC, there is a marked reduction in butyrate levels, a condition predisposing to intestinal permeability, increased inflammation, and dysbiosis [161,162]. The consumption of probiotics such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium has been shown to increase the production of butyrate in the colon. Consistently, the supplementation with L. casei, L. acidophilus, L. lactis, B. bifidum, B. longum, and B. infantis improved the quality of life for CRC patients by ameliorating the inflammatory status in the intestine [163]. In CRC patients, probiotics were shown to synergize with chemotherapy by improving their therapeutic efficacy and reducing the side effects. The co-administration of L. acidophilus and L. casei improved the efficacy of the chemotherapeutic drug 5-FU, increasing its pro-apoptotic efficiency [164]. In this same line, CRC patients co-treated with L. rhamnosus could be treated with lower doses of 5-FU and showed reduced episodes of diarrhea and abdominal pain and required shorter hospitalization compared to patients treated with only the chemotherapeutics [165]. Another study proved a synergism between 5-FU and the cell-free supernatant of Lactobacillus plantarum [166]. Probiotic treatment showed efficacy as perioperative therapy as well. Lactobacillus bacteria administered before and after surgery reduced proliferation, growth, and invasion of CRC cells, decreased enteropathogenic bacteria in blood, improved diarrhea, restored the integrity of gut mucosa, and stimulated the systemic immune system [167,168]. Post-operative complications were reduced in CRC patients treated with Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus [169,170]. Patients treated with chemotherapy supplemented with Bifidobacterium breve demonstrated increased microbiota diversity, a lower frequency of fever, and a reduced risk of infections [169]. The administration of specific Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium strains reduced radiotherapy-related gut toxicity and diarrhea [171,172].
Probiotics were revealed to be useful for CRC treatment also in combination with immunotherapy. In this respect, it was found that SCFA-producing bacteria were more abundant in responders, while Bacteroides were more abundant in non-responders to PD-1/PD-L1 therapies [173]. Particularly, in intestinal cancer patients, an increased ratio of Prevotella and Ruminococcaceae vs. Bacteroides was associated with a good response to immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy [174].
To give a balanced overview of the state-of-the-art, we must also consider the other side of the coin. Two of the most important issues that need to be taken into account are that probiotic treatment may not work in immunocompromised patients and that it is not advisable for patients with serious dysbiosis associated with a leaky intestinal barrier. In the latter case, the risk of septicemia and acute complications must be carefully considered. Here, the use of postbiotics (which do not contain living bacteria), enriched with enzymes, proteins, vitamins, and short-chain fatty acids, could be an alternative to bring the benefits at no or very minimized risk.
In Table 1, we summarize the main preclinical studies and clinical trials with their pros and cons and limitations.

Table 1.
List of preclinical research and clinical trials of the beneficial effects of probiotics administration in colorectal cancer management. The table reports an overview of the main probiotic strains tested in preclinical and clinical research, focusing on the molecular mechanisms of action, the dosage and the duration of the intervention, study design (experimental model for preclinical studies and inclusion criteria for clinical settings), and a summary of the advantages and current limitations (in term of study design, safety concerns, interaction with chemo/immunotherapy, lack of mechanistic insights). N/A, not applicable.
To maximize the benefits of probiotic and postbiotic treatments, we need to make use of the “omics” technologies to better understand the potential of probiotic strains. One other limitation is that most studies are focused on a relatively small number of species, many of which are not indigenous to the human and mouse gut.
The future is to personalize probiotic therapy for patients based on the accurate assessment of the type and severity of intestinal inflammation, immune performance, genetic and epigenetic predisposition, microbiota composition, and lifestyle factors. To this end, we should take advantage of testing probiotics and postbiotics efficacy (and dose) in appropriate in vitro models using organoids (that include intestinal and immune cells), the so-called “gut-on-chip”, and even better if reconstructed in a microfluidic chamber mimicking the dynamic changes in the TME [198,199].
2. Highlights and Concluding Remarks
Dysbiosis plays a significant role in the development and progression of CRC. Environmental factors, including diet, infections, and drugs, can disrupt the intestinal bacterial flora, which consequently may affect SCFAs and vitamin synthesis, increase stress responses, cause immune dysregulation, and increase susceptibility to DNA alterations. Over time, these changes lead to chronic inflammation, immune dysfunction, and metabolic alterations that can contribute to the development of conditions such as allergies, obesity, irritable bowel syndrome, IBD, and eventually CRC.
Autophagy plays a crucial role in maintaining cellular homeostasis through the turnover of damaged proteins and organelles. Gut bacteria and their secretions influence the level of autophagy in intestinal epithelial cells, and reciprocally, dysregulation of autophagy can influence the composition and function of the gut microbiota. This bidirectional relationship, in which autophagy impacts microbial balance and dysbiosis affects autophagic regulation, plays a significant role in the development of CRC.
Probiotics are live microorganisms that, when supplemented in equilibrate formulas, provide beneficial effects to the host. They are primarily lactic acid bacteria from genera such as Lactobacillus, Streptococcus, Enterococcus, Lactococcus, Leuconostoc, Bifidobacterium, and Saccharomyces. The therapeutic and preventive effects of probiotics are largely due to their ability to maintain a state of eubiosis, ensuring intestinal health. Probiotics help maintain gut health by protecting the intestinal mucosa, reducing the release of carcinogenic and oxidative molecules, and modulating immune responses, inflammation, autophagy, apoptosis, and cell differentiation. They also compete with harmful bacteria for nutrients and space, producing antimicrobial substances that limit the proliferation of pathogenic microbes, thereby preventing dysbiosis. The implementation of probiotics in CRC therapy is not only related to their ability to reduce the risk of CRC development and progression but also their potential to synergize with immunotherapy and chemotherapy while decreasing their unpleasant side effects [200]. In conclusion, the supplementation of probiotics pre- and/or post-surgery may improve prognosis and quality of life and reduce the recurrence of CRC [153,154,201]. In CRC patients, adjuvant therapy with probiotics decreases the occurrence of septicemia, the incidence of post-operative infections and diarrhea, and the rate of post-operative antibiotic use.
Yet, it is to be stressed that, despite the promising and encouraging results, not all probiotics showed positive health effects in CRC patients, emphasizing the need for further investigations. However, the in vitro and in vivo evidence paves the way for future translational research and development of probiotic- and postbiotic-based therapeutics for more personalized and targeted treatments of colorectal cancer.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.G., L.V., A.F., and C.I.; literature search, formal analysis, and data curation, B.G., A.V., A.A., M.P., and C.M.; writing—original draft preparation, B.G., L.V., and A.F.; writing—review and editing, C.I. and A.F.; visualization, figures, and tables B.G., L.V., A.V., C.M., and A.F.; supervision, C.I.; project administration, A.A. and M.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
B.G. was supported with PhD fellowship granted by Comoli, Ferrari & SpA (Novara, Italy). L.V. was supported with a post-doctoral fellowship granted by Probiotical S.p.A (Novara, Italy). A.F. is a recipient of a post-doctoral fellowship granted by Fondazione Veronesi (FUV 2025) (Milan, Italy). Thanks are due to Associazione per la Ricerca Medica “Ippocrate-Rhazi” (Novara, Italy) and to Consorzio Interuniversitario per le Biotecnologie (CIB, Trieste, Italy) for the support. This review article is part of the PhD thesis discussed by Beatrice Garavaglia on 26 February 2025. We mention this to anticipate that the overlapping text does not count as self-plagiarism.
Conflicts of Interest
A.V., A.A., and M.P. are employees of the company Probiotical S.p.A., which commercializes probiotic strains. All other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valle, L.; Vilar, E.; Tavtigian, S.V.; Stoffel, E.M. Genetic predisposition to colorectal cancer: Syndromes, genes, classification of genetic variants and implications for precision medicine. J. Pathol. 2019, 247, 574–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Fantini, M.C.; Guadagni, I. From inflammation to colitis-associated colorectal cancer in inflammatory bowel disease: Pathogenesis and impact of current therapies. Dig. Liver Dis. 2021, 53, 558–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roshandel, G.; Ghasemi-Kebria, F.; Malekzadeh, R. Colorectal Cancer: Epidemiology, Risk Factors, and Prevention. Cancers 2024, 16, 1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Fadlallah, H.; El Masri, J.; Fakhereddine, H.; Youssef, J.; Chemaly, C.; Doughan, S.; Abou-Kheir, W. Colorectal cancer: Recent advances in management and treatment. World J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 15, 1136–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kumar, A.; Gautam, V.; Sandhu, A.; Rawat, K.; Sharma, A.; Saha, L. Current and emerging therapeutic approaches for colorectal cancer: A comprehensive review. World J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2023, 15, 495–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Xie, Y.H.; Chen, Y.X.; Fang, J.Y. Comprehensive review of targeted therapy for colorectal cancer. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 2020, 5, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, M.S.; Karuniawati, H.; Jairoun, A.A.; Urbi, Z.; Ooi, J.; John, A.; Lim, Y.C.; Kibria, K.M.K.; Mohiuddin, A.K.M.; Ming, L.C.; et al. Colorectal Cancer: A Review of Carcinogenesis, Global Epidemiology, Current Challenges, Risk Factors, Preventive and Treatment Strategies. Cancers 2022, 14, 1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Morgan, E.; Arnold, M.; Gini, A.; Lorenzoni, V.; Cabasag, C.J.; Laversanne, M.; Vignat, J.; Ferlay, J.; Murphy, N.; Bray, F. Global burden of colorectal cancer in 2020 and 2040: Incidence and mortality estimates from GLOBOCAN. Gut 2023, 72, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuruya, A.; Kuwahara, A.; Saito, Y.; Yamaguchi, H.; Tsubo, T.; Suga, S.; Inai, M.; Aoki, Y.; Takahashi, S.; Tsutsumi, E.; et al. Ecophysiological consequences of alcoholism on human gut microbiota: Implications for ethanol-related pathogenesis of colon cancer. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Munteanu, C.; Schwartz, B. Interactions between Dietary Antioxidants, Dietary Fiber and the Gut Microbiome: Their Putative Role in Inflammation and Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Vernia, F.; Longo, S.; Stefanelli, G.; Viscido, A.; Latella, G. Dietary Factors Modulating Colorectal Carcinogenesis. Nutrients 2021, 13, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rooks, M.G.; Garrett, W.S. Gut microbiota, metabolites and host immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lozupone, C.A.; Stombaugh, J.I.; Gordon, J.I.; Jansson, J.K.; Knight, R. Diversity, stability and resilience of the human gut microbiota. Nature 2012, 489, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rinninella, E.; Raoul, P.; Cintoni, M.; Franceschi, F.; Miggiano, G.A.D.; Gasbarrini, A.; Mele, M.C. What is the Healthy Gut Microbiota Composition? A Changing Ecosystem across Age, Environment, Diet, and Diseases. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Parizadeh, M.; Arrieta, M.C. The global human gut microbiome: Genes, lifestyles, and diet. Trends Mol. Med. 2023, 29, 789–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quaglio, A.E.V.; Grillo, T.G.; De Oliveira, E.C.S.; Di Stasi, L.C.; Sassaki, L.Y. Gut microbiota, inflammatory bowel disease and colorectal cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 28, 4053–4060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ionescu, V.A.; Gheorghe, G.; Georgescu, T.F.; Buica, V.; Catanescu, M.-S.; Cercel, I.-A.; Budeanu, B.; Budan, M.; Bacalbasa, N.; Diaconu, C. Exploring the Role of the Gut Microbiota in Colorectal Cancer Development. Gastrointest. Disord. 2024, 6, 526–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lee, H.K. Potential Role of the Gut Microbiome In Colorectal Cancer Progression. Front. Immunol. 2022, 12, 807648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Moreira, M.M.; Carriço, M.; Capelas, M.L.; Pimenta, N.; Santos, T.; Ganhão-Arranhado, S.; Mäkitie, A.; Ravasco, P. The impact of pre-, pro- and synbiotics supplementation in colorectal cancer treatment: A systematic review. Front. Oncol. 2024, 14, 1395966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tan, J.; McKenzie, C.; Potamitis, M.; Thorburn, A.N.; Mackay, C.R.; Macia, L. The role of short-chain fatty acids in health and disease. Adv. Immunol. 2014, 121, 91–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaźmierczak-Siedlecka, K.; Marano, L.; Merola, E.; Roviello, F.; Połom, K. Sodium butyrate in both prevention and supportive treatment of colorectal cancer. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 1023806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Singh, V.; Lee, G.; Son, H.; Koh, H.; Kim, E.S.; Unno, T.; Shin, J.H. Butyrate producers, “The Sentinel of Gut”: Their intestinal significance with and beyond butyrate, and prospective use as microbial therapeutics. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1103836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Nguyen, L.H.; Goel, A.; Chung, D.C. Pathways of Colorectal Carcinogenesis. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Cao, Q.; Tian, Y.; Deng, Z.; Yang, F.; Chen, E. Epigenetic Alteration in Colorectal Cancer: Potential Diagnostic and Prognostic Implications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Jansen, M.; Menko, F.H.; Brosens, L.A.; Giardiello, F.M.; Offerhaus, G.J. Establishing a clinical and molecular diagnosis for hereditary colorectal cancer syndromes: Present tense, future perfect? Gastrointest. Endosc. 2014, 80, 1145–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Jeong, S. Mutation Hotspots in the β-Catenin Gene: Lessons from the Human Cancer Genome Databases. Mol. Cells 2019, 42, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Clevers, H. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in development and disease. Cell 2006, 127, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, K.; Gan, W.J. Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway in the Development and Progression of Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Manag. Res. 2023, 15, 435–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhao, H.; Ming, T.; Tang, S.; Ren, S.; Yang, H.; Liu, M.; Tao, Q.; Xu, H. Wnt signaling in colorectal cancer: Pathogenic role and therapeutic target. Mol. Cancer 2022, 21, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markowitz, S.D.; Bertagnolli, M.M. Molecular origins of cancer: Molecular basis of colorectal cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 2449–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ionescu, V.A.; Gheorghe, G.; Bacalbasa, N.; Chiotoroiu, A.L.; Diaconu, C. Colorectal Cancer: From Risk Factors to Oncogenesis. Medicina 2023, 59, 1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Dziubańska-Kusibab, P.J.; Berger, H.; Battistini, F.; Bouwman, B.A.M.; Iftekhar, A.; Katainen, R.; Cajuso, T.; Crosetto, N.; Orozco, M.; Aaltonen, L.A.; et al. Colibactin DNA-damage signature indicates mutational impact in colorectal cancer. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1063–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodwin, A.C.; Destefano Shields, C.E.; Wu, S.; Huso, D.L.; Wu, X.; Murray-Stewart, T.R.; Hacker-Prietz, A.; Rabizadeh, S.; Woster, P.M.; Sears, C.L.; et al. Polyamine catabolism contributes to enterotoxigenic Bacteroides fragilis-induced colon tumorigenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 15354–15359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wang, X.; Allen, T.D.; May, R.J.; Lightfoot, S.; Houchen, C.W.; Huycke, M.M. Enterococcus faecalis induces aneuploidy and tetraploidy in colonic epithelial cells through a bystander effect. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 9909–9917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sobhani, I.; Bergsten, E.; Couffin, S.; Amiot, A.; Nebbad, B.; Barau, C.; de’Angelis, N.; Rabot, S.; Canoui-Poitrine, F.; Mestivier, D.; et al. Colorectal cancer-associated microbiota contributes to oncogenic epigenetic signatures. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 24285–24295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Donohoe, D.R.; Holley, D.; Collins, L.B.; Montgomery, S.A.; Whitmore, A.C.; Hillhouse, A.; Curry, K.P.; Renner, S.W.; Greenwalt, A.; Ryan, E.P.; et al. A gnotobiotic mouse model demonstrates that dietary fiber protects against colorectal tumorigenesis in a microbiota- and butyrate-dependent manner. Cancer Discov. 2014, 4, 1387–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Allen, J.; Sears, C.L. Impact of the gut microbiome on the genome and epigenome of colon epithelial cells: Contributions to colorectal cancer development. Genome Med. 2019, 11, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Fellows, R.; Denizot, J.; Stellato, C.; Cuomo, A.; Jain, P.; Stoyanova, E.; Balázsi, S.; Hajnády, Z.; Liebert, A.; Kazakevych, J.; et al. Microbiota derived short chain fatty acids promote histone crotonylation in the colon through histone deacetylases. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sun, J.; Chen, S.; Zang, D.; Sun, H.; Sun, Y.; Chen, J. Butyrate as a promising therapeutic target in cancer: From pathogenesis to clinic (Review). Int. J. Oncol. 2024, 64, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Allen, J.; Hao, S.; Sears, C.L.; Timp, W. Epigenetic Changes Induced by Bacteroides fragilis Toxin. Infect. Immun. 2019, 87, e00447-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Xing, J.; Liao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wang, D.; Tang, D. Impacts of MicroRNAs Induced by the Gut Microbiome on Regulating the Development of Colorectal Cancer. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 804689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ambalam, P.; Dave, J.M.; Nair, B.M.; Vyas, B.R. In vitro mutagen binding and antimutagenic activity of human Lactobacillus rhamnosus 231. Anaerobe 2011, 17, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pithva, S.P.; Ambalam, P.S.; Ramoliya, J.M.; Dave, J.M.; Vyas, B.R. Antigenotoxic and Antimutagenic Activities of Probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus Vc against N-Methyl-N’-Nitro-N-Nitrosoguanidine. Nutr. Cancer 2015, 67, 1142–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heydari, Z.; Rahaie, M.; Alizadeh, A.M.; Agah, S.; Khalighfard, S.; Bahmani, S. Effects of Lactobacillus acidophilus and Bifidobacterium bifidum Probiotics on the Expression of MicroRNAs 135b, 26b, 18a and 155, and Their Involving Genes in Mice Colon Cancer. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2019, 11, 1155–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahmy, C.A.; Gamal-Eldeen, A.M.; El-Hussieny, E.A.; Raafat, B.M.; Mehanna, N.S.; Talaat, R.M.; Shaaban, M.T. Bifidobacterium longum Suppresses Murine Colorectal Cancer through the Modulation of oncomiRs and Tumor Suppressor miRNAs. Nutr. Cancer 2019, 71, 688–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mederle, A.L.; Semenescu, A.; Drăghici, G.A.; Dehelean, C.A.; Vlăduț, N.-V.; Nica, D.V. Sodium Butyrate: A Multifaceted Modulator in Colorectal Cancer Therapy. Medicina 2025, 61, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Klionsky, D.J. Life and Death Decisions-The Many Faces of Autophagy in Cell Survival and Cell Death. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Klionsky, D.J.; Abdel-Aziz, A.K.; Abdelfatah, S.; Abdellatif, M.; Abdoli, A.; Abel, S.; Abeliovich, H.; Abildgaard, M.H.; Abudu, Y.P.; Acevedo-Arozena, A.; et al. Guidelines for the use and interpretation of assays for monitoring autophagy (4th edition)1. Autophagy 2021, 17, 1–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Vidoni, C.; Ferraresi, A.; Secomandi, E.; Vallino, L.; Dhanasekaran, D.N.; Isidoro, C. Epigenetic targeting of autophagy for cancer prevention and treatment by natural compounds. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2020, 66, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidoni, C.; Vallino, L.; Ferraresi, A.; Secomandi, E.; Salwa, A.; Chinthakindi, M.; Galetto, A.; Dhanasekaran, D.N.; Isidoro, C. Epigenetic control of autophagy in women’s tumors: Role of non-coding RNAs. J. Cancer Metastasis Treat. 2021, 7, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuwajit, C.; Ferraresi, A.; Titone, R.; Thuwajit, P.; Isidoro, C. The metabolic cross-talk between epithelial cancer cells and stromal fibroblasts in ovarian cancer progression: Autophagy plays a role. Med. Res. Rev. 2018, 38, 1235–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ferraresi, A.; Girone, C.; Esposito, A.; Vidoni, C.; Vallino, L.; Secomandi, E.; Dhanasekaran, D.N.; Isidoro, C. How Autophagy Shapes the Tumor Microenvironment in Ovarian Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 599915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ferraresi, A.; Girone, C.; Maheshwari, C.; Vallino, L.; Dhanasekaran, D.N.; Isidoro, C. Ovarian Cancer Cell-Conditioning Medium Induces Cancer-Associated Fibroblast Phenoconversion through Glucose-Dependent Inhibition of Autophagy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Shao, L.N.; Zhu, B.S.; Xing, C.G.; Yang, X.D.; Young, W.; Cao, J.P. Effects of autophagy regulation of tumor-associated macrophages on radiosensitivity of colorectal cancer cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 13, 2661–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, M.R.; Kim, M.S.; Oh, J.E.; Kim, Y.R.; Song, S.Y.; Kim, S.S.; Ahn, C.H.; Yoo, N.J.; Lee, S.H. Frameshift mutations of autophagy-related genes ATG2B, ATG5, ATG9B and ATG12 in gastric and colorectal cancers with microsatellite instability. J. Pathol. 2009, 217, 702–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Lv, L.; Lu, K.; Li, H.; Zhang, W.; Cui, T. Autophagy: Dual roles and perspective for clinical treatment of colorectal cancer. Biochimie 2023, 206, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzoor, S.; Muhammad, J.S.; Maghazachi, A.A.; Hamid, Q. Autophagy: A Versatile Player in the Progression of Colorectal Cancer and Drug Resistance. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 924290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Jo, Y.K.; Kim, S.C.; Park, I.J.; Park, S.J.; Jin, D.H.; Hong, S.W.; Cho, D.H.; Kim, J.C. Increased expression of ATG10 in colorectal cancer is associated with lymphovascular invasion and lymph node metastasis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e52705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Jo, Y.K.; Roh, S.A.; Lee, H.; Park, N.Y.; Choi, E.S.; Oh, J.H.; Park, S.J.; Shin, J.H.; Suh, Y.A.; Lee, E.K.; et al. Polypyrimidine tract-binding protein 1-mediated down-regulation of ATG10 facilitates metastasis of colorectal cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2017, 385, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Hou, N.; Faried, A.; Tsutsumi, S.; Kuwano, H. Inhibition of autophagy augments 5-fluorouracil chemotherapy in human colon cancer in vitro and in vivo model. Eur. J. Cancer 2010, 46, 1900–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qureshi-Baig, K.; Kuhn, D.; Viry, E.; Pozdeev, V.I.; Schmitz, M.; Rodriguez, F.; Ullmann, P.; Koncina, E.; Nurmik, M.; Frasquilho, S.; et al. Hypoxia-induced autophagy drives colorectal cancer initiation and progression by activating the PRKC/PKC-EZR (ezrin) pathway. Autophagy 2020, 16, 1436–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lévy, J.; Cacheux, W.; Bara, M.A.; L’Hermitte, A.; Lepage, P.; Fraudeau, M.; Trentesaux, C.; Lemarchand, J.; Durand, A.; Crain, A.M.; et al. Intestinal inhibition of Atg7 prevents tumour initiation through a microbiome-influenced immune response and suppresses tumour growth. Nat. Cell Biol. 2015, 17, 1062–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Qu, X. Heterozygous deletion of ATG5 in Apc(Min/+) mice promotes intestinal adenoma growth and enhances the antitumor efficacy of interferon-gamma. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2015, 16, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lucas, C.; Salesse, L.; Hoang, M.H.T.; Bonnet, M.; Sauvanet, P.; Larabi, A.; Godfraind, C.; Gagnière, J.; Pezet, D.; Rosenstiel, P.; et al. Autophagy of Intestinal Epithelial Cells Inhibits Colorectal Carcinogenesis Induced by Colibactin-Producing Escherichia coli in ApcMin/+ Mice. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1373–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Li, J.; Zhou, L.; Han, J.; Liu, R.; Zhang, H.; Ning, T.; Gao, Z.; Liu, B.; Chen, X.; et al. The c-Myc/miR-27b-3p/ATG10 regulatory axis regulates chemoresistance in colorectal cancer. Theranostics 2020, 10, 1981–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhai, H.; Song, B.; Xu, X.; Zhu, W.; Ju, J. Inhibition of autophagy and tumor growth in colon cancer by miR-502. Oncogene 2013, 32, 1570–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tan, S.; Shi, H.; Ba, M.; Lin, S.; Tang, H.; Zeng, X.; Zhang, X. miR-409-3p sensitizes colon cancer cells to oxaliplatin by inhibiting Beclin-1-mediated autophagy. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 37, 1030–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trincheri, N.F.; Follo, C.; Nicotra, G.; Peracchio, C.; Castino, R.; Isidoro, C. Resveratrol-induced apoptosis depends on the lipid kinase activity of Vps34 and on the formation of autophagolysosomes. Carcinogenesis 2008, 29, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, T.; Cai, L.D.; Liu, Y.H.; Li, S.; Gan, W.J.; Li, X.M.; Wang, J.R.; Guo, P.D.; Zhou, Q.; Lu, X.X.; et al. Ube2v1-mediated ubiquitination and degradation of Sirt1 promotes metastasis of colorectal cancer by epigenetically suppressing autophagy. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 11, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Huo, H.Z.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Wang, B.; Qin, J.; Liu, W.Y.; Gu, Y. Dramatic suppression of colorectal cancer cell growth by the dual mTORC1 and mTORC2 inhibitor AZD-2014. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 443, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.X.; Li, C.Y.; Peng, R.Q.; Wu, X.J.; Wang, H.Y.; Wan, D.S.; Zhu, X.F.; Zhang, X.S. The expression of beclin 1 is associated with favorable prognosis in stage IIIB colon cancers. Autophagy 2009, 5, 303–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, C.A.; Lee, C.T.; Lee, J.C.; Wang, Y.W.; Huang, C.T.; Lan, S.H.; Lin, P.C.; Lin, B.W.; Tian, Y.F.; Liu, H.S.; et al. MiR-338-5p promotes metastasis of colorectal cancer by inhibition of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, catalytic subunit type 3-mediated autophagy pathway. EBioMedicine 2019, 43, 270–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zheng, S.; Zhong, Y.F.; Tan, D.M.; Xu, Y.; Chen, H.X.; Wang, D. miR-183-5p enhances the radioresistance of colorectal cancer by directly targeting ATG5. J. Biosci. 2019, 44, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garavaglia, B.; Vallino, L.; Amoruso, A.; Pane, M.; Ferraresi, A.; Isidoro, C. The role of gut microbiota, immune system, and autophagy in the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic approaches. Asp. Mol. Med. 2024, 4, 100056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, K.M.; Barlow, P.G.; Henderson, P.; Stevens, C. Interactions Between Autophagy and the Unfolded Protein Response: Implications for Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2019, 25, 661–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iida, T.; Onodera, K.; Nakase, H. Role of autophagy in the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 1944–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhou, M.; Xu, W.; Wang, J.; Yan, J.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, C.; Ge, W.; Wu, J.; Du, P.; Chen, Y. Boosting mTOR-dependent autophagy via upstream TLR4-MyD88-MAPK signalling and downstream NF-κB pathway quenches intestinal inflammation and oxidative stress injury. EBioMedicine 2018, 35, 345–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Nighot, P.K.; Hu, C.A.; Ma, T.Y. Autophagy enhances intestinal epithelial tight junction barrier function by targeting claudin-2 protein degradation. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 7234–7246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wong, M.; Ganapathy, A.S.; Suchanec, E.; Laidler, L.; Ma, T.; Nighot, P. Intestinal epithelial tight junction barrier regulation by autophagy-related protein ATG6/beclin 1. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2019, 316, C753–C765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhang, C.; Yan, J.; Xiao, Y.; Shen, Y.; Wang, J.; Ge, W.; Chen, Y. Inhibition of Autophagic Degradation Process Contributes to Claudin-2 Expression Increase and Epithelial Tight Junction Dysfunction in TNF-α Treated Cell Monolayers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yang, L.; Liu, C.; Zhao, W.; He, C.; Ding, J.; Dai, R.; Xu, K.; Xiao, L.; Luo, L.; Liu, S.; et al. Impaired Autophagy in Intestinal Epithelial Cells Alters Gut Microbiota and Host Immune Responses. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84, e00880-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Liu, X.; Yin, L.; Shen, S.; Hou, Y. Inflammation and cancer: Paradoxical roles in tumorigenesis and implications in immunotherapies. Genes Dis. 2021, 10, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Borowczak, J.; Szczerbowski, K.; Maniewski, M.; Kowalewski, A.; Janiczek-Polewska, M.; Szylberg, A.; Marszałek, A.; Szylberg, Ł. The Role of Inflammatory Cytokines in the Pathogenesis of Colorectal Carcinoma-Recent Findings and Review. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Muthusami, S.; Ramachandran, I.K.; Babu, K.N.; Krishnamoorthy, S.; Guruswamy, A.; Queimado, L.; Chaudhuri, G.; Ramachandran, I. Role of Inflammation in the Development of Colorectal Cancer. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug. Targets 2021, 21, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Zhu, L.; Liu, H.; Feng, X.; Zhang, C.; Liu, B.; Li, T.; Liu, L.; Chang, H.; Sun, J.; et al. Altered gut metabolites and metabolic reprogramming involved in the pathogenesis of colitis-associated colorectal cancer and the transition of colon “inflammation to cancer”. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2025, 253, 116553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, S.C.; Itzkowitz, S.H. Colorectal Cancer in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Mechanisms and Management. Gastroenterology 2022, 162, 715–730.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sato, Y.; Tsujinaka, S.; Miura, T.; Kitamura, Y.; Suzuki, H.; Shibata, C. Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Colorectal Cancer: Epidemiology, Etiology, Surveillance, and Management. Cancers 2023, 15, 4154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Fanizza, J.; Bencardino, S.; Allocca, M.; Furfaro, F.; Zilli, A.; Parigi, T.L.; Fiorino, G.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L.; Danese, S.; D’Amico, F. Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Colorectal Cancer. Cancers 2024, 16, 2943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Heo, G.; Lee, Y.; Im, E. Interplay between the Gut Microbiota and Inflammatory Mediators in the Development of Colorectal Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Turano, M.; Cammarota, F.; Duraturo, F.; Izzo, P.; De Rosa, M. Role of IL-6/IL-6R in the Development and Management of Colon Cancer. Membranes 2021, 11, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mager, L.F.; Wasmer, M.H.; Rau, T.T.; Krebs, P. Cytokine-Induced Modulation of Colorectal Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2016, 6, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Nagasaki, T.; Hara, M.; Nakanishi, H.; Takahashi, H.; Sato, M.; Takeyama, H. Interleukin-6 released by colon cancer-associated fibroblasts is critical for tumour angiogenesis: Anti-interleukin-6 receptor antibody suppressed angiogenesis and inhibited tumour-stroma interaction. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 110, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sun, Q.; Shang, Y.; Sun, F.; Dong, X.; Niu, J.; Li, F. Interleukin-6 Promotes Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Cell Invasion through Integrin β6 Upregulation in Colorectal Cancer. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2020, 2020, 8032187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhang, T.; Liu, L.; Lai, W.; Zeng, Y.; Xu, H.; Lan, Q.; Su, P.; Chu, Z. Interaction with tumor-associated macrophages promotes PRL-3-induced invasion of colorectal cancer cells via MAPK pathway-induced EMT and NF-κB signaling-induced angiogenesis. Oncol. Rep. 2019, 41, 2790–2802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Knüpfer, H.; Preiss, R. Serum interleukin-6 levels in colorectal cancer patients--a summary of published results. Int. J. Colorectal Dis. 2010, 25, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orecchioni, M.; Ghosheh, Y.; Pramod, A.B.; Ley, K. Macrophage Polarization: Different Gene Signatures in M1(LPS+) vs. Classically and M2(LPS-) vs. Alternatively Activated Macrophages. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wang, S.; Liu, G.; Li, Y.; Pan, Y. Metabolic Reprogramming Induces Macrophage Polarization in the Tumor Microenvironment. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 840029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wan, G.; Xie, M.; Yu, H.; Chen, H. Intestinal dysbacteriosis activates tumor-associated macrophages to promote epithelial-mesenchymal transition of colorectal cancer. Innate. Immun. 2018, 24, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhou, D.; Li, Y. Gut microbiota and tumor-associated macrophages: Potential in tumor diagnosis and treatment. Gut Microbes 2023, 15, 2276314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kikuchi, T.; Mimura, K.; Ashizawa, M.; Okayama, H.; Endo, E.; Saito, K.; Sakamoto, W.; Fujita, S.; Endo, H.; Saito, M.; et al. Characterization of tumor-infiltrating immune cells in relation to microbiota in colorectal cancers. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2020, 69, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Jiang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Shi, P.; Liu, Q.; Sun, Y. Dietary Nondigestible Polysaccharides Ameliorate Colitis by Improving Gut Microbiota and CD4+ Differentiation, as Well as Facilitating M2 Macrophage Polarization. JPEN J. Parenter. Enteral. Nutr. 2019, 43, 401–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribatti, D.; Tamma, R. A revisited concept. Tumors: Wounds that do not heal. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2018, 128, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veettil, S.K.; Wong, T.Y.; Loo, Y.S.; Playdon, M.C.; Lai, N.M.; Giovannucci, E.L.; Chaiyakunapruk, N. Role of Diet in Colorectal Cancer Incidence: Umbrella Review of Meta-analyses of Prospective Observational Studies. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e2037341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lewandowska, A.; Rudzki, G.; Lewandowski, T.; Stryjkowska-Góra, A.; Rudzki, S. Risk Factors for the Diagnosis of Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Control 2022, 29, 10732748211056692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rubio, K.; Hernández-Cruz, E.Y.; Rogel-Ayala, D.G.; Sarvari, P.; Isidoro, C.; Barreto, G.; Pedraza-Chaverri, J. Nutriepigenomics in Environmental-Associated Oxidative Stress. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Conti, L.; Corn, M.D.; Scazzocchio, B.; Varì, R.; D’Archivio, M.; Varano, B.; Masella, R.; Gessani, S. Dietary fatty acids and adipose tissue inflammation at the crossroad between obesity and colorectal cancer. J. Cancer Metastasis Treat. 2019, 5, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Maravilla, E.; Boucard, A.S.; Mohseni, A.H.; Taghinezhad, S.S.; Cortes-Perez, N.G.; Bermúdez-Humarán, L.G. Role of Gut Microbiota and Probiotics in Colorectal Cancer: Onset and Progression. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rosenberg, E. Diversity of bacteria within the human gut and its contribution to the functional unity of holobionts. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2024, 10, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gagnière, J.; Raisch, J.; Veziant, J.; Barnich, N.; Bonnet, R.; Buc, E.; Bringer, M.A.; Pezet, D.; Bonnet, M. Gut microbiota imbalance and colorectal cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 501–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ahmad, A.; Mahmood, N.; Raza, M.A.; Mushtaq, Z.; Saeed, F.; Afzaal, M.; Hussain, M.; Amjad, H.W.; Al-Awadi, H.M. Gut microbiota and their derivatives in the progression of colorectal cancer: Mechanisms of action, genome and epigenome contributions. Heliyon 2024, 10, e29495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Al Bander, Z.; Nitert, M.D.; Mousa, A.; Naderpoor, N. The Gut Microbiota and Inflammation: An Overview. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 7618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Liu, P.; Wang, Y.; Yang, G.; Zhang, Q.; Meng, L.; Xin, Y.; Jiang, X. The role of short-chain fatty acids in intestinal barrier function, inflammation, oxidative stress, and colonic carcinogenesis. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 165, 105420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivaprakasam, S.; Bhutia, Y.D.; Yang, S.; Ganapathy, V. Short-Chain Fatty Acid Transporters: Role in Colonic Homeostasis. Compr. Physiol. 2017, 8, 299–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hou, K.; Wu, Z.X.; Chen, X.Y.; Wang, J.Q.; Zhang, D.; Xiao, C.; Zhu, D.; Koya, J.B.; Wei, L.; Li, J.; et al. Microbiota in health and diseases. Signal. Transduct. Target Ther. 2022, 7, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sobhani, I.; Tap, J.; Roudot-Thoraval, F.; Roperch, J.P.; Letulle, S.; Langella, P.; Corthier, G.; Tran Van Nhieu, J.; Furet, J.P. Microbial dysbiosis in colorectal cancer (CRC) patients. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Castellarin, M.; Warren, R.L.; Freeman, J.D.; Dreolini, L.; Krzywinski, M.; Strauss, J.; Barnes, R.; Watson, P.; Allen-Vercoe, E.; Moore, R.A.; et al. Fusobacterium nucleatum infection is prevalent in human colorectal carcinoma. Genome Res. 2012, 22, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rubinstein, M.R.; Wang, X.; Liu, W.; Hao, Y.; Cai, G.; Han, Y.W. Fusobacterium nucleatum promotes colorectal carcinogenesis by modulating E-cadherin/β-catenin signaling via its FadA adhesin. Cell Host Microbe 2013, 14, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ye, X.; Wang, R.; Bhattacharya, R.; Boulbes, D.R.; Fan, F.; Xia, L.; Adoni, H.; Ajami, N.J.; Wong, M.C.; Smith, D.P.; et al. Fusobacterium Nucleatum Subspecies Animalis Influences Proinflammatory Cytokine Expression and Monocyte Activation in Human Colorectal Tumors. Cancer Prev. Res. 2017, 10, 398–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Lim, K.C.; Huang, J.; Saidi, R.F.; Sears, C.L. Bacteroides fragilis enterotoxin cleaves the zonula adherens protein, E-cadherin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 14979–14984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wu, S.; Morin, P.J.; Maouyo, D.; Sears, C.L. Bacteroides fragilis enterotoxin induces c-Myc expression and cellular proliferation. Gastroenterology 2003, 124, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, L.; Thiele Orberg, E.; Geis, A.L.; Chan, J.L.; Fu, K.; DeStefano Shields, C.E.; Dejea, C.M.; Fathi, P.; Chen, J.; Finard, B.B.; et al. Bacteroides fragilis Toxin Coordinates a Pro-carcinogenic Inflammatory Cascade via Targeting of Colonic Epithelial Cells. Cell Host Microbe 2018, 23, 203–214.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lu, R.; Wu, S.; Zhang, Y.G.; Xia, Y.; Liu, X.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, H.; Schaefer, K.L.; Zhou, Z.; Bissonnette, M.; et al. Enteric bacterial protein AvrA promotes colonic tumorigenesis and activates colonic beta-catenin signaling pathway. Oncogenesis 2014, 3, e105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Drewes, J.L.; Chen, J.; Markham, N.O.; Knippel, R.J.; Domingue, J.C.; Tam, A.J.; Chan, J.L.; Kim, L.; McMann, M.; Stevens, C.; et al. Human Colon Cancer-Derived Clostridioides difficile Strains Drive Colonic Tumorigenesis in Mice. Cancer Discov. 2022, 12, 1873–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kumar, R.; Herold, J.L.; Schady, D.; Davis, J.; Kopetz, S.; Martinez-Moczygemba, M.; Murray, B.E.; Han, F.; Li, Y.; Callaway, E.; et al. Streptococcus gallolyticus subsp. gallolyticus promotes colorectal tumor development. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Balamurugan, R.; Rajendiran, E.; George, S.; Samuel, G.V.; Ramakrishna, B.S. Real-time polymerase chain reaction quantification of specific butyrate-producing bacteria, Desulfovibrio and Enterococcus faecalis in the feces of patients with colorectal cancer. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2008, 23, 1298–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemati, M.; Omrani, G.R.; Ebrahimi, B.; Montazeri-Najafabady, N. The Beneficial Effects of Probiotics via Autophagy: A Systematic Review. Biomed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 2931580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Plaza-Diaz, J.; Ruiz-Ojeda, F.J.; Gil-Campos, M.; Gil, A. Mechanisms of Action of Probiotics. Adv. Nutr. 2019, 10, S49–S66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kahouli, I.; Tomaro-Duchesneau, C.; Prakash, S. Probiotics in colorectal cancer (CRC) with emphasis on mechanisms of action and current perspectives. J. Med. Microbiol. 2013, 62, 1107–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, L.; Hua, H.; Liu, L.; Mao, Y.; Wang, R. Interactions between toll-like receptors signaling pathway and gut microbiota in host homeostasis. Immun. Inflamm. Dis. 2024, 12, e1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yesudhas, D.; Gosu, V.; Anwar, M.A.; Choi, S. Multiple roles of toll-like receptor 4 in colorectal cancer. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lowe, E.L.; Crother, T.R.; Rabizadeh, S.; Hu, B.; Wang, H.; Chen, S.; Shimada, K.; Wong, M.H.; Michelsen, K.S.; Arditi, M. Toll-like receptor 2 signaling protects mice from tumor development in a mouse model of colitis-induced cancer. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Jang, Y.J.; Kim, W.K.; Han, D.H.; Lee, K.; Ko, G. Lactobacillus fermentum species ameliorate dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis by regulating the immune response and altering gut microbiota. Gut Microbes 2019, 10, 696–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Round, J.L.; Lee, S.M.; Li, J.; Tran, G.; Jabri, B.; Chatila, T.A.; Mazmanian, S.K. The Toll-like receptor 2 pathway establishes colonization by a commensal of the human microbiota. Science 2011, 332, 974–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Shi, J.; Li, H.; Liang, S.; Evivie, S.; Huo, G.; Li, B.; Liu, F. Selected lactobacilli strains inhibit inflammation in LPS-induced RAW264.7 macrophages by suppressing the TLR4-mediated NF-κB and MAPKs activation. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 42, e107621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molska, M.; Reguła, J. Potential Mechanisms of Probiotics Action in the Prevention and Treatment of Colorectal Cancer. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Cristofori, F.; Dargenio, V.N.; Dargenio, C.; Miniello, V.L.; Barone, M.; Francavilla, R. Anti-Inflammatory and Immunomodulatory Effects of Probiotics in Gut Inflammation: A Door to the Body. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 578386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Torkamaneh, M.; Torfeh, M.; Jouriani, F.H.; Sepehr, A.; Ashrafian, F.; Aghamohammad, S.; Rohani, M. Investigating the crucial role of selected Bifidobacterium probiotic strains in preventing or reducing inflammation by affecting the autophagy pathway. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2023, 76, ovad135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallino, L.; Garavaglia, B.; Visciglia, A.; Amoruso, A.; Pane, M.; Ferraresi, A.; Isidoro, C. Cell-free Lactiplantibacillus plantarum OC01 supernatant suppresses IL-6-induced proliferation and invasion of human colorectal cancer cells: Effect on β-Catenin degradation and induction of autophagy. J. Tradit. Complement. Med. 2023, 13, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Garavaglia, B.; Vallino, L.; Ferraresi, A.; Amoruso, A.; Pane, M.; Isidoro, C. Probiotic-Derived Metabolites from Lactiplantibacillus plantarum OC01 Reprogram Tumor-Associated Macrophages to an Inflammatory Anti-Tumoral Phenotype: Impact on Colorectal Cancer Cell Proliferation and Migration. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mazziotta, C.; Tognon, M.; Martini, F.; Torreggiani, E.; Rotondo, J.C. Probiotics Mechanism of Action on Immune Cells and Beneficial Effects on Human Health. Cells 2023, 12, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hou, H.; Chen, D.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, W.; Liu, T.; Wang, S.; Dai, X.; Wang, B.; Zhong, W.; Cao, H. Gut microbiota-derived short-chain fatty acids and colorectal cancer: Ready for clinical translation? Cancer Lett. 2022, 526, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.B.; Wang, P.Y.; Wang, X.; Wan, Y.L.; Liu, Y.C. Butyrate enhances intestinal epithelial barrier function via up-regulation of tight junction protein Claudin-1 transcription. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2012, 57, 3126–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burger-van Paassen, N.; Vincent, A.; Puiman, P.J.; van der Sluis, M.; Bouma, J.; Boehm, G.; van Goudoever, J.B.; van Seuningen, I.; Renes, I.B. The regulation of intestinal mucin MUC2 expression by short-chain fatty acids: Implications for epithelial protection. Biochem. J. 2009, 420, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakajima, A.; Nakatani, A.; Hasegawa, S.; Irie, J.; Ozawa, K.; Tsujimoto, G.; Suganami, T.; Itoh, H.; Kimura, I. The short chain fatty acid receptor GPR43 regulates inflammatory signals in adipose tissue M2-type macrophages. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kibbie, J.J.; Dillon, S.M.; Thompson, T.A.; Purba, C.M.; McCarter, M.D.; Wilson, C.C. Butyrate directly decreases human gut lamina propria CD4 T cell function through histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibition and GPR43 signaling. Immunobiology 2021, 226, 152126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Luo, S.; Li, Z.; Mao, L.; Chen, S.; Sun, S. Sodium butyrate induces autophagy in colorectal cancer cells through LKB1/AMPK signaling. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 75, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Hu, J.; Wang, M.; Yuan, H.; Xing, Y.; Zhou, X.; Ding, M.; Chen, W.; Qu, B.; Zhu, L. CISD2 Promotes Proliferation of Colorectal Cancer Cells by Inhibiting Autophagy in a Wnt/β-Catenin-Signaling-Dependent Pathway. Biochem. Genet. 2023, 61, 615–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, W.; Evans, P.M.; Chen, X.; He, X.; Liu, C. Adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) differentially regulates beta-catenin phosphorylation and ubiquitination in colon cancer cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 17751–17757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Fu, J.; Huang, Y.; Fu, C. Mechanism of APC truncation involved in colorectal cancer tumorigenesis (Review). Oncol. Lett. 2024, 29, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Garavaglia, B.; Vallino, L.; Ferraresi, A.; Esposito, A.; Salwa, A.; Vidoni, C.; Gentilli, S.; Isidoro, C. Butyrate Inhibits Colorectal Cancer Cell Proliferation through Autophagy Degradation of β-Catenin Regardless of APC and β-Catenin Mutational Status. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Brasiel, P.G.A.; Dutra Luquetti, S.C.P.; Peluzio, M.D.C.G.; Novaes, R.D.; Gonçalves, R.V. Preclinical Evidence of Probiotics in Colorectal Carcinogenesis: A Systematic Review. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2020, 65, 3197–3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz, B.C.S.; Sarandy, M.M.; Messias, A.C.; Gonçalves, R.V.; Ferreira, C.L.L.F.; Peluzio, M.C.G. Preclinical and clinical relevance of probiotics and synbiotics in colorectal carcinogenesis: A systematic review. Nutr. Rev. 2020, 78, 667–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertkova, I.; Hijova, E.; Chmelarova, A.; Mojzisova, G.; Petrasova, D.; Strojny, L.; Bomba, A.; Zitnan, R. The effect of probiotic microorganisms and bioactive compounds on chemically induced carcinogenesis in rats. Neoplasma 2010, 57, 422–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Singh, N.K.; Sinha, P.R. Inhibition of 1, 2-dimethylhydrazine induced colon genotoxicity in rats by the administration of probiotic curd. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2010, 37, 1373–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.H.; Shim, Y.Y.; Cha, S.K.; Reaney, M.J.T.; Chee, K.M. Effect of Lactobacillus acidophilus KFRI342 on the development of chemically induced precancerous growths in the rat colon. J. Med. Microbiol. 2012, 61, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghanavati, R.; Akbari, A.; Mohammadi, F.; Asadollahi, P.; Javadi, A.; Talebi, M.; Rohani, M. Lactobacillus species inhibitory effect on colorectal cancer progression through modulating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2020, 470, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appleyard, C.B.; Cruz, M.L.; Isidro, A.A.; Arthur, J.C.; Jobin, C.; De Simone, C. Pretreatment with the probiotic VSL#3 delays transition from inflammation to dysplasia in a rat model of colitis-associated cancer. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2011, 301, G1004-13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Do, E.J.; Hwang, S.W.; Kim, S.Y.; Ryu, Y.M.; Cho, E.A.; Chung, E.J.; Park, S.; Lee, H.J.; Byeon, J.S.; Ye, B.D.; et al. Suppression of colitis-associated carcinogenesis through modulation of IL-6/STAT3 pathway by balsalazide and VSL#3. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 31, 1453–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.M.; Yu, Y.N.; Wang, J.L.; Lin, Y.W.; Kong, X.; Yang, C.Q.; Yang, L.; Liu, Z.J.; Yuan, Y.Z.; Liu, F.; et al. Decreased dietary fiber intake and structural alteration of gut microbiota in patients with advanced colorectal adenoma. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 97, 1044–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weir, T.L.; Manter, D.K.; Sheflin, A.M.; Barnett, B.A.; Heuberger, A.L.; Ryan, E.P. Stool microbiome and metabolome differences between colorectal cancer patients and healthy adults. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Golkhalkhali, B.; Rajandram, R.; Paliany, A.S.; Ho, G.F.; Wan Ishak, W.Z.; Johari, C.S.; Chin, K.F. Strain-specific probiotic (microbial cell preparation) and omega-3 fatty acid in modulating quality of life and inflammatory markers in colorectal cancer patients: A randomized controlled trial. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 14, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldwin, C.; Millette, M.; Oth, D.; Ruiz, M.T.; Luquet, F.M.; Lacroix, M. Probiotic Lactobacillus acidophilus and L. casei mix sensitize colorectal tumoral cells to 5-fluorouracil-induced apoptosis. Nutr. Cancer 2010, 62, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osterlund, P.; Ruotsalainen, T.; Korpela, R.; Saxelin, M.; Ollus, A.; Valta, P.; Kouri, M.; Elomaa, I.; Joensuu, H. Lactobacillus supplementation for diarrhea related to chemotherapy of colorectal cancer: A randomised study. Br. J. Cancer 2007, 97, 1028–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- An, J.; Ha, E.M. Combination Therapy of Lactobacillus plantarum Supernatant and 5-Fluouracil Increases Chemosensitivity in Colorectal Cancer Cells. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 26, 1490–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishikawa, H.; Akedo, I.; Otani, T.; Suzuki, T.; Nakamura, T.; Takeyama, I.; Ishiguro, S.; Miyaoka, E.; Sobue, T.; Kakizoe, T. Randomized trial of dietary fiber and Lactobacillus casei administration for prevention of colorectal tumors. Int. J. Cancer 2005, 116, 762–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Qin, H.; Yang, Z.; Xia, Y.; Liu, W.; Yang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yang, Z.; Wang, Y.; et al. Randomised clinical trial: The effects of perioperative probiotic treatment on barrier function and post-operative infectious complications in colorectal cancer surgery—A doubleblind study. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 33, 50–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wada, M.; Nagata, S.; Saito, M.; Shimizu, T.; Yamashiro, Y.; Matsuki, T.; Asahara, T.; Nomoto, K. Effects of the enteral administration of Bifidobacterium breve on patients undergoing chemotherapy for pediatric malignancies. Support. Care Cancer 2010, 18, 751–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotzampassi, K.; Stavrou, G.; Damoraki, G.; Georgitsi, M.; Basdanis, G.; Tsaousi, G.; Giamarellos-Bourboulis, E.J. A Four-Probiotics Regimen Reduces Postoperative Complications After Colorectal Surgery: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study. World J. Surg. 2015, 39, 2776–2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urbancsek, H.; Kazar, T.; Mezes, I.; Neumann, K. Results of a double-blind, randomized study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of Antibiophilus in patients with radiation-induced diarrhoea. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2001, 13, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chitapanarux, I.; Chitapanarux, T.; Traisathit, P.; Kudumpee, S.; Tharavichitkul, E.; Lorvidhaya, V. Randomized controlled trial of live lactobacillus acidophilus plus bifidobacterium bifidum in prophylaxis of diarrhea during radiotherapy in cervical cancer patients. Radiat. Oncol. 2010, 5, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Shakhpazyan, N.K.; Mikhaleva, L.M.; Bedzhanyan, A.L.; Gioeva, Z.V.; Mikhalev, A.I.; Midiber, K.Y.; Pechnikova, V.V.; Biryukov, A.E. Exploring the Role of the Gut Microbiota in Modulating Colorectal Cancer Immunity. Cells 2024, 13, 1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Peng, Z.; Cheng, S.; Kou, Y.; Wang, Z.; Jin, R.; Hu, H.; Zhang, X.; Gong, J.F.; Li, J.; Lu, M.; et al. The Gut Microbiome Is Associated with Clinical Response to Anti-PD-1/PD-L1 Immunotherapy in Gastrointestinal Cancer. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2020, 8, 1251–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pace, F.; Pace, M.; Quartarone, G. Probiotics in digestive diseases: Focus on Lactobacillus GG. Minerva Gastroenterol. Dietol. 2015, 6, 273–292. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Holzapfel, W.H.; Haberer, P.; Snel, J.; Schillinger, U.; Huis in’t Veld, J.H. Overview of gut flora and probiotics. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1998, 41, 85–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guarner, F.; Malagelada, J.R. Gut flora in health and disease. Lancet 2003, 361, 512–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Round, J.L.; Mazmanian, S.K. The gut microbiota shapes intestinal immune responses during health and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Reid, G.; Jass, J.; Sebulsky, M.T.; McCormick, J.K. Potential uses of probiotics in clinical practice. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2003, 16, 658–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gianotti, L.; Morelli, L.; Galbiati, F.; Rocchetti, S.; Coppola, S.; Beneduce, A.; Gilardini, C.; Zonenschain, D.; Nespoli, A.; Braga, M. A randomized double-blind trial on perioperative administration of probiotics in colorectal cancer patients. World J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 16, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mego, M.; Chovanec, J.; Vochyanova-Andrezalova, I.; Konkolovsky, P.; Mikulova, M.; Reckova, M.; Miskovska, V.; Bystricky, B.; Beniak, J.; Medvecova, L.; et al. Prevention of irinotecan induced diarrhea by probiotics: A randomized double blind, placebo controlled pilot study. Complement. Ther. Med. 2015, 23, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mego, M.; Kasperova, B.; Chovanec, J.; Danis, R.; Reckova, M.; Bystricky, B.; Konkolovsky, P.; Jurisova, S.; Porsok, S.; Vaclav, V.; et al. The beneficial effect of probiotics in the prevention of irinotecan-induced diarrhea in colorectal cancer patients with colostomy: A pooled analysis of two probiotic trials (Probio-SK-003 and Probio-SK-005) led by Slovak Cooperative Oncology Group. Front Oncol. 2024, 14, 1438657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chen, X.; Fruehauf, J.; Goldsmith, J.D.; Xu, H.; Katchar, K.K.; Koon, H.W.; Zhao, D.; Kokkotou, E.G.; Pothoulakis, C.; Kelly, C.P. Saccharomyces boulardii inhibits EGF receptor signaling and intestinal tumor growth in Apc(min) mice. Gastroenterology 2009, 137, 914–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Azcárate-Peril, M.A.; Sikes, M.; Bruno-Bárcena, J.M. The intestinal microbiota, gastrointestinal environment and colorectal cancer: A putative role for probiotics in prevention of colorectal cancer? Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2011, 301, G401–G424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Theodoropoulos, G.E.; Memos, N.A.; Peitsidou, K.; Karantanos, T.; Spyropoulos, B.G.; Zografos, G. Synbiotics and gastrointestinal function-related quality of life after elective colorectal cancer resection. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2016, 29, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chen, C.C.; Lin, W.C.; Kong, M.S.; Shi, H.N.; Walker, W.A.; Lin, C.Y.; Huang, C.T.; Lin, Y.C.; Jung, S.M.; Lin, T.Y. Oral inoculation of probiotics Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM suppresses tumour growth both in segmental orthotopic colon cancer and extra-intestinal tissue. Br. J. Nutr. 2012, 107, 1623–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hibberd, A.A.; Lyra, A.; Ouwehand, A.C.; Rolny, P.; Lindegren, H.; Cedgård, L.; Wettergren, Y. Intestinal microbiota is altered in patients with colon cancer and modified by probiotic intervention. BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 2017, 4, e000145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lee, H.A.; Kim, H.; Lee, K.W.; Park, K.Y. Dead Nano-Sized Lactobacillus plantarum Inhibits Azoxymethane/Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colon Cancer in Balb/c Mice. J. Med. Food. 2015, 18, 1400–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stene, C.; Xu, J.; Fallone de Andrade, S.; Palmquist, I.; Molin, G.; Ahrné, S.; Thorlacius, H.; Johnson, L.B.; Jeppsson, B. Synbiotics protected radiation-induced tissue damage in rectal cancer patients: A controlled trial. Clin. Nutr. 2025, 49, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlini, M.; Grieco, M.; Spoletini, D.; Menditto, R.; Napoleone, V.; Brachini, G.; Mingoli, A.; Marcellinaro, R. Implementation of the gut microbiota prevents anastomotic leaks in laparoscopic colorectal surgery for cancer:the results of the MIRACLe study. Updates Surg. 2022, 74, 1253–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deol, P.K.; Khare, P.; Bishnoi, M.; Kondepudi, K.K.; Kaur, I.P. Coadministration of ginger extract-Lactobacillus acidophilus (cobiotic) reduces gut inflammation and oxidative stress via downregulation of COX-2, i-NOS, and c-Myc. Phytother. Res. 2018, 32, 1950–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Deeb, N.M.; Yassin, A.M.; Al-Madboly, L.A.; El-Hawiet, A. A novel purified Lactobacillus acidophilus 20079 exopolysaccharide, LA-EPS-20079, molecularly regulates both apoptotic and NF-κB inflammatory pathways in human colon cancer. Microb. Cell Fact. 2018, 17, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhuo, Q.; Yu, B.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, R.; Xie, J.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, S. Lysates of Lactobacillus acidophilus combined with CTLA-4-blocking antibodies enhance antitumor immunity in a mouse colon cancer model. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 20128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lin, P.Y.; Li, S.C.; Lin, H.P.; Shih, C.K. Germinated brown rice combined with Lactobacillus acidophilus and Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis inhibits colorectal carcinogenesis in rats. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 7, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Desrouillères, K.; Millette, M.; Bagheri, L.; Maherani, B.; Jamshidian, M.; Lacroix, M. The synergistic effect of cell wall extracted from probiotic biomass containing Lactobacillus acidophilus CL1285, L. casei LBC80R, and L. rhamnosus CLR2 on the anticancer activity of cranberry juice-HPLC fractions. J. Food Biochem. 2020, 44, e13195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacouton, E.; Chain, F.; Sokol, H.; Langella, P.; Bermúdez-Humarán, L.G. Probiotic Strain Lactobacillus casei BL23 Prevents Colitis-Associated Colorectal Cancer. Front Immunol. 2017, 8, 1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sharma, M.; Shukla, G. Administration of Metabiotics Extracted From Probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus MD 14 Inhibit Experimental Colorectal Carcinogenesis by Targeting Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway. Front Oncol. 2020, 10, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Valiei, A.; Aminian-Dehkordi, J.; Mofrad, M.R.K. Gut-on-a-chip models for dissecting the gut microbiology and physiology. APL Bioeng. 2023, 7, 011502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Palamà, M.E.F.; Aiello, M.; Borka, G.; Furci, J.; Parodi, I.; Firpo, G.; Scaglione, S. A Dynamic Double-Flow Gut-On-Chip Model for Predictive Absorption Studies In Vitro. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2025, 10, 2401661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, R.; Shafi, S.; Yang, Y.; Liu, G.; Liu, S.B. Research progress of intestinal microbiota in targeted therapy and immunotherapy of colorectal cancer. J. Cancer Metastasis Treat. 2024, 10, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.W.; Du, P.; Gao, J.; Yang, B.R.; Fang, W.J.; Ying, C.M. Preoperative probiotics decrease postoperative infectious complications of colorectal cancer. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2012, 343, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).