Pseudoaneurysm Versus Chronic Expanding Hematoma on MRI: Hematoma-like Lesions with Distinct Therapeutic Strategies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. MRI Acquisition
2.3. Image Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. MRI Features Regarding Morphology, Internal Characteristics, Pulsatile Artifact, and Relationship to Adjacent Structures
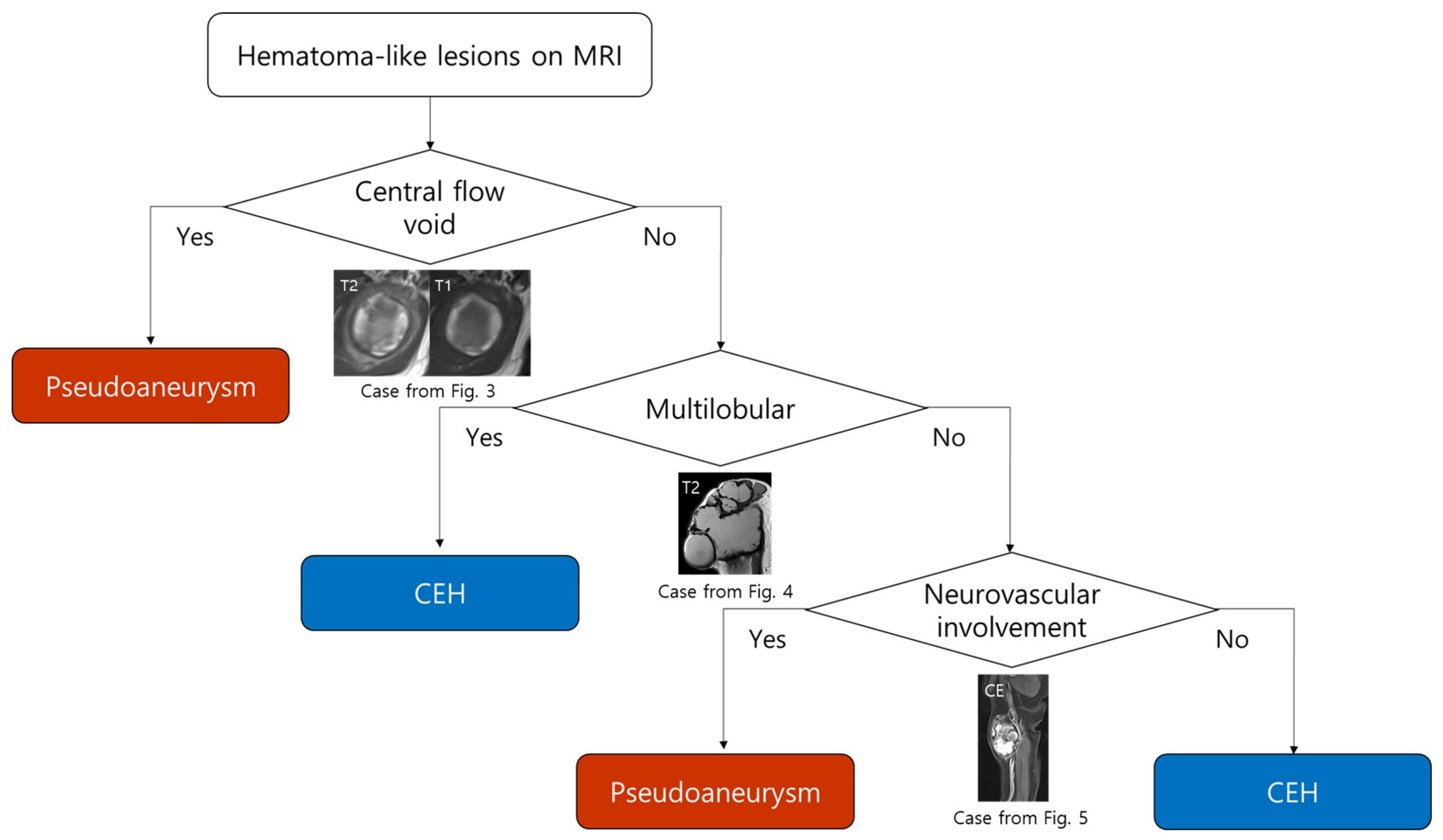
3.3. MRI-Based Diagnostic Flowchart for Differentiating Pseudoaneurysm and CEH
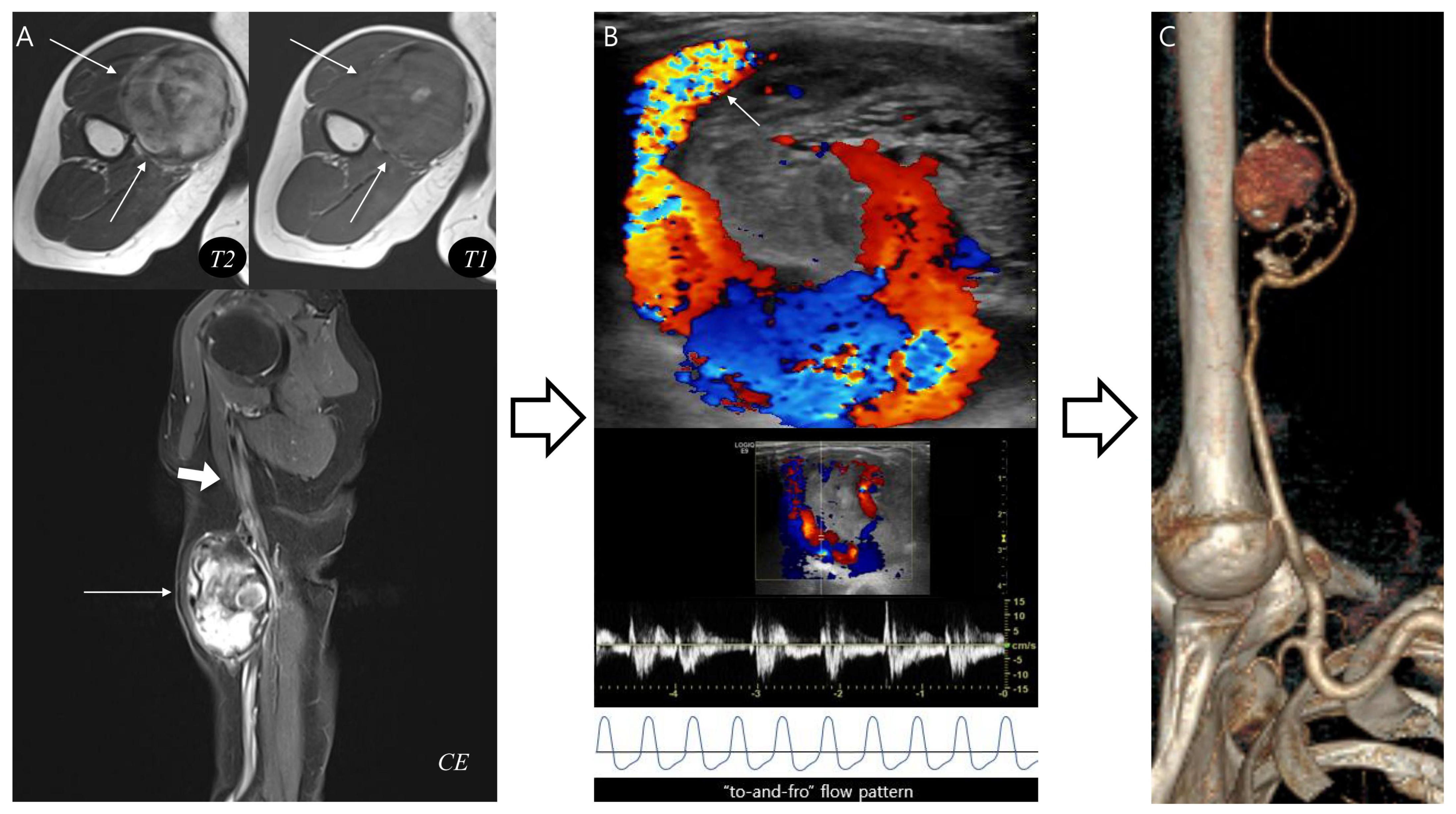
3.4. Application of the Diagnostic Flowchart: Representative Cases
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bruno, F.; Arrigoni, F.; Mariani, S.; Splendiani, A.; Di Cesare, E.; Masciocchi, C.; Barile, A. Advanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of soft tissue tumors: Techniques and applications. La Radiol. Med. 2019, 124, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frassica, F.J.; Khanna, J.A.; McCarthy, E.F. The role of MR imaging in soft tissue tumor evaluation: Perspective of the orthopedic oncologist and musculoskeletal pathologist. Magn. Reson. Imaging Clin. N. Am. 2000, 8, 915–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Lee, S.K.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, J.H. Pitfalls of Diffusion-Weighted Imaging: Clinical Utility of T2 Shine-through and T2 Black-out for Musculoskeletal Diseases. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- van Vliet, M.; Kliffen, M.; Krestin, G.P.; van Dijke, C.F. Soft tissue sarcomas at a glance: Clinical, histological, and MR imaging features of malignant extremity soft tissue tumors. Eur. Radiol. 2009, 19, 1499–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Lee, T.; Oh, E.; Yoon, Y.C. Temporal Evolution of a Chronic Expanding Organizing Hematoma on MRI, Including Functional MR Imaging Techniques: A Case Report. Investig. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2017, 21, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Jee, W.-H.; Whang, Y.S.; Jung, C.K.; Chung, Y.-G.; Lee, S.-Y. Benign versus Malignant Soft-Tissue Tumors: Differentiation with 3T Magnetic Resonance Image Textural Analysis Including Diffusion-Weighted Imaging. Investig. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2021, 25, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra Del Carpio, G.; Tapia Viñé, M.; Torena, N.; Bernabeu Taboada, D. Chronic expanding hematoma. Radiol. (Engl. Ed.) 2023, 65 (Suppl. S2), S78–S82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, I.S.; Song, Y.S.; Choi, Y.J.; Kim, J.I.; Choi, K.-U.; Kim, K.; Kang, S.; Grimm, R.; Nickel, M.D. Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced MRI in the Evaluation of Soft Tissue Tumors and Tumor-Like Lesions: Technical Principles and Clinical Applications. Korean J. Radiol. 2025, 26, 1054–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araki, Y.; Yamamoto, N.; Higuchi, T.; Tsuchiya, H. A Traumatic Intermuscular Hematoma Mimicking a Soft-tissue Tumor: A Case Report and Literature Review. In Vivo 2022, 36, 3018–3022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ward, W.G.; Sr Rougraff, B.; Quinn, R.; Damron, T.; O’Connor, M.I.; Turcotte, R.E.; Cline, M. Tumors masquerading as hematomas. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2007, 465, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albert, S.; Daniel, S.; Gouse, M.; Cherian, V.M. Case of pseudoaneurysm mimicking a soft tissue sarcoma: A diagnostic pitfall. Malays. J. Med. Sci. 2015, 22, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sreenivas, M.; Nihal, A.; Ettles, D.F. Chronic haematoma or soft-tissue neoplasm? A diagnostic dilemma. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 2004, 124, 495–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sule, A.A.; Sah, S.; Kwan, J.; Punamiya, S.; Shelat, V.G. Visceral Arterial Pseudoaneurysms—A Clinical Review. Medicina 2025, 61, 1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, A.; Matsuda, S. Chronic expanding hematoma: A late complication 45 years after thoracoplasty. J. Thorac. Dis. 2017, 9, E6–E9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, P.A.; Martinez, M.; Thompson, S.N.; Masinter, D.; Campbell, J.E.; Campbell, J.R., II; AbuRahma, A.F. Ten-Year Experience of Vascular Surgeon Management of Iatrogenic Pseudoaneurysms: Do Anticoagulant and/or Antiplatelet Medications Matter? Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2016, 30, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sueyoshi, E.; Sakamoto, I.; Nakashima, K.; Minami, K.; Hayashi, K. Visceral and peripheral arterial pseudoaneurysms. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2005, 185, 741–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamoto, A.; Okamoto, T.; Matsuda, S. Chronic Expanding Hematoma in the Extremities: A Clinical Problem of Adhesion to the Surrounding Tissues. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 4634350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Dohan, A.; Darnige, L.; Sapoval, M.; Pellerin, O. Spontaneous soft tissue hematomas. Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2015, 96, 789–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goyal, S.; Rangankar, V.; Deshmukh, S.; Prabhu, A.; Johnson, S. MRI Evaluation of Soft Tissue Tumors and Tumor-Like Lesions of Extremities. Cureus 2023, 15, e37047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Vadapalli, R.; Hegde, G.; Botchu, R. MRI imaging of soft tissues tumours and tumour like lesions-SLAM approach. J. Clin. Orthop. Trauma 2022, 28, 101872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gassenmaier, S.; Tsiflikas, I.; Maennlin, S.; Urla, C.; Warmann, S.W.; Schaefer, J.F. Retrospective accuracy analysis of MRI based lesion size measurement in neuroblastic tumors: Which sequence should we choose? BMC Med. Imaging 2020, 20, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Reid, J.D.; Kommareddi, S.; Lankerani, M.; Park, M.C. Chronic expanding hematomas. A clinicopathologic entity. JAMA 1980, 244, 2441–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, T.; Nakata, H.; Watanabe, H.; Maeda, H.; Toyonaga, T.; Hashimoto, H.; Nakamura, T. The radiological findings in chronic expanding hematoma. Skelet. Radiol. 1999, 28, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomori, J.M.; Grossman, R.I.; Goldberg, H.I.; Zimmerman, R.A.; Bilaniuk, L.T. Intracranial hematomas: Imaging by high-field MR. Radiology 1985, 157, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saad, N.E.; Saad, W.E.; Davies, M.G.; Waldman, D.L.; Fultz, P.J.; Rubens, D.J. Pseudoaneurysms and the role of minimally invasive techniques in their management. RadioGraphics 2005, 25 (Suppl. S1), S173–S189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prince, M.R.; Yucel, E.K.; Kaufman, J.A.; Harrison, D.C.; Geller, S.C. Dynamic gadolinium-enhanced three-dimensional abdominal MR arteriography. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 1993, 3, 877–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seginer, A.; Niry, D.; Furman-Haran, E.; Kolb, H.; Schmidt, R. Reducing blood flow pulsation artifacts in 3D time-of-flight angiography by locally scrambling the order of the acquisition at 3 T and 7 T. Magn. Reson. Med. 2024, 92, 2081–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soma, T.; Hayashi, N.; Sato, Y.; Ogura, T.; Uehara, M.; Watanabe, H.; Kitoh, Y. A Fundamental Study on the Removal of Vascular Pulsation Artifacts Using U-Net-Based Deep Neural Network. Cureus 2025, 17, e85400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Holzapfel, K.; Regler, J.; Baum, T.; Rechl, H.; Specht, K.; Haller, B.; von Eisenhart-Rothe, R.; Gradinger, R.; Rummeny, E.J.; Woertler, K. Local Staging of Soft-Tissue Sarcoma: Emphasis on Assessment of Neurovascular Encasement-Value of MR Imaging in 174 Confirmed Cases. Radiology 2015, 275, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landis, J.R.; Koch, G.G. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 1977, 33, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno Real, D.; de Araújo Martins-Romêo, D. Imaging of pseudoaneurysms: Key diagnostic findings, causes and complications. Radiol. (Engl. Ed.) 2025, 67, 202–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehman, V.T.; Brinjikji, W.; Mossa-Basha, M.; Lanzino, G.; Rabinstein, A.A.; Kallmes, D.F.; Huston, J. Conventional and high-resolution vessel wall MRI of intracranial aneurysms: Current concepts and new horizons. J. Neurosurg. 2018, 128, 969–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, W.B.; Wang, W.Z.; Sun, S.; Mi, Y.C.; Xu, Q.; Chen, Y.E.; Yang, S.; Tao, D.; Xu, W.; Xu, C. Interventional therapy for renal artery pseudoaneurysms. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2012, 13, 1595–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samim, M.; Mandell, J.; Smith, S.; Kapoor, N.; Czuczman, G. Arterial pseudoaneurysms of the shoulder mimicking other entities: Utilization of pulsation artifact on musculoskeletal MR for accurate diagnosis in 2 cases. Skelet. Radiol. 2017, 46, 1119–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Cheng, J.-L.; Li, H.-L.; Wang, J. Formation and suppression technique for motion and flow artifacts on magnetic resonance imaging. Zhongguo Yi Liao Qi Xie Za Zhi = Chin. J. Med. Instrum. 2009, 33, 116–119. [Google Scholar]
- Pravdivtseva, M.; Gaidzik, F.; Berg, P.; Hoffman, C.; Rivera, L.; Medero, R.; Bodart, L.; Roldan--Alzate, A.; Speidel, M.A.; Johnson, K.M.; et al. Pseudo-Enhancement in Intracranial Aneurysms on Black-Blood MRI: Effects of Flow Rate, Spatial Resolution, and Additional Flow Suppression. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2021, 54, 888–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, A.; McLoughlin, E.; Patel, A.; James, S.L.; Botchu, R.; Davies, A.M. Osteochondroma-induced pseudoaneurysms of the extremities mimicking sarcoma: A report of seven contemporary and one historical case. Clin. Radiol. 2020, 75, 642.e9–642.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahed, K.; Khazai, B.; Umpierrez, M.; Subhawong, T.K.; Singer, A.D. Pitfalls in soft tissue sarcoma imaging: Chronic expanding hematomas. Skelet. Radiol. 2018, 47, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyasaka, Y.; Hiyama, T.; Kuno, H.; Shinozaki, T.; Sakashita, S.; Kobayashi, T. Characteristic imaging findings in a patient with chronic expanding hematoma on the floor of the mouth. Int. Cancer Conf. J. 2023, 12, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ito, T.; Nakahara, T.; Takeuchi, S.; Uchi, H.; Takahara, M.; Moroi, Y.; Furue, M. Four cases of successfully treated chronic expanding soft tissue hematoma. Ann. Dermatol. 2014, 26, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]



| Pseudoaneurysm | CEH | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 6) | (n = 6) | ||
| Age (years) | 70.7 ± 10.6 | 66.3 ± 5.6 | 0.403 |
| Sex | 1.000 | ||
| Male (%) | 3 (50.0) | 4 (66.7) | |
| Female (%) | 3 (50.0) | 2 (33.3) | |
| Depth | |||
| Subcutaneous fat layer (%) | 0 (0.0) | 5 (83.3) | 0.015 |
| Fascial layer (%) | 0 (0.0) | 2 (33.3) | 0.454 |
| Muscle (%) | 6 (100.0) | 3 (50.0) | 0.181 |
| Maximum size (cm) | 6.1 ± 3.3 | 13.5 ± 3.9 | 0.005 |
| Pseudoaneurysm | CEH | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 6) | (n = 6) | ||
| Morphology | 0.0024 | ||
| Multilobular | 0 (0.0%) | 6 (100.0%) | |
| Ovoid | 6 (100.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | |
| Outermost peripheral low SI on T1WI | 6 (100.0%) | 6 (100.0%) | 1.000 |
| Inner peripheral high SI on T1WI | 5 (83.3%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0.015 |
| Central high SI on T1WI | 4 (66.7%) | 6 (100.0%) | 0.454 |
| Central flow void on T1,T2WI | 6 (100.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0.002 |
| Septation | 0 (0.0%) | 5 (83.3%) | 0.015 |
| Nodular enhancement | 4 (66.7%) | 5 (83.3%) | 1.000 |
| Pulsatile artifact | 3 (50.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0.181 |
| Neurovascular bundle involvement | 6 (100.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0.002 |
| MRI Feature | Kappa | 95% CI | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Morphology | 0.80 | 0.45–1.00 | 0.003 |
| Outermost peripheral low SI on T1WI | 1.00 | 1.00–1.00 | <0.001 |
| Inner peripheral high SI on T1WI | 0.78 | 0.42–1.00 | 0.004 |
| Central high SI on T1WI | 0.74 | 0.35–0.98 | 0.006 |
| Central flow void on T1,T2WI | 0.80 | 0.41–1.00 | 0.003 |
| Septation | 1.00 | 1.00–1.00 | <0.001 |
| Nodular enhancement | 1.00 | 1.00–1.00 | <0.001 |
| Pulsatile artifact | 1.00 | 1.00–1.00 | <0.001 |
| Neurovascular bundle involvement | 1.00 | 1.00–1.00 | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, S.K.; Kim, J.-H.; Kim, J.-Y. Pseudoaneurysm Versus Chronic Expanding Hematoma on MRI: Hematoma-like Lesions with Distinct Therapeutic Strategies. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 2834. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13112834
Lee SK, Kim J-H, Kim J-Y. Pseudoaneurysm Versus Chronic Expanding Hematoma on MRI: Hematoma-like Lesions with Distinct Therapeutic Strategies. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(11):2834. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13112834
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Seul Ki, Jun-Ho Kim, and Jee-Young Kim. 2025. "Pseudoaneurysm Versus Chronic Expanding Hematoma on MRI: Hematoma-like Lesions with Distinct Therapeutic Strategies" Biomedicines 13, no. 11: 2834. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13112834
APA StyleLee, S. K., Kim, J.-H., & Kim, J.-Y. (2025). Pseudoaneurysm Versus Chronic Expanding Hematoma on MRI: Hematoma-like Lesions with Distinct Therapeutic Strategies. Biomedicines, 13(11), 2834. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13112834





