Systemic Immune Profiling Reveals Candidate Biomarkers in Luminal A Breast Cancer: A Comparative Pilot Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants and Sample Collection
2.2. Characterization of Immune Cells by Flow Cytometry
2.3. Flow Cytometry Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Cellularity Characterization in Samples from Patients with Luminal A Breast Cancer
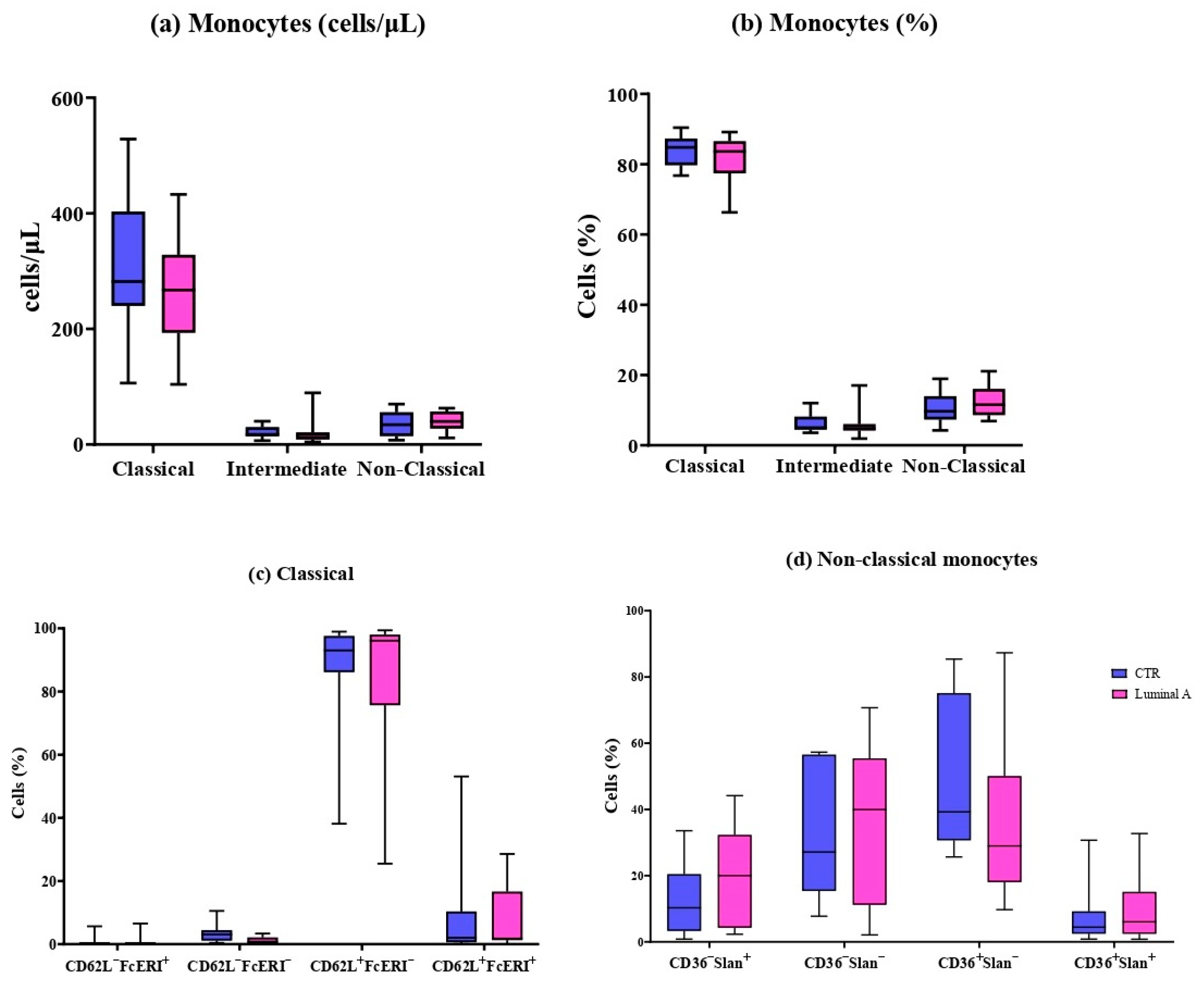
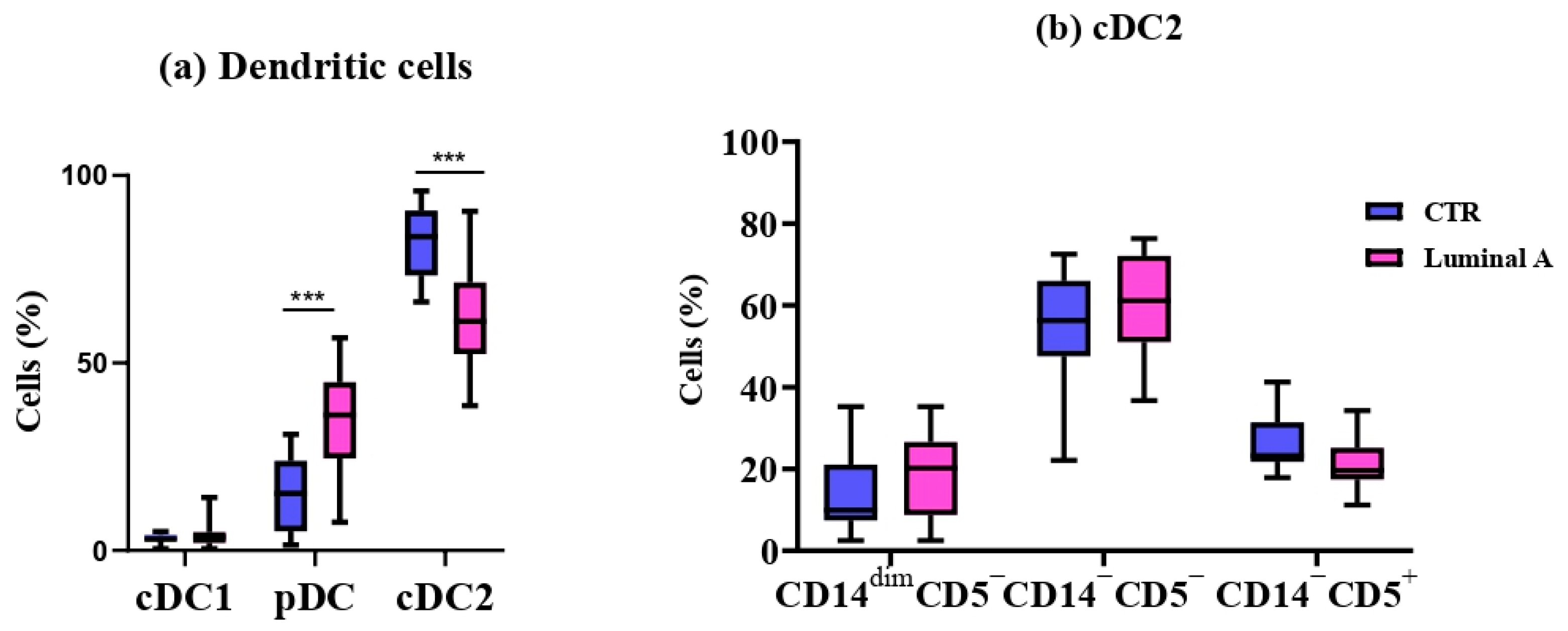
3.2. Detailed Immunophenotyping of 11 Monocyte and 6 Dendritic Cell Subpopulations
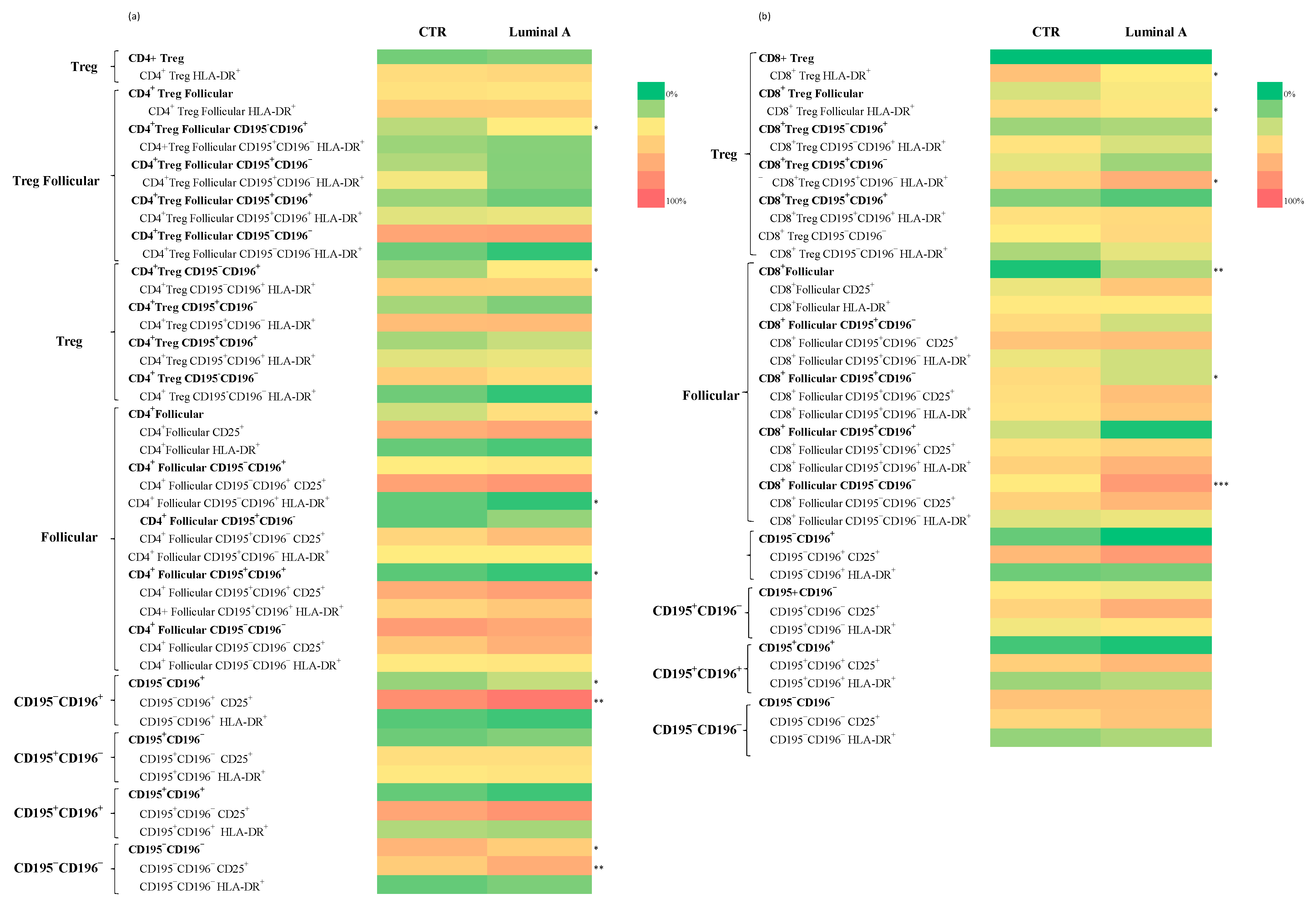
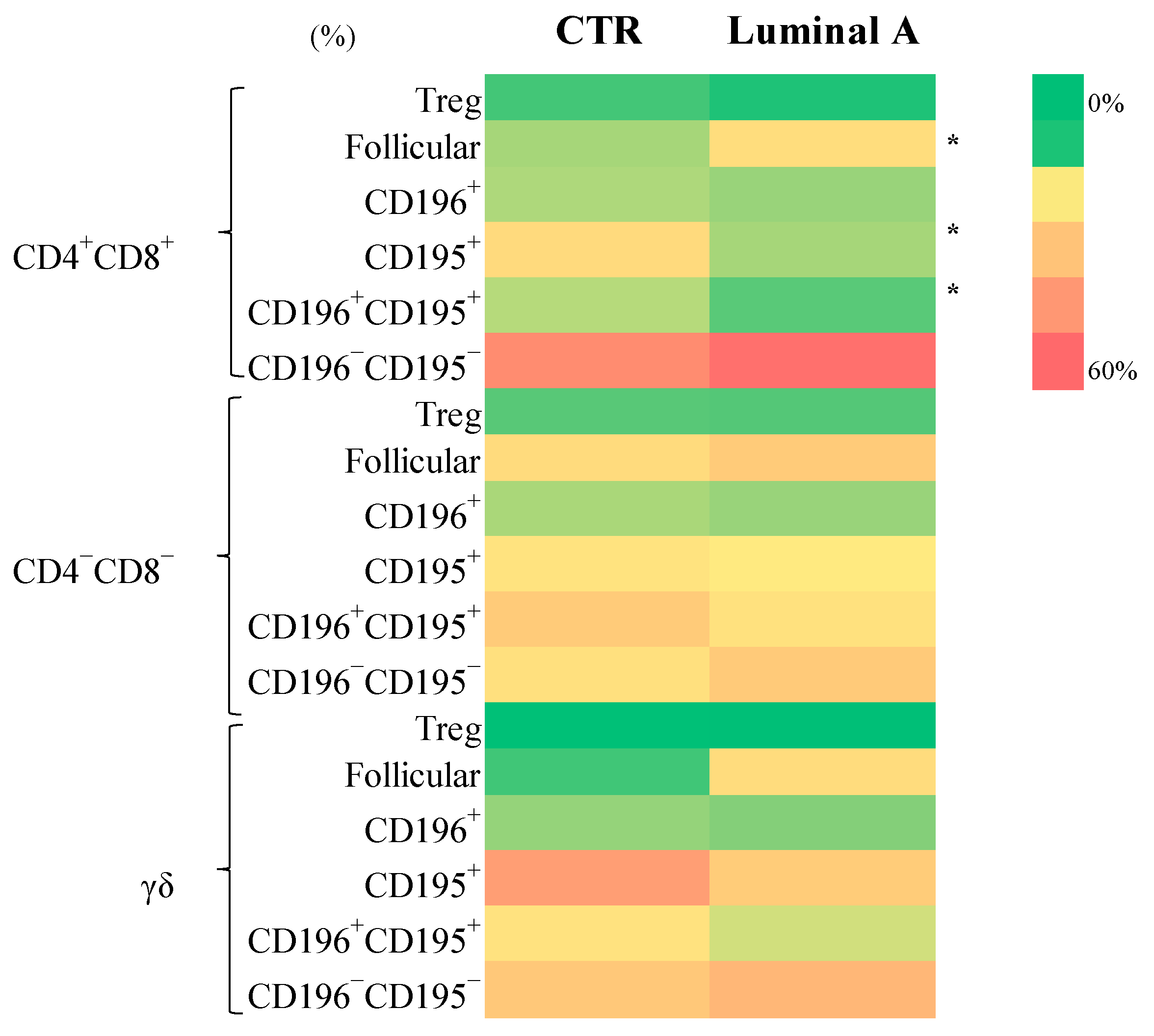
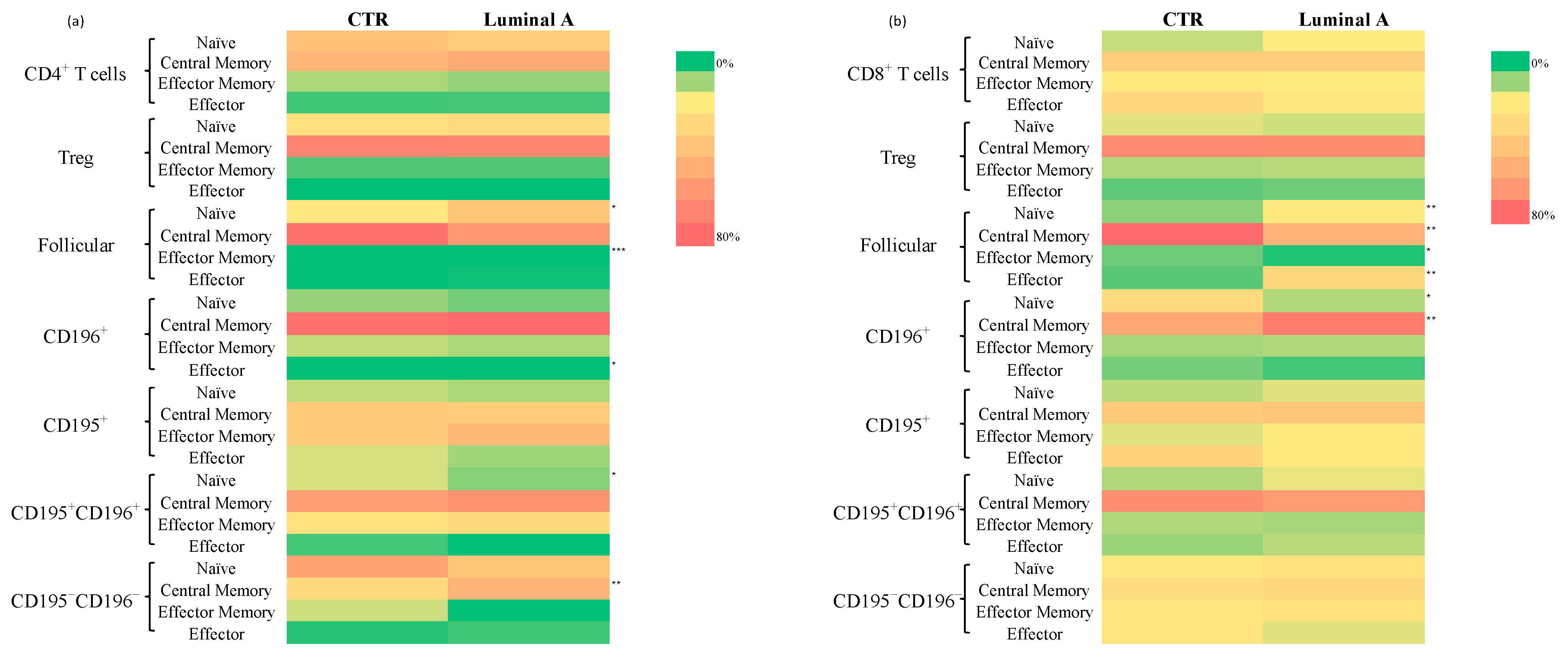
3.3. Extensive Immunophenotypic Characterization of 234 T Cell Subsets
Analysis of T Cell Subpopulations in CD4+ and CD8+ Cells in Control and Luminal A Breast Cancer
3.4. Diagnostic Performance of Biomarkers in the Classification of Luminal A Breast Cancer
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candanedo-Gonzalez, F.; Lilia Remirez-Castellanos, A.; Salazar-Gomez, U.; Valenzuela-Gonzalez, W.; Chavira-Macias, C.; Gamboa-Dominguez, A. Breast Cancer Heterogeneity and Its Implication in Precision Therapy. In Latest Research on Breast Cancer [Working Title]; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Łukasiewicz, S.; Czeczelewski, M.; Forma, A.; Baj, J.; Sitarz, R.; Stanisławek, A. Breast Cancer—Epidemiology, Risk Factors, Classification, Prognostic Markers, and Current Treatment Strategies—An Updated Review. Cancers 2021, 13, 4287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira Almeida, C.; Correia-da-Silva, G.; Teixeira, N.; Amaral, C. Influence of Tumor Microenvironment on the Different Breast Cancer Subtypes and Applied Therapies. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2024, 223, 116178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höller, A.; Nguyen-Sträuli, B.D.; Frauchiger-Heuer, H.; Ring, A. Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarkers of Luminal Breast Cancer: Where Are We Now? Breast Cancer 2023, 15, 525–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moura, T.; Caramelo, O.; Silva, I.; Silva, S.; Gonçalo, M.; Portilha, M.A.; Moreira, J.N.; Gil, A.M.; Laranjeira, P.; Paiva, A. Early-Stage Luminal B-like Breast Cancer Exhibits a More Immunosuppressive Tumor Microenvironment than Luminal A-like Breast Cancer. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huertas-Caro, C.A.; Ramírez, M.A.; Rey-Vargas, L.; Bejarano-Rivera, L.M.; Ballen, D.F.; Nuñez, M.; Mejía, J.C.; Sua-Villegas, L.F.; Cock-Rada, A.; Zabaleta, J.; et al. Tumor Infiltrating Lymphocytes (TILs) Are a Prognosis Biomarker in Colombian Patients with Triple Negative Breast Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 21324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liefaard, M.C.; Van Der Voort, A.; Van Seijen, M.; Thijssen, B.; Sanders, J.; Vonk, S.; Mittempergher, L.; Bhaskaran, R.; De Munck, L.; Van Leeuwen-Stok, A.E.; et al. Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes in HER2-Positive Breast Cancer Treated with Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy and Dual HER2-Blockade. npj Breast Cancer 2024, 10, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heras-Murillo, I.; Adán-Barrientos, I.; Galán, M.; Wculek, S.K.; Sancho, D. Dendritic Cells as Orchestrators of Anticancer Immunity and Immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 21, 257–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, N.A.M.; Garner, H.; Van Dyk, E.; Champanhet, E.; Klaver, C.; Duijst, M.; Voorwerk, L.; Nederlof, I.; Voorthuis, R.; Liefaard, M.C.; et al. Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Modifies the Systemic Immune Landscape and Alters Neutrophil Functionality. npj Breast Cancer 2025, 11, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philip, M.; Schietinger, A. CD8+ T Cell Differentiation and Dysfunction in Cancer. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2022, 22, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polanczyk, M.J.; Hopke, C.; Vandenbark, A.A.; Offner, H. Estrogen-Mediated Immunomodulation Involves Reduced Activation of Effector T Cells, Potentiation of Treg Cells, and Enhanced Expression of the PD-1 Costimulatory Pathway. J. Neurosci. Res. 2006, 84, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto, G.A.; Rosenstein, Y. Oestradiol Potentiates the Suppressive Function of Human CD4+ CD25+ Regulatory T Cells by Promoting Their Proliferation. Immunology 2006, 118, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuliano, A.E.; Edge, S.B.; Hortobagyi, G.N. Eighth Edition of the AJCC Cancer Staging Manual: Breast Cancer. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2018, 25, 1783–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Der Burg, M.; Kalina, T.; Perez-Andres, M.; Vlkova, M.; Lopez-Granados, E.; Blanco, E.; Bonroy, C.; Sousa, A.E.; Kienzler, A.-K.; Wentink, M.; et al. The EuroFlow PID Orientation Tube for Flow Cytometric Diagnostic Screening of Primary Immunodeficiencies of the Lymphoid System. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palazón-Carrión, N.; Jiménez-Cortegana, C.; Sánchez-León, M.L.; Henao-Carrasco, F.; Nogales-Fernández, E.; Chiesa, M.; Caballero, R.; Rojo, F.; Nieto-García, M.-A.; Sánchez-Margalet, V.; et al. Circulating Immune Biomarkers in Peripheral Blood Correlate with Clinical Outcomes in Advanced Breast Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 14426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gago-Dominguez, M.; Matabuena, M.; Redondo, C.M.; Patel, S.P.; Carracedo, A.; Ponte, S.M.; Martínez, M.E.; Castelao, J.E. Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio and Breast Cancer Risk: Analysis by Subtype and Potential Interactions. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Li, Y.; Tan, S.; Cheng, T.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, L. Pretreatment Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio Is Associated with Immunotherapy Efficacy in Patients with Advanced Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez Rodriguez, G.; Abrahamsson, A.; Jensen, L.D.E.; Dabrosin, C. Estradiol Promotes Breast Cancer Cell Migration via Recruitment and Activation of Neutrophils. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2017, 5, 234–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, X.; Chen, D.; Yu, J. Radiotherapy Combined with Immunotherapy: The Dawn of Cancer Treatment. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wang, W.; Hu, S.; Jia, B.; Tuo, B.; Sun, H.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Sun, Z. Radiotherapy Remodels the Tumor Microenvironment for Enhancing Immunotherapeutic Sensitivity. Cell Death Dis. 2023, 14, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dash, S.P.; Gupta, S.; Sarangi, P.P. Monocytes and Macrophages: Origin, Homing, Differentiation, and Functionality during Inflammation. Heliyon 2024, 10, e29686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kos, K.; Salvagno, C.; Wellenstein, M.D.; Aslam, M.A.; Meijer, D.A.; Hau, C.-S.; Vrijland, K.; Kaldenbach, D.; Raeven, E.A.M.; Schmittnaegel, M.; et al. Tumor-Associated Macrophages Promote Intratumoral Conversion of Conventional CD4+ T Cells into Regulatory T Cells via PD-1 Signalling. OncoImmunology 2022, 11, 2063225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Tang, Z.; Gao, S.; Li, C.; Feng, Y.; Zhou, X. Tumor-Associated Macrophages: Recent Insights and Therapies. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paek, S.H.; Kim, H.G.; Lee, J.W.; Woo, J.; Kwon, H.; Kim, J.B.; Lim, W.; Kim, J.R.; Moon, B.-I.; Paik, N.-S. Circulating Plasmacytoid and Myeloid Dendritic Cells in Breast Cancer Patients: A Pilot Study. J. Breast Cancer 2019, 22, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, H.H.; Or, Y.Z.; Shrestha, S.; Loh, J.T.; Lim, C.L.; Ong, Z.; Woo, A.R.E.; Su, I.-H.; Lin, V.C.L. Estrogen Reprograms the Activity of Neutrophils to Foster Protumoral Microenvironment during Mammary Involution. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 46485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, P.; Wang, J.; Jin, H.; Song, X.; Yan, J.; Kang, Y.; Zhao, L.; An, X.; Du, X.; Chen, X.; et al. Induction of Regulatory T Cells by Physiological Level Estrogen. J. Cell. Physiol. 2008, 214, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, H.; Nakayamada, S.; Tanaka, Y. Differentiation, Functions, and Roles of T Follicular Regulatory Cells in Autoimmune Diseases. Inflamm. Regen. 2021, 41, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, X.; Guo, Q.; Pan, Z.; Xu, X.; Shao, X.; Wang, X. The Characteristics and Novel Clinical Implications of CD4+CXCR5+Foxp3+ Follicular Regulatory T Cells in Breast Cancer. Ann. Transl. Med. 2021, 9, 1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-H.; Park, H.-J.; Park, H.-S.; Lee, J.-U.; Ko, C.; Gye, M.C.; Choi, J.-M. Estrogen Receptor α in T Cells Suppresses Follicular Helper T Cell Responses and Prevents Autoimmunity. Exp. Mol. Med. 2019, 51, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moura, T.; Laranjeira, P.; Caramelo, O.; Gil, A.M.; Paiva, A. Breast Cancer and Tumor Microenvironment: The Crucial Role of Immune Cells. Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variable | n = 13 |
|---|---|
| Age | |
| Mean ± SD | 63 ± 7 |
| Histological Grade, n (%) | |
| I | 10 (77%) |
| II | 3 (23%) |
| III | 0 (0%) |
| Ki-67, n (%) | |
| >5 | 8 (67%) |
| 5–10 | 3 (25%) |
| 10–15 | 1 (8%) |
| Tumor Size, n (%) | |
| 5–10 mm | 3 (23%) |
| 10–20 mm | 8 (62%) |
| <20 mm | 2 (15%) |
| Lymph Node Status, n (%) | |
| N0 | 10 (77%) |
| N1 | 3 (23%) |
| N2 | 0 (0%) |
| Cells Type | Controls | Luminal A | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| WBC (cells/μL) | 4914 ± 1492 | 6012 ± 1450 | 0.06 |
| Eosinophils (cells/μL) | 116 ± 95 | 78 ± 51 | 0.22 |
| Eosinophils (%) | 2.25 ± 1.59 | 1.41 ± 1.12 | 0.09 |
| Neutrophils (cells/μL) | 2881 ± 1188 | 3679 ± 1070 * | 0.05 |
| Neutrophils (%) | 58 ± 9.78 | 62 ± 11 | 0.37 |
| Monocytes (cells/μL) | 354 ± 137 | 328 ± 122 | 0.49 |
| Monocytes (%) | 7.21 ± 2.08 | 5.67 ± 2.64 * | 0.034 |
| Lymphocytes (cells/μL) | 1512 ± 585 | 1843 ± 895 | 0.27 |
| Lymphocytes (%) | 32 ± 9.37 | 31 ± 11.7 | 0.63 |
| T cells (cells/μL) | 1031 ± 615 | 1204 ± 629 | 0.40 |
| T cells (%) (within lymphocytes) | 21 ± 10 | 20 ± 10 | 0.65 |
| Dendritic cells (cells/μL) | 16 ± 6.19 | 14 ± 5.88 | 0.53 |
| Dendritic cells (%) | 0.33 ± 0.10 | 0.24 ± 0.12 * | 0.029 |
| Basophils (cells/μL) | 36 ± 27 | 35 ± 19 | 0.85 |
| Basophils (%) | 0.74 ± 0.44 | 0.57 ± 0.25 | 0.24 |
| Dendritic Cell Subtypes | Controls | Luminal A | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| cDC1 (cells/uL) | 0.52 ± 0.32 | 0.71 ± 0.88 | 0.78 |
| cDC1 (%) | 0.0105 ± 0.005 | 0.012 ± 0.0156 | 0.374 |
| pDC (cells/uL) | 2.31 ± 1.85 | 4.88 ± 2.94 * | 0.017 |
| pDC (%) | 0.049 ± 0.037 | 0.085 ± 0.056 | 0.095 |
| cDC2 (cells/uL) | 13 ± 5.64 | 8.49 ± 3.15 * | 0.04 |
| cDC2 (%) | 0.26 ± 0.088 | 0.146 ± 0.065 *** | 0.0001 |
| T Cells | Controls | Luminal A | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| CD4+ (cells/μL) | 499 ± 192 | 630 ± 342 | 0.26 |
| CD4+ (%) | 61 ± 12 | 64 ± 11 | 0.54 |
| CD8+ (cells/μL) | 251 ± 163 | 341 ± 291 | 0.35 |
| CD8+ (%) | 33 ± 12 | 30 ± 9.46 | 0.40 |
| CD4+CD8+ (cells/μL) | 9.05 ± 4.77 | 24 ± 30 | 0.10 |
| CD4+CD8+ (%) | 1.41 ± 1.21 | 2.70 ± 3.16 | 0.16 |
| CD4−CD8− (cells/μL) | 3.42 ± 2.84 | 5.82 ± 5.16 | 0.17 |
| CD4−CD8− (%) | 0.59 ± 0.33 | 0.62 ± 0.20 | 0.49 |
| γδ (cells/μL) | 24 ± 21 | 27 ± 30 | 0.77 |
| γδ (%) | 3.31± 3.25 | 2.57 ± 3.04 | 0.45 |
| T Cells | Controls | Luminal A | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| CD4+ CD25+ | 49 ± 11 | 67 ± 12 ** | 0.001 |
| CD4+ HLA-DR+ | 9.14 ± 6.98 | 8.11 ± 2.6 | 0.87 |
| CD8+ CD25+ | 39 ± 39 | 59 ± 40 | 0.21 |
| CD8+ HLA-DR+ | 20 ± 9.47 | 16 ± 11 | 0.23 |
| CD4+CD8+ CD25+ | 44 ± 27 | 51 ± 30 | 0.48 |
| CD4+CD8+ HLA-DR+ | 17 ± 12 | 12 ± 7.73 | 0.16 |
| CD4−CD8− CD25+ | 24 ± 13 | 23 ± 6.13 | 0.99 |
| CD4−CD8− HLA-DR+ | 33 ± 19 | 33 ± 15 | 0.99 |
| γδ CD25+ | 19 ± 17 | 19 ± 14 | 0.93 |
| Biomarker | Threshold | Sensitivity | Specificity | AUC | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cDC2 | 0.69 | 69 | 100 | 0.86 | <0.0001 |
| pDC | 0.69 | 69 | 100 | 0.87 | <0.0001 |
| CD4+ Follicular | 20 | 62 | 93 | 0.77 | 0.015 |
| CD4+ Treg CD195−CD196+ | 12.28 | 57 | 92 | 0.79 | 0.012 |
| CD4+CD8+ CD195+ | 11.94 | 77 | 85 | 0.81 | 0.006 |
| CD8+ Follicular | 2.55 | 85 | 64 | 0.80 | 0.007 |
| CD8+ Follicular CD195−CD196− | 29 | 85 | 62 | 0.87 | 0.0014 |
| CD8+ Follicular | 2.41 | 85 | 57 | 0.80 | 0.007 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moura, T.; Caramelo, O.; Silva, I.; Silva, S.; Laranjeira, P.; Paiva, A. Systemic Immune Profiling Reveals Candidate Biomarkers in Luminal A Breast Cancer: A Comparative Pilot Study. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 2787. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13112787
Moura T, Caramelo O, Silva I, Silva S, Laranjeira P, Paiva A. Systemic Immune Profiling Reveals Candidate Biomarkers in Luminal A Breast Cancer: A Comparative Pilot Study. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(11):2787. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13112787
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoura, Tânia, Olga Caramelo, Isabel Silva, Sandra Silva, Paula Laranjeira, and Artur Paiva. 2025. "Systemic Immune Profiling Reveals Candidate Biomarkers in Luminal A Breast Cancer: A Comparative Pilot Study" Biomedicines 13, no. 11: 2787. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13112787
APA StyleMoura, T., Caramelo, O., Silva, I., Silva, S., Laranjeira, P., & Paiva, A. (2025). Systemic Immune Profiling Reveals Candidate Biomarkers in Luminal A Breast Cancer: A Comparative Pilot Study. Biomedicines, 13(11), 2787. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13112787







