Interleukin 6 for the Prediction of Chorioamnionitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Data Synthesis and Statistical Analysis
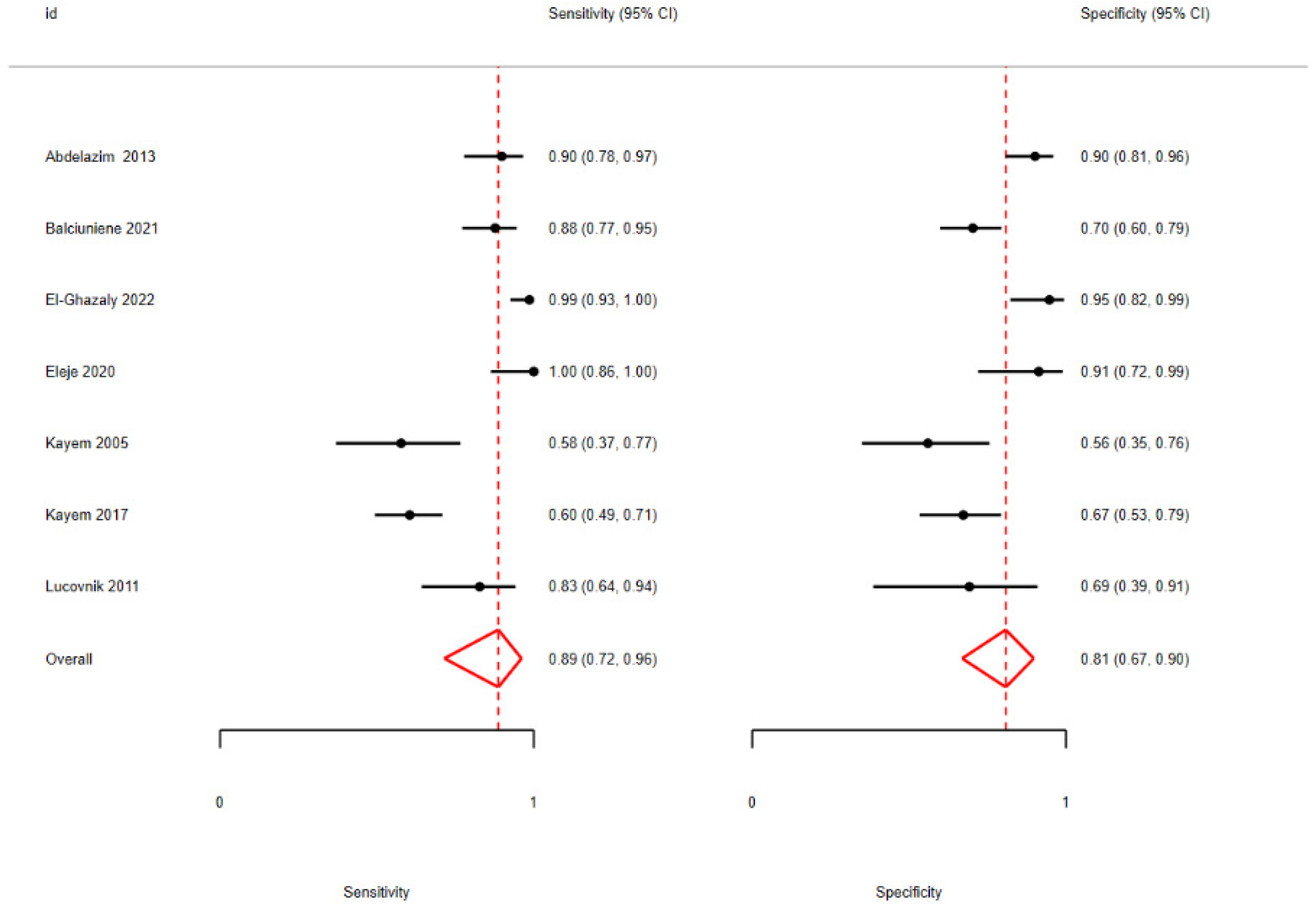
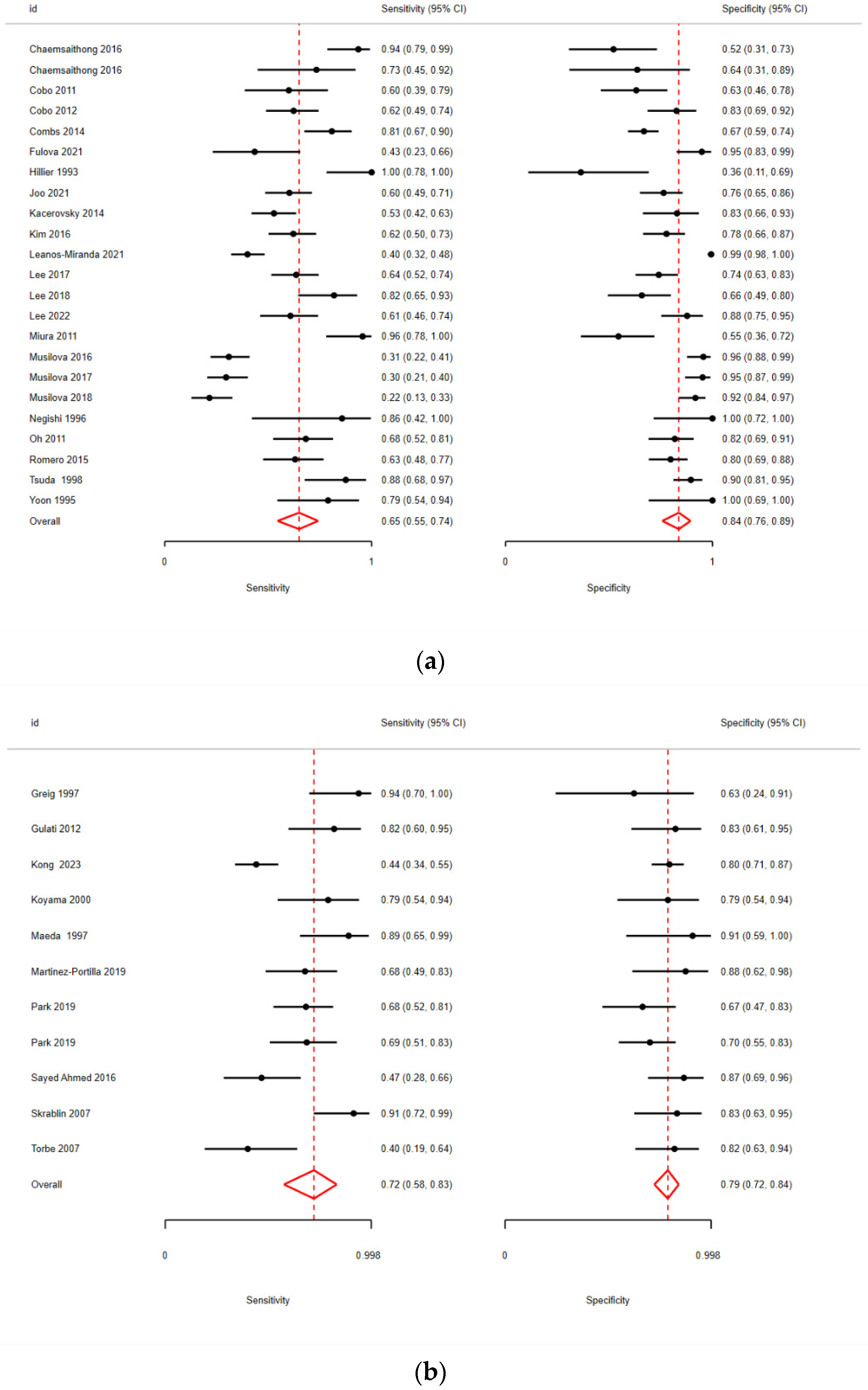
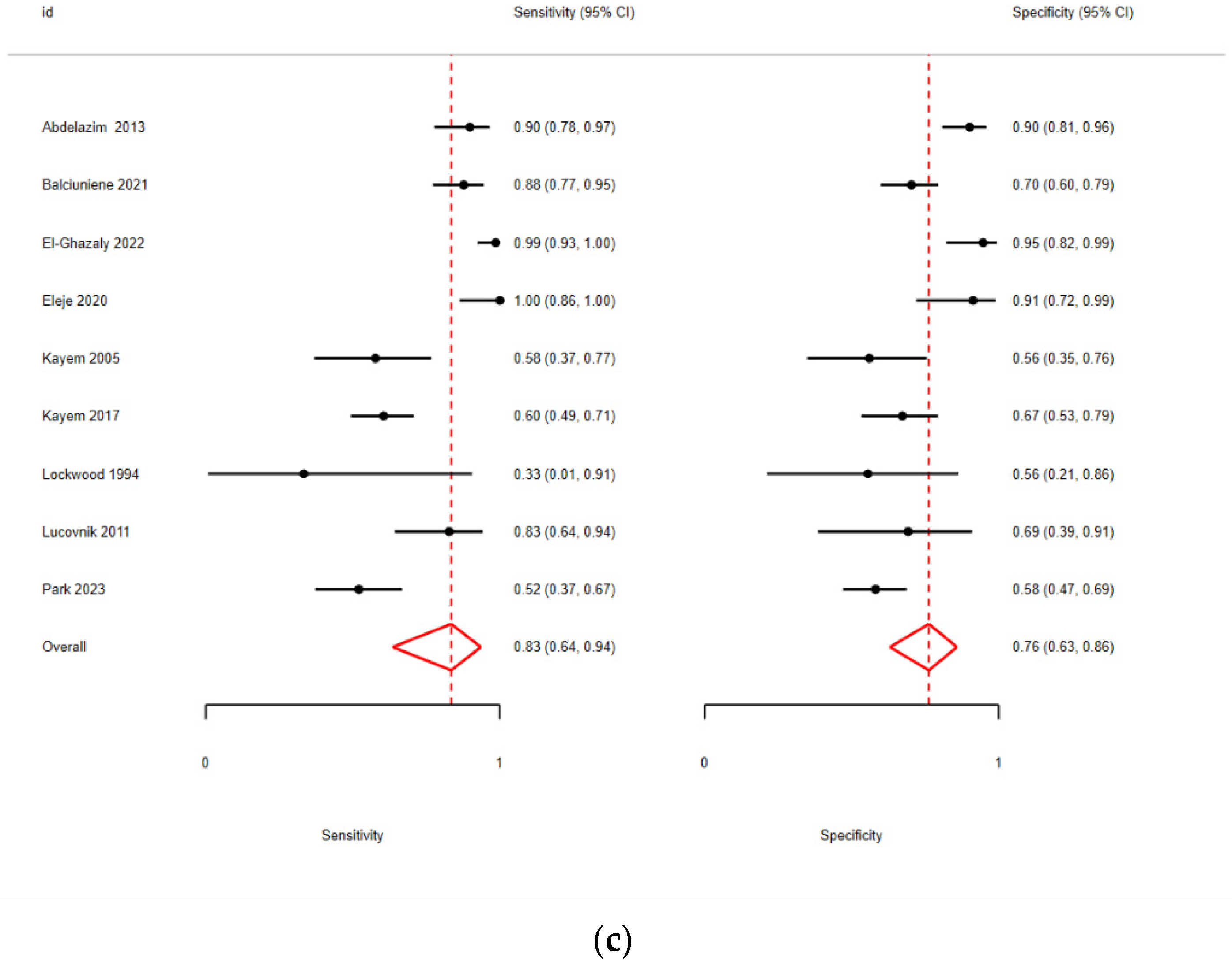
3. Results
3.1. Study Selection and Study Characteristics
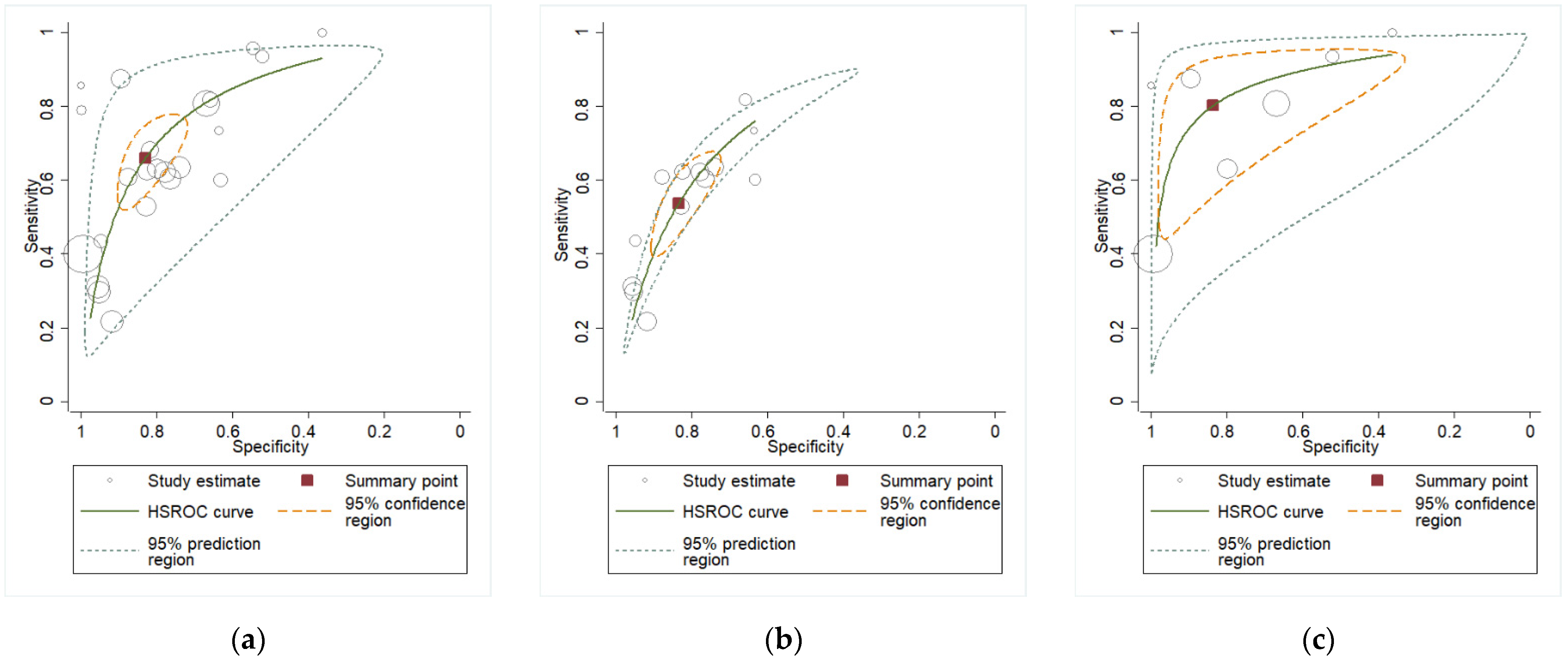
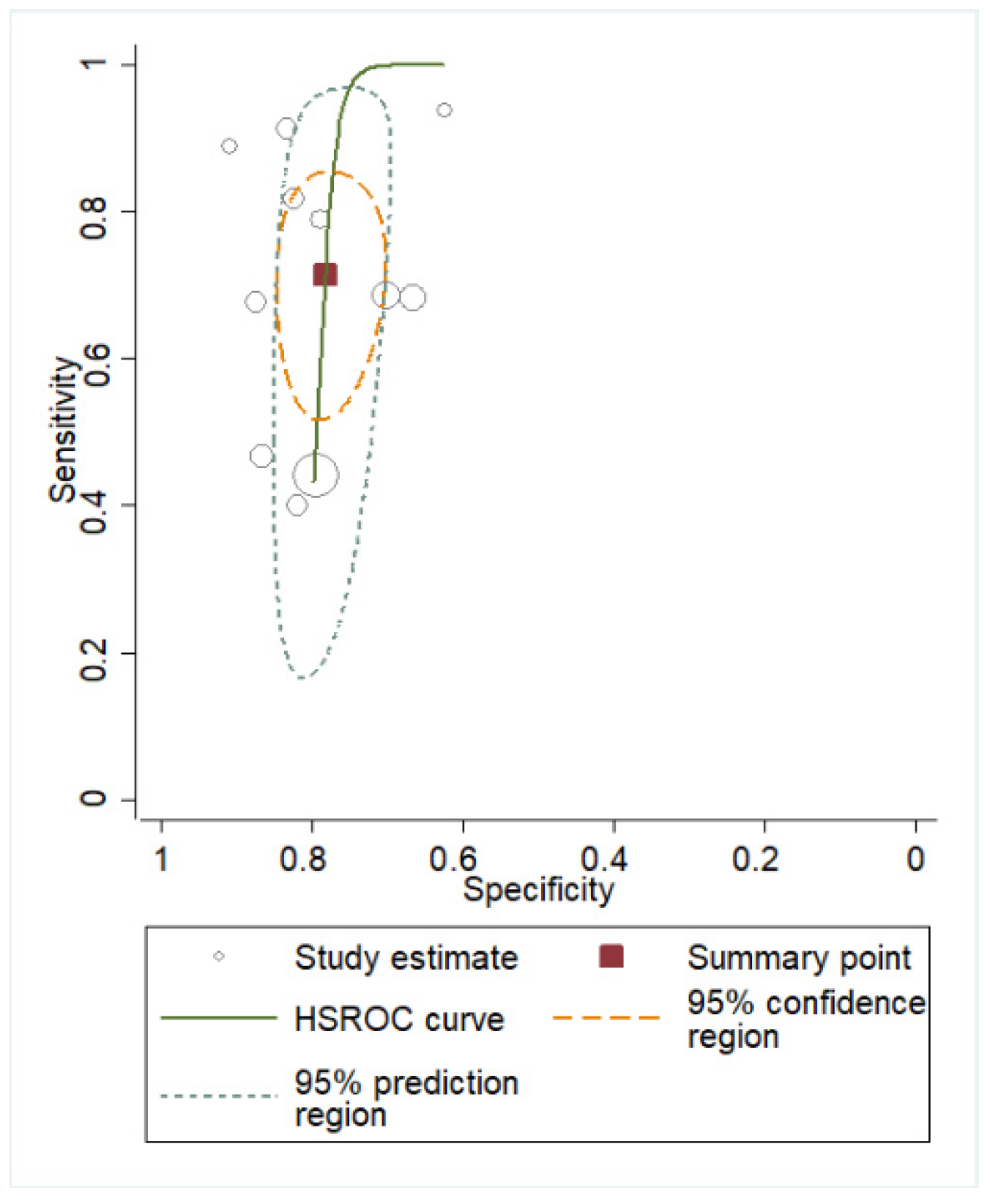
3.2. Quantitative Analysis
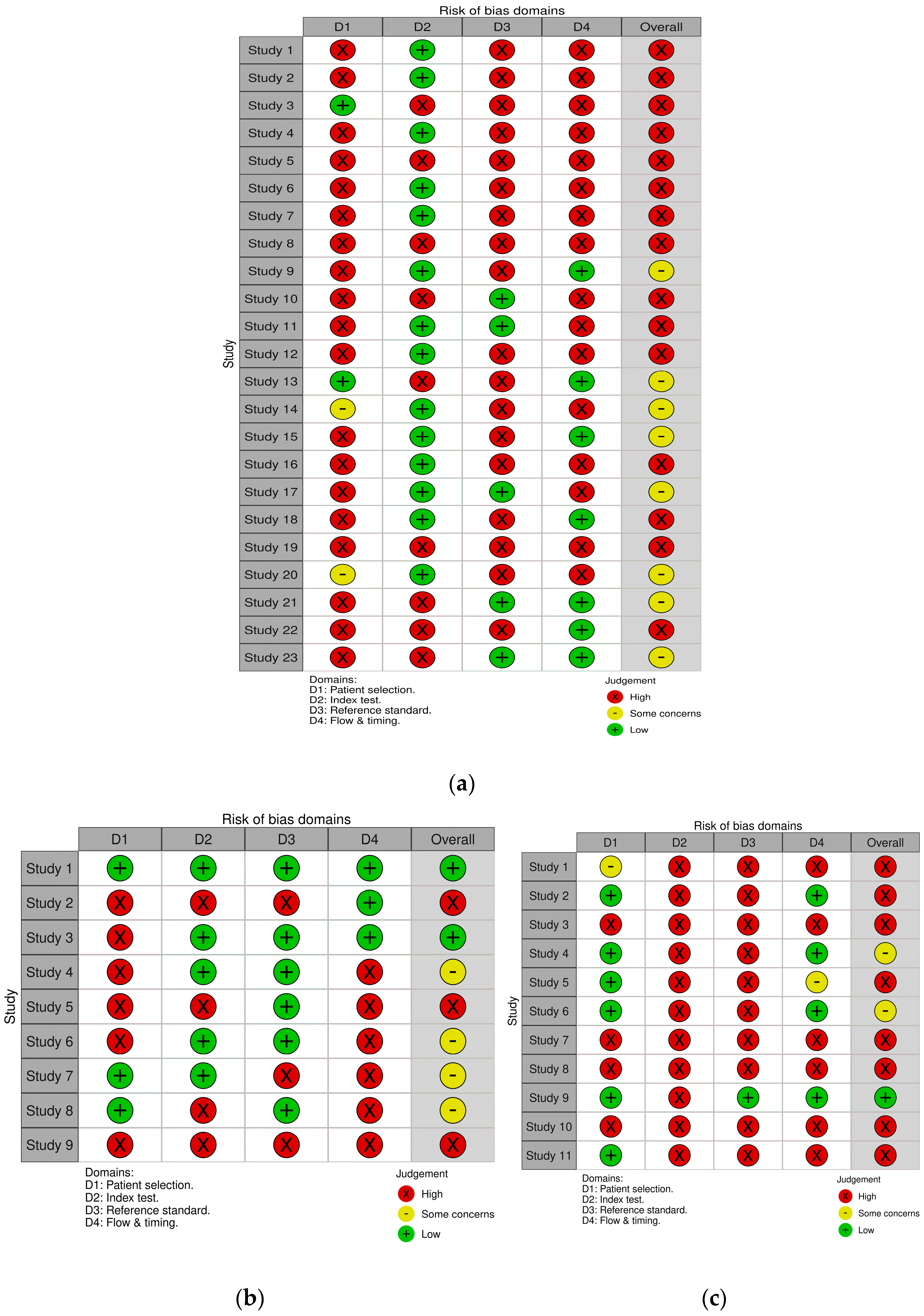
3.3. Quality Assessment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tita, A.T.N.; Andrews, W.W. Diagnosis and Management of Clinical Chorioamnionitis. Clin. Perinatol. 2010, 37, 339–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, R.S.; Blanco, J.D.; St Clair, P.J.; Castaneda, Y.S. Quantitative bacteriology of amniotic fluid from women with clinical intraamniotic infection at term. J. Infect. Dis. 1982, 145, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kachikis, A.; Eckert, L.O.; Walker, C.; Bardají, A.; Varricchio, F.; Lipkind, H.S.; Diouf, K.; Huang, W.-T.; Mataya, R.; Bittaye, M.; et al. Chorioamnionitis: Case definition & guidelines for data collection, analysis, and presentation of immunization safety data. Vaccine 2019, 37, 7610–7622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redline, R.W.; Faye-Petersen, O.; Heller, D.; Qureshi, F.; Savell, V.; Vogler, C.; The Society for Pediatric Pathology, Perinatal Section, Amniotic Fluid Infection Nosology Committee. Amniotic infection syndrome: Nosology and reproducibility of placental reaction patterns. Pediatr. Dev. Pathol. 2003, 6, 435–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garry, D.; Figueroa, R.; Aguero-Rosenfeld, M.; Martinez, E.; Visintainer, P.; Tejani, N. A comparison of rapid amniotic fluid markers in the prediction of microbial invasion of the uterine cavity and preterm delivery. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 1996, 175, 1336–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.A.; Lee, Y.S.; Seo, K. Assessment of predictive markers for placental inflammatory response in preterm births. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooqui, R.; Siddiqui, Q.U.A. Diagnostic accuracy of procalcitonin in maternal plasma to detect early intra-amniotic infection in preterm premature rupture of the membranes with respect of highvaginal swab as gold standard. Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2022, 38, 310–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Park, K.H.; Joo, E.; Lee, M.J.; Choi, B.Y. Potential of plasma inflammatory and angiogenic mediators for predicting spontaneous preterm delivery, intraamniotic infection/inflammation, and composite neonatal morbidity/mortality in women with early preterm premature rupture of membranes. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2024, 91, e13809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobo, T.; Ferrero, S.; Haavisto, A.; Luokola, P.; Sanchez-Garcia, A.B.; Bosch, J.; Gené, A.; Murillo, C.; Rueda, C.; la Presa, B.G.-D.; et al. A multivariable prediction model for intra-amniotic infection in patients with preterm labor and intact membranes including a point of care system that measures amniotic fluid MMP-8. J. Perinat. Med. 2024, 52, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yang, L.; Wang, Y.; Huai, L.; Shi, B.; Zhang, D.; Xu, W.; Cui, D. Interleukin-6 related signaling pathways as the intersection between chronic diseases and sepsis. Mol. Med. Camb. Mass. 2025, 31, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, E.; Park, K.H.; Kim, Y.M.; Ahn, K.; Hong, S. Maternal Plasma and Amniotic Fluid LBP, Pentraxin 3, Resistin, and IGFBP-3: Biomarkers of Microbial Invasion of Amniotic Cavity and/or Intra-amniotic Inflammation in Women with Preterm Premature Rupture of Membranes. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2021, 36, e279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Ghazaly, T.E.; Abdelazim, I.A.; Elshabrawy, A. Interleukin-6 bedside test in detecting chorioamnionitis in women with preterm premature rupture of fetal membranes. Ginekol. Pol. 2022, 93, 835–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, B.; Sun, L.; Liu, K. Predicting chorioamnionitis in patients with preterm premature rupture of membranes using inflammatory indexes: A retrospective study. Taiwan. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2023, 62, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramaswamy, V.; Horton, J.; Vandermeer, B.; Buscemi, N.; Miller, S.; Yager, J. Systematic review of biomarkers of brain injury in term neonatal encephalopathy. Pediatr. Neurol. 2009, 40, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohkuma, K.; Ono, T.; Oshima, Y.; So, K.; Tsumura, K.; Yamasaki, F.; Nakura, Y.; Yanagihara, I.; Nomiyama, M.; Yokoyama, M. Diagnostic accuracy of amniotic fluid interleukin-6 for fetal inflammatory response syndrome. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. 2023, 49, 1498–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Brennan, S.E.; Glanville, J.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiting, P.F.; Rutjes, A.W.S.; Westwood, M.E.; Mallett, S.; Deeks, J.J.; Reitsma, J.B.; Leeflang, M.M.G.; Sterne, J.A.C.; Bossuyt, P.M.; The QUADAS-2 Group. QUADAS-2: A revised tool for the quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies. Ann. Intern. Med. 2011, 155, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulova, V.; Hostinska, E.; Studnickova, M.; Huml, K.; Zapletalova, J.; Halek, J.; Pilka, R. Transabdominal amniocentesis in expectant management of preterm premature rupture of membranes: A single center prospective study. Biomed. Pap. 2021, 165, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.M.; Park, K.H.; Jung, E.Y.; Kook, S.Y.; Park, H.; Jeon, S.J. Inflammatory proteins in maternal plasma, cervicovaginal and amniotic fluids as predictors of intra-amniotic infection in preterm premature rupture of membranes. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0200311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musilova, I.; Andrys, C.; Drahosova, M.; Zednikova, B.; Hornychova, H.; Pliskova, L.; Zemlickova, H.; Jacobsson, B.; Kacerovsky, M. Late preterm prelabor rupture of fetal membranes: Fetal inflammatory response and neonatal outcome. Pediatr. Res. 2018, 83, 630–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.M.; Park, K.H.; Jung, E.Y.; Jang, J.A.; Yoo, H.N. Frequency and clinical significance of short cervix in patients with preterm premature rupture of membranes. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musilova, I.; Andrys, C.; Drahosova, M.; Soucek, O.; Pliskova, L.; Stepan, M.; Bestvina, T.; Maly, J.; Jacobsson, B.; Kacerovsky, M. Amniotic fluid cathepsin-G in pregnancies complicated by the preterm prelabor rupture of membranes. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2017, 30, 2097–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musilova, I.; Andrys, C.; Drahosova, M.; Soucek, O.; Kutova, R.; Pliskova, L.; Spacek, R.; Laudanski, P.; Jacobsson, B.; Kacerovsky, M. Amniotic fluid calreticulin in pregnancies complicated by the preterm prelabor rupture of membranes. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2016, 29, 3921–3929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.A.; Park, K.H.; Lee, S.M. Non-Invasive Prediction of Histologic Chorioamnionitis in Women with Preterm Premature Rupture of Membranes. Yonsei Med. J. 2016, 57, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaemsaithong, P.; Romero, R.; Korzeniewski, S.J.; Martinez-Varea, A.; Dong, Z.; Yoon, B.H.; Hassan, S.S.; Chaiworapongsa, T.; Yeo, L. A point of care test for interleukin-6 in amniotic fluid in preterm prelabor rupture of membranes: A step toward the early treatment of acute intra-amniotic inflammation/infection. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2016, 29, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kacerovsky, M.; Musilova, I.; Hornychova, H.; Kutova, R.; Pliskova, L.; Kostal, M.; Jacobsson, B. Bedside assessment of amniotic fluid interleukin-6 in preterm prelabor rupture of membranes. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2014, 211, 385.e1–385.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobo, T.; Kacerovsky, M.; Palacio, M.; Hornychova, H.; Hougaard, D.M.; Skogstrand, K.; Jacobsson, B. A prediction model of histological chorioamnionitis and funisitis in preterm prelabor rupture of membranes: Analyses of multiple proteins in the amniotic fluid. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2012, 25, 1995–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobo, T.; Palacio, M.; Martínez-Terrón, M.; Navarro-Sastre, A.; Bosch, J.; Filella, X.; Gratacós, E. Clinical and inflammatory markers in amniotic fluid as predictors of adverse outcomes in preterm premature rupture of membranes. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2011, 205, 126.e1–126.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.M.; Park, K.H.; Joo, E.; Jeong, D.E.; Lee, J.E.; Lee, K.; Shin, S. High-throughput analysis of amniotic fluid proteins associated with histological chorioamnionitis in preterm premature rupture of membranes using an antibody-based microarray. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2022, 88, e13595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leaños-Miranda, A.; Nolasco-Leaños, A.G.; Carrillo-Juárez, R.I.; Molina-Pérez, C.J.; Isordia-Salas, I.; Ramírez-Valenzuela, K.L. Interleukin-6 in Amniotic Fluid: A Reliable Marker for Adverse Outcomes in Women in Preterm Labor and Intact Membranes. Fetal Diagn. Ther. 2021, 48, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaemsaithong, P.; Romero, R.; Korzeniewski, S.J.; Martinez-Varea, A.; Dong, Z.; Yoon, B.H.; Hassan, S.S.; Chaiworapongsa, T.; Yeo, L. A rapid interleukin-6 bedside test for the identification of intra-amniotic inflammation in preterm labor with intact membranes. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2016, 29, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, R.; Miranda, J.; Chaemsaithong, P.; Chaiworapongsa, T.; Kusanovic, J.P.; Dong, Z.; Ahmed, A.I.; Shaman, M.; Lannaman, K.; Yoon, B.H.; et al. Sterile and microbial-associated intra-amniotic inflammation in preterm prelabor rupture of membranes. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2015, 28, 1394–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combs, C.A.; Gravett, M.; Garite, T.J.; Hickok, D.E.; Lapidus, J.; Porreco, R.; Rael, J.; Grove, T.; Morgan, T.K.; Clewell, W.; et al. Amniotic fluid infection, inflammation, and colonization in preterm labor with intact membranes. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2014, 210, 125.e1–125.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negishi, H.; Yamada, H.; Mikuni, M.; Kishida, T.; Okuyama, K.; Sagawa, T.; Makinoda, S.; Fujimoto, S. Correlation between cytokine levels of amniotic fluid and histological chorioamnionitis in preterm delivery. J. Perinat. Med. 1996, 24, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuda, A.; Ikegami, T.; Hirano, H.; Sanada, H.; Ogawa, M.; Sasaki, M.; Tanaka, T. The relationship between amniotic fluid interleukin-6 concentration and histologic evidence of chorioamnionitis. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 1998, 77, 515–520. [Google Scholar]
- Hillier, S.L.; Witkin, S.S.; Krohn, M.A.; Watts, D.H.; Kiviat, N.B.; Eschenbach, D.A. The relationship of amniotic fluid cytokines and preterm delivery, amniotic fluid infection, histologic chorioamnionitis, and chorioamnion infection. Obstet. Gynecol. 1993, 81, 941–948. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, K.J.; Park, K.H.; Kim, S.N.; Jeong, E.H.; Lee, S.Y.; Yoon, H.Y. Predictive value of intra-amniotic and serum markers for inflammatory lesions of preterm placenta. Placenta 2011, 32, 732–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, H.; Ogawa, M.; Hirano, H.; Sanada, H.; Sato, A.; Obara, M.; Terada, Y. Neutrophil elastase and interleukin-6 in amniotic fluid as indicators of chorioamnionitis and funisitis. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2011, 158, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, B.H.; Romero, R.; Kim, C.J.; Jun, J.K.; Gomez, R.; Choi, J.H.; Syu, H.C. Amniotic fluid interleukin-6: A sensitive test for antenatal diagnosis of acute inflammatory lesions of preterm placenta and prediction of perinatal morbidity. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 1995, 172, 960–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balciuniene, G.; Gulbiniene, V.; Dumalakiene, I.; Viliene, R.; Bartkeviciene, D.; Pilypiene, I.; Drasutiene, G.S.; Ramasauskaite, D. Prognostic Markers for Chorioamnionitis: IL-6, TNF-α, and MMP-8 in Vaginally Obtained Amniotic Fluid. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eleje, G.U.; Ukah, C.O.; Onyiaorah, I.V.; Ezugwu, E.C.; Ugwu, E.O.; Ohayi, S.R.; Eleje, L.I.; Egeonu, R.O.; Ezebialu, I.U.; Obiora, C.C.; et al. Diagnostic value of Chorioquick for detecting chorioamnionitis in women with premature rupture of membranes. Int. J. Gynecol. Obstet. 2020, 149, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayem, G.; Batteux, F.; Girard, N.; Schmitz, T.; Willaime, M.; Maillard, F.; Jarreau, P.H.; Goffinet, F. Predictive value of vaginal IL-6 and TNFα bedside tests repeated until delivery for the prediction of maternal-fetal infection in cases of premature rupture of membranes. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2017, 211, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucovnik, M.; Kornhauser-Cerar, L.; Premru-Srsen, T.; Gmeiner-Stopar, T.; Derganc, M. Neutrophil defensins but not interleukin-6 in vaginal fluid after preterm premature rupture of membranes predict fetal/neonatal inflammation and infant neurological impairment. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 2011, 90, 908–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayem, G.; Goffinet, F.; Batteux, F.; Jarreau, P.H.; Weill, B.; Cabrol, D. Detection of interleukin-6 in vaginal secretions of women with preterm premature rupture of membranes and its association with neonatal infection: A rapid immunochromatographic test. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2005, 192, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelazim, I.A. Relation between interleukin-6 in the cervicovaginal fluid and subclinical chorioamnionitis in patients with preterm premature rupture of membranes. Asian Pac. J. Reprod. 2013, 2, 38–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.H.; Lee, K.N.; Oh, E.; Im, E.M. Inflammatory biomarkers in the cervicovaginal fluid to identify histologic chorioamnionitis and funisitis in women with preterm labor. Cytokine 2023, 169, 156308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lockwood, C.J.; Ghidini, L.; Wein, R.; Lapinski, R.; Casal, D.; Berkowitz, R.L. Increased interleukin-6 concentrations in cervical secretions are associated with preterm delivery. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 1994, 171, 1097–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.W.; Park, K.H.; Lee, J.E.; Kim, Y.M.; Lee, S.J.; Cheon, D.H. Antibody Microarray Analysis of Plasma Proteins for the Prediction of Histologic Chorioamnionitis in Women with Preterm Premature Rupture of Membranes. Reprod. Sci. 2019, 26, 1476–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Portilla, R.J.; Hawkins-Villarreal, A.; Alvarez-Ponce, P.; Chinolla-Arellano, Z.L.; Moreno-Espinosa, A.L.; Sandoval-Mejia, A.L.; Moreno-Uribe, N. Maternal Serum Interleukin-6: A Non-Invasive Predictor of Histological Chorioamnionitis in Women with Preterm-Prelabor Rupture of Membranes. Fetal Diagn. Ther. 2019, 45, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayed Ahmed, W.A.; Ahmed, M.R.; Mohamed, M.L.; Hamdy, M.A.; Kamel, Z.; Elnahas, K.M. Maternal serum interleukin-6 in the management of patients with preterm premature rupture of membranes. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2016, 29, 3162–3166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulati, S.; Agrawal, S.; Raghunandan, C.; Bhattacharya, J.; Saili, A.; Agarwal, S.; Sharma, D. Maternal serum interleukin-6 and its association with clinicopathological infectious morbidity in preterm premature rupture of membranes: A prospective cohort study. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2012, 25, 1428–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.W.; Park, K.H.; Kook, S.Y.; Jung, Y.M.; Kim, Y.M. Immune biomarkers in maternal plasma to identify histologic chorioamnionitis in women with preterm labor. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2019, 299, 725–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torbé, A.; Czajka, R.; Kordek, A.; Rzepka, R.; Kwiatkowski, S.; Rudnicki, J. Maternal serum proinflammatory cytokines in preterm labor with intact membranes: Neonatal outcome and histological associations. Eur. Cytokine Netw. 2007, 18, 102–107. [Google Scholar]
- Koyama, M.; Ito, S.; Nakajima, A.; Shimoya, K.; Azuma, C.; Suehara, N.; Murata, Y.; Tojo, H. Elevations of group II phospholipase A2 concentrations in serum and amniotic fluid in association with preterm labor. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2000, 183, 1537–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, K.; Matsuzaki, N.; Fuke, S.; Mitsud, N.; Shimoya, K.; Nakayama, M.; Suehara, N.; Aono, T. Value of the Maternal Interleukin 6 Level for Determination of Histologic Chorioamnionitis in Preterm Delivery. Gynecol. Obstet. Investig. 1997, 43, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greig, P.; Murtha, A.; Jimmerson, C.; Herbert, W.; Roitmanjohnson, B.; Allen, J. Maternal Serum Interleukin-6 During Pregnancy and During Term and Preterm Labor. Obstet. Gynecol. 1997, 90, 465–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Škrablin, S.; Lovrić, H.; Banović, V.; Kralik, S.; Dijaković, A.; Kalafatić, D. Maternal plasma interleukin-6, interleukin-1β and C-reactive protein as indicators of tocolysis failure and neonatal outcome after preterm delivery. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2007, 20, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etyang, A.K.; Omuse, G.; Mukaindo, A.M.; Temmerman, M. Maternal inflammatory markers for chorioamnionitis in preterm prelabour rupture of membranes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of diagnostic test accuracy studies. Syst. Rev. 2020, 9, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanzarone, V.; Polkinghorne, A.; Eslick, G.; Branley, J. Diagnostic tests for the prediction of histological chorioamnionitis and funisitis in pregnant women with preterm premature rupture of membranes: A systematic review. Aust. N. Z. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2025, 65, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, C.C.; Chang, J.H.; Lin, H.Y.; Cheng, P.J.; Su, B.H. Intrauterine inflammation, infection, or both (Triple I): A new concept for chorioamnionitis. Pediatr. Neonatol. 2018, 59, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cobo, T.; Burgos-Artizzu, X.P.; Ferrero, S.; Balcells, J.; Bosch, J.; Gené, A.; Murillo, C.; Rueda, C.; Boada, D.; Sánchez-Antón, M.T.; et al. External validation of a non-invasive vaginal tool to assess the risk of intra-amniotic inflammation in pregnant women with preterm labor and intact membranes. J. Perinat. Med. 2024, 53, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, T.; Senkow, K.J.; Nguyen, M.B.; Patel, P.V.; Sandepudi, K.; Cooper, L.A.; Goldstein, J.A. Quantitative Modeling to Characterize Maternal Inflammatory Response of Histologic Chorioamnionitis in Placental Membranes. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2024, 92, e13944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]




| Author | Year | Study Design | Fluid | N | Cut-off | Subgroup | Gestational Age | Assay Method | Sampling Timing |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Joo [11] | 2021 | Retro | AF | 150 | 2.60 (pre) | PPROM | 24 + 0 to 33 + 6 | ELISA | Admission |
| Fulova [18] | 2021 | Pros | AF | 62 | 1.00 (pre) | PPROM | 22 + 0 to 34 + 0 | POC | Admission |
| Lee [19] | 2018 | Retro | AF | 74 | 1.48 (opt) | PPROM | 21 + 0 to 34 + 0 | Luminex | Admission |
| Musilova [20] | 2018 | Pros | AF | 159 | 0.74 (pre) | PPROM | 34 + 0 to 36 + 6 | POC | Admission |
| Lee [21] | 2017 | Retro | AF | 151 | 1.5 (opt) | PPROM | 21 + 0–33 + 6 | ELISA | Admission |
| Musilova [22] | 2017 | Retro | AF | 154 | 0.74 (pre) | PPROM | 24 + 0 to 36 + 6 | POC | Admission |
| Musilova [23] | 2016 | Pros | AF | 168 | 0.74 (pre) | PPROM | 24 + 0 to 36 + 6 | POC | Admission |
| Kim [24] | 2016 | Retro | AF | 146 | 2.40 (opt) | PPROM | 20 + 0 to 33 + 6 | ELISA | Admission |
| Chaemsaithong [25] | 2016 | Retro | AF | 26 | 0.74 (pre) | PPROM | 20 + 0 to 35 + 0 | POC | - |
| Kacerovsky [26] | 2014 | Pros | AF | 124 | 0.32 (opt) | PPROM | 24 + 0 to 36 + 6 | POC | - |
| Cobo [27] | 2012 | Pros | AF | 107 | 0.02 (pre) | PPROM | 23 + 0 to 36 + 6 | Luminex M | Admission |
| Cobo [28] | 2011 | Pros | AF | 63 | 1.43 (pre) | PPROM | <34 + 0 | ELISA | First 48 h |
| Lee [29] | 2022 | Retro | AF | 100 | 5.57 (opt) | PPROM | 24 + 0 to 34 + 0 | ELISA | Admission |
| Leaños-Miranda [30] | 2021 | Pros | AF | 452 | 2.60 (pre) | PTL | <36 + 0 | ELISA | - |
| Chaemsaithong [31] | 2016 | Retro | AF | 54 | 2.60 (pre) | PTL | 20 + 0 to 35 + 0 | ELISA | - |
| Romero [32] | 2015 | Retro | AF | 125 | 2.60 (pre) | PTL | 20 + 0 to 36 + 6 | ELISA | - |
| Combs [33] | 2014 | Pros | AF | 218 | 2.60 (pre) | PTL | 15 + 0 to 36 + 6 | ELISA | Admission |
| Negishi [34] | 1996 | Pros | AF | 18 | 0.60 (pre) | PTL | 24 + 0 to 36 + 0 | ELISA | - |
| Tsuda [35] | 1998 | Pros | AF | 110 | 3.5 (opt) | PTL | 16 + 0 to 32 + 0 | ELISA | Admission |
| Hillier [36] | 1993 | Pros | AF | 26 | 1.5 (pre) | PTL | 24 + 0 to 34 + 0 | ELISA | 7 days before |
| Oh [37] | 2011 | Retro | AF | 99 | 2.60 (opt) | PPROM/PTL | 21 + 0 to 35 + 0 | ELISA | Admission |
| Miura [38] | 2011 | Retro | AF | 56 | 11.27 (opt) | TA PTL/PPROM | 24 + 0 to 35 + 0 | ELISA | Admission |
| Yoon [39] | 1995 | Pros | AF | 29 | 17 (opt) | PPROM/PTL | 24 + 0 to 35 + 0 | ELISA | Admission |
| El-Ghazaly [12] | 2022 | Pros | CVF | 110 | 0.1 (pre) | PPROM | 24 + 0 to 34 + 0 | POC | Admission + TOP/induction |
| Balciuniene [40] | 2021 | Pros | CVF | 156 | 1.39 (opt) | PPROM | 22 + 0 to 34 + 6 | ELISA | Every second day |
| Eleje [41] | 2020 | Pros | CVF | 48 | 0.1 (pre) | PPROM | 24 + 0 to 36 + 6 | POC | Before DCE |
| Kayem [42] | 2017 | Pros | CVF | 141 | 0.1 (pre) | PPROM | 24 + 0 to 37 + 0 | POC | 7 days before |
| Lucovnik [43] | 2011 | Pros | CVF | 42 | 1.045 (opt) | PPROM | 23 + 6 to 31 + 6 | CLIA | Admission |
| Kayem [44] | 2005 | Pros | CVF | 51 | 0.1(pre) | PPROM | 24 + 6 to 34 + 6 | POC | Admission |
| Abdelazim [45] | 2013 | Pros | CVF | 120 | 0.1 (pre) | PPROM | 34 + 0 to 37 + 0 | POC | - |
| Park [46] | 2023 | Retro | CVF | 134 | 0.096 (opt) | PTL | 23 + 0 to 34 + 0 | ELISA | Admission |
| Lockwood [47] | 1994 | Pros | CVF | 12 | 0.25 (opt) | PPROM/PTL | 24 + 0 to 36 + 0 | ELISA | <28 days before |
| Kong [13] | 2023 | Retro | PL | 206 | 8.252 (opt) | PPROM | 30 + 0 to 35 + 0 | CLIA | Within 12 h |
| Park [48] | 2019 | Retro | PL | 82 | 3.87 (opt) | PPROM | 23 + 0 to 34 + 6 | ELISA | Admission |
| Martinez-Portilla [49] | 2019 | Pros | PL | 47 | 19.5 (opt) | PPROM | 26 + 0 to 36 + 6 | ELISA | Admission |
| Sayed Ahmed [50] | 2016 | Pros | PL | 60 | 8.5 (opt) | PPROM | 24 + 0 to 34 + 0 | ELISA | Admission + TOP/onset of labor |
| Gulati [51] | 2012 | PL | 45 | 8 (opt) | PPROM | 24 + 0 to 34 + 0 | ELISA | Admission + Onset of labor + 48 h + day 7 | |
| Park [52] | 2019 | Retro | PL | 74 | 5.88 (opt) | PTL | 23 + 0 to 34 + 6 | ELISA | Admission |
| Torbé [53] | 2007 | Pros | PL | 48 | 40 (opt) | PTL | 24 + 0 to 34 + 0 | ELISA | - |
| Koyama [54] | 2000 | Pros | PL | 38 | 7.5 (opt) | PTL | 23 + 0 to 36 + 0 | ELISA | - |
| Maeda [55] | 1997 | Pros | PL | 29 | 7.5 (opt) | PTL | 22 + 0 to 34 + 0 | ELISA | Delivery |
| Greig [56] | 1997 | Pros | PL | 20 | 6 (opt) | PTL–PTD | 22 + 0 to 34 + 0 | ELISA | - |
| Skrablin [57] | 2007 | Pros | PL | 47 | 29.1 (opt) | PTL/PPROM | 27 + 0 to 33 + 0 | ELISA | Admission |
| Measure | AF Overall (95% CI) |
|---|---|
| DOR | 9.53 (6.59–13.77) |
| LR+ | 3.90 (2.83–5.37) |
| LR− | 0.41 (0.32–0.52) |
| AUC | 0.82 (0.78–0.85) |
| Measure | Plasma Overall (95% CI) |
|---|---|
| DOR | 9.06 (4.88–16.82) |
| LR+ | 3.30 (2.52–4.31) |
| LR− | 0.36 (0.24–0.55) |
| AUC | 0.79 (0.76–0.83) |
| Measure | CVF Overall (95% CI) | CVF PPROM (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|
| DOR | 16.16 (3.13–83.37) | 33.03 (5.56–196.24) |
| LR+ | 3.51 (1.85–6.68) | 4.62 (2.30–9.30) |
| LR− | 0.21 (0.08–0.60) | 0.14 (0.05–0.43) |
| AUC | 0.85 (0.82–0.88) | 0.91 (0.88–0.93) |
| Measure | AF PPROM (95% CI) | AF PTL (95% CI) | z | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DOR | 5.87 (4.49–7.66) | 20.80 (7.93–54.58) | 2.479 | 0.013 |
| LR+ | 3.25 (2.52–4.19) | 4.91 (1.79–13.44) | 0.776 | 0.437 |
| LR− | 0.55 (0.47–0.65) | 0.24 (0.13–0.44) | 2.591 | 0.010 |
| AUC | 0.76 (0.72–0.80) | 0.88 (0.85–0.91) | 5.004 | <0.00001 |
| Measure | Plasma PPROM (95% CI) | Plasma PTL (95% CI) | z | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DOR | 5.82 (3.16–10.72) | 9.93 (3.58–27.56) | 0.881 | 0.379 |
| LR+ | 2.89 (2.09–3.99) | 3.12 (2.05–4.74) | 0.284 | 0.776 |
| LR− | 0.50 (0.35–0.69) | 0.31 (0.15–0.64) | 1.128 | 0.259 |
| AUC | 0.80 (0.76–0.83) | 0.77 (0.74–0.81) | 0.860 | 0.390 |
| Measure | Predefined (95% CI) | Optimal (95% CI) | z | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DOR | 8.90 (5.36–14.76) | 9.93 (5.89–16.76) | 1.112 | 0.266 |
| LR+ | 4.06 (2.49–6.62) | 3.51 (2.55–4.84) | 0.483 | 0.629 |
| LR− | 0.46 (0.34–0.62) | 0.35 (0.25–0.49) | 0.297 | 0.766 |
| AUC | 0.80 (0.76–0.83) | 0.83 (0.79–0.86) | 1.183 | 0.237 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Solomou, E.; Kalampokas, E.; Michailides, C.; Sergentanis, T.N.; Kalampokas, T. Interleukin 6 for the Prediction of Chorioamnionitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 2577. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13112577
Solomou E, Kalampokas E, Michailides C, Sergentanis TN, Kalampokas T. Interleukin 6 for the Prediction of Chorioamnionitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(11):2577. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13112577
Chicago/Turabian StyleSolomou, Eleni, Emmanouil Kalampokas, Christos Michailides, Theodoros N. Sergentanis, and Theodoros Kalampokas. 2025. "Interleukin 6 for the Prediction of Chorioamnionitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Biomedicines 13, no. 11: 2577. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13112577
APA StyleSolomou, E., Kalampokas, E., Michailides, C., Sergentanis, T. N., & Kalampokas, T. (2025). Interleukin 6 for the Prediction of Chorioamnionitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Biomedicines, 13(11), 2577. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13112577