Enhancing Lesion Detection in Rat CT Images: A Deep Learning-Based Super-Resolution Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Approval
2.2. Dataset Acquisition and Composition
2.3. Dataset Partitioning and Preprocessing
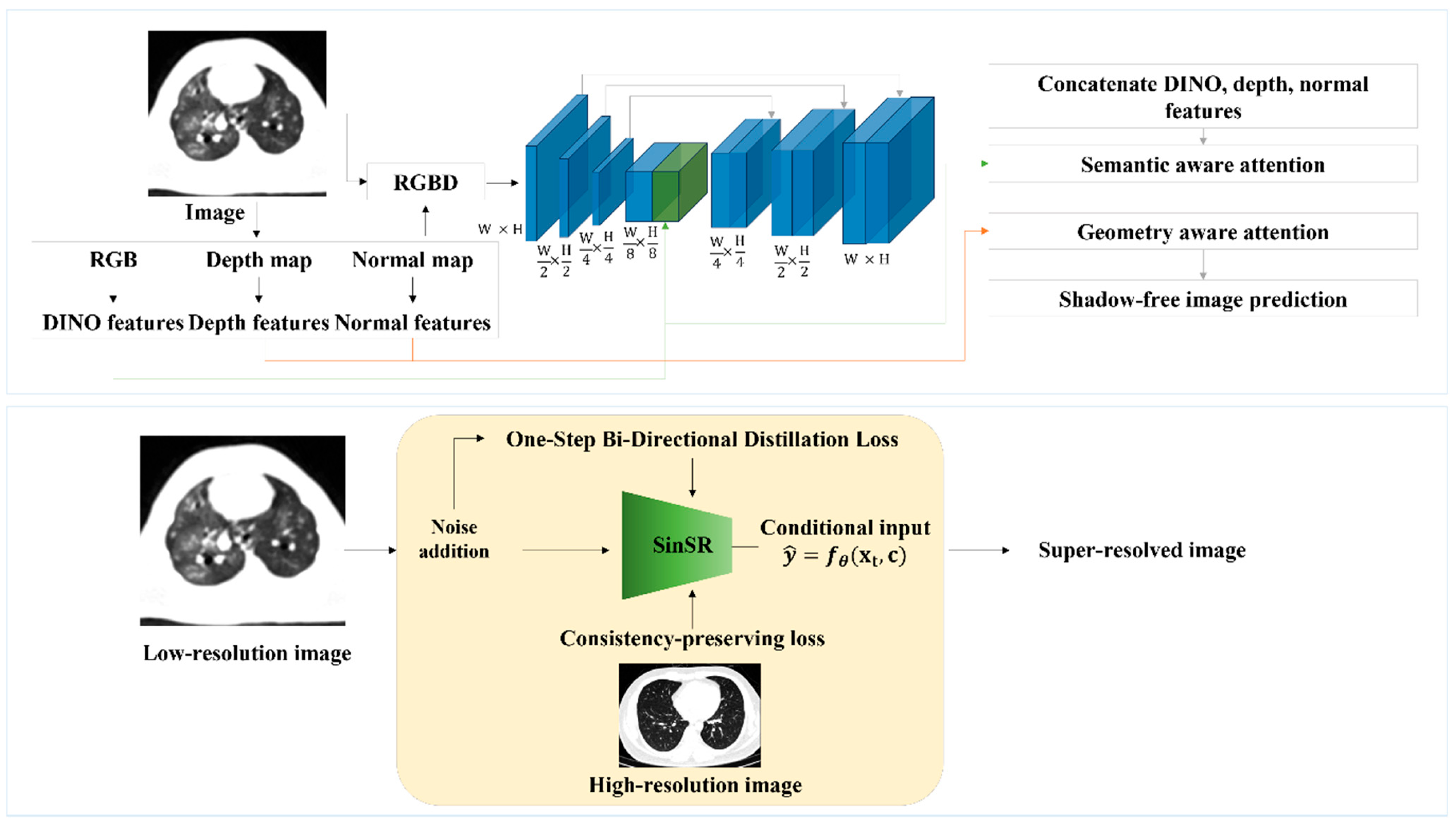
2.4. Network Architectures
2.5. Training Strategies
2.6. Evaluation Metrics
2.7. Subjective Image Quality Assessment
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
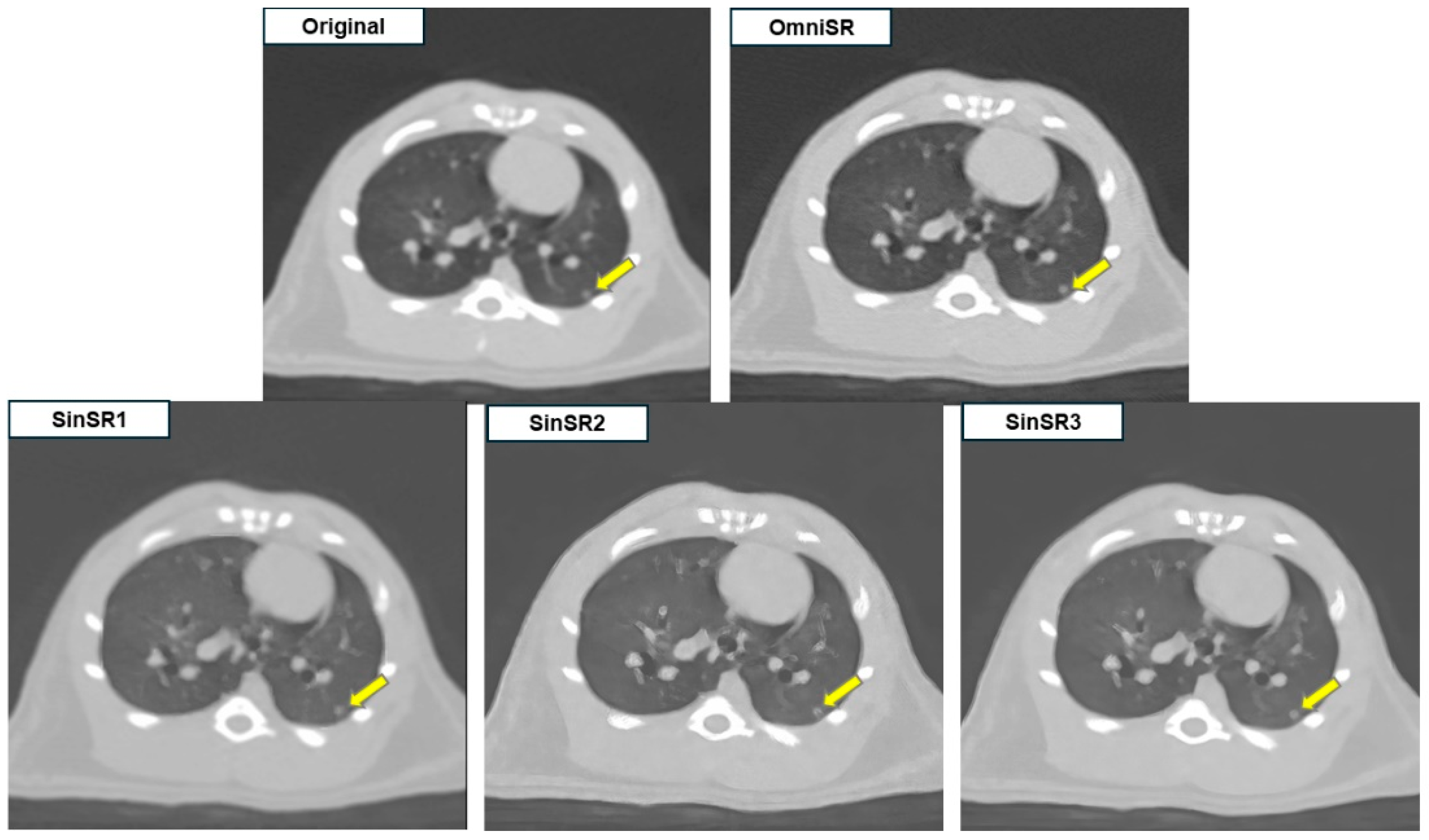
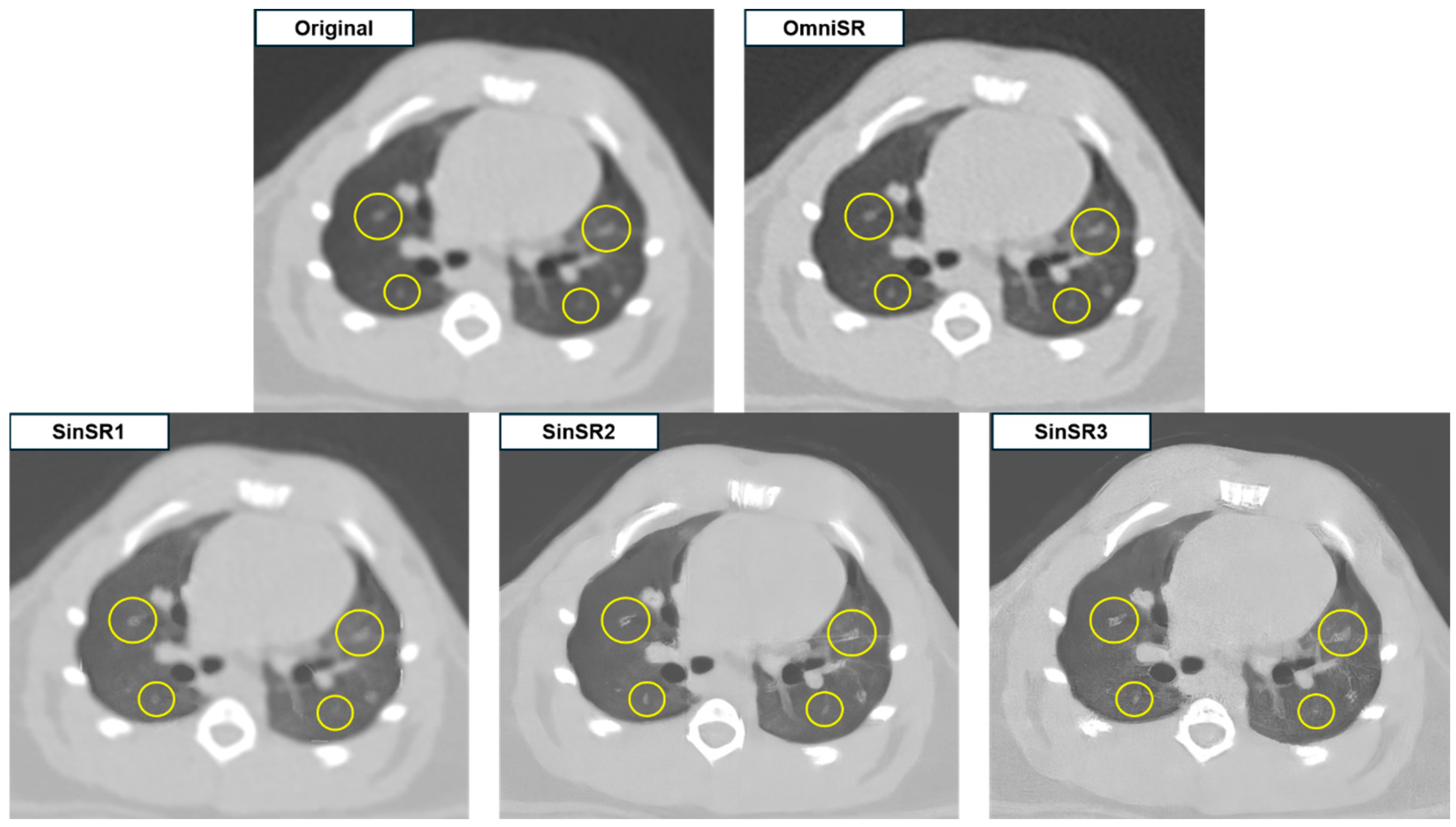
3.1. Objective Image Analysis
3.2. Subjective Image Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, C.; Jeong, S.H.; Kim, J.; Kang, J.Y.; Nam, Y.J.; Togloom, A.; Cha, J.; Lee, K.Y.; Lee, C.H.; Park, E.-K.; et al. Evaluation of the effect of filtered ultrafine particulate matter on bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis in a rat model using computed tomography, histopathologic analysis, and RNA sequencing. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 22672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashiro, J.; Rubio, G.A.; Limper, A.H.; Williams, K.; Elliot, S.J.; Ninou, I.; Aidinis, V.; Tzouvelekis, A.; Glassberg, M.K. Exploring animal models that resemble idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Front. Med. 2017, 4, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badea, C.T.; Drangova, M.; Holdsworth, D.W.; Johnson, G.A. In vivo small-animal imaging using micro-CT and digital subtraction angiography. Phys. Med. Biol. 2008, 53, R319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.R.; Lee, K.; Park, C.W.; Song, J.A.; Shin, D.Y.; Park, Y.J.; Chung, K.H. Polyhexamethylene guanidine phosphate aerosol particles induce pulmonary inflammatory and fibrotic responses. Arch. Toxicol. 2016, 90, 617–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Jeong, S.H.; Baek, Y.-W.; Lee, H.; Sa, J.K.; Lee, J.Y.; Lee, Y.-S.; Nam, Y.J.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.; et al. Deciphering the toxicity of polyhexamethylene guanidine phosphate in lung carcinogenesis: Mutational profiles and molecular mechanisms. Chemosphere 2024, 368, 143785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, R.G.; Moore, B.B.; Chambers, R.C.; Eickelberg, O.; Konigshoff, M.; Kolb, M.; Laurent, G.J.; Nanthakumar, C.B.; Olman, M.A.; Pardo, A.; et al. An official American Thoracic Society workshop report: Use of animal models for the preclinical assessment of potential therapies for pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2017, 56, 667–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, S.H.; Lee, H.; Nam, Y.J.; Kang, J.Y.; Lee, H.; Choi, J.Y.; Lee, Y.-S.; Kim, J.; Park, Y.H.; Park, S.A.; et al. Longitudinal long term follow up investigation on the carcinogenic impact of polyhexamethylene guanidine phosphate in rat models. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 7178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, D.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, X. Medical image super-resolution reconstruction algorithms based on deep learning: A survey. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2023, 238, 107590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Hwang, D.; Kim, K.Y.; Kang, S.K.; Kim, Y.K.; Lee, J.S. Computed tomography super-resolution using deep convolutional neural network. Phys. Med. Biol. 2018, 63, 145011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, X.; Wang, Y.; Wu, C. Computed Tomography (CT) Image Quality Enhancement via a Uniform Framework Integrating Noise Estimation and Super-Resolution Networks. Sensors 2019, 19, 3348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, B.; Son, S.; Kim, H.; Nah, S.; Lee, K.M. Enhanced deep residual networks for single image super-resolution. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, K.; Li, K.; Wang, L.; Zhong, B.; Fu, Y. Image Super-Resolution Using Very Deep Residual Channel Attention Networks. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Milan, Italy, 4 October 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, W.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Guo, L.; Chau, L.-P.; Liu, Z.; Qiao, Y.; Kot, A.C.; Wen, B. SinSR: Diffusion-Based Image Super-Resolution in a Single Step. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, C.; Yong, Y. Edge-enhanced with feedback attention network for image super-resolution. Sensors 2021, 21, 2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, Y.; Fan, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, L.; Huang, T.S.; Shi, H. Image super-resolution with cross-scale non-local attention and exhaustive self-exemplars mining. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.; Xu, C.; Tang, L.; Meng, Y.; Xu, W.; Wang, J.; Xu, J. OmniSR-M: A rock sheet with a multi-branch structure image super-resolution lightweight method. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.; Park, H.; Lee, S.M.; Seo, J.B.; Kim, N. Lung segmentation on HRCT and volumetric CT for diffuse interstitial lung disease using deep convolutional neural networks. J. Digit. Imaging 2019, 32, 1019–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maier-Hein, L.; Reinke, A.; Godau, P.; Tizabi, M.D.; Buettner, F.; Christodoulou, E.; Glocker, B.; Isensee, F.; Kleesiek, J.; Kozubek, M.; et al. Metrics reloaded: Recommendations for image analysis validation. Nat. Methods 2024, 21, 195–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyad, M.; Sarhan, A.M.; Arafa, M. A modified Adam algorithm for deep neural network optimization. Neural Comput. Appl. 2023, 35, 17095–17112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horé, A.; Ziou, D. Image quality metrics: PSNR vs. SSIM. In Proceedings of the 2010 20th International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Istanbul, Turkey, 23–26 August 2010; pp. 2366–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sara, U.; Akter, M.; Uddin, M.S. Image quality assessment through FSIM, SSIM, MSE and PSNR—A comparative study. J. Comput. Commun. 2019, 7, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landis, J.R.; Koch, G.G. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 1977, 33, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Han, D.; Kim, M.; Hong, J. Evaluation of AI-based super-resolution model in CT for dose reduction method: A phantom study. Egypt. J. Radiol. Nucl. Med. 2025, 56, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Shen, S.; Gao, W.; Hsu, W.; Cong, J. Computed tomography image enhancement using 3D convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Deep Learning in Medical Image Analysis, Granada, Spain, 20 September 2018; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ledig, C.; Theis, L.; Huszar, F.; Caballero, J.; Cunningham, A.; Acosta, A.; Aitken, A.; Tehani, A.; Totz, J.; Wang, Z.; et al. Photo-realistic single image super-resolution using a generative adversarial network. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
| Group | Exposure Condition | No. of Rats | No. of CT Scans |
|---|---|---|---|
| Naïve | None (no exposure, no vehicle) | 10 | 10 |
| Vehicle control (saline) | 0 mg/kg, saline instillation | 10 | 10 |
| Low-dose instillation | PHMG-p low | 10 | 10 |
| Intermediate-dose instillation | PHMG-p medium | 10 | 10 |
| High-dose instillation | PHMG-p high | 10 | 10 |
| PM group | PHMG-p + PM | 10 | 10 |
| Instillation control | PHMG-p + saline | 10 | 10 |
| Tumor cohort | PHMG-p 0.9 mg/kg (multiple follow-up CTs) | 24 | 72 |
| Inhalation control | Clean air | 20 | 20 |
| Low-dose inhalation | PHMG-p 0.01 mg/m3 | 20 | 20 |
| Intermediate-dose inhalation | PHMG-p 0.03 mg/m3 | 20 | 20 |
| High-dose inhalation | PHMG-p 0.09 mg/m3 | 20 | 20 |
| Model | PSNR (dB) | SSIM |
|---|---|---|
| OmniSR | 29.21 ± 1.46 | 0.71 ± 0.09 |
| SinSR1 | 33.64 ± 1.30 | 0.70 ± 0.06 |
| SinSR2 | 31.25 ± 1.17 | 0.69 ± 0.08 |
| SinSR3 | 32.01 ± 1.09 | 0.72 ± 0.08 |
| OmniSR | SinSR1 | SinSR2 | SinSR3 | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Margin of lesions | R1 | 4.07 ± 0.73 | 1.09 ± 0.32 | 1.10 ± 0.33 | 1.81 ± 0.90 | N/A |
| R2 | 3.88 ± 0.76 | 1.09 ± 0.32 | 1.10 ± 0.33 | 1.75 ± 0.82 | N/A | |
| Mean | 3.97 ± 0.75 | 1.09 ± 0.32 * | 1.10 ± 0.33 *† | 1.78 ± 0.86 *§ | <0.001 | |
| Nodule/mass detectability | R1 | 4.51 ± 0.85 | 1.25 ± 0.66 | 1.25 ± 0.66 | 1.50 ± 0.70 | N/A |
| R2 | 4.40 ± 0.83 | 1.15 ± 0.52 | 1.16 ± 0.53 | 1.67 ± 0.81 | N/A | |
| Mean | 4.46 ± 0.84 | 1.20 ± 0.59 * | 1.20 ± 0.60 *† | 1.58 ± 0.76 *§ | <0.001 | |
| Anatomic structure similarity | R1 | 3.00 ± 0.00 | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 2.06 ± 0.91 | N/A |
| R2 | 3.00 ± 0.00 | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 2.20 ± 0.90 | N/A | |
| Mean | 3.00 ± 0.00 | 1.00 ± 0.00 * | 1.00 ± 0.00 *† | 2.13 ± 0.90 *§ | <0.001 | |
| Image noise | R1 | 3.00 ± 0.00 | 3.55 ± 0.50 | 3.55 ± 0.50 | 4.00 ± 0.00 | N/A |
| R2 | 3.00 ± 0.00 | 3.51 ± 0.50 | 3.48 ± 0.50 | 3.80 ± 0.40 | N/A | |
| Mean | 3.00 ± 0.00 | 3.53 ± 0.50 * | 3.51 ± 0.50 *† | 3.90 ± 0.30 *§ | <0.001 | |
| Image artifact | R1 | 3.00 ± 0.00 | 1.67 ± 0.47 | 1.49 ± 0.50 | 1.69 ± 0.47 | N/A |
| R2 | 2.94 ± 0.24 | 1.65 ± 0.48 | 1.53 ± 0.50 | 1.72 ± 0.45 | N/A | |
| Mean | 2.97 ± 0.17 | 1.66 ± 0.48 * | 1.51 ± 0.50 *† | 1.71 ± 0.46 *†§ | <0.001 | |
| Overall image quality | R1 | 4.78 ± 0.42 | 1.66 ± 0.74 | 1.77 ± 0.71 | 3.14 ± 0.79 | N/A |
| R2 | 4.71 ± 0.48 | 1.65 ± 0.73 | 1.76 ± 0.70 | 3.08 ± 0.77 | N/A | |
| Mean | 4.75 ± 0.45 | 1.66 ± 0.73 * | 1.77 ± 0.70 *† | 3.11 ± 0.78 *§ | <0.001 |
| OmniSR | SinSR1 | SinSR2 | SinSR3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lesion margin | 0.613 (0.474, 0.735) | 1.000 (1.000, 1.000) | 1.000 (1.000, 1.000) | 0.801 (0.684, 0.898) |
| Detectability of lung lesions (nodules/masses) | 0.684 (0.531, 0.805) | 0.724 (0.450, 0.936) | 0.703 (0.436, 0.909) | 0.779 (0.651, 0.887) |
| Anatomic structure similarity | 1.000 (1.000, 1.000) | 1.000 (1.000, 1.000) | 1.000 (1.000, 1.000) | 0.812 (0.699, 0.897) |
| Image noise | 1.000 (1.000, 1.000) | 0.920 (0.838, 0.980) | 0.861 (0.763, 0.940) | N/A |
| Image artifact | 1.000 (1.000, 1.000) | 0.955 (0.888, 1.000) | 0.840 (0.721, 0.940) | 0.832 (0.708, 0.947) |
| Overall image quality | 0.767 (0.608, 0.911) | 0.934 (0.875, 0.987) | 0.932 (0.869, 0.986) | 0.880 (0.796, 0.943) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ham, S.; Jeong, S.H.; Lee, H.; Nam, Y.J.; Lee, H.; Choi, J.Y.; Lee, Y.-S.; Park, Y.H.; Park, S.A.; Kim, W.; et al. Enhancing Lesion Detection in Rat CT Images: A Deep Learning-Based Super-Resolution Study. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 2421. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13102421
Ham S, Jeong SH, Lee H, Nam YJ, Lee H, Choi JY, Lee Y-S, Park YH, Park SA, Kim W, et al. Enhancing Lesion Detection in Rat CT Images: A Deep Learning-Based Super-Resolution Study. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(10):2421. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13102421
Chicago/Turabian StyleHam, Sungwon, Sang Hoon Jeong, Hong Lee, Yoon Jeong Nam, Hyejin Lee, Jin Young Choi, Yu-Seon Lee, Yoon Hee Park, Su A Park, Wooil Kim, and et al. 2025. "Enhancing Lesion Detection in Rat CT Images: A Deep Learning-Based Super-Resolution Study" Biomedicines 13, no. 10: 2421. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13102421
APA StyleHam, S., Jeong, S. H., Lee, H., Nam, Y. J., Lee, H., Choi, J. Y., Lee, Y.-S., Park, Y. H., Park, S. A., Kim, W., Choi, H., Kim, H., Lee, J.-H., & Kim, C. (2025). Enhancing Lesion Detection in Rat CT Images: A Deep Learning-Based Super-Resolution Study. Biomedicines, 13(10), 2421. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13102421







