The Impact of miR-21-5p, miR-145-5p and miR-382-5p Expression in Gastric Adenocarcinoma Cells on Lymphatic Spread Capability
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Study Subjects
3.2. Univariate Analysis of the Correlation Between miRNA and Pathological Characteristics
3.3. Multivariate Analysis of the Correlation Between miRNA and Pathological Characteristics
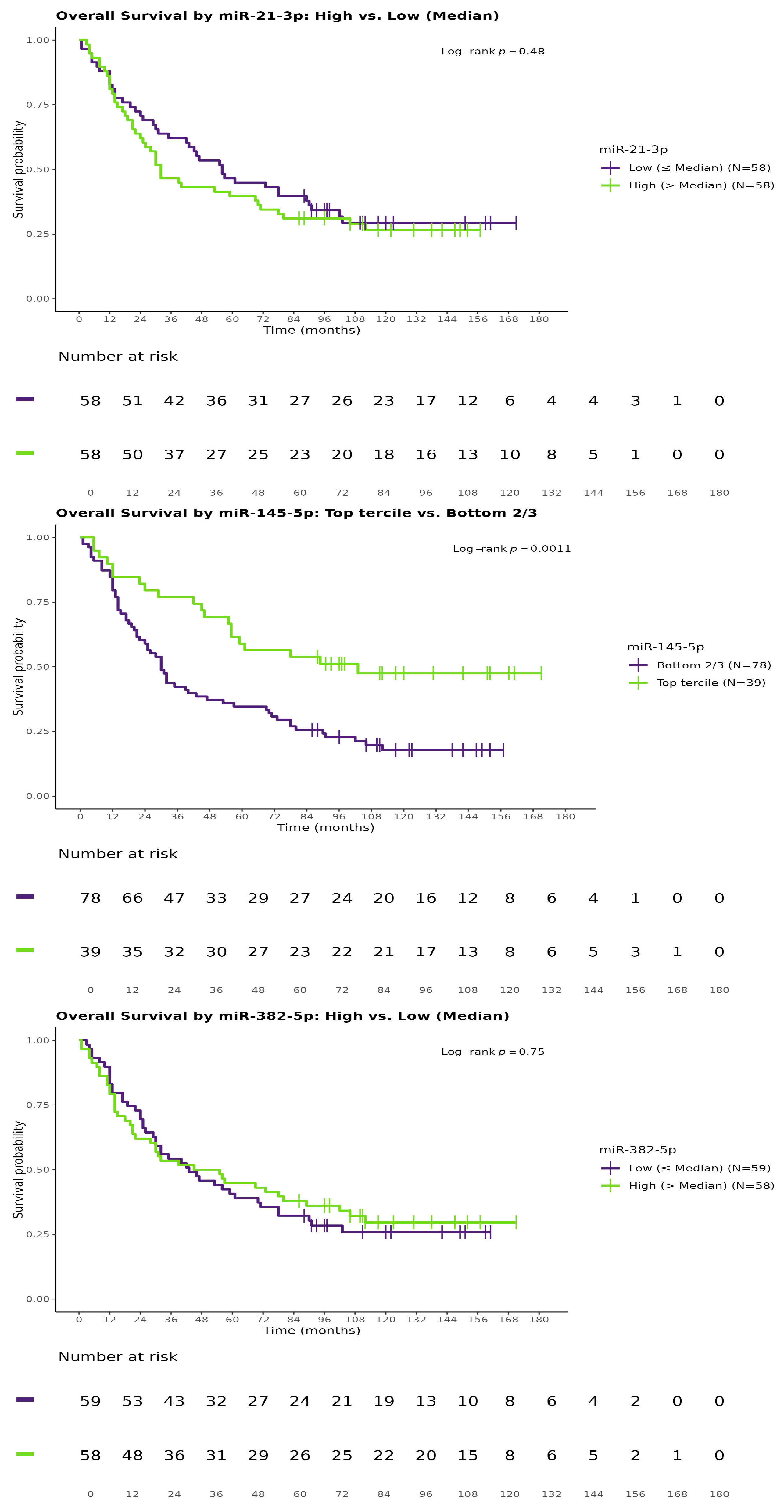
3.4. Analysis of the Correlation Between miRNA and Survival
4. Discussion
Limitations of the Study
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FFPE | Formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded |
| NGS | Next-generation sequencing |
| qPCR | Quantitative polymerase chain reaction |
| OR | Odds ratio |
| HR | Hazard ratio |
| AJCC | American Joint Committee on Cancer |
| pTNM | Pathological tumor-node-metastasis |
| MOMA | Aarhus University Molecular Medicine |
| 5-FU | 5-Fluorouracil |
| PTEN | Phosphatase and tensin homolog |
| ANGPT2 | Angiopoietin-2 |
| NLR | Nod-like receptor |
References
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.Y.; Liang, H. Clinical significance of lymph node metastasis in gastric cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 3967–3975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Lai, M. The microRNA network and tumor metastasis. Oncogene 2010, 29, 937–948. [Google Scholar]
- Hayes, J.; Peruzzi, P.P.; Lawler, S. MicroRNAs in cancer: Biomarkers, functions and therapy. Trends Mol. Med. 2014, 20, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vakilzadehian, N.; Moradi, Y.; Allela, O.Q.B.; Al-Hussainy, A.F.; Al-Nuaimi, A.M.A.; Al-Hussein, R.K.; Jawad, M.J.; Gandomkar, H.; Moradi, S. Non-coding RNA in the regulation of gastric cancer tumorigenesis: Focus on microRNAs and exosomal microRNAs. Int. J. Mol. Cell. Med. 2025, 13, 417–435. [Google Scholar]
- Bakinowska, E.; Kiełbowski, K.; Skórka, P.; Dach, A.; Olejnik-Wojciechowska, J.; Szwedkowicz, A.; Pawlik, A. Non-coding RNA as biomarkers and their role in the pathogenesis of gastric cancer—A narrative review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.M.; Wang, C.S.; Tsai, C.Y.; Huang, H.W.; Chi, H.C.; Lin, Y.H.; Lu, P.H.; Lin, K.H. Potential diagnostic, prognostic and therapeutic targets of microRNAs in human gastric cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.H.; Kuang, Z.Y.; Zhu, G.H.; Ni, B.Y.; Li, J. Multifaceted role of microRNAs in gastric cancer stem cells: Mechanisms and potential biomarkers. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2024, 16, 300–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalajahi, H.G.; Yari, A.H.; Amini, M.; Catal, T.; Youshanlui, M.A.; Pourbagherian, O.; Zhmurov, C.S.; Mokhtarzadeh, A. Therapeutic effect of microRNA-21 on differentially expressed hub genes in gastric cancer based on systems biology. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 21906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Qin, Y. Role of miRNA-145-5p in cancer (Review). Oncol. Rep. 2025, 53, 39. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, V.Y.; Chu, K.M. MiRNA as potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets for gastric cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 10432–10439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Song, B.; Wei, M.; Fang, J.; Xu, Y. miR-145-5p suppresses the proliferation, migration and invasion of gastric cancer epithelial cells via the ANGPT2/NOD_LIKE_RECEPTOR axis. Cancer Cell Int. 2020, 20, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Guan, D.H.; Bi, R.X.; Xie, J.; Yang, C.H.; Jiang, Y.H. Prognostic value of microRNAs in gastric cancer: A meta-analysis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 55489–55510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, Z.; Gao, C.; Chen, P.; Chen, J.; Liu, W.; Lu, H. miR-21 plays a pivotal role in gastric cancer pathogenesis and progression. Lab. Investig. 2008, 88, 1358–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koopaie, M.; Arian-Kia, S.; Manifar, S.; Fatahzadeh, M.; Kolahdooz, S.; Davoudi, M. Expression of salivary miRNAs, clinical, and demographic features in the early detection of gastric cancer: A statistical and machine learning analysis. J. Gastrointest. Cancer 2025, 56, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.H.; Bai, Z.Z.; Niu, X.D.; Zhu, C.I.; Liang, T.; Hu, Y.L.; Gao, Z.H.; Da, M.X. Serum extracellular vesicle-derived miR-21-5p and miR-26a-5p as non-invasive diagnostic potential biomarkers for gastric cancer: A preliminary study. Int. J. Biol. Markers 2024, 39, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.X.; Qiu, X.M.; Xu, C.H.; Guo, J.Q. miRNA-145-5p inhibits gastric cancer progression via the serpin family E member 1–extracellular signal-regulated kinase-1/2 axis. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2024, 16, 2123–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciesielski, M.; Szajewski, M.; Peksa, R.; Lewandowska, M.A.; Zielinski, J.; Walczak, J.; Szefel, J.; Kruszewski, W.J. The relationship between HER2 overexpression and angiogenesis in gastric cancer. Medicine 2018, 97, e12851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seok, J.K.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, M.J.; Lee, Y.M. MicroRNA-382 induced by HIF-1α is an angiogenic miR targeting the tumor suppressor phosphatase and tensin homolog. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 8062–8072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paduch, R. The role of lymphangiogenesis and angiogenesis in tumor metastasis. Cell. Oncol. 2016, 39, 397–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.B.; Edge, S.B.; Greene, F.L.; Byrd, D.R.; Brookland, R.K.; Washington, M.K.; Gershenwald, J.E.; Compton, C.C.; Hess, K.R.; Sullivan, D.C.; et al. (Eds.) AJCC Cancer Staging Manual, 8th ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Mueller, C.; Gao, G.; Flotte, T.R. The 2024 Nobel Prize: Impact of the discovery of miRNA on the field to gene therapy. Hum. Gene Ther. 2025, 36, 726–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilan, F.; Amini, M.; Doustvandi, M.A.; Tohidast, M.; Baghbanzadeh, A.; Hosseini, S.S.; Mokhtarzadeh, A.; Baradaran, B. Simultaneous suppression of miR-21 and restoration of miR-145 in gastric cancer cells; a promising strategy for inhibition of cell proliferation and migration. BioImpacts 2024, 14, 27764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.T.; Wang, Y.W.; Xing, A.Y.; Shi, D.B.; Zhang, H.; Guo, X.Y.; Xu, J.; Gao, P. Prognostic value of microRNA signature in patients with gastric cancers. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Cai, Q.; Jiang, Z.; Liu, B.; Zhu, Z.; Li, C. Prognostic role of microRNA-21 in gastric cancer: A meta-analysis. Med. Sci. Monit. 2014, 20, 1668–1674. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Fan, Z.; Liu, F.; Zuo, J. Hsa-miR-21 and Hsa-miR-29 in tissue as potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for gastric cancer. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 37, 1454–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wen, X.; Hu, X.L.; Cheng, L.Z.; Yu, J.Y.; Wei, Z.B. Downregulation of miR-145-5p correlates with poor prognosis in gastric cancer. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2016, 20, 3026–3030. [Google Scholar]
- de Jong, M.H.S.; Gisbertz, S.S.; van Berge Henegouwen, M.I.; Draaisma, W.A. Prevalence of nodal metastases in the individual lymph node stations for different T-stages in gastric cancer: A systematic review. Updates Surg. 2023, 75, 281–290. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.G.; Li, J.F.; Yu, B.Q.; Zhu, Z.G.; Liu, B.Y.; Yan, M.I.N. microRNA-21 promotes tumor proliferation and invasion in gastric cancer by targeting PTEN. Oncol. Rep. 2012, 27, 1019–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, S.H.; Wu, C.W.; Li, A.F.; Chi, C.W.; Lin, W.C. miR-21 microRNA expression in human gastric carcinomas and its clinical association. Anticancer Res. 2008, 28, 907–911. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Sun, J.; Xu, J.; Li, Q.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, Q. miR-21 is a promising novel biomarker for lymph node metastasis in patients with gastric cancer. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2012, 2012, 640168. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Takagi, T.; Iio, A.; Nakagawa, Y.; Naoe, T.; Tanigawa, N.; Akao, Y. Decreased expression of microRNA-143 and -145 in human gastric cancers. Oncology 2009, 77, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naito, Y.; Yasuno, K.; Tagawa, H.; Sakamoto, N.; Oue, N.; Yashiro, M.; Sentani, K.; Goto, K.; Shinmei, S.; Oo, H.Z.; et al. MicroRNA-145 is a potential prognostic factor of scirrhous type gastric cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 32, 1720–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Wu, S.; Xiao, J.; Zhang, Z. Ferroptosis: Opening up potential targets for gastric cancer treatment. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2024, 479, 2863–2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, A.N.; Jung, Y.; Jang, H.; Lee, E.; Bae, H.I.; Son, T.; Kwon, O.; Chung, H.Y.; Yu, W.; Lee, Y.M. Clinical significance and prognostic role of hypoxia-induced microRNA 382 in gastric adenocarcinoma. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0223608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, M.J.; Carbajal, J.; Alfaro, A.L.; Saravia, L.G.; Zanabria, D.; Araujo, J.M.; Quispe, L.; Zevallos, A.; Buleje, J.L.; Cho, C.E.; et al. Characteristics of gastric cancer around the world. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2023, 181, 103841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Histopathological Feature/Survival | n = 123 |
| pTNM | |
| I | 22 (17.9%) |
| II | 34 (27.6%) |
| III | 62 (50.4%) |
| IV | 5 (4.1%) |
| N+ | 88 (71.6%) |
| Mean (median) number of metastatic lymph nodes | 6.0 (3) |
| Mean (median) number of resected lymph nodes | 21.8 (20) |
| Mucinous component | 28 (22.8%) |
| Lauren histopathological type | |
| 1 Intestinal | 60 (48.8%) |
| 2 Diffuse | 35 (28.5%) |
| 3 Mixed | 28 (22.8%) |
| Survival | |
| 12 months | 101 (82.1%) |
| 24 months | 79 (64.2%) |
| 36 months | 63 (51.2%) |
| 48 months | 56 (45.5%) |
| 60 months | 50 (40.7%) |
| hsa-miR-21-5p | hsa-miR-145-5p | hsa-miR-382-5p | ||
| pT | is-2 [n = 33] | 2.57 (0.2–16.23) | 22.34 (3.26–229.1) | 0.01 (0–0.21) |
| 3–4 [n = 90] | 7.72 (0.89–26.3) | 8.68 (0.91–26.4) | 0.02 (0–0.66) | |
| p | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.0984 | |
| pN | N0 [n = 35] | 3.28 (0.89–26.2) | 17.17 (1.67–229.1) | 0.01 (0–0.21) |
| N+ [n = 88] | 7.25 (0.2–26.3) | 10.58 (0.91–29.87) | 0.02 (0–0.66) | |
| p | 0.0097 | 0.0077 | 0.0948 | |
| M | M0 [n = 118] | 6.49 (0.2–26.3) | 12.05 (0.91–229.1) | 0.02 (0–0.66) |
| M1 [n = 5] | 7.32 (2.04–12.66) | 11.92 (5.25–22.78) | 0.02 (0–0.41) | |
| p | 0.9897 | 0.8376 | 0.9591 | |
| pTNM stage | I–II [n = 56] | 4.78 (0.2–26.3) | 13.54 (1.67–229.1) | 0.01 (0–0.21) |
| III–IV [n = 67] | 7.71 (1.58–24.71) | 9.66 (0.91–26.4) | 0.02 (0–0.66) | |
| p | 0.0072 | 0.0211 | 0.0718 | |
| Mucinous | No [n = 95] | 6.72 (0.2–26.3) | 10.19 (0.91–229.1) | 0.02 (0–0.66) |
| Yes [n = 28] | 5.91 (1.24–17.88) | 14.76 (2.51–39.65) | 0.01 (0–0.07) | |
| p | 0.9781 | 0.0563 | 0.0262 | |
| Tumor location | Cardia [n = 42] | 7.26 (1.06–26.3) | 8.19 (0.91–29.92) | 0.01 (0–0.49) |
| Other [n = 81] | 5.63 (0.2–26.2) | 13.14 (1.28–229.1) | 0.02 (0–0.66) | |
| p | 0.0646 | 0.0055 | 0.2395 | |
| Lauren | Intestinal [n = 59] | 7.1 (0.2–26.3) | 8.31 (0.91–229.1) | 0.01 (0–0.21) |
| Diffuse [n = 35] | 4.75 (1.24–19.42) | 14.8 (4.7–39.65) | 0.02 (0–0.66) | |
| Mixed [n = 27] | 4.25 (1.68–24.71) | 11.71 (2.37–27.24) | 0.03 (0–0.49) | |
| p | 0.1814 | 0.0037 | 0.1607 | |
| hsa-miR-21-5p | hsa-miR-145-5p | hsa-miR-382-5p | ||||
| r | p | r | p | r | p | |
| Number of nodes with metastasis | 0.15 | 0.0992 | −0.18 | 0.046 | 0.2 | 0.0262 |
| miRNA | Outcome | HR/OR | 95% CI | p-Value | Adjusted HR/OR | 95% CI Adjusted | Adjusted p-Value |
| hsa-miR-145-5p | Hazard ratio | 0.78 | 0.64–0.95 | 0.013 | 0.79 | 0.65–0.97 | 0.025 |
| 3-year survival | 1.863 | 1.28–2.82 | 0.0019 | 1.851 | 1.26–2.83 | 0.0028 | |
| 4-year survival | 1.738 | 1.2–2.61 | 0.005 | 1.7 | 1.16–2.58 | 0.0087 | |
| 5-year survival | 1.521 | 1.06–2.25 | 0.0273 | 1.459 | 1.01–2.18 | 0.0539 | |
| Node metastasis | 0.572 | 0.36–0.86 | 0.0099 | 0.597 | 0.38–0.89 | 0.0174 | |
| hsa-miR-21-5p | Hazard ratio | 1.12 | 0.91–1.39 | 0.2746 | 1.1 | 0.88–1.37 | 0.4022 |
| 3-year survival | 0.651 | 0.45–0.93 | 0.0219 | 0.657 | 0.45–0.95 | 0.0279 | |
| 4-year survival | 0.739 | 0.51–1.05 | 0.0989 | 0.754 | 0.52–1.09 | 0.1332 | |
| 5-year survival | 0.817 | 0.57–1.17 | 0.2711 | 0.845 | 0.58–1.23 | 0.3761 | |
| Node metastasis | 1.646 | 1.1–2.53 | 0.0178 | 1.613 | 1.07–2.49 | 0.025 | |
| hsa-miR-382-5p | Hazard ratio | 0.6 | 0.09–4.07 | 0.602 | 0.43 | 0.06–2.98 | 0.3932 |
| 3-year survival | 0.575 | 0.02–12.06 | 0.7176 | 0.898 | 0.03–21.34 | 0.9467 | |
| 4-year survival | 1.271 | 0.06–27.73 | 0.8751 | 2.25 | 0.08–56.4 | 0.6146 | |
| 5-year survival | 2.045 | 0.09–45.71 | 0.6404 | 4.434 | - | 0.3696 | |
| Node metastasis | 49.627 | - | 0.1475 | 49.658 | - | 0.1527 |
| miRNA | Outcome | HR/OR | 95% CI | p-Value | Adjusted HR/OR | 95% CI Adjusted | Adjusted p-Value |
| hsa-miR-145-5p | Hazard ratio | 0.78 | 0.64–0.95 | 0.013 | 0.77 | 0.62–0.96 | 0.0222 |
| 3-year survival | 1.863 | 1.28–2.82 | 0.0019 | 1.871 | 1.25–2.91 | 0.0034 | |
| 4-year survival | 1.738 | 1.2–2.61 | 0.005 | 1.705 | 1.15–2.62 | 0.0103 | |
| 5-year survival | 1.521 | 1.06–2.25 | 0.0273 | 1.463 | 1.00–2.21 | 0.0576 | |
| Node metastasis | 0.572 | 0.36–0.86 | 0.0099 | 0.544 | 0.33–0.84 | 0.0093 | |
| hsa-miR-21-5p | Hazard ratio | 1.12 | 0.91–1.39 | 0.2746 | 1.06 | 0.84–1.33 | 0.6279 |
| 3-year survival | 0.651 | 0.45–0.93 | 0.0219 | 0.698 | 0.47–1.02 | 0.0674 | |
| 4-year survival | 0.739 | 0.51–1.05 | 0.0989 | 0.804 | 0.55–1.18 | 0.2636 | |
| 5-year survival | 0.817 | 0.57–1.17 | 0.2711 | 0.906 | 0.61–1.34 | 0.62 | |
| Node metastasis | 1.646 | 1.1–2.53 | 0.0178 | 1.756 | 1.15–2.76 | 0.0112 | |
| hsa-miR-382-5p | Hazard ratio | 0.6 | 0.09–4.07 | 0.602 | 0.49 | 0.07–3.23 | 0.4593 |
| 3-year survival | 0.575 | 0.02–12.06 | 0.7176 | 0.737 | 0.02–19.64 | 0.8584 | |
| 4-year survival | 1.271 | 0.06–27.73 | 0.8751 | 1.932 | 0.06–53.55 | 0.6988 | |
| 5-year survival | 2.045 | 0.09–45.71 | 0.6404 | 3.693 | - | 0.458 | |
| Node metastasis | 49.627 | - | 0.1475 | 40.766 | - | 0.1738 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ciesielski, M.; Lewandowska, M.A.; Szajewski, M.; Pastuszak, K.; Kurek, P.; Zieliński, J.; Walczak, J.; Pęksa, R.; Kruszewski, W.J. The Impact of miR-21-5p, miR-145-5p and miR-382-5p Expression in Gastric Adenocarcinoma Cells on Lymphatic Spread Capability. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 2393. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13102393
Ciesielski M, Lewandowska MA, Szajewski M, Pastuszak K, Kurek P, Zieliński J, Walczak J, Pęksa R, Kruszewski WJ. The Impact of miR-21-5p, miR-145-5p and miR-382-5p Expression in Gastric Adenocarcinoma Cells on Lymphatic Spread Capability. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(10):2393. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13102393
Chicago/Turabian StyleCiesielski, Maciej, Marzena Anna Lewandowska, Mariusz Szajewski, Krzysztof Pastuszak, Piotr Kurek, Jacek Zieliński, Jakub Walczak, Rafał Pęksa, and Wiesław Janusz Kruszewski. 2025. "The Impact of miR-21-5p, miR-145-5p and miR-382-5p Expression in Gastric Adenocarcinoma Cells on Lymphatic Spread Capability" Biomedicines 13, no. 10: 2393. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13102393
APA StyleCiesielski, M., Lewandowska, M. A., Szajewski, M., Pastuszak, K., Kurek, P., Zieliński, J., Walczak, J., Pęksa, R., & Kruszewski, W. J. (2025). The Impact of miR-21-5p, miR-145-5p and miR-382-5p Expression in Gastric Adenocarcinoma Cells on Lymphatic Spread Capability. Biomedicines, 13(10), 2393. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13102393






