Diagnostic Accuracy of DaTQUANT® Versus BasGanV2™ for 123I-Ioflupane Brain SPECT: A Machine Learning-Based Differentiation of Parkinson’s Disease and Essential Tremor
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. SPECT Protocol
2.2. Image Processing
2.3. Statistical Analysis
2.4. Machine Learning Analysis
2.4.1. Hyperparameter Tuning
- ClT
- Measure of the quality of a split = {‘gini’, ‘entropy’}
- Depth of the tree = {2, 3, 4}
- k-NN
- Number of neighbours = {1, 2, 3, 4}
- SVM
- Regularisation parameter C = {0.1, 1, 10, 100, 1000}
- Kernel = {‘linear’, ‘rbf’}
- Kernel coefficient for ‘rbf’ = {1, 0.1, 0.01, 0.001, 0.0001}
2.4.2. Performance Estimation
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hauser, R.A.; Grosset, D.G. [123I]FP-CIT (DaTscan) SPECT Brain Imaging in Patients with Suspected Parkinsonian Syndromes. J. Neuroimaging 2012, 22, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graebner, A.K.; Tarsy, D.; Shih, L.C.; Vanderhorst, V.; Kulkarni, O.; Kaplan, S.; Simon, D.K. Clinical Impact of 123I-Ioflupane SPECT (DaTscan) in a Movement Disorder Center. Neurodegener. Dis. 2017, 17, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bega, D.; Kuo, P.H.; Chalkidou, A.; Grzeda, M.T.; Macmillan, T.; Brand, C.; Sheikh, Z.H.; Antonini, A. Clinical Utility of DaTscan in Patients with Suspected Parkinsonian Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. npj Parkinsons Dis. 2021, 7, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seibyl, J.P.; Kupsch, A.; Booij, J.; Grosset, D.G.; Costa, D.C.; Hauser, R.A.; Darcourt, J.; Bajaj, N.; Walker, Z.; Marek, K.; et al. Individual-Reader Diagnostic Performance and between-Reader Agreement in Assessment of Subjects with Parkinsonian Syndrome or Dementia Using 123I-Ioflupane Injection (DaTscan) Imaging. J. Nucl. Med. 2014, 55, 1288–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booij, J.; Dubroff, J.; Pryma, D.; Yu, J.; Agarwal, R.; Lakhani, P.; Kuo, P.H. Diagnostic Performance of the Visual Reading of 123I-Ioflupane SPECT Images With or Without Quantification in Patients With Movement Disorders or Dementia. J. Nucl. Med. 2017, 58, 1821–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, P.H.; Cella, P.; Chou, Y.-H.; Arkhipenko, A.; Fisher, J.M. Optimal DaTQUANT Thresholds for Diagnostic Accuracy of Dementia with Lewy Bodies (DLB) and Parkinson’s Disease (PD). Tomography 2024, 10, 1608–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morbelli, S.; Arnaldi, D.; Cella, E.; Raffa, S.; Donegani, M.I.; Capitanio, S.; Massa, F.; Miceli, A.; Filippi, L.; Chincarini, A.; et al. Striatal Dopamine Transporter SPECT Quantification: Head-to-Head Comparison between Two Three-Dimensional Automatic Tools. EJNMMI Res. 2020, 10, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syed, A.B.; Zoga, A.C. Artificial Intelligence in Radiology: Current Technology and Future Directions. Semin. Musculoskelet. Radiol. 2018, 22, 540–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saboury, B.; Morris, M.; Siegel, E. Future Directions in Artificial Intelligence. Radiol. Clin. N. Am. 2021, 59, 1085–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascianelli, S.; Scialpi, M.; Amici, S.; Forini, N.; Minestrini, M.; Fravolini, M.L.; Sinzinger, H.; Schillaci, O.; Palumbo, B. Role of Artificial Intelligence Techniques (Automatic Classifiers) in Molecular Imaging Modalities in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2017, 14, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez, J.D.; Matias-Guiu, J.A.; Cabrera-Martín, M.N.; Risco-Martín, J.L.; Ayala, J.L. An Application of Machine Learning with Feature Selection to Improve Diagnosis and Classification of Neurodegenerative Disorders. BMC Bioinform. 2019, 20, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kale, M.; Wankhede, N.; Pawar, R.; Ballal, S.; Kumawat, R.; Goswami, M.; Khalid, M.; Taksande, B.; Upaganlawar, A.; Umekar, M.; et al. AI-Driven Innovations in Alzheimer’s Disease: Integrating Early Diagnosis, Personalized Treatment, and Prognostic Modelling. Ageing Res. Rev. 2024, 101, 102497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.-S. Application of Artificial Intelligence in Nuclear Neuroimaging. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2024, 58, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwabuchi, Y.; Nakahara, T.; Kameyama, M.; Yamada, Y.; Hashimoto, M.; Matsusaka, Y.; Osada, T.; Ito, D.; Tabuchi, H.; Jinzaki, M. Impact of a Combination of Quantitative Indices Representing Uptake Intensity, Shape, and Asymmetry in DAT SPECT Using Machine Learning: Comparison of Different Volume of Interest Settings. EJNMMI Res. 2019, 9, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuvoli, S.; Spanu, A.; Fravolini, M.L.; Bianconi, F.; Cascianelli, S.; Madeddu, G.; Palumbo, B. [123I]Metaiodobenzylguanidine (MIBG) Cardiac Scintigraphy and Automated Classification Techniques in Parkinsonian Disorders. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2020, 22, 703–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poli, G.L.; Bianchi, C.; Guerra, U.P. Use of the BasGan Algorithm for [123I]FP-CIT SPECT Quantification: A Phantom Study. Q. J. Nucl. Med. Mol Imaging 2013, 57, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Blagus, R.; Lusa, L. SMOTE for High-Dimensional Class-Imbalanced Data. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 14, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.; Kwak, I.-Y. Mastering Data Visualization with Python: Practical Tips for Researchers. J. Minim. Invasive Surg. 2023, 26, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pajankar, A. Introduction to Data Visualization with Seaborn. In Hands-on Matplotlib; Apress: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2022; pp. 243–267. ISBN 978-1-4842-7409-5. [Google Scholar]
- Tinaz, S.; Chow, C.; Kuo, P.H.; Krupinski, E.A.; Blumenfeld, H.; Louis, E.D.; Zubal, G. Semiquantitative Analysis of Dopamine Transporter Scans in Patients With Parkinson Disease. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2018, 43, e1–e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morbelli, S.; Esposito, G.; Arbizu, J.; Barthel, H.; Boellaard, R.; Bohnen, N.I.; Brooks, D.J.; Darcourt, J.; Dickson, J.C.; Douglas, D.; et al. EANM Practice Guideline/SNMMI Procedure Standard for Dopaminergic Imaging in Parkinsonian Syndromes 1.0. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2020, 47, 1885–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Missir, E.; Begley, P.; Jessop, M.; Singh, N.; Aplin, M.; McMeekin, H.; Parekh, P.; Raczek, M.; Dizdarevic, S. Quantitative [123]I-Ioflupane DaTSCAN Single-Photon Computed Tomography-Computed Tomography in Parkinsonism. Nucl. Med. Commun. 2023, 44, 843–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Augimeri, A.; Cherubini, A.; Cascini, G.L.; Galea, D.; Caligiuri, M.E.; Barbagallo, G.; Arabia, G.; Quattrone, A. CADA—Computer-Aided DaTSCAN Analysis. EJNMMI Phys 2016, 3, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palumbo, B.; Fravolini, M.L.; Nuvoli, S.; Spanu, A.; Paulus, K.S.; Schillaci, O.; Madeddu, G. Comparison of Two Neural Network Classifiers in the Differential Diagnosis of Essential Tremor and Parkinson’s Disease by 123I-FP-CIT Brain SPECT. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2010, 37, 2146–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palumbo, B.; Fravolini, M.L.; Buresta, T.; Pompili, F.; Forini, N.; Nigro, P.; Calabresi, P.; Tambasco, N. Diagnostic Accuracy of Parkinson Disease by Support Vector Machine (SVM) Analysis of 123I-FP-CIT Brain SPECT Data: Implications of Putaminal Findings and Age. Medicine 2014, 93, e228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palumbo, B.; Bianconi, F.; Nuvoli, S.; Spanu, A.; Fravolini, M.L. Artificial Intelligence Techniques Support Nuclear Medicine Modalities to Improve the Diagnosis of Parkinson’s Disease and Parkinsonian Syndromes. Clin. Transl. Imaging 2021, 9, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuvoli, S.; Bianconi, F.; Rondini, M.; Lazzarato, A.; Marongiu, A.; Fravolini, M.L.; Cascianelli, S.; Amici, S.; Filippi, L.; Spanu, A.; et al. Differential Diagnosis of Alzheimer Disease vs. Mild Cognitive Impairment Based on Left Temporal Lateral Lobe Hypomethabolism on 18F-FDG PET/CT and Automated Classifiers. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhou, Y.; Dvornek, N.C.; Gu, Y.; Ventola, P.; Duncan, J.S. Efficient Shapley Explanation For Features Importance Estimation Under Uncertainty. In Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2020; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 12261, pp. 792–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloch, L.; Friedrich, C.M. Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative Data Analysis with Shapley Values for Automatic Subject Selection in Alzheimer’s Disease Data Sets Using Interpretable Machine Learning. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2021, 13, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenblatt, M.; Tejavibulya, L.; Camp, C.C.; Jiang, R.; Westwater, M.L.; Noble, S.; Scheinost, D. Power and Reproducibility in the External Validation of Brain-Phenotype Predictions. bioRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Malhotra, Y.; Parikh, J. Integrative Approach for Early Detection of Parkinson’s Disease and Atypical Parkinsonian Syndromes Leveraging Hemodynamic Parameters, Motion Data & Advanced AI Models. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2025, 271, 108989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Xu, X.; Guo, X.; Li, Z.; Dong, B.; Qi, C.; Yang, C.; Zhou, D.; Wang, J.; Song, L.; et al. Improving Reliability of Movement Assessment in Parkinson’s Disease Using Computer Vision-Based Automated Severity Estimation. J. Parkinsons Dis. 2025, 15, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najmi, A.H.; Ariaei, A.; Khezri, M.; Noroozi, M.; Bafrani, M.A.; Gheysari, A.; Sabetghadam, F.; Ahmadi, M.; Sadeghi, M.; Mayeli, M.; et al. Longitudinal Assessment of Parkinson’s Motor Symptoms and Dopaminergic Dysfunction Patterns Using DaTSCAN. Clin. Park. Relat. Disord. 2025, 12, 100331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
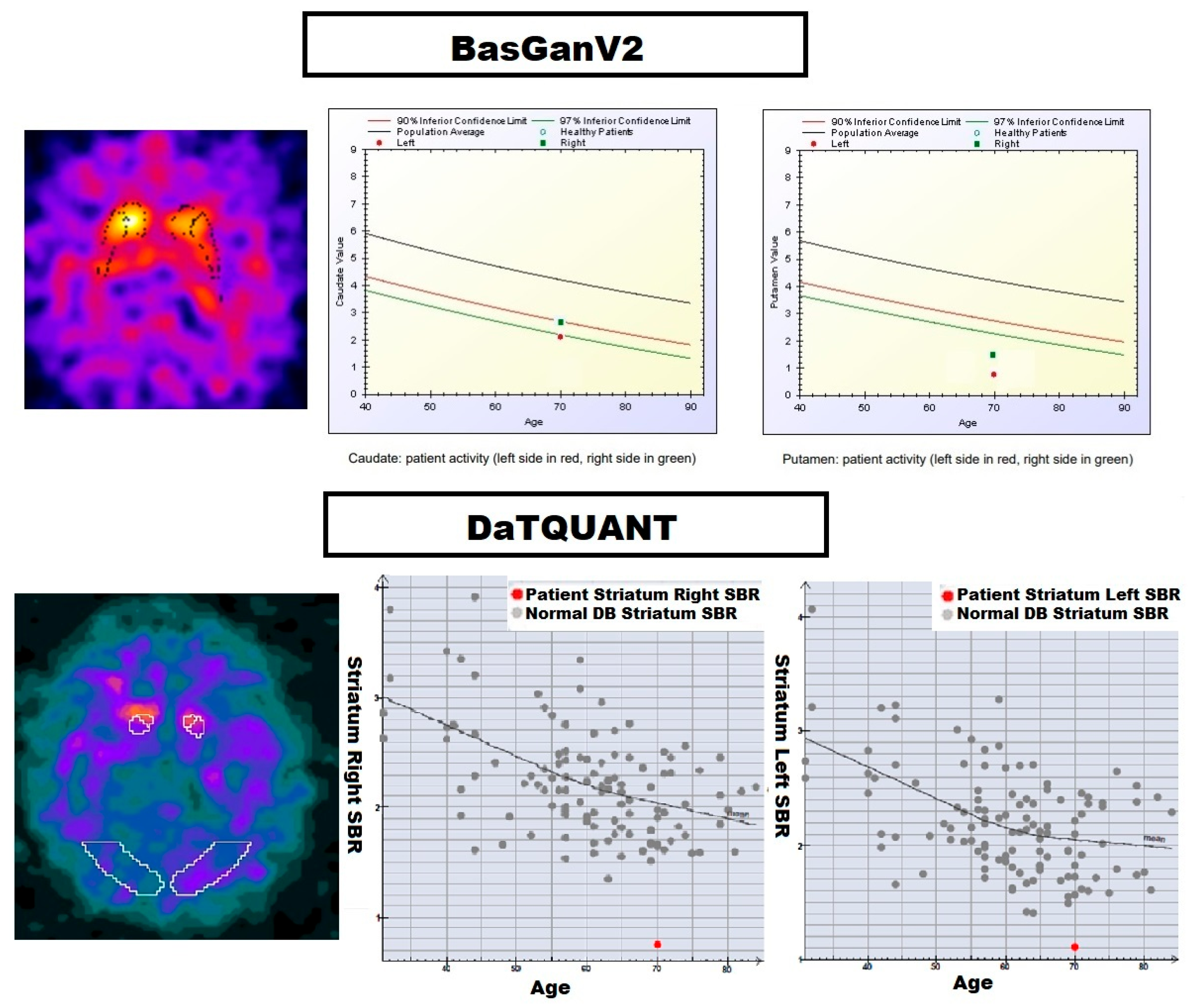
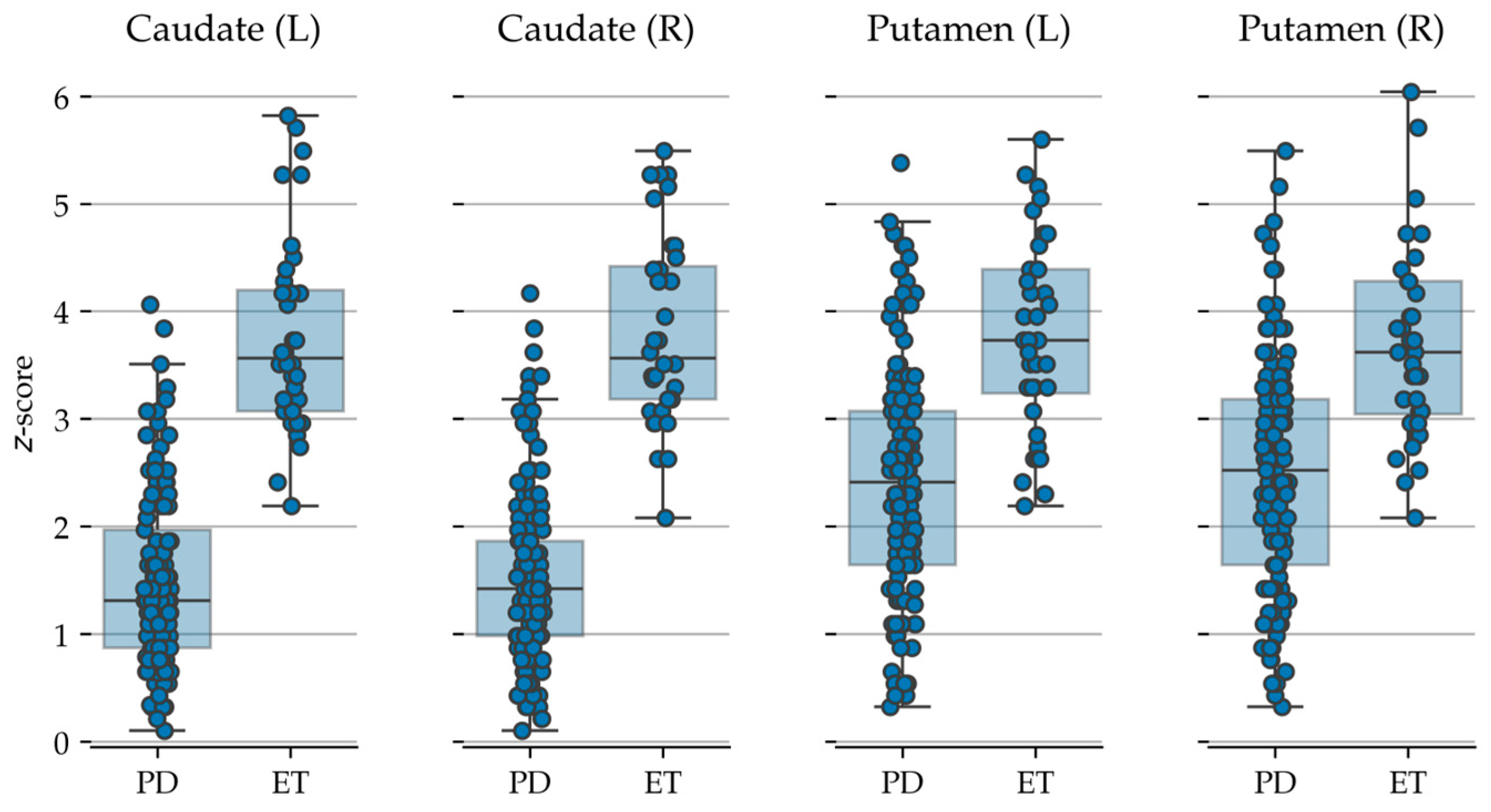
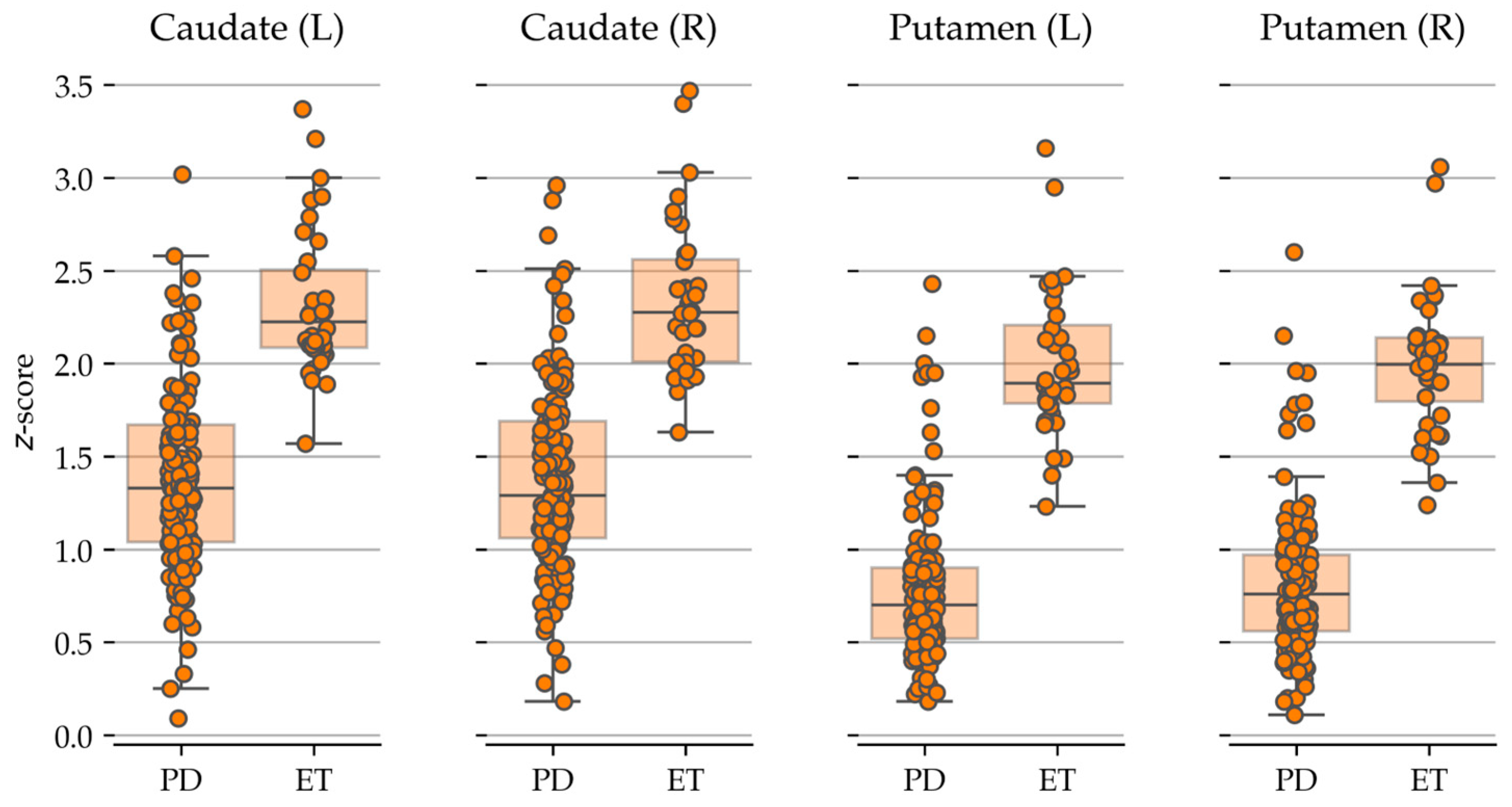
| Group | Number of Patients | Gender (M/F) | Age Range (Years) | HY Stage | UPDRS Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parkinson’s Disease (PD) | 133 | 86/47 | 44–85 | 0.5–1.5 | 6–38 |
| Essential Tremor (ET) | 36 | 12/24 | 37–82 | N/A | N/A |
| Area | Semi-Quantitative Analysis Tool | PD | ET | p-Value | p-Value (Corrected) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Caudate (L) | DaTQUANT® | 1.37 ± 0.49 | 2.32 ± 0.39 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Caudate (R) | 1.38 ± 0.50 | 2.33 ± 0.43 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| Putamen (L) | 0.78 ± 0.41 | 2.00 ± 0.40 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| Putamen (R) | 0.81 ± 0.40 | 2.00 ± 0.38 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| Caudate (L) | BasGanV2™ | 1.50 ± 0.81 | 3.77 ± 0.92 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Caudate (R) | 1.52 ± 0.81 | 3.82 ± 0.88 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| Putamen (L) | 2.44 ± 1.07 | 3.76 ± 0.90 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| Putamen (R) | 2.49 ± 1.07 | 3.69 ± 0.90 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| ClT | K-NN | SVM | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acc | Sn | Sp | Acc | Sn | Sp | Acc | Sn | Sp | |
| DaTQUANT® | 93.8 | 92.7 | 96.0 | 93.2 | 93.2 | 93.1 | 94.5 | 92.8 | 97.5 |
| BasGanV2™ | 90.9 | 90.2 | 92.0 | 91.7 | 91.0 | 92.9 | 91.9 | 91.2 | 93.1 |
| p-Value (Acc) | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Palumbo, B.; Filippi, L.; Marongiu, A.; Bianconi, F.; Fravolini, M.L.; Danieli, R.; Frantellizzi, V.; De Vincentis, G.; Spanu, A.; Nuvoli, S. Diagnostic Accuracy of DaTQUANT® Versus BasGanV2™ for 123I-Ioflupane Brain SPECT: A Machine Learning-Based Differentiation of Parkinson’s Disease and Essential Tremor. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 2367. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13102367
Palumbo B, Filippi L, Marongiu A, Bianconi F, Fravolini ML, Danieli R, Frantellizzi V, De Vincentis G, Spanu A, Nuvoli S. Diagnostic Accuracy of DaTQUANT® Versus BasGanV2™ for 123I-Ioflupane Brain SPECT: A Machine Learning-Based Differentiation of Parkinson’s Disease and Essential Tremor. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(10):2367. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13102367
Chicago/Turabian StylePalumbo, Barbara, Luca Filippi, Andrea Marongiu, Francesco Bianconi, Mario Luca Fravolini, Roberta Danieli, Viviana Frantellizzi, Giuseppe De Vincentis, Angela Spanu, and Susanna Nuvoli. 2025. "Diagnostic Accuracy of DaTQUANT® Versus BasGanV2™ for 123I-Ioflupane Brain SPECT: A Machine Learning-Based Differentiation of Parkinson’s Disease and Essential Tremor" Biomedicines 13, no. 10: 2367. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13102367
APA StylePalumbo, B., Filippi, L., Marongiu, A., Bianconi, F., Fravolini, M. L., Danieli, R., Frantellizzi, V., De Vincentis, G., Spanu, A., & Nuvoli, S. (2025). Diagnostic Accuracy of DaTQUANT® Versus BasGanV2™ for 123I-Ioflupane Brain SPECT: A Machine Learning-Based Differentiation of Parkinson’s Disease and Essential Tremor. Biomedicines, 13(10), 2367. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13102367








