Assessing the Heterogeneous Treatment Effects of Glucocorticoids in Infants and Toddlers with Severe Pneumonia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Population and Study Design
2.2. Covariates, Exposure, and Outcomes
2.3. Model Construction and HTE Analysis
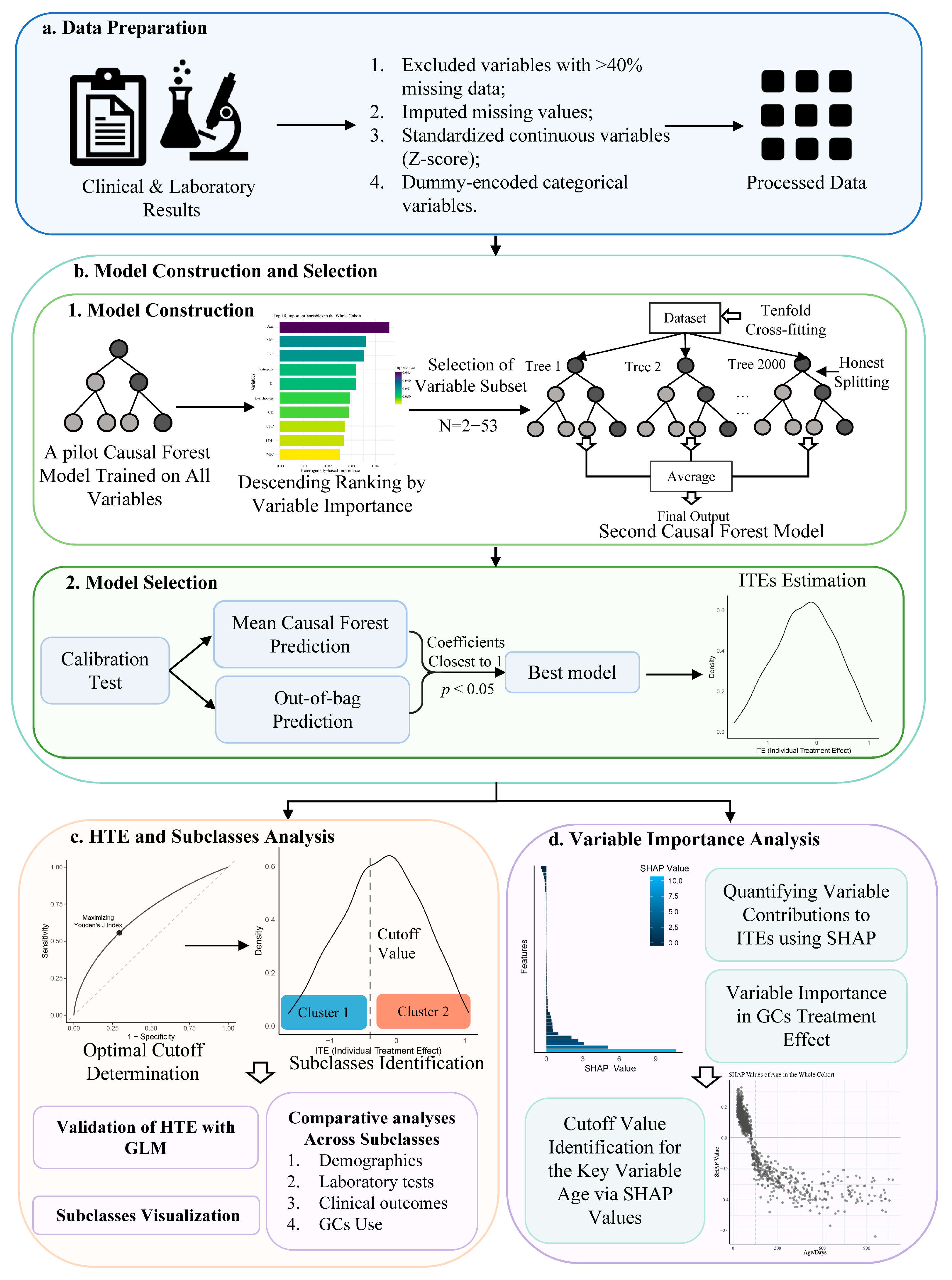
2.3.1. Data Preparation
2.3.2. Model Construction and Selection
2.3.3. HTE and Subclasses Analysis
2.3.4. Variable Importance Analysis
2.4. Sensitivity Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Participant Characteristics
3.2. Subclass Identification and Intergroup Analysis in the Whole Cohort
3.3. Subclass Identification and Intergroup Analysis in the MV Group
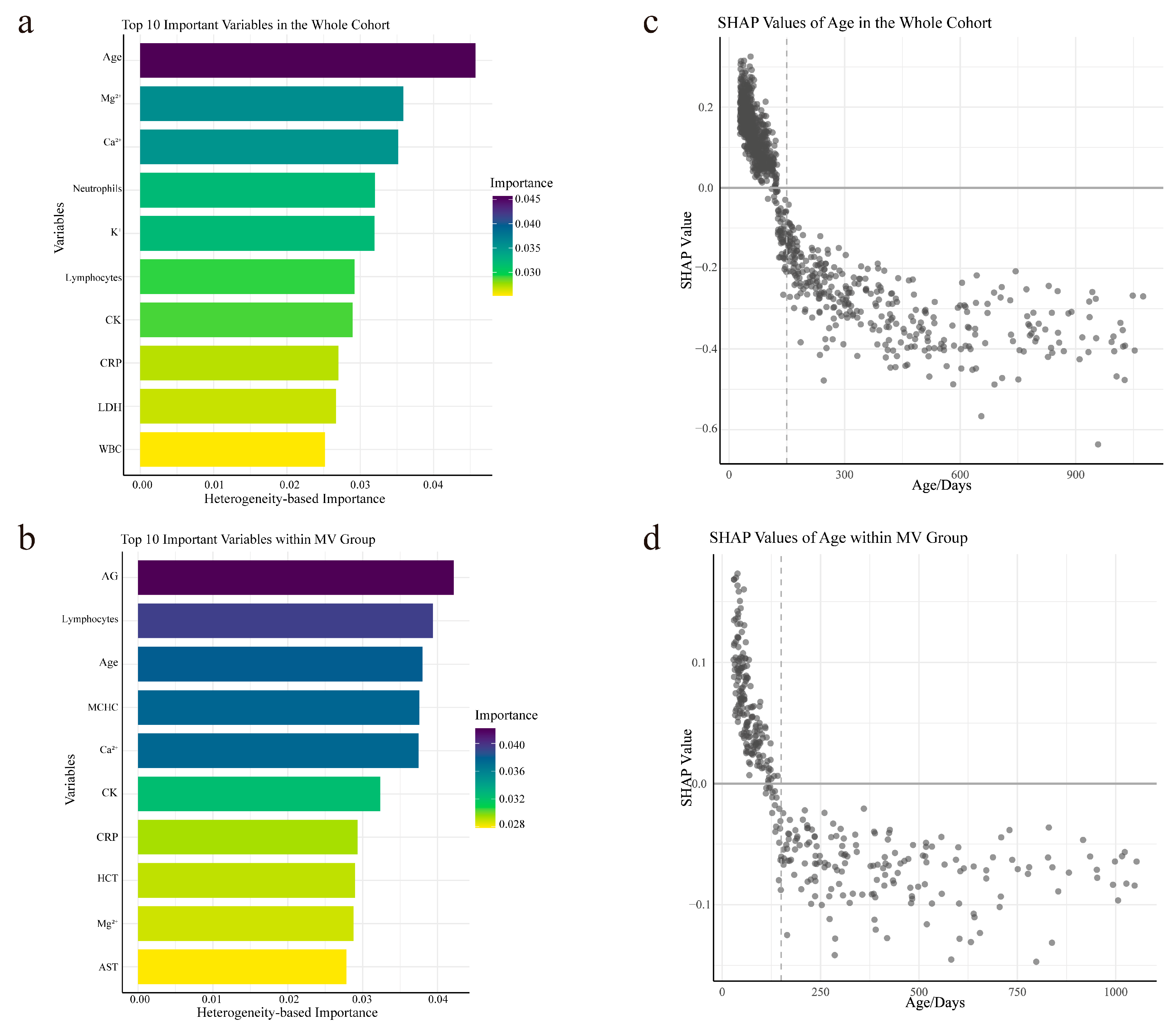
3.4. Variable Importance Analysis and Personalized Analysis of Age via SHAP
3.5. Sensitivity Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CAP | Community-acquired pneumonia |
| GCs | Glucocorticoids |
| HTE | Heterogeneous treatment effect |
| ITEs | Individual treatment effects |
| SHAP | Shapley Additive Explanations |
| ICU | Intensive care unit |
| RSV | Respiratory Syncytial Virus |
References
- Lee, G.E.; Lorch, S.A.; Sheffler-Collins, S.; Kronman, M.P.; Shah, S.S. National Hospitalization Trends for Pediatric Pneumonia and Associated Complications. Pediatrics 2010, 126, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimwood, K.; Chang, A.B. Long-Term Effects of Pneumonia in Young Children. Pneumonia 2015, 6, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrows, B.; Knudson, R.J.; Lebowitz, M.D. The Relationship of Childhood Respiratory Illness to Adult Obstructive Airway Disease. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1977, 115, 751–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, A.; Skalsky, K.; Avni, T.; Carrara, E.; Leibovici, L.; Paul, M. Corticosteroids for Pneumonia. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 2017, CD007720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, C.A.; Nigro, N.; Briel, M.; Schuetz, P.; Ullmer, E.; Suter-Widmer, I.; Winzeler, B.; Bingisser, R.; Elsaesser, H.; Drozdov, D.; et al. Adjunct Prednisone Therapy for Patients with Community-Acquired Pneumonia: A Multicentre, Double-Blind, Randomised, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Lancet 2015, 385, 1511–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijvis, S.C.; Hardeman, H.; Remmelts, H.H.; Heijligenberg, R.; Rijkers, G.T.; van Velzen-Blad, H.; Voorn, G.P.; van de Garde, E.M.; Endeman, H.; Grutters, J.C.; et al. Dexamethasone and Length of Hospital Stay in Patients with Community-Acquired Pneumonia: A Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Lancet 2011, 377, 2023–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Serrano, S.; Dorca, J.; Garcia-Vidal, C.; Fernández-Sabé, N.; Carratalà, J.; Fernández-Agüera, A.; Corominas, M.; Padrones, S.; Gudiol, F.; Manresa, F. Effect of Corticosteroids on the Clinical Course of Community-Acquired Pneumonia: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Crit. Care 2011, 15, R96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, A.; Sibila, O.; Ferrer, M.; Polverino, E.; Menendez, R.; Mensa, J.; Gabarrús, A.; Sellarés, J.; Restrepo, M.I.; Anzueto, A.; et al. Effect of Corticosteroids on Treatment Failure Among Hospitalized Patients With Severe Community-Acquired Pneumonia and High Inflammatory Response: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2015, 313, 677–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Confalonieri, M.; Urbino, R.; Potena, A.; Piattella, M.; Parigi, P.; Puccio, G.; Della Porta, R.; Giorgio, C.; Blasi, F.; Umberger, R.; et al. Hydrocortisone Infusion for Severe Community-Acquired Pneumonia. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 171, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dequin, P.F.; Meziani, F.; Quenot, J.P.; Kamel, T.; Ricard, J.D.; Badie, J.; Reignier, J.; Heming, N.; Plantefève, G.; Souweine, B.; et al. Hydrocortisone in Severe Community-Acquired Pneumonia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 1931–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittermans, E.; Vestjens, S.M.T.; Spoorenberg, S.M.C.; Blok, W.L.; Grutters, J.C.; Janssen, R.; Rijkers, G.T.; Smeenk, F.W.J.M.; Voorn, G.P.; van de Garde, E.M.W.; et al. Adjunctive Treatment with Oral Dexamethasone in Non-ICU Patients Hospitalised with Community-Acquired Pneumonia: A Randomised Clinical Trial. Eur. Respir. J. 2021, 58, 2002535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meduri, G.U.; Shih, M.-C.; Bridges, L.; Martin, T.J.; El-Solh, A.; Seam, N.; Davis-Karim, A.; Umberger, R.; Anzueto, A.; Sriram, P.; et al. Low-Dose Methylprednisolone Treatment in Critically Ill Patients with Severe Community-Acquired Pneumonia. Intensive Care Med. 2022, 48, 1009–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snijders, D.; Daniels, J.M.A.; de Graaff, C.S.; van der Werf, T.S.; Boersma, W.G. Efficacy of Corticosteroids in Community-Acquired Pneumonia. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 181, 975–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, N.; Kulkarni, A.; Snow, T.A.C.; Ambler, G.; Singer, M.; Arulkumaran, N. Effect of Corticosteroids on Mortality and Clinical Cure in Community-Acquired Pneumonia: A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and Meta-Regression of Randomized Control Trials. Chest 2023, 163, 484–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitre, T.; Abdali, D.; Chaudhuri, D.; Pastores, S.M.; Nei, A.M.; Annane, D.; Rochwerg, B.; Zeraatkar, D. Corticosteroids in Community-Acquired Bacterial Pneumonia: A Systematic Review, Pairwise and Dose-Response Meta-Analysis. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2023, 38, 2593–2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RECOVERY Collaborative Group; Horby, P.; Lim, W.S.; Emberson, J.R.; Mafham, M.; Bell, J.L.; Linsell, L.; Staplin, N.; Brightling, C.; Ustianowski, A.; et al. Dexamethasone in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 693–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, J.; Baek, K.S.; Lee, S. The Effects of Systemic Corticosteroid on Pediatric Community-Acquired Pneumonia: Comprehensive Review. Life Cycle 2022, 2, e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozsurekci, Y.; Aykac, K.; Demir, O.O.; Ilbay, S.; Kesici, S.; Karakaya, J.; Cengiz, A.B. Methylprednisolone Use in Children with Severe Pneumonia Caused by Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2. Pediatr. Int. 2023, 65, e15603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, L.; Xu, S.; Li, H.; Chu, C.; Liu, Q.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, W.; Huang, L. Low-Dose Corticosteroid Treatment in Children With Mycoplasma Pneumoniae Pneumonia: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Front. Pediatr. 2020, 8, 566371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagy, B.; Gaspar, I.; Papp, A.; Bene, Z.; Nagy, B., Jr.; Voko, Z.; Balla, G. Efficacy of Methylprednisolone in Children with Severe Community Acquired Pneumonia. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2013, 48, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Sol, I.S.; Li, D.; Choi, M.; Choi, Y.J.; Lee, K.S.; Seo, J.H.; Lee, Y.J.; Yang, H.-J.; Kim, H.H. Efficacy of Glucocorticoids for the Treatment of Macrolide Refractory Mycoplasma Pneumonia in Children: Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. BMC Pulm. Med. 2019, 19, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Luo, J.; Liu, E.; Xu, X.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, F.; Li, S.; Fu, Z. Effects of Prednisolone on Refractory Mycoplasma Pneumoniae Pneumonia in Children. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2014, 49, 377–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.Y.; Yang, E.A.; Rhim, J.-W.; Han, S.B. Effects of Antiviral Therapy and Glucocorticoid Therapy on Fever Duration in Pediatric Patients with Influenza. Medicina 2021, 57, 1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambroggio, L.; Test, M.; Metlay, J.P.; Graf, T.R.; Blosky, M.A.; Macaluso, M.; Shah, S.S. Adjunct Systemic Corticosteroid Therapy in Children With Community-Acquired Pneumonia in the Outpatient Setting. J. Pediatric Infect. Dis. Soc. 2015, 4, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, A.K.; Hall, M.; Lee, G.E.; Kronman, M.P.; Sheffler-Collins, S.; Shah, S.S. Adjunct Corticosteroids in Children Hospitalized with Community-Acquired Pneumonia. Pediatrics 2011, 127, e255–e263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagarro, A.; Otheo, E.; Baquero-Artigao, F.; Navarro, M.-L.; Velasco, R.; Ruiz, M.; Penín, M.; Moreno, D.; Rojo, P.; Madero, R.; et al. Dexamethasone for Parapneumonic Pleural Effusion: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Clinical Trial. J. Pediatr. 2017, 185, 117–123.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.-C.; Wang, J.-Y.; Chang, S.-M.; Chang, Y.-C.; Tsai, Y.-F.; Wu, A.C.; Huang, J.-L.; Tsai, H.-J. Association of Oral Corticosteroid Bursts With Severe Adverse Events in Children. JAMA Pediatr. 2021, 175, 723–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varadhan, R.; Seeger, J.D. Estimation and Reporting of Heterogeneity of Treatment Effects. In Developing a Protocol for Observational Comparative Effectiveness Research: A User’s Guide; Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US): Rockville, MD, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Sinha, P.; Spicer, A.; Delucchi, K.L.; McAuley, D.F.; Calfee, C.S.; Churpek, M.M. Comparison of Machine Learning Clustering Algorithms for Detecting Heterogeneity of Treatment Effect in Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: A Secondary Analysis of Three Randomised Controlled Trials. eBioMedicine 2021, 74, 103697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wager, S.; Athey, S. Estimation and Inference of Heterogeneous Treatment Effects Using Random Forests. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2018, 113, 1228–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athey, S.; Imbens, G. Recursive Partitioning for Heterogeneous Causal Effects. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 7353–7360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiba, K.; Daoud, A.; Kino, S.; Nishi, D.; Kondo, K.; Kawachi, I. Uncovering Heterogeneous Associations of Disaster-Related Traumatic Experiences with Subsequent Mental Health Problems: A Machine Learning Approach. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2022, 76, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osawa, I.; Goto, T.; Kudo, D.; Hayakawa, M.; Yamakawa, K.; Kushimoto, S.; Foster, D.M.; Kellum, J.A.; Doi, K. Targeted Therapy Using Polymyxin B Hemadsorption in Patients with Sepsis: A Post-Hoc Analysis of the JSEPTIC-DIC Study and the EUPHRATES Trial. Crit. Care 2023, 27, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Jian, B.; Chen, X.; Liu, M.; Zhang, S.; Fu, G.; Li, G.; Liang, M.; Tian, T.; Wu, Z. Heterogeneous Treatment Effects of Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting in Ischemic Cardiomyopathy: A Machine Learning Causal Forest Analysis. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2023, 168, 1462–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, C.; Shen, Y.; Sun, S.; Zhou, J.; Li, J.; Su, G.; Michalopoulou, E.; Peng, W.; Gu, Y.; Guo, W.; et al. Artificial Intelligence in Breast Imaging: Current Situation and Clinical Challenges. Exploration 2023, 3, 20230007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edward, J.A.; Josey, K.; Bahn, G.; Caplan, L.; Reusch, J.E.B.; Reaven, P.; Ghosh, D.; Raghavan, S. Heterogeneous Treatment Effects of Intensive Glycemic Control on Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events in the ACCORD and VADT Trials: A Machine-Learning Analysis. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2022, 21, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goligher, E.C.; Lawler, P.R.; Jensen, T.P.; Talisa, V.; Berry, L.R.; Lorenzi, E.; McVerry, B.J.; Chang, C.-C.H.; Leifer, E.; Bradbury, C.; et al. Heterogeneous Treatment Effects of Therapeutic-Dose Heparin in Patients Hospitalized for COVID-19. JAMA 2023, 329, 1066–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China. State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine Guideline for Diagnosis and Treatment of Community-Acquired Pneumonia in Children (2019 Version). Chin. J. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2019, 12, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China. Reference Intervals of Blood Cell Analysis for Children. Available online: http://www.nhc.gov.cn/wjw/s9492/202105/a85d8b64e0384c98aed8f3157860ee44/files/1739781618961_15816.pdf (accessed on 15 September 2024).
- National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China. Reference Intervals of Clinical Biochemistry Tests Commonly Used for Children. Available online: http://www.nhc.gov.cn/wjw/s9492/202105/3d5159ef7619452b9842ea9520189a11/files/1739781620270_69076.pdf (accessed on 15 September 2024).
- Liu, P.; Li, S.; Zheng, T.; Wu, J.; Fan, Y.; Liu, X.; Gong, W.; Xie, H.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; et al. Subphenotyping Heterogeneous Patients with Chronic Critical Illness to Guide Individualised Fluid Balance Treatment Using Machine Learning: A Retrospective Cohort Study. eClinicalMedicine 2023, 59, 101970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibshirani, J.; Athey, S.; Friedberg, R.; Hadad, V.; Hirshberg, D.; Miner, L.; Sverdrup, E.; Wager, S.; Wright, M. Grf: Generalized Random Forests; The R Foundation: Vienna, Austria, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Athey, S.; Wager, S. Estimating Treatment Effects with Causal Forests: An Application. Obs. Stud. 2019, 5, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavanaugh, J.E.; Neath, A.A. The Akaike Information Criterion: Background, Derivation, Properties, Application, Interpretation, and Refinements. WIREs Comput. Stat. 2019, 11, e1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundberg, S.M.; Lee, S.-I. A Unified Approach to Interpreting Model Predictions. In Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; Curran Associates Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 4768–4777. [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg, S.M.; Nair, B.; Vavilala, M.S.; Horibe, M.; Eisses, M.J.; Adams, T.; Liston, D.E.; Low, D.K.-W.; Newman, S.-F.; Kim, J.; et al. Explainable Machine-Learning Predictions for the Prevention of Hypoxaemia during Surgery. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 2, 749–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molnar, C.; Casalicchio, G.; Bischl, B. Iml: An R Package for Interpretable Machine Learning. J. Open Source Softw. 2018, 3, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Yadlowsky, S. Calibration Error for Heterogeneous Treatment Effects. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, Virtual, 28–30 March 2022; PMLR. pp. 9280–9303. [Google Scholar]
- Wittermans, E.; van de Garde, E.M.; Voorn, G.P.; Aldenkamp, A.F.; Janssen, R.; Grutters, J.C.; Bos, W.J.W. Neutrophil Count, Lymphocyte Count and Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio in Relation to Response to Adjunctive Dexamethasone Treatment in Community-Acquired Pneumonia. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2022, 96, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirracchio, R.; Venkatesh, B.; Legrand, M. Low-Dose Corticosteroids for Critically Ill Adults With Severe Pulmonary Infections: A Review. JAMA 2024, 332, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Woensel, J.B.M.; Vyas, H.; on behalf of the STAR Trial Group. Dexamethasone in Children Mechanically Ventilated for Lower Respiratory Tract Infection Caused by Respiratory Syncytial Virus: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 39, 1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-N.; Zhang, Y.-F.; Xu, Q.; Qiu, Y.; Lu, Q.-B.; Wang, T.; Zhang, X.-A.; Lin, S.-H.; Lv, C.-L.; Jiang, B.-G.; et al. Infection and Co-Infection Patterns of Community-Acquired Pneumonia in Patients of Different Ages in China from 2009 to 2020: A National Surveillance Study. Lancet Microbe 2023, 4, e330–e339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, A.K.; Hollander, G.A.; McMichael, A. Evolution of the Immune System in Humans from Infancy to Old Age. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2015, 282, 20143085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cillóniz, C.; Ewig, S.; Polverino, E.; Marcos, M.A.; Esquinas, C.; Gabarrús, A.; Mensa, J.; Torres, A. Microbial Aetiology of Community-Acquired Pneumonia and Its Relation to Severity. Thorax 2011, 66, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Cluster 1 | Cluster 2 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Outcomes | Treatment | β(log-time) | 95%CI | p | Adjusted p | β(log-time) | 95%CI | p | Adjusted p |
| Whole Cohort | |||||||||
| Duration of ICU stay (Days) | GC Use | −0.16 | [−0.25,−0.08] | <0.001 * | <0.001 * | 0.46 | [0.37,0.55] | <0.001 * | <0.001 * |
| Duration of GC treatment | −0.01 | [−0.02,0.01] | 0.50 | 0.57 | 0.07 | [0.06,0.09] | <0.001 * | <0.001 * | |
| GC treatment intensity | −0.14 | [−0.20,−0.08] | <0.001 * | <0.001 * | 0.34 | [0.26,0.40] | <0.001 * | <0.001 * | |
| Time to GC initiation | 0.01 | [−0.05,0.07] | 0.75 | 0.78 | 0.01 | [−0.02,0.03] | 0.64 | 0.70 | |
| Mechanically Ventilated Group | |||||||||
| Duration of ICU stay (Days) | GC Use | −0.34 | [−0.46,−0.24] | <0.001 * | <0.001 * | 0.36 | [0.28,0.46] | <0.001 * | <0.001 * |
| Duration of GC treatment | −0.02 | [−0.04,−0.004] | 0.02 * | 0.03 * | 0.06 | [0.04,0.07] | <0.001 * | <0.001 * | |
| GC treatment intensity | −0.21 | [−0.30,−0.13] | <0.001 * | <0.001 * | 0.26 | [0.19,0.34] | <0.001 * | <0.001 * | |
| Time to GC initiation | −0.005 | [−0.08,0.07] | 0.89 | 0.89 | −0.04 | [−0.10,0.01] | 0.10 | 0.13 | |
| Mechanical Ventilation Duration (Hours) | GC Use | −0.35 | [−0.51,−0.19] | <0.001 * | <0.001 * | 0.46 | [0.34,0.60] | <0.001 * | <0.001 * |
| Duration of GC treatment | −0.01 | [−0.041,0.01] | 0.33 | 0.42 | 0.07 | [0.05,0.09] | <0.001 * | <0.001 * | |
| GC treatment intensity | −0.29 | [−0.42,−0.17] | <0.001 * | <0.001 * | 0.30 | [0.19,0.42] | <0.001 * | <0.001 * | |
| Time to GC initiation | −0.05 | [−0.16,0.06] | 0.37 | 0.44 | 0.08 | [0.03,0.14] | 0.006 * | 0.009 * | |
| Overall | Cluster 1 | Cluster 2 | p | Adjusted p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristics | 1116 | 446 | 670 | ||
| Age (Median [IQR], Days) | 82.50 [51.00,200.00] | 216.00 [98.00,433.75] | 58.00 [43.00,88.75] | <0.001 * | <0.001 * |
| Patients Requiring Mechanical Ventilation (%) | 368 (32.97) | 209 (46.86) | 159 (23.73) | <0.001 * | <0.001 * |
| The duration of ICU stay, Days (median [IQR]) | 5.96 [4.71,8.24] | 6.71 [5.08,8.79] | 5.79 [4.08,7.92] | <0.001 * | <0.001 * |
| Mechanical Ventilation Duration, Hours (median [IQR]) | 109.10 [69.67,158.93] | 109.83 [68.75,140.99] | 106.62 [70.21,178.00] | 0.27 | 0.31 |
| Patients Receiving GC Treatment (%) | 273 (24.46) | 190 (42.60) | 83 (12.39) | <0.001 * | <0.001 * |
| The duration of GC treatment, Days (mean (SD)) | 5.70 (2.26) | 5.48 (1.95) | 6.18 (2.79) | 0.02 * | 0.03 * |
| GC treatment intensity, mg/(kg·day) (mean (SD)) | 1.24 (0.45) | 1.23 (0.45) | 1.28 (0.45) | 0.38 | 0.43 |
| Time to GC initiation, Days (median [IQR]) | 0.00 [0.00,1.00] | 0.00 [0.00,0.00] | 0.00 [0.00,1.00] | 0.02 * | 0.03 * |
| Comorbidities | 310 (27.78) | 149 (32.89) | 160 (23.88) | <0.001 * | 0.001 * |
| Circulatory System Disease (%) | 174 (15.59) | 83 (18.61) | 91 (13.58) | 0.03 * | 0.04 * |
| Blood Disease (%) | 62 (5.56) | 46 (10.31) | 16 (2.39) | <0.001 * | <0.001 * |
| Respiratory Disease (%) | 29 (2.60) | 14 (3.14) | 15 (2.24) | 0.46 | 0.52 |
| Digestive Disease (%) | 63 (5.65) | 15 (3.36) | 48 (7.16) | 0.01 * | 0.02 * |
| Nervous System Disease(%) | 38 (3.41) | 23 (5.16) | 15 (2.24) | 0.01 * | 0.02 * |
| Chromosomal Anomalies(%) | 17 (1.52) | 13 (2.91) | 4 (0.60) | 0.004 * | 0.009 * |
| Overall | Cluster 1 | Cluster 2 | p | Adjusted p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1116 | 446 | 670 | |||
| Viral Infection (%) | 499 (44.71) | 182 (40.81) | 317 (47.31) | 0.04 * | 0.06 |
| Influenza B (%) | 10 (1.06) | 3 (0.80) | 7 (1.23) | 0.75 | 0.79 |
| Parainfluenza virus (%) | 97 (10.28) | 36 (9.57) | 61 (10.74) | 0.64 | 0.76 |
| Respiratory syncytial virus (%) | 365 (38.67) | 121 (32.18) | 244 (42.96) | 0.001 * | 0.003 * |
| Influenza A (%) | 24 (2.54) | 15 (3.99) | 9 (1.58) | 0.04 * | 0.07 |
| Adenovirus (%) | 33 (3.50) | 22 (5.85) | 11 (1.94) | 0.003 * | 0.007 * |
| Atypical Infection (%) | 56 (6.20) | 37 (8.30) | 19 (2.84) | <0.001 * | <0.001 * |
| Mycoplasma pneumoniae (%) | 54 (5.98) | 37 (8.30) | 17 (2.54) | <0.001 * | <0.001 * |
| Chlamydophila pneumoniae (%) | 2 (0.22) | 0 (0.00) | 2 (0.30) | 0.65 | 0.76 |
| Bacterial Infection (%) | 433 (38.80) | 195 (43.72) | 238 (35.52) | 0.007 * | 0.02 * |
| Escherichia coli (%) | 38 (3.99) | 15 (4.01) | 23 (4.03) | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Haemophilus influenzae (%) | 96 (10.07) | 55 (14.55) | 41 (7.13) | <0.001 * | 0.001 * |
| Klebsiella pneumoniae (%) | 94 (9.86) | 44 (11.76) | 50 (8.73) | 0.16 | 0.22 |
| Streptococcus pneumoniae (%) | 99 (10.39) | 51 (13.56) | 48 (8.41) | 0.02 * | 0.03 * |
| Staphylococcus aureus (%) | 162 (17.00) | 52 (13.83) | 110 (19.06) | 0.044 * | 0.07 |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa (%) | 19 (2.00) | 12 (3.20) | 7 (1.23) | 0.06 | 0.09 |
| Acinetobacter baumannii (%) | 31 (3.25) | 15 (4.02) | 16 (2.80) | 0.40 | 0.52 |
| Overall | Cluster 1 | Cluster 2 | p | Adjusted p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristics | 368 | 159 | 209 | ||
| Age, Days (Median [IQR]) | 127.00 [61.00,338.50] | 240.00 [104.00,472.50] | 85.00 [51.00,210.00] | <0.001 * | <0.001 * |
| The duration of ICU stay, Days (median [IQR]) | 7.04 [5.83,9.97] | 7.54 [5.85,10.48] | 7.04 [5.83,9.88] | 0.60 | 0.72 |
| Mechanical Ventilation Duration, Hours (median [IQR]) | 109.35 [70.30,163.43] | 120.61 [77.72,180.98] | 94.32 [69.95,154.08] | 0.02 * | 0.04 * |
| Patients Receiving GC Treatment (%) | 154 (41.85) | 90 (56.60) | 64 (30.62) | <0.001 * | <0.001 * |
| The duration of GC treatment, Days (mean (SD)) | 5.86 (2.39) | 5.47 (1.89) | 6.41 (2.89) | 0.02 * | 0.04 * |
| GC treatment intensity, mg/(kg·day) (mean (SD)) | 1.20 (0.41) | 1.19 (0.36) | 1.22 (0.49) | 0.69 | 0.78 |
| Time to GC initiation, Days (median [IQR]) | 0.00 [0.00,1.00] | 0.00 [0.00,1.00] | 0.00 [0.00,1.00] | 0.27 | 0.37 |
| Comorbidities | 132 (35.87) | 62 (38.99) | 70 (33.49) | 0.89 | 1.00 |
| Circulatory System Disease (%) | 74 (20.11) | 30 (18.87) | 44 (21.05) | 0.33 | 0.62 |
| Blood Disease (%) | 39 (10.60) | 23 (14.47) | 16 (7.66) | 0.05 | 0.35 |
| Respiratory Disease (%) | 15 (4.08) | 9 (5.66) | 6 (2.87) | 0.28 | 0.61 |
| Digestive Disease (%) | 11 (2.99) | 3 (1.89) | 8 (3.83) | 0.44 | 0.64 |
| Nervous System Disease (%) | 20 (5.43) | 11 (6.92) | 9 (4.31) | 0.39 | 0.63 |
| Chromosomal Anomalies (%) | 12 (3.26) | 5 (3.14) | 7 (3.35) | 1.00 | 1.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ying, Z.; Ge, H.; Han, W.; Hu, G.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, J.; Song, L.; Qu, D.; Jin, Z. Assessing the Heterogeneous Treatment Effects of Glucocorticoids in Infants and Toddlers with Severe Pneumonia. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 2333. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13102333
Ying Z, Ge H, Han W, Hu G, Zhu Z, Wang J, Song L, Qu D, Jin Z. Assessing the Heterogeneous Treatment Effects of Glucocorticoids in Infants and Toddlers with Severe Pneumonia. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(10):2333. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13102333
Chicago/Turabian StyleYing, Zhoumeng, Haiyan Ge, Wei Han, Ge Hu, Zhenchen Zhu, Jinhua Wang, Lan Song, Dong Qu, and Zhengyu Jin. 2025. "Assessing the Heterogeneous Treatment Effects of Glucocorticoids in Infants and Toddlers with Severe Pneumonia" Biomedicines 13, no. 10: 2333. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13102333
APA StyleYing, Z., Ge, H., Han, W., Hu, G., Zhu, Z., Wang, J., Song, L., Qu, D., & Jin, Z. (2025). Assessing the Heterogeneous Treatment Effects of Glucocorticoids in Infants and Toddlers with Severe Pneumonia. Biomedicines, 13(10), 2333. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13102333







