Dopamine and Serotonin Transporter Genes Regulation in Highly Sensitive Individuals during Stressful Conditions: A Focus on Genetics and Epigenetics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Procedure
2.3. Behavioral Tests
2.3.1. The 12-Item HSP Scale
2.3.2. Perceived Stress Scale (PSS-10)
2.3.3. Interaction between HSP and PSS
2.4. Molecular Studies
2.4.1. Salivary Samples Collection
2.4.2. DNA Extraction and Methylation Study
2.4.3. Exosomal miRNAs Extraction and Real-Time PCR
2.4.4. SERT 5-HTTLPR and DAT1 VNTR Genotype
2.4.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Sample Characteristics
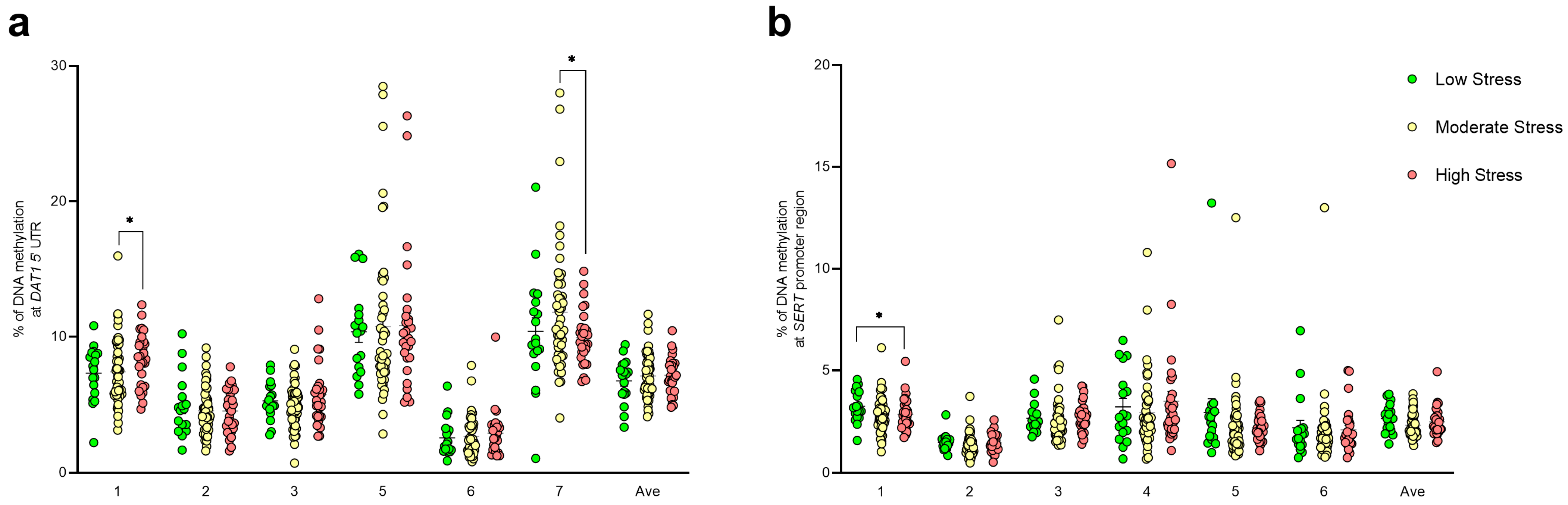
3.2. DNA Methylation Studies
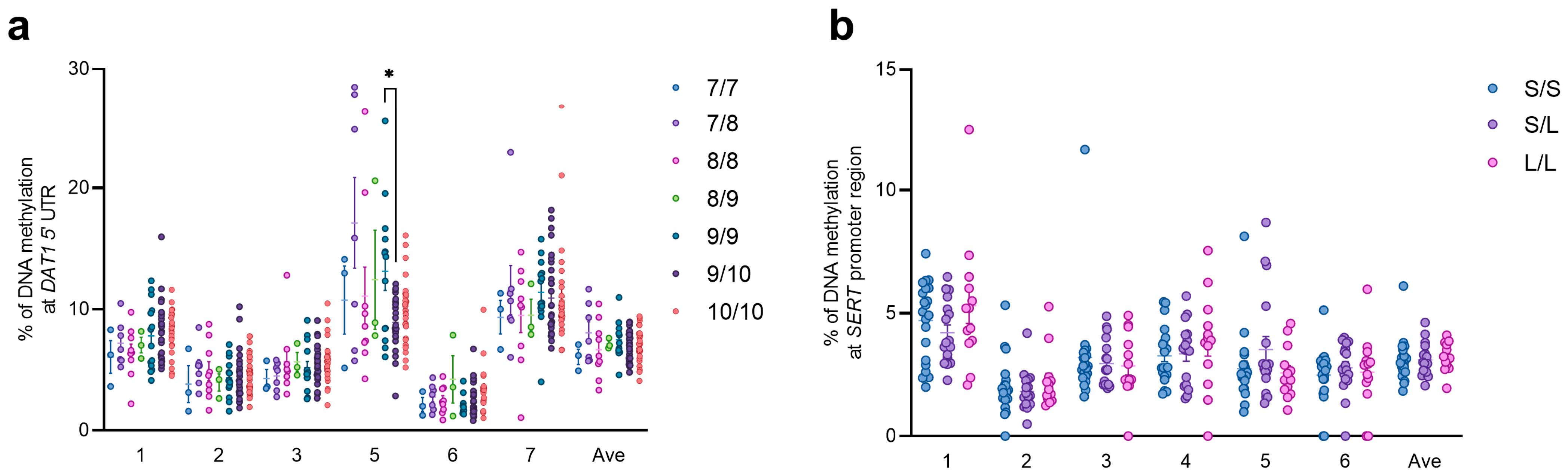
3.3. Genetic Analysis
3.4. miRNAs Analysis
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arnett, J.J. Emerging Adulthood: A Theory of Development from the Late Teens through the Twenties. Am. Psychol. 2000, 55, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbayannis, G.; Franco, D.; Wong, S.; Galdamez, J.; Romeo, R.D.; Bauer, E.P. Differential Effects of Stress on Fear Learning and Activation of the Amygdala in Pre-Adolescent and Adult Male Rats. Neuroscience 2017, 360, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosmans, G.; Young, J.F.; Hankin, B.L. NR3C1 Methylation as a Moderator of the Effects of Maternal Support and Stress on Insecure Attachment Development. Dev. Psychol. 2018, 54, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, J.J.; Cole, S.W.; Bower, J.E.; Irwin, M.R.; Taylor, S.E.; Arevalo, J.; Fuligni, A.J. Daily Interpersonal Stress, Sleep Duration, and Gene Regulation during Late Adolescence. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2019, 103, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chubar, V.; Vaessen, T.; den Noortgate, W.V.; Lutin, E.; Bosmans, G.; Bekaert, B.; Van Leeuwen, K.; Calders, F.; Weyn, S.; Bijttebier, P.; et al. Mild Daily Stress, in Interaction with NR3C1 DNA Methylation Levels, Is Linked to Alterations in the HPA Axis and ANS Response to Acute Stress in Early Adolescents. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2023, 150, 106045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogan, D.P.; Astone, N.M. The Transition to Adulthood. Annu. Rev. Sociol. 1986, 12, 109–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lally, M.; Valentine-French, S. Lifespan Development: A Psychological Perspective; College of Lake County: Grayslake, IL, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Matud, M.P.; Díaz, A.; Bethencourt, J.M.; Ibáñez, I. Stress and Psychological Distress in Emerging Adulthood: A Gender Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeo, R.D. The Impact of Stress on the Structure of the Adolescent Brain: Implications for Adolescent Mental Health. Brain Res. 2017, 1654, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scales, P.C.; Benson, P.L.; Oesterle, S.; Hill, K.G.; Hawkins, J.D.; Pashak, T.J. The Dimensions of Successful Young Adult Development: A Conceptual and Measurement Framework. Appl. Dev. Sci. 2015, 20, 150–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanahan, M.J. Pathways to Adulthood in Changing Societies: Variability and Mechanisms in Life Course Perspective. Annu. Rev. Sociol. 2000, 26, 667–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spear, L.P. The Adolescent Brain and Age-Related Behavioral Manifestations. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2000, 24, 417–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pozos-Radillo, B.E.; Preciado-Serrano, M.d.L.; Acosta-Fernández, M.; Aguilera-Velasco, M.d.l.Á.; Delgado-García, D.D. Academic Stress as a Predictor of Chronic Stress in University Students. Psicol. Educ. 2014, 20, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannito, L.; Annunzi, E.; Viganò, C.; Dell’Osso, B.; Vismara, M.; Sacco, P.L.; Palumbo, R.; D’Addario, C. The Role of Stress and Cognitive Absorption in Predicting Social Network Addiction. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karyotaki, E.; Cuijpers, P.; Albor, Y.; Alonso, J.; Auerbach, R.P.; Bantjes, J.; Bruffaerts, R.; Ebert, D.D.; Hasking, P.; Kiekens, G.; et al. Sources of Stress and Their Associations with Mental Disorders among College Students: Results of the World Health Organization World Mental Health Surveys International College Student Initiative. Front. Psychol. 2020, 11, 1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.H.; Stevens, C.; Wong, S.H.M.; Yasui, M.; Chen, J.A. The Prevalence and Predictors of Mental Health Diagnoses and Suicide among U.S. College Students: Implications for Addressing Disparities in Service Use. Depress. Anxiety 2019, 36, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedrelli, P.; Nyer, M.; Yeung, A.; Zulauf, C.; Wilens, T. College Students: Mental Health Problems and Treatment Considerations. Acad. Psychiatry 2015, 39, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, C.; Okuda, M.; Wright, C.; Hasin, D.S.; Grant, B.F.; Liu, S.-M.; Olfson, M. Mental Health of College Students and Their Non-College-Attending Peers: Results from the National Epidemiologic Study on Alcohol and Related Conditions. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2008, 65, 1429–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, K.J.; Menon, K.R.; Thattil, A. Academic Stress and Its Sources Among University Students. Biomed. Pharmacol. J. 2018, 11, 531–537. [Google Scholar]
- Saleh, A.; Potter, G.G.; McQuoid, D.R.; Boyd, B.; Turner, R.; MacFall, J.R.; Taylor, W.D. Effects of Early Life Stress on Depression, Cognitive Performance and Brain Morphology. Psychol. Med. 2017, 47, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Lee, J.; Yoo, S.; Suh, S.; Chung, S.; Lee, S.A. The Psychometric Properties of the Stress and Anxiety to Viral Epidemics-6 Items: A Test in the U.S. General Population. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 746244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natalia, J.R.; Bernathsius, J. Highly Sensitive Person dan Dampaknya terhadap Kesehatan Mental. J. Keperawatan Jiwa 2019, 7, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pluess, M.; Lionetti, F.; Aron, E.N.; Aron, A. People Differ in Their Sensitivity to the Environment: An Integrated Theory, Measurement and Empirical Evidence. J. Res. Personal. 2023, 104, 104377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aron, E.N.; Aron, A. Sensory-Processing Sensitivity and Its Relation to Introversion and Emotionality. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 1997, 73, 345–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iimura, S.; Yano, K.; Ishii, Y. Environmental Sensitivity in Adults: Psychometric Properties of the Japanese Version of the Highly Sensitive Person Scale 10-Item Version. J. Personal. Assess. 2023, 105, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pluess, M. Individual Differences in Environmental Sensitivity. Child Dev. Perspect. 2015, 9, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benham, G. The Highly Sensitive Person: Stress and Physical Symptom Reports. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2006, 40, 1433–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greven, C.U.; Lionetti, F.; Booth, C.; Aron, E.N.; Fox, E.; Schendan, H.E.; Pluess, M.; Bruining, H.; Acevedo, B.; Bijttebier, P.; et al. Sensory Processing Sensitivity in the Context of Environmental Sensitivity: A Critical Review and Development of Research Agenda. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2019, 98, 287–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakermans-Kranenburg, M.J.; Ijzendoorn, M.H. van Differential Susceptibility to Rearing Environment Depending on Dopamine-Related Genes: New Evidence and a Meta-Analysis. Dev. Psychopathol. 2011, 23, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chen, C.; Moyzis, R.; Stern, H.; He, Q.; Li, H.; Li, J.; Zhu, B.; Dong, Q. Contributions of Dopamine-Related Genes and Environmental Factors to Highly Sensitive Personality: A Multi-Step Neuronal System-Level Approach. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homberg, J.R.; Kyzar, E.J.; Nguyen, M.; Norton, W.H.; Pittman, J.; Poudel, M.K.; Gaikwad, S.; Nakamura, S.; Koshiba, M.; Yamanouchi, H.; et al. Understanding Autism and Other Neurodevelopmental Disorders through Experimental Translational Neurobehavioral Models. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2016, 65, 292–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schinka, J.A.; Busch, R.M.; Robichaux-Keene, N. A Meta-Analysis of the Association between the Serotonin Transporter Gene Polymorphism (5-HTTLPR) and Trait Anxiety. Mol. Psychiatry 2004, 9, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minelli, A.; Bonvicini, C.; Scassellati, C.; Sartori, R.; Gennarelli, M. The Influence of Psychiatric Screening in Healthy Populations Selection: A New Study and Meta-Analysis of Functional 5-HTTLPR and Rs25531 Polymorphisms and Anxiety-Related Personality Traits. BMC Psychiatry 2011, 11, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delli Colli, C.; Borgi, M.; Poggini, S.; Chiarotti, F.; Cirulli, F.; Penninx, B.W.J.H.; Benedetti, F.; Vai, B.; Branchi, I. Time Moderates the Interplay between 5-HTTLPR and Stress on Depression Risk: Gene x Environment Interaction as a Dynamic Process. Transl. Psychiatry 2022, 12, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miño, V.; San Martín, C.; Alfaro, F.; Miguez, G.; Laborda, M.A.; Bacigalupo, F.; Quezada-Scholz, V. Meta-Analysis of the Effect of 5HTTLPR Polymorphism in Fear Learning. Learn. Motiv. 2023, 82, 101889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesch, K.-P.; Bengel, D.; Heils, A.; Sabol, S.Z.; Greenberg, B.D.; Petri, S.; Benjamin, J.; Müller, C.R.; Hamer, D.H.; Murphy, D.L. Association of Anxiety-Related Traits with a Polymorphism in the Serotonin Transporter Gene Regulatory Region. Science 1996, 274, 1527–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonda, X.; Fountoulakis, K.N.; Juhasz, G.; Rihmer, Z.; Lazary, J.; Laszik, A.; Akiskal, H.S.; Bagdy, G. Association of the s Allele of the 5-HTTLPR with Neuroticism-Related Traits and Temperaments in a Psychiatrically Healthy Population. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2009, 259, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Yi, J.; Wang, X.; Zhu, X.; Yao, S. Serotonin Transporter Gene Polymorphism (5-HTTLPR) L Allele Interacts with Stress to Increase Anxiety Symptoms in Chinese Adolescents: A Multiwave Longitudinal Study. BMC Psychiatry 2015, 15, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zuschlag, Z.D.; Compean, E.; Nietert, P.; Lauzon, S.; Hamner, M.; Wang, Z. Dopamine Transporter (DAT1) Gene in Combat Veterans with PTSD: A Case-Control Study. Psychiatry Res. 2021, 298, 113801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadow, K.D.; Roohi, J.; DeVincent, C.J.; Hatchwell, E. Association of ADHD, Tics, and Anxiety with Dopamine Transporter (DAT1) Genotype in Autism Spectrum Disorder. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 2008, 49, 1331–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreher, J.-C.; Kohn, P.; Kolachana, B.; Weinberger, D.R.; Berman, K.F. Variation in Dopamine Genes Influences Responsivity of the Human Reward System. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 617–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plomin, R.; Haworth, C.M.A.; Davis, O.S.P. Common Disorders Are Quantitative Traits. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 10, 872–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keers, R.; Coleman, J.R.I.; Lester, K.J.; Roberts, S.; Breen, G.; Thastum, M.; Bögels, S.; Schneider, S.; Heiervang, E.; Meiser-Stedman, R.; et al. A Genome-Wide Test of the Differential Susceptibility Hypothesis Reveals a Genetic Predictor of Differential Response to Psychological Treatments for Child Anxiety Disorders. Psychother. Psychosom. 2016, 85, 146–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuffin, P.; Rijsdijk, F.; Andrew, M.; Sham, P.; Katz, R.; Cardno, A. The Heritability of Bipolar Affective Disorder and the Genetic Relationship to Unipolar Depression. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2003, 60, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caspi, A.; McClay, J.; Moffitt, T.E.; Mill, J.; Martin, J.; Craig, I.W.; Taylor, A.; Poulton, R. Role of Genotype in the Cycle of Violence in Maltreated Children. Science 2002, 297, 851–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caspi, A.; Sugden, K.; Moffitt, T.E.; Taylor, A.; Craig, I.W.; Harrington, H.; McClay, J.; Mill, J.; Martin, J.; Braithwaite, A.; et al. Influence of Life Stress on Depression: Moderation by a Polymorphism in the 5-HTT Gene. Science 2003, 301, 386–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellia, F.; Vismara, M.; Annunzi, E.; Cifani, C.; Benatti, B.; Dell’Osso, B.; D’Addario, C. Genetic and Epigenetic Architecture of Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder: In Search of Possible Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarkers. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2021, 137, 554–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isles, A.R. Neural and Behavioral Epigenetics; What It Is, and What Is Hype. Genes Brain Behav. 2015, 14, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiele, M.A.; Domschke, K. Epigenetics at the Crossroads between Genes, Environment and Resilience in Anxiety Disorders. Genes Brain Behav. 2018, 17, e12423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lionetti, F.; Dumpfrey, R.S.C.; Richetin, J.; Fasolo, M.; Nocentini, A.; Penolazzi, B.; Pluess, M.; Santona, A.; Spinelli, M.; Preti, E. Is Environmental Sensitivity a Unique Trait? A Multi-Sample Study on the Association between Sensitivity, Personality, and Psychological Adjustment. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2024, 217, 112463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Addario, C.; Macellaro, M.; Bellia, F.; Benatti, B.; Annunzi, E.; Palumbo, R.; Conti, D.; Fasciana, F.; Vismara, M.; Varinelli, A.; et al. In Search for Biomarkers in Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder: New Evidence on Saliva as a Practical Source of DNA to Assess Epigenetic Regulation. Curr. Med. Chem. 2021, 29, 5782–5791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Jia, L.; Zheng, Y.; Li, W. Salivary Exosomes: Emerging Roles in Systemic Disease. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 14, 633–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallo, A.; Tandon, M.; Alevizos, I.; Illei, G.G. The Majority of MicroRNAs Detectable in Serum and Saliva Is Concentrated in Exosomes. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, P.R.; Han, S.; Hing, B.; Nagahama, Y.; Gaul, L.N.; Heinzman, J.T.; Grossbach, A.J.; Close, L.; Dlouhy, B.J.; Howard, M.A.; et al. Genome-Wide DNA Methylation Comparison between Live Human Brain and Peripheral Tissues within Individuals. Transl. Psychiatry 2019, 9, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Addario, C.; Pucci, M.; Bellia, F.; Girella, A.; Sabatucci, A.; Fanti, F.; Vismara, M.; Benatti, B.; Ferrara, L.; Fasciana, F.; et al. Regulation of Oxytocin Receptor Gene Expression in Obsessive–Compulsive Disorder: A Possible Role for the Microbiota-Host Epigenetic Axis. Clin. Epigenetics 2022, 14, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smolewska, K.A.; McCabe, S.B.; Woody, E.Z. A Psychometric Evaluation of the Highly Sensitive Person Scale: The Components of Sensory-Processing Sensitivity and Their Relation to the BIS/BAS and “Big Five”. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2006, 40, 1269–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lionetti, F.; Aron, A.; Aron, E.N.; Burns, G.L.; Jagiellowicz, J.; Pluess, M. Dandelions, Tulips and Orchids: Evidence for the Existence of Low-Sensitive, Medium-Sensitive and High-Sensitive Individuals. Transl. Psychiatry 2018, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, S.; Kamarck, T.; Mermelstein, R. A Global Measure of Perceived Stress. J. Health Soc. Behav. 1983, 24, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diotaiuti, P.; Valente, G.; Mancone, S. Validation Study of the Italian Version of Temporal Focus Scale: Psychometric Properties and Convergent Validity. BMC Psychol. 2021, 9, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goode, M.R.; Cheong, S.Y.; Li, N.; Ray, W.C.; Bartlett, C.W. Collection and Extraction of Saliva DNA for next Generation Sequencing. J. Vis. Exp. 2014, 51697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anzani, S.; Cannito, L.; Bellia, F.; Di Domenico, A.; Dell’Osso, B.; Palumbo, R.; D’Addario, C. OXTR Gene DNA Methylation Levels Are Associated with Discounting Behavior with Untrustworthy Proposers. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dejeux, E.; Abdalaoui, H.E.; Gut, I.G.; Tost, J. Identification and Quantification of Differentially Methylated Loci by the PyrosequencingTM Technology. In DNA Methylation: Methods and Protocols; Tost, J., Ed.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 189–205. ISBN 978-1-59745-522-0. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, X. miRDB: An Online Database for Prediction of Functional microRNA Targets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D127–D131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sookoian, S.; Gemma, C.; García, S.I.; Gianotti, T.F.; Dieuzeide, G.; Roussos, A.; Tonietti, M.; Trifone, L.; Kanevsky, D.; González, C.D.; et al. Short Allele of Serotonin Transporter Gene Promoter Is a Risk Factor for Obesity in Adolescents. Obesity 2007, 15, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinohara, M.; Mizushima, H.; Hirano, M.; Shioe, K.; Nakazawa, M.; Hiejima, Y.; Ono, Y.; Kanba, S. Eating Disorders with Binge-Eating Behaviour Are Associated with the s Allele of the 3’-UTR VNTR Polymorphism of the Dopamine Transporter Gene. J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 2004, 29, 134–137. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Annunzi, E.; Cannito, L.; Bellia, F.; Mercante, F.; Vismara, M.; Benatti, B.; Di Domenico, A.; Palumbo, R.; Adriani, W.; Dell’Osso, B.; et al. Mild Internet Use Is Associated with Epigenetic Alterations of Key Neurotransmission Genes in Salivary DNA of Young University Students. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 22192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardi, L.D.; Carpentieri, V.; Pascale, E.; Pucci, M.; D’Addario, C.; Cerniglia, L.; Adriani, W.; Cimino, S. Involvement of DAT1 Gene on Internet Addiction: Cross-Correlations of Methylation Levels in 5′-UTR and 3’-UTR Genotypes, Interact with Impulsivity and Attachment-Driven Quality of Relationships. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 7956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannon, M.J.; Michelhaugh, S.K.; Wang, J.; Sacchetti, P. The Human Dopamine Transporter Gene: Gene Organization, Transcriptional Regulation, and Potential Involvement in Neuropsychiatric Disorders. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2001, 11, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shumay, E.; Fowler, J.S.; Volkow, N.D. Genomic Features of the Human Dopamine Transporter Gene and Its Potential Epigenetic States: Implications for Phenotypic Diversity. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adriani, W.; Romano, E.; Pucci, M.; Pascale, E.; Cerniglia, L.; Cimino, S.; Tambelli, R.; Curatolo, P.; Granstrem, O.; Maccarrone, M.; et al. Potential for Diagnosis versus Therapy Monitoring of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: A New Epigenetic Biomarker Interacting with Both Genotype and Auto-Immunity. Eur. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2018, 27, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiers, C.E.; Shumay, E.; Volkow, N.D.; Frieling, H.; Kotsiari, A.; Lindenmeyer, J.; Walter, H.; Bermpohl, F. Effects of Depressive Symptoms and Peripheral DAT Methylation on Neural Reactivity to Alcohol Cues in Alcoholism. Transl. Psychiatry 2015, 5, e648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chmielowiec, K.; Chmielowiec, J.; Masiak, J.; Strońska-Pluta, A.; Lachowicz, M.; Boroń, A.; Larysz, D.; Dzitkowska-Zabielska, M.; Cięszczyk, P.; Grzywacz, A. DNA Methylation of the Dopamine Transporter DAT1 Gene—Bliss Seekers in the Light of Epigenetics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillemacher, T.; Frieling, H.; Hartl, T.; Wilhelm, J.; Kornhuber, J.; Bleich, S. Promoter Specific Methylation of the Dopamine Transporter Gene Is Altered in Alcohol Dependence and Associated with Craving. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2009, 43, 388–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubino, A.; D’Addario, C.; Di Bartolomeo, M.; Michele Salamone, E.; Locuratolo, N.; Fattapposta, F.; Vanacore, N.; Pascale, E. DNA Methylation of the 5′-UTR DAT1 Gene in Parkinson’s Disease Patients. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2020, 142, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mollet, I.G.; Malm, H.A.; Wendt, A.; Orho-Melander, M.; Eliasson, L. Integrator of Stress Responses Calmodulin Binding Transcription Activator 1 (Camta1) Regulates miR-212/miR-132 Expression and Insulin Secretion. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 18440–18452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, C.; Yang, Y.; Du, L.; Wang, H. Calmodulin-Binding Transcription Activators and Perspectives for Applications in Biotechnology. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 10379–10385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serafini, G.; Pompili, M.; Hansen, K.F.; Obrietan, K.; Dwivedi, Y.; Shomron, N.; Girardi, P. The Involvement of microRNAs in Major Depression, Suicidal Behavior, and Related Disorders: A Focus on miR-185 and miR-491-3p. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2014, 34, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glavina Jelaš, I.; Dević, I.; Karlović, D. Cloninger’s Temperament and Character Dimensions and Dopaminergic Genes: DAT1 VNTR and COMT Val158Met Polymorphisms. Psychiatr. Danub. 2018, 30, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuke, S.; Suo, S.; Takahashi, N.; Koike, H.; Sasagawa, N.; Ishiura, S. The VNTR Polymorphism of the Human Dopamine Transporter (DAT1) Gene Affects Gene Expression. Pharmacogenom. J. 2001, 1, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catale, C.; Lo Iacono, L.; Martini, A.; Heil, C.; Guatteo, E.; Mercuri, N.B.; Viscomi, M.T.; Palacios, D.; Carola, V. Early Life Social Stress Causes Sex- and Region-Dependent Dopaminergic Changes That Are Prevented by Minocycline. Mol. Neurobiol. 2022, 59, 3913–3932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubol, M.; Trichard, C.; Leroy, C.; Granger, B.; Tzavara, E.T.; Martinot, J.-L.; Artiges, E. Lower Midbrain Dopamine Transporter Availability in Depressed Patients: Report from High-Resolution PET Imaging. J. Affect. Disord. 2020, 262, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, J.H.; Krüger, S.; Wilson, A.A.; Christensen, B.K.; Goulding, V.S.; Schaffer, A.; Minifie, C.; Houle, S.; Hussey, D.; Kennedy, S.H. Lower Dopamine Transporter Binding Potential in Striatum during Depression. Neuroreport 2001, 12, 4121–4125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriya, H.; Tiger, M.; Tateno, A.; Sakayori, T.; Masuoka, T.; Kim, W.; Arakawa, R.; Okubo, Y. Low Dopamine Transporter Binding in the Nucleus Accumbens in Geriatric Patients with Severe Depression. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2020, 74, 424–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pizzagalli, D.A.; Berretta, S.; Wooten, D.; Goer, F.; Pilobello, K.T.; Kumar, P.; Murray, L.; Beltzer, M.; Boyer-Boiteau, A.; Alpert, N.; et al. Assessment of Striatal Dopamine Transporter Binding in Individuals With Major Depressive Disorder: In Vivo Positron Emission Tomography and Postmortem Evidence. JAMA Psychiatry 2019, 76, 854–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beach, S.R.H.; Brody, G.H.; Todorov, A.A.; Gunter, T.D.; Philibert, R.A. Methylation at SLC6A4 Is Linked to Family History of Child Abuse: An Examination of the Iowa Adoptee Sample. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 2010, 153B, 710–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsson, C.A.; Foley, D.L.; Parkinson-Bates, M.; Byrnes, G.; McKenzie, M.; Patton, G.C.; Morley, R.; Anney, R.J.L.; Craig, J.M.; Saffery, R. Prospects for Epigenetic Research within Cohort Studies of Psychological Disorder: A Pilot Investigation of a Peripheral Cell Marker of Epigenetic Risk for Depression. Biol. Psychol. 2010, 83, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philibert, R.A.; Sandhu, H.; Hollenbeck, N.; Gunter, T.; Adams, W.; Madan, A. The Relationship of 5HTT (SLC6A4) Methylation and Genotype on mRNA Expression and Liability to Major Depression and Alcohol Dependence in Subjects from the Iowa Adoption Studies. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 2008, 147B, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alasaari, J.S.; Lagus, M.; Ollila, H.M.; Toivola, A.; Kivimäki, M.; Vahtera, J.; Kronholm, E.; Härmä, M.; Puttonen, S.; Paunio, T. Environmental Stress Affects DNA Methylation of a CpG Rich Promoter Region of Serotonin Transporter Gene in a Nurse Cohort. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leibold, N.K.; Weidner, M.T.; Ziegler, C.; Ortega, G.; Domschke, K.; Lesch, K.P.; Van Den Hove, D.L.; Schruers, K.R. DNA Methylation in the 5-HTT Regulatory Region Is Associated with CO2-Induced Fear in Panic Disorder Patients. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2020, 36, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.-J.; Kim, J.-M.; Stewart, R.; Kim, S.-Y.; Bae, K.-Y.; Kim, S.-W.; Shin, I.-S.; Shin, M.-G.; Yoon, J.-S. Association of SLC6A4 Methylation with Early Adversity, Characteristics and Outcomes in Depression. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2013, 44, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issler, O.; Haramati, S.; Paul, E.D.; Maeno, H.; Navon, I.; Zwang, R.; Gil, S.; Mayberg, H.S.; Dunlop, B.W.; Menke, A.; et al. MicroRNA 135 Is Essential for Chronic Stress Resiliency, Antidepressant Efficacy, and Intact Serotonergic Activity. Neuron 2014, 83, 344–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotlib, I.H.; Joormann, J.; Minor, K.L.; Hallmayer, J. HPA Axis Reactivity: A Mechanism Underlying the Associations Among 5-HTTLPR, Stress, and Depression. Biol. Psychiatry 2008, 63, 847–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belsky, J.; Bakermans-Kranenburg, M.J.; van IJzendoorn, M.H. For Better and For Worse: Differential Susceptibility to Environmental Influences. Curr. Dir. Psychol. Sci. 2007, 16, 300–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
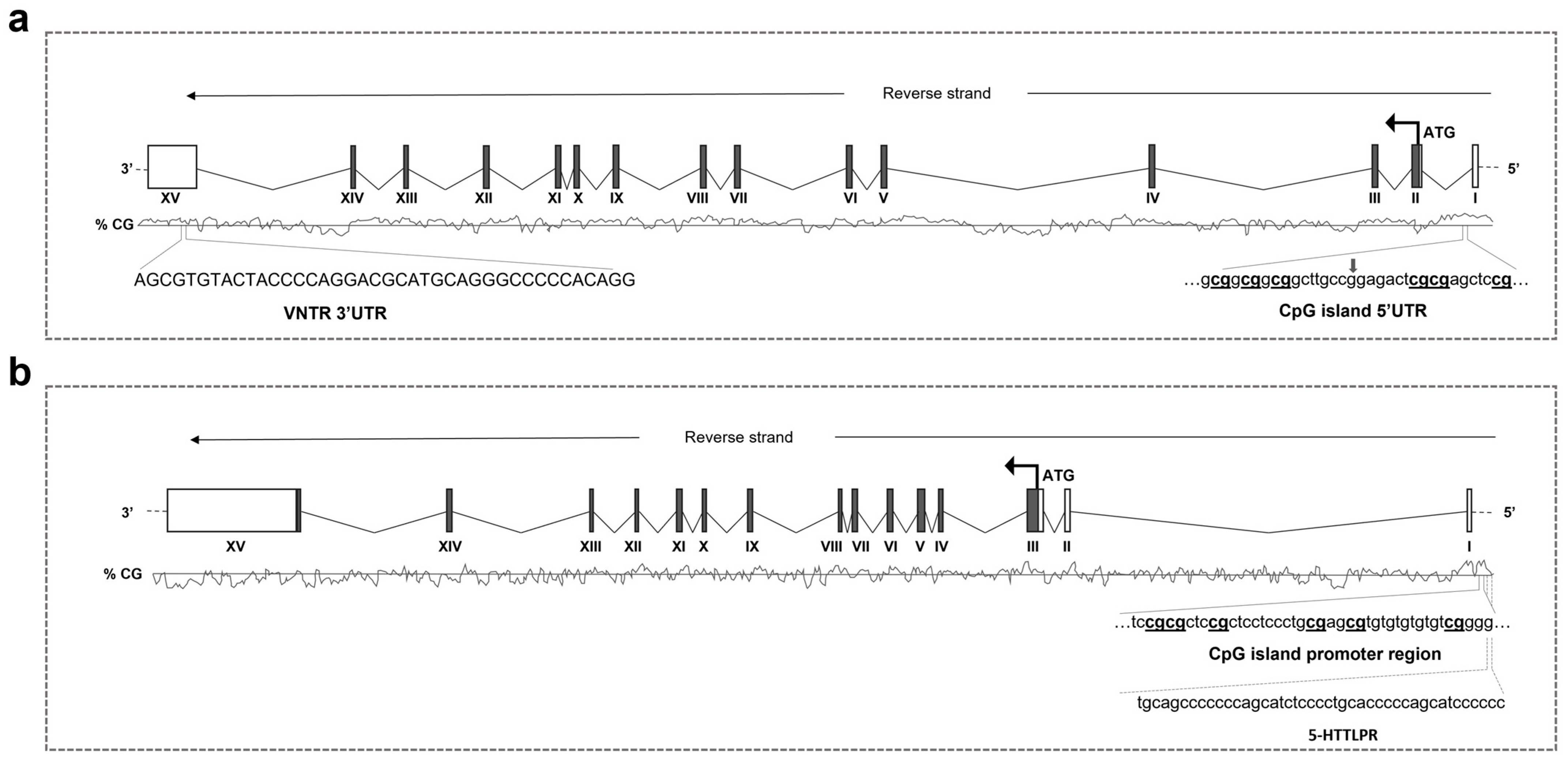




| Gene | GeneGlobe ID | Sequence Analysed | CpG Sites | Genomic Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DAT1 | PM00022064 | GCGGCGGCGGCTTGCCRGAGACTCGCGAGCTCCGC | 6 | Chr5, bp 1444718-1444679 |
| SERT | PM00065625 | CCCCGACACACACACACGCTCGCAGGGAGGAGCGGAGCGCGGA | 6 | Chr17, bp 30235935-30235893 |
| miRNA | GeneGlobe ID | miRbase Accession | Mature miRNA Sequence |
|---|---|---|---|
| hsa-miR-26a-5p | YP00206023 | MIMAT0000082 | UUCAAGUAAUCCAGGAUAGGCU |
| U6 snRNA | YP02119464 | U6snRNA | |
| hsa-miR-132-3p | YP00206035 | MIMAT0000426 | UAACAGUCUACAGCCAUGGUCG |
| hsa-miR-491-5p | YP00204695 | MIMAT0002807 | AGUGGGGAACCCUUCCAUGAGG |
| hsa-miR-16-5p | YP00205702 | MIMAT0000069 | UAGCAGCACGUAAAUAUUGGCG |
| hsa-miR-135 | YP00204762 | MIMAT0000428 | UAUGGCUUUUUAUUCCUAUGUGA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bellia, F.; Piccinini, A.; Annunzi, E.; Cannito, L.; Lionetti, F.; Dell’Osso, B.; Adriani, W.; Dainese, E.; Di Domenico, A.; Pucci, M.; et al. Dopamine and Serotonin Transporter Genes Regulation in Highly Sensitive Individuals during Stressful Conditions: A Focus on Genetics and Epigenetics. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2149. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12092149
Bellia F, Piccinini A, Annunzi E, Cannito L, Lionetti F, Dell’Osso B, Adriani W, Dainese E, Di Domenico A, Pucci M, et al. Dopamine and Serotonin Transporter Genes Regulation in Highly Sensitive Individuals during Stressful Conditions: A Focus on Genetics and Epigenetics. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(9):2149. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12092149
Chicago/Turabian StyleBellia, Fabio, Alessandro Piccinini, Eugenia Annunzi, Loreta Cannito, Francesca Lionetti, Bernardo Dell’Osso, Walter Adriani, Enrico Dainese, Alberto Di Domenico, Mariangela Pucci, and et al. 2024. "Dopamine and Serotonin Transporter Genes Regulation in Highly Sensitive Individuals during Stressful Conditions: A Focus on Genetics and Epigenetics" Biomedicines 12, no. 9: 2149. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12092149
APA StyleBellia, F., Piccinini, A., Annunzi, E., Cannito, L., Lionetti, F., Dell’Osso, B., Adriani, W., Dainese, E., Di Domenico, A., Pucci, M., Palumbo, R., & D’Addario, C. (2024). Dopamine and Serotonin Transporter Genes Regulation in Highly Sensitive Individuals during Stressful Conditions: A Focus on Genetics and Epigenetics. Biomedicines, 12(9), 2149. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12092149








